The Diagnostic Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence in Radiological Markers of Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH) on Non-Contrast CT Scans of the Brain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Imaging Review
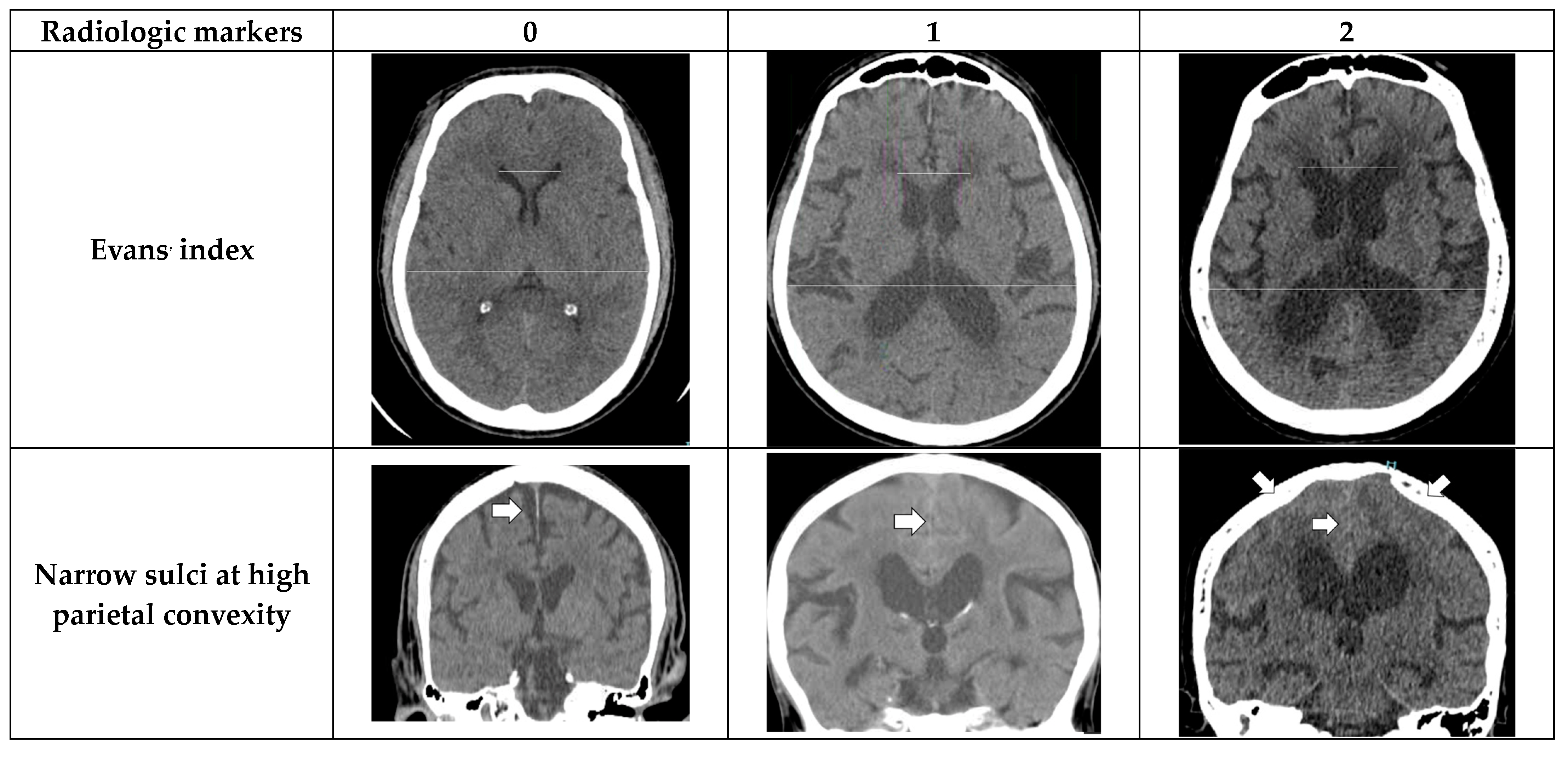
2.3. Radiologic Parameters
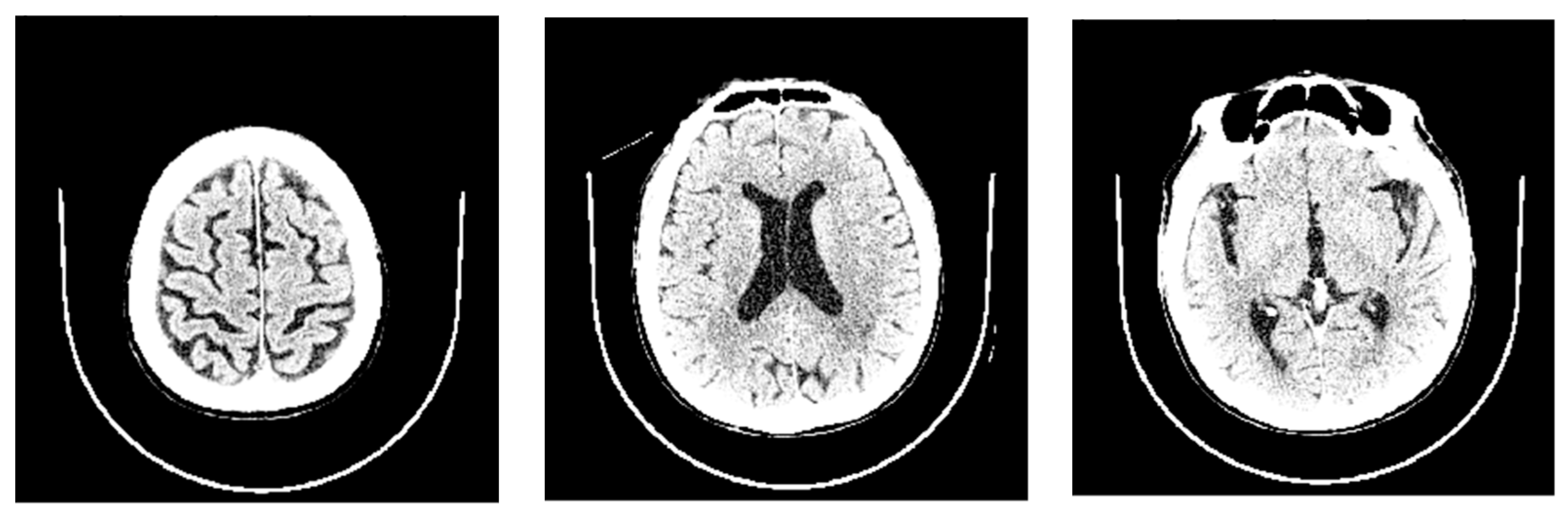
- Evans’ index: The ratio between the maximal width of the frontal horns of the lateral ventricles (B–C) by the maximal width of the inner table of the cranium in the same axial image [9].
- Narrow parietal sulci: At high-convexity and parafalcine region assessed in both axial planes in the most superior slices and coronal plane [10].
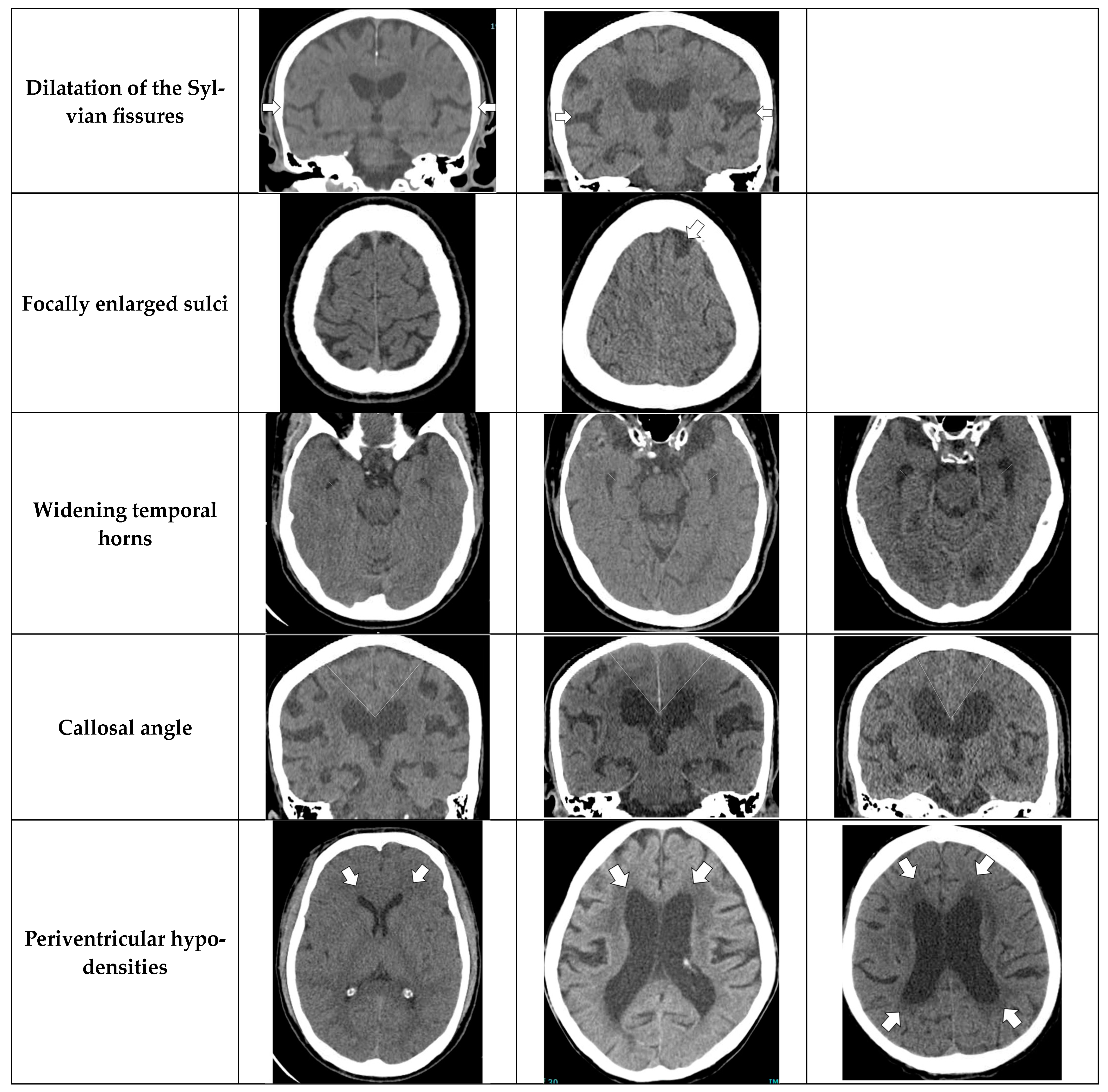
- Dilation of the Sylvian fissures: Reported as present or not present in the coronal plane compared with surrounding sulci [11].
- Focally enlarged sulci: Compared with surrounding sulci, usually found in coronal or axial planes [12].
- Temporal horns: Reported as mean width of the right and left side, measuring in the axial plane [11].
- Callosal angle: Angle between the lateral ventricles in the coronal plane through the posterior commissure perpendicular to the intercommissural plane [13].
- Periventricular hypodensities: Along the lateral ventricles graded as not present, present as a cap around frontal horns or confluently extending around the lateral ventricles [14].
2.4. AI Evaluation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
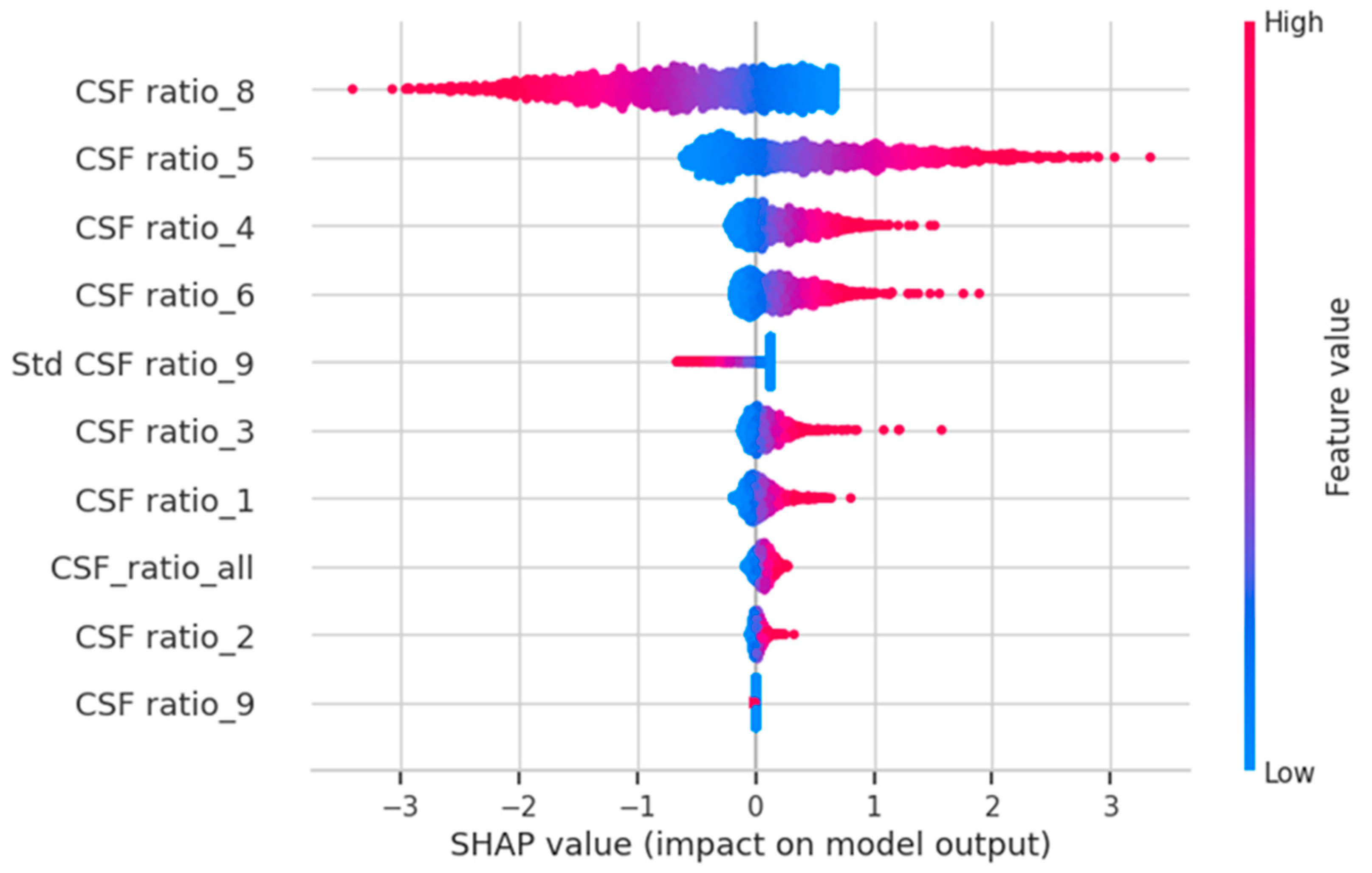
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Damasceno, B.P. Neuroimaging in normal pressure hydrocephalus. Dement. Neuropsychol. 2015, 9, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kockum, K.; Virhammar, J.; Riklund, K.; Söderström, L.; Larsson, E.-M.; Laurell, K. Standardized image evaluation in patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: Consistency and reproducibility. Neuroradiology 2019, 61, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kockum, K.; Lilja-Lund, O.; Larsson, E.-M.; Rosell, M.; Söderström, L.; Virhammar, J.; Laurell, K. The idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus Radscale: A radiological scale for structured evaluation. Eur. J. Neurol. 2017, 25, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Ye, Q.; Yang, X.; Chen, J.; Ma, H.; Xia, J.; Del Ser, J.; Yang, G. AI-based medical e-diagnosis for fast and automatic ventricular volume measurement in patients with normal pressure hydrocephalus. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 35, 16011–16020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, M.G.; Quattrone, A.; Sarica, A.; Vescio, B.; Buonocore, J.; Vaccaro, M.G.; Aracri, F.; Calomino, C.; Gramigna, V.; Quattrone, A. Cortical atrophy distinguishes idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus from progressive supranuclear palsy: A machine learning approach. Park. Relat. Disord. 2022, 103, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Lin, Z.M.; Chen, Y.; Hao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. Evaluation of an artificial intelligent hydrocephalus diagnosis model based on transfer learning. Medicine 2020, 99, e21229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Wen, J.; Wei, J. Progression in Neuroimaging of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 700269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townley, R.A.; Botha, H.; Graff-Radford, J.; Boeve, B.F.; Petersen, R.C.; Senjem, M.L.; Knopman, D.S.; Lowe, V.; Jack, C.R.; Jones, D.T. 18F-FDG PET-CT pattern in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. NeuroImage Clin. 2018, 18, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, W.A.J. An encephalographic ratio for estimating ventricular enlargement and cerebral atrophy. Arch. Neurol. Psychiatry 1942, 47, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, M.; Honda, S.; Yuasa, T.; Iwamura, A.; Shibata, E.; Ohba, H. Narrow CSF space at high convexity and high midline areas in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus detected by axial and coronal MRI. Neuroradiology 2007, 50, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virhammar, J.; Laurell, K.; Cesarini, K.G.; Larsson, E.M. Preoperative prognostic value of MRI findings in 108 patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 2311–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holodny, A.I.; George, A.E.; de Leon, M.J.; Golomb, J.; Kalnin, A.J.; Cooper, P.R. Focal dilation and paradoxical collapse of cortical fissures and sulci in patients with normal-pressure hydrocephalus. J. Neurosurg. 1998, 89, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, K.; Kanda, T.; Harada, A.; Miyamoto, N.; Kawaguchi, T.; Shimada, K.; Ohkawa, S.; Uemura, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Mori, E. Clinical impact of the callosal angle in the diagnosis of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Eur. Radiol. 2008, 18, 2678–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazekas, F.; Chawluk, J.B.; Alavi, A.; Hurtig, H.I.; Zimmerman, R.A. MR signal abnormalities at 1.5 T in Alzheimer’s dementia and normal aging. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1987, 149, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.04597. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1505.04597 (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- SPM12 Software—Statistical Parametric Mapping. Available online: https://www.fil.ion.ucl.ac.uk/spm/software/spm12/ (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Delving Deep into Rectifiers: Surpassing Human-Level Performance on ImageNet Classification. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Las Condes, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1026–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1412.6980. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980 (accessed on 2 August 2023).
- Andersson, J.; Rosell, M.; Kockum, K.; Lilja-Lund, O.; Söderström, L.; Laurell, K. Prevalence of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: A prospective, population-based study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.M.; Nitrini, R.; Román, G.C. Normal-pressure hydrocephalus: A critical review. Dement Neuropsychol. 2019, 13, 133–143, Erratum in Dement Neuropsychol. 2019, 13, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maytal, J.; Alvarez, L.; Elkin, C.; Shinnar, S.; Maytal, L.A.J.; Hanrahan, C.J.; Shah, L.M.; Perrich, K.D.; Goodwin, D.W.; Hecht, P.J.; et al. External hydrocephalus: Radiologic spectrum and differentiation from cerebral atrophy. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1987, 148, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, A.K.; Holl, E.; Kitchen, N.D.; Watkins, L.D. Evans’ index revisited: The need for an alternative in normal pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 2011, 68, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Brutto, O.H.; Mera, R.M.; Gladstone, D.; Sarmiento-Bobadilla, M.; Cagino, K.; Zambrano, M.; Costa, A.F.; Sedler, M.J. Inverse relationship between the evans index and cognitive performance in non-disabled, stroke-free, community-dwelling older adults. A population-based study. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2018, 169, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambarki, K.; Israelsson, H.; Wåhlin, A.; Birgander, R.; Eklund, A.; Malm, J. Brain ventricular size in healthy elderly: Comparison between Evans index and volume measurement. Neurosurgery 2010, 67, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narita, W.; Nishio, Y.; Baba, T.; Iizuka, O.; Ishihara, T.; Matsuda, M.; Iwasaki, M.; Tominaga, T.; Mori, E. High-Convexity Tightness Predicts the Shunt Response in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 1831–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.; Lee, A.; Li, H.; Ong, N.Y.X.; Keong, N.; Chen, R.; Chan, L.L. Callosal angle in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: Small angular mal-rotations of the coronal plane affect measurement reliability. Neuroradiology 2021, 63, 1659–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tullberg, M.; Jensen, C.; Ekholm, S.; Wikkelso, C. Normal pressure hydrocephalus: Vascular white matter changes on MRI must not exclude patients from shunt surgery. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2001, 22, 1665–1673. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Xia, J. Application of Evans Index in Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Patients: A Mini Review. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 13, 783092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Moghekar, A.; Shi, W.; Blitz, A.M.; Mori, S. Systematic volumetric analysis predicts response to CSF drainage and outcome to shunt surgery in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 4972–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscas, G.; Matteuzzi, T.; Becattini, E.; Orlandini, S.; Battista, F.; Laiso, A.; Nappini, S.; Limbucci, N.; Renieri, L.; Carangelo, B.R.; et al. Development of machine learning models to prognosticate chronic shunt-dependent hydrocephalus after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir. 2020, 162, 3093–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Khan, A.; Majeti, S.; Pham, J.; Nguyen, C.; Tran, P.; Iyer, V.; Shelat, A.; Chen, J.; Manjunath, B.S. Automated Segmentation and Connectivity Analysis for Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. BME Front. 2022, 2022, 9783128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.Y.-L.; Leow, S.M.H.; Bea, K.T.; Cheng, W.K.; Phoong, S.W.; Hong, Z.-W.; Chen, Y.-L. Mitigating the Multicollinearity Problem and Its Machine Learning Approach: A Review. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

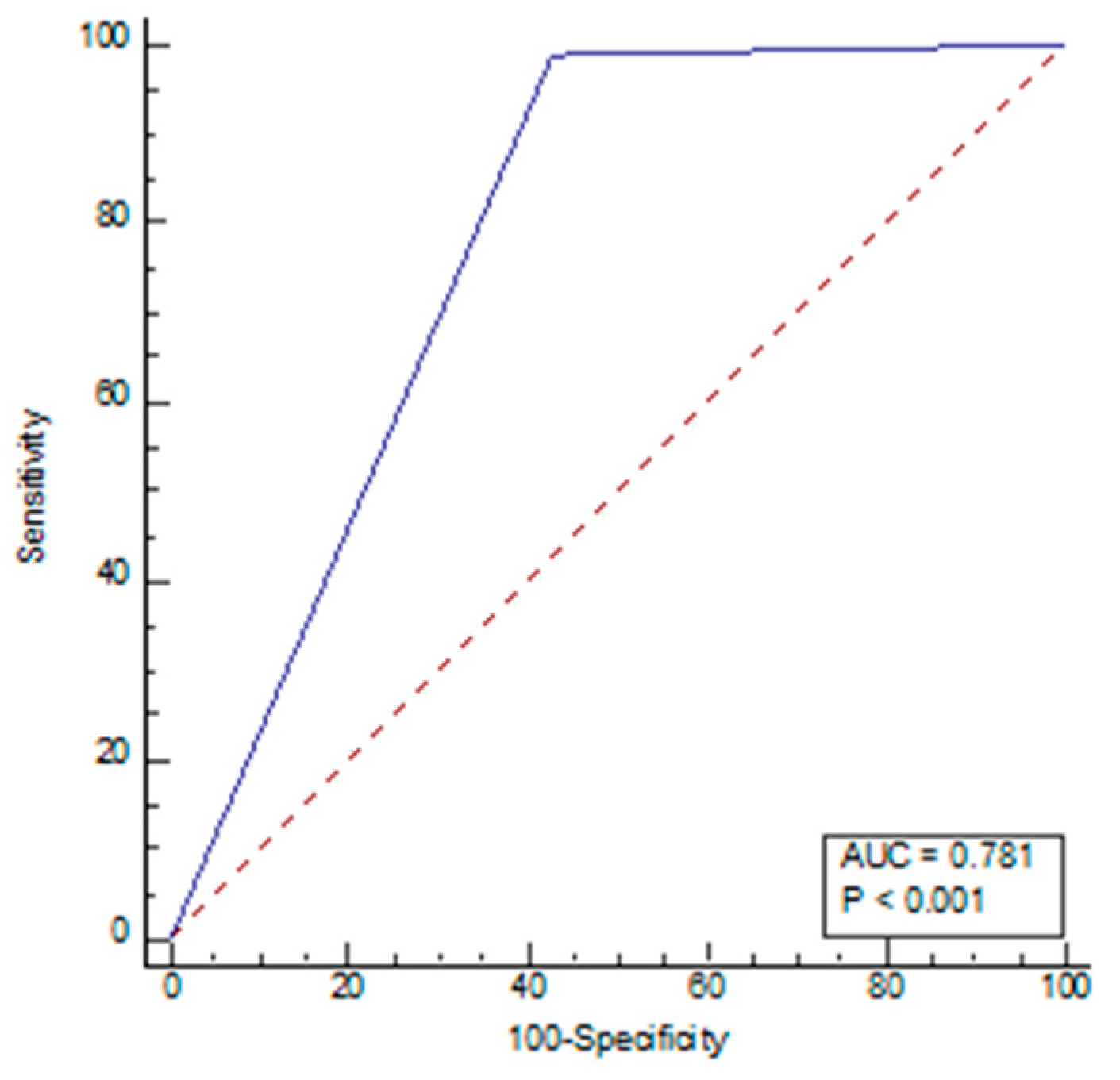
| Variables | All (n = 217) | Normal (n = 112) | NPH (n = 105) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (M:F) | 105 (48.4%):112 (51.6%) | 55 (49.1%):57 (50.9%) | 60 (57.1%):45 (42.9%) | 0.236 |
| Age (years) | 65.4 ± 17.8 | 55.7 ± 19.2 | 75.7 ± 8.0 | <0.001 |
| Gait disturbance | 99 (45.6%) | 0 (0%) | 99 (94.3%) | <0.001 |
| Urinary incontinence | 77 (35.5%) | 0 (0%) | 77 (73.3%) | <0.001 |
| Memory impairment | 61 (28.1%) | 0 (0%) | 61 (58.1%) | <0.001 |
| HT * | 122 (56.2%) | 49 (43.8%) | 73 (69.5%) | <0.001 |
| T2DM | 72 (33.2%) | 26 (23.2%) | 46 (43.8%) | <0.001 |
| DLP | 80 (36.9%) | 42 (37.5%) | 38 (36.2%) | 0.842 |
| Old CVA | 42 (19.4%) | 21 (18.8%) | 21 (20.0%) | 0.816 |
| CKD | 21 (9.7%) | 1 (0.9%) | 10 (9.5%) | 0.941 |
| CAD | 20 (9.2%) | 8 (7.1%) | 12 (11.4%) | 0.275 |
| Parkinson’s disease | 23 (10.6%) | 0 (0%) | 23 (21.9%) | <0.001 |
| Dementia | 20 (9.2%) | 3 (2.7%) | 17 (16.2%) | <0.001 |
| OA knee | 11 (5.1%) | 6 (5.4%) | 5 (4.8%) | 0.842 |
| Variable | 1 Crude OR * (95% CI) ** | p-Value | 2 Adjusted OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evans’ index | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||
| 0 | Ref. *** | Ref. | ||
| 1 | 12.77 (4.68–34.88) | 3.49 (1.07–11.42) | ||
| 2 | 395.3 (73.91–2114.10) | 38.37 (6.04–243.56) | ||
| Dilatation of Sylvian fissures | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||
| 0 | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| 1 | 23.25 (11.12–48.62) | 3.07 (1.04–9.08) | ||
| Focally enlarged sulci | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||
| 0 | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| 1 | 25.499 (0.762–85.30) | 7.88 (1.28–48.25) | ||
| Widening temporal horns | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||
| 0 | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| 1 | 30 (12.83–70.13) | 5.35 (1.88–15.16) | ||
| 2 | 132 (28.86–603.79) | 12.55 (2.15–73.31) |
| Total Score | Normal | NPH | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 46 (100%) | 0 | <0.0001 |
| 1 | 30 (96.8%) | 1 (3.2%) | <0.0001 |
| 2 | 15 (75%) | 5 (25%) | 0.028 |
| 3 | 12 (63.2%) | 7 (36.8%) | 0.292 |
| 4 | 7 (38.9%) | 11 (61.1%) | 0.259 |
| 5 | 1 (5.6%) | 17 (94.4%) | <0.0001 |
| 6 | 1 (5%) | 19 (95%) | <0.0001 |
| 7 | 0 | 19 (100%) | <0.0001 |
| 8 | 0 | 11 (100%) | <0.0001 |
| 9 | 0 | 9 (100%) | 0.002 |
| 10 | 0 | 4 (100%) | 0.037 |
| 11 | 0 | 2 (100%) | 0.142 |
| 12 | 0 | 0 | N/A |
| Score | Result of Predicted NPH |
|---|---|
| 0–2 | Negative |
| 3–4 | Borderline |
| ≥5 | Positive |
| Variables | Radiologists | AI *** |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 77.14% | 99.05% |
| Specificity | 98.21% | 57.14% |
| NPV * | 82.09% | 98.46% |
| PPV ** | 97.59% | 68.42% |
| Accuracy | 88.02% | 77.42% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Songsaeng, D.; Nava-apisak, P.; Wongsripuemtet, J.; Kingchan, S.; Angkoondittaphong, P.; Phawaphutanon, P.; Supratak, A. The Diagnostic Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence in Radiological Markers of Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH) on Non-Contrast CT Scans of the Brain. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2840. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13172840
Songsaeng D, Nava-apisak P, Wongsripuemtet J, Kingchan S, Angkoondittaphong P, Phawaphutanon P, Supratak A. The Diagnostic Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence in Radiological Markers of Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH) on Non-Contrast CT Scans of the Brain. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(17):2840. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13172840
Chicago/Turabian StyleSongsaeng, Dittapong, Poonsuta Nava-apisak, Jittsupa Wongsripuemtet, Siripra Kingchan, Phuriwat Angkoondittaphong, Phattaranan Phawaphutanon, and Akara Supratak. 2023. "The Diagnostic Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence in Radiological Markers of Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH) on Non-Contrast CT Scans of the Brain" Diagnostics 13, no. 17: 2840. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13172840
APA StyleSongsaeng, D., Nava-apisak, P., Wongsripuemtet, J., Kingchan, S., Angkoondittaphong, P., Phawaphutanon, P., & Supratak, A. (2023). The Diagnostic Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence in Radiological Markers of Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH) on Non-Contrast CT Scans of the Brain. Diagnostics, 13(17), 2840. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13172840






