Digital Pathology Implementation in Private Practice: Specific Challenges and Opportunities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Our Laboratory
2.2. Information Technology Infrastructure and Tracking System
2.3. Imaging, Server and Storage Technology
2.4. Pathologists’ Workstations
- Workstation HP Z2 G5 Tower, Intel i7-10700, 16 GB RAM, 512 GB SSD; Radeon Pro W5500 graphic card; Monitor HP Z24N G3 24” (for reporting on LIS) and LG Clinical Monitor LED IPS 27” 16:9 8MP 4K 27HJ712C (for WSI viewing);
- HP ProOne 600 AIO, Intel Core i5-9500, 8 GB RAM, 256 GB SSD; Intel UHD Graphics 630 graphic card; LCD wide screen FHD IPS 21,5” (for reporting on LIS) and LG Clinical Monitor LED IPS 27” 16:9 8MP 4K 27HJ712C (for WSI viewing).
2.5. LIS and IMS Integration
2.6. Quality Control
2.7. Validation
3. Results
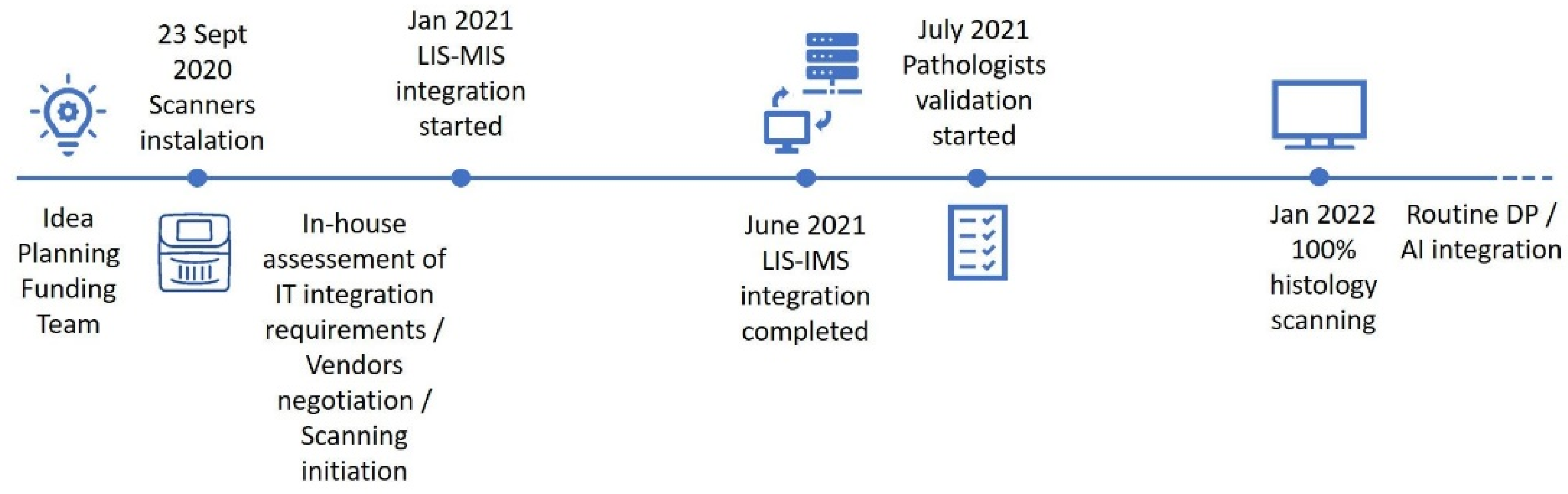
3.1. Implementation Track, Challenges and Opportunities
3.2. Quality Control
3.3. Validation
4. Discussion
4.1. Implementation Track, Challenges and Opportunities
4.2. Quality Control
4.3. Validation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fraggetta, F.; Caputo, A.; Guglielmino, R.; Pellegrino, M.G.; Runza, G.; L’Imperio, V.A. Survival Guide for the Rapid Transition to a Fully Digital Workflow: The “Caltagirone Example”. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betmouni, S. Diagnostic digital pathology implementation: Learning from the digital health experience. Digit. Health 2021, 7, 20552076211020240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schüffler, P.J.; Geneslaw, L.; Yarlagadda, D.V.K.; Hanna, M.G.; Samboy, J.; Stamelos, E.; Vanderbilt, C.; Philip, J.; Jean, M.H.; Corsale, L.; et al. Integrated digital pathology at scale: A solution for clinical diagnostics and cancer research at a large academic medical center. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2021, 28, 1874–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraggetta, F.; Garozzo, S.; Zannoni, G.F.; Pantanowitz, L.; Rossi, E.D. Routine Digital Pathology Workflow: The Catania Experience. J. Patho.l Inform. 2017, 8, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Stathonikos, N.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Spoto, C.P.; Verdaasdonk MA, M.; van Diest, P.J. Being fully digital: Perspective of a Dutch academic pathology laboratory. Histopathology 2019, 75, 621–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stathonikos, N.; Nguyen, T.Q.; van Diest, P.J. Rocky road to digital diagnostics: Implementation issues and exhilarating experiences. J. Clin. Pathol. 2021, 74, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retamero, J.A.; Aneiros-Fernandez, J.; Del Moral, R.G. Complete Digital Pathology for Routine Histopathology Diagnosis in a Multicenter Hospital Network. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2020, 144, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanna, M.G.; Reuter, V.E.; Samboy, J.; England, C.; Corsale, L.; Fine, S.W.; Agaram, N.P.; Stamelos, E.; Yagi, Y.; Hameed, M.; et al. Implementation of Digital Pathology Offers Clinical and Operational Increase in Efficiency and Cost Savings. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2019, 143, 1545–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quigley, J.C.; Lujan, G.; Hartman, D.; Parwani, A.; Roehmholdt, B.; Van Meter, B.; Ardon, O.; Hanna, M.G.; Kelly, D.; Sowards, C.; et al. Dissecting the Business Case for Adoption and Implementation of Digital Pathology: A White Paper from the Digital Pathology Association. J. Pathol. Inform. 2021, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, S.W.; Plass, M.; Moinfar, F. Digital Pathology: Advantages, Limitations and Emerging Perspectives. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallua, J.D.; Brunner, A.; Zelger, B.; Schirmer, M.; Haybaeck, J. The future of pathology is digital. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 153040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bera, K.; Schalper, K.A.; Rimm, D.L.; Velcheti, V.; Madabhushi, A. Artificial intelligence in digital pathology—New tools for diagnosis and precision oncology. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Drug Administration. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf20/DEN200080.pdf (accessed on 4 November 2021).
- Echle, A.; Rindtorff, N.T.; Brinker, T.J.; Luedde, T.; Pearson, A.T.; Kather, J.N. Deep learning in cancer pathology: A new generation of clinical biomarkers. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, S.P.; Neto, P.C.; Fraga, J.; Montezuma, D.; Monteiro, A.; Monteiro, J.; Ribeiro, L.; Gonçalves, S.; Pinto, I.M.; Cardoso, J.S. CAD systems for colorectal cancer from WSI are still not ready for clinical acceptance. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royal College of Pathologists. Best Practice Recommendations for Digital Pathology. 2018. Available online: https://www.rcpath.org/resourceLibrary/best-practicerecommendations-for-implementing-digital-pathology-pdf (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Williams, B.J.; Treanor, D. Practical guide to training and validation for primary diagnosis with digital pathology. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 73, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baidoshvili, A.; Bucur, A.; van Leeuwen, J.; van der Laak, J.; Kluin, P.; van Diest, P.J. Evaluating the benefits of digital pathology implementation: Time savings in laboratory logistics. Histopathology 2018, 73, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.; Ahlers, S.M.; Stratman, C.; Aridor, O.; Pantanowitz, L.; Fine, J.L.; Kuzmishin, J.A.; Montalto, M.C.; Parwani, A.V. Can digital pathology result in cost savings? A financial projection for digital pathology implementation at a large integrated health care organization. J. Pathol. Inform. 2014, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloy, C.; Vale, J.; Curado, M.; Polónia, A.; Campelos, S.; Caramelo, A.; Sousa, R.; Sobrinho-Simões, M. Digital Pathology Workflow Implementation at IPATIMUP. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, M.G.; Ardon, O.; Reuter, V.E.; Sirintrapun, S.J.; England, C.; Klimstra, D.S.; Hameed, M.R. Integrating digital pathology into clinical practice. Mod Pathol. Mod. Pathol. 2021, 35, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, M.G.; Reuter, V.E.; Ardon, O.; Kim, D.; Sirintrapun, S.J.; Schüffler, P.J.; Busam, K.J.; Sauter, J.L.; Brogi, E.; Tan, L.K.; et al. Validation of a digital pathology system including remote review during the COVID-19 pandemic. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 2115–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retamero, J.A.; Aneiros-Fernandez, J.; Del Moral, R.G. Microscope? No, Thanks: User Experience With Complete Digital Pathology for Routine Diagnosis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2020, 144, 672–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.J.; Salama, M.E.; Henricks, W.H.; Pantanowitz, L. Implementation of Whole Slide Imaging for Clinical Purposes: Issues to Consider From the Perspective of Early Adopters. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2017, 141, 944–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Griffin, J.; Treanor, D. Digital pathology in clinical use: Where are we now and what is holding us back? Histopathology 2017, 70, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraggetta, F.; L’Imperio, V.; Ameisen, D.; Carvalho, R.; Leh, S.; Kiehl, T.R.; Serbanescu, M.; Racoceanu, D.; Della Mea, V.; Polonia, A.; et al. Best Practice Recommendations for the Implementation of a Digital Pathology Workflow in the Anatomic Pathology Laboratory by the European Society of Digital and Integrative Pathology (ESDIP). Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Challenges |
|
| Opportunities |
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montezuma, D.; Monteiro, A.; Fraga, J.; Ribeiro, L.; Gonçalves, S.; Tavares, A.; Monteiro, J.; Macedo-Pinto, I. Digital Pathology Implementation in Private Practice: Specific Challenges and Opportunities. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020529
Montezuma D, Monteiro A, Fraga J, Ribeiro L, Gonçalves S, Tavares A, Monteiro J, Macedo-Pinto I. Digital Pathology Implementation in Private Practice: Specific Challenges and Opportunities. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(2):529. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020529
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontezuma, Diana, Ana Monteiro, João Fraga, Liliana Ribeiro, Sofia Gonçalves, André Tavares, João Monteiro, and Isabel Macedo-Pinto. 2022. "Digital Pathology Implementation in Private Practice: Specific Challenges and Opportunities" Diagnostics 12, no. 2: 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020529
APA StyleMontezuma, D., Monteiro, A., Fraga, J., Ribeiro, L., Gonçalves, S., Tavares, A., Monteiro, J., & Macedo-Pinto, I. (2022). Digital Pathology Implementation in Private Practice: Specific Challenges and Opportunities. Diagnostics, 12(2), 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020529






