Concordance between Three PD-L1 Immunohistochemical Assays in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) in a Multicenter Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.2. Immunohistochemical Assays and Evaluation
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics and PD-L1 Staining by 22C3 Pharma Dx and SP263 Assays
3.2. Concordance among Pathologists
3.3. Concordance among Assays
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laura, Q.M.; Chow, M.D. Head and Neck Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 60–72. [Google Scholar]
- Warnakulasuriya, S. Global epidemiology of oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 2009, 45, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, E.E.W.; Soulières, D.; Le Tourneau, C.; Dinis, J.; Licitra, L.; Ahn, M.-J.; Soria, A.; Machiels, J.-P.; Mach, N.; Mehra, R.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus methotrexate, docetaxel, or cetuximab for recurrent or metastatic head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma (KEYNOTE-040): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2018, 393, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtness, B.; Harrington, K.J.; Greil, R.; Soulières, D.; Tahara, M.; de Castro, G., Jr.; Psyrri, A.; Basté, N.; Neupane, P.; Bratland, A.; et al. Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-048): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2019, 394, 1915–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Approves Pembrolizumab for First-Line Treatment of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-pembrolizumab-first-line-treatment-head-and-neck-squamous-cell-carcinoma#:~:text=squamous%20cell%20carcinoma-,FDA%20approves%20pembrolizumab%20for%20first%2Dline%20treatment%20of,and%20neck%20squamous%20cell%20carcinoma&text=On%20June%2010%2C%202019%2C%20the,squamous%20cell%20carcinoma%20(HNSCC) (accessed on 6 November 2019).
- EMA. Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) Assessment Report EMEA/H/C/003820/II/0065. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/variation-report/keytruda-h-c-3820-ii-0065-epar-assessment-report-variation_en.pdf (accessed on 17 October 2020).
- Emancipator, K.; Huang, L.; Aurora-Garg, D.; Bal, T.; Cohen, E.E.W.; Harrington, K.; Soulières, D.; Le Tourneau, C.; Licitra, L.; Burtness, B.; et al. Comparing programmed death ligand 1 scores for predicting pembrolizumab efficacy in head and neck cancer. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 34, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girolami, I.; Pantanowitz, L.; Barberis, M.; Paolino, G.; Brunelli, M.; Vigliar, E.; Munari, E.; Satturwar, S.; Troncone, G.; Eccher, A. Challenges facing pathologists evaluating PD-L1 in head & neck squamous cell carcinoma. J. Oral. Pathol. Med. 2021, 50, 864–873. [Google Scholar]
- Paolino, G.; Pantanowitz, L.; Barresi, V.; Pagni, F.; Munari, E.; Moretta, L.; Brunelli, M.; Bariani, E.; Vigliar, E.; Pisapia, P.; et al. PD-L1 evaluation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Insights regarding specimens, heterogeneity and therapy. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2021, 226, 153605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, A.; Barberis, M.; Franco, R.; De Luca, G.; Pace, M.V.; Staibano, S.; Volante, M.; Buttitta, F.; Guerini-Rocco, E.; Righi, L.; et al. Multicenter Comparison of 22C3 PharmDx (Agilent) and SP263 (Ventana) Assays to Test PD-L1 Expression for NSCLC Patients to Be Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Büttner, R.; Gosney, J.R.; Skov, B.G.; Adam, J.; Motoi, N.; Bloom, K.J.; Dietel, M.; Longshore, J.W.; López-Ríos, F.; Penault-Llorca, F.; et al. Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Immunohistochemistry Testing: A Review of Analytical Assays and Clinical Implementation in Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3867–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ruiter, E.J.; Mulder, F.J.; Koomen, B.M.; Speel, E.-J.; Hout, M.F.C.M.V.D.; de Roest, R.H.; Bloemena, E.; Devriese, L.A.; Willems, S.M. Comparison of three PD-L1 immunohistochemical assays in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Mod. Pathol. 2020, 34, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eccher, A.; Fontanini, G.; Fusco, N.; Girolami, I.; Graziano, P.; Rocco, E.; Martini, M.; Morbini, P.; Pantanowitz, L.; Parwani, A.; et al. Digital slides as an effective tool for programmed death ligand 1 combined positive score assessment and training: Lessons learned from the “Programmed death ligand 1 key learning program in Head-and-Neck squamous cell carcinoma”. J. Pathol. Inform. 2021, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerbelli, B.; Girolami, I.; Eccher, A.; Costarelli, L.; Taccogna, S.; Scialpi, R.; Benevolo, M.; Lucante, T.; Luigi Alò, P.; Stella, F.; et al. Evaluating PD-L1 in Head & Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Concordance between 22C3 PharmaDx and SP263 assays on whole sections from a multicenter study. Histopathology 2022, 80, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Girolami, I.; Pantanowitz, L.; Munari, E.; Martini, M.; Nocini, R.; Bisi, N.; Molteni, G.; Marchioni, D.; Ghimenton, C.; Brunelli, M.; et al. Prevalence of PD-L1 expression in head and neck squamous precancerous lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Head Neck 2020, 42, 3018–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassanelli, M.; Sioletic, S.; Martini, M.; Giacinti, S.; Viterbo, A.; Staddon, A.; Liberati, F.; Ceribelli, A. Heterogeneity of PD-L1 Expression and Relationship with Biology of NSCLC. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 3789–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossi, E.D.; Martini, M.; Bd, S.C.; Cenci, T.; Bd, P.S.; Angrisani, B.; Ricci, C.; Lanza, P.; Lombardi, C.P.; Pontecorvi, A.; et al. Analysis of immunocytochemical and molecular BRAF expression in thyroid carcinomas: A cytohistologic institutional experience. Cancer Cytopathol. 2014, 122, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munari, E.; Mariotti, F.R.; Quatrini, L.; Bertoglio, P.; Tumino, N.; Vacca, P.; Eccher, A.; Ciompi, F.; Brunelli, M.; Martignoni, G.; et al. PD-1/PD-L1 in Cancer: Pathophysiological, Diagnostic and Therapeutic Aspects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 12, 5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pembrolizumab for Untreated Metastatic or Unresectable Recurrent Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta661 (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Hodgson, A.; Slodkowska, E.; Jungbluth, A.; Liu, S.; Vesprini, D.; Enepekides, D.; Higgins, K.; Katabi, N.; Xu, B.; Downes, M.R. PD-L1 Immunohistochemistry Assay Concordance in Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder and Hypopharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2018, 42, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosta, S.; Boldorini, R.; Bono, F.; Brambilla, V.; Dainese, E.; Fusco, N.; Gianatti, A.; L’Imperio, V.; Morbini, P.; Pagni, F. PD-L1 Testing and Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck: A Multicenter Study on the Diagnostic Reproducibility of Different Protocols. Cancers 2021, 13, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ock, C.-Y.; Kim, S.; Keam, B.; Kim, S.; Ahn, Y.-O.; Chun, J.K.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, T.M.; Kwon, S.K.; Jeon, Y.K.; et al. Changes in programmed death-ligand 1 expression during cisplatin treatment in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 97920–97927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naruse, T.; Yanamoto, S.; Okuyama, K.; Ohmori, K.; Tsuchihashi, H.; Furukawa, K.; Yamada, S.I.; Umeda, M. Immunohistochemical Study of PD-1/PD-L1 Axis Expression in Oral Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinomas: Effect of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on Local Recurrence. Pathol. Oncol. Res. POR 2020, 26, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pflumio, C.; Thomas, J.; Salleron, J.; Faivre, J.; Borel, C.; Dolivet, G.; Sastre-Garau, X.; Geoffrois, L. Expression of immune response biomarkers (PD-L1, p16, CD3+ and CD8+ TILs) in recurrent head and neck squamous cell carcinoma within previously irradiated areas. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 45, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Shao, C. Radiotherapy-Mediated Immunomodulation and Anti-Tumor Abscopal Effect Combining Immune Checkpoint Blockade. Cancers 2020, 12, 2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| n = 40 | |
|---|---|
| Age, mean (±SD) | 63 (7.7) |
| Gender, n (%) | |
| Male | 26 (65) |
| Female | 14 (35) |
| Stage, n (%) | |
| metastatic | 31 (77.5) |
| unresectable recurrent | 9 (22.5) |
| Tumor location, n (%) | |
| Oropharynx | 18 (45) |
| Hypopharynx | 15 (37.5) |
| Larynx | 5 (12.5) |
| Metastatic sites | 2 (5) |
| HPV status (p16), n (%) | |
| Positive | 7 (35) |
| Negative | 13 (65) |
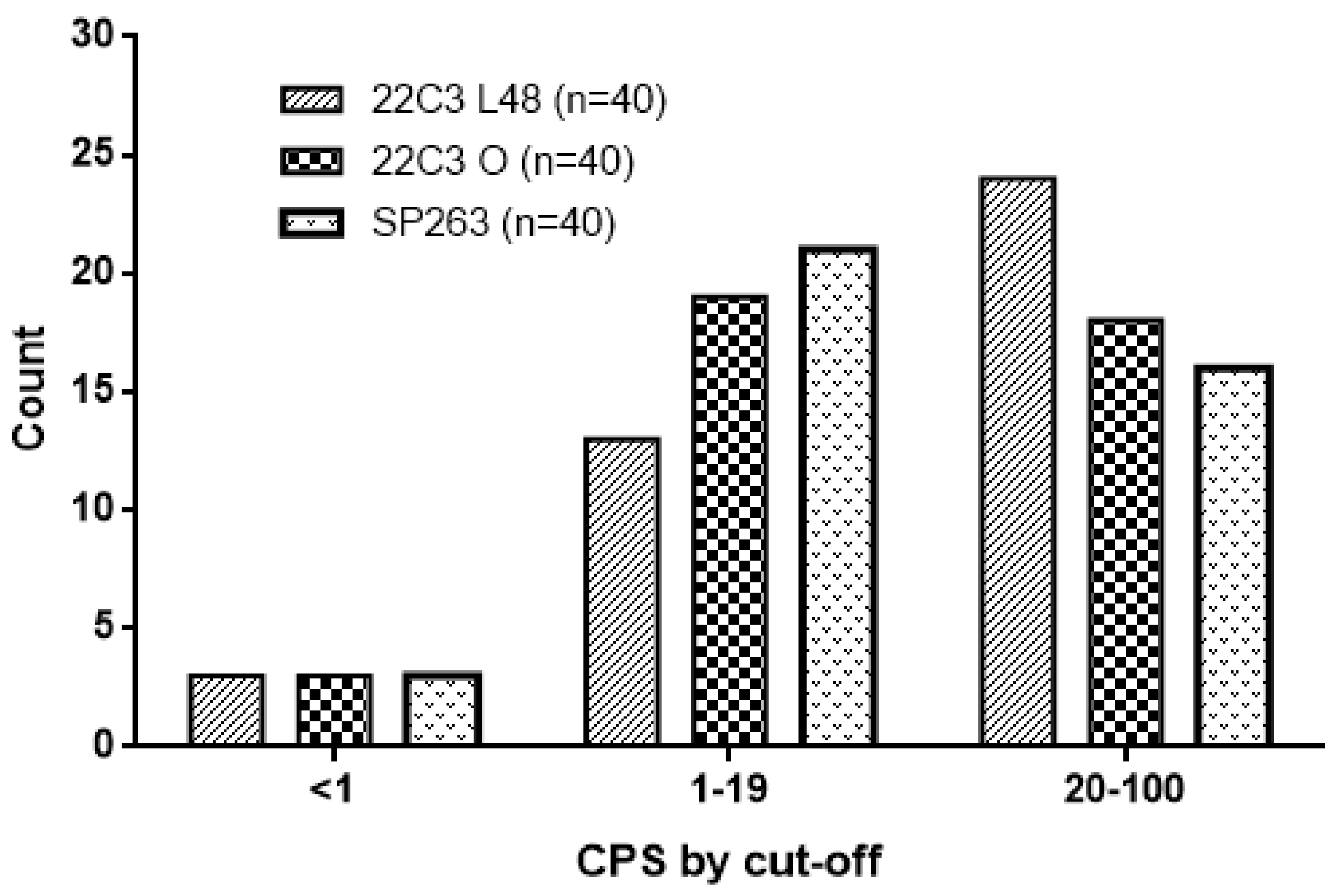
| PD-L1 expression 22C3 Auto L48 n (%) | |
| <1 | 3 (7.5) |
| 1–<20 | 13 (32.5) |
| ≥20 | 24 (60) |
| PD-L1 expression 22C3 Omnis, n (%) | |
| <1 | 3 (7.5) |
| 1–<20 | 19 (47.5) |
| ≥20 | 18 (45) |
| PD-L1 expression SP263, n (%) | |
| <1 | 3 (7.5) |
| 1–<20 | 21 (52.5) |
| ≥20 | 16 (40) |
| Concordance among Raters—ICC | 22C3 Omnis | 0.938 (CI 0.914 to 0.957) |
| SP263 | 0.930 (CI 0.899 to 0.953) | |
| 22C3 Autostainer | 0.914 (CI 0.881 to 0.941) | |
| Concordance among Raters for Cut-Off Categories—Fleiss’ Kappa | 22C3 Omnis | Range 0.675–0.848 |
| SP263 | Range 0.720–0.880 | |
| 22C3 Autostainer | Range 0.748–0.895 | |
| Concordance among Assays—ICC | 22C3 Omnis vs. SP263 | Range 0.874–0.993 |
| SP263 vs. 22C3 Autostainer | Range 0.532–0.807 | |
| 22C3 Autostainer vs. 22C3 Omnis | Range 0.686–0.924 | |
| Concordance among Assays for Cut-Off Categories—Cohen’s Kappa for Single Rater | 22C3 Omnis vs. SP263 | Range 0.642–0.796 |
| SP263 vs. 22C3 Autostainer | Range 0.522–0.687 | |
| 22C3 Autostainer vs. 22C3 Omnis | Range 0.681–0.823 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guerini Rocco, E.; Eccher, A.; Girolami, I.; Graziano, P.; Fontanini, G.; Vigliar, E.; Troncone, G.; Barberis, M.; Morbini, P.; Martini, M. Concordance between Three PD-L1 Immunohistochemical Assays in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) in a Multicenter Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020477
Guerini Rocco E, Eccher A, Girolami I, Graziano P, Fontanini G, Vigliar E, Troncone G, Barberis M, Morbini P, Martini M. Concordance between Three PD-L1 Immunohistochemical Assays in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) in a Multicenter Study. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(2):477. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020477
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuerini Rocco, Elena, Albino Eccher, Ilaria Girolami, Paolo Graziano, Gabriella Fontanini, Elena Vigliar, Giancarlo Troncone, Massimo Barberis, Patrizia Morbini, and Maurizio Martini. 2022. "Concordance between Three PD-L1 Immunohistochemical Assays in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) in a Multicenter Study" Diagnostics 12, no. 2: 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020477
APA StyleGuerini Rocco, E., Eccher, A., Girolami, I., Graziano, P., Fontanini, G., Vigliar, E., Troncone, G., Barberis, M., Morbini, P., & Martini, M. (2022). Concordance between Three PD-L1 Immunohistochemical Assays in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) in a Multicenter Study. Diagnostics, 12(2), 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020477










