Contrast Administration Impacts CT-Based Radiomics of Colorectal Liver Metastases and Non-Tumoral Liver Parenchyma Revealing the “Radiological” Tumour Microenvironment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
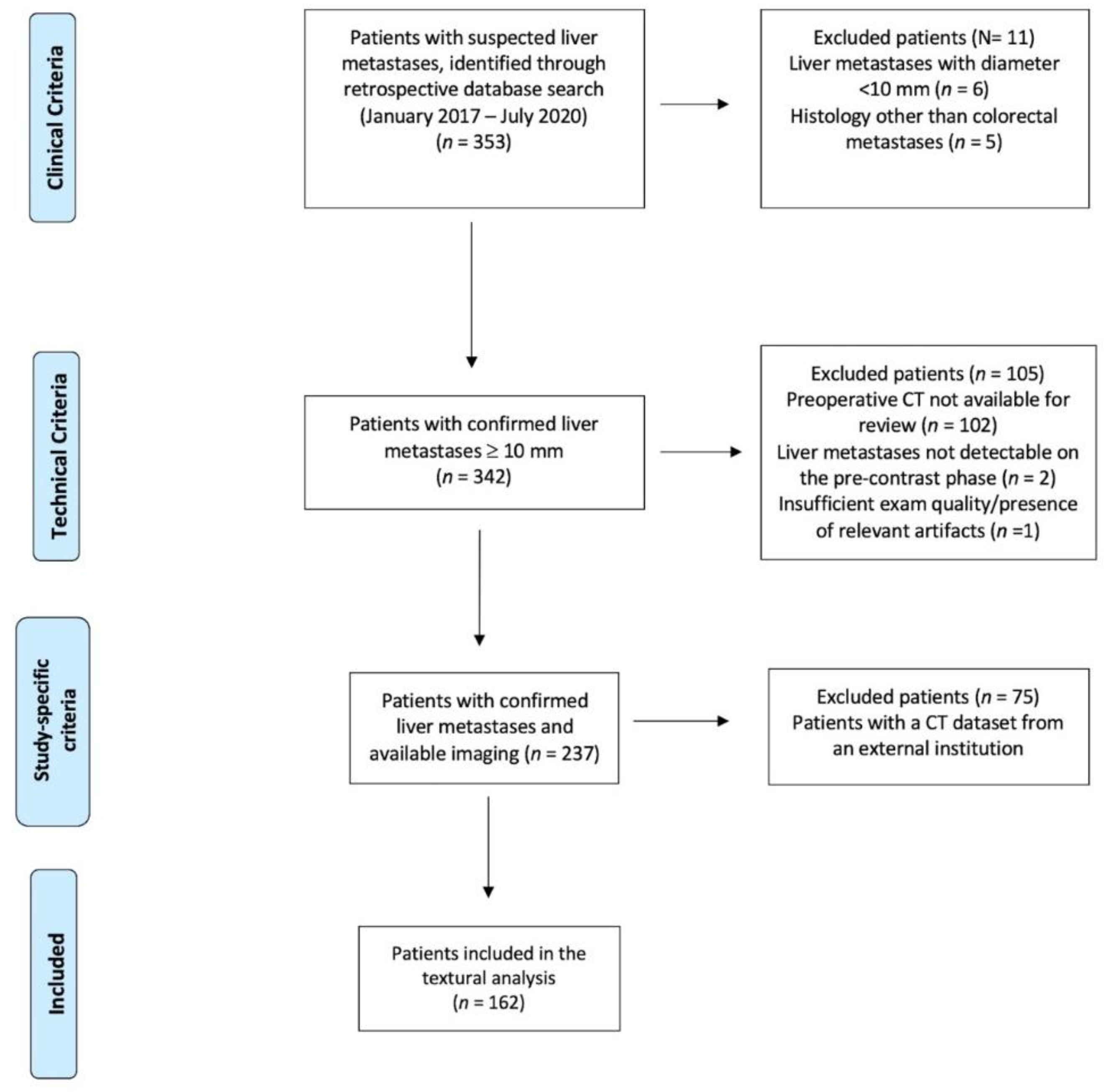
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Image Acquisition
2.3. Image Analysis
2.4. Features Selection and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
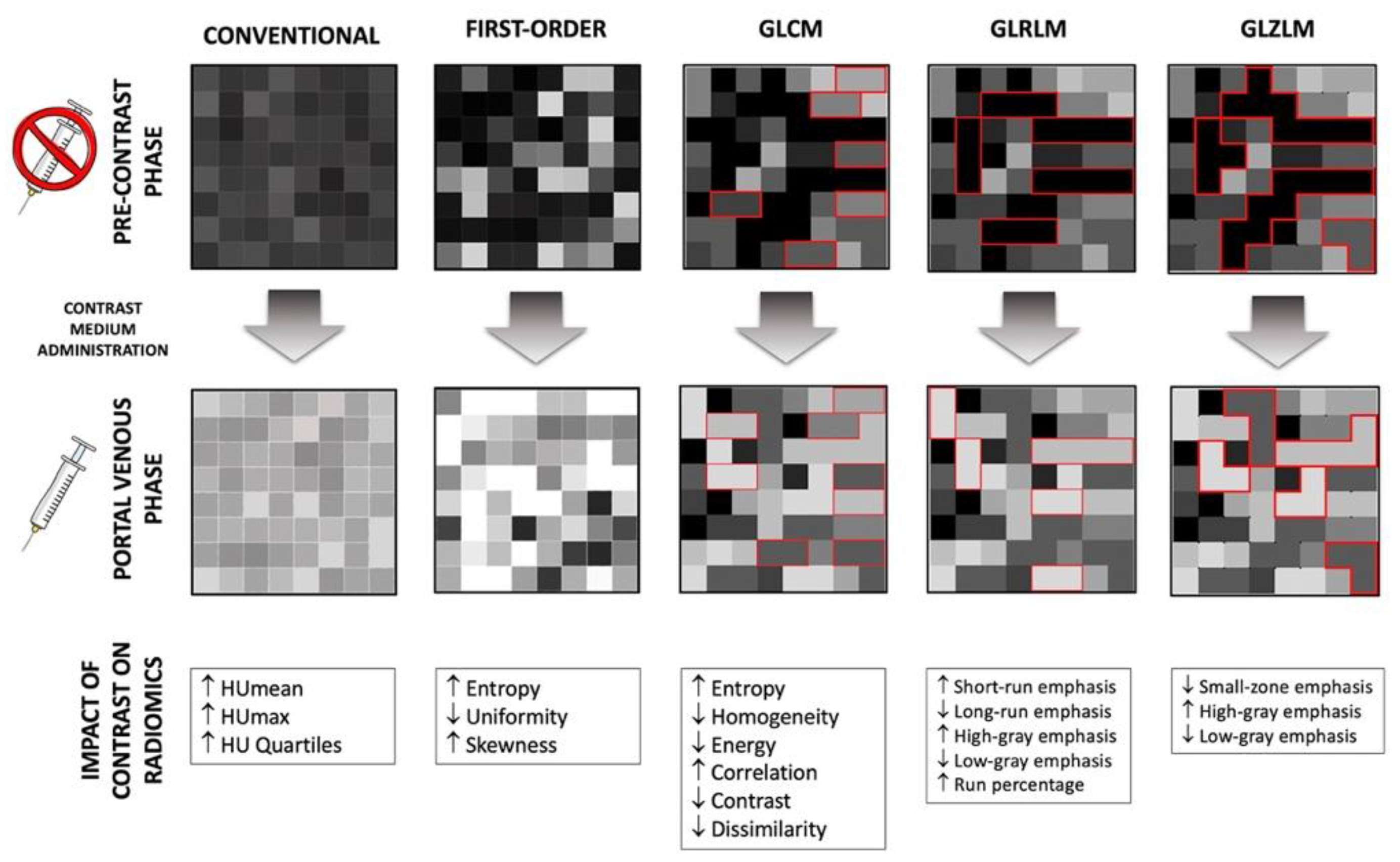
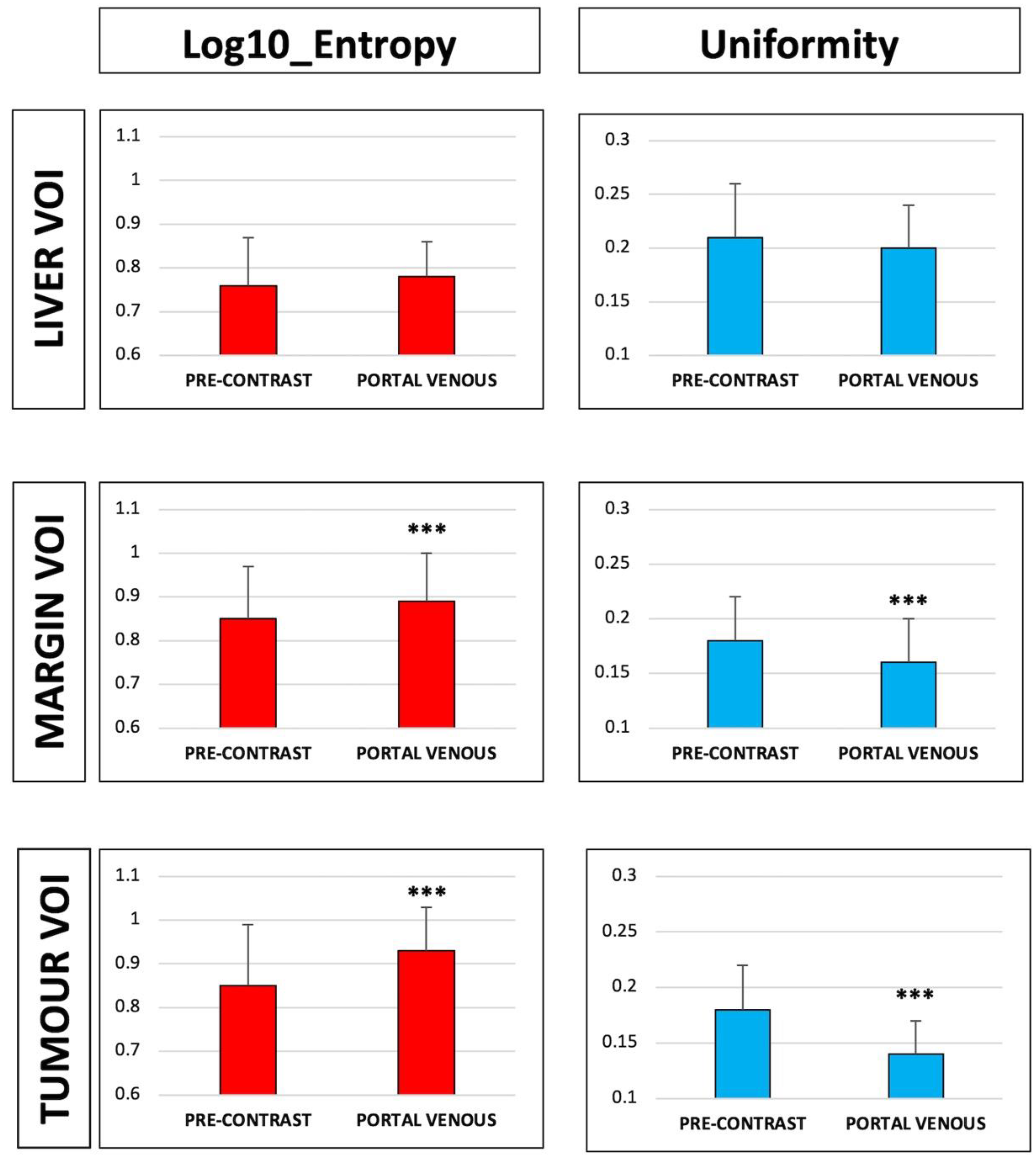
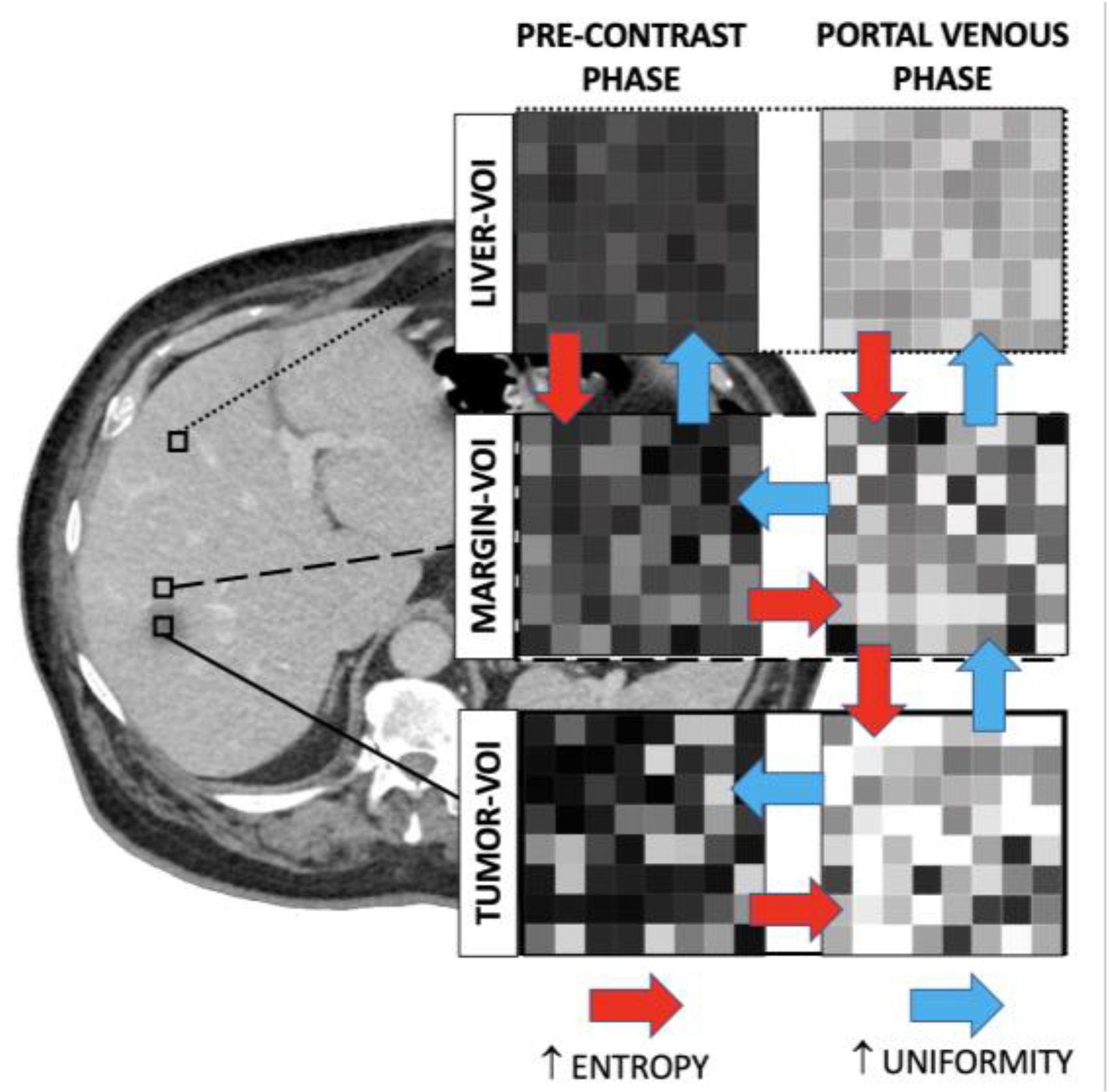
3.1. Radiomic Features of the Tumour VOI
3.2. Radiomic Features of the Margin VOI
3.3. Radiomic Features of the Liver VOI
3.4. Comparison of Radiomic Features across VOIs of the Same Series
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Massague, J.; Obenauf, A.C. Metastatic colonization by circulating tumour cells. Nature 2016, 529, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Cervantes, A.; Adam, R.; Sobrero, A.; Van Krieken, J.H.; Aderka, D.; Aranda Aguilar, E.; Bardelli, A.; Benson, A.; Bodoky, G.; et al. ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1386–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creasy, J.M.; Sadot, E.; Koerkamp, B.G.; Chou, J.F.; Gonen, M.; Kemeny, N.E.; Balachandran, V.P.; Kingham, T.P.; DeMatteo, R.P.; Allen, P.J.; et al. Actual 10-year survival after hepatic resection of colorectal liver metastases: What factors preclude cure? Surgery 2018, 163, 1238–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigano, L.; Procopio, F.; Cimino, M.M.; Donadon, M.; Gatti, A.; Costa, G.; Del Fabbro, D.; Torzilli, G. Is Tumor Detachment from Vascular Structures Equivalent to R0 Resection in Surgery for Colorectal Liver Metastases? An Observational Cohort. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 1352–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, J.C.; Petre, E.N.; Sofocleous, C.T. Thermal Ablation of Metastatic Colon Cancer to the Liver. Semin. Intervent. Radiol. 2019, 36, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, R.; Pascal, G.; Castaing, D.; Azoulay, D.; Delvart, V.; Paule, B.; Levi, F.; Bismuth, H. Tumor progression while on chemotherapy: A contraindication to liver resection for multiple colorectal metastases? Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 1052–1064; discussion 1061–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigano, L.; Darwish, S.S.; Rimassa, L.; Cimino, M.; Carnaghi, C.; Donadon, M.; Procopio, F.; Personeni, N.; Del Fabbro, D.; Santoro, A.; et al. Progression of Colorectal Liver Metastases from the End of Chemotherapy to Resection: A New Contraindication to Surgery? Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 25, 1676–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, S.; Chun, Y.S.; Kopetz, S.E.; Vauthey, J.N. Biomarkers in colorectal liver metastases. Br. J. Surg. 2018, 105, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouquet, A.; Blot, C.; Allard, M.A.; Lazure, T.; Sebbagh, M.; Gayet, M.; Lewin, M.; Adam, R.; Penna, C.; Sa Cunha, A.; et al. What is the Prognostic Value of a Discordant Radiologic and Pathologic Response in Patients Undergoing Resection of Colorectal Liver Metastases after Preoperative Chemotherapy? Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachet, J.B.; Moreno-Lopez, N.; Vigano, L.; Marchese, U.; Gelli, M.; Raoux, L.; Truant, S.; Laurent, C.; Herrero, A.; Le Roy, B.; et al. BRAF mutation is not associated with an increased risk of recurrence in patients undergoing resection of colorectal liver metastases. Br. J. Surg 2019, 106, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollini, M.; Antunovic, L.; Chiti, A.; Kirienko, M. Towards clinical application of image mining: A systematic review on artificial intelligence and radiomics. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 2656–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; de Jong, E.E.C.; van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; Larue, R.; Even, A.J.G.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thawani, R.; McLane, M.; Beig, N.; Ghose, S.; Prasanna, P.; Velcheti, V.; Madabhushi, A. Radiomics and radiogenomics in lung cancer: A review for the clinician. Lung Cancer 2018, 115, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakabayashi, T.; Ouhmich, F.; Gonzalez-Cabrera, C.; Felli, E.; Saviano, A.; Agnus, V.; Savadjiev, P.; Baumert, T.F.; Pessaux, P.; Marescaux, J.; et al. Radiomics in hepatocellular carcinoma: A quantitative review. Hepatol. Int. 2019, 13, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fiz, F.; Vigano, L.; Gennaro, N.; Costa, G.; La Bella, L.; Boichuk, A.; Cavinato, L.; Sollini, M.; Politi, L.S.; Chiti, A.; et al. Radiomics of Liver Metastases: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2020, 12, 2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dam, P.J.; van der Stok, E.P.; Teuwen, L.A.; Van den Eynden, G.G.; Illemann, M.; Frentzas, S.; Majeed, A.W.; Eefsen, R.L.; Coebergh van den Braak, R.R.J.; Lazaris, A.; et al. International consensus guidelines for scoring the histopathological growth patterns of liver metastasis. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 1427–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vigano, L.; Soldani, C.; Franceschini, B.; Cimino, M.; Lleo, A.; Donadon, M.; Roncalli, M.; Aghemo, A.; Di Tommaso, L.; Torzilli, G. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Macrophages in Intrahepatic Cholangiocellular Carcinoma. Impact on Prognosis after Complete Surgery. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2019, 23, 2216–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, H.L.; Liu, Q.P.; Sun, S.W.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, F.P.; Yang, G.; Yan, X.; Zhang, Y.D.; Liu, X.S. Radiomic analysis of contrast-enhanced CT predicts microvascular invasion and outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nioche, C.; Orlhac, F.; Boughdad, S.; Reuze, S.; Goya-Outi, J.; Robert, C.; Pellot-Barakat, C.; Soussan, M.; Frouin, F.; Buvat, I. LIFEx: A Freeware for Radiomic Feature Calculation in Multimodality Imaging to Accelerate Advances in the Characterization of Tumor Heterogeneity. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4786–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganeshan, B.; Miles, K.A.; Young, R.C.; Chatwin, C.R. Hepatic entropy and uniformity: Additional parameters that can potentially increase the effectiveness of contrast enhancement during abdominal CT. Clin. Radiol. 2007, 62, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, K.A.; Ganeshan, B.; Hayball, M.P. CT texture analysis using the filtration-histogram method: What do the measurements mean? Cancer Imaging 2013, 13, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, J.; Hu, C.; Qiu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Meng, H.; Wang, K.; Dong, H.; Wei, H.; Yin, Y. Characterization of microvessels and parenchyma in in-line phase contrast imaging CT: Healthy liver, cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2019, 9, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, M.; Ronald, J.; Vernuccio, F.; Nelson, R.C.; Ramirez-Giraldo, J.C.; Solomon, J.; Patel, B.N.; Samei, E.; Marin, D. Reproducibility of CT Radiomic Features within the Same Patient: Influence of Radiation Dose and CT Reconstruction Settings. Radiology 2019, 293, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghavi, M.; Trebeschi, S.; Simoes, R.; Meek, D.B.; Beckers, R.C.J.; Lambregts, D.M.J.; Verhoef, C.; Houwers, J.B.; van der Heide, U.A.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; et al. Machine learning-based analysis of CT radiomics model for prediction of colorectal metachronous liver metastases. Abdom. Radiol. (NY) 2021, 46, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creasy, J.M.; Cunanan, K.M.; Chakraborty, J.; McAuliffe, J.C.; Chou, J.; Gonen, M.; Kingham, V.S.; Weiser, M.R.; Balachandran, V.P.; Drebin, J.A.; et al. Differences in Liver Parenchyma are Measurable with CT Radiomics at Initial Colon Resection in Patients that Develop Hepatic Metastases from Stage II/III Colon Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 28, 1982–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badic, B.; Desseroit, M.C.; Hatt, M.; Visvikis, D. Potential Complementary Value of Noncontrast and Contrast Enhanced CT Radiomics in Colorectal Cancers. Acad. Radiol. 2019, 26, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Wei, J.; Tong, T.; Sheng, W.; Zhang, Y.; Han, Y.; Gu, D.; Hong, N.; Ye, Y.; Tian, J.; et al. Prediction of Histopathologic Growth Patterns of Colorectal Liver Metastases with a Noninvasive Imaging Method. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 4587–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzese, C.; Foley, K.; Whybra, P.; Hurt, C.; Crosby, T.; Spezi, E. Discovery of stable and prognostic CT-based radiomic features independent of contrast administration and dimensionality in oesophageal cancer. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.M.; Park, S.J.; Han, J.K. CT reconstruction algorithms affect histogram and texture analysis: Evidence for liver parenchyma, focal solid liver lesions, and renal cysts. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 4008–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahon, R.N.; Ghita, M.; Hugo, G.D.; Weiss, E. ComBat harmonization for radiomic features in independent phantom and lung cancer patient computed tomography datasets. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 015010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masokano, I.B.; Liu, W.; Xie, S.; Marcellin, D.F.H.; Pei, Y.; Li, W. The application of texture quantification in hepatocellular carcinoma using CT and MRI: A review of perspectives and challenges. Cancer Imaging 2020, 20, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.Y.; Huang, Y.Q.; Yang, Z.X.; Ying, D.; Zeng, M.S.; Rao, S.X. Potential of MR histogram analyses for prediction of response to chemotherapy in patients with colorectal hepatic metastases. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 2009–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dercle, L.; Lu, L.; Schwartz, L.H.; Qian, M.; Tejpar, S.; Eggleton, P.; Zhao, B.; Piessevaux, H. Radiomics Response Signature for Identification of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Sensitive to Therapies Targeting EGFR Pathway. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2020, 112, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.E.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.S.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Cho, S.J.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, J.H. Quality of science and reporting of radiomics in oncologic studies: Room for improvement according to radiomics quality score and TRIPOD statement. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwanenburg, A.; Vallieres, M.; Abdalah, M.A.; Aerts, H.; Andrearczyk, V.; Apte, A.; Ashrafinia, S.; Bakas, S.; Beukinga, R.J.; Boellaard, R.; et al. The Image Biomarker Standardization Initiative: Standardized Quantitative Radiomics for High-Throughput Image-based Phenotyping. Radiology 2020, 295, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Patients’ Cohort (n = 162 Patients) | |
|---|---|
| Feature | Median (Range)-# (%) |
| Age (years) | 62 (39–82) |
| Sex | |
| Male | 100 (61.7%) |
| Female | 62 (38.3%) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.4 (18.0–40.3) |
| Number of liver metastases per patient | 2 (1–5) |
| Size of liver metastases (mm) | 32 (10–71) |
| Preoperative chemotherapy | 124 (76.5%) |
| >6 cycles | 69 (42.6%) |
| Interval between CT and surgery (days) | 23 (1–65) |
| VOIs | |
| Number of analyzed Tumor VOIs | 409 |
| Volume of metastases (mL, Tumor VOI) | 4.1 (0.55–380) |
| Number of analyzed Margin VOIs | 409 |
| Volume of Margin VOI (mL) | 9.6 (3.4–107.2) |
| Number of analyzed Liver VOIs | 162 |
| Volume of Liver VOI (mL) | 1.96 (fixed value) |
| Class | Feature | Pre-Contrast Phase (Mean ± SD) | Portal Phase (Mean ± SD) | p | Class | Feature | Pre-Contrast Phase (Mean ± SD) | Portal Phase (Mean ± SD) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional (Intensity) | MIN | −73 ± 171 | −14 ± 94 | <0.001 | Gray-Level Run Length Matrices (GLRLM) | GLRLM_SRE | 0.87 ± 0.03 | 0.89 ± 0.03 | <0.001 |
| MEAN | 39 ± 30 | 71 ± 25 | <0.001 | GLRLM_LRE | 1.72 ± 0.28 | 1.64 ± 0.24 | <0.001 | ||
| STD. DEVIATION | 24 ± 32 | 22 ± 10 | <0.001 | GLRLM_LGRE | 1.01 × 10−4 ± 7.89 × 10−5 | 866 × 10−5± 5.02 × 10−6 | <0.001 | ||
| MAX | 127 ± 133 | 163 ± 100 | <0.001 | GLRLM_HGRE | 10,933.98 ± 515.11 | 11,619.98 ± 531.51 | <0.001 | ||
| Q1 | 26 ± 51 | 57 ± 24 | <0.001 | GLRLM_SRLGE | 8.90 × 10−5 ± 7.70 × 10−5 | 7.66 × 10−5± 4.79 × 10−6 | <0.001 | ||
| Q2 | 41 ± 22 | 70 ± 25 | <0.001 | GLRLM_SRHGE | 9558 ± 625 | 10,297 ± 678 | <0.001 | ||
| Q3 | 53 ± 18 | 85 ± 26 | <0.001 | GLRLM_LRLGE | 1.68 × 10−4 ± 9.21 × 10−5 | 1.43 × 10−4 ± 2.35 × 10−5 | <0.001 | ||
| First Order | HISTO_Skewness | −0.29 ± 2.08 | 0.14 ± 1.19 | <0.001 | GLRLM_LRHGE | 18,797 ± 3034 | 18,998 ± 2652 | 0.317 | |
| HISTO_Kurtosis | 11.16 ± 28.13 | 5.85 ± 17.82 | 0.013 | GLRLM_GLNU | 704 ± 1422 | 855 ± 1868 | 0.197 | ||
| HISTO_Entropy_log10 | 0.85 ± 0.14 | 0.93 ± 0.10 | <0.001 | GLRLM_RLNU | 3500 ± 6687 | 3696 ± 6933 | 0.684 | ||
| HISTO_Entropy_log2 | 2.83 ± 0.47 | 3.08 ± 0.34 | <0.001 | GLRLM_RP | 0.84 ± 0.05 | 0.85 ± 0.04 | <0.001 | ||
| HISTO_Energy (=Uniformity) | 0.18 ± 0.04 | 0.14 ± 0.03 | <0.001 | Gray-Level Zone Length Matrices (GLZLM) | GLZLM_SZE | 0.60 ± 0.06 | 0.58 ± 0.05 | <0.001 | |
| Gray-Level Colocalization Matrices (GLCM) | GLCM_Homogeneity (=inverse difference) | 0.51 ± 0.06 | 0.49 ± 0.05 | <0.001 | GLZLM_LZE | 12,042 ± 29,885 | 9120 ± 30,290 | 0.005 | |
| GLCM_Energy (=Angular second moment) | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | <0.001 | GLZLM_LGZE | 1.14 × 10−4 ± 2.12 × 10−4 | 8.61 × 10−5 ± 1.53 × 10−5 | <0.001 | ||
| GLCM_Contrast (=Variance) | 18.8 ± 180.71 | 6.24 ± 6.51 | <0.001 | GLZLM_HGZE | 10,906 ± 763 | 11,779 ± 539 | <0.001 | ||
| GLCM_Correlation | 0.30 ± 0.15 | 0.37 ± 0.14 | <0.001 | GLZLM_SZLGE | 7.47 × 10−5 ± 1.97 × 10−4 | 5.02 × 10−5 ± 1.21 × 10−5 | <0.001 | ||
| GLCM_Entropy_log10 | 1.62 ± 0.23 | 1.73 ± 0.19 | <0.001 | GLZLM_SZHGE | 6519 ± 680 | 6867 ± 642 | <0.001 | ||
| GLCM_Entropy_log2(=Joint entropy) | 5.37 ± 0.77 | 5.37 ± 0.77 | <0.001 | GLZLM_LZLGE | 1.11 ± 2.74 | 0.80 ± 2.64 | 0.002 | ||
| GLCM_Dissimilarity | 1.83 ± 2.69 | 1.78 ± 0.52 | <0.001 | GLZLM_LZHGE | 1.31 × 108 ± 3.26 × 10−8 | 1.04 × 108 ± 3.49 × 10−8 | 0.011 | ||
| NGLDM | NGLDM_Coarseness | 8.47 ± 1.14 | 1.00 ± 1.49 | 0.350 | GLZLM_GLNU | 112.06 ± 63 | 58 ± 82.71 | 0.473 | |
| NGLDM_Contrast | 0.06 ± 0.11 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | <0.001 | GLZLM_ZLNU | 218 ± 403 | 211 ± 336 | 0.783 | ||
| NGLDM_Busyness | 0.34 ± 0.54 | 0.29 ± 0.46 | 0.266 | GLZLM_ZP | 0.14 ± 0.08 | 0.16 ± 0.08 | 0.004 |
| Class | Feature | Pre-Contrast Phase (Mean ± SD) | Portal Phase (Mean ± SD) | p | Class | Feature | Pre-Contrast Phase (Mean ± SD) | Portal Phase (Mean ± SD) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional (Intensity) | MIN | −127 ± 232 | −43 ± 162 | <0.001 | Gray-level run Length matrices (GLRLM) | GLRLM_SRE | 0.87 ± 0.03 | 0.87 ± 0.03 | 0.023 |
| MEAN | 45 ± 23 | 103 ± 21 | <0.001 | GLRLM_LRE | 1.75 ± 0.23 | 1.72 ± 0.21 | 0.046 | ||
| STD. DEVIATION | 27 ± 38 | 24 ± 23 | <0.001 | GLRLM_LGRE | 1.05 × 10−4 ± 1.16 × 10−4 | 8.62 × 10−5 ± 7.46 × 10−5 | <0.001 | ||
| MAX | 136 ± 171 | 206 ± 167 | <0.001 | GLRLM_HGRE | 11,067.4 ± 378.82 | 12,307.37 ± 440.84 | <0.001 | ||
| Q1 | 36 ± 33 | 93 ± 20 | <0.001 | GLRLM_SRLGE | 9.21 × 10−5 ± 1.08 × 10−4 | 7.56 × 10−5 ± 6.85 × 10−5 | <0.001 | ||
| Q2 | 49 ± 11 | 105 ± 19 | <0.001 | GLRLM_SRHGE | 9609.64 ± 454.57 | 10,745.25 ± 527.76 | <0.001 | ||
| Q3 | 60 ± 11 | 117 ± 19 | <0.001 | GLRLM_LRLGE | 1.76 × 10−4 ± 1.63 × 10−4 | 1.46 × 10−4± 1.10 × 10−4 | <0.001 | ||
| First Order | HISTO_Skewness | −1.00 ± 2.42 | −0.68 ± 1.79 | 0.034 | GLRLM_LRHGE | 19,381.46 ± 2681.14 | 21,141.18 ± 2710.60 | <0.001 | |
| HISTO_Kurtosis | 14.62 ± 29.94 | 10.94 ± 26.47 | 0.002 | GLRLM_GLNU | 1198.74 ± 1220.89 | 1061.56 ± 1051.90 | 0.089 | ||
| HISTO_Entropy_log10 | 0.85 ± 0.12 | 0.89 ± 0.11 | <0.001 | GLRLM_RLNU | 5238.95 ± 5155.42 | 5329.76 ± 5355.55 | 0.807 | ||
| HISTO_Entropy_log2 | 2.83 ± 0.41 | 2.95 ± 0.35 | <0.001 | GLRLM_RP | 0.83 ± 0.04 | 0.84 ± 0.03 | 0.025 | ||
| HISTO_Energy (=Uniformity) | 0.18 ± 0.04 | 0.16 ± 0.04 | <0.001 | Gray-Level Zone Length Matrices (GLZLM) | GLZLM_SZE | 0.61 ± 0.04 | 0.59 ± 0.03 | <0.001 | |
| Gray-Level Colocalization Matrices (GLCM) | GLCM_Homogeneity (=inverse difference) | 0.52 ± 0.05 | 0.51 ± 0.05 | 0.008 | GLZLM_LZE | 11,321.33 ± 15,687.66 | 8373.28 ± 10,870.41 | 0.001 | |
| GLCM_Energy (=Angular second moment) | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | <0.001 | GLZLM_LGZE | 1.24 × 10−4 ± 1.93 × 10−4 | 9.26 × 10−5 ± 1.26 × 10−4 | <0.001 | ||
| GLCM_Contrast (=Variance) | 12.12 ± 54.31 | 6.21 ± 12.81 | 0.021 | GLZLM_HGZE | 10,901.23 ± 786.09 | 12,177.28 ± 616.16 | <0.001 | ||
| GLCM_Correlation | 0.34 ± 0.16 | 0.38 ± 0.12 | <0.001 | GLZLM_SZLGE | 7.95 × 10−5 ± 1.39 × 10−4 | 5.56 × 10−5 ± 7.45 × 10−5 | <0.001 | ||
| GLCM_Entropy_log10 | 1.63 ± 0.21 | 1.69 ± 1.18 | <0.001 | GLZLM_SZHGE | 6576.90 ± 546.54 | 7209.92 ± 477.19 | <0.001 | ||
| GLCM_Entropy_log2(=Joint entropy) | 5.42 ± 0.68 | 5.63 ± 0.61 | <0.001 | GLZLM_LZLGE | 1.02 ± 1.41 | 0.68 ± 0.89 | <0.001 | ||
| GLCM_Dissimilarity | 1.67 ± 1.01 | 1.63 ± 0.37 | 0.019 | GLZLM_LZHGE | 1.26 × 108 ± 1.74 × 10−8 | 1.03 × 108 ± 1.33 × 10−8 | 0.039 | ||
| NGLDM | NGLDM_Coarseness | 1.55 × 10−3± 1.23 × 10−3 | 1.79 × 10−3± 1.79 × 10−3 | 0.026 | GLZLM_GLNU | 105.01 ± 101.20 | 98.23 ± 94.25 | 0.327 | |
| NGLDM_Contrast | 0.04 ± 0.16 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.039 | GLZLM_ZLNU | 366.34 ± 417.51 | 363.53 ± 387.52 | 0.921 | ||
| NGLDM_Busyness | 0.46 ± 0.46 | 0.33 ± 0.27 | <0.001 | GLZLM_ZP | 0.12 ± 0.05 | 0.13 ± 0.04 | 0.016 |
| Class | Feature | Pre-Contrast Phase (Mean ± SD) | Portal Phase (Mean ± SD) | p | CLASS | Class | Feature | Pre-Contrast Phase (Mean ± SD) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional (Intensity) | MIN | −1 ± 77 | 59 ± 23 | <0.001 | Gray-level Run length Matrices (GLRLM) | GLRLM_SRE | 0.85 ± 0.03 | 0.86 ± 0.03 | 0.602 |
| MEAN | 54 ± 12 | 106 ± 20 | <0.001 | GLRLM_LRE | 1.87 ± 0.28 | 1.85 ± 0.26 | 0.486 | ||
| STD. DEVIATION | 15 ± 9 | 15 ± 3 | 0.011 | GLRLM_LGRE | 8.96 × 10−5 ± 5.79 × 10−6 | 8.11 × 10−5 ± 2.99 × 10−6 | <0.001 | ||
| MAX | 102 ± 25 | 167 ± 31 | <0.001 | GLRLM_HGRE | 11,232 ± 257 | 12,364 ± 440 | <0.001 | ||
| Q1 | 45 ± 12 | 96 ± 20 | <0.001 | GLRLM_SRLGE | 7.65 × 10−5 ± 6.24 × 10−6 | 6.93 × 10−5 ± 3.41 × 10−6 | <0.001 | ||
| Q2 | 54 ± 12 | 106± 20 | <0.001 | GLRLM_SRHGE | 9586 ± 439 | 10,577 ± 541 | <0.001 | ||
| Q3 | 64 ± 14 | 115 ± 20 | <0.001 | GLRLM_LRLGE | 1.67 × 10−4 ± 2.64 × 10−5 | 1.50 × 10−4 ± 2.15 × 10−5 | <0.001 | ||
| First Order | HISTO_Skewness | −0.07 ± 0.63 | 0.24 ± 0.41 | <0.001 | GLRLM_LRHGE | 20,976 ± 3240 | 22,812 ± 3252 | <0.001 | |
| HISTO_Kurtosis | 3.55 ± 4.41 | 3.73 ± 1.13 | <0.001 | GLRLM_GLNU | 188 ± 43 | 185 ± 41 | 0.506 | ||
| HISTO_Entropy_log10 | 0.76 ± 0.11 | 0.78 ± 0.08 | 0.201 | GLRLM_RLNU | 687 ± 211 | 703 ± 221 | 0.515 | ||
| HISTO_Entropy_log2 | 2.53 ± 0.35 | 2.57 ± 0.28 | 0.201 | GLRLM_RP | 0.81 ± 0.04 | 0.81 ± 0.04 | 0.551 | ||
| HISTO_ENERGY (=Uniformity) | 0.21 ± 0.05 | 0.20 ± 0.04 | 0.230 | Gray-Level Zone Length Matrices (GLZLM) | GLZLM_SZE | 0.60 ± 0.04 | 0.59 ± 0.04 | 0.006 | |
| Gray-level Colocalization Matrices (GLCM) | GLCM_Homogeneity (=Inverse difference) | 0.53 ± 0.06 | 0.53 ± 0.05 | 0.229 | GLZLM_LZE | 2700 ± 1929 | 2506 ± 1897 | 0.024 | |
| GLCM_Energy (=Angular second moment) | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.109 | GLZLM_LGZE | 9.21 × 10−5 ± 3.57 × 10−5 | 8.09 × 10−5 ± 3.04 × 10−6 | <0.001 | ||
| GLCM_Contrast (=Variance) | 4.23 ± 7.32 | 3.71 ± 1.50 | 0.377 | GLZLM_HGZE | 11,222 ± 313 | 12,406 ± 456 | <0.001 | ||
| GLCM_Correlation | 0.17 ± 0.07 | 0.21 ± 0.08 | <0.001 | GLZLM_SZLGE | 5.60 × 10−5 ± 2.90 × 10−5 | 4.77 × 10−5 ± 4.20 × 10−6 | <0.001 | ||
| GLCM_Entropy_log10 | 1.50 ± 0.21 | 1.53 ± 0.17 | 0.135 | GLZLM_SZHGE | 6757 ± 471 | 7309 ± 591 | <0.001 | ||
| GLCM_Entropy_log2 (=Joint entropy) | 4.97 ± 0.68 | 5.08 ± 0.55 | 0.135 | GLZLM_LZLGE | 0.24 ± 0.17 | 0.20 ± 0.15 | 0.043 | ||
| GLCM_Dissimilarity | 1.45 ± 0.58 | 1.45 ± 0.30 | 0.936 | GLZLM_LZHGE | 3.04 × 107 ± 2.18 × 10−7 | 3.10 × 107 ± 2.36 × 10−7 | 0.817 | ||
| NGLDM | NGLDM_Coarseness | 0.01 ± 0 | 0.01 ± 0 | 0.964 | GLZLM_GLNU | 17.42 ± 4.68 | 16.65 ± 4.83 | 0.151 | |
| NGLDM_Contrast | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.009 | GLZLM_ZLNU | 43.68 ± 54.59 | 40.75 ± 22.18 | 0.531 | ||
| NGLDM_Busyness | 0.15 ± 0.04 | 0.13 ± 0.04 | <0.001 | GLZLM_ZP | 0.10 ± 0.05 | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 0.856 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fiz, F.; Costa, G.; Gennaro, N.; la Bella, L.; Boichuk, A.; Sollini, M.; Politi, L.S.; Balzarini, L.; Torzilli, G.; Chiti, A.; et al. Contrast Administration Impacts CT-Based Radiomics of Colorectal Liver Metastases and Non-Tumoral Liver Parenchyma Revealing the “Radiological” Tumour Microenvironment. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11071162
Fiz F, Costa G, Gennaro N, la Bella L, Boichuk A, Sollini M, Politi LS, Balzarini L, Torzilli G, Chiti A, et al. Contrast Administration Impacts CT-Based Radiomics of Colorectal Liver Metastases and Non-Tumoral Liver Parenchyma Revealing the “Radiological” Tumour Microenvironment. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(7):1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11071162
Chicago/Turabian StyleFiz, Francesco, Guido Costa, Nicolò Gennaro, Ludovico la Bella, Alexandra Boichuk, Martina Sollini, Letterio S. Politi, Luca Balzarini, Guido Torzilli, Arturo Chiti, and et al. 2021. "Contrast Administration Impacts CT-Based Radiomics of Colorectal Liver Metastases and Non-Tumoral Liver Parenchyma Revealing the “Radiological” Tumour Microenvironment" Diagnostics 11, no. 7: 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11071162
APA StyleFiz, F., Costa, G., Gennaro, N., la Bella, L., Boichuk, A., Sollini, M., Politi, L. S., Balzarini, L., Torzilli, G., Chiti, A., & Viganò, L. (2021). Contrast Administration Impacts CT-Based Radiomics of Colorectal Liver Metastases and Non-Tumoral Liver Parenchyma Revealing the “Radiological” Tumour Microenvironment. Diagnostics, 11(7), 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11071162









