Relationship between Eccentricity and Volume Determined by Spectral Algorithms Applied to Spatially Registered Bi-Parametric MRI and Prostate Tumor Aggressiveness: A Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
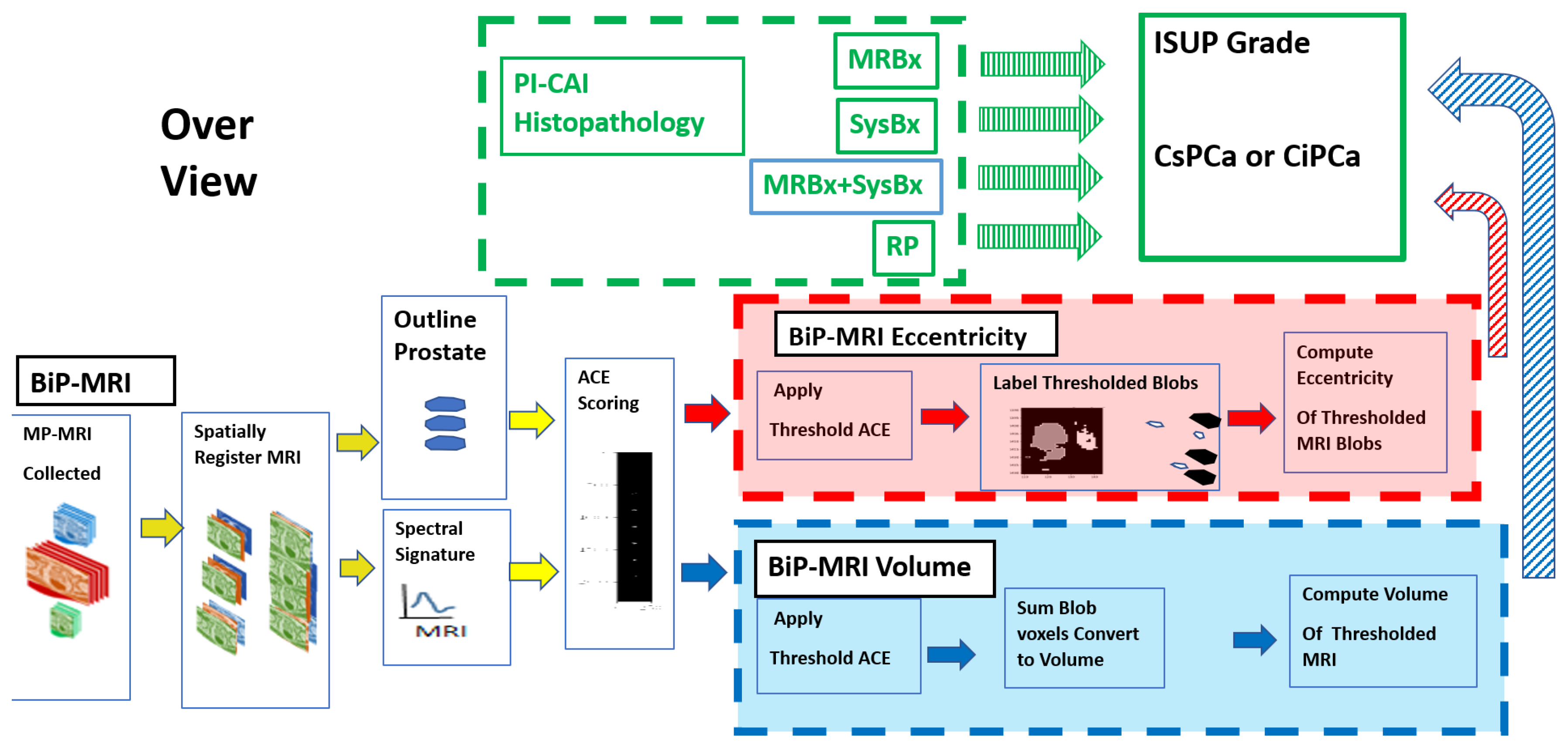
2.1. Overview
2.2. Study Design and Population
2.3. Spatial Registered Hypercube Assembly: MRI Components, Sequences
2.4. Spatial Registered Hypercube Assembly, Pre- Image Processing Analysis
2.5. Adaptive Cosine Estimator (ACE) Algorithm
2.6. Tumor Volume Measurements, Supervised Target Detection
2.7. Labeling and Blob Generation
2.8. Eccentricity Calculation
2.9. Univariate and Multivariate Fitting
2.10. Logistic Regression
2.11. Receiver Operator Characteristic
3. Results
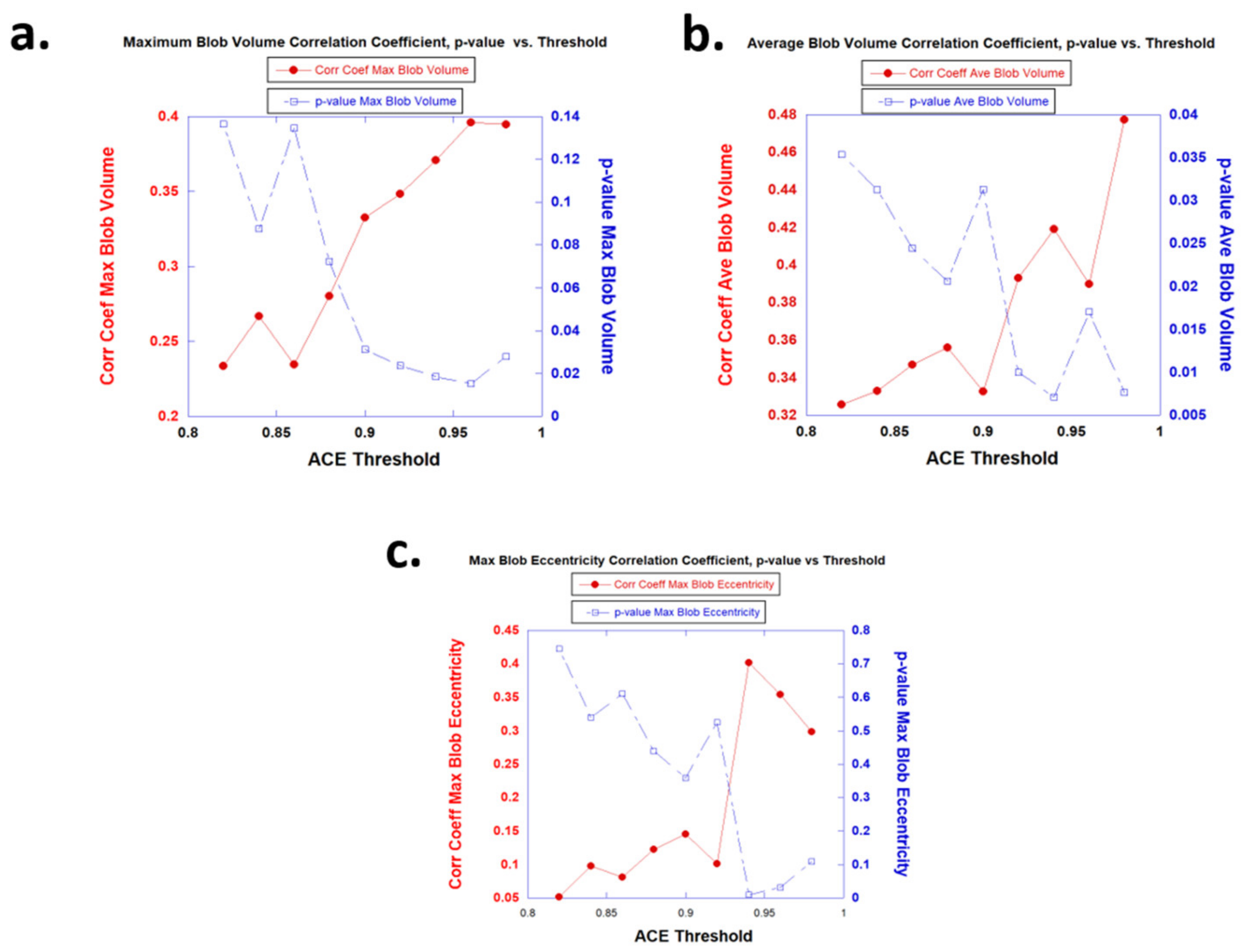
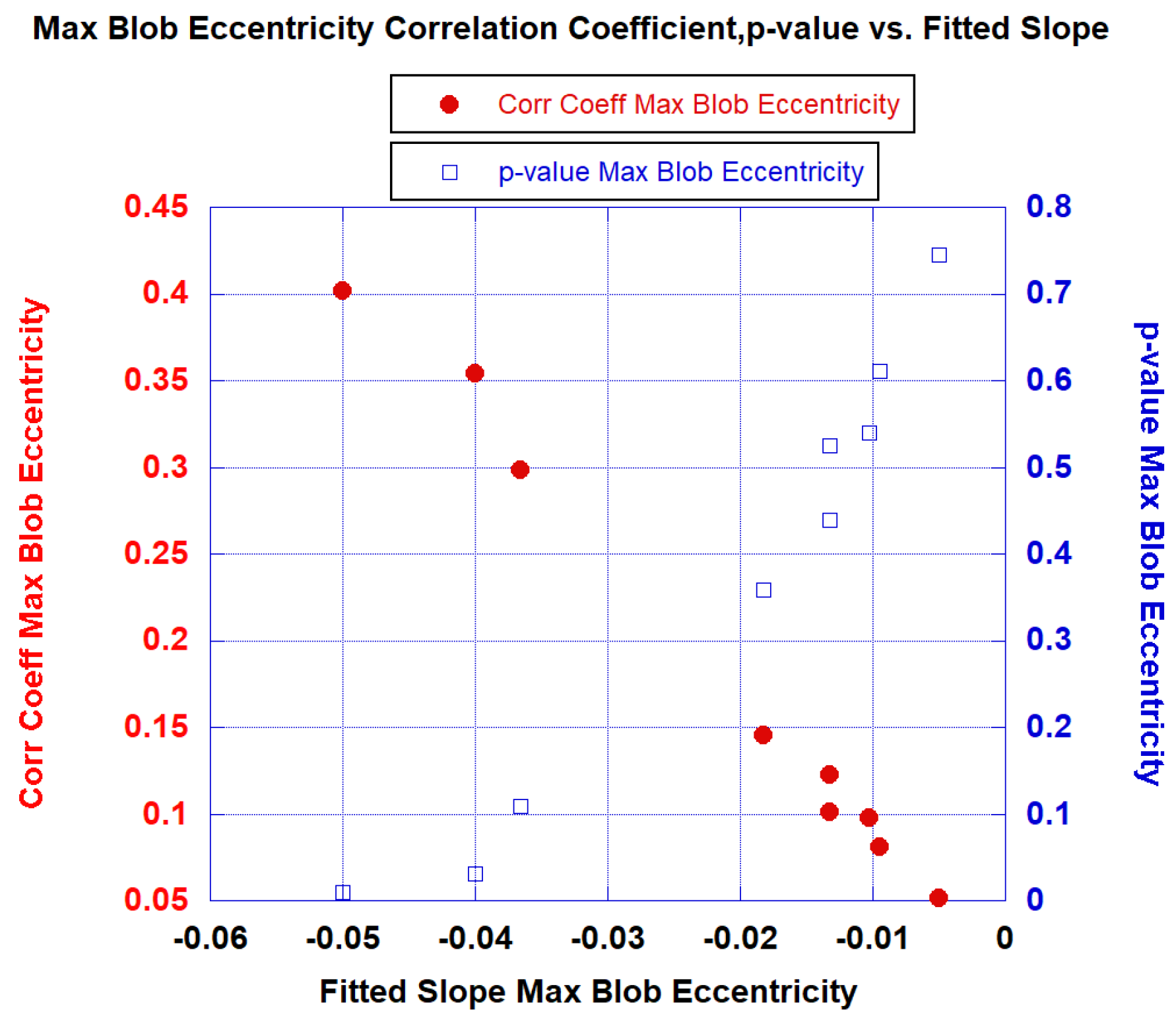
3.1. Univariate Fits
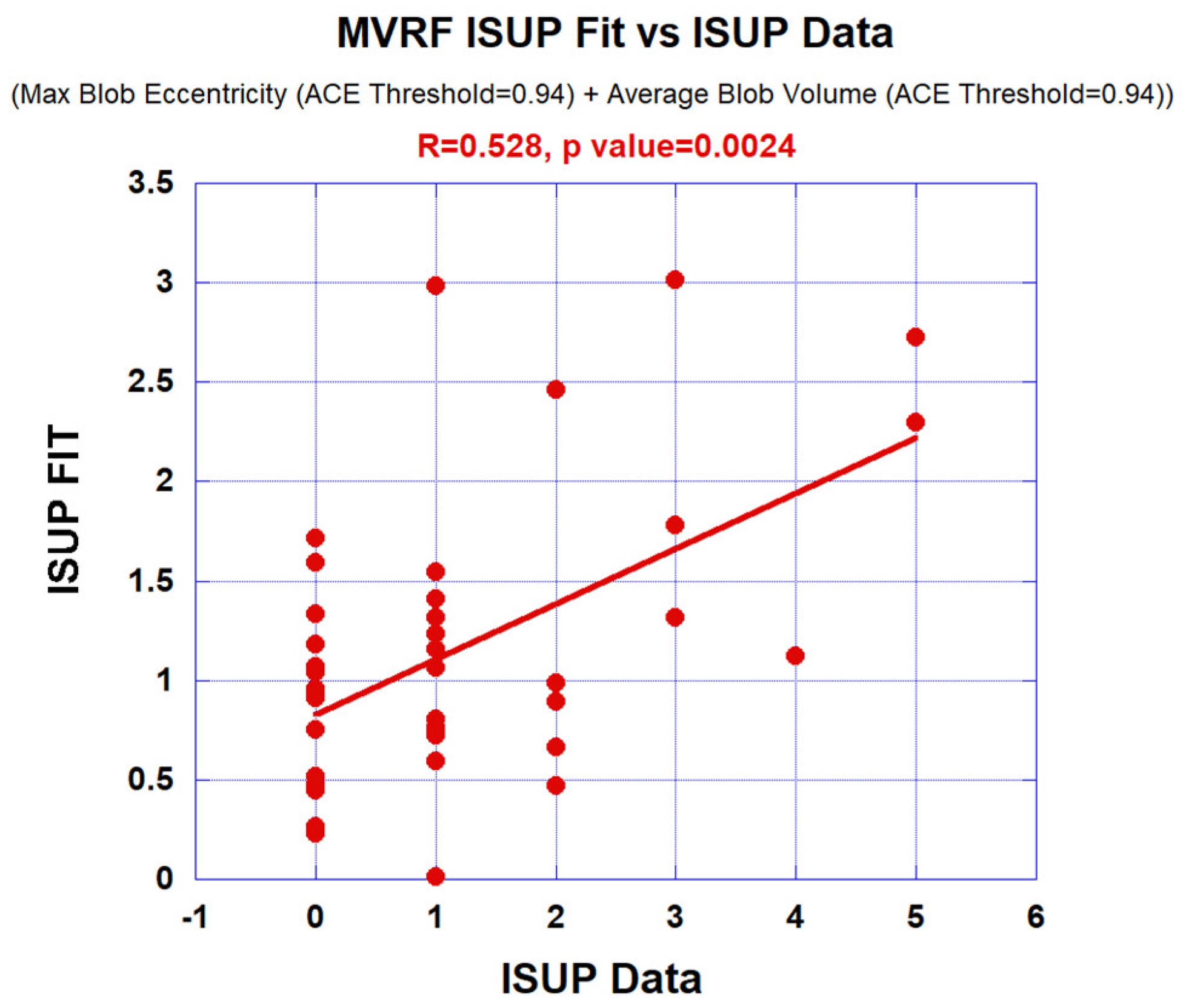
3.2. Multivariate Fits
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Adaptive Cosine Estimator (ACE)
Appendix A.2. Eccentricity Calculation
Appendix A.3. Tumor Volume Measurements, Supervised Target Detection
Appendix A.4. Univariate and Multivariate Fitting
Appendix A.5. Receiver Operator Characteristic
References
- Aus, G.; Abbou, C.C.; Pacik, D.; Schmid, H.P.; Van Poppel, H.; Wolff, J.M.; Zattoni, F. EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 2001, 40, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shariat, S.F.; Roehrborn, C.G. Using biopsy to detect prostate cancer. Rev. Urol. 2008, 10, 262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gayet, M.; van der Aa, A.; Beerlage, H.P.; Schrier, B.P.; Mulders, P.F.; Wijkstra, H. The value of magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasonography (MRI/US)-fusion biopsy platforms in prostate cancer detection: A systematic review. BJU Int. 2016, 117, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Irshad, H.; Veillard, A.; Roux, L.; Racoceanu, D. Methods for nuclei detection, segmentation, and classification in digital histopathology: A review—Current status and future potential. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 7, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeb, S.; Vellekoop, A.; Ahmed, H.U.; Catto, J.; Emberton, M.; Nam, R.; Rosario, D.J.; Scattoni, V.; Lotan, Y. Systematic review of complications of prostate biopsy. Eur. Urol. 2013, 64, 876–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjurlin, M.A.; Wysock, J.S.; Taneja, S.S. Optimization of prostate biopsy: Review of technique and complications. Urol. Clin. 2014, 41, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahab, S.A.; Verma, S. Review of Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System version 2. Future Oncol. 2016, 12, 2479–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohestani, K.; Wallström, J.; Dehlfors, N.; Sponga, O.M.; Månsson, M.; Josefsson, A.; Carlsson, S.; Hellström, M.; Hugosson, J. Performance and inter-observer variability of prostate MRI (PI-RADS version 2) outside high-volume centres. Scand. J. Urol. 2019, 53, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twilt, J.J.; van Leeuwen, K.G.; Huisman, H.J.; Fütterer, J.J.; de Rooij, M. Artificial intelligence based algorithms for prostate cancer classification and detection on magnetic resonance imaging: A narrative review. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, R.; Simone, C.B., 2nd; Skinner, W.; Turkbey, B.; Choyke, P. Pilot study for supervised target detection applied to spatially registered multiparametric MRI in order to non-invasively score prostate cancer. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 94, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, R.; Simone, C.B., 2nd; Turkbey, B.; Choyke, P. Algorithms applied to spatially registered multi-parametric MRI for prostate tumor volume measurement. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2021, 11, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, R.; Simone, C.B., 2nd; Turkbey, B.; Choyke, P. Correlation of prostate tumor eccentricity and Gleason scoring from prostatectomy and multi-parametric-magnetic resonance imaging. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2021, 11, 4235–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, R.; Simone, C.B., 2nd; Turkbey, B.; Choyke, P. Development and testing quantitative metrics from multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging that predict Gleason score for prostate tumors. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2022, 12, 1859–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, R.; Turkbey, B.; Choyke, P.; Simone, C.B., 2nd. Combining and Analyzing Novel Multi-parametric MRI Metrics for Predicting Gleason Score. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2022, 12, 3844–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, R.; Turkbey, B.; Choyke, P.; Simone, C.B., 2nd. Pilot Study for Generating and Assessing Nomograms and Decision Curves Analysis to Predict Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer Using Only Spatially Registered Multi-Parametric MRI. Front. Oncol. Sec. Genitourin. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1066498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, R.; Turkbey, B.; Choyke, P.L.; Simone, C.B., 2nd. Application of Spectral Algorithm Applied to Spatially Registered Bi-Parametric MRI to Predict Prostate Tumor Aggressiveness: A Pilot Study. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawaideh, J.P.; Sala, E.; Shaida, N.; Koo, B.; Warren, A.Y.; Carmisciano, L.; Saeb-Parsy, K.; Gnanapragasam, V.J.; Kastner, C.; Barrett, T. Diagnostic accuracy of biparametric versus multiparametric prostate MRI: Assessment of contrast benefit in clinical practice. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 4039–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, K.K.; King, A.; Galgano, S.J.; Sherrer, R.L.; Gordetsky, J.B.; Rais-Bahrami, S. Financial implications of biparametric prostate MRI. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2020, 23, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofts, P.S. T1-Weighted DCE Imaging Concepts: Modelling, Acquisition and Analysis. Magnetom. Flash 2010, 3, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Egevad, L.; Delahunt, B.; Srigley, J.R.; Samaratunga, H. International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) grading of prostate cancer—An ISUP consensus on contemporary grading. APMIS 2016, 124, 433–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Twilt, J.J.; Bosma, J.S.; Van Ginneken, B.; Yakar, D.; Elschot, M.; Veltman, J.; Fütterer, J.; de Rooij, M.; Huisman, H. Artificial Intelligence and Radiologists at Prostate Cancer Detection in MRI: The PI-CAI Challenge (Study Protocol). Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/6624726#.ZGvT2nbMKM9 (accessed on 28 April 2023).
- Ahdoot, M.; Wilbur, A.R.; Reese, S.E.; Lebastchi, A.H.; Mehralivand, S.; Gomella, P.T.; Bloom, J.; Gurram, S.; Siddiqui, M.; Pinsky, P.; et al. MRI-Targeted, Systematic, and Combined Biopsy for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawcett, T. An Introduction to ROC Analysis. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 861–874. [Google Scholar]
- Manolakis, D.; Shaw, G. Detection algorithms for hyperspectral imaging applications. IEEE Sign. Process. Mag. 2002, 19, 29–43. [Google Scholar]
- Samet, H.; Tamminen, M. Efficient Component Labeling of Images of Arbitrary Dimension Represented by Linear Bintrees. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1988, 10, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulos, E.C. Introduction to multivariate regression analysis. Hippokratia 2010, 14 (Suppl. 1), 23–28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hosmer, D.W., Jr.; Lemeshow, S.; Sturdivant, R.X. Applied Logistic Regression, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000; ISBN 978-0-471-35632-5. [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez, I.; Rios-Ibacache, O.; Caprile, P.; Gonzalez, J.; San Francisco, I.F.; Besa, C. MRI-Based Surrogate Imaging Markers of Aggressiveness in Prostate Cancer: Development of a Machine Learning Model Based on Radiomic Features. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, M.S.; Seo, M.; Kwang Kim, K.G.; Park, I.A.; Moon, W.K. Quantitative MRI morphology of invasive breast cancer: Correlation with immunohistochemical biomarkers and subtypes. Acta Radiol. 2015, 56, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.J.; Park, H.; Lee, H.Y.; Sohn, I.; Ahn, J.; Lee, S.H. Prediction of tumor doubling time of lung adenocarcinoma using radiomic margin characteristics. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 2600–2609. [Google Scholar]
- Baba, T.; Uramoto, H.; Takenaka, M.; Oka, S.; Shigematsu, Y.; Shimokawa, H.; Hanagiri, T.; Tanaka, F. The tumour shape of lung adenocarcinoma is related to the postoperative prognosis. Interact. CardioVascular Thorac. Surg. 2012, 15, 73–76. [Google Scholar]
- Thornton, S.T.; Marion, J.B. Classical Dynamics of Particles & Systems, 5th ed.; Cengage Learning: Independence, KY, USA, 2003; ISBN -10 0534408966. [Google Scholar]

| Clinical Features | Median [Minimum, Maximum] |
|---|---|
| Age (Years) | 65.14 [50.00, 78.00] |
| PSA Median (ng/mL) | 13.49 [1.50, 81.95] |
| Prostate Volume Median (mL) | 60.6 [19.00, 192.00] |
| ISUP Grade | Patient # |
| 0 | 17 |
| 1 | 14 |
| 2 | 5 |
| 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 1 |
| 5 | 2 |
| Univariate Variable | ACE Treshold | R | p-Value | AUC [95% CI] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ave Blob Vol (mL) | 0.90 | 0.333 | 0.0313 | 0.641 [0.167–1.0] |
| Max Blob Vol (mL) | 0.90 | 0.333 | 0.0313 | 0.892 [0.667–1.0] |
| Max Blob Eccentricity | 0.90 | 0.145 | 0.358 | 0.466 [0.0–0.917] |
| Ave Blob Vol (mL) | 0.92 | 0.393 | 0.010 | 0.641 [0.167–1.0] |
| Max Blob Vol (mL) | 0.92 | 0.348 | 0.0238 | 0.959 [0.80–1.0] |
| Max Blob Eccentricity | 0.92 | 0.100 | 0.525 | 0.500 [0–0.917] |
| Ave Blob Vol (mL) | 0.94 | 0.419 | 0.00712 | 0.701 [0.333–1.0] |
| Max Blob Vol (mL) | 0.94 | 0.371 | 0.0185 | 0.949 [0.778–1.0] |
| Max Blob Eccentricity | 0.94 | 0.402 | 0.0102 | 0.896 [0.630–1.0] |
| Ave Blob Vol (mL) | 0.96 | 0.390 | 0.0171 | 0.0 [0.0–0.0] |
| Max Blob Vol (mL) | 0.96 | 0.396 | 0.0152 | 0.364 [0.091–0.636] |
| Max Blob Eccentricity | 0.96 | 0.354 | 0.0315 | 0.443 [0.125–0.727] |
| Age (Years) | NA | 0.045 | 0.778 | 0.450 [0.182–0.75] |
| PSA (nG/mL) | NA | 0.153 | 0.339 | 0.418 [0.0–0.909] |
| Prostate Volume (mL) | NA | 0.174 | 0.271 | 0.464 [0.167–0.767] |
| ACE Threshold | Independent Variable 1 | R1 (p Value) | Independent Variable 2 | R2 (p Value) | R12 (F-Statistic Probability) | AUC [95% CI] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.90 | Max Blob Eccentricity | −0.145 (0.303) | Average Blob Volume | 0.333 (0.029) | 0.367 (0.0593) | 0.542 [0.250–0.833] |
| 0.90 | Max Blob Eccentricity | −0.145 (0.551) | Max Blob Volume | 0.333 (0.044) | 0.345 (0.0847) | 0.869 [0.636–1.0] |
| 0.92 | Max Blob Eccentricity | −0.101 (0.646) | Average Blob Volume | 0.393 (0.0102) | 0.399 (0.034) | 0.640 [0.182–1.0] |
| 0.92 | Max Blob Eccentricity | −0.101 (0.780) | Max Blob Volume | 0.348 (0.0310) | 0.351 (0.0772) | 0.959 [0.80–1.0] |
| 0.94 | Max Blob Eccentricity | −0.402 (0.028) | Average Blob Volume | 0.419 (0.0190) | 0.528 (0.0024) | 0.896 [0.625–1.0] |
| 0.94 | Max Blob Eccentricity | −0.402 (0.037) | Max Blob Volume | 0.371 (0.068) | 0.484 (0.00716) | 0.949 [0.778–1.0] |
| 0.96 | Max Blob Eccentricity | −0.354 (0.019) | Average Blob Volume | 0.390 (0.011) | 0.530 (0.00372) | 0.084 [0–0.3] |
| 0.96 | Max Blob Eccentricity | −0.354 (0.018) | Max Blob Volume | 0.396 (0.009) | 0.536 (0.0032) | 0.448 [0.182–0.727] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mayer, R.; Turkbey, B.; Choyke, P.L.; Simone, C.B., II. Relationship between Eccentricity and Volume Determined by Spectral Algorithms Applied to Spatially Registered Bi-Parametric MRI and Prostate Tumor Aggressiveness: A Pilot Study. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3238. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13203238
Mayer R, Turkbey B, Choyke PL, Simone CB II. Relationship between Eccentricity and Volume Determined by Spectral Algorithms Applied to Spatially Registered Bi-Parametric MRI and Prostate Tumor Aggressiveness: A Pilot Study. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(20):3238. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13203238
Chicago/Turabian StyleMayer, Rulon, Baris Turkbey, Peter L. Choyke, and Charles B. Simone, II. 2023. "Relationship between Eccentricity and Volume Determined by Spectral Algorithms Applied to Spatially Registered Bi-Parametric MRI and Prostate Tumor Aggressiveness: A Pilot Study" Diagnostics 13, no. 20: 3238. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13203238
APA StyleMayer, R., Turkbey, B., Choyke, P. L., & Simone, C. B., II. (2023). Relationship between Eccentricity and Volume Determined by Spectral Algorithms Applied to Spatially Registered Bi-Parametric MRI and Prostate Tumor Aggressiveness: A Pilot Study. Diagnostics, 13(20), 3238. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13203238







