Impact of Different Cell Counting Methods in Molecular Monitoring of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Blood Collection and White Blood Cell Isolation
2.3. White Blood Cells Count
2.4. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.5. Quantification of BCR-ABL1 and ABL1 Transcripts
2.6. Software and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
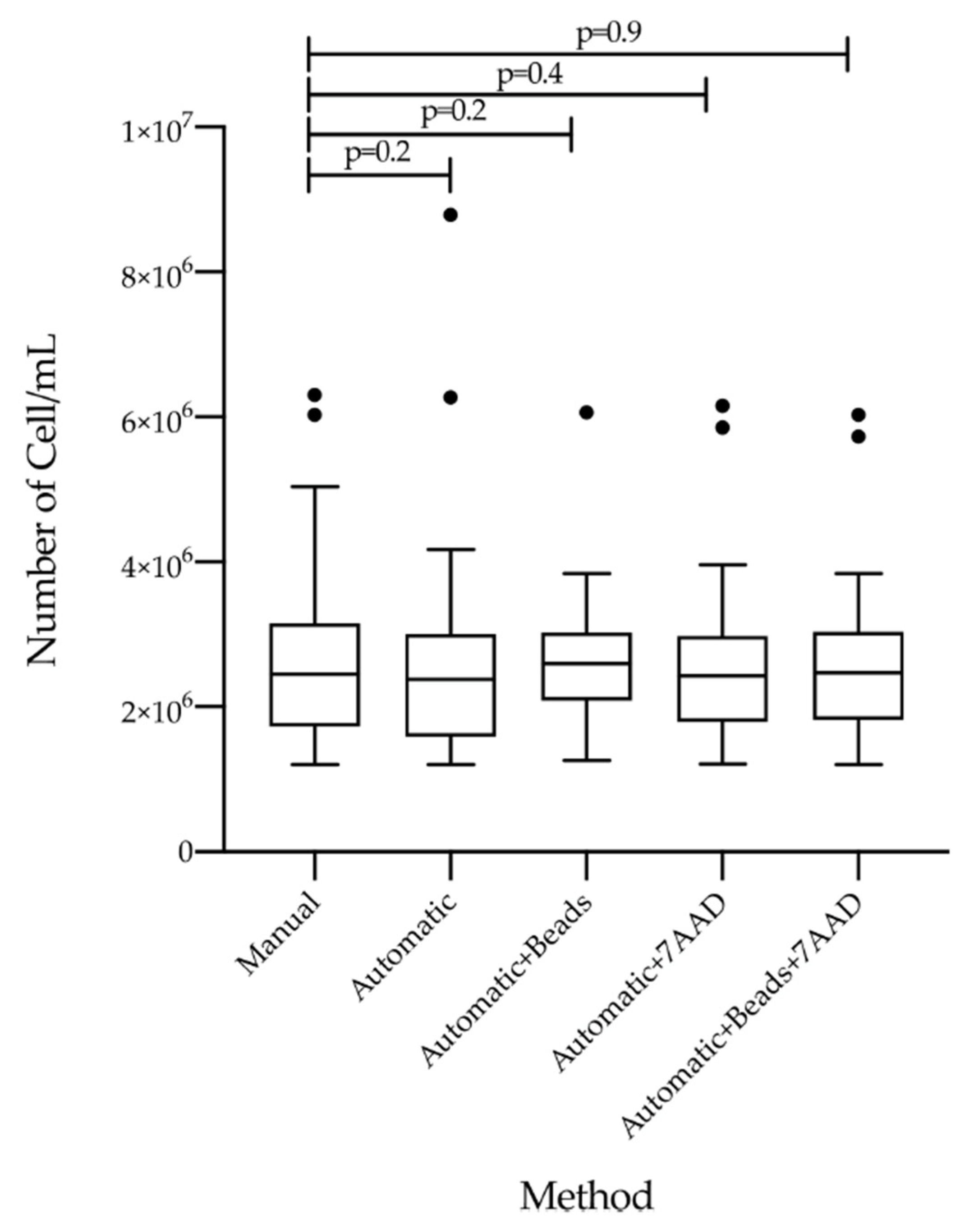
3.2. Comparison of Count Efficiency and RNA Isolation by Five Different Measurement Methods
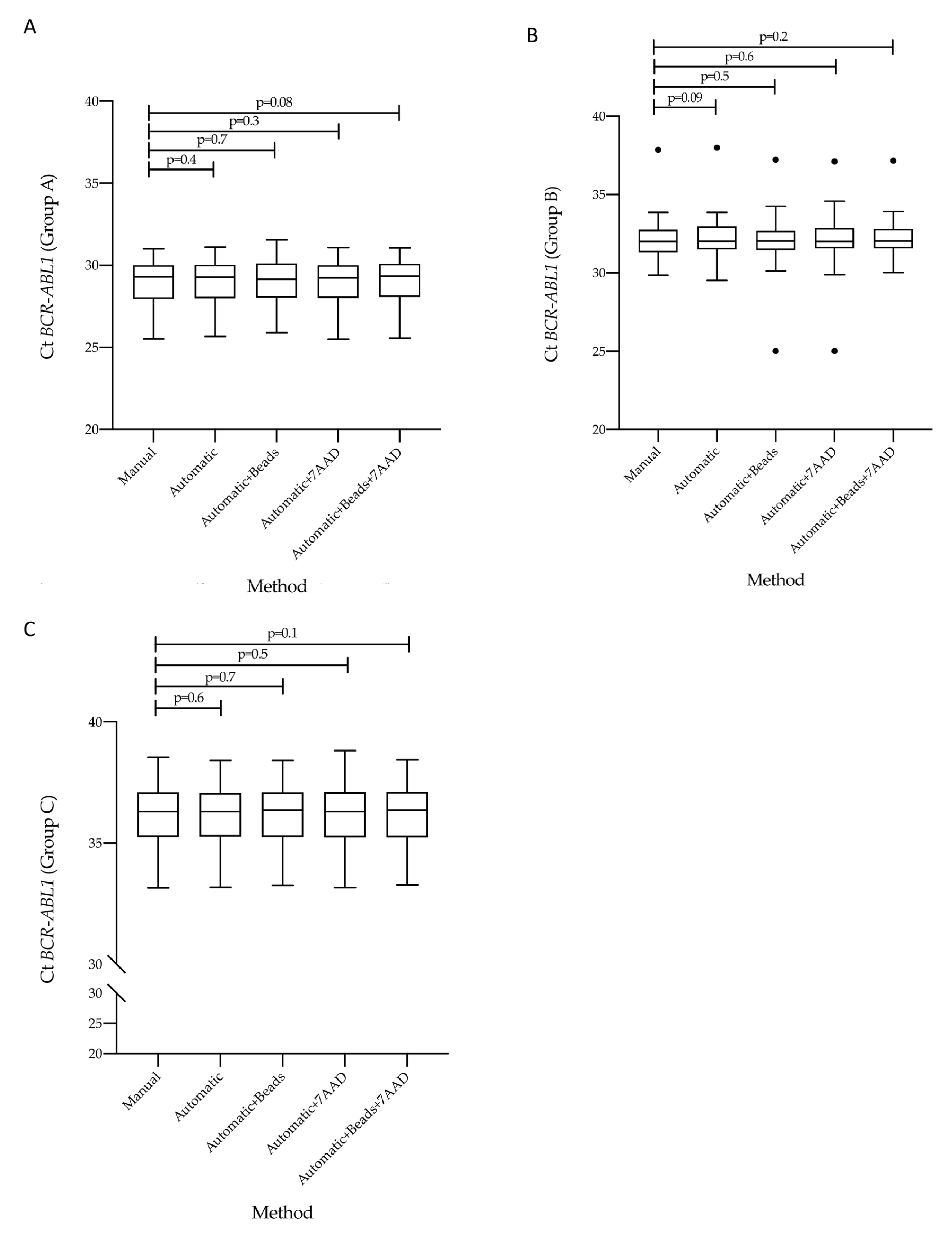
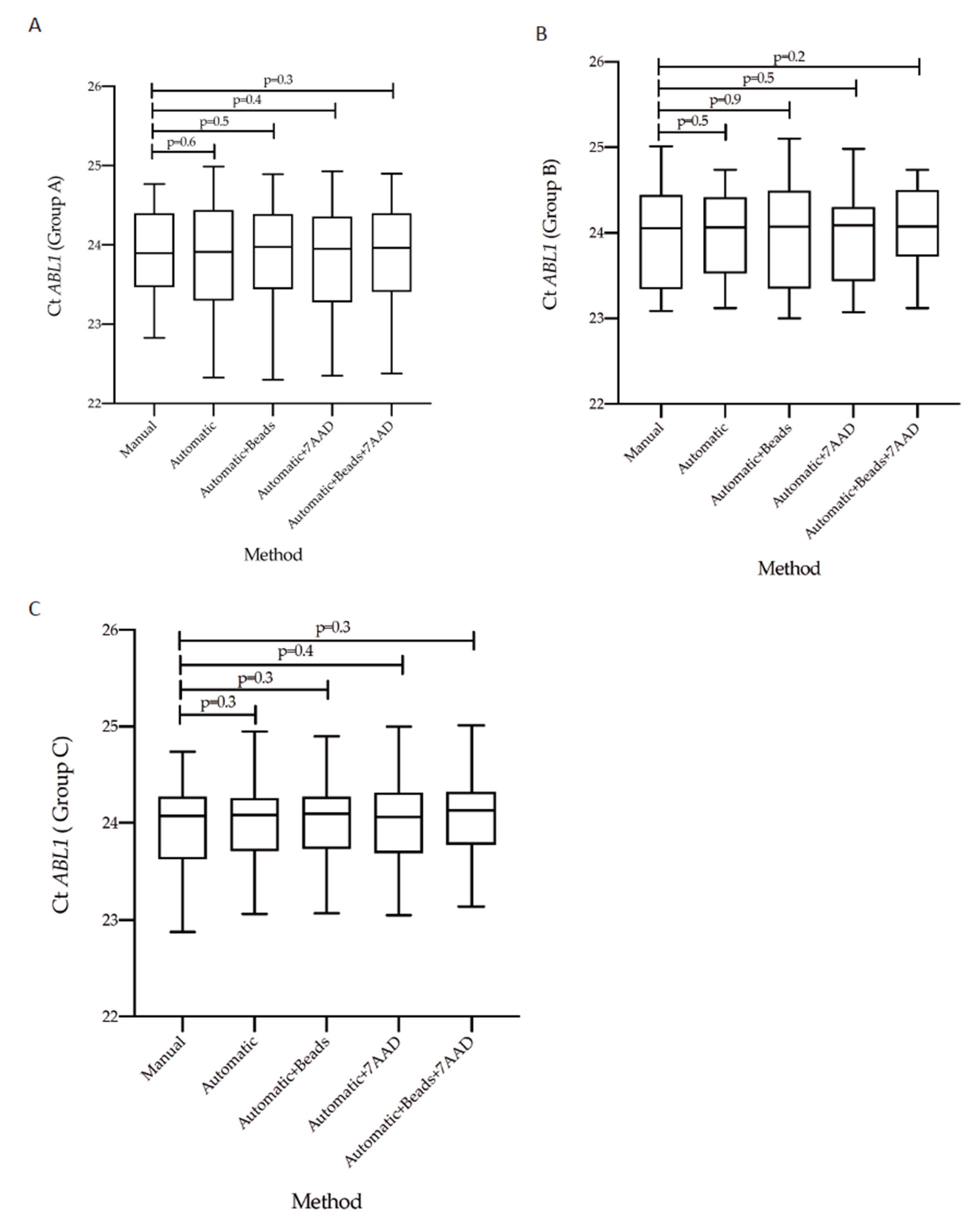
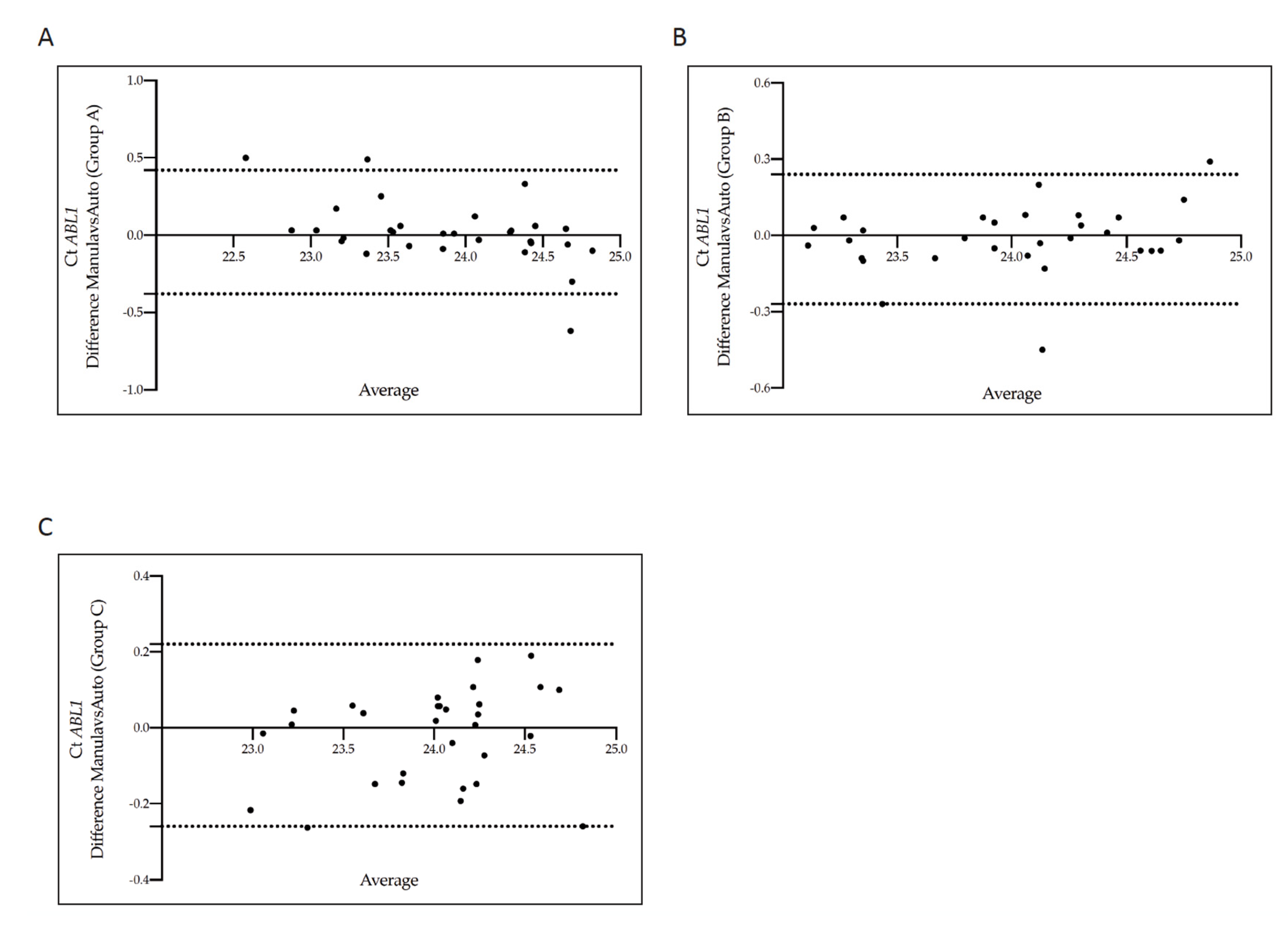
3.3. Concordance of Cycle Threshold Values for BCR-ABL1 and ABL1 Genes According to the Five Counting Methods
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quintas-Cardama, A.; Cortes, J. Molecular biology of bcr-abl1–positive chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2009, 113, 1619–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jabbour, E.; Kantarjian, H. Chronic myeloid leukemia: 2020 update on diagnosis, therapy and monitoring. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 691–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apperley, J.F. Chronic myeloid leukaemia. Lancet 2015, 385, 1447–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, R. Mechanisms of BCR–ABL in the pathogenesis of chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, Y.; Nhiayi, M.K.; Tse, E.; Cheng, J.; Massimino, M.; Durden, D.L.; Vigneri, P.; Wang, J.Y. Knockout Serum Replacement Promotes Cell Survival by Preventing BIM from Inducing Mitochondrial Cytochrome C Release. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140585. [Google Scholar]
- Massimino, M.; Vigneri, P.; Stella, S.; Tirro, E.; Pennisi, M.S.; Parrinello, L.N.; Vetro, C.; Manzella, L.; Stagno, F.; Di Raimondo, F. Combined Inhibition of Bcl2 and Bcr-Abl1 Exercises Anti-Leukemia Activity but Does Not Eradicate the Primitive Leukemic Cells. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochhaus, A.; Larson, R.A.; Guilhot, F.; Radich, J.P.; Branford, S.; Hughes, T.P.; Baccarani, M.; Deininger, M.W.; Cervantes, F.; Fujihara, S.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Imatinib Treatment for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leotta, S.; Markovic, U.; Pirosa, M.C.; Stella, S.; Tringali, S.; Martino, M.; Specchia, G.; Carluccio, P.; Risitano, A.M.; Grimaldi, F.; et al. The role of ponatinib in adult BCR-ABL1 positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia after allogeneic transplantation: A real-life retrospective multicenter study. Ann. Hematol. 2021, 100, 1743–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, V.; White, H.E.; Gerrard, G.; Mobius, S.; Saussele, S.; Franke, G.N.; Mahon, F.X.; Talmaci, R.; Colomer, D.; Soverini, S.; et al. Assessment of individual molecular response in chronic myeloid leukemia patients with atypical BCR-ABL1 fusion transcripts: Recommendations by the EUTOS cooperative network. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 147, 3081–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagnetti, F.; Di Raimondo, F.; De Vivo, A.; Spitaleri, A.; Gugliotta, G.; Fabbiano, F.; Capodanno, I.; Mannina, D.; Salvucci, M.; Antolino, A.; et al. A population-based study of chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated with imatinib in first line. Am. J. Hematol. 2017, 92, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccarani, M.; Deininger, M.W.; Rosti, G.; Hochhaus, A.; Soverini, S.; Apperley, J.F.; Cervantes, F.; Clark, R.E.; Cortes, J.E.; Guilhot, F.; et al. European LeukemiaNet recommendations for the management of chronic myeloid leukemia: 2013. Blood 2013, 122, 872–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochhaus, A.; Baccarani, M.; Silver, R.T.; Schiffer, C.; Apperley, J.F.; Cervantes, F.; Clark, R.E.; Cortes, J.E.; Deininger, M.W.; Guilhot, F.; et al. European LeukemiaNet 2020 recommendations for treating chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2020, 34, 966–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosti, G.; Castagnetti, F.; Gugliotta, G.; Baccarani, M. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukaemia: Which, when, for whom? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soverini, S.; Bavaro, L.; De Benedittis, C.; Martelli, M.; Iurlo, A.; Orofino, N.; Sica, S.; Sora, F.; Lunghi, F.; Ciceri, F.; et al. Prospective assessment of NGS-detectable mutations in CML patients with nonoptimal response: The NEXT-in-CML study. Blood 2020, 135, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massimino, M.; Stella, S.; Tirro, E.; Pennisi, M.S.; Vitale, S.R.; Puma, A.; Romano, C.; Di Gregorio, S.; Tomarchio, C.; Di Raimondo, F.; et al. ABL1-Directed Inhibitors for CML: Efficacy, Resistance and Future Perspectives. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 2457–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, S.; Zammit, V.; Vitale, S.R.; Pennisi, M.S.; Massimino, M.; Tirro, E.; Forte, S.; Spitaleri, A.; Antolino, A.; Siracusa, S.; et al. Clinical Implications of Discordant Early Molecular Responses in CML Patients Treated with Imatinib. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahon, F.X. Discontinuation of TKI therapy and ‘functional’ cure for CML. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2016, 29, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccarani, M. Treatment-free remission in chronic myeloid leukemia: Floating between expectation and evidence. Leukemia 2017, 31, 1015–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saussele, S.; Richter, J.; Hochhaus, A.; Mahon, F.X. The concept of treatment-free remission in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2016, 30, 1638–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, N.C.; Hochhaus, A.; Muller, M.C. Molecular monitoring of chronic myeloid leukemia: Principles and interlaboratory standardization. Ann. Hematol. 2015, 94, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroni, L.; Wilson, G.; Gerrard, G.; Mason, J.; Grimwade, D.; White, H.E.; de Castro, D.G.; Austin, S.; Awan, A.; Burt, E.; et al. Guidelines for the measurement of BCR-ABL1 transcripts in chronic myeloid leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 153, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzo, B.; Gottardi, E.M.; Errichiello, S.; Daraio, F.; Barate, C.; Galimberti, S. Monitoring Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: How Molecular Tools May Drive Therapeutic Approaches. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muller, M.C.; Erben, P.; Saglio, G.; Gottardi, E.; Nyvold, C.G.; Schenk, T.; Ernst, T.; Lauber, S.; Kruth, J.; Hehlmann, R.; et al. Harmonization of BCR-ABL mRNA quantification using a uniform multifunctional control plasmid in 37 international laboratories. Leukemia 2008, 22, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hughes, T.; Deininger, M.; Hochhaus, A.; Branford, S.; Radich, J.; Kaeda, J.; Baccarani, M.; Cortes, J.; Cross, N.C.; Druker, B.J.; et al. Monitoring CML patients responding to treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Review and recommendations for harmonizing current methodology for detecting BCR-ABL transcripts and kinase domain mutations and for expressing results. Blood 2006, 108, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stella, S.; Gottardi, E.M.; Favout, V.; Barragan Gonzalez, E.; Errichiello, S.; Vitale, S.R.; Fava, C.; Luciano, L.; Stagno, F.; Grimaldi, F.; et al. The Q-LAMP Method Represents a Valid and Rapid Alternative for the Detection of the BCR-ABL1 Rearrangement in Philadelphia-Positive Leukemias. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stella, S.; Vitale, S.R.; Massimino, M.; Puma, A.; Tomarchio, C.; Pennisi, M.S.; Tirro, E.; Romano, C.; Martorana, F.; Stagno, F.; et al. A Novel System for Semiautomatic Sample Processing in Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia: Increasing Throughput without Impacting on Molecular Monitoring at Time of SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.P.; Saglio, G.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Guilhot, F.; Niederwieser, D.; Rosti, G.; Nakaseko, C.; De Souza, C.A.; Kalaycio, M.E.; Meier, S.; et al. Early molecular response predicts outcomes in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase treated with frontline nilotinib or imatinib. Blood 2014, 123, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, M.; Carol, B. Factors Affecting Haemocytometer Counts of Sperm Concentration in Human Semen. J. Reprod. Fertil. 1964, 8, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massimino, M.; Tirro, E.; Stella, S.; Manzella, L.; Pennisi, M.S.; Romano, C.; Vitale, S.R.; Puma, A.; Tomarchio, C.; Di Gregorio, S.; et al. Impact of the Breakpoint Region on the Leukemogenic Potential and the TKI Responsiveness of Atypical BCR-ABL1 Transcripts. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 669469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirosa, M.C.; Leotta, S.; Cupri, A.; Stella, S.; Martino, E.A.; Scalise, L.; Sapienza, G.; Calafiore, V.; Mauro, E.; Spadaro, A.; et al. Long-Term Molecular Remission Achieved by Antibody Anti-CD22 and Ponatinib in a Patient Affected by Ph’+ Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Relapsed after Second Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Case Report. Chemotherapy 2018, 63, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, M.S.; Stella, S.; Vitale, S.R.; Puma, A.; Di Gregorio, S.; Romano, C.; Tirro, E.; Massimino, M.; Antolino, A.; Siragusa, S.; et al. BCR-ABL1 Doubling-Times and Halving-Times May Predict CML Response to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vigneri, P.; Stagno, F.; Stella, S.; Cupri, A.; Forte, S.; Massimino, M.; Antolino, A.; Siragusa, S.; Mannina, D.; Impera, S.S.; et al. High BCR-ABL/GUS(IS) Levels at Diagnosis of Chronic Phase CML Are Associated with Unfavorable Responses to Standard-Dose Imatinib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 7189–7198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cross, N.C.; White, H.E.; Muller, M.C.; Saglio, G.; Hochhaus, A. Standardized definitions of molecular response in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2012, 26, 2172–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cross, N.C.; White, H.E.; Colomer, D.; Ehrencrona, H.; Foroni, L.; Gottardi, E.; Lange, T.; Lion, T.; Machova Polakova, K.; Dulucq, S.; et al. Laboratory recommendations for scoring deep molecular responses following treatment for chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2015, 29, 999–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deininger, M.W. Molecular monitoring in CML and the prospects for treatment-free remissions. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2015, 2015, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shanmuganathan, N.; Hughes, T.P. Molecular monitoring in CML: How deep? How often? How should it influence therapy? Blood 2018, 132, 2125–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cadena-Herrera, D.; Esparza-De Lara, J.E.; Ramirez-Ibanez, N.D.; Lopez-Morales, C.A.; Perez, N.O.; Flores-Ortiz, L.F.; Medina-Rivero, E. Validation of three viable-cell counting methods: Manual, semi-automated, and automated. Biotechnol. Rep. 2015, 7, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.C.; Lin, W.; Yagami, M.; Tseng, D.; Miyashita-Lin, E.; Singh, N.; Lin, A.; Shih, S.J. Validation of cell density and viability assays using Cedex automated cell counter. Biologicals 2010, 38, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Fernandez, C.; Hervas, D.; Rivas-Sendra, A.; Marin, M.P.; Segui-Simarro, J.M. Comparison of six different methods to calculate cell densities. Plant Methods 2018, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Characteristics | N. |
|---|---|
| Age | |
| Median | 63 |
| Range | 25–82 |
| Follow up | |
| Median (mo.) | 60 |
| Range | 5–105 |
| Sex (pts n.) | |
| Male | 53 (58.9%) |
| Female | 37 (41.1%) |
| Leukocyte count (×109/L) | |
| Median | 9.85 |
| Range | 6.20–20.8 |
| Platelet count (×109/L) | |
| Median | 350 |
| Range | 80–758 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | |
| Median | 12.5 |
| Range | 10.8–14.5 |
| Transcript Type | |
| e13a2 (b2a2) | 34 |
| e14a2 (b3a2) | 48 |
| e13a2 and e14a2 | 8 |
| Molecular response | |
| GROUP A (10% > BCR-ABL1/ABL1IS > 1%) | 30 |
| GROUP B (1% ≥ BCR-ABL1/ABL1IS > 0.1%) | 30 |
| GROUP C (0.1% ≥ BCR-ABL1/ABL1IS > 0.01%) | 30 |
| Cells Isolation | RNA Isolation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protocol | Cells/mL Median Range | Total Cells Median Range | ng/µL Median Range | 260/280 Median Range | 260/230 Median Range |
| Manual | 2.46 × 106 (1.20 × 106–6.30 × 106) | 1.23 × 108 (6.00 × 107–3.15 × 108) | 123.00 (80–223.5) | 1.9 (1.9–2.0) | 2.1 (2.0–2.2) |
| Automatic (PBS with cells) | 2.46 × 106 (1.20 × 106–6.27 × 106) | 1.23 × 108 (6.00 × 107–3.14 × 108) | 120.35 (75–256.4) | 1.9 (1.90–2.0) | 2.1 (2.0–2.2) |
| Automatic + beads | 2.60 × 106 (1.26 × 106–6.06 × 106) | 1.30 × 108 (6.30 × 107–3.03 × 108) | 118.12 (75–200.4) | 1.9 (1.90–2.0) | 2.1 (2.0–2.2) |
| Automatic + 7AAD | 2,43 × 106 (1.22 × 106–6.16 × 106) | 1.22 × 108 (6.10 × 107–3.08 × 108) | 126.00 (78–232.5) | 1.9 (1.9–2.0) | 2.1 (2.0–2.2) |
| Automatic + 7AAD + beads | 2,47 × 106 (1.20 × 106–6.04 × 106) | 1.24 × 108 (6.00 × 107–3.02 × 108) | 116.65 (75–223.3) | 1.9 (1.90–2.0) | 2.1 (2.0–2.2) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stella, S.; Vitale, S.R.; Stagno, F.; Massimino, M.; Puma, A.; Tomarchio, C.; Pennisi, M.S.; Tirrò, E.; Romano, C.; Di Raimondo, F.; et al. Impact of Different Cell Counting Methods in Molecular Monitoring of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051051
Stella S, Vitale SR, Stagno F, Massimino M, Puma A, Tomarchio C, Pennisi MS, Tirrò E, Romano C, Di Raimondo F, et al. Impact of Different Cell Counting Methods in Molecular Monitoring of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(5):1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051051
Chicago/Turabian StyleStella, Stefania, Silvia Rita Vitale, Fabio Stagno, Michele Massimino, Adriana Puma, Cristina Tomarchio, Maria Stella Pennisi, Elena Tirrò, Chiara Romano, Francesco Di Raimondo, and et al. 2022. "Impact of Different Cell Counting Methods in Molecular Monitoring of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients" Diagnostics 12, no. 5: 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051051
APA StyleStella, S., Vitale, S. R., Stagno, F., Massimino, M., Puma, A., Tomarchio, C., Pennisi, M. S., Tirrò, E., Romano, C., Di Raimondo, F., Cacciola, E., Cacciola, R., & Manzella, L. (2022). Impact of Different Cell Counting Methods in Molecular Monitoring of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients. Diagnostics, 12(5), 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051051







