Diagnosis of Early Mycosis Fungoides
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. General Features of Early MF for Diagnosis
3. Algorithm for Diagnosis of Early Mycosis Fungoides
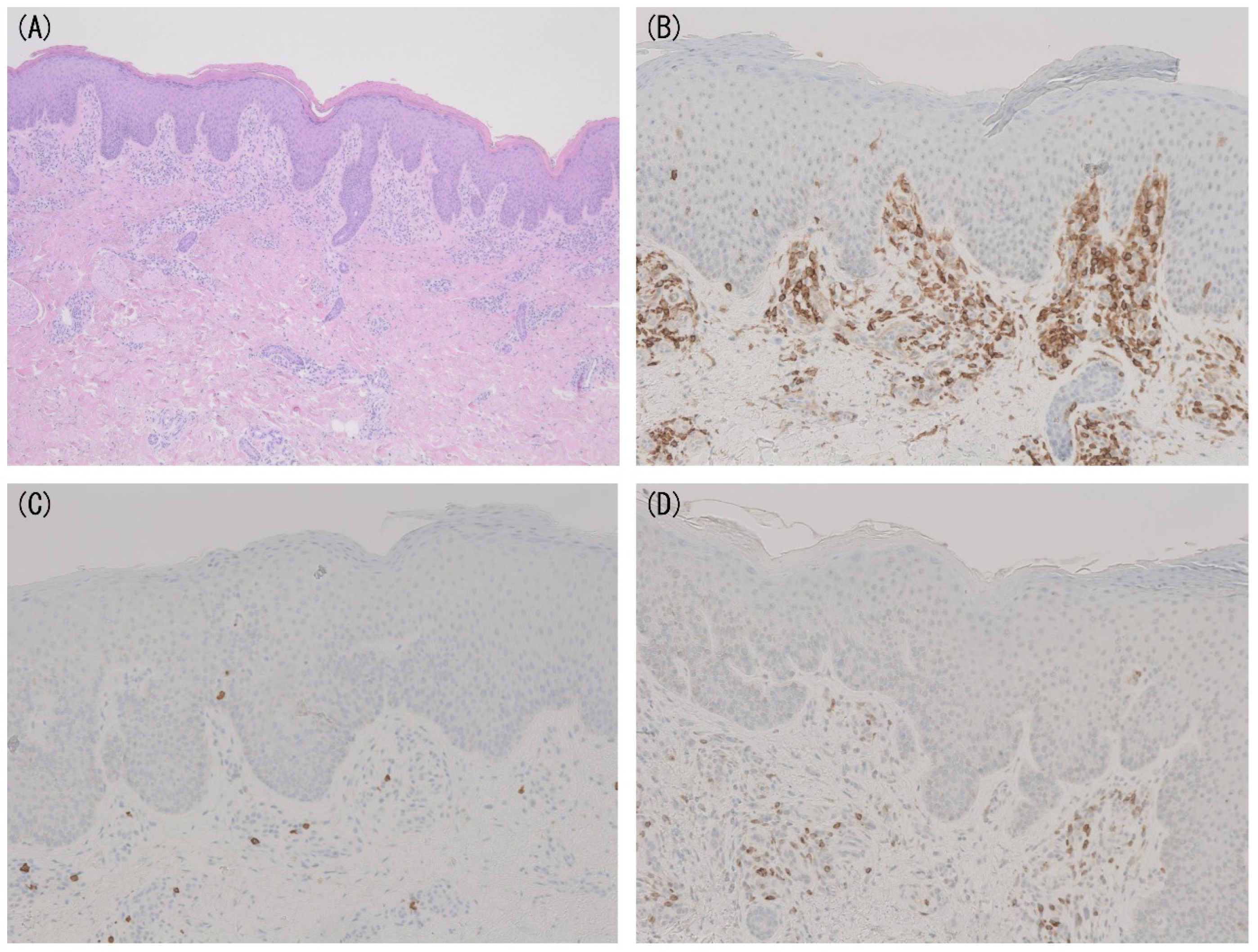
4. Novel Diagnostic Markers of Early MF
5. Next-Generation High-Throughput Sequencing
6. MicroRNA for the Diagnosis of Early MF
7. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Willemze, R.; Jaffe, E.S.; Burg, G.; Cerroni, L.; Berti, E.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Ralfkiaer, E.; Chimenti, S.; Diaz-Perez, J.L.; Duncan, L.M.; et al. WHO-EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood 2005, 105, 3768–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujii, K.; Hamada, T.; Shimauchi, T.; Asai, J.; Fujisawa, Y.; Ihn, H.; Katoh, N. Cutaneous lymphoma in Japan, 2012–2017: A nationwide study. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2020, 97, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuka, M.; Hamada, T.; Miyagaki, T.; Shimauchi, T.; Yonekura, K.; Kiyohara, E.; Fujita, H.; Izutsu, K.; Okuma, K.; Kawai, K.; et al. Outlines of the Japanese guidelines for the management of primary cutaneous lymphomas. J. Dermatol. 2021, 48, e49–e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemze, R.; Cerroni, L.; Kempf, W.; Berti, E.; Facchetti, F.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Jaffe, E.S. The 2018 update of the WHO-EORTC classification for primary cutaneous lymphomas. Blood 2019, 133, 1703–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agar, N.S.; Wedgeworth, E.; Crichton, S.; Mitchell, T.; Cox, M.; Ferreira, S.; Robson, A.; Calonje, E.; Stefanato, C.M.; Wain, E.M.; et al. Survival Outcomes and Prognostic Factors in Mycosis Fungoides/Sézary Syndrome: Validation of the Revised International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas/European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Staging Proposal. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4730–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaglino, P.; Pimpinelli, N.; Berti, E.; Calzavara-Pinton, P.; Alfonso Lombardo, G.; Rupoli, S.; Alaibac, M.; Bottoni, U.; Carbone, A.; Fava, P.; et al. Time course, clinical pathways, and long-term hazards risk trends of disease progression in patients with classic mycosis fungoides: A multicenter, retrospective follow-up study from the Italian Group of Cutaneous Lymphomas. Cancer 2012, 118, 5830–5839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilson, D.; Whittaker, S.; Child, F.; Scarisbrick, J.; Illidge, T.; Parry, E.; Mustapa, M.M.; Exton, L.; Kanfer, E.; Rezvani, K.; et al. British Association of Dermatologists and U.K. Cutaneous Lymphoma Group guidelines for the management of primary cutaneous lymphomas. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 180, 496–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willemze, R.; Hodak, E.; Zinzani, P.L.; Specht, L.; Ladetto, M. Primary cutaneous lymphomas: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, iv149–iv154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta-Shah, N.; Horwitz, S.M.; Ansell, S.; Ai, W.Z.; Barnes, J.; Barta, S.K.; Clemens, M.W.; Dogan, A.; Fisher, K.; Goodman, A.M.; et al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Primary Cutaneous Lymphomas, Version 2.2020: Featured Updates to the NCCN Guidelines. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2020, 18, 522–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zackheim, H.S.; Koo, J.; LeBoit, P.E.; McCalmont, T.H.; Bowman, P.H.; Kashani-Sabet, M.; Jones, C.; Zehnder, J. Psoriasiform mycosis fungoides with fatal outcome after treatment with cyclosporine. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2002, 47, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugaya, M. Is blocking IL-4 receptor alpha beneficial for patients with mycosis fungoides or Sézary syndrome? J. Dermatol. 2021, 48, e225–e226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Cabala, C.A. Diagnosis of T-cell lymphoid proliferations of the skin: Putting all the pieces together. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmo, A.; Patrizi, A.; Bardazzi, F.; Pileri, A. Erythroderma: Psoriasis or lymphoma? A diagnostic challenge and therapeutic pitfall. Ital. J. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodak, E.; Amitay-Laish, I. Mycosis fungoides: A great imitator. Clin. Dermatol. 2019, 37, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitteldorf, C.; Stadler, R.; Sander, C.A.; Kempf, W. Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides. JDDG J. Der Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2018, 16, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zackheim, H.S.; Kashani-Sabet, M.; Amin, S. Topical Corticosteroids for Mycosis Fungoides. Arch. Dermatol. 1998, 134, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pimpinelli, N.; Olsen, E.A.; Santucci, M.; Vonderheid, E.; Haeffner, A.C.; Stevens, S.; Burg, G.; Cerroni, L.; Dreno, B.; Glusac, E.; et al. Defining early mycosis fungoides. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2005, 53, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, S.R.; Chandler, W.M.; Abuzeid, M.; Hossler, E.W.; Ferringer, T.; Elston, D.M.; LeBoit, P.E. Eosinophils in mycosis fungoides: An uncommon finding in the patch and plaque stages. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2012, 34, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuckols, J.D.; Shea, C.R.; Horenstein, M.G.; Burchette, J.L.; Prieto, V.G. Quantitation of intraepidermal T-cell subsets in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue helps in the diagnosis of mycosis fungoides. J. Cutan. Pathol. 1999, 26, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.; Fullen, D.; Carlson, J.A. Low CD7 expression in benign and malignant cutaneous lymphocytic infiltrates: Experience with an antibody reactive with paraffin-embedded tissue. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2002, 24, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, G.S.; Hong, S.R.; Sasaki, D.T.; Abel, E.A.; Hoppe, R.T.; Warnke, R.A.; Morhenn, V.B. Leu-8/CD7 antigen expression by CD3+ T cells: Comparative analysis of skin and blood in mycosis fungoides/Sézary syndrome relative to normal blood values. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1990, 22, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcó, N.; Servitje, O.; Llucià, M.; Bertran, J.; Limón, A.; Carmona, M.; Romagosa, V.; Peyrí, J. Genotypic analysis of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: A comparative study of Southern blot analysis with polymerase chain reaction amplification of the T-cell receptor-gamma gene. Br. J. Dermatol. 1997, 137, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, G.S. Analysis of clonality in cutaneous T cell lymphoma and associated diseases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 941, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schachter, O.; Tabibian-Keissar, H.; Debby, A.; Segal, O.; Baum, S.; Barzilai, A. Evaluation of the polymerase chain reaction–based T-cell receptor β clonality test in the diagnosis of early mycosis fungoides. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 83, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, N.; Flaig, M.J.; Yazdi, A.S.; Sander, C.A. The value of molecular analysis by PCR in the diagnosis of cutaneous lymphocytic infiltrates. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2002, 29, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, A.; Takahama, H.; Kato, T.; Kubota, Y.; Kurokawa, K.; Nishioka, K.; Mizoguchi, M.; Yamamoto, K. Clonotypic Analysis of T Cells Infiltrating the Skin of Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: Evidence for Antigen-Driven Accumulation of T Cells. Hum. Immunol. 1996, 48, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guitart, J.; Magro, C. Cutaneous T-cell lymphoid dyscrasia: A unifying term for idiopathic chronic dermatoses with persistent T-cell clones. Arch. Dermatol. 2007, 143, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurber, S.E.; Zhang, B.; Kim, Y.H.; Schrijver, I.; Zehnder, J.; Kohler, S. T-cell clonality analysis in biopsy specimens from two different skin sites shows high specificity in the diagnosis of patients with suggested mycosis fungoides. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2007, 57, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandergriff, T.; Nezafati, K.A.; Susa, J.; Karai, L.; Sanguinetti, A.; Hynan, L.; Ambruzs, J.M.; Oliver, D.H.; Pandya, A.G. Defining early mycosis fungoides: Validation of a diagnostic algorithm proposed by the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2015, 42, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, G.M.; Quintella, D.C.; Niemeyer-Corbellini, J.P.; Ferreira, L.C.; Ramos-E-Silva, M.; Cuzzi, T. Validation of an algorithm based on clinical, histopathological and immunohistochemical data for the diagnosis of early-stage mycosis fungoides. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2020, 95, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuraitis, D.; McBurney, E.; Boh, E. Utility of clonal T-cell rearrangement study in the diagnosis of early mycosis fungoides. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 85, 1040–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; He, X.; Dave, V.P.; Zhang, Y.; Hua, X.; Nicolas, E.; Xu, W.; Roe, B.A.; Kappes, D.J. The zinc finger transcription factor Th-POK regulates CD4 versus CD8 T-cell lineage commitment. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 433, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, R.; Huang, Y.; Su, M.; Xiao, C.; Martinka, M.; Dutz, J.P.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Molecular markers of early-stage mycosis fungoides. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 1698–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morimura, S.; Sugaya, M.; Suga, H.; Miyagaki, T.; Ohmatsu, H.; Fujita, H.; Asano, Y.; Tada, Y.; Kadono, T.; Sato, S. TOX expression in different subtypes of cutaneous lymphoma. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2014, 306, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Luo, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Q. TOX Acts an Oncological Role in Mycosis Fungoides. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, A.M.; Jansen, P.M.; Willemze, R. TOX expression in cutaneous T-cell lymphomas: An adjunctive diagnostic marker that is not tumour-specific and not restricted to the CD4(+) CD8(−) phenotype. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 175, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGirt, L.; Degesys, C.; Johnson, V.; Zic, J.; Zwerner, J.; Eischen, C. TOX expression and role in CTCL. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2016, 30, 1497–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ibrahim, M.A.-H.; Mohamed, A.; Soltan, M. Thymocyte selection–associated high-mobility group box as a potential diagnostic marker differentiating hypopigmented mycosis fungoides from early vitiligo: A pilot study. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, Y.; Mashima, E.; Saito-Sasaki, N.; Nakamura, M. The Role of Cell Adhesion Molecule 1 (CADM1) in Cutaneous Malignancies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, H.; Nishikata, I.; Shiraga, T.; Akamatsu, E.; Fukami, T.; Hidaka, T.; Kubuki, Y.; Okayama, A.; Hamada, K.; Okabe, H.; et al. Overexpression of a cell adhesion molecule, TSLC1, as a possible molecular marker for acute-type adult T-cell leukemia. Blood 2004, 105, 1204–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahata, S.; Morishita, K. CADM1/TSLC1 is a novel cell surface marker for adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. J. Clin. Exp. Hematop. 2012, 52, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuki, A.; Shinkuma, S.; Hayashi, R.; Fujikawa, H.; Kato, T.; Homma, E.; Hamade, Y.; Onodera, O.; Matsuoka, M.; Shimizu, H.; et al. CADM1 is a diagnostic marker in early-stage mycosis fungoides: Multicenter study of 58 cases. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 79, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, W.-K.; Armstrong, R.; Arai, S.; Desmarais, C.; Hoppe, R.; Kim, Y.H. Minimal Residual Disease Monitoring with High-Throughput Sequencing of T Cell Receptors in Cutaneous T Cell Lymphoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 214ra171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sufficool, K.E.; Lockwood, C.M.; Abel, H.J.; Hagemann, I.S.; Schumacher, J.A.; Kelley, T.W.; Duncavage, E.J. T-cell clonality assessment by next-generation sequencing improves detection sensitivity in mycosis fungoides. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 73, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kirsch, I.R.; Watanabe, R.; O’Malley, J.T.; Williamson, D.W.; Scott, L.-L.; Elco, C.P.; Teague, J.E.; Gehad, A.; Lowry, E.L.; LeBoeuf, N.R.; et al. TCR sequencing facilitates diagnosis and identifies mature T cells as the cell of origin in CTCL. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 308ra158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Masson, A.; O’Malley, J.T.; Elco, C.P.; Garcia, S.S.; DiVito, S.J.; Lowry, E.L.; Tawa, M.; Fisher, D.C.; Devlin, P.M.; Teague, J.E.; et al. High-throughput sequencing of the T cell receptor β gene identifies aggressive early-stage mycosis fungoides. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaar5894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rea, B.; Haun, P.; Emerson, R.; Vignali, M.; Farooqi, M.; Samimi, S.; Elenitsas, R.; Kirsch, I.; Bagg, A. Role of high-throughput sequencing in the diagnosis of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J. Clin. Pathol. 2018, 71, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, C.; Boisson, M.; Ram-Wolff, C.; Sadoux, A.; Louveau, B.; Vignon-Pennamen, M.; Rivet, J.; Cayuela, J.; Dobos, G.; Moins-Teisserenc, H.; et al. Diagnostic performance of high-throughput sequencing of the T-cell receptor beta gene for the diagnosis of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 185, 679–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluud, M.; Willerslev-Olsen, A.; Gjerdrum, L.M.R.; Lindahl, L.M.; Buus, T.B.; Andersen, M.H.; Bonefeld, C.M.; Krejsgaard, T.; Litvinov, I.V.; Iversen, L.; et al. MicroRNAs in the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, Prognosis and Targeted Treatment of Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphomas. Cancers 2020, 12, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralfkiaer, U.; Hagedorn, P.H.; Bangsgaard, N.; Løvendorf, M.; Ahler, C.B.; Svensson, L.; Kopp, K.L.; Vennegaard, M.T.; Lauenborg, B.; Zibert, J.R.; et al. Diagnostic microRNA profiling in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL). Blood 2011, 118, 5891–5900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marstrand, T.; Ahler, C.B.; Ralfkiaer, U.; Clemmensen, A.; Kopp, K.L.; Sibbesen, N.A.; Krejsgaard, T.; Litman, T.; Wasik, M.A.; Bonefeld, C.M.; et al. Validation of a diagnostic microRNA classifier in cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. Leuk. Lymphoma 2013, 55, 957–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralfkiaer, U.; Lindahl, L.M.; Lindal, L.; Litman, T.; Gjerdrum, L.M.R.; Ahler, C.B.; Gniadecki, R.; Marstrand, T.; Fredholm, S.; Iversen, L.; et al. MicroRNA expression in early mycosis fungoides is distinctly different from atopic dermatitis and advanced cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 7207–7217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dusílková, N.; Bašová, P.; Polívka, J.; Kodet, O.; Kulvait, V.; Pešta, M.; Trněný, M.; Stopka, T. Plasma miR-155, miR-203, and miR-205 are Biomarkers for Monitoring of Primary Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphomas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, X.; Wang, B.; Li, K.; Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Xue, F.; Shi, R.; Zheng, J. MicroRNA Signatures in Diagnosis and Prognosis of Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 2024–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Motamedi, M.; Xiao, M.; Iyer, A.; Gniadecki, R. Patterns of Gene Expression in Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma: Systematic Review of Transcriptomic Studies in Mycosis Fungoides. Cells 2021, 10, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinov, I.; Netchiporouk, E.; Cordeiro, B.; Doré, M.-A.; Moreau, L.; Pehr, K.; Gilbert, M.; Zhou, Y.; Sasseville, D.; Kupper, T.S. The Use of Transcriptional Profiling to Improve Personalized Diagnosis and Management of Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma (CTCL). Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2820–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Criteria | Scoring System |
|---|---|
| Clinical Basic Persistent and/or progressive patches/thin plaques Additional (1) Non-sun-exposed location (2) Size/shape variation (3) Poikiloderma | 2 points for basic criteria and 2 additional criteria 1 point for basic criteria and 1 additional criterion |
| Histopathological Basic Superficial lymphoid infiltrate Additional (1) Epidermotropism without spongiosis (2) Lymphocytic atypia | 2 points for basic criteria and 2 additional criteria 1 point for basic criteria and 1 additional criterion |
| Molecular biology (1) Clonal T-cell receptor rearrangement | 1 point for clonality |
| Immunopathological (Immunohistochemical) (1) <50% CD2+, CD3+, and/or CD5+ T cells (2) <10% CD7+ T cells (3) Epidermal/dermal discordance of CD2, CD3, CD5, or CD7 (T-cell antigen deficiency confined to the epidermis) | 1 point for one or more criteria |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miyagaki, T. Diagnosis of Early Mycosis Fungoides. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1721. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11091721
Miyagaki T. Diagnosis of Early Mycosis Fungoides. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(9):1721. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11091721
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiyagaki, Tomomitsu. 2021. "Diagnosis of Early Mycosis Fungoides" Diagnostics 11, no. 9: 1721. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11091721
APA StyleMiyagaki, T. (2021). Diagnosis of Early Mycosis Fungoides. Diagnostics, 11(9), 1721. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11091721






