B-Lines Lung Ultrasonography Simulation Using Finite Element Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
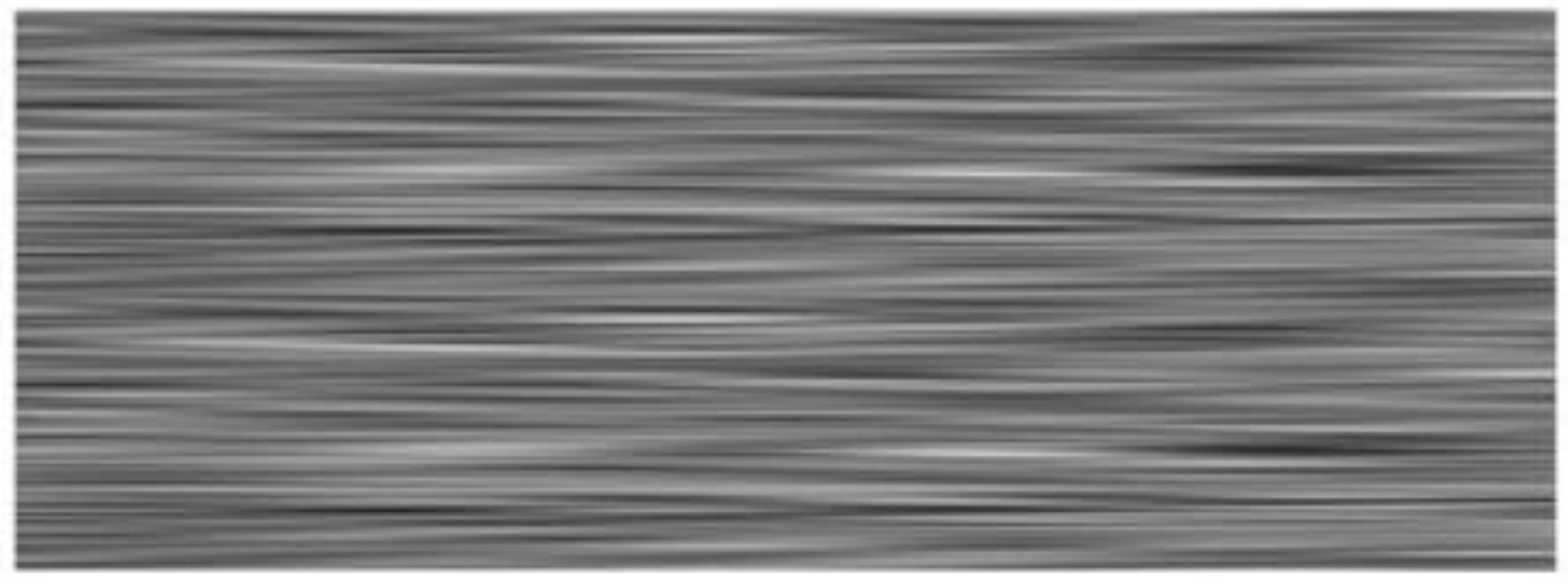
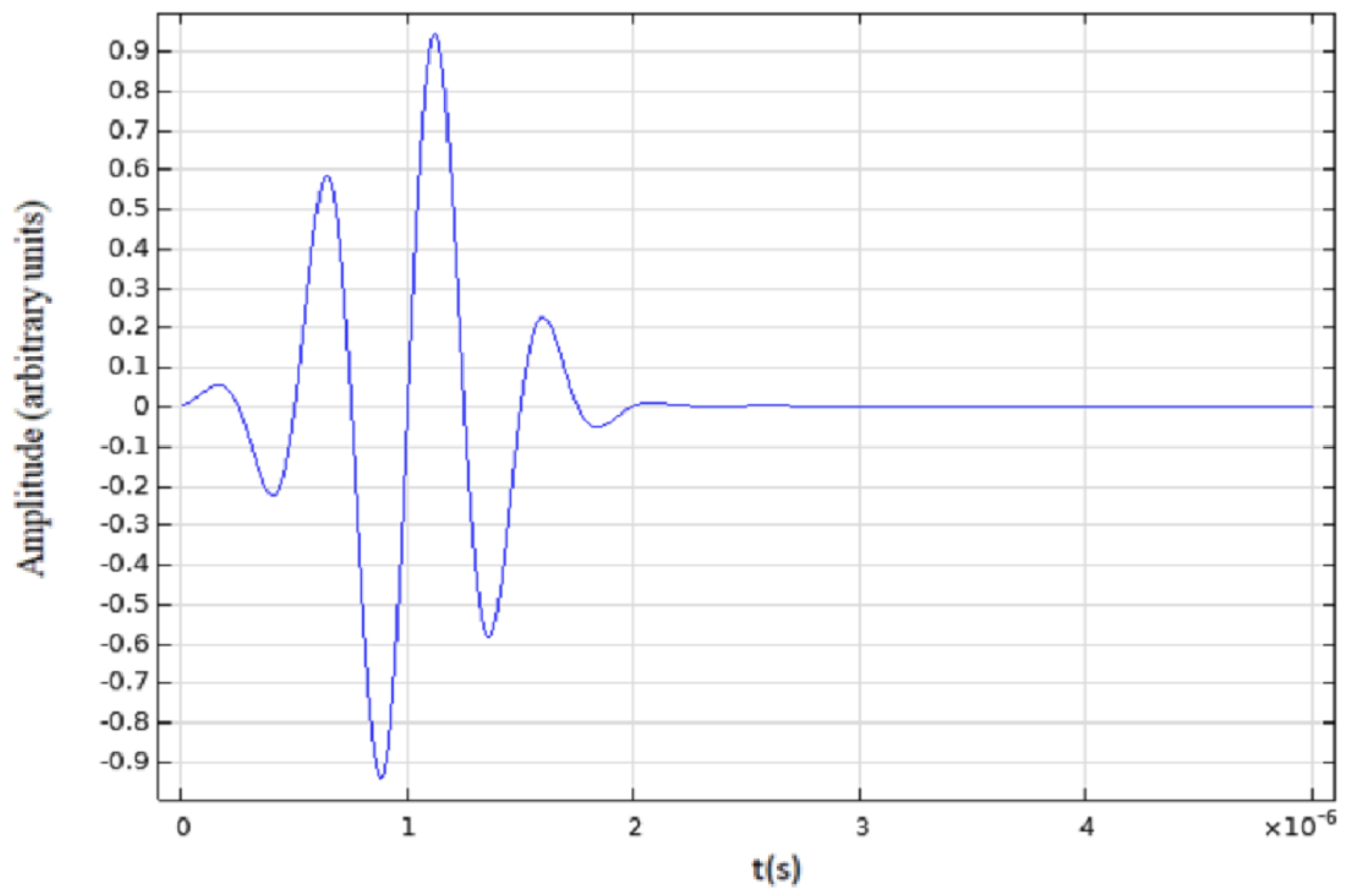
2.1. Ultrasound Propagation Simulation Techniques
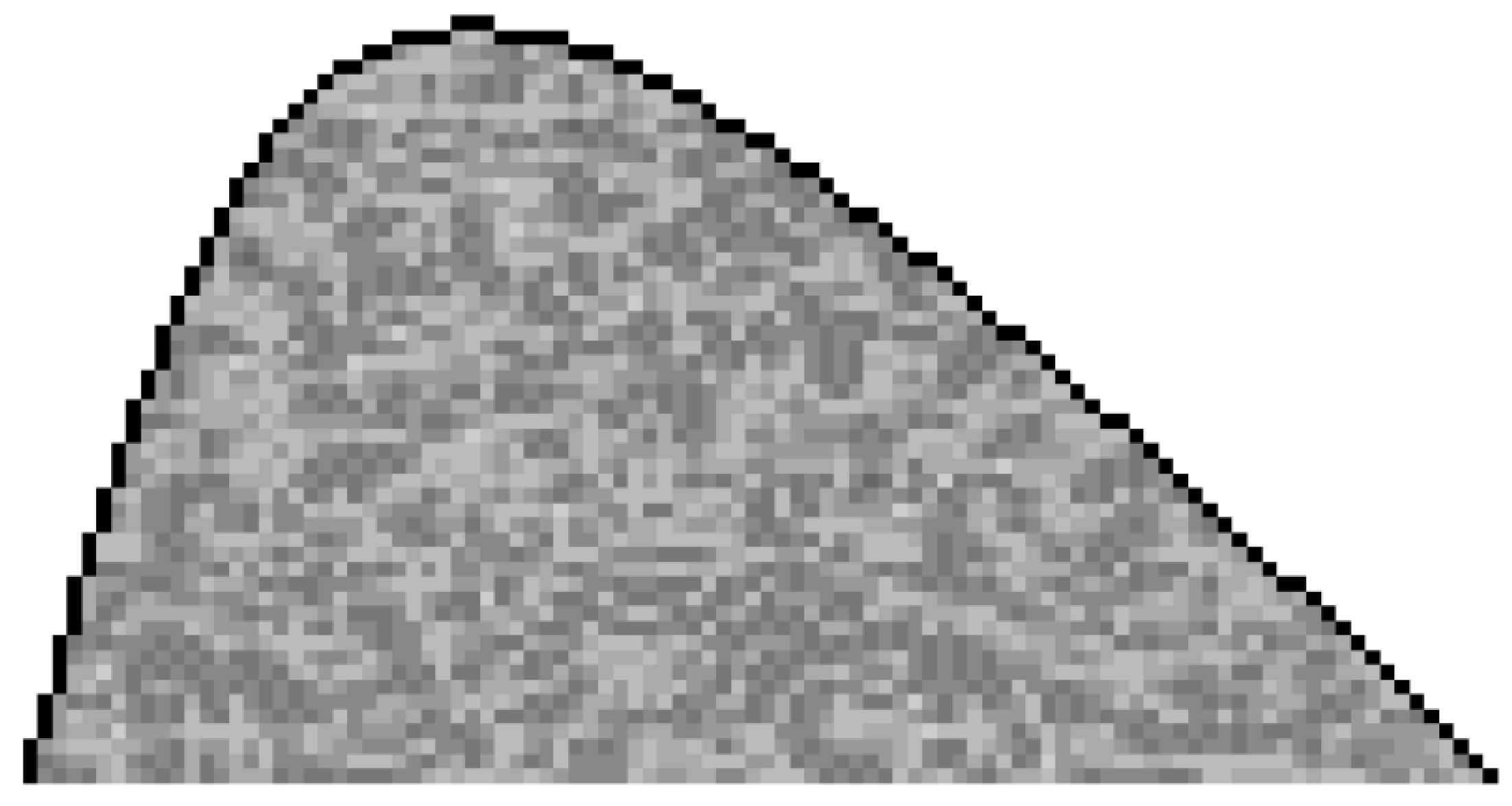
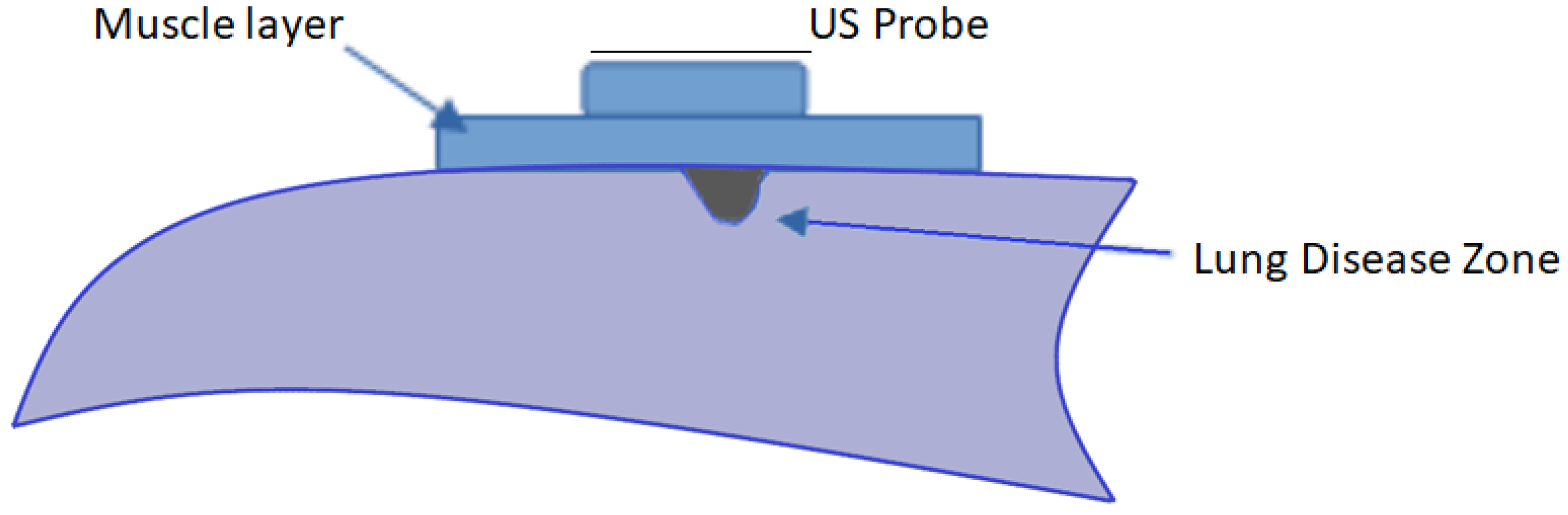
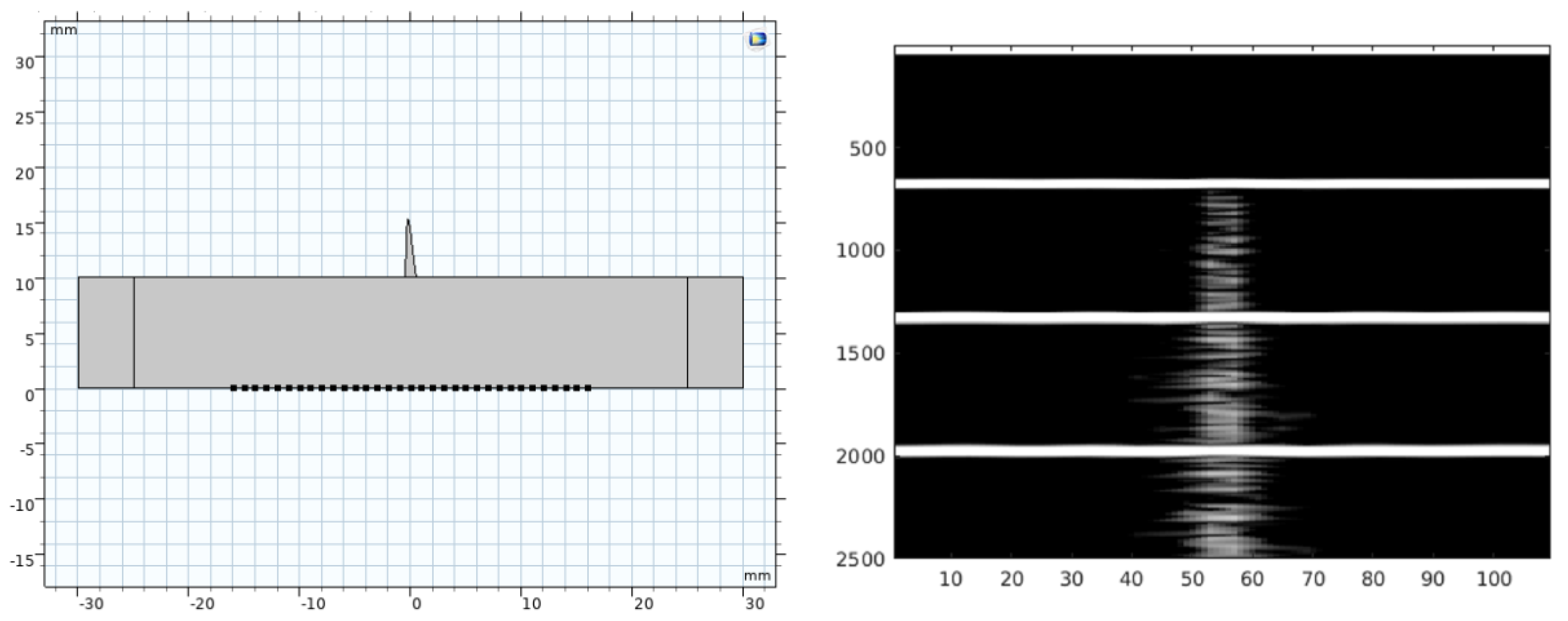
2.2. COMSOL® Models
2.3. COMSOL® Strategy
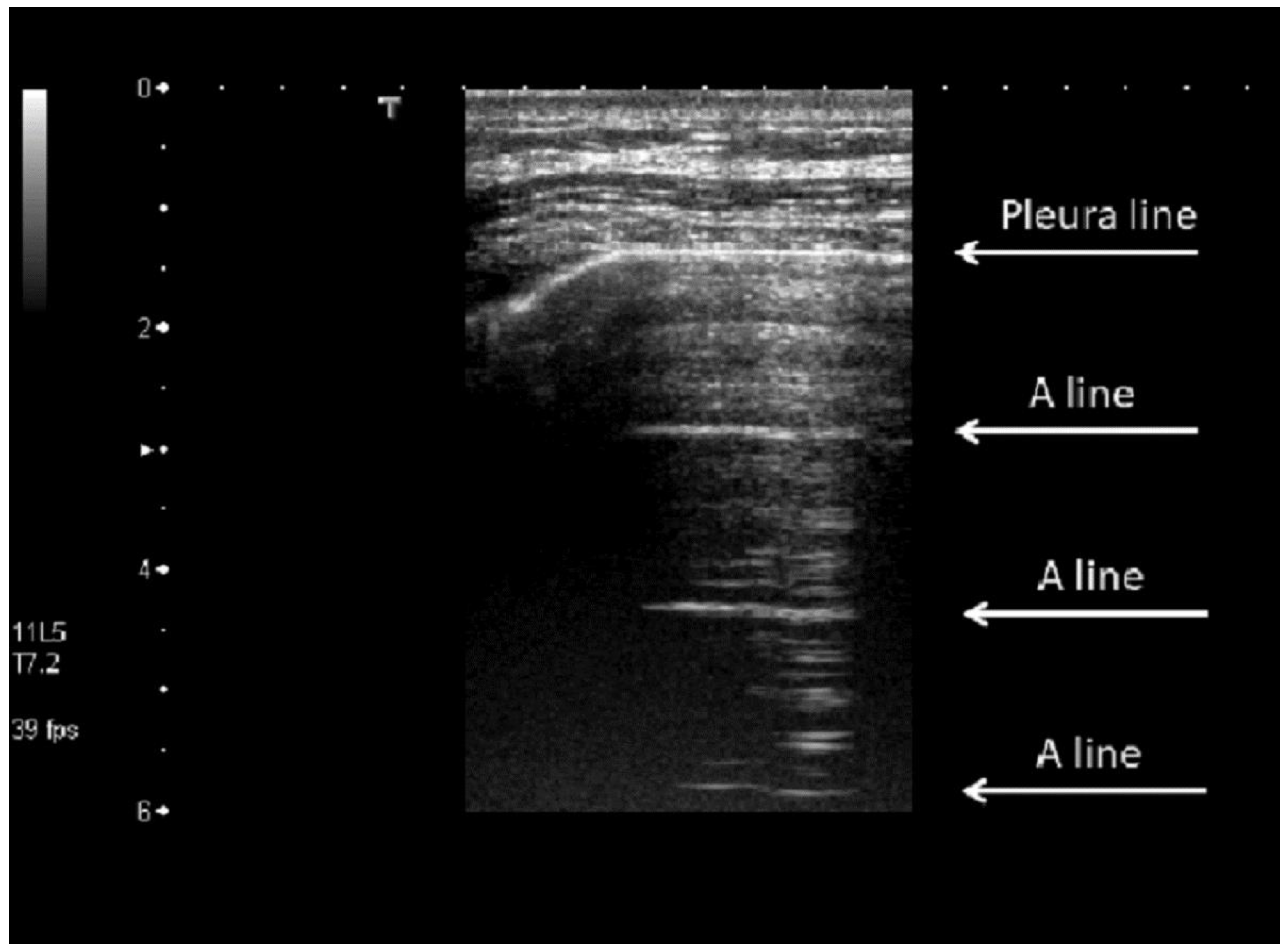
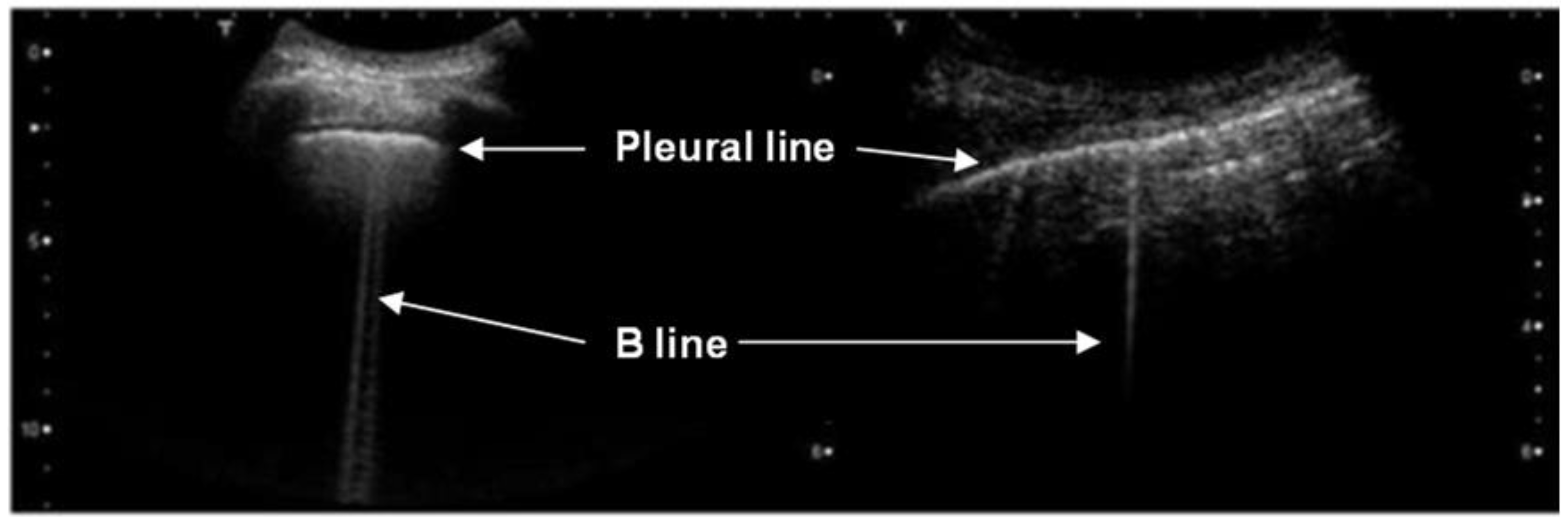
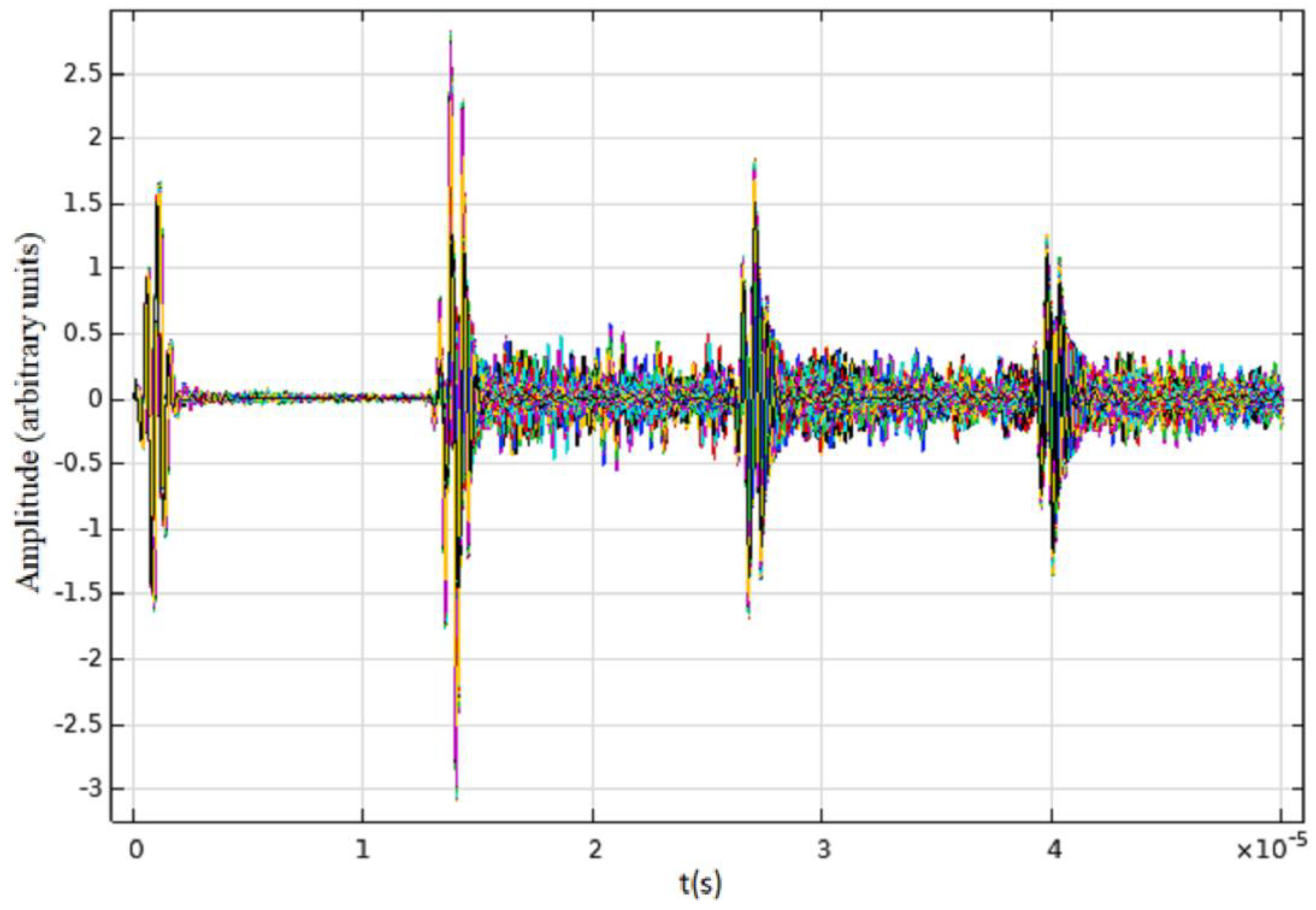
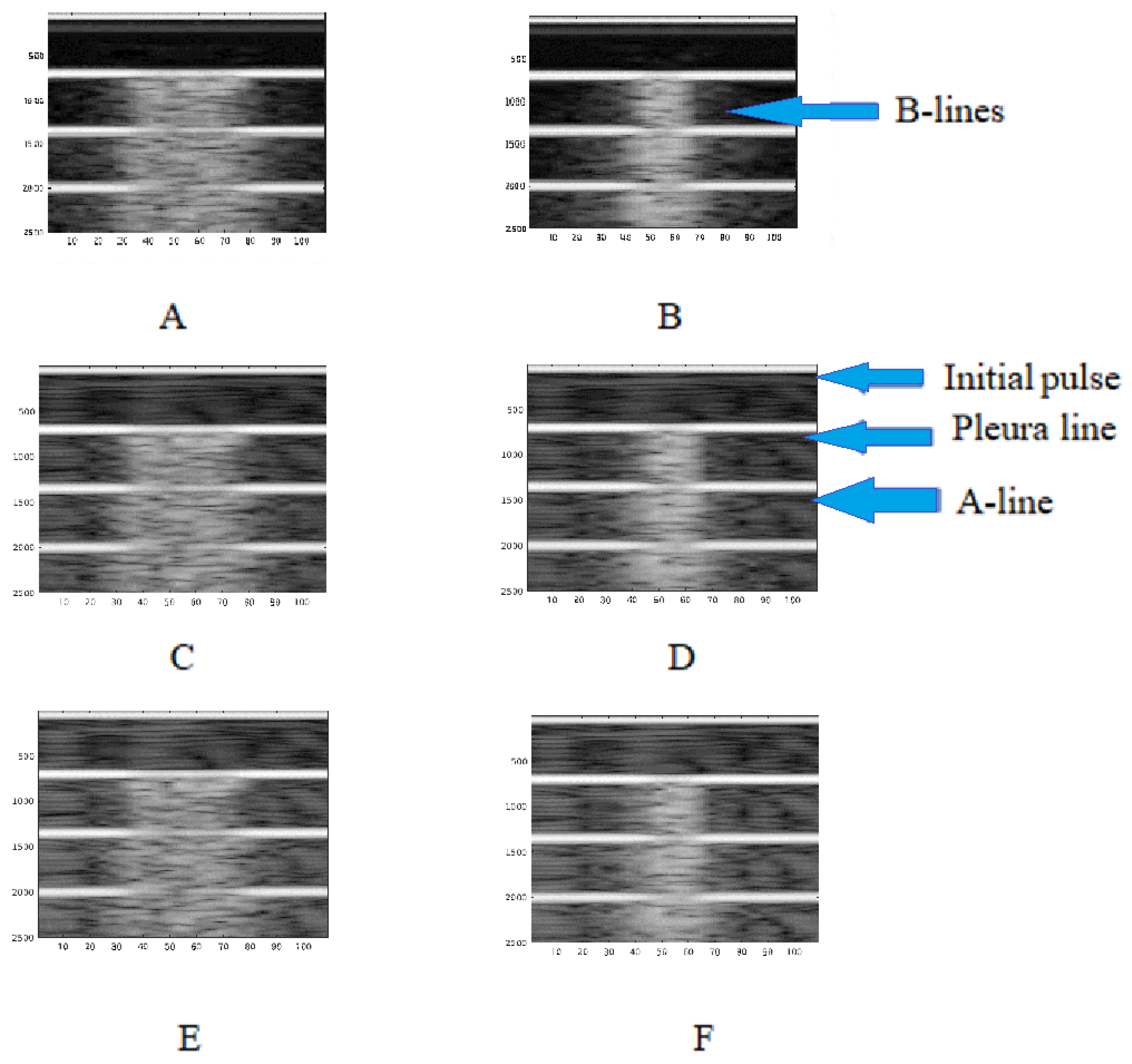
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lichtenstein, D.A. Lung ultrasound in the critically ill. Ann. Intensive Care 2014, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargani, L. Lung ultrasound: A new tool for the cardiologist. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound 2011, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demi, L.; Wolfram, F.; Klersy, C.; De Silvestri, A.; Ferretti, V.V.; Muller, M.; Miller, D.; Feletti, F.; Wełnicki, M.; Buda, N.; et al. New International Guidelines and Consensus on the Use of Lung Ultrasound. J. Ultrasound Med. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stassen, J.; Bax, J.J. How to do lung ultrasound. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 23, 447–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, M.F.H. The Utility of Ultrasound Extends Beyond Interstitial Pneumonia Assessment in COVID-19 Patients. Acad. Radiol. 2020, 27, 1332–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Yu, K.; Zhao, Q.; Tian, R.; Xie, H.; Xie, L.; Deng, P.; Xie, G.; Bao, A.; Du, J. Lung Ultrasound Score in Evaluating the Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pneumonia. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2020, 46, 2938–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldati, G.; Smargiassi, A.; Inchingolo, R.; Buonsenso, D.; Perrone, T.; Briganti, D.F.; Perlini, S.; Torri, E.; Mariani, A.; Mossolani, E.E.; et al. Proposal for International Standardization of the Use of Lung Ultrasound for Patients with COVID-19: A Simple, Quantitative, Reproducible Method. J. Ultrasound Med. 2020, 39, 1413–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpicelli, G. Lung Sonography. J. Ultrasound Med. 2013, 32, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldati, G.; Copetti, R.; Sher, S. Sonographic Interstitial Syndrome: The Sound of Lung Water. J. Ultrasound Med. 2009, 28, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demi, M.; Soldati, G.; Demi, L. On the artefactual information of ultrasound lung images: A lines and B lines. In Proceedings of the 176th Meeting of Acoustical Society of America 2018 Acoustics Week in Canada, Victoria, BC, Canada, 5–9 November 2018; p. 020003. [Google Scholar]
- Oelze, M.L.; Miller, R.J.; Blue, J.P.; Zachary, J.F.; O’Brien, W.D. Estimation of the acoustic impedance of lung versus level of inflation for different species and ages of animals. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 124, 2340–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buda, N.; Andruszkiewicz, P.; Czuczwar, M.; Gola, W.; Kosiak, W.; Nowakowski, P.; Sporysz, K. Consensus of the Study Group for Point-of-Care Lung Ultrasound in the intensive care management of COVID-19 patients. Anaesthesiol. Intensive Ther. 2020, 52, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelosi, P.; Tonelli, R.; Torregiani, C.; Baratella, E.; Confalonieri, M.; Battaglini, D.; Marchioni, A.; Confalonieri, P.; Clini, E.; Salton, F.; et al. Different Methods to Improve the Monitoring of Noninvasive Respiratory Support of Patients with Severe Pneumonia/ARDS Due to COVID-19: An Update. JCM 2022, 11, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruaro, B.; Baratella, E.; Confalonieri, P.; Confalonieri, M.; Vassallo, F.G.; Wade, B.; Geri, P.; Pozzan, R.; Caforio, G.; Marrocchio, C.; et al. High-Resolution Computed Tomography and Lung Ultrasound in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: Which One to Choose? Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpicelli, G.; Elbarbary, M.; Blaivas, M.; Lichtenstein, D.A.; Mathis, G.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Melniker, L.; Gargani, L.; Noble, V.E.; Via, G.; et al. International evidence-based recommendations for point-of-care lung ultrasound. Intensive Care Med. 2012, 38, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhemad, B.; Mongodi, S.; Via, G.; Rouquette, I. Ultrasound for “Lung Monitoring” of Ventilated Patients. Anesthesiology 2015, 122, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargent, A.; Chatelain, E.; Kreitmann, L.; Quenot, J.-P.; Cour, M.; Argaud, L. The COVID-LUS study group Lung ultrasound score to monitor COVID-19 pneumonia progression in patients with ARDS. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpicelli, G.; Gargani, L.; Perlini, S.; Spinelli, S.; Barbieri, G.; Lanotte, A.; Casasola, G.G.; Nogué-Bou, R.; Lamorte, A.; Agricola, E.; et al. Lung ultrasound for the early diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia: An international multicenter study. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugarà, M.; Tamburrini, S.; Coppola, M.G.; Oliva, G.; Fiorini, V.; Catalano, M.; Carbone, R.; Saturnino, P.P.; Rosano, N.; Pesce, A.; et al. The Role of Lung Ultrasound in SARS-CoV-19 Pneumonia Management. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demi, M.; Prediletto, R.; Soldati, G.; Demi, L. Physical Mechanisms Providing Clinical Information From Ultrasound Lung Images: Hypotheses and Early Confirmations. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2020, 67, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peschiera, E.; Mento, F.; Demi, L. Numerical study on lung ultrasound B-line formation as a function of imaging frequency and alveolar geometriesa. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2021, 149, 2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.A.M.; Pastrana-Chalco, M.; Teixeira, C.A.; Pereira, W.C.A. Simulation of Lung Ultrasonography Phantom for Acquisition of A-lines and B-lines Artifacts. In XXVII Brazilian Congress on Biomedical Engineering; Bastos-Filho, T.F., de Oliveira Caldeira, E.M., Frizera-Neto, A., Eds.; IFMBE Proceedings; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 83, pp. 2045–2050. ISBN 978-3-030-70600-5. [Google Scholar]
- COMSOL Multiphysics® Reference Manual v. 6.1. Available online: http://www.comsol.com (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- Simulation Software for Analyzing Acoustics and Vibrations. Available online: https://www.comsol.com/acoustics-module (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- MATLAB Documentation. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- Sjodin, B. How to Generate Randomized Inhomogeneous Material Data|COMSOL Blog. Available online: https://www.comsol.com/blogs/how-to-generate-randomized-inhomogeneous-material-data/ (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- Dunn, F. Attenuation and speed of ultrasound in lung. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1986, 80, 1248–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, A.; Via, G.; Melniker, L.; Goffi, A.; Tavazzi, G.; Neri, L.; Villen, T.; Hoppmann, R.; Mojoli, F.; Noble, V.; et al. Multi-organ point-of-care ultrasound for COVID-19 (PoCUS4COVID): International expert consensus. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonsenso, D.; Piano, A.; Raffaelli, F.; Bonadia, N.; Donati, K.D.G.; Franceschi, F. Point-of-Care Lung Ultrasound findings in novel coronavirus disease-19 pnemoniae: A case report and potential applications during COVID-19 outbreak. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 2776–2780. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mento, F.; Demi, L. On the influence of imaging parameters on lung ultrasound B-line artifacts, in vitro study. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 148, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avruch, L.; Cooperberg, P.L. The ring-down artifact. J. Ultrasound Med. 1985, 4, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louvet, A.; Bourgeois, J.-M. Lung ring-down artifact as a sign of pulmonary alveolar-interstitial disease. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2008, 49, 374–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treeby, B.E.; Cox, B.T. k-Wave: MATLAB toolbox for the simulation and reconstruction of photoacoustic wave fields. J. Biomed. Opt. 2010, 15, 021314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameda, T.; Kamiyama, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Kanayama, Y.; Taniguchi, N. Ultrasonic B-Line–Like Artifacts Generated with Simple Experimental Models Provide Clues to Solve Key Issues in B-Lines. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 45, 1617–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldati, G.; Smargiassi, A.; Demi, L.; Inchingolo, R. Artifactual Lung Ultrasonography: It Is a Matter of Traps, Order, and Disorder. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, F.A.M.d.; Moreno, E.; Pereira, W.C.d.A. B-Lines Lung Ultrasonography Simulation Using Finite Element Method. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2751. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112751
Silva FAMd, Moreno E, Pereira WCdA. B-Lines Lung Ultrasonography Simulation Using Finite Element Method. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(11):2751. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112751
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Fellipe Allevato Martins da, Eduardo Moreno, and Wagner Coelho de Albuquerque Pereira. 2022. "B-Lines Lung Ultrasonography Simulation Using Finite Element Method" Diagnostics 12, no. 11: 2751. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112751
APA StyleSilva, F. A. M. d., Moreno, E., & Pereira, W. C. d. A. (2022). B-Lines Lung Ultrasonography Simulation Using Finite Element Method. Diagnostics, 12(11), 2751. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112751






