A New Perspective on the Renin-Angiotensin System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Role of RAAS in Regulating Arterial Blood Pressure
2.1. Renin
2.2. Angiotensinogen and Related Peptides
2.3. Aldosterone
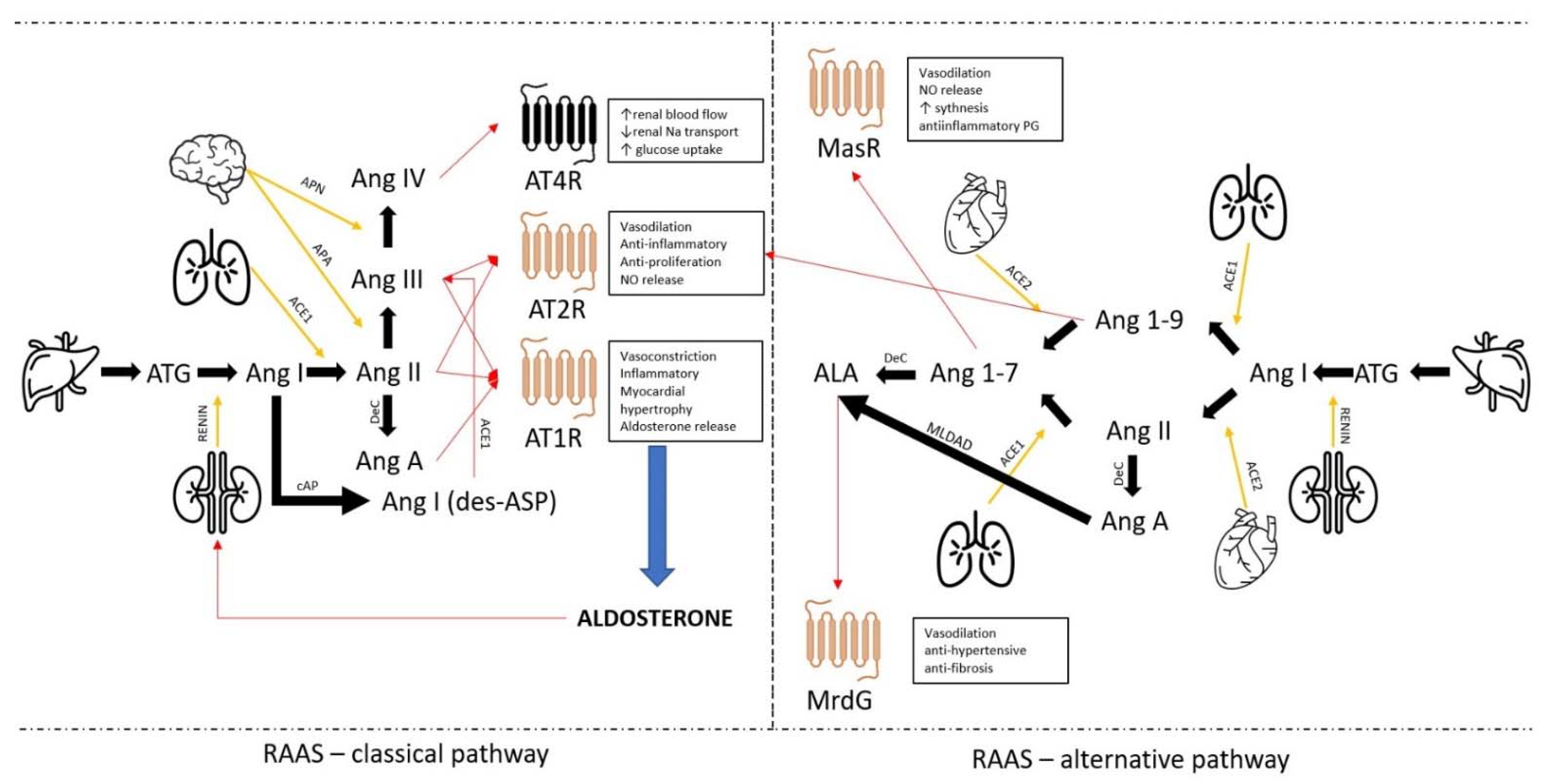
3. RAAS Classical Pathway
3.1. Angiotensin Convertase Enzyme Type 1 (ACE1)
3.2. Angiotensin II
3.3. Angiotensin III
3.4. Angiotensin IV
3.5. Other Important Enzymes-Aminopeptidase A and N
3.6. Angiotensin A
4. Alternative Pathway of RAAS
4.1. Angiotensin 1–7
4.2. Angiotensin 1–9
4.3. Alamandine
4.4. Angiotensin Convertase Enzyme Type II (ACE2)
5. Local Renin-Angiotensin System-Role of Angiotensin’s Peptides in Heart Failure
6. Novels and New Perspective on RAAS
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsao, C.W.; Aday, A.W.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Alonso, A.; Beaton, A.Z.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Boehme, A.K.; Buxton, A.E.; Carson, A.P.; Commodore-Mensah, Y.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2022 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2022, 145, 153–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, G. Diagnosis, Epidemiology, and Management of Hypertension in Children. Pediatrics 2016, 138, e20153616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, J.; Kurschat, C.; Reuter, H. Arterial Hypertension: Diagnosis and Treatment. Dtsch. Ärzteblatt Int. 2018, 115, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navar, L.G. Physiology: Hemodynamics, Endothelial Function, Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System, Sympathetic Nervous System. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2014, 8, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seccia, T.M.; Caroccia, B.; Maiolino, G.; Cesari, M.; Rossi, G.P. Arterial Hypertension, Aldosterone, and Atrial Fibrillation. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2019, 21, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mello, W.C. Local Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Systems and Cardiovascular Diseases. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 101, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holappa, M.; Vapaatalo, H.; Vaajanen, A. Many Faces of Renin-Angiotensin System-Focus on Eye. Open Ophthalmol. J. 2017, 11, 122–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittana, N. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2–Angiotensin 1-7/1-9 System: Novel Promising Targets for Heart Failure Treatment. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 32, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaszczewska-Markowska, M.; Sagan, M.; Bogunia-Kubik, K. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)-physiology and molecular mechanisms of functioning. Postep. Hig. Med. Dosw. (Online) 2016, 70, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, L.; Eldahshan, W.; Fagan, S.C.; Ergul, A. Within the Brain: The Renin Angiotensin System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, A. Control of Renin Synthesis and Secretion. Am. J. Hypertens. 2012, 25, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damkjær, M.; Isaksson, G.L.; Stubbe, J.; Jensen, B.L.; Assersen, K.; Bie, P. Renal Renin Secretion as Regulator of Body Fluid Homeostasis. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2013, 465, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Chen, L.; Faulhaber-Walter, R.; Oppermann, M.; Huang, Y.; Mizel, D.; Briggs, J.P.; Schnermann, J. Regulation of Renin Secretion and Expression in Mice Deficient in Β1- and Β2-Adrenergic Receptors. Hypertension 2007, 50, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beierwaltes, W.H. The Role of Calcium in the Regulation of Renin Secretion. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2010, 298, F1–F11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiannikouris, F.; Karounos, M.; Charnigo, R.; English, V.L.; Rateri, D.L.; Daugherty, A.; Cassis, L.A. Adipocyte-Specific Deficiency of Angiotensinogen Decreases Plasma Angiotensinogen Concentration and Systolic Blood Pressure in Mice. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2012, 302, R244–R251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschepper, C.F. Angiotensinogen: Hormonal Regulation and Relative Importance in the Generation of Angiotensin II. Kidney Int. 1994, 46, 1561–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Cassis, L.A.; Kooi, C.W.V.; Daugherty, A. Structure and Functions of Angiotensinogen. Hypertens. Res. 2016, 39, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaluddin, M.; Meng, T.; Sun, J.; Boldogh, I.; Han, Y.; Brasier, A.R. Angiotensin II Induces Nuclear Factor (NF)-ΚB1 Isoforms to Bind the Angiotensinogen Gene Acute-Phase Response Element: A Stimulus-Specific Pathway for NF-ΚB Activation. Mol. Endocrinol. 2000, 14, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Belova, L.A. Angiotensin II-Generating Enzymes. Biochemistry. Biokhimiia 2000, 65, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellomo, R.; Wunderink, R.G.; Szerlip, H.; English, S.W.; Busse, L.W.; Deane, A.M.; Khanna, A.K.; McCurdy, M.T.; Ostermann, M.; Young, P.J.; et al. Angiotensin I and Angiotensin II Concentrations and Their Ratio in Catecholamine-Resistant Vasodilatory Shock. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habiyakare, B.; Alsaadon, H.; Mathai, M.L.; Hayes, A.; Zulli, A. Reduction of Angiotensin A and Alamandine Vasoactivity in the Rabbit Model of Atherogenesis: Differential Effects of Alamandine and Ang(1-7). Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 95, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umpierrez, G.E.; Cantey, P.; Smiley, D.; Palacio, A.; Temponi, D.; Luster, K.; Chapman, A. Primary Aldosteronism in Diabetic Subjects With Resistant Hypertension. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 1699–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Náray-Fejes-Tóth, A.; Fejes-Tóth, G. The Sgk, an Aldosterone-Induced Gene in Mineralocorticoid Target Cells, Regulates the Epithelial Sodium Channel. Kidney Int. 2000, 57, 1290–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaddam, K.K.; Pimenta, E.; Husain, S.; Calhoun, D.A. Aldosterone and Cardiovascular Disease. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2009, 34, 51–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.; Fullerton, M.; Dilley, R.; Funder, J. Mineralocorticoids, Hypertension, and Cardiac Fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 2578–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studdy, P.R.; Lapworth, R.; Bird, R. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme and Its Clinical Significance—A Review. J. Clin. Pathol. 1983, 36, 938–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, R.M.; Siragy, H.M. Newly Recognized Components of the Renin-Angiotensin System: Potential Roles in Cardiovascular and Renal Regulation. Endocr. Rev. 2003, 24, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, V.; Goswami, B. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE). Clin. Chim. Acta 2022, 524, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, S.A. The Renin-Angiotensin Aldosterone System: Pathophysiological Role and Pharmacologic Inhibition. J. Manag. Care Pharm. 2007, 13, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, B.; Smith, T.L.; Dubey, P.; Zapadka, M.E.; Torti, F.M.; Willingham, M.C.; Tallant, E.A.; Gallagher, P.E. Angiotensin-(1-7) Attenuates Metastatic Prostate Cancer and Reduces Osteoclastogenesis. Prostate 2013, 73, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Awan, F.R. Hypertension Regulating Angiotensin Peptides in the Pathobiology of Cardiovascular Disease. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2018, 40, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaux, A.; Fournie-Zaluski, M.C.; Llorens-Cortes, C. Angiotensin III: A Central Regulator of Vasopressin Release and Blood Pressure. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 12, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devynck, M.A.; Pernollet, M.G.; Matthews, P.G.; Khosla, M.C.; Bumpus, F.M.; Meyer, P. Specific Receptors for Des-Asp 1-Angiotensin II (‘angiotensin III’) in Rat Adrenals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 4029–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, J.W.; Felix, D. Angiotensin-Sensitive Neurons in the Rat Paraventricular Nucleus: Relative Potencies of Angiotensin II and Angiotensin III. Brain Res. 1987, 410, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens-Cortès, C. Orally Active Aminopeptidase A Inhibitors Reduce Blood Pressure: A New Strategy for Treating Hypertension. Biol. Aujourdhui 2014, 208, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaux-Le Goazigo, A.; Iturrioz, X.; Fassot, C.; Claperon, C.; Roques, B.P.; Llorens-Cortes, C. Role of Angiotensin III in Hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2005, 7, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammelgaard, I.; Wamberg, S.; Bie, P. Systemic Effects of Angiotensin III in Conscious Dogs during Acute Double Blockade of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone-System. Acta Physiol. 2006, 188, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yugandhar, V.G.; Clark, M.A. Angiotensin III: A Physiological Relevant Peptide of the Renin Angiotensin System. Peptides 2013, 46, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, S.Y.; Fernando, R.; Peck, G.; Ye, S.Y.; Mendelsohn, F.A.O.; Jenkins, T.A.; Albiston, A.L. The Angiotensin IV/AT4 Receptor. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 2728–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.W.; Harding, J.W. The Brain Angiotensin System and Extracellular Matrix Molecules in Neural Plasticity, Learning, and Memory. Prog. Neurobiol. 2004, 72, 263–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenkei, Z.; Palkovits, M.; Corvol, P.; Llorens-Cortès, C. Expression of Angiotensin Type-1 (AT1) and Type-2 (AT2) Receptor MRNAs in the Adult Rat Brain: A Functional Neuroanatomical Review. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 1997, 18, 383–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, F.A.; Rowland, N.E.; Fregly, M.J. Angiotensin-Related Intakes of Water and NaCl in Fischer 344 and Sprague-Dawley Rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1992, 262, R382–R388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, W.L.; Roques, B.P.; Llorens-Cortes, C.; Speth, R.C.; Harding, J.W.; Wright, J.W. Roles of Brain Angiotensins II and III in Thirst and Sodium Appetite. Brain Res. 2005, 1060, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournie-Zaluski, M.C.; Fassot, C.; Valentin, B.; Djordjijevic, D.; Reaux-Le Goazigo, A.; Corvol, P.; Roques, B.P.; Llorens-Cortes, C. Brain Renin-Angiotensin System Blockade by Systemically Active Aminopeptidase A Inhibitors: A Potential Treatment of Salt-Dependent Hypertension. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 7775–7780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marc, Y.; Boitard, S.E.; Balavoine, F.; Azizi, M.; Llorens-Cortes, C. Targeting Brain Aminopeptidase A: A New Strategy for the Treatment of Hypertension and Heart Failure. Can J. Cardiol. 2020, 36, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, V.; Vanholder, R.; van der Giet, M.; Tölle, M.; Karadogan, S.; Gobom, J.; Furkert, J.; Oksche, A.; Krause, E.; Tran, T.N.A.; et al. Mass-Spectrometric Identification of a Novel Angiotensin Peptide in Human Plasma. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Smolders, I.; Vanderheyden, P.; Demaegdt, H.; van Eeckhaut, A.; Vauquelin, G.; Lukaszuk, A.; Tourwé, D.; Chai, S.Y.; Albiston, A.L.; et al. Pressor and Renal Hemodynamic Effects of the Novel Angiotensin A Peptide Are Angiotensin II Type 1A Receptor Dependent. Hypertension 2011, 57, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badejo, A.; Greco, A.J.; Casey, D.B.; Cook, J.L.; Murthy, S.N.; Kadowitz, P.J. Analysis of Hemodynamic Responses and the Proliferative Effect of the Novel Angiotensin Peptide Angiotensin, A. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 935.2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, M.; Alenina, N.; Andrade-Navarro, M.A.; Santos, R.A. Mas and Its Related G Protein-Coupled Receptors, Mrgprs. Pharmacol. Rev. 2014, 66, 1080–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkowicz, M.; Chlopicki, S.; Smolenski, R.T. Perspectives for Angiotensin Profiling with Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry to Evaluate ACE/ACE2 Balance in Endothelial Dysfunction and Vascular Pathologies. Pharmacol. Rep. 2015, 67, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, P.L.; Kangussu, L.M.; da Silva, L.G.; Castro, C.H.; Santos, R.A.S.; Ferreira, A.J.; Ferreira, A.J. Cardiovascular Effects of Small Peptides of the Renin Angiotensin System. Physiol. Rep. 2017, 5, e13505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautner, R.Q.; Villela, D.C.; Fraga-Silva, R.A.; Silva, N.; Verano-Braga, T.; Costa-Fraga, F.; Jankowski, J.; Jankowski, V.; Sousa, F.; Alzamora, A.; et al. Discovery and Characterization of Alamandine: A Novel Component of the Renin-Angiotensin System. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, F.C.; Okuda, T.; Dong, X.; Zylka, M.J.; Chen, C.L.; Anderson, D.J.; Kuner, R.; Ma, Q. Mechanisms of Compartmentalized Expression of Mrg Class G-Protein-Coupled Sensory Receptors. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorrez, L.; Laudadio, I.; van Deun, K.; Quintens, R.; Hendrickx, N.; Granvik, M.; Lemaire, K.; Schraenen, A.; van Lommel, L.; Lehnert, S.; et al. Tissue-Specific Disallowance of Housekeeping Genes: The Other Face of Cell Differentiation. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, V.B.; Zhong, J.C.; Grant, M.B.; Oudit, G.Y. Role of the ACE2/Angiotensin 1–7 Axis of the Renin–Angiotensin System in Heart Failure. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1313–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Basu, R.; Guo, D.; Chow, F.L.; Byrns, S.; Schuster, M.; Loibner, H.; Wang, X.H.; Penninger, J.M.; Kassiri, Z.; et al. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Suppresses Pathological Hypertrophy, Myocardial Fibrosis, and Cardiac Dysfunction. Circulation 2010, 122, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyerstedt, S.; Casaro, E.B.; Rangel, É.B. COVID-19: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) Expression and Tissue Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Gheblawi, M.; Oudit, G.Y. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2: A Double-Edged Sword. Circulation 2020, 142, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, G.; Bhat, G. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and heart failure. Cardiol. Clin. 2014, 32, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roger, V.L.; Go, A.S.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Benjamin, E.J.; Berry, J.D.; Borden, W.B.; Bravata, D.M.; Dai, S.; Ford, E.S.; Fox, C.S. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2012 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2012, 125, 2–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haschke, M.; Schuster, M.; Poglitsch, M.; Loibner, H.; Salzberg, M.; Bruggisser, M.; Penninger, J.; Krähenbühl, S. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of recombinant human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in healthy human subjects. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2013, 52, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchnowski, P. N-Terminal of the Prohormone Brain Natriuretic Peptide Predicts Postoperative Cardiogenic Shock Requiring Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCollum, L.T.; Gallagher, P.E.; Ann Tallant, E. Angiotensin-(1-7) attenuates angiotensin II-induced cardiac remodeling associated with upregulation of dual-specificity phosphatase 1. Am. J. Physiol Heart Circ. Physiol. 2012, 302, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartupee, J.; Mann, D.L. Neurohormonal activation in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamargo, M.; Tamargo, J. Future Drug Discovery in Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Intervention. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2017, 12, 827–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Q.; Wu, Y.; Nag, S.; Hussain, T. Estimation of Angiotensin Peptides in Biological Samples by LC/MS Method. Anal Methods 2014, 6, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurray, J.J.; Packer, M.; Desai, A.S.; Gong, J.; Lefkowitz, M.P.; Rizkala, A.R.; Rouleau, J.; Shi, V.C.; Solomon, S.D.; Swedberg, K.; et al. Dual angiotensin receptor and neprilysin inhibition as an alternative to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in patients with chronic systolic heart failure: Rationale for and design of the Prospective comparison of ARNI with ACEI to Determine Impact on Global Mortality and morbidity in Heart Failure trial (PARADIGM-HF). Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2013, 15, 1062–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, P.K.; Claggett, B.L.; Solomon, S.D.; McMurray, J.J.; Packer, M.; Zile, M.R.; Desai, A.S.; Rouleau, J.L.; Swedberg, K.; Fonarow, G.C. Estimated 5-Year Number Needed to Treat to Prevent Cardiovascular Death or Heart Failure Hospitalization With Angiotensin Receptor-Neprilysin Inhibition vs. Standard Therapy for Patients With Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction: An Analysis of Data From the PARADIGM-HF Trial. JAMA Cardiol. 2018, 3, 1226–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martyniak, A.; Tomasik, P.J. A New Perspective on the Renin-Angiotensin System. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13010016
Martyniak A, Tomasik PJ. A New Perspective on the Renin-Angiotensin System. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartyniak, Adrian, and Przemysław J. Tomasik. 2023. "A New Perspective on the Renin-Angiotensin System" Diagnostics 13, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13010016
APA StyleMartyniak, A., & Tomasik, P. J. (2023). A New Perspective on the Renin-Angiotensin System. Diagnostics, 13(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13010016




