Detection of Erosive Changes on Smooth Surfaces with and without Orthodontic Brackets Using an Intraoral Scanner—An In Vitro Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Selection and Preparation
- A = 6% citric acid/pH value 1.6;
- B = Coca-Cola/pH value 2.6;
- C = Redbull/pH value 3.6;
- D = Powerade/pH-value 3.9;
- E = Control group, deionized water/pH-value 7.0.
2.2. Measurement with Intraoral Scanner and Acid Exposure
2.3. Quantitative Light-Induced Fluorescence (QLF)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Clinical Relevance
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lussi, A.; Carvalho, T.S. Erosive tooth wear: A multifactorial condition of growing concern and increasing knowledge. In Monographs in Oral Science, 2nd ed.; Lussi, A., Ganss, C., Eds.; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 25, pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlueter, N.; Luka, B. Erosive tooth wear—A review on global prevalence and on its prevalence in risk groups. Br. Dent. J. 2018, 224, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leven, A.J.; Ashley, M. Epidemiology, aetiology and prevention of tooth wear. Br. Dent. J. 2023, 234, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, C.E.; Brandao, A.C.S.; Bícego-Pereira, E.C.; Del Bel Cury, A.A.; Cury, J.A.; Tenuta, L.M.A. Effect of pH and titratable acidity on enamel and dentine erosion. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 5867–5873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambon, D.L.; Brand, H.S.; Boutkabout, C.; Levie, D.; Veerman, E.C. Patterns in consumption of potentially erosive beverages among adolescent school children in the Netherlands. Int. Dent. J. 2011, 61, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundararaj, D.; Venkatachalapathy, S.; Tandon, A.; Pereira, A. Critical evaluation of incidence and prevalence of white spot lesions during fixed orthodontic appliance treatment: A metaanalysis. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2015, 5, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Attin, T.; Wegehaupt, F.J. Methods for assessment of dental erosion. In Monographs in Oral Science, 2nd ed.; Lussi, A., Ganss, C., Eds.; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 25, pp. 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, D.; Ganss, C.; Lussi, A. Basic Erosive Wear Examination (BEWE): A new scoring system for scientific and clinical needs. Clin. Oral Investig. 2008, 12 (Suppl. S1), S65–S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, A.K.; Omar, R.; Carlsson, G.E.; Johansson, A. Dental erosion and its growing importance in clinical practice: From past to present. Int. J. Dent. 2012, 2012, 632907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganss, C. Definition of erosion and links to tooth wear. In Monographs in Oral Science; Lussi, A., Ed.; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2006; Volume 20, pp. 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Schlueter, N.; Hara, A.; Shellis, R.P.; Ganss, C. Methods for the measurement and characterization of erosion in enamel and dentine. Caries Res. 2011, 45 (Suppl. S1), 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, M.; Joshi, N.; Kathariya, R.; Angadi, P.; Raikar, S. Techniques to Evaluate Dental Erosion: A Systematic Review of Literature. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, ZE01–ZE07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, A.C.; Phillips, T.S.; Zimmerman, R.; Scaramucci, T.; Amaechi, B.T. Monitoring erosive tooth wear with intraoral 3D scanner: A feasibility study. Am. J. Dent. 2022, 35, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Witecy, C.; Ganss, C.; Wöstmann, B.; Schlenz, M.B.; Schlenz, M.A. Monitoring of Erosive Tooth Wear with Intraoral Scanners In Vitro. Caries Res. 2021, 55, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michou, S.; Vannahme, C.; Ekstrand, K.R.; Benetti, A.R. Detecting early erosive tooth wear using an intraoral scanner system. J. Dent. 2020, 100, 103445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlenz, M.A.; Schlenz, M.B.; Wöstmann, B.; Jungert, A.; Ganss, C. Intraoral scanner-based monitoring of tooth wear in young adults: 12-month results. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 1869–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlenz, M.A.; Schlenz, M.B.; Wöstmann, B.; Glatt, A.S.; Ganss, C. Intraoral scanner-based monitoring of tooth wear in young adults: 24-month results. Clin. Oral Investig. 2023, 27, 2775–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochoa-López, G.; Cascos, R.; Antonaya-Martín, J.L.; Revilla-León, M.; Gómez-Polo, M. Influence of ambient light conditions on the accuracy and scanning time of seven intraoral scanners in complete-arch implant scans. J. Dent. 2022, 121, 104138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulic, A.; Tveit, A.B.; Wang, N.J.; Hove, L.H.; Espelid, I.; Skaare, A.B. Reliability of two clinical scoring systems for dental erosive wear. Caries Res. 2010, 44, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaraudanjoki, V.; Laitala, M.L.; Tjäderhane, L.; Pesonen, P.; Lussi, A.; Anttonen, V. Association of erosive tooth wear and dental caries in Northern Finland Birth Cohort 1966—An epidemiological cross-sectional study. BMC Oral Health 2016, 17, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganss, C.; Lussi, A. (Eds.) Diagnosis of erosive tooth wear. In Monographs in Oral Science, 2nd ed.; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 25, pp. 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, T.S.; Colon, P.; Ganss, C.; Huysmans, M.C.; Lussi, A.; Schlueter, N.; Schmalz, G.; Shellis, R.P.; Tveit, A.B.; Wiegand, A. Consensus report of the European Federation of Conservative Dentistry: Erosive tooth wear-diagnosis and management. Clin. Oral Investig. 2015, 19, 1557–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marro, F.; De Lat, L.; Martens, L.; Jacquet, W.; Bottenberg, P. Monitoring the progression of erosive tooth wear (ETW) using BEWE index in casts and their 3D images: A retrospective longitudinal study. J. Dent. 2018, 73, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marro, F.; Jacquet, W.; Martens, L.; Keeling, A.; Bartlett, D.; O’Toole, S. Quantifying increased rates of erosive tooth wear progression in the early permanent dentition. J. Dent. 2020, 93, 103282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulfman, C.; Koenig, V.; Mainjot, A.K. Wear measurement of dental tissues and materials in clinical studies: A systematic review. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, 825–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Toole, S.; Osnes, C.; Bartlett, D.; Keeling, A. Investigation into the validity of WearCompare, a purpose-built software to quantify erosive tooth wear progression. Dent. Mater. 2019, 35, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, D.; O’Toole, S. Tooth wear and aging. Aus. Dent. J. 2019, 64 (Suppl. S1), S59–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makrygiannakis, M.A.; Kaklamanos, E.G.; Milosevic, A.; Athanasiou, A.E. Tooth Wear during Orthodontic Treatment with Fixed Appliances: A Systematic Review. J. Orthod. 2018, 45, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwangi, C.W.; Richmond, S.; Hunter, M.L. Relationship between malocclusion, orthodontic treatment, and tooth wear. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2009, 136, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heukamp, J.; Korbmacher-Steiner, H.; Schmidt, S.; Neumann, C.M.; Bottenberg, P.; Jablonski-Momeni, A. Remineralisation capability of silver diamine fluoride in artificial enamel lesions on smooth surfaces using quantitative light-induced fluorescence measurements in-vitro. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jablonski-Momeni, A.; Müller, M.; Korbmacher-Steiner, H.; Bottenberg, P. Ability of a Blue Hemoglobin-Based Liquid as a Novel Technology to Stain Initial Enamel Demineralization: A Proof-of-Concept in vitro Study. Caries Res. 2022, 56, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jablonski-Momeni, A.; Sambale, J.; Gaerttner, L.; Nothelfer, R.; Korbmacher-Steiner, H. Use of bioluminescence measurements for detection of artificial demineralization adjacent to orthodontic brackets. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2023, 84, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, K.; Nikaido, T.; Ikeda, M.; Foxton, R.M.; Tagami, J. Relationship between fluorescence loss of QLF and depth of demineralization in an enamel erosion model. Dent. Mat. J. 2009, 28, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganss, C.; Klimek, J.; Schwarz, N. A comparative profilometric in vitro study of the susceptibility of polished and natural human enamel and dentine surfaces to erosive demineralization. Arch. Oral Biol. 2000, 45, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michou, S.; Vannahme, C.; Bakhshandeh, A.; Ekstrand, K.R.; Benetti, A.R. Intraoral scanner featuring transillumination for proximal caries detection. An in vitro validation study on permanent posterior teeth. J Dent. 2022, 116, 103841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, A.K.; Lingström, P.; Birkhed, D. Comparison of factors potentially related to the occurrence of dental erosion in high- and low-erosion groups. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2002, 110, 204–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lussi, A.; Jaeggi, T. Erosion-diagnosis and risk factors. Clin. Oral Investig. 2008, 12 (Suppl. S1), 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsunni, A.A. Energy Drink Consumption: Beneficial and Adverse Health Effects. Int. J. Health Sci. 2015, 9, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karda, B.; Jindal, R.; Mahajan, S.; Sandhu, S.; Sharma, S.; Kaur, R. To Analyse the Erosive Potential of Commercially Available Drinks on Dental Enamel and Various Tooth Coloured Restorative Materials—An In-vitro Study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, ZC117–ZC121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrowska, A.; Szymański, W.; Kołodziejczyk, L.; Bołtacz-Rzepkowska, E. Evaluation of the Erosive Potential of Selected Isotonic Drinks: In Vitro Studies. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2016, 25, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, R.; Vicente, A.; Ortiz, A.J.; Bravo, L.A. The effects of two soft drinks on bond strength, bracket microleakage, and adhesive remnant on intact and sealed enamel. Eur. J. Orthod. 2011, 33, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammad, S.M.; Enan, E.T. In vivo effects of two acidic soft drinks on shear bond strength of metal orthodontic brackets with and without resin infiltration treatment. Angle Orthod. 2013, 83, 648–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasha, A.; Sindhu, D.; Nayak, R.S.; Mamatha, J.; Chaitra, K.R.; Vishwakarma, S. The Effect of Two Soft Drinks on Bracket Bond Strength and on Intact and Sealed Enamel: An In Vitro Study. J. Int. Oral Health 2015, 7 (Suppl. S2), 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Bastani, P.; Manchery, N.; Samadbeik, M.; Ha, D.H.; Do, L.G. Digital Health in Children’s Oral and Dental Health: An Overview and a Bibliometric Analysis. Children 2022, 9, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntovas, P.; Michou, S.; Benetti, A.R.; Bakhshandeh, A.; Ekstrand, K.; Rahiotis, C.; Kakaboura, A. Occlusal caries detection on 3D models obtained with an intraoral scanner. A validation study. J. Dent. 2023, 131, 104457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
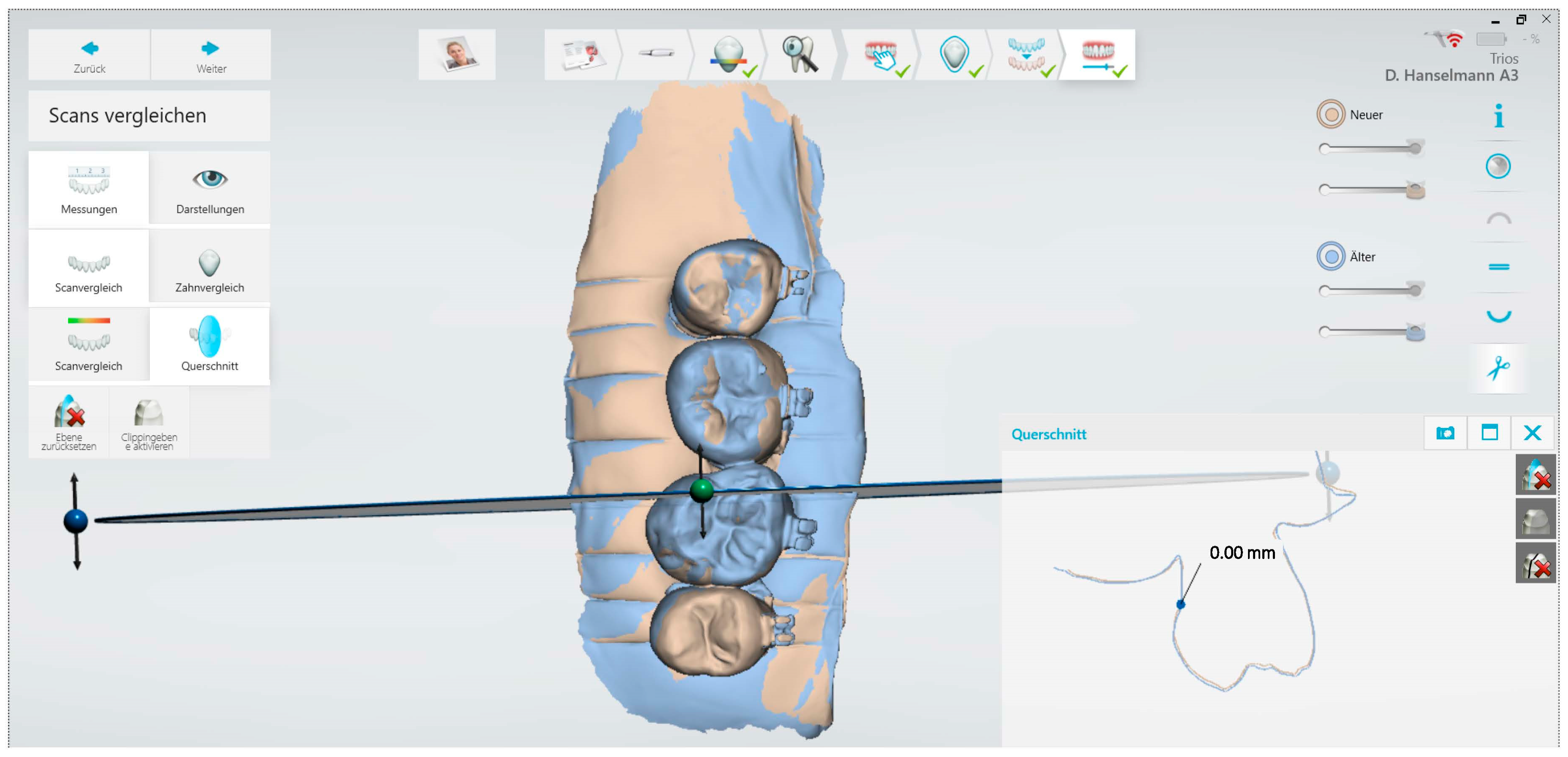



| Group | Min-Max (T0_T1)/µm | Median (T0_T1)/µm | Min-Max (T0_T2)/µm | Median (T0_T2)/µm | Min-Max (T0_T2)/µm | Median (T0_T2)/µm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0–5 | 0 | 0–15 | 10 | 10–20 | 12.5 |
| A Bracket | 0–10 | 0 | 0–20 | 10 | 0–20 | 10 |
| B | 0–5 | 0 | 0–15 | 10 | 0–20 | 15 |
| B Bracket | 0–10 | 0 | 0–10 | 0 | 0–20 | 10 |
| C | 0 | 0 | 0–5 | 0 | 0–15 | 7.5 |
| C Bracket | 0 | 0 | 0–10 | 0 | 0–10 | 0 |
| D | 0–5 | 0 | 0–5 | 0 | 0–10 | 5 |
| D Bracket | 0 | 0 | 0–10 | 0 | 0–10 | 0 |
| E | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| E Bracket | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Group | Min-Max ΔF T1 (%) | Median ΔF T1 (%) | Min-Max ΔF T2 (%) | Median ΔF T2 (%) | Min-Max ΔF T3 (%) | Median ΔF T3 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | −8.6–0 | −5.6 | −16.7–0 | −2.5 | −11.6–0 | −6.2 |
| A Bracket | −12.7–0 | 0 | −10.6–0 | −3.0 | −22.0–0 | −5.9 |
| B | −20.1–0 | −5.6 | −24.9–0 | −6.0 | −16.5–0 | −6.1 |
| B Bracket | −15.3–0 | 0 | −16.6–0 | 0 | −20.1–0 | 0 |
| C | −13.2–0 | −5.9 | −17.9–0 | −6.1 | −12.4–0 | −5.8 |
| C Bracket | −11.8–0 | −5.3 | −15.3–0 | −5.7 | −10.3–0 | 0 |
| D | −10.0–0 | −6.8 | −9.1–0 | −7.1 | −9.3–0 | −7.0 |
| D Bracket | −8.7–0 | 0 | −9.6–0 | 0 | −8.1–0 | 0 |
| E | −13.1–0 | 0 | −5.8–0 | 0 | −5.6–0 | 0 |
| E Bracket | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jablonski-Momeni, A.; Hanselmann, F.; Bottenberg, P.; Korbmacher-Steiner, H. Detection of Erosive Changes on Smooth Surfaces with and without Orthodontic Brackets Using an Intraoral Scanner—An In Vitro Study. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3232. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13203232
Jablonski-Momeni A, Hanselmann F, Bottenberg P, Korbmacher-Steiner H. Detection of Erosive Changes on Smooth Surfaces with and without Orthodontic Brackets Using an Intraoral Scanner—An In Vitro Study. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(20):3232. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13203232
Chicago/Turabian StyleJablonski-Momeni, Anahita, Franka Hanselmann, Peter Bottenberg, and Heike Korbmacher-Steiner. 2023. "Detection of Erosive Changes on Smooth Surfaces with and without Orthodontic Brackets Using an Intraoral Scanner—An In Vitro Study" Diagnostics 13, no. 20: 3232. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13203232
APA StyleJablonski-Momeni, A., Hanselmann, F., Bottenberg, P., & Korbmacher-Steiner, H. (2023). Detection of Erosive Changes on Smooth Surfaces with and without Orthodontic Brackets Using an Intraoral Scanner—An In Vitro Study. Diagnostics, 13(20), 3232. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13203232







