Chest CT Severity Score and Systemic Inflammatory Biomarkers as Predictors of the Need for Invasive Mechanical Ventilation and of COVID-19 Patients’ Mortality
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Systemic Inflammatory Markers
2.4. Chest CT Severity Score
2.5. Vaccination Status
2.6. Study Outcomes
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19)—World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 (accessed on 9 August 2022).
- Mureșan, A.V.; Russu, E.; Arbănași, E.M.; Kaller, R.; Hosu, I.; Arbănași, E.M.; Voidăzan, S.T. Negative Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Kidney Disease Management—A Single-Center Experience in Romania. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muresan, A.V.; Russu, E.; Arbanasi, E.M.; Kaller, R.; Voidăzan, S.T.; Arbanasi, E.M. Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Vascular Surgery Unit Activity in Central Romania. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinreich, D.M.; Sivapalasingam, S.; Norton, T.; Ali, S.; Gao, H.; Bhore, R.; Xiao, J.; Hooper, A.T.; Hamilton, J.D.; Musser, B.J.; et al. REGEN-COV Antibody Combination and Outcomes in Outpatients with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moline, H.L.; Whitaker, M.; Deng, L.; Rhodes, J.C.; Milucky, J.; Pham, H.; Patel, K.; Anglin, O.; Reingold, A.; Chai, S.J.; et al. Effectiveness of COVID-19 Vaccines in Preventing Hospitalization Among Adults Aged ≥ 65 Years—COVID-NET, 13 States, February–April 2021. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharif, W.; Qurashi, A. Effectiveness of COVID-19 Diagnosis and Management Tools: A Review. Radiogr. Lond 2021, 27, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyit, M.; Avci, E.; Nar, R.; Senol, H.; Yilmaz, A.; Ozen, M.; Oskay, A.; Aybek, H. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio, Lymphocyte to Monocyte Ratio and Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio to Predict the Severity of COVID-19. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 40, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaim, S.; Chong, J.H.; Sankaranarayanan, V.; Harky, A. COVID-19 and Multiorgan Response. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2020, 45, 100618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.S.; de Sá, K.S.G.; Ishimoto, A.Y.; Becerra, A.; Oliveira, S.; Almeida, L.; Gonçalves, A.V.; Perucello, D.B.; Andrade, W.A.; Castro, R.; et al. Inflammasomes Are Activated in Response to SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Are Associated with COVID-19 Severity in Patients. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 218, e20201707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, D.Q.; Zou, B.; Yang, H.; Hui, W.Z.; Rui, F.; Yee, N.T.S.; Liu, C.; Nerurkar, S.N.; Kai, J.C.Y.; et al. Epidemiology of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Characteristics, Risk Factors, and Outcomes. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrilli, C.M.; Jones, S.A.; Yang, J.; Rajagopalan, H.; O’Donnell, L.; Chernyak, Y.; Tobin, K.A.; Cerfolio, R.J.; Francois, F.; Horwitz, L.I. Factors Associated with Hospital Admission and Critical Illness among 5279 People with Coronavirus Disease 2019 in New York City: Prospective Cohort Study. BMJ 2020, 369, m1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ding, M.; Dong, X.; Zhang, J.; Kursat Azkur, A.; Azkur, D.; Gan, H.; Sun, Y.; Fu, W.; Li, W.; et al. Risk Factors for Severe and Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: A Review. Allergy 2021, 76, 428–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, W.-J.; Ni, Z.-Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.-H.; Ou, C.-Q.; He, J.-X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.-L.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhazzani, W.; Evans, L.; Alshamsi, F.; Moller, M.H.; Ostermann, M.; Prescott, H.C.; Arabi, Y.M.; Loeb, M.; Ng Gong, M.; Fan, E.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guidelines on the Management of Adults With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in the ICU: First Update. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, e219–e234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Collazo, E.; Avendaño-Ortiz, J.; Martín-Quirós, A.; Aguirre, L.A. Immune Response and COVID-19: A Mirror Image of Sepsis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 2479–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, P.; Palumbo, M.M.; Bruno, F.; Picchi, G.; Iacopino, A.; Acanfora, C.; Sgalambro, F.; Arrigoni, F.; Ciccullo, A.; Cosimini, B.; et al. Automated Quantitative Lung CT Improves Prognostication in Non-ICU COVID-19 Patients beyond Conventional Biomarkers of Disease. Diagn. Basel Switz. 2021, 11, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baikpour, M.; Carlos, A.; Morasse, R.; Gissel, H.; Perez-Gutierrez, V.; Nino, J.; Amaya-Suarez, J.; Ali, F.; Toledano, T.; Arampulikan, J.; et al. Role of a Chest X-ray Severity Score in a Multivariable Predictive Model for Mortality in Patients with COVID-19: A Single-Center, Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skopljanac, I.; Ivelja, M.P.; Barcot, O.; Brdar, I.; Dolic, K.; Polasek, O.; Radic, M. Role of Lung Ultrasound in Predicting Clinical Severity and Fatality in COVID-19 Pneumonia. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regolo, M.; Vaccaro, M.; Sorce, A.; Stancanelli, B.; Colaci, M.; Natoli, G.; Russo, M.; Alessandria, I.; Motta, M.; Santangelo, N.; et al. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) Is a Promising Predictor of Mortality and Admission to Intensive Care Unit of COVID-19 Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanini, S.; Montaldo, C.; Nicastri, E.; Vairo, F.; Agrati, C.; Petrosillo, N.; Scognamiglio, P.; Antinori, A.; Puro, V.; Di Caro, A.; et al. COVID-19 Disease-Temporal Analyses of Complete Blood Count Parameters over Course of Illness, and Relationship to Patient Demographics and Management Outcomes in Survivors and Non-Survivors: A Longitudinal Descriptive Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahat, R.K.; Panda, S.; Rathore, V.; Swain, S.; Yadav, L.; Sah, S.P. The Dynamics of Inflammatory Markers in Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19) Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2021, 11, 100727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citu, C.; Gorun, F.; Motoc, A.; Sas, I.; Gorun, O.M.; Burlea, B.; Tuta-Sas, I.; Tomescu, L.; Neamtu, R.; Malita, D.; et al. The Predictive Role of NLR, d-NLR, MLR, and SIRI in COVID-19 Mortality. Diagn. Basel Switz. 2022, 12, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, J.; Suter, F.; Furrer, E.; Sendoel, A.; Stüssi-Helbling, M.; Huber, L.C. Neutrophile-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) Identifies Patients with Coronavirus Infectious Disease 2019 (COVID-19) at High Risk for Deterioration and Mortality-A Retrospective, Monocentric Cohort Study. Diagn. Basel Switz. 2022, 12, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, C.; Mao, Z.; Xiao, M.; Wang, L.; Qi, S.; Zhou, F. Predictive Values of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio on Disease Severity and Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Crit. Care Lond. Engl. 2020, 24, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simadibrata, D.M.; Calvin, J.; Wijaya, A.D.; Ibrahim, N.A.A. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio on Admission to Predict the Severity and Mortality of COVID-19 Patients: A Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 42, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Kannan, S.; Khanna, P.; Singh, A.K. Role of Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Count Ratio (PLR), as a Prognostic Indicator in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Yang, L.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ning, K.; Su, D. Temporal Relationship between Serial RT-PCR Results and Serial Chest CT Imaging, and Serial CT Changes in Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) Pneumonia: A Descriptive Study of 155 Cases in China. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, G.; Gaba, W.; Shah, A.; Helali, A.A.; Raidullah, E.; Ali, A.A.; Elghazali, M.; Ahmed, D.; Kaabi, S.A.; Almazrouei, S. Correlation between Chest CT Severity Scores and the Clinical Parameters of Adult Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia. Radiol. Res. Pract. 2021, 2021, 6697677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Li, X.; Guo, D.; Wu, L.; Chen, T.; Fang, Z.; Chen, L.; Zeng, W.; Yang, R. CT Quantitative Analysis and Its Relationship with Clinical Features for Assessing the Severity of Patients with COVID-19. Korean J. Radiol. 2020, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yu, H.; Zhang, S. The Indispensable Role of Chest CT in the Detection of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 1638–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Fang, Y.; Li, W.; Pan, C.; Qin, P.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, M.; Liao, Y.; Li, S. CT Image Visual Quantitative Evaluation and Clinical Classification of Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 4407–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salaffi, F.; Carotti, M.; Tardella, M.; Borgheresi, A.; Agostini, A.; Minorati, D.; Marotto, D.; Di Carlo, M.; Galli, M.; Giovagnoni, A.; et al. The Role of a Chest Computed Tomography Severity Score in Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia. Med. (Baltim.) 2020, 99, e22433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Wu, J.; Wu, F.; Guo, D.; Chen, L.; Fang, Z.; Li, C. The Clinical and Chest CT Features Associated With Severe and Critical COVID-19 Pneumonia. Investig. Radiol. 2020, 55, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Zhen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, Q.; Luo, Y.; Gao, C.; Zeng, W. Chest CT Severity Score: An Imaging Tool for Assessing Severe COVID-19. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging 2020, 2, e200047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.; Bernheim, A.; Mei, X.; Zhang, N.; Huang, M.; Zeng, X.; Cui, J.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Fayad, Z.A.; et al. CT Imaging Features of 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-NCoV). Radiology 2020, 295, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellos, I.; Tavernaraki, K.; Stefanidis, K.; Michalopoulou, O.; Lourida, G.; Korompoki, E.; Thanou, I.; Thanos, L.; Pefanis, A.; Argyraki, A. Chest CT Severity Score and Radiological Patterns as Predictors of Disease Severity, ICU Admission, and Viral Positivity in COVID-19 Patients. Respir. Investig. 2021, 59, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmokadem, A.H.; Mounir, A.M.; Ramadan, Z.A.; Elsedeiq, M.; Saleh, G.A. Comparison of Chest CT Severity Scoring Systems for COVID-19. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 3501–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermali, M.; Khalsa, R.K.; Pillai, K.; Ismail, Z.; Harky, A. The Role of Biomarkers in Diagnosis of COVID-19—A Systematic Review. Life Sci. 2020, 254, 117788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, L.; Xu, M.; Wu, J.; Luo, D.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Song, X.; Zhou, X. Prognostic Value of Interleukin-6, C-Reactive Protein, and Procalcitonin in Patients with COVID-19. J. Clin. Virol. Off. Publ. Pan Am. Soc. Clin. Virol. 2020, 127, 104370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payen, D.; Cravat, M.; Maadadi, H.; Didelot, C.; Prosic, L.; Dupuis, C.; Losser, M.-R.; De Carvalho Bittencourt, M. A Longitudinal Study of Immune Cells in Severe COVID-19 Patients. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 580250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumagalli, C.; Rozzini, R.; Vannini, M.; Coccia, F.; Cesaroni, G.; Mazzeo, F.; Cola, M.; Bartoloni, A.; Fontanari, P.; Lavorini, F.; et al. Clinical Risk Score to Predict In-Hospital Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e040729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawaz, M.; Langer, H.; May, A.E. Platelets in Inflammation and Atherogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 3378–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drugescu, A.; Roca, M.; Zota, I.M.; Costache, A.-D.; Gavril, O.I.; Gavril, R.S.; Vasilcu, T.F.; Mitu, O.; Esanu, I.M.; Roca, I.-C.; et al. Value of the Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio in Predicting CPET Performance in Patients with Stable CAD and Recent Elective PCI. Med. Kaunas Lith. 2022, 58, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtul, A.; Yarlioglues, M.; Murat, S.N.; Ergun, G.; Duran, M.; Kasapkara, H.A.; Demircelik, M.B.; Cetin, M.; Ocek, A.H. Usefulness of the Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Predicting Angiographic Reflow after Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Patients with Acute ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Am. J. Cardiol. 2014, 114, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbănași, E.M.; Mureșan, A.V.; Coșarcă, C.M.; Kaller, R.; Bud, T.I.; Hosu, I.; Voidăzan, S.T.; Arbănași, E.M.; Russu, E. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Impact on Predicting Outcomes in Patients with Acute Limb Ischemia. Life 2022, 12, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taşoğlu, I.; Çiçek, O.F.; Lafcı, G.; Kadiroğulları, E.; Sert, D.E.; Demir, A.; Cavus, U.; Colak, N.; Songur, M.; Hodo, B. Usefulness of Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio as a Predictor of Amputation after Embolectomy for Acute Limb Ischemia. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2014, 28, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mureșan, A.V.; Russu, E.; Arbănași, E.M.; Kaller, R.; Hosu, I.; Arbănași, E.M.; Voidăzan, S.T. The Predictive Value of NLR, MLR, and PLR in the Outcome of End-Stage Kidney Disease Patients. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunoren, O.; Akkus, G.; Sezal, D.T.; Ciftcioglu, M.; Guzel, F.B.; Isiktas, S.; Torun, G.I.; Uyan, M.; Sokmen, M.F.; Sevim, H.A.; et al. Does Neutrophyl to Lymphocyte Ratio Really Predict Chronic Kidney Disease Progression? Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2019, 51, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russu, E.; Mureșan, A.V.; Arbănași, E.M.; Kaller, R.; Hosu, I.; Voidăzan, S.; Arbănași, E.M.; Coșarcă, C.M. The Predictive Role of NLR and PLR in Outcome and Patency of Lower Limb Revascularization in Patients with Femoropopliteal Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Zhuang, L.; Shen, Y.; Geng, Y.; Yu, S.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Meng, Z.; Wang, P.; Chen, Z. A Novel Systemic Inflammation Response Index (SIRI) for Predicting the Survival of Patients with Pancreatic Cancer after Chemotherapy. Cancer 2016, 122, 2158–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, Z.; Du, H.; Zhang, W.; Che, G.; Liu, L. Novel Systemic Inflammation Response Index to Predict Prognosis after Thoracoscopic Lung Cancer Surgery: A Propensity Score-Matching Study. ANZ J. Surg. 2019, 89, E507–E513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.-J.; Qian, L.-Q.; Ding, Z.-P.; Luo, Q.-Q.; Zhao, H.; Xia, W.-Y.; Fu, Y.-Y.; Feng, W.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, W.; et al. Prognostic Value of Inflammatory Biomarkers in Patients With Stage I Lung Adenocarcinoma Treated With Surgical Dissection. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 711206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical Course and Risk Factors for Mortality of Adult Inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yu, J.; He, W.; Chen, L.; Yuan, G.; Dong, F.; Chen, W. Risk Factors for Death in 1859 Subjects with COVID-19. Leukemia 2020, 34, 2173–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fois, A.G.; Paliogiannis, P.; Scano, V.; Cau, S.; Babudieri, S.; Perra, R.; Ruzzittu, G.; Zinellu, E.; Pirina, P.; Carru, C.; et al. The Systemic Inflammation Index on Admission Predicts In-Hospital Mortality in COVID-19 Patients. Molecules 2020, 25, 5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moisa, E.; Corneci, D.; Negoita, S.; Filimon, C.R.; Serbu, A.; Negutu, M.I.; Grintescu, I.M. Dynamic Changes of the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, Systemic Inflammation Index, and Derived Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Independently Predict Invasive Mechanical Ventilation Need and Death in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasselli, G.; Greco, M.; Zanella, A.; Albano, G.; Antonelli, M.; Bellani, G.; Bonanomi, E.; Cabrini, L.; Carlesso, E.; Castelli, G.; et al. Risk Factors Associated With Mortality Among Patients With COVID-19 in Intensive Care Units in Lombardy, Italy. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santus, P.; Radovanovic, D.; Saderi, L.; Marino, P.; Cogliati, C.; Filippis, G.D.; Rizzi, M.; Franceschi, E.; Pini, S.; Giuliani, F.; et al. Severity of Respiratory Failure at Admission and In-Hospital Mortality in Patients with COVID-19: A Prospective Observational Multicentre Study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e043651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, B.M.; Lippi, G. Chronic Kidney Disease Is Associated with Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Infection. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2020, 52, 1193–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, S.; Turgutalp, K.; Arici, M.; Odabas, A.R.; Altiparmak, M.R.; Aydin, Z.; Cebeci, E.; Basturk, T.; Soypacaci, Z.; Sahin, G.; et al. Mortality Analysis of COVID-19 Infection in Chronic Kidney Disease, Haemodialysis and Renal Transplant Patients Compared with Patients without Kidney Disease: A Nationwide Analysis from Turkey. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 2083–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ERA-EDTA Council; ERACODA Working Group Chronic Kidney Disease Is a Key Risk Factor for Severe COVID-19: A Call to Action by the ERA-EDTA. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 87–94. [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei, S.M.H.; Rahimi, H.; Moghaddas, F.; Rajebi, H. Predictive Value of CT in the Short-Term Mortality of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pneumonia in Nonelderly Patients: A Case-Control Study. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 132, 109298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Chen, C.; Hu, Y.; Lv, W.; Ai, T.; Xia, L. Chest CT Imaging Features and Severity Scores as Biomarkers for Prognostic Prediction in Patients with COVID-19. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tharwat, S.; Saleh, G.A.; Saleh, M.; Mounir, A.M.; Abdelzaher, D.G.; Salah, A.M.; Nassar, M.K. Chest CT Total Severity Score on Admission to Predict In-Hospital Mortality in COVID-19 Patients with Acute and Chronic Renal Impairment. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamad, D.A.; Aly, M.M.; Abdelhameid, M.A.; Ahmed, S.A.; Shaltout, A.S.; Abdel-Moniem, A.E.; Ragheb, A.M.R.; Attia, M.N.; Meshref, T.S. Combined Blood Indexes of Systemic Inflammation as a Mirror to Admission to Intensive Care Unit in COVID-19 Patients: A Multicentric Study. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2022, 12, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalbant, A.; Demirci, T.; Kaya, T.; Aydın, A.; Altındiş, M.; Güçlü, E. Can Prognostic Nutritional Index and Systemic Immune-Inflammatory Index Predict Disease Severity in COVID-19? Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e14544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | All Patients n = 267 | Survivors n = 185 | Non-Survivors n = 82 | p Value (OR; CI 95%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age mean ± SD (min-max) | 71.19 ± 10.25 (33–94) | 70.01 ± 8.99 (46–91) | 73.85 ± 12.29 (33–94) | 0.01 |
| Male sex no. (%) | 159 (59.55%) | 112 (60.54%) | 47 (57.32%) | 0.62 (0.87; 0.51–1.48) |
| Comorbidities & Risk Factors | ||||
| AH, no. (%) | 167 (62.55%) | 116 (62.70%) | 51 (62.20%) | 0.93 (0.97; 0.57–1.67) |
| IHD, no. (%) | 145 (54.31%) | 97 (52.43%) | 48 (58.54%) | 0.35 (1.28; 0.75–2.16) |
| AF, no. (%) | 79 (29.59%) | 43 (23.24%) | 36 (43.90%) | 0.0008 (2.58; 1.48–4.49) |
| CHF, no. (%) | 130 (48.69%) | 81 (43.78%) | 49 (59.76%) | 0.01 (1.90; 1.12–3.23) |
| MI, no. (%) | 80 (29.96%) | 50 (27.03%) | 30 (36.59%) | 0.11 (1.55; 0.89–2.71) |
| T2D, no. (%) | 116 (43.45%) | 82 (44.32%) | 34 (41.46%) | 0.66 (0.88; 0.52–1.50) |
| COPD, no. (%) | 62 (23.22%) | 44 (23.78%) | 18 (21.95%) | 0.74 (0.90; 0.48–1.68) |
| Dyslipidemia, no. (%) | 150 (56.18%) | 95 (51.35%) | 55 (67.07%) | 0.01 (1.92; 1.12–3.32) |
| PAD, no. (%) | 120 (44.94%) | 85 (45.95%) | 35 (42.68%) | 0.62 (0.87; 0.51–1.48) |
| CKD, no. (%) | 57 (21.35%) | 30 (16.22%) | 27 (32.93%) | 0.002 (2.54; 1.38–4.64) |
| CVA, no. (%) | 76 (28.46%) | 46 (24.86%) | 30 (36.59%) | 0.051 (1.74; 0.99–3.05) |
| Obesity, no. (%) | 69 (44.94%) | 49 (26.49%) | 20 (24.39%) | 0.71 (0.89; 0.49–1.63) |
| Tobacco, no. (%) | 99 (37.08%) | 68 (36.76%) | 31 (37.80%) | 0.87 (1.04; 0.61–1.78) |
| Chest CT Findings | ||||
| Consolidation, no. (%) | 95 (35.58%) | 62 (33.51%) | 33 (40.24%) | 0.29 |
| Pleural Effusion, no. (%) | 38 (14.23%) | 26 (14.05%) | 12 (14.63%) | 0.90 |
| Ground Glass-Opacities, no. (%) | 167 (62.55%) | 114 (61.62%) | 53 (64.63%) | 0.63 |
| Right Upper Lobe, mean ± SD | 2.30 ± 1.19 | 1.97 ± 1.15 | 3.04 ± 0.94 | <0.0001 |
| Right Middle Lobe, mean ± SD | 2.58 ± 1.29 | 2.25 ± 1.29 | 3.32 ± 0.96 | <0.0001 |
| Right Lower Lobe, mean ± SD | 2.84 ± 1.15 | 2.54 ± 1.14 | 3.52 ± 0.83 | <0.0001 |
| Left Upper Lobe, mean ± SD | 2.12 ± 1.10 | 1.79 ± 1.02 | 2.85 ± 0.93 | <0.0001 |
| Left Lower Lobe, mean ± SD | 2.74 ± 1.17 | 2.40 ± 1.16 | 3.51 ± 0.75 | <0.0001 |
| Total System Score. mean ± SD | 12.57 ± 5.26 | 10.95 ± 5.07 | 16.24 ± 3.78 | <0.0001 |
| Vaccination Status | ||||
| UNVACCINATED, no. (%) | 69 (25.84%) | 37 (20%) | 32 (39.02%) | 0.001 |
| PARTIALLY VACCINATED, no. (%) | 54 (20.22%) | 35 (18.91%) | 19 (23.17%) | 0.42 |
| FULLY VACCINATED, no. (%) | 144 (53.93%) | 113 (61.08%) | 31 (37.80%) | 0.0005 |
| Laboratory Data | ||||
| Hemoglobin g/dL, median [Q1–Q3] | 12.51 [10.73–13.9] | 12.56 [10.7–13.81] | 12.50 [10.96–14.2] | 0.21 |
| Hematocrit %, median [Q1–Q3] | 38.99 [32.74–42.75] | 38.4 [32.5–42.3] | 39.1 [33.32–44.5] | 0.10 |
| Neutrophils ×103/uL, median [Q1–Q3] | 7.6 [5.86–10.93] | 6.82 [5.27–8.95] | 10.59 [7.50–13.73] | <0.0001 |
| Lymphocytes ×103/uL, median [Q1–Q3] | 1.58 [1.09–2.09] | 1.79 [1.41–2.26] | 1.05 [0.63–1.41] | <0.0001 |
| Monocyte ×103/uL, median [Q1–Q3] | 0.64 [0.46–0.88] | 0.61 [0.46–0.81] | 0.73 [0.56–1.08] | 0.0006 |
| PLT ×103/uL, median [Q1–Q3] | 257 [207.05–318] | 257 [212–314.5] | 257.5 [206–338.85] | 0.43 |
| Glucose mg/dL, median [Q1–Q3] | 118 [97–149.5] | 107 [95–139.5] | 139 [116.02–175.12] | <0.0001 |
| Cholesterol mg/dL, median [Q1–Q3] | 177.7 [144.25–212.7] | 179.2 [144.9–214.4] | 164.95 [143.6–205.47] | 0.13 |
| Triglyceride mg/dL, median [Q1–Q3] | 114.8 [91.3–166.95] | 114.8 [92.7–160] | 113.95 [88.32–169.7] | 0.49 |
| Potassium mmol/L, median [Q1–Q3] | 4.59 [4.09–5.37] | 4.79 [4.3–5.49] | 4.18 [3.77–4.99] | <0.0001 |
| Sodium mmol/L, median [Q1–Q3] | 140 [139–141] | 140 [139–141] | 140 [139–142] | 0.11 |
| BUN mg/dL, median [Q1–Q3] | 43.6 [33–56.05] | 42.4 [33.3–54.7] | 46.55 [32.55–67.8] | 0.10 |
| Creatinine mg/dL, median [Q1–Q3] | 0.94 [0.75–1.15] | 0.94 [0.75–1.14] | 0.92 [0.78–1.23] | 0.25 |
| MLR, median [Q1–Q3] | 0.40 [0.27–0.67] | 0.33 [0.24–0.47] | 0.75 [0.51–1.25] | <0.0001 |
| NLR, median [Q1–Q3] | 4.90 [2.88–9.79] | 3.73 [2.61–5.78] | 11.04 [7.77–18.24] | <0.0001 |
| SII, median [Q1–Q3] | 1408.12 [721.44–2464.28] | 1012.58 [618.39–1599.85] | 2613.55 [1950.20–5024.20] | <0.0001 |
| SIRI, median [Q1–Q3] | 3.03 [1.68–7.27] | 2.21 [1.41–4.04] | 9.13 [5.10–12.76] | <0.0001 |
| AISI, median [Q1–Q3] | 856.54 [416.97–2224.48] | 594.41 [350.51–1180.64] | 2349.60 [1310.65–3817.96] | <0.0001 |
| IL-6, median [Q1–Q3] | 19.43 [10.54–48.34] | 14.31 [9.08–24.75] | 69.9 [32.42–147.4] | <0.0001 |
| Outcomes | ||||
| IMV, no. (%) | 60 (22.47%) | 15 (8.11%) | 45 (54.88%) | <0.0001 |
| Mortality, no. (%) | 82 (30.71%) | - | 82 (30.71%) | <0.0001 |
| IMV + Mortality, no. (%) | 45 (16.85%) | - | 45 (16.85%) | <0.0001 |
| Hospital stays, day median [Q1-Q3] | 8 [6–13] | 8 [6–11] | 12 [6–17.75] | 0.0005 |
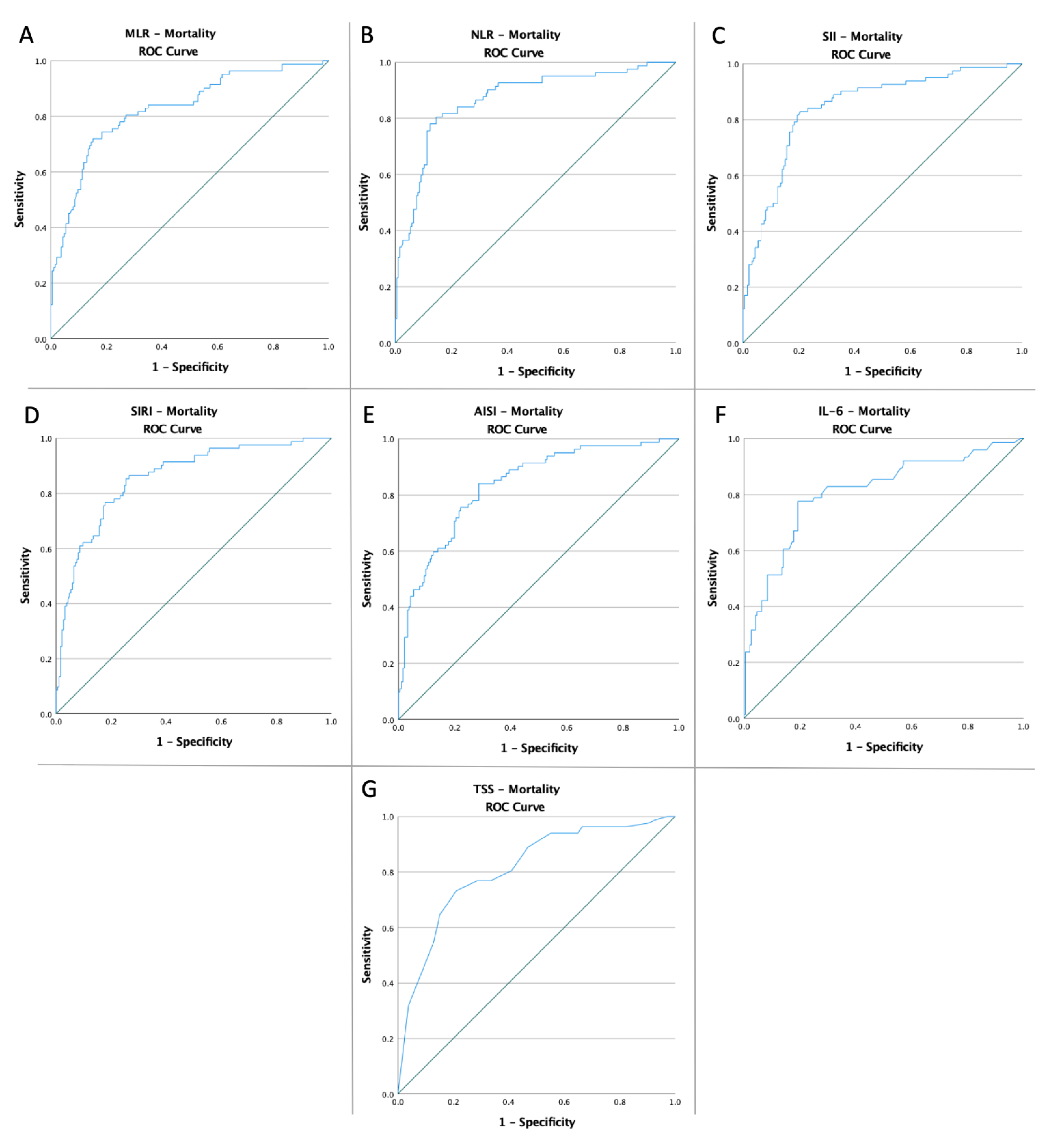
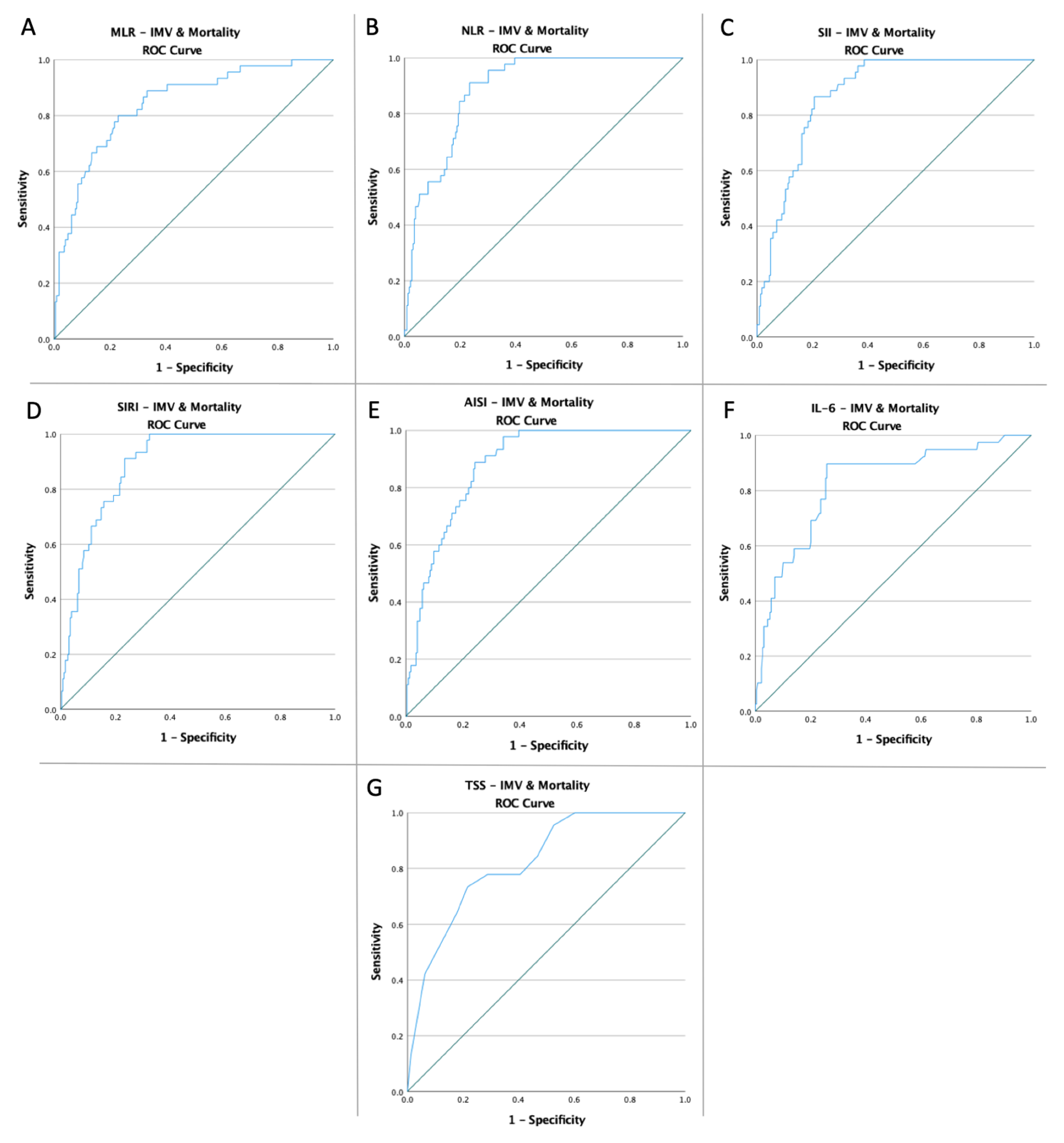
| Variables | Cut-Off | AUC | Std. Error | 95% CI | Sensitivity | Specificity | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMV | |||||||
| MLR NLR SII | 0.54 | 0.783 | 0.033 | 0.717–0.848 | 70% | 76.8% | <0.0001 |
| 6.82 | 0.827 | 0.029 | 0.771–0.883 | 76.7% | 76.3% | <0.0001 | |
| 2166.04 | 0.814 | 0.030 | 0.756–0.873 | 71.7% | 79.8% | <0.0001 | |
| SIRI | 3.66 | 0.822 | 0.029 | 0.765–0.880 | 90% | 66.2% | <0.0001 |
| AISI | 994.76 | 0.813 | 0.030 | 0.754–0.871 | 88.3% | 67.6% | <0.0001 |
| IL-6 | 30.95 | 0.762 | 0.034 | 0.695–0.830 | 74.1% | 75.6% | <0.0001 |
| TSS | 16.50 | 0.807 | 0.032 | 0.745–0.870 | 70% | 81.2% | <0.0001 |
| Mortality | |||||||
| MLR NLR SII | 0.54 | 0.826 | 0.029 | 0.771–0.882 | 74.4% | 81.6% | <0.0001 |
| 6.97 | 0.869 | 0.025 | 0.820–0.911 | 80.5% | 85.4% | <0.0001 | |
| 1739.36 | 0.845 | 0.026 | 0.794–0.896 | 82.9% | 79.5% | <0.0001 | |
| SIRI | 3.84 | 0.858 | 0.025 | 0.809–0.907 | 86.6% | 73.5% | <0.0001 |
| AISI | 973.59 | 0.836 | 0.026 | 0.784–0.888 | 84.1% | 71.4% | <0.0001 |
| IL-6 | 28.17 | 0.808 | 0.031 | 0.747–0.870 | 77.6% | 80.6% | <0.0001 |
| TSS | 15.50 | 0.811 | 0.029 | 0.754–0.867 | 73.2% | 78.9% | <0.0001 |
| IMV & Mortality | |||||||
| MLR NLR SII | 0.55 | 0.842 | 0.032 | 0.780–0.905 | 80% | 77% | <0.0001 |
| 6.97 | 0.887 | 0.021 | 0.846–0.928 | 91.1% | 76.6% | <0.0001 | |
| 2166.04 | 0.876 | 0.022 | 0.833–0.918 | 86.7% | 79.3% | <0.0001 | |
| SIRI | 4.70 | 0.892 | 0.020 | 0.852–0.931 | 93.3% | 72.5% | <0.0001 |
| AISI | 1403.56 | 0.880 | 0.022 | 0.838–0.922 | 88.9% | 75.7% | <0.0001 |
| IL-6 | 30.95 | 0.825 | 0.037 | 0.753–0.897 | 89.7% | 74.1% | <0.0001 |
| TSS | 16.50 | 0.823 | 0.031 | 0.762–0.884 | 73.3% | 78.4% | <0.0001 |
| IMV | Mortality | IMV & Mortality | |
|---|---|---|---|
| low-MLR vs. high-MLR | 18/170 (10.59%) vs. 42/97 (43.30%) p < 0.0001 OR:6.44 CI: (3.42–12.13) | 21/170 (12.35%) vs. 61/97 (62.89%) p < 0.0001 OR:11.38 CI: (6.18–20.97) | 9/170 (5.29%) vs. 36/97 (37.11%) p < 0.0001 OR:10.55 CI: (4.80–23.20) |
| low-NLR vs. high-NLR | 14/172 (8.14%) vs. 46/95 (48.42%) p < 0.0001 OR:10.59 CI: (5.37–20.88) | 16/174 (9.20%) vs. 66/93 (70.97%) p < 0.0001 OR:24.13 CI: (12.20–47.73) | 4/174 (2.30%) vs. 41/93 (44.09%) p < 0.0001 OR:33.50 CI: (11.46–97.95) |
| low-SII vs. high-SII | 17/182 (9.34%) vs. 43/85 (50.59%) p < 0.0001 OR:9.93 CI: (5.15–19.14) | 14/161 (8.70%) vs. 68/106 (64.15%) p < 0.0001 OR:18.78 CI: (9.54–36.97) | 6/182 (3.30%) vs. 39/85 (45.88%) p < 0.0001 OR:24.86 CI: (9.92–62.32) |
| low-SIRI vs. high-SIRI | 6/143 (4.20%) vs. 54/124 (43.55%) p < 0.0001 OR:17.61 CI: (7.22–42.94) | 11/147 (7.48%) vs. 71/120 (59.17%) p < 0.0001 OR:17.91 CI: (8.77–36.58) | 3/164 (1.83%) vs. 42/103 (40.78%) p < 0.0001 OR:36.95 CI: (11.04–123.64) |
| low-AISI vs. high-AISI | 7/147 (4.76%) vs. 53/120 (44.17%) p < 0.0001 OR:15.82 CI: (6.82–36.65) | 13/145 (8.97%) vs. 69/122 (56.56%) p < 0.0001 OR:13.21 CI: (6.74–25.90) | 5/173 (2.89%) vs. 40/94 (42.55%) p < 0.0001 OR:24.88 CI: (9.35–66.24) |
| low-IL-6 vs. high-IL-6 | 15/173 (8.67%) vs. 45/94 (47.87%) p < 0.0001 OR:9.67 CI: (4.96–18.83) | 17/171 (9.94%) vs. 63/96 (65.63%) p < 0.0001 OR:17.29 CI: (8.98–33.27) | 4/173 (2.31%) vs. 41/94 (43.62%) p < 0.0001 OR:32.68 CI: (11.18–95.48) |
| low-TSS vs. high-TSS | 15/168 (8.93%) vs. 45/99 (45.45%) p < 0.0001 OR:8.50 CI: (4.38–16.47) | 29/186 (15.59%) vs. 53/81 (65.43%) p < 0.0001 OR:10.24 CI: (5.59–18.77) | 10/158 (6.33%) vs. 35/99 (35.35%) p < 0.0001 OR:8.09 CI: (3.77–17.33) |
| IMV | Mortality | IMV & Mortality | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p Value | OR | 95% CI | p Value | OR | 95% CI | p Value | |
| Age > 70 AF CHF | 1.97 | 1.07–3.63 | 0.02 | 2.49 | 1.43–4.35 | 0.001 | 2.87 | 1.38–5.96 | 0.005 |
| 2.22 | 1.22–4.04 | 0.009 | 2.58 | 1.48–4.49 | <0.001 | 2.21 | 1.14–4.27 | 0.01 | |
| 1.51 | 0.84–2.69 | 0.16 | 1.90 | 1.12–3.23 | 0.01 | 2.17 | 1.11–4.22 | 0.02 | |
| MI | 1.35 | 0.73–2.48 | 0.33 | 1.55 | 0.89–2.71 | 0.11 | 1.36 | 0.69–2.67 | 0.37 |
| Dyslipidemia | 2.13 | 1.15–3.96 | 0.01 | 1.93 | 1.12–3.32 | 0.01 | 2.16 | 1.08–4.35 | 0.02 |
| CKD | 1.31 | 0.66–2.57 | 0.43 | 2.53 | 1.38–4.64 | 0.003 | 2.14 | 1.05–4.33 | 0.03 |
| CVA | 0.89 | 0.46–1.70 | 0.72 | 1.74 | 0.99–3.05 | 0.052 | 1.32 | 0.66–2.62 | 0.42 |
| Unvaccinated | 1.90 | 1.01–3.55 | 0.04 | 3.02 | 1.69–5.40 | <0.001 | 2.97 | 1.47–6.00 | 0.002 |
| Fully Vaccinated | 0.16 | 0.08–0.33 | <0.001 | 0.46 | 0.27–0.79 | 0.006 | 0.23 | 0.11–0.51 | <0.001 |
| high-MLR high-NLR high-SII | 6.44 | 3.42–12.13 | <0.001 | 6.49 | 2.51–22.24 | <0.001 | 11.85 | 5.37–26.14 | <0.001 |
| 10.59 | 5.37–20.88 | <0.001 | 24.13 | 12.20–47.73 | <0.001 | 33.51 | 11.46–97.95 | <0.001 | |
| 9.93 | 5.15–19.14 | <0.001 | 18.78 | 9.54–36.97 | <0.001 | 24.87 | 9.92–62.32 | <0.001 | |
| high-SIRI | 17.61 | 7.22–42.94 | <0.001 | 17.91 | 8.77–36.58 | <0.001 | 36.95 | 11.04–123.64 | <0.001 |
| high-AISI | 15.82 | 6.86–36.65 | <0.001 | 13.21 | 6.74–25.90 | <0.001 | 24.88 | 9.35–66.24 | <0.001 |
| high-IL-6 | 8.88 | 4.55–17.30 | <0.001 | 14.45 | 7.55–27.61 | <0.001 | 25.06 | 8.54–73.51 | <0.001 |
| high-TSS | 8.50 | 4.38–16.47 | <0.001 | 10.24 | 5.59–18.77 | <0.001 | 8.64 | 4.03–18.48 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Halmaciu, I.; Arbănași, E.M.; Kaller, R.; Mureșan, A.V.; Arbănași, E.M.; Bacalbasa, N.; Suciu, B.A.; Cojocaru, I.I.; Runcan, A.I.; Grosu, F.; et al. Chest CT Severity Score and Systemic Inflammatory Biomarkers as Predictors of the Need for Invasive Mechanical Ventilation and of COVID-19 Patients’ Mortality. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2089. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12092089
Halmaciu I, Arbănași EM, Kaller R, Mureșan AV, Arbănași EM, Bacalbasa N, Suciu BA, Cojocaru II, Runcan AI, Grosu F, et al. Chest CT Severity Score and Systemic Inflammatory Biomarkers as Predictors of the Need for Invasive Mechanical Ventilation and of COVID-19 Patients’ Mortality. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(9):2089. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12092089
Chicago/Turabian StyleHalmaciu, Ioana, Emil Marian Arbănași, Réka Kaller, Adrian Vasile Mureșan, Eliza Mihaela Arbănași, Nicolae Bacalbasa, Bogdan Andrei Suciu, Ioana Iulia Cojocaru, Andreea Ioana Runcan, Florin Grosu, and et al. 2022. "Chest CT Severity Score and Systemic Inflammatory Biomarkers as Predictors of the Need for Invasive Mechanical Ventilation and of COVID-19 Patients’ Mortality" Diagnostics 12, no. 9: 2089. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12092089
APA StyleHalmaciu, I., Arbănași, E. M., Kaller, R., Mureșan, A. V., Arbănași, E. M., Bacalbasa, N., Suciu, B. A., Cojocaru, I. I., Runcan, A. I., Grosu, F., Vunvulea, V., & Russu, E. (2022). Chest CT Severity Score and Systemic Inflammatory Biomarkers as Predictors of the Need for Invasive Mechanical Ventilation and of COVID-19 Patients’ Mortality. Diagnostics, 12(9), 2089. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12092089







