Cell-Free miRNAs as Non-Invasive Biomarkers in Brain Tumors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
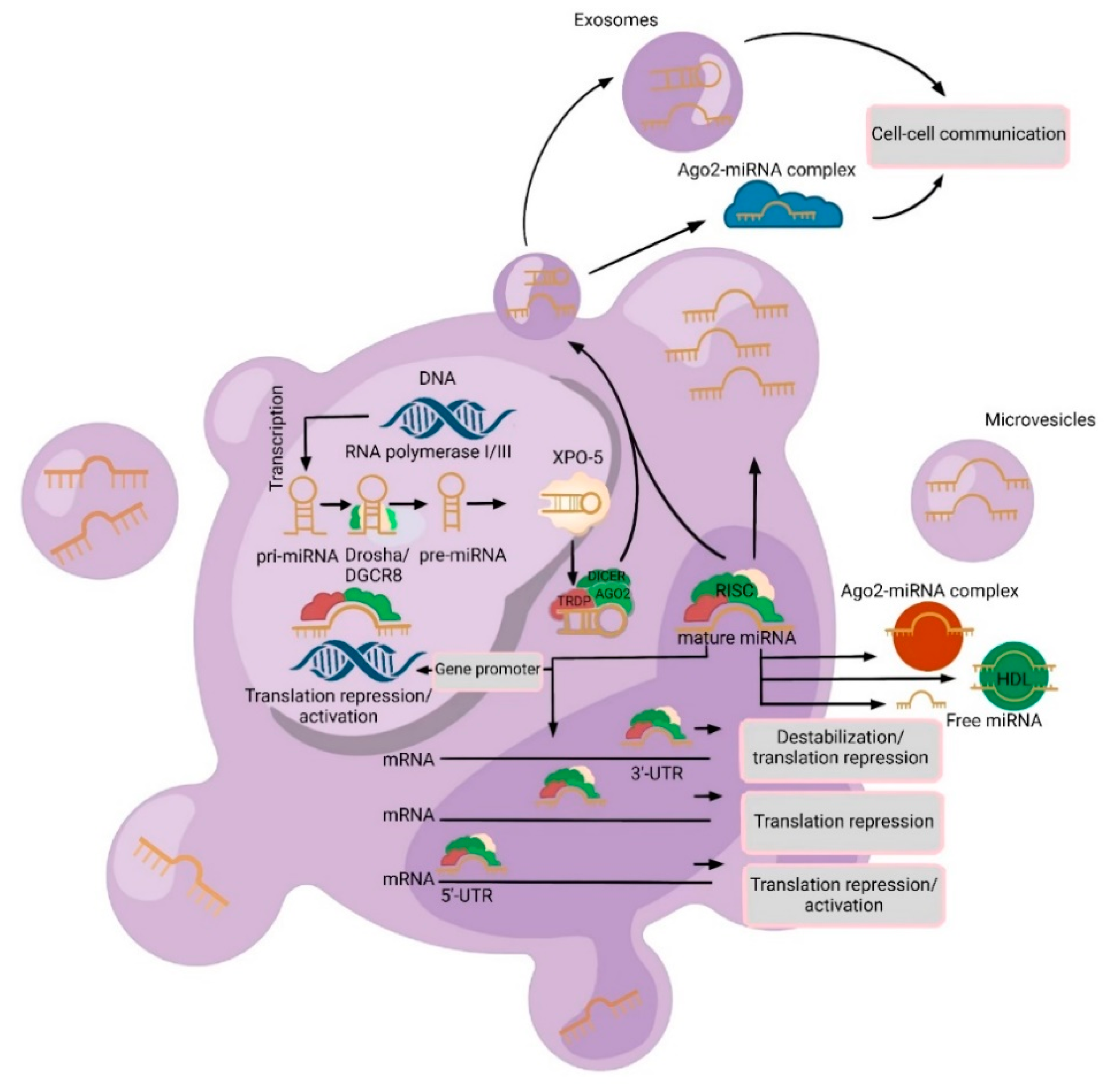
2. Varieties and Mechanisms of Cell-Free miRNAs Secretion
3. Advantages of Cell-Free miRNAs
3.1. Diagnostic Utility
3.2. Detection of Tumor Recurrence
3.3. Monitoring Treatment Response
4. Cerebrospinal Fluid or Blood?
5. Cell-Free miRNAs as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers
6. Future Perspectives and Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gritsch, S.; Batchelor, T.T.; Gonzalez Castro, L.N. Diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic implications of the 2021 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system. Cancer 2022, 128, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boire, A.; Brastianos, P.K.; Garzia, L.; Valiente, M. Brain metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandu, H.; Wen, P.Y.; Huang, R.Y. Imaging in neuro-oncology. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2018, 11, 1756286418759865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, H.; Harting, R.; de Vries, R.; Ali, M.; Wurdinger, T.; Best, M.G. Blood-Based Biomarkers for Glioma in the Context of Gliomagenesis: A Systematic Review. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 665235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halawa, T.; Baeesa, S.; Fadul, M.M.; Badahdah, A.A.; Enani, M.; Fathaddin, A.A.; Kawass, D.; Alkhotani, A.; Bahakeem, B.; Kurdi, M.; et al. The Role of Liquid Biopsy in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of WHO Grade 4 Astrocytoma. Cureus 2023, 15, e41221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagès, M.; Rotem, D.; Gydush, G.; Reed, S.; Rhoades, J.; Ha, G.; Lo, C.; Fleharty, M.; Duran, M.; Jones, R.; et al. Liquid biopsy detection of genomic alterations in pediatric brain tumors from cell-free DNA in peripheral blood, CSF, and urine. Neuro-oncology 2022, 24, 1352–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Qu, C.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, Z. Liquid biopsy: Early and accurate diagnosis of brain tumor. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 148, 2347–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdipour, P.; Javan, F.; Jouibari, M.F.; Khaleghi, M.; Mehrazin, M. Evolutionary model of brain tumor circulating cells: Cellular galaxy. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 12, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sufianov, A.; Kostin, A.; Begliarzade, S.; Kudriashov, V.; Ilyasova, T.; Liang, Y.; Mukhamedzyanov, A.; Beylerli, O. Exosomal non coding RNAs as a novel target for diabetes mellitus and its complications. Noncoding RNA Res. 2023, 8, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sippl, C.; Teping, F.; Ketter, R.; Braun, L.; Tremmel, L.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.; Oertel, J.; Urbschat, S. The Influence of Distinct Regulatory miRNAs of the p15/p16/RB1/E2F Pathway on the Clinical Progression of Glioblastoma Multiforme. World Neurosurg. 2019, 132, e900–e908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gareev, I.; Kudriashov, V.; Sufianov, A.; Begliarzade, S.; Ilyasova, T.; Liang, Y.; Beylerli, O. The role of long non-coding RNA ANRIL in the development of atherosclerosis. Noncoding RNA Res. 2022, 7, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beylerli, O.; Gareev, I.; Sufianov, A.; Ilyasova, T.; Guang, Y. Long noncoding RNAs as promising biomarkers in cancer. Noncoding RNA Res. 2022, 7, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lianidou, E.; Pantel, K. Liquid biopsies. Genes. Chromosomes Cancer 2019, 58, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sufianov, A.; Begliarzade, S.; Beilerli, A.; Liang, Y.; Ilyasova, T.; Beylerli, O. Circular RNAs as biomarkers for lung cancer. Noncoding RNA Res. 2022, 8, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wortzel, I.; Dror, S.; Kenific, C.M.; Lyden, D. Exosome-Mediated Metastasis: Communication from a Distance. Dev. Cell 2019, 49, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, E.N.; Mourot, L.; Rakobowchuk, M. Exercise-Derived Microvesicles: A Review of the Literature. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 2025–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, J.Q.; Liu, J.L.; Tian, L. Exosomes in tumor microenvironment: Novel transporters and biomarkers. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu-Gruttadauria, J.; Xiao, Y.; Gebert, L.F.; MacRae, I.J. Beyond the seed: Structural basis for supplementary microRNA targeting by human Argonaute2. EMBO J. 2019, 1, e101153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, A. Preface for Brain Tumor Pathology vol.40 issue 2: (Special issue for the 40th Annual Meeting of the Japan Society of Brain Tumor Pathology). Brain Tumor Pathol. 2023, 40, 45–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popp, I.; Weber, W.A.; Combs, S.E.; Yuh, W.T.C.; Grosu, A.L. Neuroimaging for Radiation Therapy of Brain Tumors. Top. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 28, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, H.; Steidl, E.; Hattingen, E.; Filipski, K.; Meissner, M.; Sebastian, M.; Koch, A.; Strzelczyk, A.; Forster, M.T.; Baumgarten, P.; et al. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Cerebral Pseudoprogression: Patterns and Categorization. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 798811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, A.; Savjani, R. The Current Landscape of Clinical Predictions from Brain Tumor Imaging. Radiol. Imaging Cancer 2022, 4, e229011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Al-Zahrani, A.; Beylerli, O.; Sufianov, R.; Talybov, R.; Meshcheryakova, S.; Sufianova, G.; Gareev, I.; Sufianov, A. Cell-free miRNAs as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in High-Grade Gliomas. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 898537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montemurro, N. Glioblastoma Multiforme and Genetic Mutations: The Issue Is Not Over Yet. An Overview of the Current Literature. J. Neurol. Surg. A Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2020, 81, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Sun, Z.; Gareev, I.; Yan, T.; Chen, X.; Ahmad, A.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, B.; Beylerli, O.; Yang, G.; et al. Exosomal miR-2276-5p in Plasma Is a Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Glioma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 671202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Li, X.; Peng, L.; Shen, X.; Dang, Y.; Zhang, G. MicroRNA-150 as a Potential Biomarker in Diagnosis of Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. Lab. 2017, 63, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Liu, J.; Quan, J.; Liu, W.; Tan, H.; Li, W. MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of glioma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 2651–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, S.S.; Nygaard, A.B.; Nielsen, M.Y.; Jensen, K.; Christensen, T. MiRNA Expression Profiles in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Blood of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. Transl. Stroke Res. 2014, 5, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargiulo, E.; Paggetti, J.; Moussay, E. Hematological Malignancy-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles and Tumor Microenvironment: The Art of Turning Foes into Friends. Cells 2019, 8, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, N.; Hu, S.; Hu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Wang, B. Quantitative proteomic characterization of microvesicles/exosomes from the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with acute bilirubin encephalopathy. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, C.E.; Verheul, C.; Willemse, E.A.J. The use of cerebrospinal fluid in biomarker studies. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2017, 146, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Hurley, J.; Roberts, D.; Chakrabortty, S.K.; Enderle, D.; Noerholm, M.; Breakefield, X.O.; Skog, J.K. Exosome-based liquid biopsies in cancer: Opportunities and challenges. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamage, T.K.J.B.; Fraser, M. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in the Developing Brain: Current Perspective and Promising Source of Biomarkers and Therapy for Perinatal Brain Injury. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 744840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Hu, S.; Zhang, L.; Xin, J.; Sun, C.; Wang, L.; Ding, K.; Wang, B. Tumor circulome in the liquid biopsies for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Theranostics 2020, 10, 4544–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.M.; Shah, R.H.; Pentsova, E.I.; Pourmaleki, M.; Briggs, S.; Distefano, N.; Zheng, Y.; Skakodub, A.; Mehta, S.A.; Campos, C.; et al. Tracking tumour evolution in glioma through liquid biopsies of cerebrospinal fluid. Nature 2019, 565, 654–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Movahedpour, A.; Khatami, S.H.; Khorsand, M.; Salehi, M.; Savardashtaki, A.; Mirmajidi, S.H.; Negahdari, B.; Khanjani, N.; Naeli, P.; Vakili, O.; et al. Exosomal noncoding RNAs: Key players in glioblastoma drug resistance. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2021, 476, 4081–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, Y.; Ohkubo, T.; Kawaji, H.; Machida, A.; Miyata, H.; Goda, S.; Roy, S.; Hayashizaki, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Yokota, T. Next-generation sequencing-based small RNA profiling of cerebrospinal fluid exosomes. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 636, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Cai, Y.; Peng, B.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Kang, F.; Hong, Q.; Yan, Y.; et al. Current Understanding of Exosomal MicroRNAs in Glioma Immune Regulation and Therapeutic Responses. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 813747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miida, T.; Yamada, T.; Seino, U.; Ito, M.; Fueki, Y.; Takahashi, A.; Kosuge, K.; Soda, S.; Hanyu, O.; Obayashi, K.; et al. Serum amyloid a (SAA)-induced remodeling of CSF-HDL. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1761, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch-Reinshagen, V.; Donkin, J.; Stukas, S.; Chan, J.; Wilkinson, A.; Fan, J.; Parks, J.S.; Kuivenhoven, J.A.; Lütjohann, D.; Pritchard, H.; et al. LCAT synthesized by primary astrocytes esterifies cholesterol on glia-derived lipoproteins. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Dong, Y.; Wang, H. microRNA-19b-3p-containing extracellular vesicles derived from macrophages promote the development of atherosclerosis by targeting JAZF1. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffman, J.D.; Fisher, P.G.; Gibbs, P. Early detection of cancer: Past, present, and future. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2015, 1, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, A.M.; Quddusi, A.; Shamim, M.S. The significance of MGMT methylation in Glioblastoma Multiforme prognosis. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2018, 68, 1137–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Che, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Su, Q.; You, C.; Lu, Y.; et al. Diagnostic and Prognostic Potential of Serum Cell-Free microRNA-214 in Glioma. World Neurosurg. 2019, 125, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, F.; Shao, N.; Li, B.; Xue, L.; Deng, D.; Xu, Y.; Lan, Q.; Peng, Y.; Yang, Y. A serum 6-miRNA panel as a novel non-invasive biomarker for meningioma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Ruan, C.; Wang, L.; Guo, H. Serum miR-100 is a potential biomarker for detection and outcome prediction of glioblastoma patients. Cancer Biomark. 2019, 24, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, K.; Lin, T.; Pang, Q.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z.; Tai, M.; Meng, F.; Zhang, J.; Wan, Y.; Mao, P.; et al. Extracellular miRNA-21 as a novel biomarker in glioma: Evidence from meta-analysis, clinical validation and experimental investigations. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 33994–34010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, J.; Feng, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, Q.; Lv, P.; Wang, F.; Gao, H.; Zhang, Y. Identification of Serum miRNA-423-5p Expression Signature in Somatotroph Adenomas. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 2019, 8516858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beylerli, O.; Khasanov, D.; Gareev, I.; Valitov, E.; Sokhatskii, A.; Wang, C.; Pavlov, V.; Khasanova, G.; Ahmad, A. Differential non-coding RNAs expression profiles of invasive and non-invasive pituitary adenomas. Noncoding RNA Res. 2021, 6, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopková, A.; Šána, J.; Večeřa, M.; Fadrus, P.; Lipina, R.; Smrčka, M.; Lojová, M.; Slabý, O. MicroRNAs in Cerebrospinal Fluid as Biomarkers in Brain Tumor Patients. Klin. Onkol. 2019, 32, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gareev, I.; Beylerli, O.; Liang, Y.; Xiang, H.; Liu, C.; Xu, X.; Yuan, C.; Ahmad, A.; Yang, G. The Role of MicroRNAs in Therapeutic Resistance of Malignant Primary Brain Tumors. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 740303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAnena, P.; Tanriverdi, K.; Curran, C.; Gilligan, K.; Freedman, J.E.; Brown, J.A.L.; Kerin, M.J. Cell-free microRNAs miR-331 and miR-195 differentiate local luminal a from metastatic breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.P.; Zhu, Z.T.; Zhang, Y.; He, C.Y. Downregulation of MicroRNA-330 Correlates with the Radiation Sensitivity and Prognosis of Patients with Brain Metastasis from Lung Cancer. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 2220–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montemurro, N.; Condino, S.; Carbone, M.; Cattari, N.; D’Amato, R.; Cutolo, F.; Ferrari, V. Brain Tumor and Augmented Reality: New Technologies for the Future. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafarzadeh, A.; Paknahad, M.H.; Nemati, M.; Jafarzadeh, S.; Mahjoubin-Tehran, M.; Rajabi, A.; Shojaie, L.; Mirzaei, H. Dysregulated expression and functions of microRNA-330 in cancers: A potential therapeutic target. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 146, 112600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, J.; Abdulsahib, W.K.; Turki Jalil, A.; Saadi Kareem, D.; Aminov, Z.; Alsaikhan, F.; Ramírez-Coronel, A.A.; Ramaiah, P.; Farhood, B. Prostate cancer and microRNAs: New insights into apoptosis. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2023, 245, 154436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirjang, S.; Mansoori, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Shajari, N.; Duijf, P.; Najafi, S.; Abedi Gaballu, F.; Nofouzi, K.; Baradaran, B. miR-330 Regulates Colorectal Cancer Oncogenesis by Targeting BACH1. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 10, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sippl, C.; Quiring, A.; Teping, F.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.; Urbschat, S.; Ketter, R.; Oertel, J. MiRNA-181d Expression Correlates in Tumor versus Plasma of Glioblastoma Patients-the Base of a Preoperative Stratification Tool for Local Carmustine Wafer Use. World Neurosurg. 2022, 159, e324–e333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualetti, F.; Barberis, A.; Zanotti, S.; Montemurro, N.; De Salvo, G.L.; Soffietti, R.; Mazzanti, C.M.; Ius, T.; Caffo, M.; Paiar, F.; et al. The impact of survivorship bias in glioblastoma research. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2023, 188, 104065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemurro, N.; Trevisi, G. Editorial: Awake surgery for brain tumors and brain connectomics. Front Oncol. 2022, 12, 1094818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morokoff, A.; Jones, J.; Nguyen, H.; Ma, C.; Lasocki, A.; Gaillard, F.; Bennett, I.; Luwor, R.; Stylli, S.; Paradiso, L.; et al. Serum microRNA is a biomarker for post-operative monitoring in glioma. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 149, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Chen, D.; Lv, T.; Li, G.; Qu, S. Serum MicroRNA-125b as a Potential Biomarker for Glioma Diagnosis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akers, J.C.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Kim, R.; Skog, J.; Nakano, I.; Pingle, S.; Kalinina, J.; Hua, W.; Kesari, S.; Mao, Y.; et al. MiR-21 in the extracellular vesicles (EVs) of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): A platform for glioblastoma biomarker development. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Sun, Y.; Tang, J. Serum miR-21 is a diagnostic and prognostic marker of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 35, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraniskin, A.; Chomiak, M.; Ahle, G.; Gress, T.; Buchholz, M.; Turewicz, M.; Eisenacher, M.; Margold, M.; Schlegel, U.; Schmiegel, W.; et al. MicroRNA-30c as a novel diagnostic biomarker for primary and secondary B-cell lymphoma of the CNS. J. Neurooncol. 2018, 137, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraniskin, A.; Kuhnhenn, J.; Schlegel, U.; Maghnouj, A.; Zöllner, H.; Schmiegel, W.; Hahn, S.; Schroers, R. Identification of microRNAs in the cerebrospinal fluid as biomarker for the diagnosis of glioma. Neuro-oncology 2012, 14, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, V.; Cirino, M.; Panepucci, R.; Peria, F.; Tirapelli, D.; Colli, B.; Carlotti, C.G., Jr. The Role of MicroRNA 181d as a Possible Biomarker Associated With Tumor Progression in Meningiomas. Cureus 2021, 13, e19158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, J.; Shimomura, A.; Kawauchi, J.; Matsuzaki, J.; Yamamoto, Y.; Takizawa, S.; Sakamoto, H.; Ohno, M.; Narita, Y.; Ochiya, T.; et al. Brain metastasis-related microRNAs in patients with advanced breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, F.; Qing, Q.; Pan, Q.; Hu, M.; Yu, H.; Yue, X. Serum exosomal miR-301a as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for human glioma. Cell Oncol. 2018, 41, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Lan, F.; Hu, M.; Pan, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J. Downregulation of serum microRNA-205 as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for human glioma. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 124, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teplyuk, N.M.; Mollenhauer, B.; Gabriely, G.; Giese, A.; Kim, E.; Smolsky, M.; Kim, R.Y.; Saria, M.G.; Pastorino, S.; Kesari, S.; et al. MicroRNAs in cerebrospinal fluid identify glioblastoma and metastatic brain cancers and reflect disease activity. Neuro-oncology 2012, 14, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemurro, N.; Pahwa, B.; Tayal, A.; Shukla, A.; De Jesus Encarnacion, M.; Ramirez, I.; Nurmukhametov, R.; Chavda, V.; De Carlo, A. Macrophages in Recurrent Glioblastoma as a Prognostic Factor in the Synergistic System of the Tumor Microenvironment. Neurol. Int. 2023, 15, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemurro, N.; Fanelli, G.N.; Scatena, C.; Ortenzi, V.; Pasqualetti, F.; Mazzanti, C.M.; Morganti, R.; Paiar, F.; Naccarato, A.G.; Perrini, P. Surgical outcome and molecular pattern characterization of recurrent glioblastoma multiforme: A single-center retrospective series. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2021, 207, 106735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, M.; Lessi, F.; Barachini, S.; Liotti, R.; Montemurro, N.; Perrini, P.; Santonocito, O.S.; Gambacciani, C.; Snuderl, M.; Pieri, F.; et al. Metabolic-imaging of human glioblastoma live tumors: A new precision-medicine approach to predict tumor treatment response early. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 969812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasqualetti, F.; Montemurro, N.; Desideri, I.; Loi, M.; Giannini, N.; Gadducci, G.; Malfatti, G.; Cantarella, M.; Gonnelli, A.; Montrone, S.; et al. Impact of recurrence pattern in patients undergoing a second surgery for recurrent glioblastoma. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2022, 122, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasqualetti, F.; Gabelloni, M.; Gonnelli, A.; Faggioni, L.; Cantarella, M.; Montrone, S.; Gadducci, G.; Giannini, N.; Montemurro, N.; Mattioni, R.; et al. Impact of temporalis muscle thickness in elderly patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma treated with radio or radio-chemotherapy. Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Innocenti, L.; Ortenzi, V.; Scarpitta, R.; Montemurro, N.; Pasqualetti, F.; Asseri, R.; Lazzi, S.; Szumera-Cieckiewicz, A.; De Ieso, K.; Perrini, P.; et al. The Prognostic Impact of Gender, Therapeutic Strategies, Molecular Background, and Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Glioblastoma: A Still Unsolved Jigsaw. Genes 2023, 14, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualetti, F.; Giampietro, C.; Montemurro, N.; Giannini, N.; Gadducci, G.; Orlandi, P.; Natali, E.; Chiarugi, P.; Gonnelli, A.; Cantarella, M.; et al. Old and New Systemic Immune-Inflammation Indexes Are Associated with Overall Survival of Glioblastoma Patients Treated with Radio-Chemotherapy. Genes 2022, 13, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, H.; Lou, J.R.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, H.; Popescu, N.I.; Lupu, F.; Lind, S.E.; Ding, W.Q. MicroRNA-19 (miR-19) regulates tissue factor expression in breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 1429–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mott, J.L.; Kobayashi, S.; Bronk, S.F.; Gores, G.J. Mir-29 regulates Mcl-1 protein expression and apoptosis. Oncogene 2007, 26, 6133–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creighton, C.J.; Fountain, M.D.; Yu, Z.; Nagaraja, A.K.; Zhu, H.; Khan, M.; Olokpa, E.; Zariff, A.; Gunaratne, P.H.; Matzuk, M.M.; et al. Molecular profiling uncovers a p53-associated role for microRNA-31 in inhibiting the proliferation of serous ovarian carcinomas and other cancers. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1906–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, P.A.; Bert, A.G.; Paterson, E.L.; Barry, S.C.; Tsykin, A.; Farshid, G.; Vadas, M.A.; Khew-Goodall, Y.; Goodall, G.J. The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Huang, K.; You, Y.; Fu, X.; Hu, L.; Song, L.; Meng, Y. Hypoxia-induced miR-210 in epithelial ovarian cancer enhances cancer cell viability via promoting proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 44, 2111–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sullivan, P.S.; Goodman, J.C.; Gunaratne, P.H.; Marchetti, D. MicroRNA-1258 suppresses breast cancer brain metastasis by targeting heparanase. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuda, H.; Xing, F.; Pandey, P.R.; Sharma, S.; Watabe, M.; Pai, S.K.; Mo, Y.Y.; Iiizumi-Gairani, M.; Hirota, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. miR-7 suppresses brain metastasis of breast cancer stem-like cells by modulating KLF4. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 1434–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, W.; Xue, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Hu, X. Down-regulationof miR-145 contributes to lung adenocarcinoma cell growth to form brain metastases. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 2027–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, S.; Ranade, A.R.; Tran, N.L.; Nasser, S.; Sridhar, S.; Korn, R.L.; Ross, J.T.; Dhruv, H.; Foss, K.M.; Sibenaller, Z.; et al. MicroRNA-328 is associated with (non-small) cell lung cancer (NSCLC) brain metastasis and mediates NSCLC migration. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 2621–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.T.; Xu, S.D.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J.F.; Ning, J.F.; Wang, S.F. MicroRNA-378 is associated with non-small cell lung cancer brain metastasis by promoting cell migration, invasion, and tumor angiogenesis. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.J.; Seol, H.J.; Park, Y.M.; Kim, K.H.; Gorospe, M.; Nam, D.H.; Kim, H.H. MicroRNA-146a suppresses metastatic activity in brain metastasis. Mol. Cells 2012, 34, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, A.; Alsidawi, S.; Jagannathan, S.; Sumita, K.; Sasaki, A.T.; Aronow, B.; Warnick, R.E.; Lawler, S.; Driscoll, J.J. The brain microenvironment negatively regulates miRNA-768-3p to promote K-ras expression and lung cancer metastasis. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gu, X.; Fang, Y.; Xiang, J.; Chen, Z. MicroRNA expression profiles in human colorectal cancers with brain metastases. Oncol. Lett. 2012, 3, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Source | Factor | Advantages | Disadvantages | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSF, blood, urine | miRNA | Specificity +/− There is a chance for the convenient and precise tracking of therapy effectiveness, and even the possibility of using it for initial tumor diagnosis, contingent on the choice of appropriate markers or panels | Sensitivity − − − Lacks distinctive tumor-specific sequences, requires a comparison with normal references, lacks standardization | [4,5] |
| CSF, blood, neurosurgical fluid (including DNA, RNA, miRNA) | EV | Specificity + + + CSF is preferable to blood because it contains fewer background signals from white blood cells | Sensitivity − Signals originating from regular cells (leukocytes, for instance), as seen in blood | [5,6] |
| CSF, blood | Cell-free nucleic acid (DNA, RNA) | Specificity + + + Molecular assessment using established techniques, simpler to collect compared to CTCs, rapid and convenient tracking of tumor progression and treatment reaction, might constitute a massive portion of the tumor and surpass localized tissue biopsies in value | Sensitivity − Might not accurately depict the entirety of the tumor, lacks a definitive established standard, contingent on the tumor’s proximity to CSF | [4,5,6] |
| CSF, blood | CTC | Specificity + + + Utilizing molecular diagnosis enables swift and effortless tracking of both tumor progression and treatment responsiveness. It has the potential to portray a pertinent portion of the tumor and could outperform conventional local tissue biopsies | Sensitivity − − − Highly uncommon, challenging to isolate, lacking established norms, might not accurately reflect the entirety of the tumor, necessitates further experimental investigations | [5,7,8] |
| Tumor | Number of Patients, n | miRNA | Regulation | Biofluid | AUC | Sensitivity, % | Specificity, % | Important Find | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glioma (WHO grades II and IV) | 47 and 44 | miR-320e, miR-223, miR-21, miR-23a | Up | Serum | 99.8 | 100.0 | 97.8 | Confirming the diagnosis of pseudo-progression | [61] |
| Glioma (WHO grades II and III–IV) | 11 and 11 | miR-125b | Down | Serum | 0.868 and 0.959 | 81.82 and 90.91 | 75.76 and 87.88 | Biomarker development, especially for WHO grade-II–IV gliomas | [62] |
| Glioblastoma | 13 | EV miR-21 | Down | CSF | 0.91 | 87.0 | 93.0 | Glioblastoma cells actively secrete EVs containing miR-21 | [63] |
| PCNSL | 56 | miR-21 | Up | Serum and CSF | 0.930 | - | - | Correlation analysis demonstrated that serum miR-21 might reflect its companions in CSF | [64] |
| JPA | 3 | miR-26a-5p | Up | Serum | 0.751 | - | - | Correlated strongly in JPA patients within both the serum and tumor tissue samples | [65] |
| SCNSL and PCNSL | 61 and 14 | miR-30c | Up | CSF | 0.86 | 90.9 | 85.5 | miR-30c may facilitate lymphoma cells to engraft into CNS by the interaction with the CELSR3 gene that controls the function of ependymal cilia and, thus, affects the circulation of CSF | [66] |
| Glioma (WHO grades II and III–IV) | 2 and 8 | miR-15b | Up | CSF | 0.96 | 90.0 | 94.9 | Biomarker development, especially for WHO gradeII–IV glioma | [67] |
| Meningioma (WHO grades II–III) | 40 | miR-197 and miR-219a, miR-34a, miR-224 and miR-375 | Up and down | Serum | 0.79 | - | - | miR-197, miR-34a, miR-375 for grade I, and miR-375 for grade II | [68] |
| Brain metastasis related to advanced breast cancer | 51 | miR-4428 and miR-4480 | Up | Serum | 0.779 and 0.781 | - | - | Specific for brain metastasis (breast cancer) | [69] |
| Glioma (WHO grades I–II and III–IV) | 38 and 62 | miR-214 | Up | Serum | 0.885 | 90.00 | 71.00 | Potential minimally invasive biomarker for tumor stratification, early detection | [44] |
| Tumor | Number of Patients, n | miRNA | Regulation | Biofluid | Important Find | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCNSL | 56 | miR-21 | Up | Serum and CSF | miR-21 as an independent and powerful predictor of overall survival | [64] |
| Glioma (WHO grades I–II and III–IV) | 38 and 62 | miR-214 | Up | Serum | miR-214 as an independent and powerful predictor of overall survival | [44] |
| Glioblastoma | 66 | Exosomal miR-301a | Up | Serum | Exosomal miR-301a as an independent and powerful predictor of overall survival | [70] |
| Glioma (WHO grades III–IV) | 64 | miR-205 | Down | Serum | miR-205 as an independent and powerful predictor of overall survival | [45] |
| Meningioma (WHO grades I–III) | 230 | miR-106a-5p, miR-219-5p, miR-375, miR-409-3p, miR-197-3p, and miR-224-5p | Up and down | Serum | Serum 6-miRNA as an independent and powerful predictor of overall survival | [45] |
| Glioblastoma, breast cancer metastasis to brain and leptomeningeal metastasis, lung cancer metastasis to brain and leptomeningeal metastasis | 19, 16, 26, 28, and 4 | miR-10b, miR-21, and miR-200 family | Up | CSF | miR-10b, miR-21, and miR-200 family as an independent and powerful predictor of overall survival of primary and metastatic brain tumors | [71] |
| MiRNA | Primary Tumor | Regulation | Potential Target | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-19a | Breast | Down | 3′-UTR of tissue factor transcript | [79] |
| miR-29c | Breast and melanoma | Down | Induced myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein MCL1 | [80] |
| miR-31 | Colon | Down | p53 | [81] |
| miR-200 | Breast and lung | Up | E-cadherin transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2 | [82] |
| miR-210 | Breast and melanoma | Up | PTP1b and HIF-1α | [83] |
| miR-1258 | Breast | Down | Heparanase | [84] |
| miR-7 | Breast | Down | KLF4 gene | [85] |
| miR-145 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Down | 3′-UTR of the JAM-A and fascin | [86] |
| miR-328 | NSCLC | Up | PRKCA gene | [87] |
| miR-378 | NSCLC | Up | MMP-7, MMP-9, and VEGF | [88] |
| miR-146-a | Breast | Down | B-catenin and hnRNPC | [89] |
| miR-768-3p | Lung and breast | Down | K-RAS | [90] |
| miR-1, miR-145, miR-146a, miR-143, miR-10b, miR-22 | Colon | Up | Multiple genes related to apoptosis and oncogenesis | [91] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beylerli, O.; Encarnacion Ramirez, M.d.J.; Shumadalova, A.; Ilyasova, T.; Zemlyanskiy, M.; Beilerli, A.; Montemurro, N. Cell-Free miRNAs as Non-Invasive Biomarkers in Brain Tumors. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2888. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13182888
Beylerli O, Encarnacion Ramirez MdJ, Shumadalova A, Ilyasova T, Zemlyanskiy M, Beilerli A, Montemurro N. Cell-Free miRNAs as Non-Invasive Biomarkers in Brain Tumors. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(18):2888. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13182888
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeylerli, Ozal, Manuel de Jesus Encarnacion Ramirez, Alina Shumadalova, Tatiana Ilyasova, Mikhail Zemlyanskiy, Aferin Beilerli, and Nicola Montemurro. 2023. "Cell-Free miRNAs as Non-Invasive Biomarkers in Brain Tumors" Diagnostics 13, no. 18: 2888. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13182888
APA StyleBeylerli, O., Encarnacion Ramirez, M. d. J., Shumadalova, A., Ilyasova, T., Zemlyanskiy, M., Beilerli, A., & Montemurro, N. (2023). Cell-Free miRNAs as Non-Invasive Biomarkers in Brain Tumors. Diagnostics, 13(18), 2888. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13182888








