Neurogenic Appendicitis: A Reappraisal of the Clinicopathological Features and Pathogenesis
Abstract
:1. Background
1.1. The Historical and Clinical Aspects of NA
1.2. The Enteric Nervous System
1.3. The Pathogenesis of NA
1.4. The Roles of NPs and Neuroplasticity in NA
1.4.1. VIP Neuropeptide
1.4.2. SP Neuropeptide
1.4.3. Serotonin and Enterochromaffin Cells
1.4.4. GAP-43 Neuropeptide
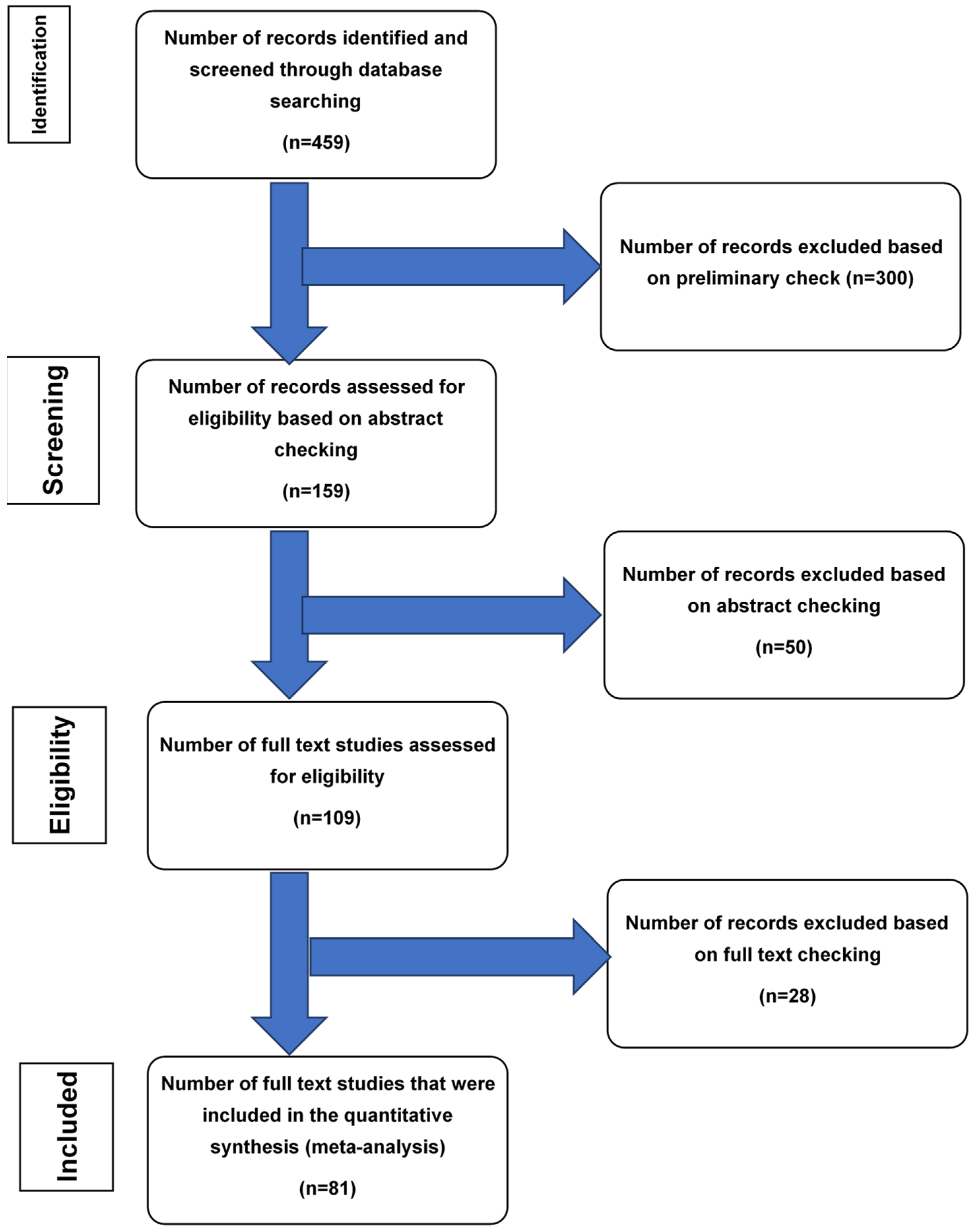
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Methods
2.2. Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Methodological Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Features of the Cases of NA
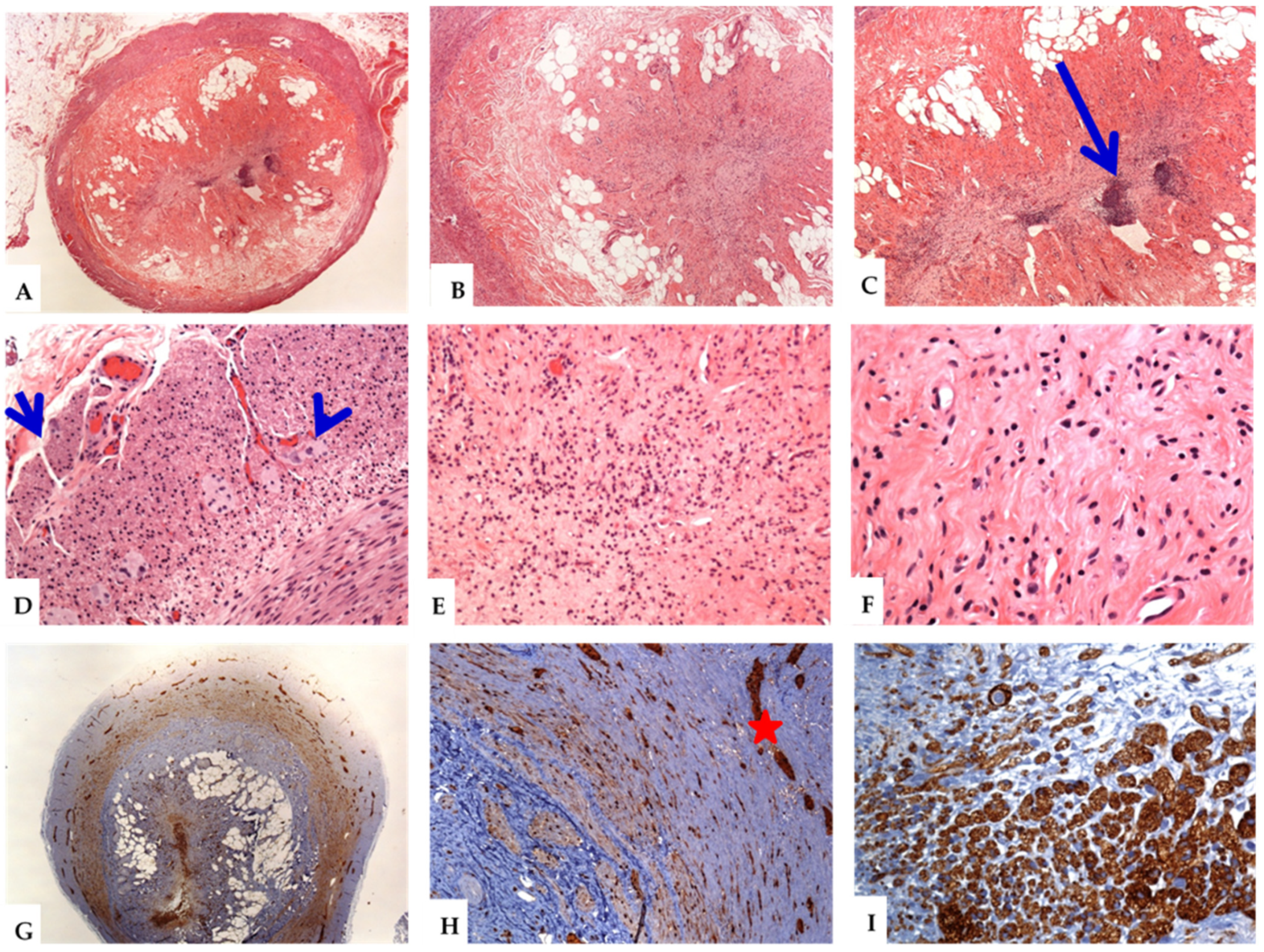
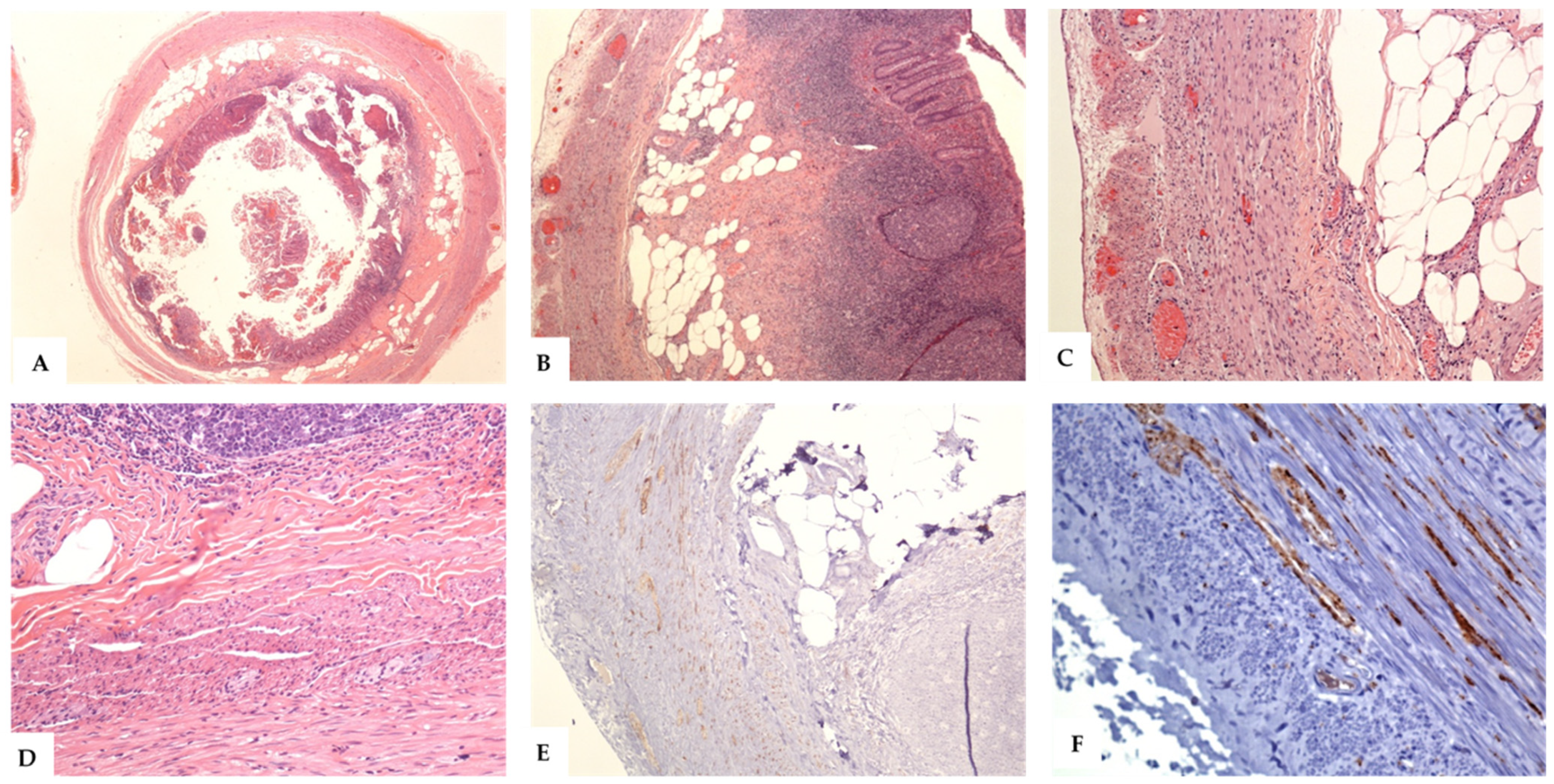
3.2. Pathological Features of the Cases of NA
3.3. Histological Variants of NA
4. Discussion
4.1. The Early, Intermediate, and Late Phases of NA (Evolving and Regressing Lesions of NA)
4.2. Neuroinflammation in NA
4.3. Acute Abdominal Pain in NA
4.4. Fibrosis in NA
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NA | neurogenic appendicitis |
| EC cells | enterochromaffin cells |
| SP | Substance P |
| NPs | neuropeptides |
| NSGs | neurosecretory granules |
References
- Buschard, K.; Kjaeldgaard, A. Investigation and analysis of the position, fixation, length and embryology of the vermiform appendix. Acta Chir. Scand. 1973, 139, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schumpelick, V.; Dreuw, B.; Ophoff, K.; Prescher, A. Appendix and cecum. Embryology, anatomy, and surgical applications. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2000, 80, 295–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, M.W.; Cherwitz, D.; Hagen, K.; Snover, D.C. Neuromas of the appendix. A light-microscopic, immunohistochemical and electron-microscopic study of 20 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1986, 10, 801–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, B.S.; Holck, S. Neurogenous hyperplasia leading to appendiceal obliteration: An immunohistochemical study of 237 cases. Histopathology 1987, 11, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, C. Neurogenic appendicopathy: A common, nearly unknown disease picture. Evaluation of 816 appendices and review of the literature. Chirurg 2001, 72, 1508–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiari, H. Neurogenic appendicopathy. J. Mt. Sinai Hosp. N. Y. 1952, 19, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Hofler, H. Neurogenic appendicopathy—A common disorder, seldom diagnosed (author’s transl). Langenbecks Arch. Chir. 1980, 351, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.; Rios, A.; Oviedo, M.I.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Parrilla, P. Neurogenic ppendicopathy. A report of 8 cases. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2017, 109, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guller, U.; Oertli, D.; Terracciano, L.; Harder, F. Neurogenic appendicopathy: A frequent, almost unknown disease picture. Evaluation of 816 appendices and review of the literature. Chirurg 2001, 72, 684–689. [Google Scholar]
- Jonas, L.; Bombil, I.; Mannell, A. Unusual histopathologies of the appendix. S. Afr. J. Surg. 2020, 58, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maresch, M.P. Ueber das VorkommenneuromartigerBildungen in obliterierten Wurmfortsätzen. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 1921, 34, 181–182. [Google Scholar]
- Masson, P. Les Lesions nerveuses de lappendicitechronique. CR Acad. Sci. 1921, 173, 262–264. [Google Scholar]
- Di Sebastiano, P.; Fink, T.; di Mola, F.F.; Weihe, E.; Innocenti, P.; Friess, H.; Buchler, M.W. Neuroimmune appendicitis. Lancet 1999, 354, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, C.; Gerharz, C.D.; Bohner, H.; Ohmann, C.; Heydrich, G.; Kramling, H.J.; Stock, W.; Rosen, D.; Kurpreugsch, K.; Roher, H.D. Neurogenic appendicopathy: A clinical disease entity? Int. J. Colorectal. Dis. 2002, 17, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, C.; Gerharz, C.D.; Bohner, H.; Ohmann, C.; Heydrich, G.; Kramling, H.J.; Stock, W.; Rosen, D.; Kurpreugsch, K.; Willnow, U.; et al. Neurogenic appendicopathy in children. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2002, 12, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Solanki, A.; Vasishta, R.K. Appendiceal neuroma: Report of an elusive neuroma. Trop. Gastroenterol. 2011, 32, 332–333. [Google Scholar]
- Furness, J.B. The enteric nervous system and neurogastroenterology. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassmann, G. Neurogenic appendicitis in the picture of neurovegetative-allergic diseases. Minerva Med. 1950, 41, 880–885. [Google Scholar]
- Gershon, M.D. The enteric nervous system: A second brain. Hosp. Pract. 1999, 34, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, A.M.; Hofstra, R.M.; Burns, A.J. Building a brain in the gut: Development of the enteric nervous system. Clin. Genet. 2013, 83, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershon, M.D. Development of the Enteric Nervous System: A Genetic Guide to the Perplexed. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 478–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schneider, S.; Wright, C.M.; Heuckeroth, R.O. Unexpected Roles for the Second Brain: Enteric Nervous System as Master Regulator of Bowel Function. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2019, 81, 235–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila, J.A.; Southard-Smith, E.M. In the Enteric Nervous System, It’s All About Connections. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 13, 346–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjolund, K.; Sanden, G.; Hakanson, R.; Sundler, F. Endocrine cells in human intestine: An immunocytochemical study. Gastroenterology 1983, 85, 1120–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar Barroso, T.V.; Petroianu, A. Neuroimmunoendocrine peptides on inflammed and morphologically normal appendices removed due to clinical acute appendicitis. Int. J. Surg. 2019, 67, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofler, H.; Kasper, M.; Heitz, P.U. The neuroendocrine system of normal human appendix, ileum and colon, and in neurogenic appendicopathy. Virchows Arch. A Pathol. Anat. Histopathol. 1983, 399, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadaki, L.; Rode, J.; Dhillon, A.P.; Dische, F.E. Fine structure of a neuroendocrine complex in the mucosa of the appendix. Gastroenterology 1983, 84, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, L.; Rolle, U.; Reen, D.J.; Puri, P. Nitrergic hyperinnervation in appendicitis and in appendices histologically classified as normal. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2003, 127, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, I.E.; Schafer, K.H.; Tieftrunk, E.; Friess, H.; Ceyhan, G.O. Neural plasticity in the gastrointestinal tract: Chronic inflammation, neurotrophic signals, and hypersensitivity. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 125, 491–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partecke, L.I.; Thiele, A.; Schmidt-Wankel, F.; Kessler, W.; Wodny, M.; Dombrowski, F.; Heidecke, C.D.; von Bernstorff, W. Appendicopathy—A clinical and diagnostic dilemma. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2013, 28, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, S.I.; Mutt, V. Polypeptide with broad biological activity: Isolation from small intestine. Science 1970, 169, 1217–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesia, S.B.; Mayr, J.; Bruder, E.; Haecker, F.M. Neurogenic appendicopathy: Clinical, macroscopic, and histopathological presentation in pediatric patients. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2013, 23, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koon, H.W.; Shih, D.; Karagiannides, I.; Zhao, D.; Fazelbhoy, Z.; Hing, T.; Xu, H.; Lu, B.; Gerard, N.; Pothoulakis, C. Substance P modulates colitis-associated fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 2300–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, U.; Chitkara, N.; Dadoo, R.C.; Singh, G.P.; Gulati, P.; Narula, S. Evaluation of plasma serotonin concentration in acute appendicitis. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 1997, 16, 18–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vasei, M.; Zakeri, Z.; Azarpira, N.; Hosseini, S.V.; Solaymani-Dodaran, M. Serotonin content of normal and inflamed appendix: A possible role of serotonin in acute appendicitis. APMIS 2008, 116, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millikin, P.D. Extraepithelial enterochromaffin cells and Schwann cells in the human appendix. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 1983, 107, 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Naik, R.; Baliga, P.; Pai, M.R. Neurogenic appendicopathy—Role of enterochromaffin cells in its pathogenesis. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 1999, 42, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oates, J.A.; Melmon, K.; Sjoerdsma, A.; Gillespie, L.; Mason, D.T. Release of a Kinin Peptide in the Carcinoid Syndrome. Lancet 1964, 1, 514–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fries, J.F.; Lindgren, J.A.; Bull, J.M. Scleroderma-like lesions and the carcinoid syndrome. Arch. Intern. Med. 1973, 131, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, D.A.; Oakley, F. Serotonin paracrine signaling in tissue fibrosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1832, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benowitz, L.I.; Routtenberg, A. GAP-43: An intrinsic determinant of neuronal development and plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 1997, 20, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paden, C.M.; Watt, J.A.; Selong, T.H.; Paterson, C.L.; Cranston, H.J. The neuronal growth-associated protein (GAP)-43 is expressed by corticotrophs in the rat anterior pituitary after adrenalectomy. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 952–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coskun, N.; Sindel, M.; Elpek, G.O. Mast cell density, neuronal hypertrophy and nerve growth factor expression in patients with acute appendicitis. Folia Morphol. 2002, 61, 237–243. [Google Scholar]
- Gomariz, R.P.; Juarranz, Y.; Abad, C.; Arranz, A.; Leceta, J.; Martinez, C. VIP-PACAP system in immunity: New insights for multitarget therapy. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1070, 51–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Rey, E.; Chorny, A.; Delgado, M. Regulation of immune tolerance by anti-inflammatory neuropeptides. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US, V.E.; Gaddum, J.H. An unidentified depressor substance in certain tissue extracts. J. Physiol. 1931, 72, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winning, L.; El Karim, I.A.; Linden, G.J.; Irwin, C.R.; Killough, S.A.; Lundy, F.T. Differential regulation of NPY and SP receptor expression in STRO-1+ve PDLSCs by inflammatory cytokines. J. Periodontal. Res. 2022, 57, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashaghi, A.; Marmalidou, A.; Tehrani, M.; Grace, P.M.; Pothoulakis, C.; Dana, R. Neuropeptide substance P and the immune response. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 4249–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinhoff, M.S.; von Mentzer, B.; Geppetti, P.; Pothoulakis, C.; Bunnett, N.W. Tachykinins and their receptors: Contributions to physiological control and the mechanisms of disease. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 265–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aubock, L.; Ratzenhofer, M. “Extraepithelial enterochromaffin cell—Nerve-fibre complexes” in the normal human appendix, and in neurogenic appendicopathy. J. Pathol. 1982, 136, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofler, H.; Aubock, L.; Ratzenhofer, M. Neurogenic appendicopathy. A facultative precursor of appendiceal carcinoids. Contribution to Feyrter’s theory of disseminated endocrine-(paracrine) cells. Norm. Pathol. Anat. 1982, 45, 1–117. [Google Scholar]
- Hofler, H.; Heitz, P.U. Neurogenic appendicopathy—An immunocytochemical study. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 1982, 94, 588–591. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bertrand, P.P.; Bertrand, R.L. Serotonin release and uptake in the gastrointestinal tract. Auton. Neurosci. 2010, 153, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Camilleri, M. Serotonin in the gastrointestinal tract. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2009, 16, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, R.; Xiao, H.; Zhao, J.; Ju, L.; Wen, Y.; Xu, Q.; Cui, X. GAP-43 is involved in the orientation of cell division by interacting with GAlphaI during neurogenesis. Int. J. Neurosci. 2020, 130, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sebastiano, P.; Fink, T.; Weihe, E.; Friess, H.; Innocenti, P.; Beger, H.G.; Buchler, M.W. Immune cell infiltration and growth-associated protein 43 expression correlate with pain in chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 1997, 112, 1648–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, T.; Di Sebastiano, P.; Buchler, M.; Beger, H.G.; Weihe, E. Growth-associated protein-43 and protein gene-product 9.5 innervation in human pancreas: Changes in chronic pancreatitis. Neuroscience 1994, 63, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, M.S.; Fitzgerald, M.; Winter, J.; Hu-Tsai, M.; Emson, P.C.; Wiese, U.; Woolf, C.J. GAP-43 mRNA in Rat Spinal Cord and Dorsal Root Ganglia Neurons: Developmental Changes and Re-expression Following Peripheral Nerve Injury. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1992, 4, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piehl, F.; Arvidsson, U.; Johnson, H.; Cullheim, S.; Dagerlind, A.; Ulfhake, B.; Cao, Y.; Elde, R.; Pettersson, R.F.; Terenius, L.; et al. GAP-43, aFGF, CCK and alpha- and beta-CGRP in rat spinal motoneurons subjected to axotomy and/or dorsal root severance. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1993, 5, 1321–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, C.M.; Brown, M.C. Expression of GAP-43 mRNA in mouse spinal cord following unilateral peripheral nerve damage: Is there a contralateral effect? Eur. J. Neurosci. 1993, 5, 1663–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walch-Patterson, A. Exemptions and Limited Institutional Review Board Review: A Practical Look at the 2018 Common Rule Requirements for Exempt Research. Ochsner. J. 2020, 20, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Group, P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arya, S.; Kaji, A.H.; Boermeester, M.A. PRISMA Reporting Guidelines for Meta-analyses and Systematic Reviews. JAMA Surg. 2021, 156, 789–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amber, S.; Mathai, A.M.; Naik, R.; Pai, M.R.; Kumar, S.; Prasad, K. Neuronal hypertrophy and mast cells in histologically negative, clinically diagnosed acute appendicitis: A quantitative immunophenotypical analysis. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 29, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbulut, S.; Tas, M.; Sogutcu, N.; Arikanoglu, Z.; Basbug, M.; Ulku, A.; Semur, H.; Yagmur, Y. Unusual histopathological findings in appendectomy specimens: A retrospective analysis and literature review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 1961–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, M.; Akbulut, S.; Kutluturk, K.; Sahin, N.; Arabaci, E.; Ara, C.; Yilmaz, S. Unusual histopathological findings in appendectomy specimens from patients with suspected acute appendicitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 4015–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeramo, C.A.; Dreifuss, N.H.; Giacone, J.; Schlottmann, F. Outcomes of Acute Appendicitis in Elderly Patients: A Single Center Analysis of 2000 Laparoscopic Appendectomies. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2020, 24, 2859–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapsa, S.; Ozolins, A.; Strumfa, I.; Gardovskis, J. Acute Appendicitis in the Elderly: A Literature Review on an Increasingly Frequent Surgical Problem. Geriatrics 2021, 6, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, R.K.; Hassn, A.M. Managing acute appendicitis. Neuroimmune appendicitis may be distinct pathological entity. BMJ 2003, 326, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Konigshoff, M.; Dumitrascu, R.; Udalov, S.; Amarie, O.V.; Reiter, R.; Grimminger, F.; Seeger, W.; Schermuly, R.T.; Eickelberg, O. Increased expression of 5-hydroxytryptamine2A/B receptors in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A rationale for therapeutic intervention. Thorax 2010, 65, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biondi, M.L.; Marasini, B.; Bianchi, E.; Agostoni, A. Plasma free and intraplatelet serotonin in patients with Raynaud’s phenomenon. Int. J. Cardiol. 1988, 19, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabab, T.; Khanabdali, R.; Moghadamtousi, S.Z.; Kadir, H.A.; Mohan, G. Neuroinflammation pathways: A general review. Int. J. Neurosci. 2017, 127, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, N.; Chugh, H.; Sakharkar, M.K.; Dhawan, U.; Chidambaram, S.B.; Chandra, R. Neuroinflammation Mechanisms and Phytotherapeutic Intervention: A Systematic Review. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 3707–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rode, J.; Dhillon, A.P.; Papadaki, L. Serotonin-immunoreactive cells in the lamina propria plexus of the appendix. Hum. Pathol. 1983, 14, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundqvist, M.; Wilander, E. Subepithelial neuroendocrine cells and carcinoid tumours of the human small intestine and appendix. A comparative immunohistochemical study with regard to serotonin, neuron-specific enolase and S-100 protein reactivity. J. Pathol. 1986, 148, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincel, O.; Goksu, M.; Turk, B.A.; Pehlivanoglu, B.; Isler, S. Unexpected findings in the routine histopathological examinations of appendectomy specimens A retrospective analysis of 1,970 patients. Ann. Ital. Chir. 2017, 88, 519–525. [Google Scholar]
- Dincel, O.; Goksu, M.; Turk, B.A.; Pehlivanoglu, B.; Isler, S. Incidental Findings in Routine Histopathological Examination of Appendectomy Specimens; Retrospective Analysis of 1970 Patients. Indian J. Surg. 2018, 80, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Puri, P.; Nemeth, L.; O’Briain, D.S.; Reen, D.J. Neuronal hypertrophy in acute appendicitis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2000, 124, 1429–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimund, E. Methysergide and retroperitoneal fibrosis. Lancet 1987, 1, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, I.; Faria, R.; Vita, P.; Vasconcelos, C. Systemic sclerosis refractory disease: From the skin to the heart. Autoimmun. Rev. 2011, 10, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Generini, S.; Matucci Cerinic, M. Raynaud’s phenomenon and vascular disease in systemic sclerosis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1999, 455, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdonald, R.A.; Robbins, S.L.; Mallory, G.K. Dermal fibrosis following subcutaneous injections of serotonin creatinine sulphate. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1958, 97, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, J.G.; Pucilowska, J.B.; Keku, T.O.; Lund, P.K. IGF-I and TGF-beta1 have distinct effects on phenotype and proliferation of intestinal fibroblasts. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2002, 283, G809–G818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantyh, P.W. Neurobiology of substance P and the NK1 receptor. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2002, 63 (Suppl. S11), 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Simard, L.C. On the Frequency of Nervous Lesions of the Vermiform Appendix: “Neuro-Appendicopathy”. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1935, 33, 518–521. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Knoflach, J.G.; Wayand, E. Neurogenic appendicitis. Acta Neuroveg. 1951, 2, 458–459. [Google Scholar]
- Triska, H. Remote sequels of appendectomy with special reference to neurogenic appendicitis. Wien. Med. Wochenschr. 1951, 101, 611–613. [Google Scholar]
- Quell, M.; Horvath, W. Neurogenic appendicopathy—Long-term results following appendectomy. Chirurg 1987, 58, 597–600. [Google Scholar]
- Emre, A.; Akbulut, S.; Bozdag, Z.; Yilmaz, M.; Kanlioz, M.; Emre, R.; Sahin, N. Routine histopathologic examination of appendectomy specimens: Retrospective analysis of 1255 patients. Int. Surg. 2013, 98, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zdichavsky, M.; Gogele, H.; Blank, G.; Kraulich, M.; Meile, T.; von Feilitzsch, M.; Wichmann, D.; Konigsrainer, A. Histological characterization of appendectomy specimens with intraoperative appearance of vascular injection. Surg. Endosc. 2013, 27, 849–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Mediators and Cells | Sources | Mechanisms of Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vasoactive intestinal peptide | Neurons and immune cells | These G protein-coupled receptors have strong anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory actions. | [13,30,31] |
| Substance P neuropeptide | Neurons, epithelial cells, endothelial cells, T cells, macrophages, some stem and progenitor cells | SP binding to its receptor neurokinin-1 alters several intestinal functions, such as inflammation and fibrosis. | [13,30,32,33]. |
| Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) | Proliferating nerve plexuses and EC cells | Serotonin plays a fibroproliferative role. | [34,35,36,37,38,39,40] |
| Growth-associated protein-43 | Nerve fibers | It is a membrane-associated phosphoprotein involved in axonal growth, synaptic remodeling, and secretion of both catecholamines and NPs. | [13,41,42] |
| Pro-fibrogenic factors (transforming growth factor1 and insulin-like growth factor 1) | Endothelial cells, mast cells, and fibroblasts | Fibrosis leads to obliteration of the appendiceal lumen and effacement of the appendiceal architecture. | [29,43] |
| No | Authors (Reference) | Year | Number of Cases | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Stanley, Cherwitz et al. | 1986 | 20 | [3] |
| 2 | Olsen and Holck | 1987 | 195 | [4] |
| 3 | Guller, Oertli et al. | 2001 | 140 | [5] |
| 4 | Franke, Gerharz et al. | 2002 | 4 | [15] |
| 5 | Amber, Mathai et al. | 2010 | 25 | [64] |
| 6 | Akbulut, Tas et al. | 2011 | 54 | [65] |
| 7 | Sesia, Mayr et al. | 2013 | 29 | [32] |
| 8 | Yilmaz, Akbulut et al. | 2013 | 134 | [66] |
| 9 | Ruiz, Rios et al. | 2017 | 8 | [8] |
| Variants | Features | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| The central variant |
| [3,5,9] |
| The submucosal variant |
| [26] |
| The intramucosal variant |
| [4,5,14,15] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hussein, M.R.A.; Al Bshabshe, A.; Elhakeem, A.A.; Elsamman, M.K. Neurogenic Appendicitis: A Reappraisal of the Clinicopathological Features and Pathogenesis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12061386
Hussein MRA, Al Bshabshe A, Elhakeem AA, Elsamman MK. Neurogenic Appendicitis: A Reappraisal of the Clinicopathological Features and Pathogenesis. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(6):1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12061386
Chicago/Turabian StyleHussein, Mahmoud Rezk Abdelwahed, Ali Al Bshabshe, Ahmed Abdelsatar Elhakeem, and Mahmoud Kamal Elsamman. 2022. "Neurogenic Appendicitis: A Reappraisal of the Clinicopathological Features and Pathogenesis" Diagnostics 12, no. 6: 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12061386
APA StyleHussein, M. R. A., Al Bshabshe, A., Elhakeem, A. A., & Elsamman, M. K. (2022). Neurogenic Appendicitis: A Reappraisal of the Clinicopathological Features and Pathogenesis. Diagnostics, 12(6), 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12061386






