Artificial Intelligence (Enhanced Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Network) for Calcium Deblooming in Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography: A Feasibility Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. CCTA and Invasive Coronary Angiography Images
2.2. Deblooming in CCTA
- Generator: Removal of the batch normalization layers from the SRGAN with the addition of residual-in-residual dense block layers to facilitate training of a deeper model.
- Discriminator: Implementation of the relativistic average discriminator to determine whether an image was more realistic rather than “real” or “fake” noted in the SRGAN.
- Loss function: Determination of the perceptual loss based on the VGG features before its activation rather than after the activation employed in the SRGAN for better monitoring of image brightness and texture.
2.3. CCTA Measurements
2.4. ICA Measurements
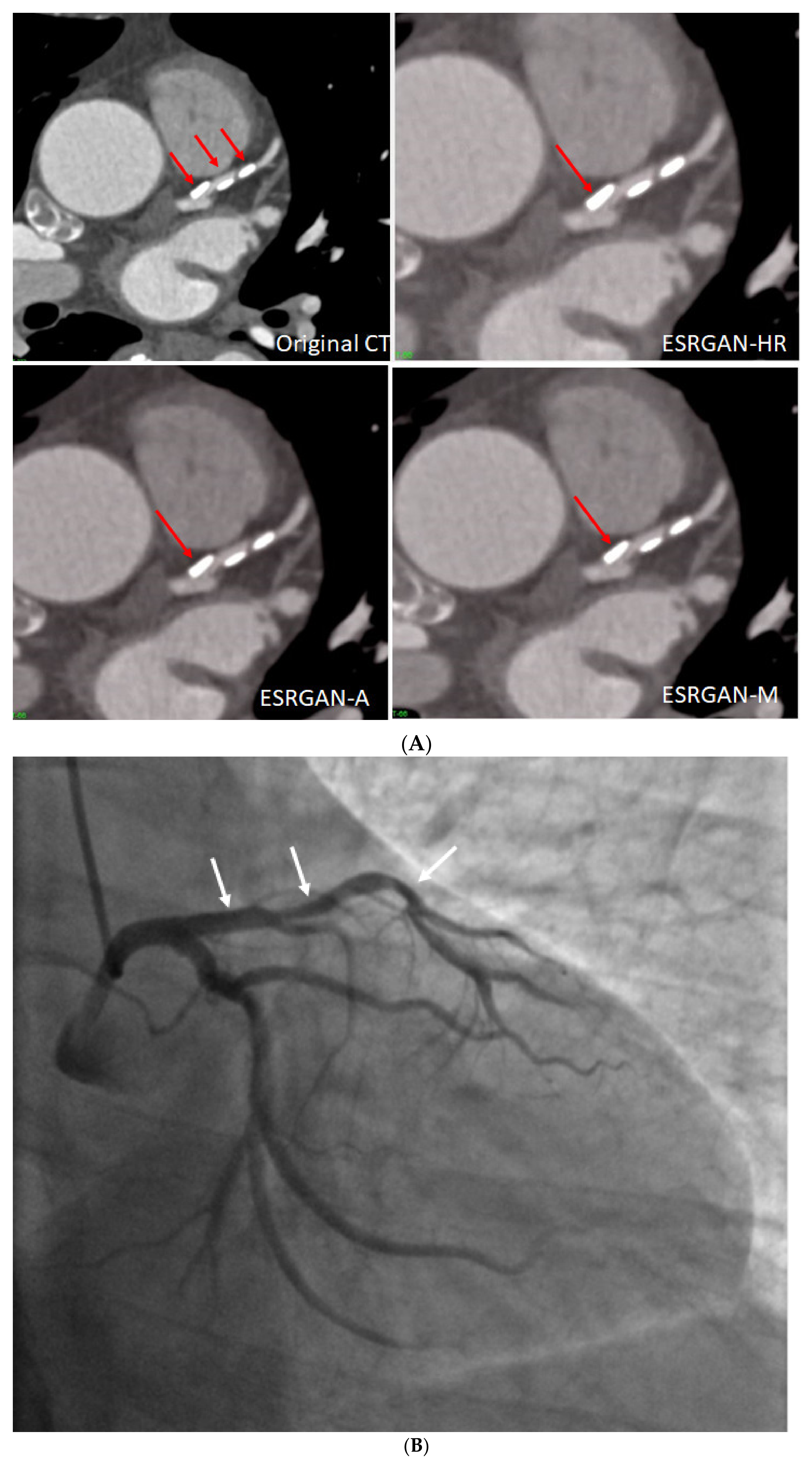
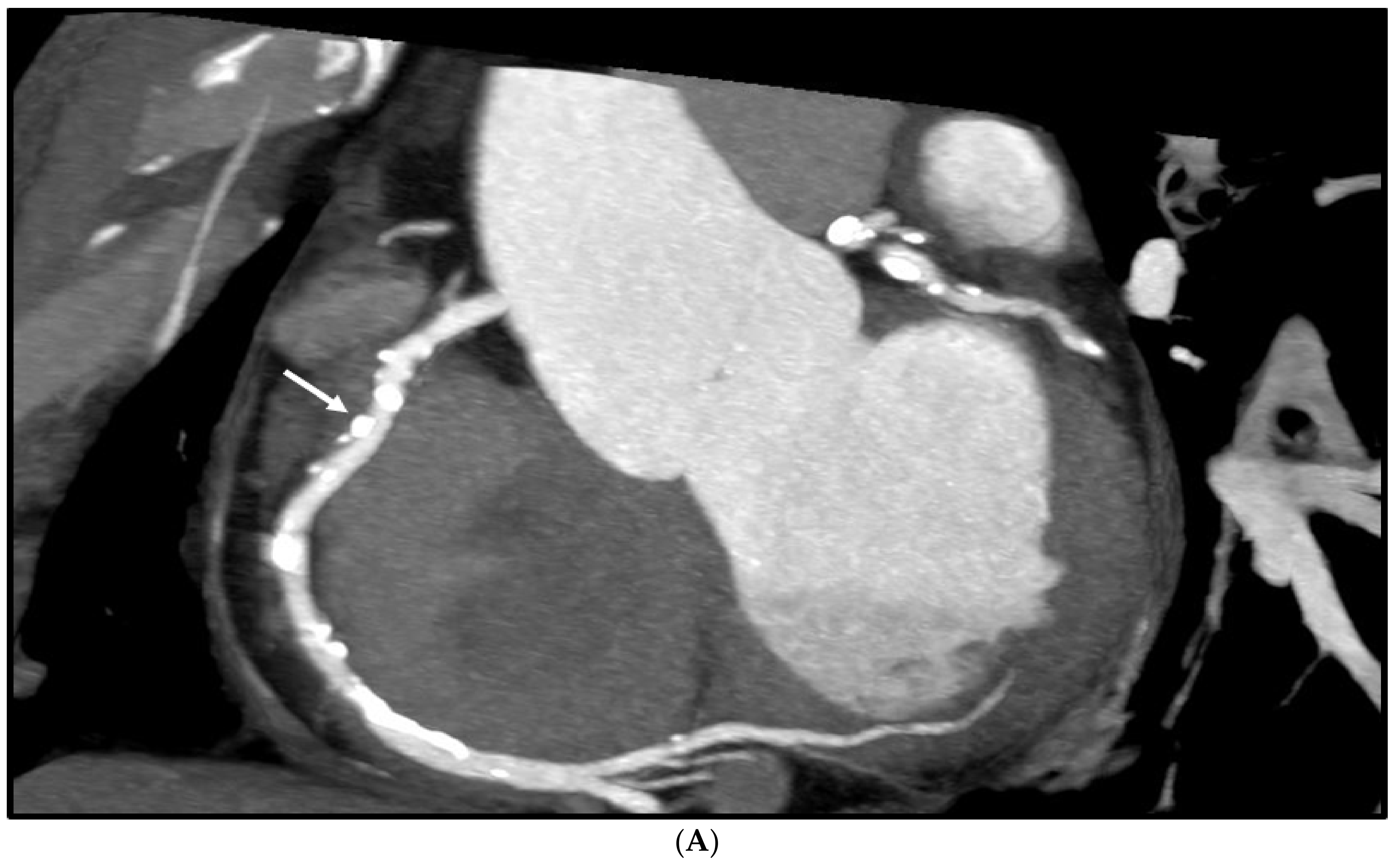
2.5. Reduction of Blooming Artifact by ESRGAN
2.6. Statistical Analysis
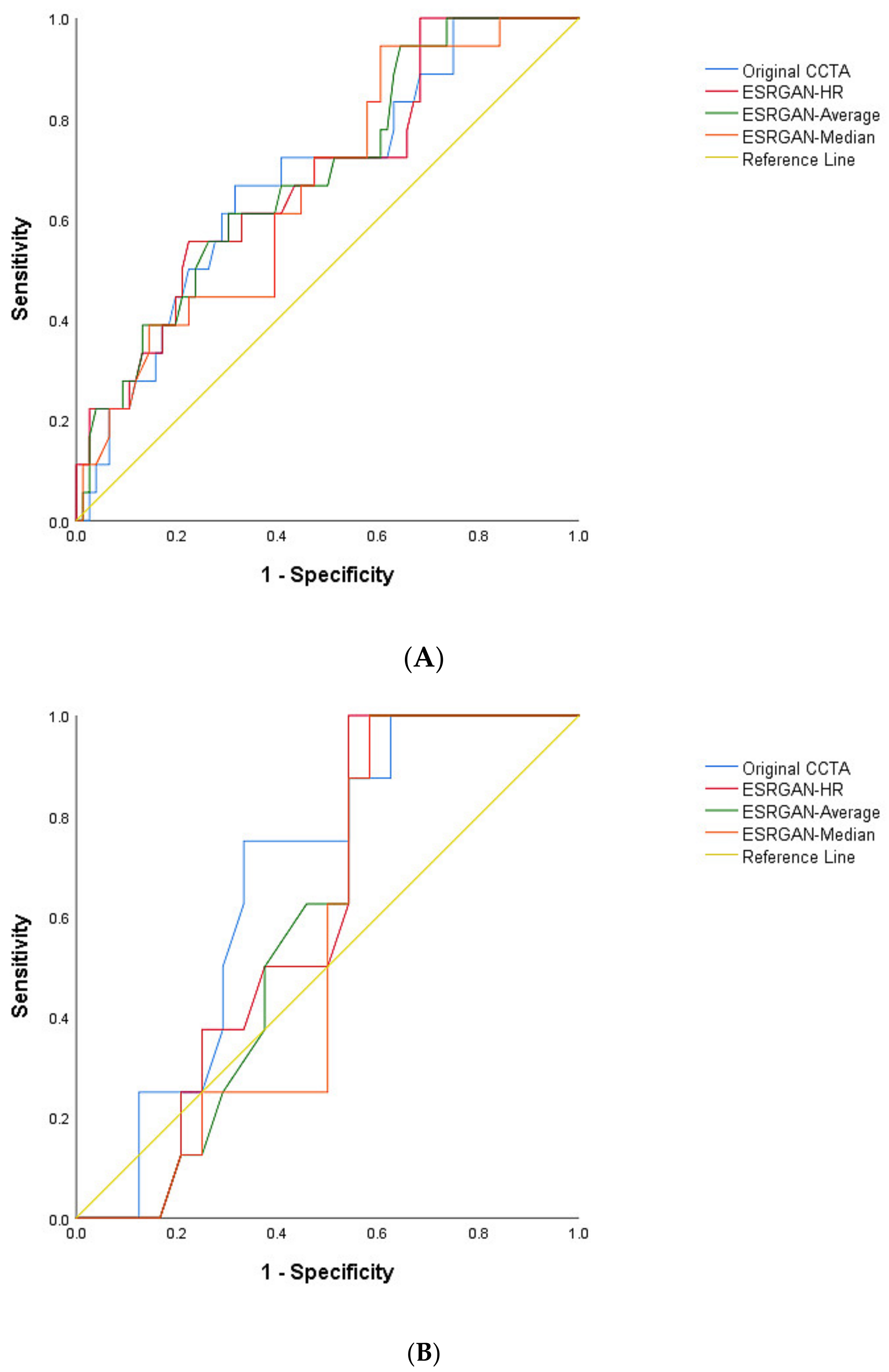
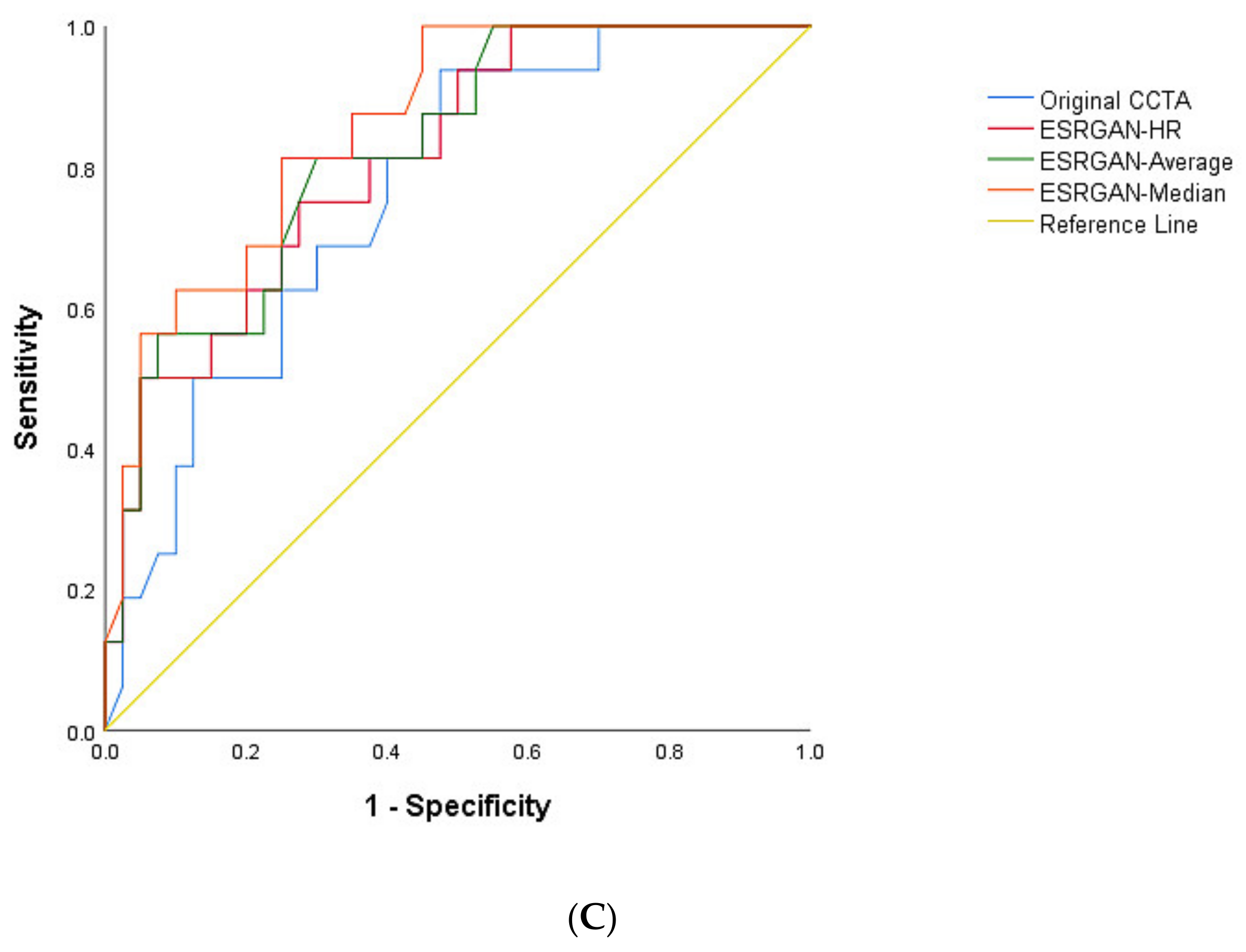
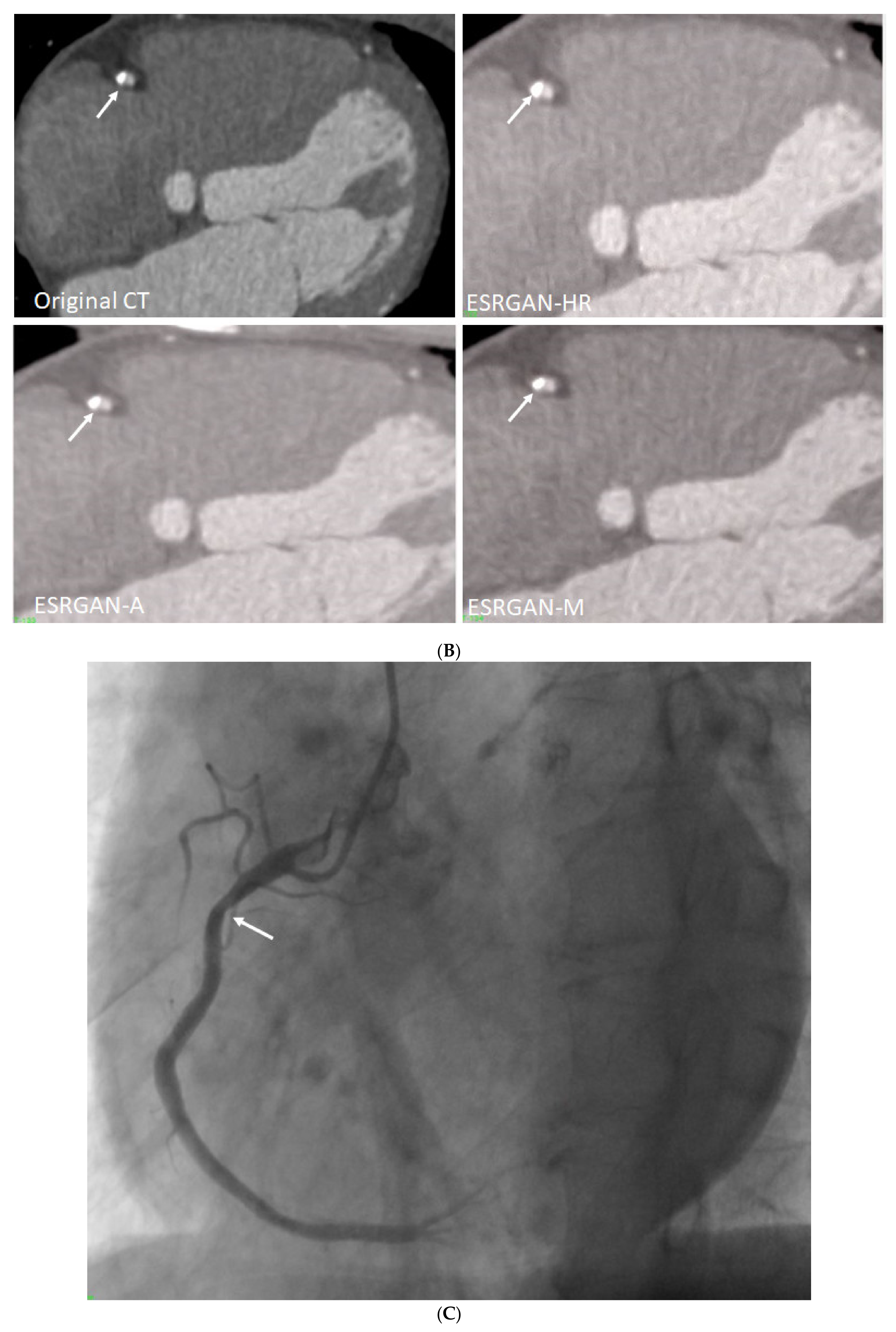
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kianoush, S.; Al Rifai, M.; Cainzos-Achirica, M.; Umapathi, P.; Graham, G.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Nasir, K.; Blaha, M.J. An update on the utility of coronary artery calcium scoring for coronary heart disease and cardiovascular disease risk prediction. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2016, 18, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Rifai, M.; McEvoy, J.W.; Nasir, K.; Rumberger, J.; Feldman, D.; Budoff, M.J.; Blaha, M.J. Traditional cardiovascular disease risk factors associated with one-year all-cause mortality among those with coronary artery calcium scores ≥400. Atherosclerosis 2015, 241, 495–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Ng, C.K.C. High calcium scores in coronary CT angiography: Effects of image post-processing on visualization and measurement of coronary lumen diameter. J. Med. Imaging Health Inform. 2015, 5, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Ng, C.K.C.; Xu, L.; Fan, Z.; Lei, J. Coronary CT angiography in heavily calcified coronary arteries: Improvement of coronary lumen visualization and coronary stenosis assessment with image postprocessing methods. Medicine 2015, 94, e2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalisz, K.; Buethe, J.; Saboo, S.S.; Abbara, S.; Halliburton, S.; Rajiah, P. Artifacts at cardiac CT: Physics and solutions. Radiographics 2016, 36, 2064–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xu, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, R.; Hsieh, J.; Sun, Z.; Fan, Z.; Leipsic, J.A. Blooming artifact reduction in coronary artery calcification by a new de-blooming algorithm: Initial study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir-McCall, J.R.; Wang, R.; Halankar, J.; Hsieh, J.; Hague, C.J.; Rosenblatt, S.; Fan, Z.; Sellers, S.L.; Murphy, D.T.; Blanke, P.; et al. Effect of a calcium deblooming algorithm on accuracy of coronary computed tomography angiography. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2020, 14, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Lei, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wynne, J.F.; Curran, W.J.; Liu, T.; Yang, X. A review on medical imaging synthesis using deep learning and its clinical applications. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2021, 22, 11–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolterink, J.M.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Leiner, T.; Vogl, T.J.; Bucher, A.M.; Išgum, I. Generative adversarial networks: A primer for radiologists. Radiographics 2021, 41, 840–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagayama, Y.; Sakabe, D.; Goto, M.; Emoto, T.; Oda, S.; Nakaura, T.; Kidoh, M.; Uetani, H.; Funama, Y.; Hirai, T. Deep learning-based reconstruction for lower-dose pediatric CT: Technical principles, image characteristics, and clinical implementations. Radiographics 2021, 41, 1936–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, S.L.; Trout, A.T.; Somasundaram, E.; Anton, C.G.; Li, Y.; Dillman, J.R. Improving image quality and reducing radiation dose for pediatric CT by using deep learning reconstruction. Radiology 2021, 298, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenfant, M.; Chevallier, O.; Comby, P.O.; Secco, G.; Haioun, K.; Ricolfi, F.; Lemogne, B.; Loffroy, R. Deep learning versus iterative reconstruction for CT pulmonary angiography in the emergency setting: Improved image quality and reduced radiation dose. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akagi, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Higaki, T.; Narita, K.; Honda, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yu, Z.; Akino, N.; Awai, K. Deep learning reconstruction improves image quality of abdominal ultra-high-resolution CT. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 6163–6171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatsugami, F.; Higaki, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Lu, Y.; Fujioka, C.; Kitagawa, T.; Kihara, Y.; Iida, M.; et al. Deep learning-based image restoration algorithm for coronary CT angiography. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 5322–5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benz, D.C.; Benetos, G.; Rampidis, G.; von Felten, E.; Bakula, A.; Sustar, A.; Kudura, K.; Messerli, M.; Fuchs, T.A.; Gebhard, C.; et al. Validation of deep-learning image reconstruction for coronary computed tomography angiography: Impact on noise, image quality and diagnostic accuracy. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2020, 14, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolterink, J.M.; Leiner, T.; Viergever, M.A.; Isgum, I. Generative adversarial networks for noise reduction in low-dose CT. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 2536–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledig, C.; Theis, L.; Huszar, F.; Caballero, J.; Cunningham, A.; Acosta, A.; Aitken, A.; Tejani, A.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yu, K.; Wu, S.; Gu, J.; Liu, Y.; Dong, C.; Qiao, Y.; Loy, C.C. ESRGAN: Enhanced super-resolution generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Workshops, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Sun, Z. Virtual intravascular endoscopy visualization of calcified coronary plaques: A novel approach of identifying plaque features for more accurate assessment of coronary lumen stenosis. Medicine 2015, 94, e805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; He, K.; Tang, X. Learning a deep convolutional network for image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Volume 8692. [Google Scholar]
- Friedrichsdorf, S.P.; Arana-Chavez, V.E.; Cattaneo, P.M.; Spin-Neto, R.; Dominguez, G.C. Effect of the software binning and averaging data during microcomputed tomography image acquisition. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Ng, C.K.C.; Squelch, A. Synchrotron radiation computed tomography assessment of calcified plaques and coronary stenosis with different slice thicknesses and beam energies on 3D printed coronary models. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2019, 9, 6–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunaga, H.; Ohta, Y.; Kaetsu, Y.; Kitao, S.; Watanabe, T.; Furuse, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Ogawa, T. Diagnostic performance of calcification-suppressed coronary CT angiography using rapid kilovolt-switching dual-energy CT. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 2794–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Du, X.; Guo, D.; Cao, L.; Gao, Y.; Bai, M.; Li, P.; Liu, J.; Li, K. Noise-based tube current reduction method with iterative reconstruction for reduction of radiation exposure in coronary CT angiography. Eur. J. Radiol. 2013, 82, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funabashi, N.; Irie, R.; Aiba, M.; Morimoto, R.; Kabashima, T.; Fujii, S.; Uehara, M.; Ozawa, K.; Takaoka, H.; Kobayashi, Y. Adaptive-iterative-dosereduction 3D with multisector-reconstruction method in 320-slice CT may maintain accurate-measurement of the Agatston-calcium- score of severe-calcification even at higher pulsating-beats and low tube-current in vitro. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 601–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontone, G.; Bertella, E.; Mushtaq, S.; Loguercio, M.; Cortinovis, S.; Baggiano, A.; Conte, E.; Annoni, A.; Formenti, A.; Beltrama, V.; et al. Coronary artery disease: Diagnostic accuracy of CT coronary angiography-A comparison of high and standard spatial resolution scanning. Radiology 2014, 271, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si-Mohamed, S.; Boccalini, S.; Lacombe, H.; Diaw, A.; Varaseh, M.; Rodesch, P.A.; Villien, M.; Tatard-Leitman, V.; Bochaton, T.; Coulon, P.; et al. Coronary CT angiography with photon-counting CT: First in-human results. Radiology 2022, 15, 211780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Xu, L.; Fan, Z. Coronary CT angiography in calcified coronary plaques: Comparison of diagnostic accuracy between bifurcation angle measurement and coronary lumen assessment for diagnosing significant coronary stenosis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 203, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sun, Z.; Cao, Y. Multislice CT angiography assessment of left coronary artery: Correlation between bifurcation angle and dimensions and development of coronary artery disease. Eur. J. Radiol. 2011, 79, e90–e95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temov, K.; Sun, Z. Coronary computed tomography angiography investigation of the association between left main coronary artery bifurcation angle and risk factors of coronary artery disease. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 32, S129–S137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, R.; Yoshioka, K.; Muranaka, K.; Chiba, T.; Ueda, T.; Sasaki, T.; Fusazaki, T.; Ehara, S. Improved evaluation of calcified segments on coronary CT angiography: A feasibility study of coronary calcium subtraction. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 29, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, C.B.; Codari, M.; van Assen, M.; de Cecco, C.N.; Vliegenthart, R. Machine learning and deep neural networks applications in computed tomography for coronary artery disease and myocardial perfusion. J. Thorac. Imaging 2020, 35 (Suppl. 1), S58–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambale-Venkatesh, B.; Yang, X.; Wu, C.O.; Liu, K.; Hundley, W.G.; McClelland, R.; Gomes, A.S.; Folsom, A.R.; Shea, S.; Guallar, E.; et al. Cardiovascular event prediction by machine learning: The multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Martin, S.; Burt, J.R.; Bagherzadeh, P.S.; Rapaka, S.; Gray, H.N.; Leonard, T.J.; Schwemmer, C.; Schoepf, U.J. Machine learning and coronary artery calcium scoring. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2020, 22, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, R.; Zhang, N.; Sun, Z.; Xu, L. Coronary artery calcium score quantification using a deep learning algorithm. Clin. Radiol. 2020, 75, 237.e11–237.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Liu, J.; Sun, Z.; Cui, Y.; He, Y.; Yang, Z. Deep learning analysis in coronary computed tomographic angiography imaging for the assessment of patients with coronary artery stenosis. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2020, 196, 105651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.Y.; Tang, C.X.; Zhang, X.L.; Chen, S.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Qiao, H.Y.; Zhou, C.S.; Xu, P.P.; Lu, M.J.; et al. Deep learning powered coronary CT angiogrphy for detecting obstructive coronary artery disease: The effect of reader experience, calcification and image quality. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 142, 109835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Xu, C.; Xu, M.; Yan, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Diagnostic improvements of deep learning-based image reconstruction for assessing calcification-related obstructive coronary artery disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 758793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroules, C.D.; Hamilton-Craig, C.; Branch, K.; Lee, J.; Cury, R.C.; Maurovich-Horvat, P.; Rubinshtein, R.; Thomas, D.; Williams, M.; Guo, Y.; et al. Coronary artery disease reporting and data system (CAD-RADS™): Inter-observer agreement for assessment categories and modifiers. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2018, 12, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Nakaura, T.; Fanama, Y.; Okimoto, T.; Sato, T.; Higaki, T.; Noda, N.; Imada, N.; Baba, Y.; Awai, K. Machine-learning intergration of CT histogram analysis to evaluate the composition of atherosclerotic plaques: Validation with IB-IVUS. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2019, 13, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolossvary, M.; De Cecco, C.N.; Feuchtner, G.; Maurich-Horvat, P. Advanced atherosclerosis imaging by CT: Radiomics, machine learning and deep learning. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2019, 13, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opincariu, D.; Benedek, T.; Chitu, M.; Rat, N.; Benedek, I. From CT to artificial intelligence for complex assessment of plaque-associated risk. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 36, 2403–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hamersvelt, R.W.; Zreik, M.; Voskuil, M.; Viergever, M.A.; Isgum, I.; Leiner, T. Deep learning analysis of left ventricular myocardium in CT angiographic intermediate-degree coronary stenosis improves the diagnostic accuracy for identification of functionally significant stenosis. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 2350–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zreik, M.; Lessmann, N.; van Hamersvelt, R.W.; Wolterink, J.M.; Voskuil, M.; Viergever, M.A.; Leiner, T.; Isgum, I. Deep learning of the myocardium in coronary CT angiography for identification of patients with functionally significant coronary artery stenosis. Med. Image Anal. 2018, 44, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, T.N.K.; Le, N.Q.K.; Le, N.H.; Tuan, L.V.; Nguyen, T.P.; Thi, C.; Kang, J.H. An AI-based prediction model for drug-drug interactions in osteoporosis and paget’s diseases from SMILES. Mol. Inform. 2022, 5, e2100264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, N.Q.K.; Huang, T.N.K.; Do, D.T.; Lam, L.H.T.; Dang, L.H.; Huynh, T.T. Radiomics-based machine learning model for efficiently classifying transcriptome subtypes in glioblastoma patients from MRI. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 132, 104320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, L.H.; Dung, N.T.; Quang, L.X.; Hung, L.Q.; Le, N.H.; Le, N.T.N.; Diem, N.T.; Nga, N.T.T.; Huang, S.H.; Le, N.Q.K. Machine learning-based prediction of drug-drug interactions for histamine antagonist hybrid chemical features. Cells 2021, 10, 3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
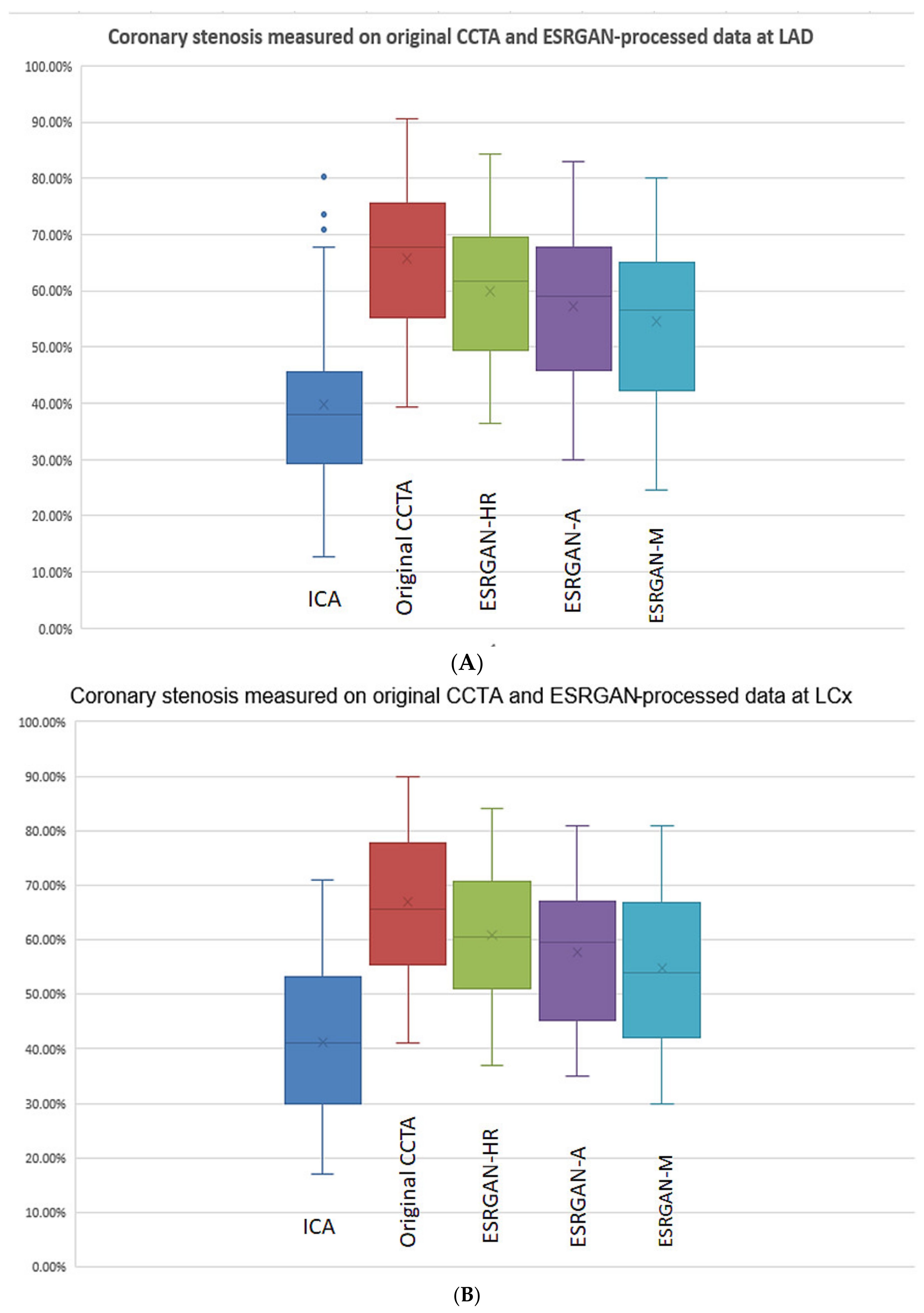
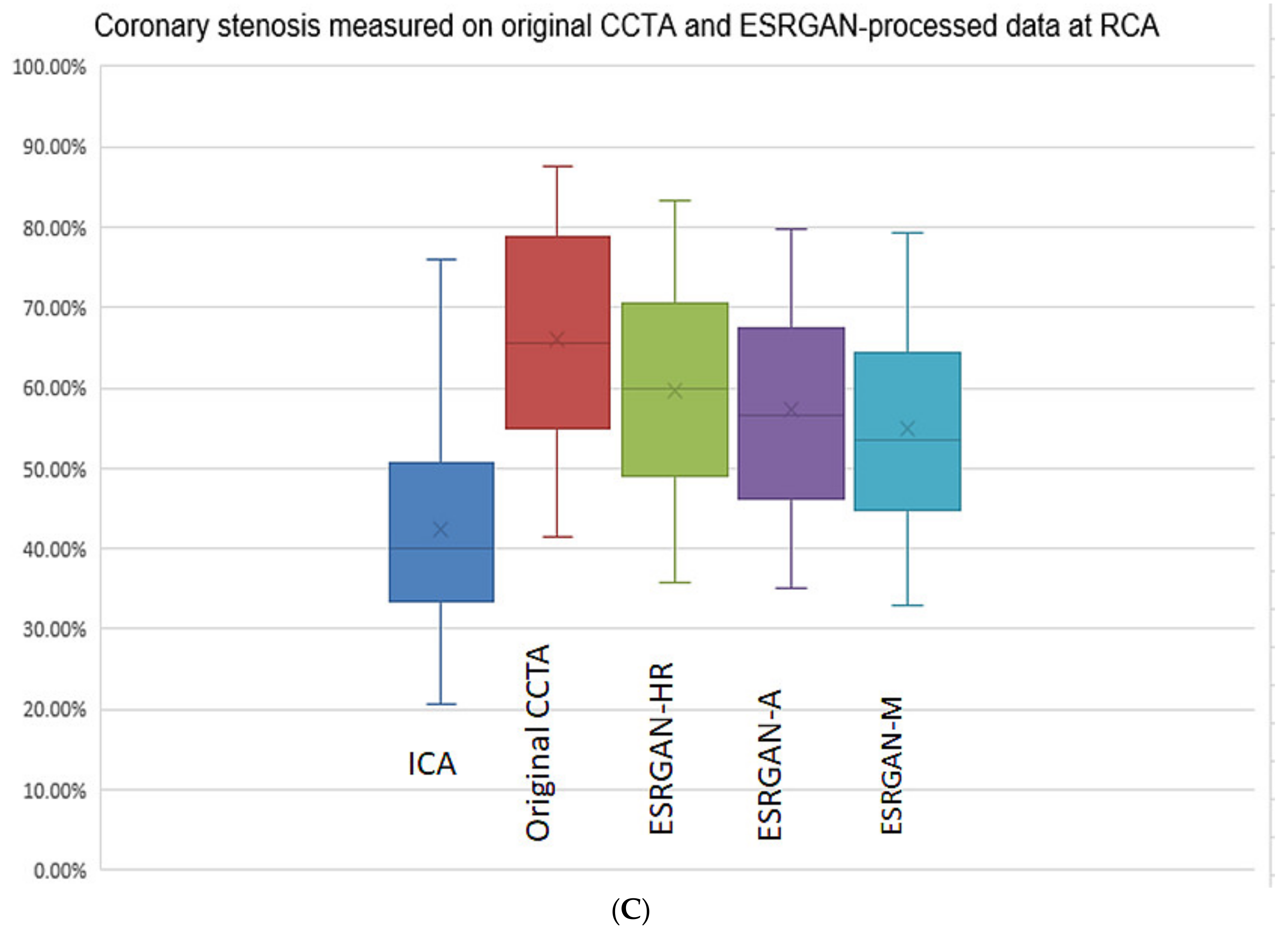
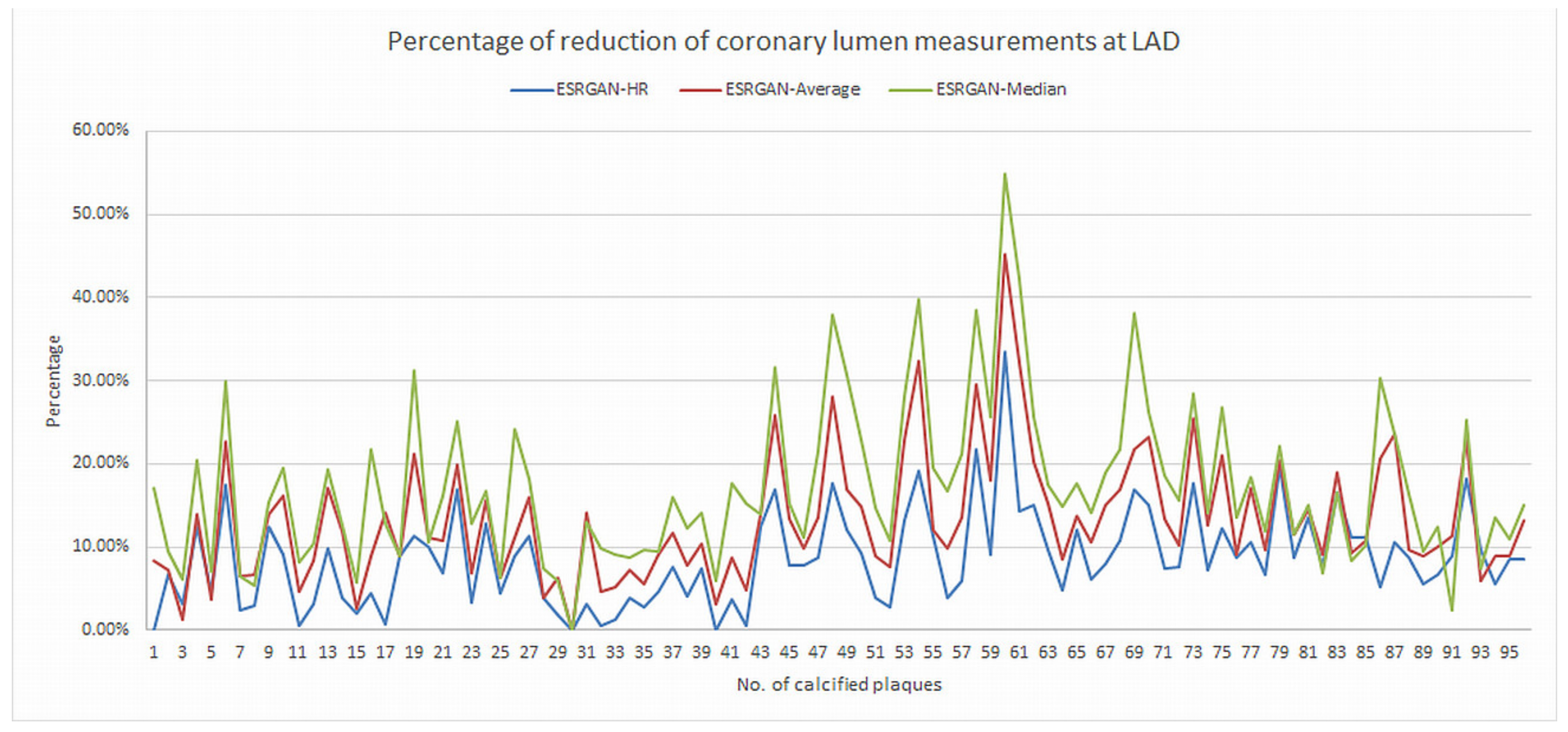
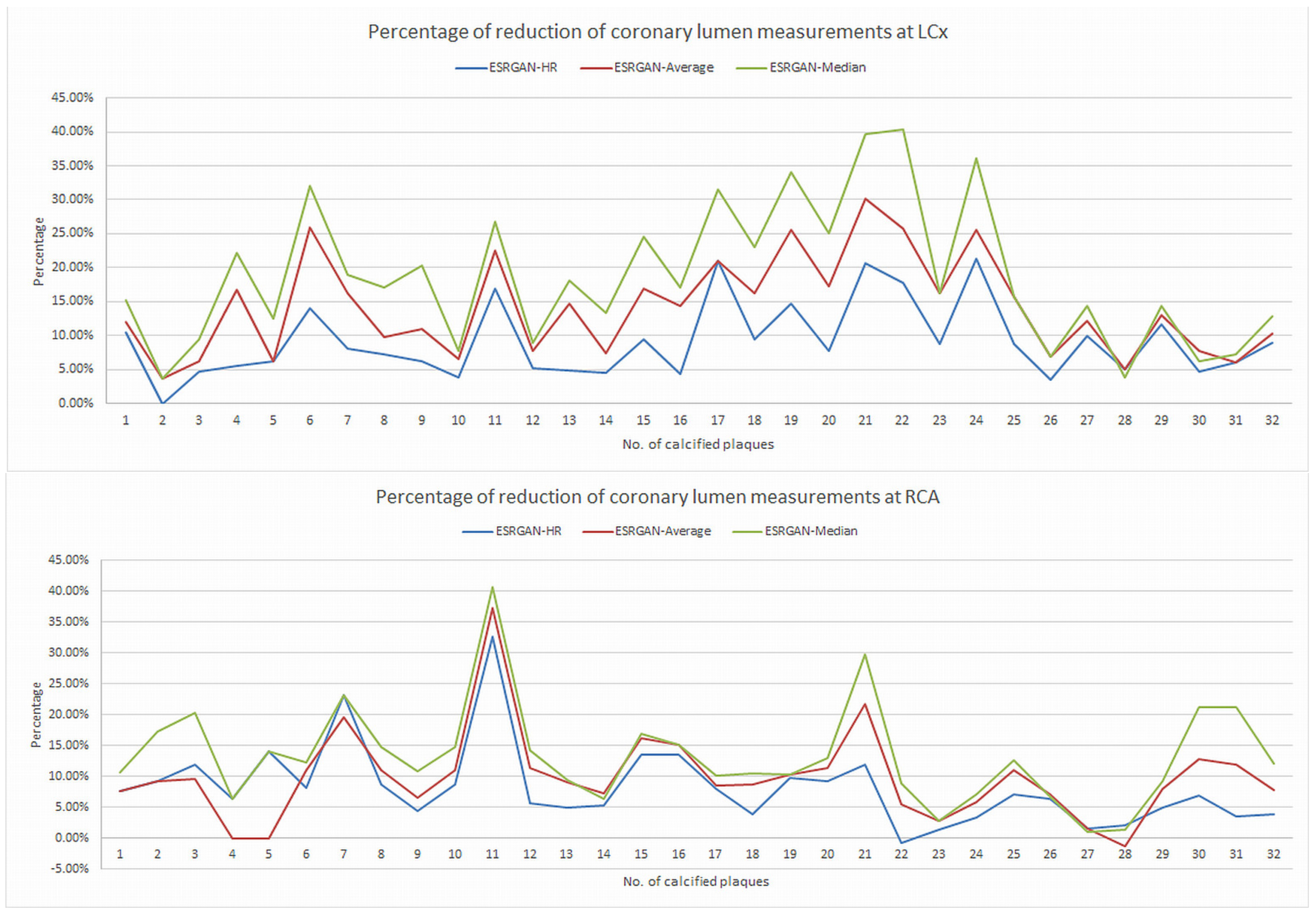
| Characteristics | Total Number of Cases (Percentage) |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 61.9 ± 9.1 |
| M/F | 41/9 |
| Coronary artery involvement | |
| 1-vessel disease | 10 (20%) |
| 2-vessel disease | 28 (56%) |
| 3-vessel disease | 12 (24%) |
| Distribution of calcified plaques at coronary arteries | |
| LAD (n = 96) | |
| 1–3 plaques | 45 (90%) |
| 4–5 plaques | 5 (10%) |
| >5 plaques | 0 |
| LCx (n = 32) | |
| 1–3 plaques | 25 (100%) |
| 4–5 plaques | 0 |
| >5 plaques | 0 |
| RCA (n = 56) | |
| 1–3 plaques | 19 (83%) |
| 4–5 plaques | 1 (4%) |
| >5 plaques | 3 (13%) |
| Coronary Arteries/No. Plaques | TP | FP | TN | FN | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | PPV (%) | NPV (%) | PLR | NLR | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LAD | |||||||||||
| Original CCTA | 18 | 61 | 17 | 0 | 100 (81.5, 100) | 21.8 (13.2, 32.6) | 22.8 (20.8, 24.9) | 100 | 1.28 (1.13, 1.43) | 0.00 | 0.68 (0.55, 0.81) |
| ESRGAN-HR | 18 | 54 | 24 | 0 | 100 (81.5, 100) | 30.8 (20.8, 42.2) | 25.0 (22.3, 27.9) | 100 | 1.44 (1.24, 1.67) | 0.00 | 0.69 (0.55, 0.82) |
| ESRGAN-Average | 17 | 49 | 29 | 1 | 94.4 (72.7, 99.8) | 37.2 (26.5, 48.9) | 25.8 (22.1, 29.8) | 96.7 (80.8, 99.5) | 1.50 (1.22, 1.84) | 0.15 (0.02, 1.02) | 0.69 (0.56, 0.82) |
| ESRGAN-Median | 17 | 46 | 32 | 1 | 94.4 (72.7, 99.8) | 41.0 (30.0, 52.7) | 26.9 (22.9, 31.4) | 96.9 (82.4, 99.5) | 1.60 (1.29, 1.99) | 0.13 (0.02, 0.93) | 0.66 (0.53, 0.79) |
| LCx | |||||||||||
| Original CCTA | 8 | 21 | 3 | 0 | 100 (63.1, 100) | 12.5 (2.6, 32.4) | 27.6 (24.7, 30.7) | 100 | 1.14 (0.98, 1.33) | 0.00 | 0.67 (0.48, 0.86) |
| ESRGAN-HR | 8 | 18 | 6 | 0 | 100 (63.1, 100) | 25.0 (9.8, 46.7) | 30.8 (26.1, 35.9) | 100 | 1.33 (1.06, 1.68) | 0.00 | 0.61 (0.41, 0.80) |
| ESRGAN-Average | 8 | 14 | 10 | 0 | 100 (63.1, 100) | 41.7 (22.1, 63.4) | 36.4 (28.9, 44.5) | 100 | 1.71 (1.22, 2.40) | 0.00 | 0.59 (0.40, 0.78) |
| ESRGAN-Median | 8 | 14 | 10 | 0 | 100 (63.1, 100) | 41.7 (22.1, 63.4) | 36.4 (28.9, 44.5) | 100 | 1.71 (1.22, 2.40) | 0.00 | 0.55 (0.36, 0.75) |
| RCA | |||||||||||
| Original CCTA | 16 | 33 | 7 | 0 | 100 (79.4, 100) | 17.5 (7.3, 32.8) | 32.7 (29.6, 35.9) | 100 | 1.21 (1.05, 1.39) | 0.00 | 0.76 (0.64, 0.89) |
| ESRGAN-HR | 16 | 23 | 17 | 0 | 100 (79.4, 100) | 42.5 (27.0, 59.1) | 41.0 (34.8, 47.6) | 100 | 1.74 (1.33, 2.27) | 0.00 | 0.81 (0.69, 0.93) |
| ESRGAN-Average | 16 | 22 | 18 | 0 | 100 (79.4, 100) | 45.0 (29.2, 61.5) | 42.1 (35.5, 49.0) | 100 | 1.82 (1.37, 2.41) | 0.00 | 0.82 (0.71, 0.94) |
| ESRGAN-Median | 16 | 18 | 22 | 0 | 100 (79.4, 100) | 55.0 (38.5, 70.7) | 47.1 (38.7, 55.6) | 100 | 2.22 (1.58, 3.13) | 0.00 | 0.86 (0.76, 0.96) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Z.; Ng, C.K.C. Artificial Intelligence (Enhanced Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Network) for Calcium Deblooming in Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography: A Feasibility Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040991
Sun Z, Ng CKC. Artificial Intelligence (Enhanced Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Network) for Calcium Deblooming in Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography: A Feasibility Study. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(4):991. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040991
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Zhonghua, and Curtise K. C. Ng. 2022. "Artificial Intelligence (Enhanced Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Network) for Calcium Deblooming in Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography: A Feasibility Study" Diagnostics 12, no. 4: 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040991
APA StyleSun, Z., & Ng, C. K. C. (2022). Artificial Intelligence (Enhanced Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Network) for Calcium Deblooming in Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography: A Feasibility Study. Diagnostics, 12(4), 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040991







