Diagnostic Value of Superb Microvascular Imaging in Differentiating Benign and Malignant Breast Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Quality Assessment
2.5. Strategy for Data Synthesis
2.6. Heterogeneity Assessment
3. Results
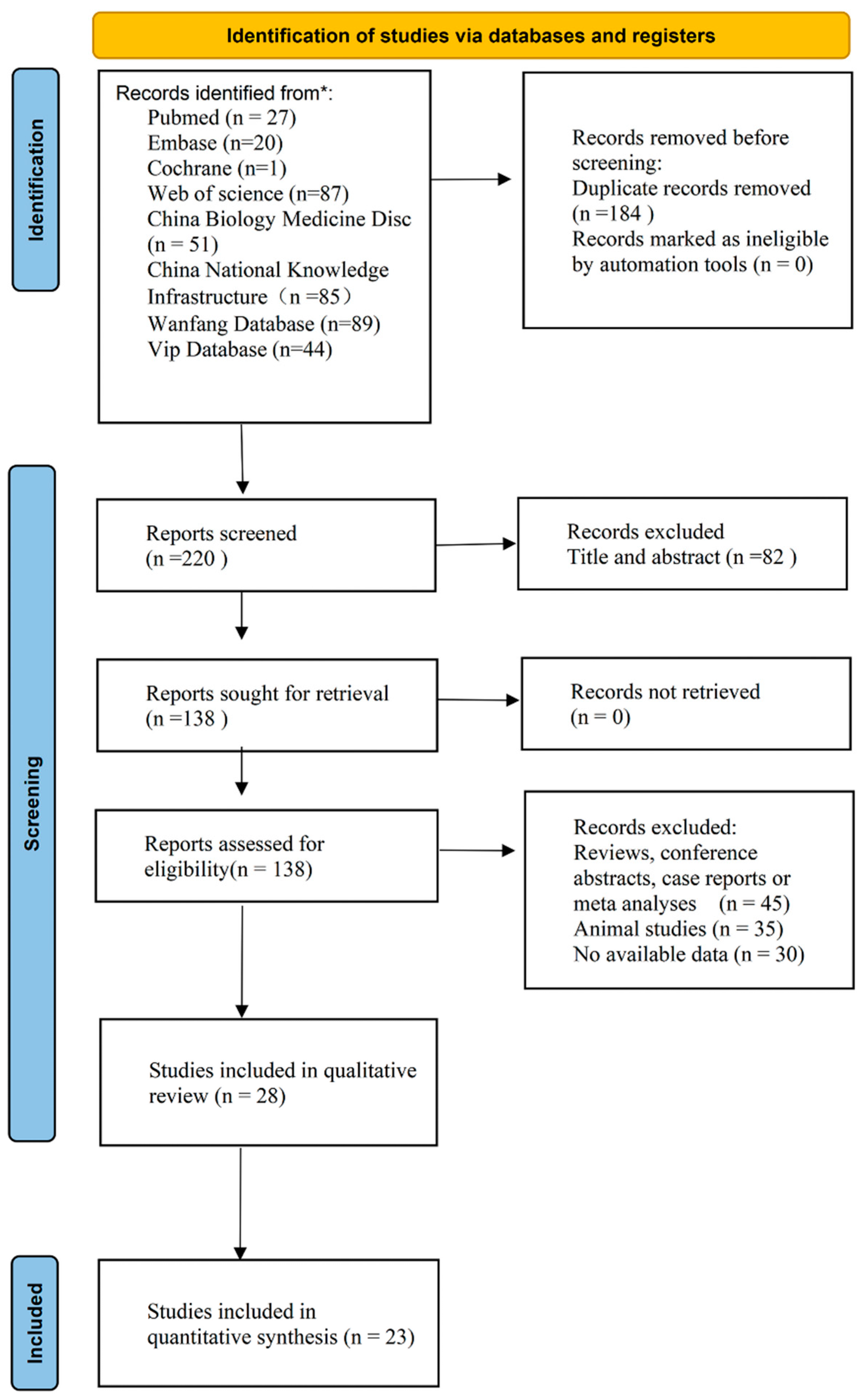
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Quality Assessment
3.4. Quantitative Synthesis
3.4.1. Diagnostic Accuracy Assessment
3.4.2. Assessment of Publication Bias
3.5. Heterogeneity Assessment
4. Discussion
4.1. Principal Results
4.2. Comparison with Previous Systematic Review
4.3. Clinical Implications of our Findings
4.4. Limitations of Our Work
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AC | Alder classification |
| AUC | area under the curve |
| CEUS | contrast-enhanced ultrasonography |
| CI | confidence interval |
| CDFI | color doppler flow imaging |
| DOR | diagnostic odds ratio |
| FP | false positive |
| FN | false negative |
| I2 | inconsistency index square |
| LR | likely ratio |
| OR | odds ratio |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| MVDP | microvascular distribution pattern |
| PDI | power Doppler imaging |
| PV | penetrating vessel |
| SE | standard error |
| SROC | summary receiver operating characteristic curve |
| SMI | superb microvascular imaging |
| VI | vascular index |
| TP | true positive |
| TN | true negative |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joko-Fru, W.Y.; Miranda-Filho, A.; Soerjomataram, I.; Egue, M.; Akele-Akpo, M.T.; N’da, G.; Assefa, M.; Buziba, N.; Korir, A.; Kamate, B.; et al. Breast cancer survival in sub-Saharan Africa by age, stage at diagnosis and human development index: A population-based registry study. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 1208–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmeliet, P.; Jain, R.K. Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 2000, 407, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, A.Y.; Seo, B.K. Up-to-date Doppler techniques for breast tumor vascularity: Superb microvascular imaging and contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Ultrasonography 2018, 37, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, B.P.; Miller, K.D. Angiogenesis of breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol 2005, 23, 1782–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, D.; León-Sosa, A.; Lugo, P.; Suquillo, D.; Torres, F.; Surre, F.; Trojman, L.; Caicedo, A. Breast cancer, screening and diagnostic tools: All you need to know. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2021, 157, 103174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, R.J.; Bostanjoglo, M.; Rademaker, J.; Maeurer, J.; Felix, R. Role of power Doppler techniques and ultrasound contrast enhancement in the differential diagnosis of focal breast lesions. Eur. Radiol. 2003, 13, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.C.; Zu, D.M.; Zhang, Y.; Shan, J.; Shi, X.R.; Deng, S.H.; Jiang, Q. A comparative study on superb microvascular imaging and conventional ultrasonography in differentiating BI-RADS 4 breast lesions. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 3202–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsberg, F.; Kuruvilla, B.; Pascua, M.B.; Chaudhari, M.H.; Merton, D.A.; Palazzo, J.P.; Goldberg, B.B. Comparing contrast-enhanced color flow imaging and pathological measures of breast lesion vascularity. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2008, 34, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokalp, G.; Topal, U.; Kizilkaya, E. Power Doppler sonography: Anything to add to BI-RADS US in solid breast masses? Eur. J. Radiol. 2009, 70, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, M.; Albukhari, A.; Alyami, J.; Mansour, R.F. Ensemble Deep-Learning-Enabled Clinical Decision Support System for Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Classification on Ultrasound Images. Biology 2022, 11, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, A.Y.; Seo, B.K.; Cha, S.H.; Yeom, S.K.; Lee, S.W.; Chung, H.H. An Innovative Ultrasound Technique for Evaluation of Tumor Vascularity in Breast Cancers: Superb Micro-Vascular Imaging. J. Breast Cancer 2016, 19, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.Z.; Huang, Y.H.; Shen, H.L.; Liu, X.T. Clinical Applications of Superb Microvascular Imaging in the Liver, Breast, Thyroid, Skeletal Muscle, and Carotid Plaques. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 38, 2811–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.; Wang, C. Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound superb microvascular imaging for breast tumor: A meta-analysis. Med. Ultrason. 2020, 22, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakdik, S.; Arslan, S.; Oncu, F.; Durmaz, M.S.; Altunkeser, A.; Eryilmaz, M.A.; Unlu, Y. Effectiveness of Superb Microvascular Imaging for the differentiation of intraductal breast lesions. Med. Ultrason. 2018, 20, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, N.; Zhu, Q.L.; Li, J.C.; Sun, Q.; Wang, H.Y.; Jiang, Y.X. Vascular index measured by smart 3-D superb microvascular imaging can help to differentiate malignant and benign breast lesion. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 5481–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongfeng, Z.; Ping, Z.; Wengang, L.; Yang, S.; Shuangming, T. Application of a Novel Microvascular Imaging Technique in Breast Lesion Evaluation. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2016, 42, 2097–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, M.D.F.; Moher, D.; Thombs, B.D.; McGrath, T.A.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Clifford, T.; Cohen, J.F.; Deeks, J.J.; Gatsonis, C.; Hooft, L.; et al. Preferred Reporting Items for a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Studies: The PRISMA-DTA Statement. JAMA 2018, 319, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsubeik, K.; Motilal, S.; Sanchez-Ramos, L.; Ramrattan, L.A.; Kaeley, G.S.; Singh, J.A. Diagnostic accuracy of salivary gland ultrasound in Sjögren’s syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2020, 12, 1759720x20973560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, R.; Cheng, J. Diagnostic accuracy of contrast-enhanced ultrasound to differentiate benign and malignant breast lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2022, 149, 110219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.W.; Lee, J.; Choi, S.H.; Huh, J.; Park, S.H. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Studies Evaluating Diagnostic Test Accuracy: A Practical Review for Clinical Researchers-Part I. General Guidance and Tips. Korean J. Radiol. 2015, 16, 1175–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, K.W.; Choi, S.H.; Huh, J.; Park, S.H. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Studies Evaluating Diagnostic Test Accuracy: A Practical Review for Clinical Researchers-Part II. Statistical Methods of Meta-Analysis. Korean J. Radiol. 2015, 16, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ades, A.E.; Lu, G.; Higgins, J.P. The interpretation of random-effects meta-analysis in decision models. Med. Decis. Mak. 2005, 25, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, C.H.; Park, S.H. Successful Publication of Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Studies Evaluating Diagnostic Test Accuracy. Korean J. Radiol. 2016, 17, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, J.J.; Macaskill, P.; Irwig, L. The performance of tests of publication bias and other sample size effects in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy was assessed. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2005, 58, 882–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Yang, D.W.; Wu, Y.X.; Xue, W.Q.; Li, D.H.; Zhang, J.B.; He, Y.Q.; Jia, W.H. Burden, trends, and risk factors for breast cancer in China from 1990 to 2019 and its predictions until 2034: An up-to-date overview and comparison with those in Japan and South Korea. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, A.; Shin, V.Y.; Ho, J.C.; Kang, E.; Nakamura, S.; Teo, S.H.; Lee, A.S.; Sng, J.H.; Ginsburg, O.M.; Kurian, A.W.; et al. Comprehensive spectrum of BRCA1 and BRCA2 deleterious mutations in breast cancer in Asian countries. J. Med. Genet. 2016, 53, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Cao, M.; Li, H.; He, S.; Chen, W. Cancer burden and trends in China: A review and comparison with Japan and South Korea. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 32, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Chang, Y.W.; Oh, E.; Hwang, J.; Kim, H.J.; Hong, S.S. Reproducibility and diagnostic performance of the vascular index of superb microvascular imaging in real-time breast ultrasonography for evaluating breast masses. Ultrasonography 2021, 40, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, G.; Li, J.; Ren, W.D. The Diagnostic Value of Superb Microvascular Imaging (SMI) in Detecting Blood Flow Signals of Breast Lesions: A Preliminary Study Comparing SMI to Color Doppler Flow Imaging. Medicine 2015, 94, e1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Kang, S.; Wang, X. Application of superb microvascular imaging and CDFI in diagnosis of breast masses. Chin. J. Med. Imaging Technol. 2015, 31, 663–667. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Luo, B.; Guan, X.; WU, H.; Xiao, X. Comparative study of superb microvascular imaging and contrast-enhanced ultrasonographic microvascular imaging in diagnosis of breast tumor. Chin. J. Ultrason. 2016, 25, 608–611. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.Y.; Chen, X.; Guan, X.F.; Wu, H.; Qin, W.; Luo, B.M. Superb microvascular imaging in diagnosis of breast lesions: A comparative study with contrast-enhanced ultrasonographic microvascular imaging. Br. J. Radiol. 2016, 89, 20160546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Chu, W.; Wang, H. Preliminary analysis of diagnostic efficiency of vascular morphology distribution in breast tumor by superb microvascular imaging. Chin. J. Ultrason. 2018, 12, 973–976. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, W. Superb microvascular imaging in diagnosis of benign and malignant breast lesions. Chin. J. Med. Imaging Technol. 2019, 12, 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Diao, X.; Zhan, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Cao, H. Role of Superb Microvascular Imaging in Differentiating Between Malignant and Benign Solid Breast Masses. Clin. Breast Cancer 2020, 20, e786–e793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Ou, B.; Wu, J.; Xiao, X.; Ruan, J.; Tian, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, B.; Yang, H.; Luo, B. Combined use of strain elastography and superb microvascular imaging with grayscale ultrasound according to the BI-RADS classification for differentiating benign from malignant solid breast masses. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2020, 74, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhan, W.; Zhou, Q.; Tao, L.; Yang, Y. The diagnostic value of smart three-dimensional superb microvascular imaging in differentiating benign and malignant breast lesions of BI-RADS 4. J. Diagn. Concepts Pract. 2020, 19, 583. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, Q.; Li, J.; Jiang, Y. Superb Microvascular Imaging Technology Can Improve the Diagnostic Efficiency of the BI-RADS System. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 634752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; An, X.; Yan, J.; Zhang, H. Application of Shear Wave Elastography and Superb Microvascular Imaging on Diagnosis of Benign Breast Lesions and Malignant Tumor. Imaging Sci. Photochem. 2020, 38, 1000. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Ji, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Yu, D.; Tian, J.; Leng, X. Application of shear wave elastography combined with superb micro-vascular imaging in diagnosing benign and malignant breast masses. Chin. J. Ultrason. 2018, 12, 143–146. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, L.; Zhu, W.; Wang, C. Value of Smart 3D SMI in the diagnosis of breast cancer. J. Dalian Med. Univ. 2020, 42, 348–351. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K. Effect of SMI combined with SWE on the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant breast tumors. Heilongjiang Med. Pharm. 2020, 43, 191–192. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, P.; Li, Y. Application value of ultrasound MicroPure imaging combined with superb microvascular imaging in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant nodules of breast. J. Bengbu Med. Coll. 2021, 46, 799–802. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, Q. The value of ultrasonic shear waves combined with superb microvascular imaging in evaluating the nature of breast cancer. Henan Med. Res. 2021, 30, 6657–6660. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Chen, Y.; He, J.; Fang, J.; Lu, Y. Study on the screening and diagnosis value of acoustic pulse radiation force imaging combined with superb microvascular imaging in early breast cancer. Imaging Res. Med. Appl. 2021, 5, 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, W.; Jin, L.; Liu, X.; Huang, S.; Zhou, H. The Diagnostic Value of Ultramicrovascular Imaging Combined with Contrast—enhanced Ultrasonography in the Diagnosis of BI-RADS 4 Breast Masses. Chin. J. ultrasound Med. 2021, 37, 974–978. [Google Scholar]
- Park, A.Y.; Kwon, M.; Woo, O.H.; Cho, K.R.; Park, E.K.; Cha, S.H.; Song, S.E.; Lee, J.H.; Cha, J.; Son, G.S.; et al. A Prospective Study on the Value of Ultrasound Microflow Assessment to Distinguish Malignant from Benign Solid Breast Masses: Association between Ultrasound Parameters and Histologic Microvessel Densities. Korean J. Radiol. 2019, 20, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Chang, Y.W. Combination of Quantitative Parameters of Shear Wave Elastography and Superb Microvascular Imaging to Evaluate Breast Masses. Korean J. Radiol. 2020, 21, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, E.Y.; Yoon, G.Y.; Cha, J.H.; Shin, H.J.; Choi, W.J.; Kim, H.H. Added Value of the Vascular Index on Superb Microvascular Imaging for the Evaluation of Breast Masses: Comparison With Grayscale Ultrasound. J. Ultrasound Med. 2021, 40, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uysal, E.; Öztürk, M.; Kilinçer, A.; Koplay, M. Comparison of the Effectiveness of Shear Wave Elastography and Superb Microvascular Imaging in the Evaluation of Breast Masses. Ultrasound Q 2021, 37, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, F.Z.; Altunkeser, A.; Körez, M.K.; Aksoy, N.; Bayramoğlu, Z.; Karagülle, M. The Importance of Superb Microvascular Imaging for the Differentiation of Malignant Breast Lesions from Benign Lesions. Eur J. Breast Health 2022, 18, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, D.D.; Carson, P.L.; Rubin, J.M.; Quinn-Reid, D. Doppler ultrasound color flow imaging in the study of breast cancer: Preliminary findings. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1990, 16, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Author | Year | Country | Age (Mean, Year) | Size (Mean, mm) | Instrument | Scale (cm/s) | lesions | SD | DC | TP | FP | TN | FN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ma | 2015 | China | 43.7 | 22.4 | Aplio 400 | 1–2 | 123 | Pro | AC | 51 | 27 | 39 | 6 |
| Li | 2015 | China | 44.1 | 18.4 | Aplio 500 | 2.6 | 146 | Retro | AC | 38 | 13 | 86 | 9 |
| Chen | 2016 | China | 44.9 | 17.7 | Aplio 400 | 1–2 | 116 | Retro | MVDP | 42 | 6 | 57 | 11 |
| Fan | 2016 | China | 47.5 | 17.5 | Aplio 500 | 1.2 | 86 | Retro | AC | 37 | 9 | 33 | 7 |
| Zhao | 2016 | China | 44.5 | 14.9 | Aplio 500 | 1.5–2.5 | 135 | Retro | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Xiao | 2016 | China | 44.1 | 18.3 | Aplio 400 | NA | 132 | Retro | MVDP | 45 | 7 | 67 | 13 |
| Xiao | 2018 | China | 47.2 | 19 | Aplio 500 | 1–2 | 105 | Retro | MVDP | 35 | 6 | 60 | 4 |
| Park | 2019 | Korea | 45.6 | 18.7 | Aplio 500 | 3 | 98 | Pro | PV | 33 | 18 | 39 | 8 |
| PARK | 2019 | Korea | 45.6 | 18.7 | Aplio 500 | 3 | 98 | Pro | VI | 33 | 15 | 42 | 8 |
| Zhang | 2019 | China | 44.9 | 23.5 | Aplio 500 | 1.2–1.6 | 236 | Pro | VI | 92 | 39 | 76 | 19 |
| Xue | 2019 | China | NA | NA | Aplio 500 | NA | 300 | Retro | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Chu | 2020 | China | 44.4 | 19.9 | Aplio 500 | 1.2 | 142 | Retro | AC | 57 | 17 | 57 | 11 |
| Jia | 2020 | China | 48 | 22.4 | Aplio 900 | NA | 114 | Retro | MVDP | 35 | 6 | 54 | 19 |
| Wang | 2020 | China | 49.9 | 29.7 | Aplio 500 | 1.2 | 94 | Retro | AC | 32 | 9 | 48 | 5 |
| Diao | 2020 | China | 54.2 | 15.3 | Aplio 500 | 2 | 85 | Retro | PV | 32 | 6 | 40 | 7 |
| DIAO | 2020 | China | 54.2 | 15.3 | Aplio 500 | 2 | 85 | Retro | MVDP | 29 | 6 | 41 | 9 |
| Lee | 2020 | Korea | 49 | 11.3 | Aplio 800 | 2.5 | 200 | Retro | VI | 72 | 42 | 73 | 13 |
| Liang | 2020 | China | 43.9 | 17.4 | Aplio 400 | 1.2 | 177 | Pro | MVDP | 57 | 6 | 93 | 19 |
| Li | 2020 | China | 49.8 | NA | Aplio 500 | NA | 208 | Retro | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Jin | 2021 | China | NA | NA | Aplio 500 | NA | 123 | Retro | AC | 63 | 9 | 36 | 15 |
| Ran | 2021 | China | 49.4 | 20.1 | Aplio 500 | 1.2 | 150 | Pro | AC | 31 | 6 | 100 | 13 |
| Xu | 2021 | China | 53.1 | 27.7 | Aplio 800 | NA | 50 | Retro | AC | 29 | 3 | 9 | 9 |
| Zuo | 2021 | China | NA | 16 | Aplio 400 | NA | 122 | Pro | MVDP | 33 | 8 | 66 | 15 |
| Chae | 2021 | Korea | 54.1 | NA | Aplio 800 | 2.5 | 70 | Retro | VI | 31 | 3 | 31 | 5 |
| Uysal | 2021 | Turkey | 50.5 | NA | Aplio 500 | 3.5 | 121 | Retro | VI | 33 | 26 | 48 | 14 |
| Cai | 2021 | China | 46.1 | 23.5 | Aplio 500 | 1–2 | 238 | Retro | VI | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Lee | 2021 | Korea | 46 | 10.7 | Aplio 800 | 2.5 | 88 | Retro | VI | 30 | 3 | 47 | 8 |
| Aralan | 2022 | Turkey | 49 | 21.9 | Aplio 300 | 1.5–2.5 | 90 | Retro | VI | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Subgroup | Study Sample | Sen [95% CI; I2, %] | Spe [95% CI; I2, %] | PLR [95% CI; I2, %] | NLR [95% CI; I2, %] | DOR [95% CI;] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country | ||||||
| China | 17 | 0.79 [0.76, 0.82; 34.61] | 0.86 * [0.81, 0.90; 82.31] | 5.5 * [4.2, 7.3; 80.03] | 0.24 [0.21, 0.28; 17.43] | 23 * [17,31] |
| Korea or Turkey | 6 | 0.80 [0.75, 0.85; 11.41] | 0.77 * [0.67 0.87; 81.65] | 3.6 * [2.2, 6.0; 63.86] | 0.25 [0.18, 0.34;43.41] | 14 * [7,30] |
| Study Design | ||||||
| Retro | 16 | 0.80 [0.77, 0.83; 22.27] | 0.85 [0.80, 0.88; 78.68] | 5.2 [3.9, 6.9; 68.84] | 0.24 [0.20, 0.27; 32.55] | 22 [15,32] |
| Pro | 7 | 0.79 [0.73, 0.84; 45.12] | 0.82 [0.68, 0.90; 90.85] | 4.3 [2.5, 7.3; 79.40] | 0.26 [0.21, 0.32; 0.00] | 17 [10,29] |
| Diagnostic Basis | ||||||
| AC | 8 | 0.82 [0.77, 0.86; 11.98] | 0.82 [0.77, 0.88; 81.02] | 4.5 [3.1, 6.6; 60.62] | 0.22 [0.18, 0.28; 0.00] | 20 [13,31] |
| PV | 2 | 0.81 [0.71, 0.89] | 0.77 * [0.67, 0.85] | 3.8 * [1.5, 9.6] | 0.25 [0.15, 0.39] | 16 * [5,52] |
| MVDP | 7 | 0.76 [0.70, 0.80; 35.69] | 0.91 * [0.88, 0.93; 0.00] | 8.1 * [6.1, 10.8; 0.00] | 0.27 [0.22, 0.33; 33.58] | 30 * [20,46] |
| VI | 6 | 0.81 [0.77, 0.85; 22.24] | 0.77 [0.64, 0.87; 82.47] | 3.6 [2.1, 6.0; 65.20] | 0.24 [0.18, 0.32; 48.02] | 15 [7,30] |
| Overall | 23 | 0.80 [0.77, 0.84; 28.32] | 0.84 [0.79, 0.88; 84.36] | 4.9 [3.8, 6.3; 76.23] | 0.24 [0.22, 0.27; 17.87] | 20 [15,27] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, J.; Lu, J.; Jin, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Guo, G.; Gong, X. Diagnostic Value of Superb Microvascular Imaging in Differentiating Benign and Malignant Breast Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112648
Feng J, Lu J, Jin C, Chen Y, Chen S, Guo G, Gong X. Diagnostic Value of Superb Microvascular Imaging in Differentiating Benign and Malignant Breast Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(11):2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112648
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Jiaping, Jianghao Lu, Chunchun Jin, Yihao Chen, Sihan Chen, Guoqiang Guo, and Xuehao Gong. 2022. "Diagnostic Value of Superb Microvascular Imaging in Differentiating Benign and Malignant Breast Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Diagnostics 12, no. 11: 2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112648
APA StyleFeng, J., Lu, J., Jin, C., Chen, Y., Chen, S., Guo, G., & Gong, X. (2022). Diagnostic Value of Superb Microvascular Imaging in Differentiating Benign and Malignant Breast Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics, 12(11), 2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112648





