Synthetic Arterial Spin Labeling MRI of the Kidneys for Evaluation of Data Processing Pipeline
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthetic ASL Data Sets
2.2. ASL Processing Pipeline
2.3. Pipeline Evaluation
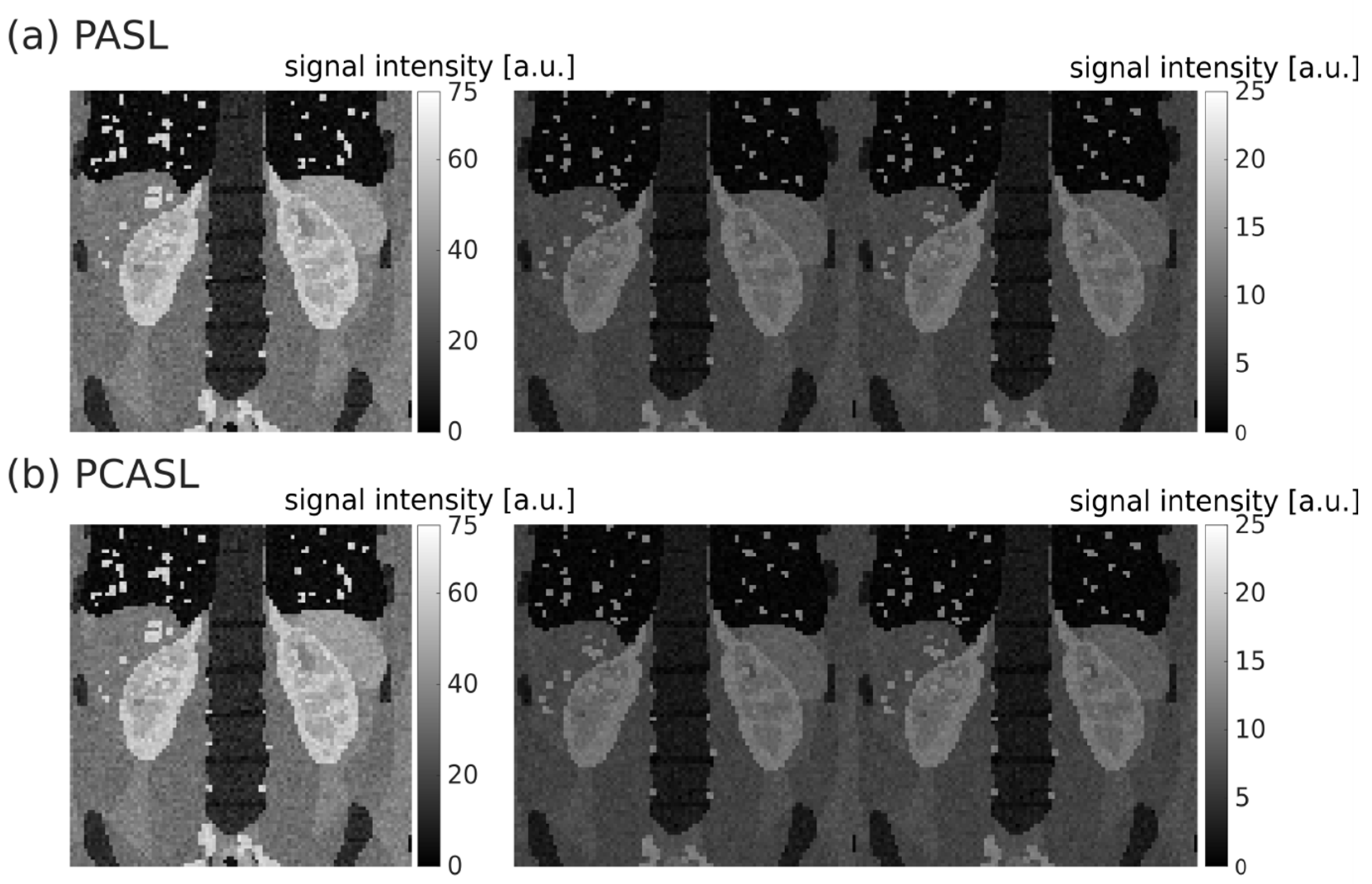
3. Results
3.1. Synthetic ASL Data Sets
3.2. Registration
3.3. Quantification
3.4. Segmentation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Rayner, H.; Thomas, M.; Milford, D. Kidney anatomy and physiology. In Understanding Kidney Diseases; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Yang, L.; Su, T.; Yang, X.; Chen, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Jiang, X. Quantitative assessment of acute kidney injury by noninvasive arterial spin labeling perfusion MRI: A pilot study. Sci. China Life Sci. 2013, 56, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, R.J.; Feehally, J.; Floege, J. Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, C.; Artunc, F.; Martirosian, P.; Schlemmer, H.P.; Schick, F.; Boss, A. Histogram analysis of renal arterial spin labeling perfusion data reveals differences between volunteers and patients with mild chronic kidney disease. Investig. Radiol. 2012, 47, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.Z.; Li, Z.C.; Zuo, P.L.; Pfeuffer, J.; Li, Y.M.; Liu, F.; Liu, R.B. Diagnostic value of renal perfusion in patients with chronic kidney disease using 3D arterial spin labeling. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 46, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.P.; Tan, H.; Thacker, J.M.; Li, W.; Zhou, Y.; Kohn, O.; Sprague, S.M.; Prasad, P.V. Evaluation of renal blood flow in chronic kidney disease using arterial spin labeling perfusion magnetic resonance imaging. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 2, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.L.; Lee, V.S. Renal perfusion imaging by MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 52, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora-Gutiérrez, J.M.; Garcia-Fernandez, N.; Slon Roblero, M.F.; Páramo, J.A.; Escalada, F.J.; Wang, D.J.; Benito, A.; Fernández-Seara, M.A. Arterial spin labeling MRI is able to detect early hemodynamic changes in diabetic nephropathy. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 46, 1810–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzman, R.S.; Wittsack, H.J.; Martirosian, P.; Zgoura, P.; Bilk, P.; Kröpil, P.; Schick, F.; Voiculescu, A.; Blondin, D. Quantification of renal allograft perfusion using arterial spin labeling MRI: Initial results. Eur. Radiol. 2010, 20, 1485–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hueper, K.; Gueler, F.; Bräsen, J.H.; Gutberlet, M.; Jang, M.S.; Lehner, F.; Richter, N.; Peperhove, M.; Martirosian, P.; Tewes, S.; et al. Functional MRI detects perfusion impairment in renal allografts with delayed graft function. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2015, 308, F1444–F1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ren, T.; Wen, C.L.; Chen, L.H.; Xie, S.S.; Cheng, Y.; Fu, Y.X.; Oesingmann, N.; de Oliveira, A.; Zuo, P.L.; Yin, J.Z.; et al. Evaluation of renal allografts function early after transplantation using intravoxel incoherent motion and arterial spin labeling MRI. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2016, 34, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notohamiprodjo, M.; Reiser, M.F.; Sourbron, S.P. Diffusion and perfusion of the kidney. Eur. J. Radiol. 2010, 76, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detre, J.A.; Leigh, J.S.; Williams, D.S.; Koretsky, A.P. Perfusion imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 1992, 23, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.S.; Detre, J.A.; Leigh, J.S.; Koretsky, A.P. Magnetic resonance imaging of perfusion using spin inversion of arterial water. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odudu, A.; Nery, F.; Harteveld, A.A.; Evans, R.G.; Pendse, D.; Buchanan, C.E.; Francis, S.T.; Fernández-Seara, M.A. Arterial spin labelling MRI to measure renal perfusion: A systematic review and statement paper. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33 (Suppl. 2), ii15–ii21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nery, F.; Gordon, I.; Thomas, D.L. Non-invasive renal perfusion imaging using arterial spin labeling MRI: Challenges and opportunities. Diagnostics 2018, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nery, F.; Buchanan, C.E.; Harteveld, A.A.; Odudu, A.; Bane, O.; Cox, E.F.; Derlin, K.; Gach, H.M.; Golay, X.; Gutberlet, M.; et al. Consensus-based technical recommendations for clinical translation of renal ASL MRI. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2020, 33, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Segars, W.P.; Sturgeon, G.; Mendonca, S.; Grimes, J.; Tsui, B.M.W. 4D XCAT phantom for multimodality imaging research. Med. Phys. 2010, 37, 4902–4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissmann, L.; Santelli, C.; Segars, W.P.; Kozerke, S. MRXCAT: Realistic numerical phantoms for cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2014, 16, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bazelaire, C.M.; Duhamel, G.D.; Rofsky, N.M.; Alsop, D.C. MR imaging relaxation times of abdominal and pelvic tissues measured in vivo at 3.0 T: Preliminary results. Radiology 2004, 230, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanisz, G.J.; Odrobina, E.E.; Pun, J.; Escaravage, E.; Graham, S.J.; Bronskill, M.J.; Henkelman, R.M. T1, T2 relaxation and magnetization transfer in tissue at 3T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2005, 54, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taso, M.; Guidon, A.; Alsop, D.C. Influence of background suppression and retrospective realignment on free-breathing renal perfusion measurement using pseudo-continuous ASL. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 81, 2439–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, R.B.; Frank, L.R.; Wong, E.C.; Siewert, S.; Warach, S.; Edelman, R.R. A general kinetic model for quantitative perfusion imaging with arterial spin labeling. Magn. Reson. Med. 1998, 40, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, D.A.; Detre, J.A.; Bolinger, L.; Insko, E.K.; Lenkinski, R.E.; Pentecost, M.J.; Leigh, J.S., Jr. Renal perfusion in humans: MR imaging with spin tagging of arterial water. Radiology 1995, 196, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Shim, W.H.; Yoon, S.K.; Oh, J.Y.; Kim, J.K.; Jung, H.; Matsuda, T.; Kim, D. Measurement of arterial transit time and renal blood flow using pseudocontinuous ASL MRI with multiple post-labeling delays: Feasibility, reproducibility, and variation. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 46, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Staring, M.; Murphy, K.; Viergever, M.A.; Pluim, J.P.W. Elastix: A toolbox for intensity-based medical image registration. IEEE 2009, 29, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamonin, D.P.; Bron, E.E.; Lelieveldt, B.P.; Smits, M.; Klein, S.; Staring, M.; Alzheimer’s Neuroimaging Initiative. Fast parallel image registration on CPU and GPU for diagnostic classification of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Neuroinform. 2014, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Pluim, J.P.; Staring, M.; Viergever, M.A. Adaptive stochastic gradient descent optimisation for image registration. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2009, 81, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huizinga, W.; Poot, D.H.; Guyader, J.M.; Klaassen, R.; Coolen, B.F.; van Kranenburg, M.; van Geuns, R.J.M.; Uitterdijk, A.; Polfliet, M.; Vandemeulebroucke, J.; et al. PCA-based groupwise image registration for quantitative MRI. Med. Image Anal. 2016, 29, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dice, L.R. Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 1945, 26, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, D.F.; Russ, T.; Waldkirch, B.I.; Tönnes, C.; Segars, W.P.; Schad, L.R.; Zöllner, F.G.; Golla, A.K. Generation of annotated multimodal ground truth datasets for abdominal medical image registration. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2021, 16, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antolak, A.G.; Jackson, E.F. Development and evaluation of an arterial spin-labeling digital reference object for quality control and comparison of data analysis applications. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019, 64, 02NT01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver-Taylor, A.M.; Hampshire, T.; Smith, N.; Stritt, M.; Petr, J.; Gregori, J.; Günther, M.; Mutsaerts, H.; Golay, X. ASLDRO: Digital reference object software for Arterial Spin Labelling. In Proceedings of the ISMRM 29th Annual Meeting, Virtual, 15–20 May 2021; Volume 2731. Available online: https://pypi.org/project/asldro/ (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Anazodo, U.; Pinto, J.; Kennedy McConnell, F.; Dounavi, M.-E.; Gould van Praag, C.; Mutsaerts, H.; Oliver-Taylor, A.; Paschoal, A.; Petr, J.; Pineda-Ordóñez, D.; et al. The Open Source Initiative for Perfusion Imaging (OSIPI) ASL MRI Challenge. In Proceedings of the ISMRM 29th Annual Meeting, Virtual, 15–20 May 2021; Volume 2714. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver-Taylor, A.; Sharma, K.; Sourbron, S.P.; Golay, X. A Renal Digital Reference Object for Arterial Spin Labelling. In Proceedings of the ISMRM Workshop Kidney MRI Biomarkers: The Route to Clinical Application, Lisbon, Portugal, 10–12 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Aramendía-Vidauretta, V. Non-Invasive Evaluation of Myocardial Perfusion in Humans Using Arterial Spin Labeling Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Doctoral Thesis, Universidad de Navarra, Pamplona, Spain, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Merrem, A.D.; Zöllner, F.G.; Reich, M.; Lundervold, A.; Rorvik, J.; Schad, L.R. A variational approach to image registration in dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI of the human kidney. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 31, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zöllner, F.G.; Šerifović-Trbalić, A.; Kabelitz, G.; Kociński, M.; Materka, A.; Rogelj, P. Image registration in dynamic renal MRI—current status and prospects. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2020, 33, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zöllner, F.G.; Sance, R.; Rogelj, P.; Ledesma-Carbayo, M.J.; Rørvik, J.; Santos, A.; Lundervold, A. Assessment of 3D DCE-MRI of the kidneys using non-rigid image registration and segmentation of voxel time courses. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2009, 33, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zöllner, F.G.; Merrem, A.D.; Peng, Y.; Roervik, J.; Lundervold, A.; Schad, L.R. Wavelet-based segmentation of renal compartments in DCE-MRI of human kidney: Initial results in patients and healthy volunteers. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2012, 36, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, B.; Ansaloni, A.; Sousa-Guimaraes, S.; Vakilzadeh, N.; Piskunowicz, M.; Vogt, B.; Stuber, M.; Burnier, M.; Pruijm, M. Reduction of cortical oxygenation in chronic kidney disease: Evidence obtained with a new analysis method of blood oxygenation level-dependent magnetic resonance imaging. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 2097–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schnurr, A.; Drees, C.; Schad, L.R.; Zöllner, F.G. Comparing sample mining schemes for CNN kidney segmentation in T1w MRI. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Functional Renal Imaging, Nottingham, UK, 15–17 October 2019; Available online: https://www.nottingham.ac.uk/research/groups/spmic/documents/3rd-renal-programme.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Zöllner, F.G.; Kociński, M.; Hansen, L.; Golla, A.K.; Trbalić, A.Š.; Lundervold, A.; Materka, A.; Rogelj, P. Kidney segmentation in renal magnetic resonance imaging-current status and prospects. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 71577–71605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zöllner, F.G.; Svarstad, E.; Munthe-Kaas, A.Z.; Schad, L.R.; Lundervold, A.; Rørvik, J. Assessment of kidney volumes from MRI: Acquisition and segmentation techniques. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2012, 199, 1060–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brumer, I.; Bauer, D.F.; Schad, L.R.; Zöllner, F.G. Synthetic Arterial Spin Labeling MRI of the Kidneys for Evaluation of Data Processing Pipeline. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1854. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12081854
Brumer I, Bauer DF, Schad LR, Zöllner FG. Synthetic Arterial Spin Labeling MRI of the Kidneys for Evaluation of Data Processing Pipeline. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(8):1854. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12081854
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrumer, Irène, Dominik F. Bauer, Lothar R. Schad, and Frank G. Zöllner. 2022. "Synthetic Arterial Spin Labeling MRI of the Kidneys for Evaluation of Data Processing Pipeline" Diagnostics 12, no. 8: 1854. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12081854
APA StyleBrumer, I., Bauer, D. F., Schad, L. R., & Zöllner, F. G. (2022). Synthetic Arterial Spin Labeling MRI of the Kidneys for Evaluation of Data Processing Pipeline. Diagnostics, 12(8), 1854. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12081854





