Cytokine Profile of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Severe COVID-19 and Possible Therapeutic Targets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in COVID-19: Where We Are Now and Where We Are Going to
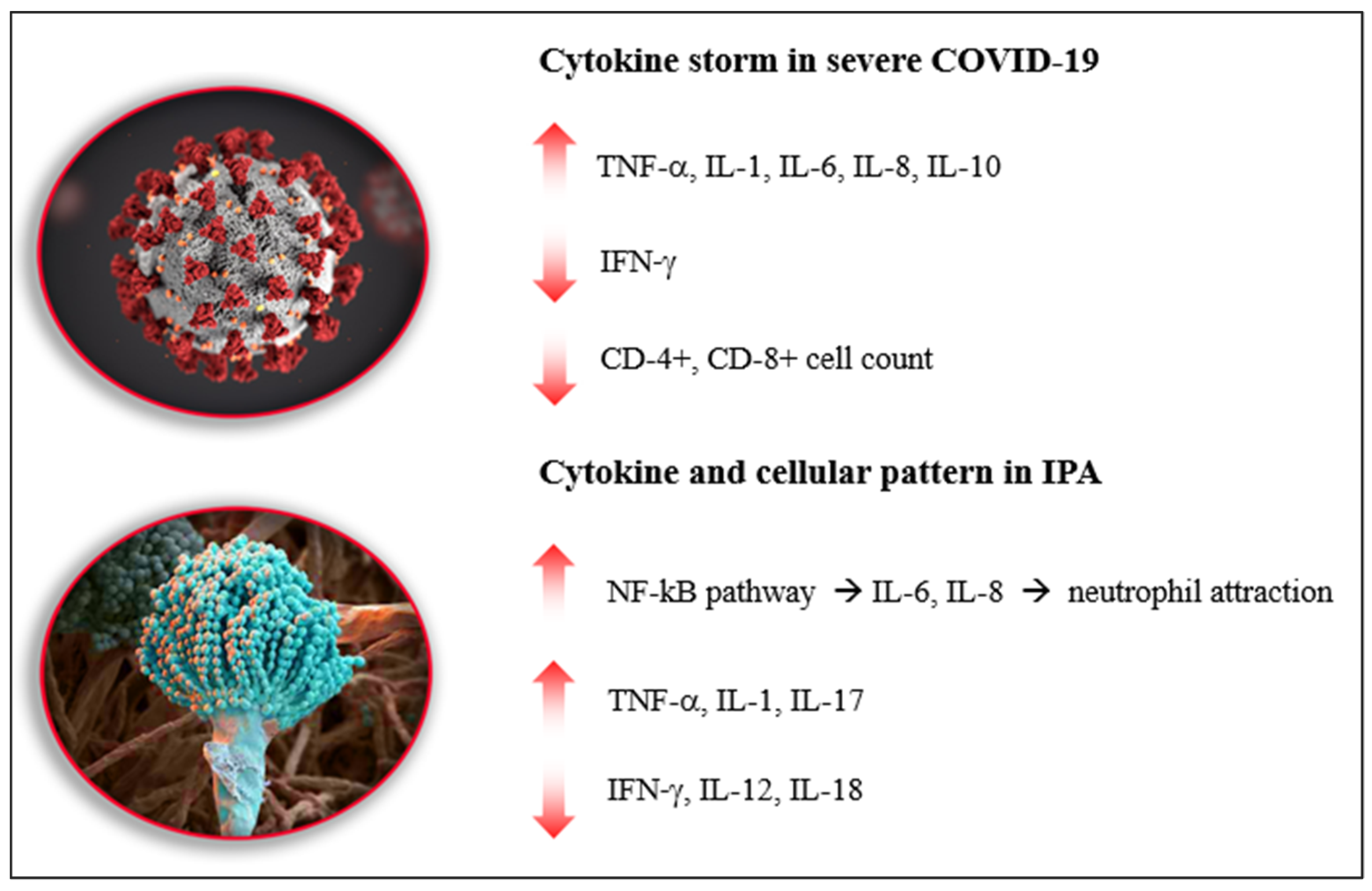
3. Cytokine Storm in Severe COVID-19
4. Cytokine Expression in IPA
5. Genetic Susceptibility to Aspergillus Infection: Possible Role in CAPA
6. Impact of COVID-19 Therapy on CAPA
7. Preventive and Therapeutic Strategies for CAPA
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, J.; Zhao, S.; Teng, T.; Abdalla, A.E.; Zhu, W.; Xie, L.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X. Systematic Comparison of Two Animal-to-Human Transmitted Human Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV. Viruses 2020, 12, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ravid, J.D.; Leiva, O.; Chitalia, V.C. Janus Kinase Signaling Pathway and Its Role in COVID-19 Inflammatory, Vascular, and Thrombotic Manifestations. Cells 2022, 11, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawson, T.M.; Moore, L.S.P.; Zhu, N.; Ranganathan, N.; Skolimowska, K.; Gilchrist, M.; Satta, G.; Cooke, G.; Holmes, A. Bacterial and Fungal Coinfection in Individuals With Coronavirus: A Rapid Review To Support COVID-19 Antimicrobial Prescribing. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 2459–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, M.; Higginson, E.; Pereira-Dias, J.; Curran, M.D.; Parmar, S.; Khokhar, F.; Cuchet-Lourenco, D.; Lux, J.; Sharma-Hajela, S.; Ravenhill, B.; et al. Ventilator-associated pneumonia in critically ill patients with COVID-19. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez Martin, C.; Madrid Martinez, E.; Gonzalez Pellicer, R.; Armero Ibanez, R.; Martinez Gonzalez, E.; Llau Pitarch, J.V. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with acute respiratory syndrome by COVID-19. Rev. Esp. Anestesiol. Reanim. 2021, 69, 48–53. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alanio, A.; Delliere, S.; Fodil, S.; Bretagne, S.; Megarbane, B. Prevalence of putative invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill patients with COVID-19. Lancet. Respir. Med. 2020, 8, e48–e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wauters, J.; Baar, I.; Meersseman, P.; Meersseman, W.; Dams, K.; De Paep, R.; Lagrou, K.; Wilmer, A.; Jorens, P.; Hermans, G. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis is a frequent complication of critically ill H1N1 patients: A retrospective study. Intensive Care Med. 2012, 38, 1761–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pauw, B.; Walsh, T.J.; Donnelly, J.P.; Stevens, D.A.; Edwards, J.E.; Calandra, T.; Pappas, P.G.; Maertens, J.; Lortholary, O.; Kauffman, C.A.; et al. Revised definitions of invasive fungal disease from the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Invasive Fungal Infections Cooperative Group and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study Group (EORTC/MSG) Consensus Group. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 1813–1821. [Google Scholar]
- Koehler, P.; Bassetti, M.; Chakrabarti, A.; Chen, S.C.A.; Colombo, A.L.; Hoenigl, M.; Klimko, N.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Oladele, R.O.; Vinh, D.C.; et al. Defining and managing COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis: The 2020 ECMM/ISHAM consensus criteria for research and clinical guidance. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, e149–e162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone, M.; Massetti, A.P.; Russo, A.; Vullo, V.; Venditti, M. Invasive aspergillosis in patients with liver disease. Med. Mycol. 2011, 49, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verweij, P.E.; Bruggemann, R.J.M.; Azoulay, E.; Bassetti, M.; Blot, S.; Buil, J.B.; Calandra, T.; Chiller, T.; Clancy, C.J.; Cornely, O.A.; et al. Taskforce report on the diagnosis and clinical management of COVID-19 associated pulmonary aspergillosis. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 819–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamoth, F.; Lewis, R.E.; Walsh, T.J.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Navigating the uncertainties of COVID-19 associated aspergillosis (CAPA): A comparison with influenza associated aspergillosis (IAPA). J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 10, 1631–1640. [Google Scholar]
- Kula, B.E.; Clancy, C.J.; Hong Nguyen, M.; Schwartz, I.S. Invasive mould disease in fatal COVID-19: A systematic review of autopsies. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e405–e414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergun, M.; Bruggemann, R.J.M.; Alanio, A.; Delliere, S.; van Arkel, A.; Bentvelsen, R.G.; Rijpstra, T.; van der Sar-van der Brugge, S.; Lagrou, K.; Janssen, N.A.F.; et al. Aspergillus Test Profiles and Mortality in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e0122921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.; Tiseo, G.; Falcone, M.; Menichetti, F. Pulmonary Aspergillosis: An Evolving Challenge for Diagnosis and Treatment. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2020, 9, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, R.; Sharma, B.R.; Tuladhar, S.; Williams, E.P.; Zalduondo, L.; Samir, P.; Zheng, M.; Sundaram, B.; Banoth, B.; Malireddi, R.K.S.; et al. Synergism of TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma Triggers Inflammatory Cell Death, Tissue Damage, and Mortality in SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Cytokine Shock Syndromes. Cell 2021, 184, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGonagle, D.; Sharif, K.; O’Regan, A.; Bridgewood, C. The Role of Cytokines including Interleukin-6 in COVID-19 induced Pneumonia and Macrophage Activation Syndrome-Like Disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janka, G.E.; Lehmberg, K. Hemophagocytic syndromes--an update. Blood Rev. 2014, 28, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubernatorova, E.O.; Gorshkova, E.A.; Polinova, A.I.; Drutskaya, M.S. IL-6: Relevance for immunopathology of SARS-CoV-2. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020, 53, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Valle, D.M.; Kim-Schulze, S.; Huang, H.H.; Beckmann, N.D.; Nirenberg, S.; Wang, B.; Lavin, Y.; Swartz, T.H.; Madduri, D.; Stock, A.; et al. An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts COVID-19 severity and survival. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, B.; Wang, C.; Tan, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Ning, L.; Chen, L.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; et al. Reduction and Functional Exhaustion of T Cells in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhao, J.; Van Rooijen, N.; Perlman, S. Evasion by stealth: Inefficient immune activation underlies poor T cell response and severe disease in SARS-CoV-infected mice. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Lee, Y.; Kim, E.; Kwak, A.; Ryoo, S.; Bae, S.H.; Azam, T.; Kim, S.; Dinarello, C.A. The Interleukin-1alpha Precursor is Biologically Active and is Likely a Key Alarmin in the IL-1 Family of Cytokines. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, W.Y.; Goodman, R.B.; Steinberg, K.P.; Ruzinski, J.T.; Radella, F., 2nd; Park, D.R.; Pugin, J.; Skerrett, S.J.; Hudson, L.D.; Martin, T.R. Cytokine balance in the lungs of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164 Pt 1, 1896–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Wu, D.; Guo, W.; Cao, Y.; Huang, D.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Yu, H.; et al. Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2620–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Li, M.; Zhou, Z.; Guan, X.; Xiang, Y. Can we use interleukin-6 (IL-6) blockade for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-induced cytokine release syndrome (CRS)? J. Autoimmun. 2020, 111, 102452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.; Fatima, R.; Assaly, R. Elevated interleukin-6 and severe COVID-19: A meta-analysis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 2283–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, R.; Leunig, A.; Pekayvaz, K.; Popp, O.; Joppich, M.; Polewka, V.; Escaig, R.; Anjum, A.; Hoffknecht, M.L.; Gold, C.; et al. Self-sustaining IL-8 loops drive a prothrombotic neutrophil phenotype in severe COVID-19. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e150862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, M.; O’Garra, A. The regulation of IL-10 production by immune cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barry, J.C.; Shakibakho, S.; Durrer, C.; Simtchouk, S.; Jawanda, K.K.; Cheung, S.T.; Mui, A.L.; Little, J.P. Hyporesponsiveness to the anti-inflammatory action of interleukin-10 in type 2 diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, L.; Zhang, H.; Dauphars, D.J.; He, Y.W. A Potential Role of Interleukin 10 in COVID-19 Pathogenesis. Trends Immunol. 2021, 42, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohl, T.M. Immune responses to invasive aspergillosis: New understanding and therapeutic opportunities. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 30, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chai, L.; Netea, M.G.; Teerenstra, S.; Earnest, A.; Vonk, A.G.; Schlamm, H.T.; Herbrecht, R.; Troke, P.F.; Kullberg, B.J. Early proinflammatory cytokines and C-reactive protein trends as predictors of outcome in invasive Aspergillosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 1454–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warris, A.; Bjorneklett, A.; Gaustad, P. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis associated with infliximab therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1099–1100. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrad, B.; Strieter, R.M.; Standiford, T.J. Role of TNF-alpha in pulmonary host defense in murine invasive aspergillosis. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar]
- Nagai, H.; Guo, J.; Choi, H.; Kurup, V. Interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha protect mice from invasive aspergillosis. J. Infect. Dis. 1995, 172, 1554–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borger, P.; Koeter, G.H.; Timmerman, J.A.; Vellenga, E.; Tomee, J.F.; Kauffman, H.F. Proteases from Aspergillus fumigatus induce interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-8 production in airway epithelial cell lines by transcriptional mechanisms. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 180, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clemons, K.V.; Grunig, G.; Sobel, R.A.; Mirels, L.F.; Rennick, D.M.; Stevens, D.A. Role of IL-10 in invasive aspergillosis: Increased resistance of IL-10 gene knockout mice to lethal systemic aspergillosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2000, 122, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roilides, E.; Dimitriadou, A.; Kadiltsoglou, I.; Sein, T.; Karpouzas, J.; Pizzo, P.A.; Walsh, T.J. IL-10 exerts suppressive and enhancing effects on antifungal activity of mononuclear phagocytes against Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 322–329. [Google Scholar]
- Cunha, C.; Goncalves, S.M.; Duarte-Oliveira, C.; Leite, L.; Lagrou, K.; Marques, A.; Lupianez, C.B.; Mesquita, I.; Gaifem, J.; Barbosa, A.M.; et al. IL-10 overexpression predisposes to invasive aspergillosis by suppressing antifungal immunity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, X.; Du, W.; Du, J.; Chi, Y.; Sun, B.; Song, Z.; Shi, J. Diagnosis values of IL-6 and IL-8 levels in serum and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Investig. Med. 2021, 69, 1344–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthikeyan, R.S.; Vareechon, C.; Prajna, N.V.; Dharmalingam, K.; Pearlman, E.; Lalitha, P. Interleukin 17 expression in peripheral blood neutrophils from fungal keratitis patients and healthy cohorts in southern India. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 211, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phadke, A.P.; Mehrad, B. Cytokines in host defense against Aspergillus: Recent advances. Med. Mycol. 2005, 43 (Suppl. S1), S173–S176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marciano, B.E.; Spalding, C.; Fitzgerald, A.; Mann, D.; Brown, T.; Osgood, S.; Yockey, L.; Darnell, D.N.; Barnhart, L.; Daub, J.; et al. Common severe infections in chronic granulomatous disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 1176–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.; Pasqualotto, A.C.; Pitzurra, L.; Romani, L.; Denning, D.W.; Rodrigues, F. Polymorphisms in toll-like receptor genes and susceptibility to pulmonary aspergillosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 618–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, N.L.; Hankinson, J.; Simpson, A.; Denning, D.W.; Bowyer, P. Reduced expression of TLR3, TLR10 and TREM1 by human macrophages in Chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis, and novel associations of VEGFA, DENND1B and PLAT. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, O960–O968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaid, M.; Kaur, S.; Sambatakou, H.; Madan, T.; Denning, D.W.; Sarma, P.U. Distinct alleles of mannose-binding lectin (MBL) and surfactant proteins A (SP-A) in patients with chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis and allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2007, 45, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, Z.; Sahin, O.S.; Yazar, S.; Bozok Cetintas, V. Genetic and epigenetic factors associated with increased severity of COVID-19. Cell Biol. Int. 2021, 45, 1158–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Veerdonk, F.L.; Bruggemann, R.J.M.; Vos, S.; De Hertogh, G.; Wauters, J.; Reijers, M.H.E.; Netea, M.G.; Schouten, J.A.; Verweij, P.E. COVID-19-associated Aspergillus tracheobronchitis: The interplay between viral tropism, host defence, and fungal invasion. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines; National Institutes of Health (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2021.
- Centeno-Lima, S.; Silveira, H.; Casimiro, C.; Aguiar, P.; do Rosario, V.E. Kinetics of cytokine expression in mice with invasive aspergillosis: Lethal infection and protection. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2002, 32, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balloy, V.; Huerre, M.; Latge, J.P.; Chignard, M. Differences in patterns of infection and inflammation for corticosteroid treatment and chemotherapy in experimental invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ng, T.T.; Robson, G.D.; Denning, D.W. Hydrocortisone-enhanced growth of Aspergillus spp.: Implications for pathogenesis. Microbiology (Reading) 1994, 140 Pt 9, 2475–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lionakis, M.S.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Glucocorticoids and invasive fungal infections. Lancet 2003, 362, 1828–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yang, X.; Lv, Z.; Zhou, T.; Liu, H.; Zou, X.; Cao, F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, B.; Chen, W.; et al. Risk Factors for Invasive Aspergillosis in Patients Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit With Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 753659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delliere, S.; Dudoignon, E.; Fodil, S.; Voicu, S.; Collet, M.; Oillic, P.A.; Salmona, M.; Depret, F.; Ghelfenstein-Ferreira, T.; Plaud, B.; et al. Risk factors associated with COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis in ICU patients: A French multicentric retrospective cohort. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 27, 790-e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenburg, C.E.; Doan, T. Azithromycin for severe COVID-19. Lancet 2020, 396, 936–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhalabi, M.; Eddin, K.A.; Ali, F.; Abbas, A. SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) pneumonia patient treated with two doses of infliximab within 2 weeks for acute severe ulcerative colitis: A case report. Medicine 2022, 101, e28722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraliakos, X.; Tsiami, S.; Vijayan, S.; Jung, H.; Barkham, N. Real-world evidence for subcutaneous infliximab (CT-P13 SC) treatment in patients with psoriatic arthritis during the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic: A case series. Clin. Case Rep. 2022, 10, e05205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiodras, S.; Samonis, G.; Boumpas, D.T.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Fungal infections complicating tumor necrosis factor alpha blockade therapy. Mayo. Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Locatelli, F.; Jordan, M.B.; Allen, C.; Cesaro, S.; Rizzari, C.; Rao, A.; Degar, B.; Garrington, T.P.; Sevilla, J.; Putti, M.C.; et al. Emapalumab in Children with Primary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1811–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cure, E.; Kucuk, A.; Cure, M.C. Can emapalumab be life saving for refractory, recurrent, and progressive cytokine storm caused by COVID-19, which is resistant to anakinra, tocilizumab, and Janus kinase inhibitors. Indian. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 53, 226–228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bechman, K.; Subesinghe, S.; Norton, S.; Atzeni, F.; Galli, M.; Cope, A.P.; Winthrop, K.L.; Galloway, J.B. A systematic review and meta-analysis of infection risk with small molecule JAK inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantini, F.; Niccoli, L.; Matarrese, D.; Nicastri, E.; Stobbione, P.; Goletti, D. Baricitinib therapy in COVID-19: A pilot study on safety and clinical impact. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 318–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi, S.; Becker, H.; Reinhardt, H.; Engelhardt, M.; Zeiser, R.; von Bubnoff, N.; Wasch, R. Ruxolitinib. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2018, 212, 119–132. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.; Merrill, S.A.; Alsawah, F.; Bockenstedt, P.; Campagnaro, E.; Devata, S.; Gitlin, S.D.; Kaminski, M.; Cusick, A.; Phillips, T.; et al. Ruxolitinib in adult patients with secondary haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: An open-label, single-centre, pilot trial. Lancet Haematol. 2019, 6, e630–e637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wei, J.; Zou, L.; Jiang, T.; Wang, G.; Chen, L.; Huang, L.; Meng, F.; Huang, L.; Wang, N.; et al. Ruxolitinib in treatment of severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A multicenter, single-blind, randomized controlled trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.R.; Roy, S.; Meszaros, E.C.; Sun, Y.; Howell, S.J.; Malemud, C.J.; Pearlman, E. JAK/STAT regulation of Aspergillus fumigatus corneal infections and IL-6/23-stimulated neutrophil, IL-17, elastase, and MMP9 activity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 100, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gresnigt, M.S.; Rekiki, A.; Rasid, O.; Savers, A.; Jouvion, G.; Dannaoui, E.; Parlato, M.; Fitting, C.; Brock, M.; Cavaillon, J.M.; et al. Reducing hypoxia and inflammation during invasive pulmonary aspergillosis by targeting the Interleukin-1 receptor. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloseily, E.M.; Weiser, P.; Crayne, C.B.; Haines, H.; Mannion, M.L.; Stoll, M.L.; Beukelman, T.; Atkinson, T.P.; Cron, R.Q. Benefit of Anakinra in Treating Pediatric Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, M.; Menon, S.; Chaimani, A.; Evrenoglou, T.; Ghosn, L.; Grana, C.; Henschke, N.; Cogo, E.; Villanueva, G.; Ferrand, G.; et al. Interleukin-1 blocking agents for treating COVID-19. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 1, CD015308. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mazzitelli, M.; Arrighi, E.; Serapide, F.; Pelle, M.C.; Tassone, B.; Lionello, R.; Marrazzo, G.; Lagana, D.; Costanzo, F.S.; Matera, G.; et al. Use of subcutaneous tocilizumab in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levi, M. Tocilizumab in severe COVID-19: A promise fulfilled. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 95, 38–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prattes, J.; Wauters, J.; Giacobbe, D.R.; Salmanton-Garcia, J.; Maertens, J.; Bourgeois, M.; Reynders, M.; Rutsaert, L.; Van Regenmortel, N.; Lormans, P.; et al. Risk factors and outcome of pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill coronavirus disease 2019 patients-a multinational observational study by the European Confederation of Medical Mycology. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 28, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arastehfar, A.; Carvalho, A.; van de Veerdonk, F.L.; Jenks, J.D.; Koehler, P.; Krause, R.; Cornely, O.A.; David, S.P.; Lass-Florl, C.; Hoenigl, M. COVID-19 Associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CAPA)-From Immunology to Treatment. J. Fungi. 2020, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzl, S.; Reisinger, A.C.; Posch, F.; Prattes, J.; Stradner, M.; Pilz, S.; Eller, P.; Schoerghuber, M.; Toller, W.; Gorkiewicz, G.; et al. Antifungal prophylaxis for prevention of COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill patients: An observational study. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.; Giuliano, S.; Vena, A.; Lucidi, C.; Falcone, M.; Raponi, G.; Merli, M.; Venditti, M. Predictors of mortality in non-neutropenic patients with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: Does galactomannan have a role? Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 80, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.; Falcone, M.; Vena, A.; Venditti, C.; Mancini, C.; Morelli, A.; Venditti, M. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in non-neutropenic patients: Analysis of a 14-month prospective clinical experience. J. Chemother. 2011, 23, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, F.; Bignell, E.; Brown, G.D.; Cook, P.C.; Warris, A. Pathogenesis of Respiratory Viral and Fungal Coinfections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2022, 35, e0009421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trecarichi, E.M.; Mazzitelli, M.; Serapide, F.; Pelle, M.C.; Tassone, B.; Arrighi, E.; Perri, G.; Fusco, P.; Scaglione, V.; Davoli, C.; et al. Clinical characteristics and predictors of mortality associated with COVID-19 in elderly patients from a long-term care facility. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Bussini, L.; Hoenigl, M.; Bartoletti, M. Prevalence of COVID-19-Associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis: Critical Review and Conclusions. J. Fungi. 2022, 8, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassetti, M.; Azoulay, E.; Kullberg, B.J.; Ruhnke, M.; Shoham, S.; Vazquez, J.; Giacobbe, D.R.; Calandra, T. EORTC/MSGERC Definitions of Invasive Fungal Diseases: Summary of Activities of the Intensive Care Unit Working Group. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, S121–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Russo, A.; Morrone, H.L.; Rotundo, S.; Trecarichi, E.M.; Torti, C. Cytokine Profile of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Severe COVID-19 and Possible Therapeutic Targets. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12061364
Russo A, Morrone HL, Rotundo S, Trecarichi EM, Torti C. Cytokine Profile of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Severe COVID-19 and Possible Therapeutic Targets. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(6):1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12061364
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusso, Alessandro, Helen Linda Morrone, Salvatore Rotundo, Enrico Maria Trecarichi, and Carlo Torti. 2022. "Cytokine Profile of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Severe COVID-19 and Possible Therapeutic Targets" Diagnostics 12, no. 6: 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12061364
APA StyleRusso, A., Morrone, H. L., Rotundo, S., Trecarichi, E. M., & Torti, C. (2022). Cytokine Profile of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Severe COVID-19 and Possible Therapeutic Targets. Diagnostics, 12(6), 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12061364






