Progress of Imaging in Diabetic Retinopathy—From the Past to the Present
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Evolutions of Contemporary Modalities in Imaging of DR
2.1. Color Fundus Photography
2.2. Ultra-Widefield (UWF) Imaging and Confocal Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscope (SLO)
2.3. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) and OCT Angiography (OCTA)
2.4. Adaptive Optics
3. General Characteristics of Imaging in DR
3.1. Mild Non Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR)
3.2. Moderate to Severe NPDR
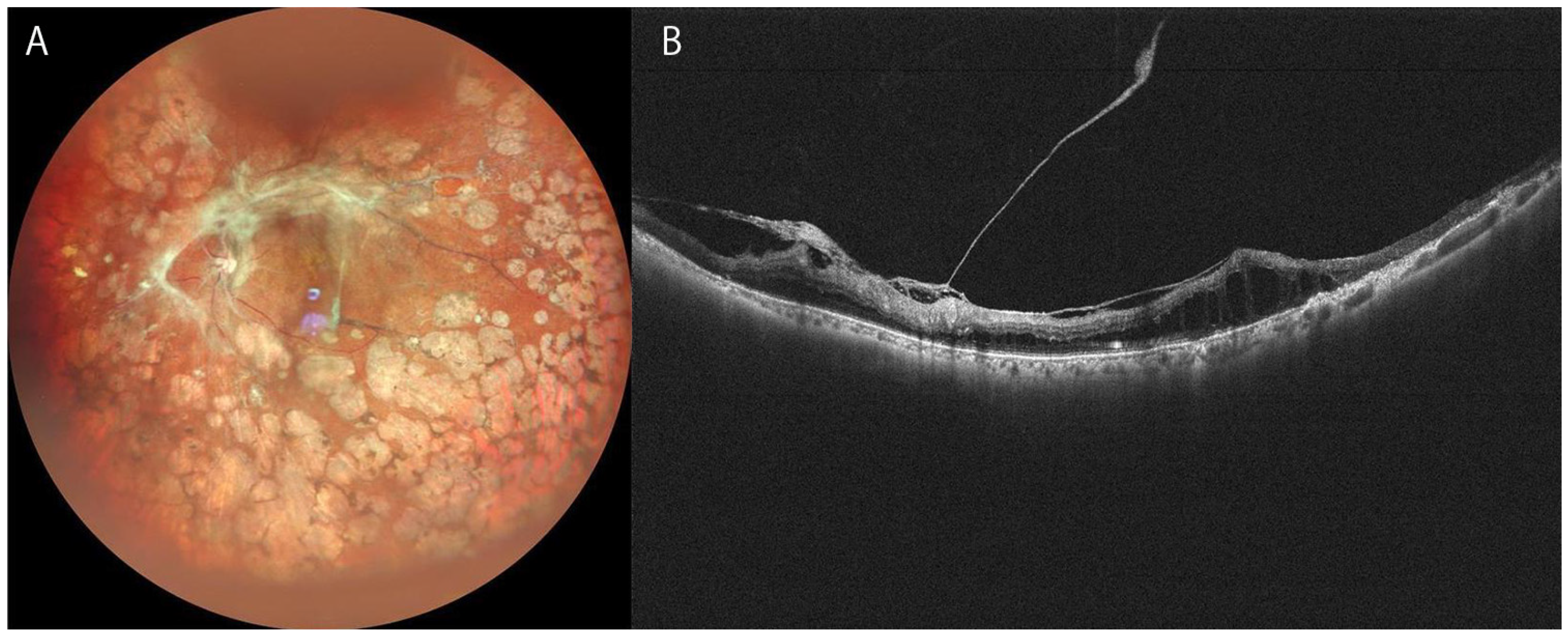
3.3. Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR)
3.4. Diabetic Macular Edema (DME)
4. Recent Topics in Imaging in DR
4.1. UWF Blue SLO Image in Detection of Retinal Ischemia
4.2. UWF-FA and Quantification of Retinal Non-Perfused Areas
4.3. WF-OCTA
4.4. Automated Diagnosis in DR
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parr, J.; Spears, G. Grading of Diabetic Retinopathy by Point-Counting on a Standardized Photographic Sample of the Retina. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1972, 74, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group. Fundus photographic risk factors for progression of diabetic retinopathy: ETDRS report number 12. Ophthalmology 1991, 98 (Suppl. 5), 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group. Diabetic retinopathy study. Report Number 6. Design, methods, and baseline results. Report Number 7. A modification of the Airlie House classification of diabetic retinopathy. Prepared by the Diabetic Retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1981, 21 Pt 2, 1–226. [Google Scholar]
- Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group. Grading diabetic retinopathy from stereoscopic color fundus photographs--an extension of the modified Airlie House classification. ETDRS report number 10. Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research. Ophthalmology 1991, 98, 786–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frambach, D.A.; Dacey, M.P.; Sadun, A. Stereoscopic Photography with a Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscope. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1993, 116, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gass, J.D.M. A Fluorescein Angiographic Study of Macular Dysfunction Secondary to Retinal Vascular Disease. IV. Diabetic retinal angiopathy. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1968, 80, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Muraoka, K. Midperipheral Fundus Involvement in Diabetic Retinopathy. Ophthalmology 1981, 88, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niki, T.; Muraoka, K.; Shimizu, K. Distribution of Capillary Nonperfusion in Early-stage Diabetic Retinopathy. Ophthalmology 1984, 91, 1431–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraoka, K.; Shimizu, K. Intraretinal Neovascularization in Diabetic Retinopathy. Ophthalmology 1984, 91, 1440–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacurariu, R.I. Low incidence of side effects following intravenous fluorescein angiography. Ann. Ophthalmol. 1982, 14, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Razvi, F.M.; Kritzinger, E.E.; Tsaloumas, M.D.; Ryder, R.E.J. Use of oral fluorescein angiography in the diagnosis of macular oedema within a diabetic retinopathy screening programme. Diabet. Med. 2001, 18, 1003–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, E.A.; Izatt, J.A.; Lin, C.P.; Fujimoto, J.G.; Schuman, J.; Hee, M.R.; Huang, D.; Puliafito, C.A. In vivo retinal imaging by optical coherence tomography. Opt. Lett. 1993, 18, 1864–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hee, M.R.; Puliafito, C.A.; Wong, C.; Duker, J.S.; Reichel, E.; Rutledge, B.; Schuman, J.; Swanson, E.A.; Fujimoto, J.G. Quantitative Assessment of Macular Edema with Optical Coherence Tomography. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1995, 113, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinthanayothin, C.; Boyce, J.F.; Williamson, T.H.; Cook, H.L.; Mensah, E.; Lal, S.; Usher, D. Automated detection of diabetic retinopathy on digital fundus images. Diabet. Med. 2002, 19, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ting, D.S.W.; Cheung, C.Y.-L.; Lim, G.; Tan, G.S.W.; Quang, N.D.; Gan, A.; Hamzah, H.; Garcia-Franco, R.; Yeo, I.Y.S.; Lee, S.Y.; et al. Development and Validation of a Deep Learning System for Diabetic Retinopathy and Related Eye Diseases Using Retinal Images from Multiethnic Populations with Diabetes. JAMA 2017, 318, 2211–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Heijden, A.A.; Abramoff, M.D.; Verbraak, F.; Van Hecke, M.V.; Liem, A.; Nijpels, G. Validation of automated screening for referable diabetic retinopathy with the IDx-DR device in the Hoorn Diabetes Care System. Acta Ophthalmol. 2018, 96, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Clarida, W.; Amelon, R.; Hernaez-Ortega, M.C.; Navea, A.; Morales-Olivas, J.; Dolz-Marco, R.; Verbraak, F.; Jorda, P.P.; van der Heijden, A.A.; et al. Validation of Automated Screening for Referable Diabetic Retinopathy with an Autonomous Diagnostic Artificial Intelligence System in a Spanish Population. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2021, 15, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Li, D.; Wei, Q.; Han, X.; Zhang, B.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Mo, B.; Hu, B.; et al. Automated detection of severe diabetic retinopathy using deep learning method. Graefes. Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2022, 260, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivannan, A.; Plskova, J.; Farrow, A.; Mckay, S.; Sharp, P.F.; Forrester, J.V. Ultra-Wide-Field Fluorescein Angiography of the Ocular Fundus. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2005, 140, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, P.J.; Russell, M.; Ma, P.E.; Isbister, C.M.; Maberley, D.A.L. Sensitivity and specificity of the optos optomap for detecting peripheral retinal lesions. Retina 2007, 27, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T.; Imai, A.; Kasamatsu, H.; Kakihara, S.; Toriyama, Y.; Murata, T. Assessment of diabetic retinopathy using two ultra-wide-field fundus imaging systems, the Clarus® and Optos™ systems. BMC Ophthalmol. 2018, 18, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schreur, V.; Larsen, M.B.; Sobrin, L.; Bhavsar, A.R.; Hollander, A.I.D.; Klevering, B.J.; Hoyng, C.B.; de Jong, E.K.; Grauslund, J.; Peto, T. Imaging diabetic retinal disease: Clinical imaging requirements. Acta Ophthalmol. 2022. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishibazawa, A.; Nagaoka, T.; Takahashi, A.; Omae, T.; Tani, T.; Sogawa, K.; Yokota, H.; Yoshida, A. Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography in Diabetic Retinopathy: A Prospective Pilot Study. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 160, 35–44.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salz, D.A.; De Carlo, T.E.; Adhi, M.; Moult, E.M.; Choi, W.; Baumal, C.R.; Witkin, A.J.; Duker, J.S.; Fujimoto, J.G.; Waheed, N.K. Select Features of Diabetic Retinopathy on Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomographic Angiography Compared with Fluorescein Angiography and Normal Eyes. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016, 134, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, O.; Ichiyama, Y.; Obata, S.; Ito, Y.; Kakinoki, M.; Sawada, T.; Saishin, Y.; Ohji, M. Comparison between wide-angle OCT angiography and ultra-wide field fluorescein angiography for detecting non-perfusion areas and retinal neovascularization in eyes with diabetic retinopathy. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2018, 256, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.C.; Lu, Y.; Zeng, R.; Katz, R.; Vingopoulos, F.; Le, R.; Laíns, I.; Wu, D.M.; et al. Comparison of widefield swept-source optical coherence tomography angiography with ultra-widefield colour fundus photography and fluorescein angiography for detection of lesions in diabetic retinopathy. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 105, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer-Schwickerath, G.R. Ophthalmology and Photography. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1968, 66, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimmer, F.; Pillat, A. Atlas Photograpischer Bilder des Menschlichen Augenhintergrundes; F Deuticke: Leipzig, Germany, 1927. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, P.S.; Walia, S.; Cavallerano, J.D.; Sun, J.K.; Dunn, C.; Bursell, S.-E.; Aiello, L.M. Comparison of Low-Light Nonmydriatic Digital Imaging with 35-mm ETDRS Seven-Standard Field Stereo Color Fundus Photographs and Clinical Examination. Telemed. e-Health 2012, 18, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.S.; Cavallerano, J.D.; Sun, J.K.; Soliman, A.Z.; Aiello, L.M.; Aiello, L.P. Peripheral Lesions Identified by Mydriatic Ultrawide Field Imaging: Distribution and Potential Impact on Diabetic Retinopathy Severity. Ophthalmology 2013, 120, 2587–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.S.; Cavallerano, J.D.; Haddad, N.M.N.; Kwak, H.; Dyer, K.H.; Omar, A.F.; Shikari, H.; Aiello, L.M.; Sun, J.K. Peripheral Lesions Identified on Ultrawide Field Imaging Predict Increased Risk of Diabetic Retinopathy Progression over 4 Years. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kernt, M.; Hadi, I.; Pinter, F.; Seidensticker, F.; Hirneiss, C.; Haritoglou, C.; Kampik, A.; Ulbig, M.W.; Neubauer, A.S. Assessment of Diabetic Retinopathy Using Nonmydriatic Ultra-Widefield Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy (Optomap) Compared with ETDRS 7-Field Stereo Photography. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 2459–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rasmussen, M.L.; Broe, R.; Frydkjaer-Olsen, U.; Olsen, B.S.; Mortensen, H.B.; Peto, T.; Grauslund, J. Comparison between Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study 7-field retinal photos and non-mydriatic, mydriatic and mydriatic steered widefield scanning laser ophthalmoscopy for assessment of diabetic retinopathy. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2015, 29, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiello, L.P.; Odia, I.; Glassman, A.R.; Melia, M.; Jampol, L.M.; Bressler, N.M.; Kiss, S.; Silva, P.S.; Wykoff, C.C.; Sun, J.K.; et al. Comparison of Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Standard 7-Field Imaging with Ultrawide-Field Imaging for Determining Severity of Diabetic Retinopathy. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2019, 137, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verma, A.; Indian Retina Research Associates (IRRA); Alagorie, A.R.; Ramasamy, K.; van Hemert, J.; Yadav, N.; Pappuru, R.R.; Tufail, A.; Nittala, M.G.; Sadda, S.R.; et al. Distribution of peripheral lesions identified by mydriatic ultra-wide field fundus imaging in diabetic retinopathy. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2020, 258, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.; Rageh, A.; Gilbert, M.; Tolls, D.; Fleming, A.; Souka, A.; El-Baha, S.; Cavallerano, J.D.; Sun, J.K.; Aiello, L.P.; et al. Factors Affecting Predominantly Peripheral Lesion Identification and Grading. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoba, C.M.P.; Ashraf, M.; Cavallerano, J.D.; Tolson, A.M.; Tolls, D.; Pellegrini, E.; Fleming, A.; Sun, J.K.; Aiello, L.P.; Silva, P.S. Association of Maximizing Visible Retinal Area by Manual Eyelid Lifting with Grading of Diabetic Retinopathy Severity and Detection of Predominantly Peripheral Lesions When Using Ultra-Widefield Imaging. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2022, 140, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedova, A.; Hajdu, D.; Datlinger, F.; Steiner, I.; Neschi, M.; Aschauer, J.; Gerendas, B.S.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U.; Pollreisz, A. Comparison of early diabetic retinopathy staging in asymptomatic patients between autonomous AI-based screening and human-graded ultra-widefield colour fundus images. Eye 2022, 36, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellmann, C.; Rubin, G.S.; Kabanarou, S.A.; Bird, A.C.; Fitzke, F.W. Fundus autofluorescence imaging compared with different confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopes. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2003, 87, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, S.; Kukimoto, N.; Kamoi, K.; Igarashi-Yokoi, T.; Yoshida, T.; Ohno-Matsui, K. Blue Widefield Images of Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscope Can Detect Retinal Ischemic Areas in Eyes with Diabetic Retinopathy. Asia-Pacific J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 10, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, J.G.; Swanson, E.A. The Development, Commercialization, and Impact of Optical Coherence Tomography. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, OCT1–OCT13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reznicek, L.; Klein, T.; Wieser, W.; Kernt, M.; Wolf, A.; Haritoglou, C.; Kampik, A.; Huber, R.; Neubauer, A.S. Megahertz ultra-wide-field swept-source retina optical coherence tomography compared to current existing imaging devices. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2014, 252, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno-Matsui, K.; Takahashi, H.; Mao, Z.; Nakao, N. Determining posterior vitreous structure by analysis of images obtained by AI-based 3D segmentation and ultrawidefield optical coherence tomography. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2021. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Nakao, N.; Shinohara, K.; Sugisawa, K.; Uramoto, K.; Igarashi-Yokoi, T.; Yoshida, T.; Ohno-Matsui, K. Posterior vitreous detachment and paravascular retinoschisis in highly myopic young patients detected by ultra-widefield OCT. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Uramoto, K.; Ohno-Matsui, K. Ultra-widefield optical coherence tomography for retinal detachment with proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Retin. Cases Brief Rep. 2020, 16, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaide, R.F.; Fujimoto, J.G.; Waheed, N.K.; Sadda, S.R.; Staurenghi, G. Optical coherence tomography angiography. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2018, 64, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiku, Y.; Hirano, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Tuchiya, A.; Nakamura, M.; Murata, T. Evaluating posterior vitreous detachment by widefield 23-mm swept-source optical coherence tomography imaging in healthy subjects. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, E.; Dikland, F.A.; van Bakel, R.; De Jesus, D.A.; Brea, L.S.; Klein, S.; van Walsum, T.; Rossant, F.; Farías, D.C.; Grieve, K.; et al. Adaptive optics ophthalmoscopy: A systematic review of vascular biomarkers. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2021, 67, 369–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, T.Y.P.; Pinhas, A.; Gan, A.; Razeen, M.; Shah, N.; Cheang, E.; Liu, C.L.; Dubra, A.; Rosen, R.B.; Chui, Y.P.T. Longitudinal imaging of microvascular remodelling in proliferative diabetic retinopathy using adaptive optics scanning light ophthalmoscopy. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2016, 36, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilkinson, C.; Ferris, F.; Klein, R.; Lee, P.; Agardh, C.D.; Davis, M.; Dills, D.; Kampik, A.; Pararajasegaram, R.; Verdaguer, J.T. Proposed international clinical diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema disease severity scales. Ophthalmology 2003, 110, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, N.P.; Shahidi, M.; Lai, W.W.; Zelkha, R. Correlation between microaneurysms and retinal thickness in diabetic macular edema. Retina 2008, 28, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akil, H.; Karst, S.; Heisler, M.; Etminan, M.; Navajas, E.; Maberley, D. Application of optical coherence tomography angiography in diabetic retinopathy: A comprehensive review. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 54, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Carlo, T.E.; Chin, A.T.; Filho, M.A.B.; Adhi, M.; Branchini, L.; Salz, D.A.; Baumal, C.R.; Crawford, C.; Reichel, E.; Witkin, A.J.; et al. Detection of microvascular changes in eyes of patients with diabetes but not clinical diabetic retinopathy using optical coherence tomography angiography. Retina 2015, 35, 2364–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, S.; Zhang, C.; Qin, H.; Xie, H.; Luo, D.; Qiu, Q.; Liu, K.; Zhang, J.; Xu, G.; Zhang, J. Hyperreflective Foci and Subretinal Fluid Are Potential Imaging Biomarkers to Evaluate Anti-VEGF Effect in Diabetic Macular Edema. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 791442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Boulton, M. The pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy: Old concepts and new questions. Eye 2002, 16, 242–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibazawa, A.; De Pretto, L.R.; Alibhai, A.Y.; Moult, E.M.; Arya, M.; Sorour, O.; Mehta, N.; Baumal, C.R.; Witkin, A.J.; Yoshida, A.; et al. Retinal Nonperfusion Relationship to Arteries or Veins Observed on Widefield Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography in Diabetic Retinopathy. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 4310–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nian, S.; Lo, A.C.Y.; Mi, Y.; Ren, K.; Yang, D. Neurovascular unit in diabetic retinopathy: Pathophysiological roles and potential therapeutical targets. Eye Vis. 2021, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.; Hu, A.; Schwartz, S.D. Ultra Wide Field Fluorescein Angiography Guided Targeted Retinal Photocoagulation (TRP). Semin. Ophthalmol. 2009, 24, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonekawa, Y.; Modi, Y.S.; Kim, L.A.; Skondra, D.; Kim, J.E.; Wykoff, C.C. American Society of Retina Specialists Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of Nonproliferative and Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy without Diabetic Macular Edema. J. Vitr. Dis. 2020, 4, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, L.; Huang, C.; Zhong, X.; Gong, Y.; Li, L.; Xu, F.; Li, C.; Lu, L.; et al. Subthreshold Pan-Retinal Photocoagulation Using Endpoint Management Algorithm for Severe Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy: A Paired Controlled Pilot Prospective Study. Ophthalmic Res. 2020, 64, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Wang, K.; Falavarjani, K.G.; Sagong, M.; Uji, A.; Ip, M.; Wykoff, C.C.; Brown, D.M.; van Hemert, J.; Sadda, S.R. Distribution of Nonperfusion Area on Ultra-widefield Fluorescein Angiography in Eyes with Diabetic Macular Edema: DAVE Study. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 180, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Fan, W.; Shi, Y.; Ip, M.S.; Wykoff, C.C.; Wang, K.; Falavarjani, K.G.; Brown, D.M.; van Hemert, J.; Sadda, S.R. Classification of Regions of Nonperfusion on Ultra-widefield Fluorescein Angiography in Patients with Diabetic Macular Edema. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 206, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehlers, J.P.; Jiang, A.C.; Boss, J.D.; Hu, M.; Figueiredo, N.; Babiuch, A.; Talcott, K.; Sharma, S.; Hach, J.; Le, T.K.; et al. Quantitative Ultra-Widefield Angiography and Diabetic Retinopathy Severity: An Assessment of Panretinal Leakage Index, Ischemic Index and Microaneurysm Count. Ophthalmology 2019, 126, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antaki, F.; Coussa, R.G.; Mikhail, M.; Archambault, C.; Lederer, D.E. The prognostic value of peripheral retinal nonperfusion in diabetic retinopathy using ultra-widefield fluorescein angiography. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2020, 258, 2681–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, P.S.; Liu, D.; Glassman, A.R.; Aiello, L.P.; Grover, S.; Kingsley, R.M.; Melia, M.; Sun, J.K.; Network, F.T.D.R. Assessment of fluorescein angiography nonperfusion in eyes with diabetic retinopathy using ultrawide field retinal imaging. Retina 2022, 42, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.F.; Shi, Y.; Hinkle, J.W.; Scott, N.L.; Fan, K.C.; Lyu, C.; Gregori, G.; Rosenfeld, P.J. Longitudinal Wide-Field Swept-Source OCT Angiography of Neovascularization in Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy after Panretinal Photocoagulation. Ophthalmol. Retin. 2018, 3, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaal, K.B.; Munk, M.R.; Wyssmueller, I.; Berger, L.E.; Zinkernagel, M.S.; Wolf, S. Vascular abnormalities in diabetic retinopathy assessed with swept-source optical coherence tomography angiography widefield imaging. Retina 2019, 39, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichi, F.; Smith, S.D.; Abboud, E.B.; Neri, P.; Woodstock, E.; Hay, S.; Levine, E.; Baumal, C.R. Wide-field optical coherence tomography angiography for the detection of proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2020, 258, 1901–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Garg, I.; Miller, J.B. Wide Field Swept Source Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography for the Evaluation of Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy and Associated Lesions: A Review. Semin. Ophthalmol. 2021, 36, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabr, H.; Chen, X.; Zevallos-Carrasco, O.M.; Viehland, C.; Dandrige, A.; Sarin, N.; Mahmoud, T.H.; Vajzovic, L.; Izatt, J.A.; Toth, C.A. Visualization from intraoperative swept-source microscope-integrated optical coherence tomography in vitrectomy for complications of proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Retina 2018, 38, S110–S120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, R.K.; Pieramici, D.J.; Gune, S.; Ghanekar, A.; Lu, N.; Quezada-Ruiz, C.; Baumal, C.R. Efficacy of Ranibizumab in Eyes with Diabetic Macular Edema and Macular Nonperfusion in RIDE and RISE. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 1568–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.K.; Lin, M.M.; Lammer, J.; Prager, S.; Sarangi, R.; Silva, P.S.; Aiello, L.P. Disorganization of the Retinal Inner Layers as a Predictor of Visual Acuity in Eyes with Center-Involved Diabetic Macular Edema. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2014, 132, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, R.; Spence, G.; Hogg, R.; Stevenson, M.; Chakravarthy, U. Disorganization of Inner Retina and Outer Retinal Morphology in Diabetic Macular Edema. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2018, 136, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitriou, E.; Sergentanis, T.N.; Lambadiari, V.; Theodossiadis, G.; Theodossiadis, P.; Chatziralli, I. Correlation between Imaging Morphological Findings and Laboratory Biomarkers in Patients with Diabetic Macular Edema. J. Diabetes Res. 2021, 2021, 6426003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szeto, S.K.; Hui, V.W.K.; Tang, F.Y.; Yang, D.; Sun, Z.H.; Mohamed, S.; Chan, C.K.M.; Lai, T.Y.Y.; Cheung, C. OCT-based biomarkers for predicting treatment response in eyes with centre-involved diabetic macular oedema treated with anti-VEGF injections: A real-life retina clinic-based study. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 2021, 319587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrelli, E.; Grosso, D.; Barresi, C.; Lari, G.; Sacconi, R.; Senni, C.; Querques, L.; Bandello, F.; Querques, G. Long-Term Visual Outcomes and Morphologic Biomarkers of Vision Loss in Eyes with Diabetic Macular Edema Treated with Anti-VEGF Therapy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 235, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Gil Moon, B.; Cho, A.R.; Yoon, Y.H. Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography of DME and Its Association with Anti-VEGF Treatment Response. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 2368–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mané, V.; Dupas, B.; Gaudric, A.; Bonnin, S.; Pedinielli, A.; Bousquet, E.; Erginay, A.; Tadayoni, R.; Couturier, A. Correlation between cystoid spaces in chronic diabetic macular edema and capillary nonperfusion detected by optical coherence tomography angiography. Retina 2016, 36, S102–S110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.-T.; Alam, M.N.; Le, D.; Hsiao, C.-C.; Yang, C.-H.; Chao, D.L.; Yao, X. OCT Angiography Biomarkers for Predicting Visual Outcomes after Ranibizumab Treatment for Diabetic Macular Edema. Ophthalmol. Retin. 2019, 3, 826–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.U.; Lee, B.R.; Kim, S.; Lee, W.J. A Novel Noninvasive Detection Method for Retinal Nonperfusion Using Confocal Red-free Imaging. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 1447–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicinelli, M.V.; Cavalleri, M.; Brambati, M.; Lattanzio, R.; Bandello, F. New imaging systems in diabetic retinopathy. Geol. Rundsch. 2019, 56, 981–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Yeo, J.H.; Son, G.; Kang, H.; Sung, Y.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.-G.; Yoon, Y.H. Efficacy of intravitreal AFlibercept injection for Improvement of retinal Nonperfusion in diabeTic retinopathY (AFFINITY study). BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e001616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, N.; Donaghue, K.C.; Liew, G.; Rogers, S.L.; Wang, J.J.; Lim, S.-W.; Jenkins, A.J.; Hsu, W.; Lee, M.L.; Wong, T.Y. Quantitative Assessment of Early Diabetic Retinopathy Using Fractal Analysis. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, W.-Y.; Fleming, A.; Robertson, G.; Uji, A.; Van Hemert, J.; Singer, M.; Sagong, M.; Ip, M.; Sadda, S.R. Fractal analysis of retinal vasculature in normal subjects on ultra-wide field fluorescein angiography. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 13, 1109–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.; Uji, A.; Wang, K.; Falavarjani, K.G.; Wykoff, C.C.; Brown, D.M.; Van Hemert, J.; Sagong, M.; Sadda, S.R.; Ip, M. Severity of diabetic macular edema correlates with retinal vascular bed area on ultra-wide field fluorescein angiography. Retina 2020, 40, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.; Nittala, M.G.; Fleming, A.; Robertson, G.; Uji, A.; Wykoff, C.C.; Brown, D.M.; van Hemert, J.; Ip, M.; Wang, K.; et al. Relationship Between Retinal Fractal Dimension and Nonperfusion in Diabetic Retinopathy on Ultrawide-Field Fluorescein Angiography. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 209, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Nittala, M.G.; Wykoff, C.C.; Brown, D.M.; Uji, A.; Van Hemert, J.; Fleming, A.; Robertson, G.; Sadda, S.R.; Ip, M. New biomarker quantifying the effect of anti-vegf therapy in eyes with proliferative diabetic retinopathy on ultrawide field fluorescein angiography. Retina 2021, 42, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.; Cavallerano, J.; Sun, J.; Silva, P.; Aiello, L. Ultrawide Field Imaging in Diabetic Retinopathy: Exploring the Role of Quantitative Metrics. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.F.; Flynn, H.W.; Sridhar, J.; Townsend, J.H.; Shi, Y.; Fan, K.C.; Scott, N.L.; Hinkle, J.W.; Lyu, C.; Gregori, G.; et al. Distribution of Diabetic Neovascularization on Ultra-Widefield Fluorescein Angiography and on Simulated Widefield OCT Angiography. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 207, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, J.K.H.; Cheung, C.; Sim, S.S.; Tan, P.C.; Tan, G.S.W.; Wong, T.Y. Retinal Imaging Techniques for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2016, 10, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheung, C.Y.; Tang, F.; Ting, D.S.W.; Tan, G.S.W.; Wong, T.Y. Artificial Intelligence in Diabetic Eye Disease Screening. Asia-Pacific J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 8, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balyen, L.; Peto, T. Promising Artificial Intelligence-Machine Learning-Deep Learning Algorithms in Ophthalmology. Asia-Pacific J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 8, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, D.S.; Peng, L.; Varadarajan, A.V.; Keane, P.A.; Burlina, P.M.; Chiang, M.F.; Schmetterer, L.; Pasquale, L.R.; Bressler, N.M.; Webster, D.R.; et al. Deep learning in ophthalmology: The technical and clinical considerations. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2019, 72, 100759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshminarayanan, V.; Kheradfallah, H.; Sarkar, A.; Balaji, J.J. Automated Detection and Diagnosis of Diabetic Retinopathy: A Comprehensive Survey. J. Imaging 2021, 7, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Carmona, S.; Alemany-Marquez, P.; Alvarez-Ramos, P.; Mayoral, E.; Aguilar-Diosdado, M. Validation of an Automated Screening System for Diabetic Retinopathy Operating under Real Clinical Conditions. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falavarjani, K.G.; Wang, K.; Khadamy, J.; Sadda, S.R. Ultra-wide-field imaging in diabetic retinopathy; an overview. J. Curr. Ophthalmol. 2016, 28, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terasaki, H.; Sonoda, S.; Shiihara, H.; Kakiuchi, N.; Funatsu, R.; Shirasawa, M.; Sakamoto, T. More effective screening for epiretinal membranes with multicolor scanning laser ophthalmoscope than with color fundus photographs. Retina 2020, 40, 1412–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Sun, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, S. Multicolor Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy Strengthens Surgeons’ Preoperative Decision-Making and Intraoperative Performance on Epiretinal Membrane. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H.; Moon, K.Y.; Jang, S.; Moon, Y. Comparison of MultiColor fundus imaging and colour fundus photography in the evaluation of epiretinal membrane. Acta Ophthalmol. 2018, 97, e533–e539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muftuoglu, I.K.; Bartsch, D.-U.; Barteselli, G.; Gaber, R.; Nezgoda, J.; Freeman, W.R. Visualization of macular pucker by multicolor scanning laser imaging. Retina 2018, 38, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Saurabh, K.; Thomas, N.R.; Chowdhury, M.; Shah, D.K. Validation of Multicolor Imaging of Diabetic Retinopathy Lesions Vis a Vis Conventional Color Fundus Photographs. Ophthalmic Surg. Lasers Imaging Retin. 2019, 50, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieczynski, J.; Kuklo, P.; Grzybowski, A. The Role of Telemedicine, In-Home Testing and Artificial Intelligence to Alleviate an Increasingly Burdened Healthcare System: Diabetic Retinopathy. Ophthalmol. Ther. 2021, 10, 445–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajalakshmi, R.; Subashini, R.; Anjana, R.M.; Mohan, V. Automated diabetic retinopathy detection in smartphone-based fundus photography using artificial intelligence. Eye 2018, 32, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellemo, V.; Lim, Z.W.; Lim, G.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Xie, Y.; Yip, M.Y.T.; Hamzah, H.; Ho, J.; Lee, X.Q.; Hsu, W.; et al. Artificial intelligence using deep learning to screen for referable and vision-threatening diabetic retinopathy in Africa: A clinical validation study. Lancet Digit. Health 2019, 1, e35–e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Fundus Ophthalmoscopy/Camera | Optos (Optos Plc) | Mirante (NIDEK) | Clarus (Carl Zeiss) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum field of view | 200° | 163° | 133° |
| Without mydriasis | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Light sources | Laser (red and green) | Laser (red, green, and blue) | LED (red, green, and blue) |
| Multimodality | FA, ICGA, FAF, OCT | FA, ICGA, FAF, Retromode, OCT, OCTA | FA, FAF |
| Features | Widest field | Mutlimodality | Color reality |
| Less than Mild NPDR | Moderate/Severe NPDR | PDR | DME | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biomicroscopy (contact or non-contact lens) | S | H | H | H |
| Color photography (1 or 2-field, 30/45°) | S | S | L | H |
| Color photography (7-field of 30°) | S | S | S | S |
| UWF color (>100°) | L | H | H | L |
| FA (30/45°) | N | S | H | H |
| UWF FA (>100°) | N | H | H | L |
| OCT | S | H | H | H |
| WF OCTA (12 mm × 12 mm) | N | H | H | L |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Horie, S.; Ohno-Matsui, K. Progress of Imaging in Diabetic Retinopathy—From the Past to the Present. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12071684
Horie S, Ohno-Matsui K. Progress of Imaging in Diabetic Retinopathy—From the Past to the Present. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(7):1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12071684
Chicago/Turabian StyleHorie, Shintaro, and Kyoko Ohno-Matsui. 2022. "Progress of Imaging in Diabetic Retinopathy—From the Past to the Present" Diagnostics 12, no. 7: 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12071684
APA StyleHorie, S., & Ohno-Matsui, K. (2022). Progress of Imaging in Diabetic Retinopathy—From the Past to the Present. Diagnostics, 12(7), 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12071684






