Vascular Complications Caused by Tibial Osteochondroma: Focus on the Literature and Presentation of a Popliteal Artery Thrombosis with Acute Lower Limb Ischemia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Focus on the Literature and Search Strategy
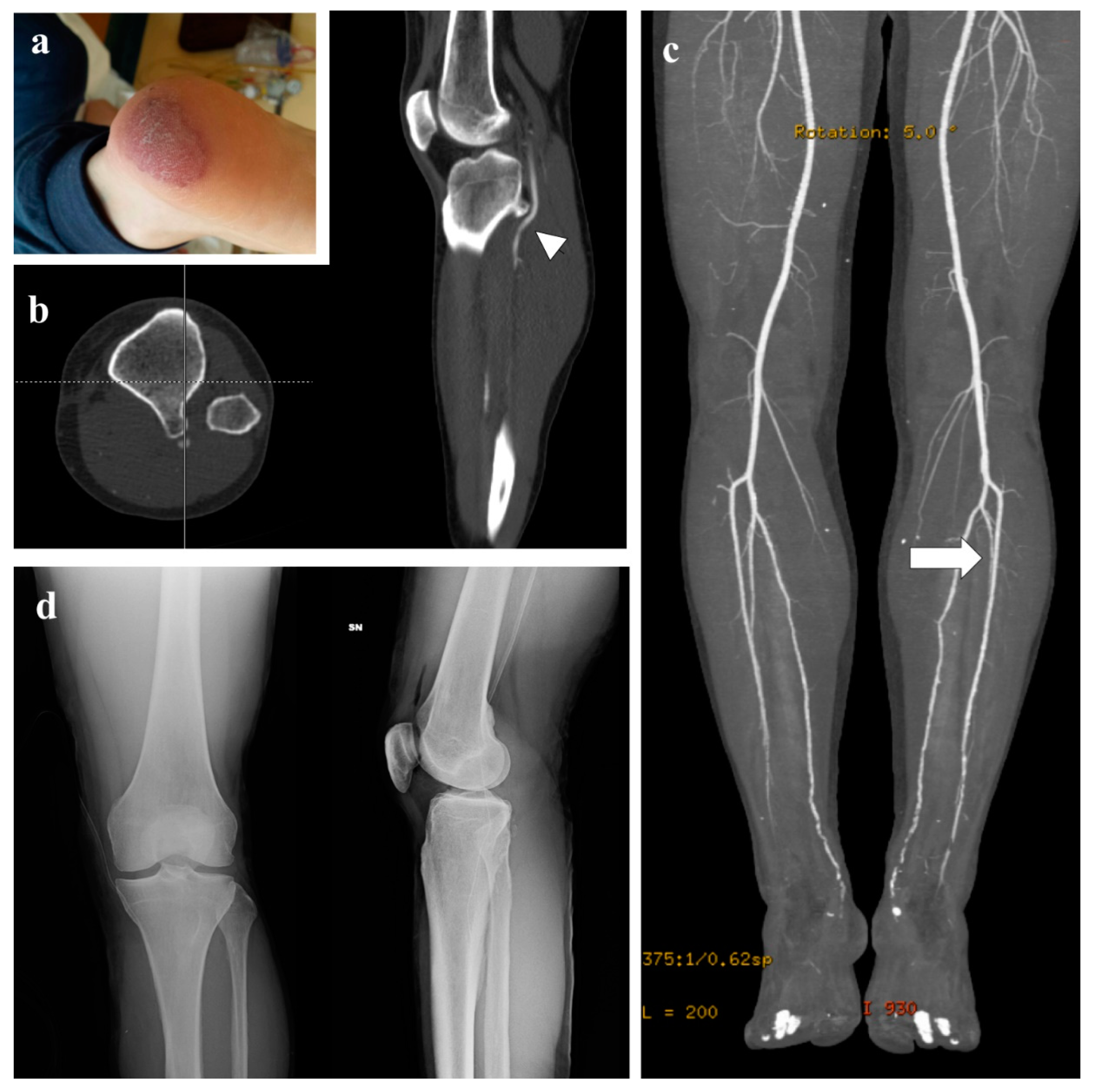
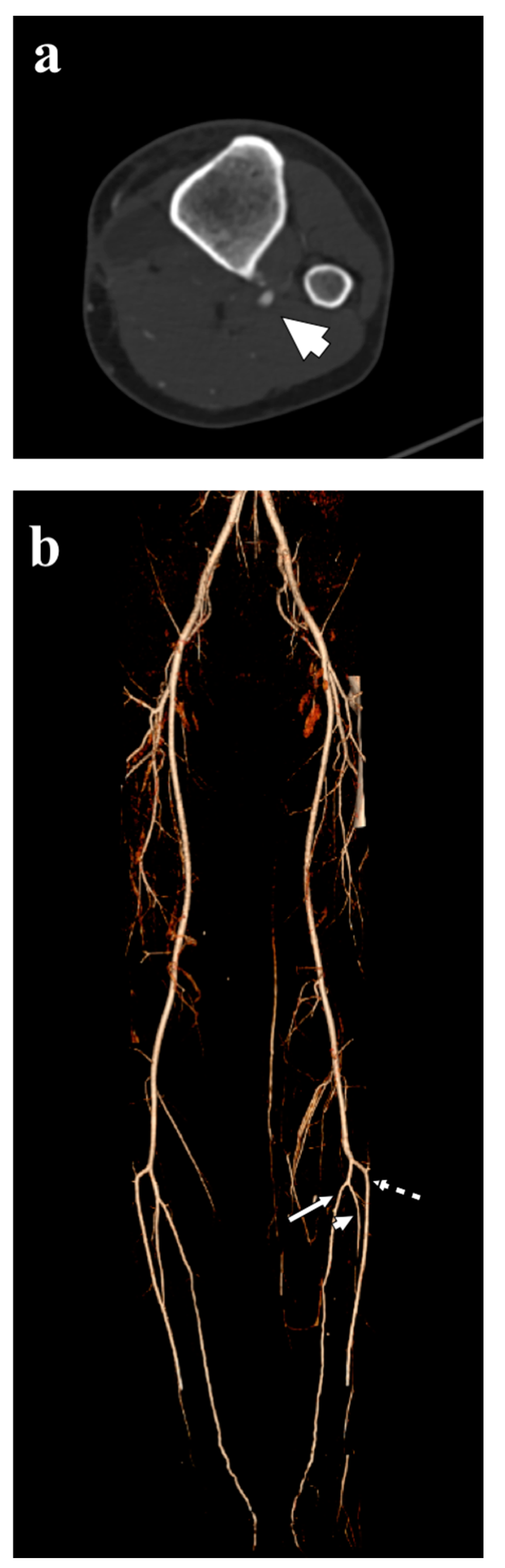
3. Representative Explanatory Case
4. Discussion
5. Diagnosis
6. Treatment
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alonso-Gómez, N.; Diego, M.C.-D.; Martínez-Izquierdo, A.; Sáinz-González, F. Unusual clinical complication: Acute lower limb ischemia caused by a tibial osteochondroma. Reumatol. Clin. 2019, 15, 182–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tepelenis, K.; Papathanakos, G.; Kitsouli, A.; Troupis, T.; Barbouti, A.; Vlachos, K.; Kanavaros, P.; Kitsoulis, P. Osteochondromas: An Updated Review of Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Clinical Presentation, Radiological Features and Treatment Options. In Vivo 2021, 35, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argyriou, C.; Drosos, G.; Tottas, S.; Tasopoulou, K.-M.; Kougioumtzis, I.; Georgiadis, G.S. A Rare Case of Tibioperoneal Arterial Trunk Entrapment Caused by a Fibular Osteochondroma. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 55, 308.e11–308.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanigawa, N.; Kariya, S.; Kojima, H.; Komemushi, A.; Fujii, H.; Sawada, S. Lower limb ischaemia caused by fractured osteochondroma of the femur. Br. J. Radiol. 2007, 80, e78–e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.; Mavrogenis, A.F.; Angelini, A.; Rimondi, E.; Battaglia, M.; Ruggieri, P. Vascular complications in orthopaedic surgery. J. Long-Term Eff. Med. Implants 2011, 21, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muneer, K.; Goyal, K.K.; Gupta, H.; Sajeev, C.G. Popliteal artery thrombosis caused by osteochondroma: A rare presentation. Heart India 2016, 4, 153–155. [Google Scholar]
- Eschelman, D.J.; Gardiner, G.A.; Deely, D.M. Osteochondroma: An Unusual Cause of Vascular Disease in Young Adults. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 1995, 6, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber-Szydło, K.; Poręba, R.; Belowska-Bień, K.; Derkacz, A.; Badowski, R.; Andrzejak, R.; Szuba, A. Popliteal artery thrombosis secondary to a tibial osteochondroma. Vasa 2011, 40, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, A.F.; Pullan, J.M. Aneurysm complicating exostosis. Br. J. Surg. 1966, 53, 929–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kover, J.H.; Schwalbe, N.; Levowitz, B.S. Popliteal aneurysm due to osteochondroma in athletic injury. N. Y. State J. Med. 1970, 70, 3001–3003. [Google Scholar]
- Metras, D.; Coulibaly, A.O.; Calvy, H.; Acquaviva, P.; Ouattara, K. Thrombose artérielle fémoro-poplitée un case exceptionnel de complication vasculaire par exostose [Arterial thrombosis of the femoro-popliteal axis. An exceptional case of vascular complication by exostosis (author’s transl)]. J. Mal. Vasc. 1981, 6, 289–291. (In French) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Männer, R.; Mäkinen, E. Angiographic findings in a false popliteal aneurysm due to osteochondroma of the femur. Pediatr. Radiol. 1975, 3, 244–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smits, A.; Pavoordt, H.V.; Moll, F. Unusual Arterial Complications Caused by an Osteochondroma of the Femur or Tibia in Young Patients. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 1998, 12, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi-Azandaryani, M.; Mendl, N.; Rademacher, A.; Hoffmann, U.; Steckmeier, B.; Heyn, J. Pseudoaneurysm of the popliteal artery due to osteochondroma of the distal femur. Vasa 2010, 39, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solhaugh, J.H.; Olerud, S.E. Pseudoaneurysm of the femoral artery caused by osteochondroma of the femur. A case report. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1975, 57, 867–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leve, L.; Kalideen, J.M. Popliteal false aneurysm complicating osteochondroma. A case report. S. Afr. Med. J. 1979, 55, 1087–1088. [Google Scholar]
- Ennker, J.; Freyschmidt, J.; Reilmann, H.; Dimovski, D.; Refmann, H. False aneurysm of the femoral artery due to an osteochondroma. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 1984, 102, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcove, R.C.; Lindeque, B.G.; Silane, M.F. Pseudoaneurysm of the Popliteal Artery with an Unusual Arteriographic Presentation. A case report. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1988, 234, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasseur, M.A.; Fabre, O. Vascular complications of osteochondromas. J. Vasc. Surg. 2000, 31, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klebuc, M.; Burrow, S.; Organek, A.; Cole, W.; Zuker, R. Osteochondroma as a Causal Agent in Popliteal Artery Pseudoaneurysms: Case Report and Literature Review. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2001, 17, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.J.R. Aneurysm of the popliteal artery secondary to trauma from an osteochondroma of the femur: A case report and review of the literature. Br. J. Surg. 1978, 65, 786–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieffer, E.; Maraval, M.; Tricot, J.F.; Natali, J. Anévrysme artériel compliquant une exostose ostéogénique de l’extrémité supérieure du tibia [Aneurysm due to an exostosis of the upper end of the tibia (author’s transl)]. Rev. Chir. Orthop. Reparatrice Appar. Mot. 1978, 64, 155–162. (In French) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferriter, P.; Hirschy, J.; Kesseler, H.; Scott, W.N. Popliteal pseudoaneurysm. A case report. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1983, 65, 695–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmir, H.; Azghari, A.; Mechchat, A.; Benzirar, A.; Idrissi, R.; Lekehel, B.; Sefiani, Y.; El Mesnaoui, A.; Ammar, F.; Bensaid, Y. Rupture d’un faux anévrisme de l’artère poplitée révélant une exostose du tibia: À propos d’un cas et revue de littérature [Rupture of a popliteal artery pseudo-aneurysm revealing a tibial osteochondroma: Case report and review of the literature]. J. Mal. Vasc. 2011, 36, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenway, G.; Resnick, D.; Bookstein, J.J. Popliteal pseudoaneurysm as a complication of an adjacent osteochondroma: Angiographic diagnosis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1979, 132, 294–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otsuka, T.; Yonezawa, M.; Kamiyama, F.; Matusita, Y.; Matui, N. Popliteal pseudoaneurysm simulating soft-tissue sarcoma: Complication of osteochondroma resection. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 6, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israels, S.; Downs, A.R. Traumatic aneurysm of the popliteal artery due to an osteochondroma of the femur. Can. J. Surg. 1980, 23, 270–272. [Google Scholar]
- Zini, F.; Negri, V. Su di un caso di pseudo-aneurisma popliteo da esostosi del femore. A case of popliteal pseudoaneurysm caused by femoral exostoses. Acta Biomed. Ateneo Parmense 1984, 55, 43–47. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Taneda, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Yano, M.; Nagahama, H.; Nakamura, E.; Niina, K.; Enomoto, Y.; Onituka, T. Popliteal Artery Pseudoaneurysm Caused by Osteochondroma. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2004, 18, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.J.-Y.; Qi, S.D.; Vaes, R.H.; Di Bella, C.; Mayer, R. Fractured osteochondroma presenting with popliteal pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of literature. J. Vasc. Surg. Cases Innov. Tech. 2020, 6, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lizama, V.; Zerbini, M.; Gagliardi, R.; Howell, L. Popliteal vein thrombosis and popliteal artery pseudoaneurysm complicating osteochondroma of the femur. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1987, 148, 783–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harrington, I.; Campbell, V.; Valazques, R.; Williams, T. Pseudoaneurysm of the Popliteal Artery as a Complication of an Osteochondroma. A review of the literature and a case report. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1991, 270, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Burkhardt, J.L.; Castilla, J.C. Postraumatic popliteal pseudoaneurysm from femoral osteochondroma: Case report and review of the literature. J. Vasc. Surg. 2003, 37, 669–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antonio, Z.P.; Alejandro, R.M.; Luis, M.R.J.; José, G.R. Femur ostochondroma and secondary pseudoaneurysm of the popliteal artery. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2006, 126, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolson, S.T.; Maloney, W.J.; James, D.R. Superficial femoral pseudoaneurysm and arterial thromboembolism caused by an osteochondroma. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 1989, 9, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asselineau, A.; Coubret, P.; Lahoud, J.C. Faux anévrysme de l’artère fémorale compliquant une exostose [False aneurysm of the femoral artery complicating exostosis]. Rev. Chir. Orthop. Reparatrice Appar. Mot. 1993, 79, 411–414. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- Argin, M.; Biçeroğlu, S.; Arkun, R.; Parildar, M. Solitary osteochondroma causing popliteal pseudoaneurysm that presented as a mass lesion. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2007, 13, 190–192. [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman, J.; Mazzucco, J.; Kwasnik, E.; Loyer, R.; Knight, D. Popliteal Pseudoaneurysm as a Complication of an Adjacent Osteochondroma. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 1994, 8, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballaro, A.; Fox, A.; Collin, J. Rupture of a popliteal artery pseudo-aneurysm secondary to a fibular osteochondroma. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 1997, 14, 151–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsushita, M.; Nishikimi, N.; Sakurai, T.; Nimura, Y. Pseudoaneurysm of the popliteal artery caused by exostosis of the femur: Case report and review of the literature. J. Vasc. Surg. 2000, 32, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davies, R.S.; Satti, U.; Duffield, R.G. Popliteal artery pseudo-aneurysm secondary to femoral osteochondroma: A case report and literature review. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2007, 89, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petratos, D.V.; Bakogiannis, K.S.; Anastasopoulos, J.N.; Matsinos, G.S.; Bessias, N.K. Popliteal artery pseudoaneurysm secondary to osteochondroma in children and adolescents: A case report and literature review. J. Surg. Orthop. Adv. 2009, 18, 205–210. [Google Scholar]
- Kalinga, M.J.; Lo, N.N.; Tan, S.K. Popliteal artery pseudoaneurysm caused by an osteochondroma—A traditional medicine massage sequelae. Singap. Med. J. 1996, 37, 443–445. [Google Scholar]
- Hasselgren, P.O.; Eriksson, B.; Lukes, P.; Seeman, T. False popliteal aneurysm caused by exostosis of the femur. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1983, 24, 540–542. [Google Scholar]
- Wiater, J.M.; Farley, F.A. Popliteal pseudoaneurysm caused by an adjacent osteochondroma: A case report and review of the literature. Am. J. Orthop. (Belle Mead NJ) 1999, 28, 412–416. [Google Scholar]
- Cardon, A.; Aillet, S.; Ledu, J.; Kerdiles, Y. Pseudo-aneurysm of the popliteal artery by femoral exostosis in a young child. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2001, 42, 241–244. [Google Scholar]
- Tóth, C.; Olvasztó, S.; Dinya, T. Femurcondylus exostosisa okozta arteria poplitea sérülés ritka esete (Esetismertetés) [Rare case of popliteal artery injury caused by distal femoral exostosis. Case report]. Magy Seb. 2001, 54, 115–117. (In Hungarian) [Google Scholar]
- Oxenius, A.; Knirsch, W.; Kretschmar, O.; Dodge-Khatami, A.; Lamprecht, E. Unclear Swelling of the Popliteal Fossa Due to a Giant Pseudoaneurysm Associated with Osteochondroma. J. Pediatr. 2009, 154, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bursztyn, M.; Stracher, M.; Sanchez, J.I.; Ramenofsky, M.; Kirwin, J.; Spero, C. Pseudoaneurysm associated with multiple osteochondromatosis. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2005, 40, 1201–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hadidy, A.M.; Al-Smady, M.M.; Haroun, A.A.; Hamamy, H.A.; Ghoul, S.M.; Shennak, A.O. Hereditary Multiple Exostoses with Pseudoaneurysm. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2007, 30, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thévenin, F.; Dumaine, V.; Feydy, A.; Campagna, R.; Guerini, H.; Richarme, D.; Drapé, J.; Bierry, G.; Babinet, A.; Anract, P.; et al. Faux anévrisme de l’artère fémorale compliquant une maladie des exostoses multiples [False aneurysm of the femoral artery in multiple exostosis syndrome]. J. Radiol. 2009, 90, 612–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaouch, N.; Alimi, F.; Kortas, C.; Limayem, F.; Braham, A.; Mlika, S.; Jerbi, S.; Ennabli, K. Complications vasculaires poplitées bilatérales d’une exostose héréditaire multiple [Bilateral popliteal artery complications of multiple hereditary exostosis]. Ann. Cardiol. Angeiol. 2011, 60, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavić, P.; Vergles, D.; Šarlija, M.; Ajduk, M.; Cupurdija, K. Pseudoaneurysm of the Popliteal Artery in a Patient with Multiple Hereditary Exostoses. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2011, 25, 268.e1–268.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhegan, I.S.; Shehzad, K.N.; Bhatti, T.S.; Waters, T.S. Acute popliteal pseudoaneurysm rupture secondary to distal femoral osteochondroma in a patient with hereditary multiple exostoses. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2012, 94, e134–e136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banno, H.; Houbballah, R.; Becquemin, J.-P. Acute Lower Extremity Ischemia due to the Popliteal Pseudoaneurysm in a 16-year-old Boy with Multiple Exostoses. Ann. Vasc. Dis. 2013, 6, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nasr, B.; Albert, B.; David, C.H.; da Fonseca, P.M.; Badra, A.; Gouny, P. Exostoses and Vascular Complications in the Lower Limbs: Two Case Reports and Review of the Literature. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2015, 29, 1315.e7–1315.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orawczyk, T.; Kuczmik, W.; Kazibudzki, M.; Ludyga, T.; Cwik, P.; Ziaja, K. Popliteal Pseudoaneurysm as a Rare Complication of a Solitary Tibial Osteochondroma. EJVES Extra 2006, 12, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duarte, O.A.P.; Neira, J.G.A.; Herazo, V.d.C.; Lara, M.F.O.; Polanco, A.L.L.; Omaña, A.F.D.; Ortiz, A.F.H. Popliteal artery pseudoaneurysm caused by non–penetrating trauma in a patient with hereditary multiple osteochondromatosis. Radiol. Case Rep. 2021, 17, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphey, M.D.; Choi, J.J.; Kransdorf, M.J.; Flemming, D.J.; Gannon, F.H. Imaging of Osteochondroma: Variants and Complications with Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation. RadioGraphics 2000, 20, 1407–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakata, T.; Mogi, K.; Sakurai, M.; Nomura, A.; Fujii, M.; Takahara, Y. Popliteal Artery Pseudoaneurysm Caused by Osteochondroma. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2017, 43, 313.e5–313.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.; Silver, M. Osteochondroma: An unusual case of claudication in a young adult. Vasc. Med. 2019, 25, 274–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Derubertis, B.G. Popliteal Artery Occlusion Secondary to Exostosis of the Femur. Perspect. Vasc. Surg. Endovasc. Ther. 2012, 24, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazick, E.; Keeling, W.B.; Armstrong, P.; Letson, D.; Back, M. Pseudoaneurysm of the Superficial Femoral Artery Associated with Osteochondroma: A Case Report. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2005, 39, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raherinantenaina, F.; Rakoto-Ratsimba, H.N.; Rajaonanahary, T.M.A. Management of extremity arterial pseudoaneurysms associated with osteochondromas. Vascular 2016, 24, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parente, B.; Fiorucci, B.; Simonte, G.; Brambilla, D.M.; Lenti, M. Osteochondromas: An Unusual Cause of Vascular Disease in Young Patients: 2 Clinical Cases. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 32, 129.e7–129.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, A.; Piazza, M.; Pagliarini, E.; Trovarelli, G.; Spertino, A.; Ruggieri, P. The Orthopedic-Vascular Multidisciplinary Approach Improves Patient Safety in Surgery for Musculoskeletal Tumors: A Large-Volume Center Experience. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotti, C.; Marone, E.M.; Brasca, L.E.; Peretti, G.M.; Chiesa, R.; Del Maschio, A.; Fraschini, G.; Camnasio, F. Pseudoaneurysm overlying an osteochondroma: A noteworthy complication. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 2010, 11, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Authors | Pts | Symptoms | Bone Site | Treatment of Vascular Lesion | Age (Years) | Exostosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Masson et al. [9] | 1 | S + P | Femur | Popliteal artery ligature + VB | 9 | Multiple |
| Refs. [10,11] | 2 | S (1), P (1) AI (1) | Femur | PAR + VB | Mean 31.5 (15–48) | Solitary |
| Refs. [12,13,14] | 4 | S (2), P (2),AI (2) | Femur | n.a. | Mean 22 (13–39) | Solitary |
| Refs. [15,16,17,18,19,20] | 7 | S (5), P (4) | Femur | Direct repair | Mean 19.7 (15–20) | Multiple |
| Shah et al. [21] | 1 | AI | Femur | PAR + direct repair | 16 | Solitary |
| Refs. [22,23,24] | 3 | S (2), P (2), AI (1) | Tibia | Flattening + VB | Mean 22 (20–23) | Solitary |
| Refs. [25,26] | 2 | S (1) P (2) | Femur | PAR + EtoEA | Mean 18.5 (16–18) | Multiple |
| Refs. [17,19,27,28,29,30] | 6 | S (6), P (4) | Femur | PAR + EtoEA | Mean 34.3 (14–51) | Solitary |
| Refs. [31,32,33,34] | 4 | S (2), P (4) | Femur | Ligature + direct repair | Mean 15.3 (9–16) | Solitary |
| Refs. [35,36,37] | 3 | S (3), P (1) AI (1) | Femur | Flattening + VB | Mean 14.3 (13–16) | Solitary |
| Refs. [38,39,40,41,42] | 5 | S (3), P (3), Pulsatile mass (1) | Femur (4) Fibula (1) | Vein patch | Mean 18.8 (13–33) | Solitary |
| Refs. [19,38,43] | 4 | S (3), P (2), AI (1) | Femur | Ligature + VB | Mean 22.3 (14–37) | Solitary |
| Hasselgren et al. [44] | 1 | S + P | Femur | Ligature + prosthetic bypass | 45 | Multiple |
| Smits et al. [13] | 1 | Calf swelling | Tibia | n.a. | 28 | Solitary |
| Wiater et al. [45] | 1 | P | Femur | VB | 17 | Multiple |
| Cardon et al. [46] | 1 | P | Femur | Resection + EtoEA | 12 | Solitary |
| Toth et al. [47] | 1 | S + P | Femur | Flattening + prosthetic bypass | 17 | Multiple |
| Oxenius et al. [48] | 1 | S + P | Femur | Pericardial patch | 13 | Solitary |
| Refs. [49,50,51,52,53,54,55] | 8 | S (5), P (4), C (2), AI (1) | Femur (8) | Flattening + VB | Mean 17.5 (12–21) | Multiple |
| Nasr et al. [56] | 1 | AI | Femur | Vein patch + EtoEA | 17 | Multiple |
| 1 | S + P | Femur | Flattening + EtoEA | 17 | Multiple | |
| Refs. [57,58] | 2 | S (1), P (2), C (1) | Tibia | Direct repair | Mean 14.5 (14–15) | Multiple |
| Present case | 1 | AI | Tibia | Thrombolytic Therapy | 34 | Solitary |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Angelini, A.; Cerchiaro, M.; Maturi, C.; Ruggieri, P. Vascular Complications Caused by Tibial Osteochondroma: Focus on the Literature and Presentation of a Popliteal Artery Thrombosis with Acute Lower Limb Ischemia. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051191
Angelini A, Cerchiaro M, Maturi C, Ruggieri P. Vascular Complications Caused by Tibial Osteochondroma: Focus on the Literature and Presentation of a Popliteal Artery Thrombosis with Acute Lower Limb Ischemia. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(5):1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051191
Chicago/Turabian StyleAngelini, Andrea, Mariachiara Cerchiaro, Carlo Maturi, and Pietro Ruggieri. 2022. "Vascular Complications Caused by Tibial Osteochondroma: Focus on the Literature and Presentation of a Popliteal Artery Thrombosis with Acute Lower Limb Ischemia" Diagnostics 12, no. 5: 1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051191
APA StyleAngelini, A., Cerchiaro, M., Maturi, C., & Ruggieri, P. (2022). Vascular Complications Caused by Tibial Osteochondroma: Focus on the Literature and Presentation of a Popliteal Artery Thrombosis with Acute Lower Limb Ischemia. Diagnostics, 12(5), 1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051191








