Escherichia coli Infection Sepsis: An Analysis of Specifically Expressed Genes and Clinical Indicators
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Data: Study Cohort and Information Collection
2.2. Data Source
2.3. DEG Identification and Functional Enrichment Analysis
2.4. PPI Network and MCODE Analysis
2.5. Weighted Gene Coexpression Network Analysis (WGCNA)
2.6. Infiltration of Immune Cells in E. coli Sepsis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. DEG Identification and Functional Enrichment
3.2. MCODE Analysis
3.3. Weighted Gene Coexpression Network Analysis (WGCNA) of E. coli Infection and Other Bacterial Infections
3.4. Potential E. coli Hub Genes
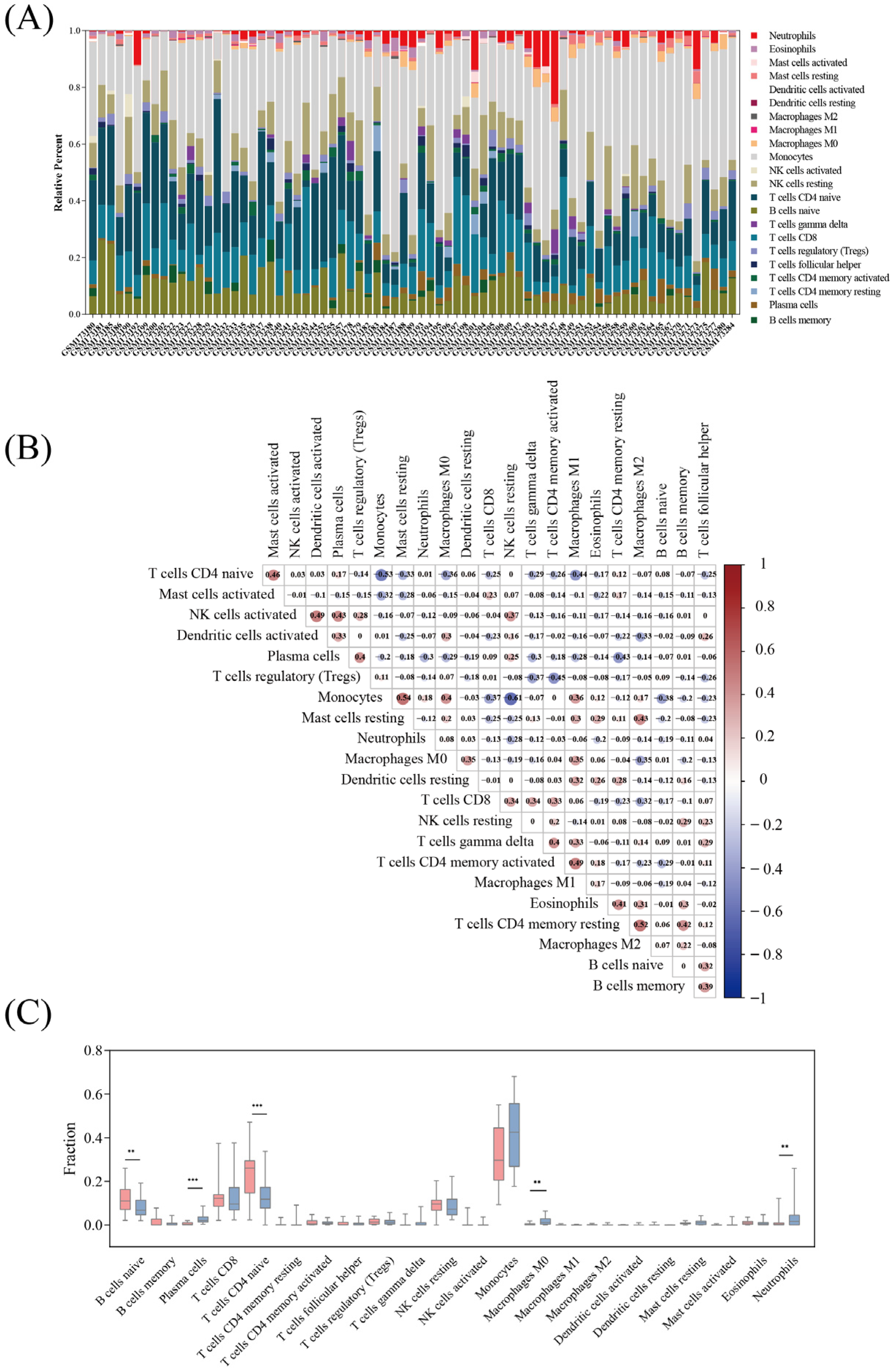
3.5. Immune Cell Infiltration
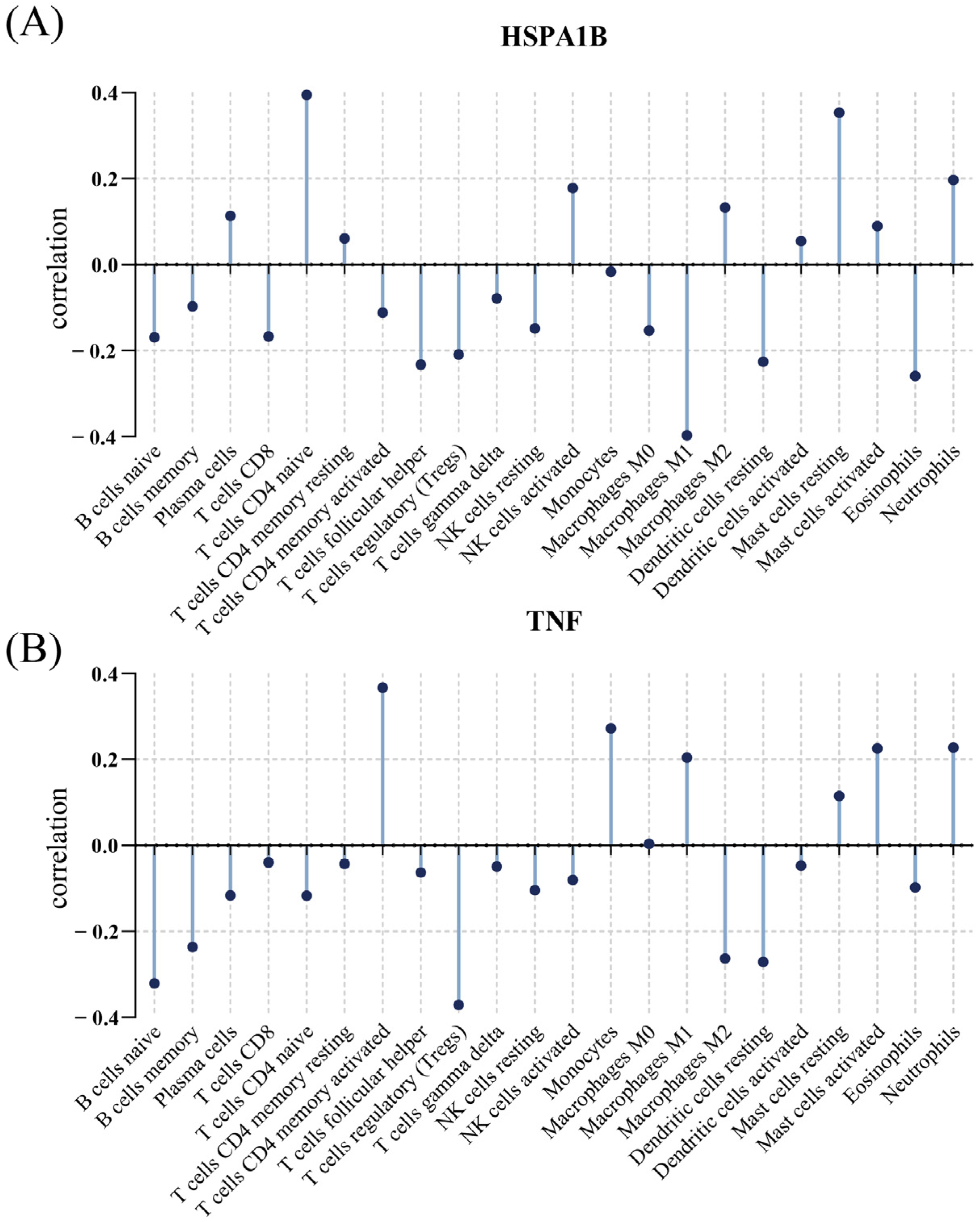
3.6. Relationship between Immunological Cells and Hub Genes
3.7. Clinical Features of E. coli Infection
3.8. Combined Analysis with Clinical Practice
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Standing up to Infectious Disease. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1.
- Rudd, K.E.; Johnson, S.C.; Agesa, K.M.; Shackelford, K.A.; Tsoi, D.; Kievlan, D.R.; Colombara, D.V.; Ikuta, K.S.; Kissoon, N.; Finfer, S.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Sepsis Incidence and Mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markwart, R.; Saito, H.; Harder, T.; Tomczyk, S.; Cassini, A.; Fleischmann-Struzek, C.; Reichert, F.; Eckmanns, T.; Allegranzi, B. Epidemiology and Burden of Sepsis Acquired in Hospitals and Intensive Care Units: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 1536–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Q.; Shao, W.X.; Wang, Q.Q.; Mao, J.H. An Imbalance of T Cell Subgroups Exists in Children with Sepsis. Microbes Infect. 2019, 21, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramilo, O.; Allman, W.; Chung, W.; Mejias, A.; Ardura, M.; Glaser, C.; Wittkowski, K.M.; Piqueras, B.; Banchereau, J.; Palucka, A.K.; et al. Gene Expression Patterns in Blood Leukocytes Discriminate Patients with Acute Infections. Blood 2007, 109, 2066–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faix, J.D. Biomarkers of Sepsis. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2013, 50, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glik, J.; Kawecki, M.; Gaździk, T.; Nowak, M. The Impact of the Types of Microorganisms Isolated from Blood and Wounds on the Results of Treatment in Burn Patients with Sepsis. Pol. Prz. Chir. 2012, 84, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croxen, M.A.; Law, R.J.; Scholz, R.; Keeney, K.M.; Wlodarska, M.; Finlay, B.B. Recent Advances in Understanding Enteric Pathogenic Escherichia Coli. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 822–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurtsen, J.; de Been, M.; Weerdenburg, E.; Zomer, A.; McNally, A.; Poolman, J. Genomics and Pathotypes of the Many Faces of Escherichia Coli. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2022, 46, fuac031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Pastor, L.; Geurtsen, J.; Baugh, B.; El Khoury, A.C.; Kalu, N.; Krishnarajah, G.; Gauthier-Loiselle, M.; Bungay, R.; Cloutier, M.; Saade, E. Economic Burden of Invasive Escherichia Coli Disease among Older Adult Patients Treated in Hospitals in the United States. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2023, 29, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshammari, M.K.; Alsanad, A.H.; Alnusayri, R.J.; Alanazi, A.S.; Shamakhi, F.Q.; Alshahrani, K.M.; Alshahrani, A.M.; Yahya, G.; Alshahrani, A.A.; Alshahrani, T.S.; et al. Risk and Diagnostic Factors and Therapy Outcome of Neonatal Early Onset Sepsis in Icu Patients of Saudi Arabia: A Systematic Review and Meta Analysis. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1206389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abernethy, J.K.; Johnson, A.P.; Guy, R.; Hinton, N.; Sheridan, E.A.; Hope, R.J. Thirty Day All-Cause Mortality in Patients with Escherichia Coli Bacteraemia in England. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 251.e1–251.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.M.; Priestap, F.; Fisher, H.; Fowler, R.A.; Heyland, D.K.; Keenan, S.P.; Longo, C.J.; Morrison, T.; Bentley, D.; Antman, N. A Prospective, Observational Registry of Patients with Severe Sepsis: The Canadian Sepsis Treatment and Response Registry. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, H.R.; Shanley, T.P.; Sakthivel, B.; Cvijanovich, N.; Lin, R.; Allen, G.L.; Thomas, N.J.; Doctor, A.; Kalyanaraman, M.; Tofil, N.M.; et al. Genome-Level Expression Profiles in Pediatric Septic Shock Indicate a Role for Altered Zinc Homeostasis in Poor Outcome. Physiol. Genom. 2007, 30, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, P.; Smith, C.L.; Forster, T.; Craigon, M.; Ross, A.J.; Khondoker, M.R.; Ivens, A.; Lynn, D.J.; Orme, J.; Jackson, A.; et al. Whole Blood Gene Expression Profiling of Neonates with Confirmed Bacterial Sepsis. Genome Data 2015, 3, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaeder, M.C.; Moorman, J.R.; Tran, C.A.; Keim-Malpass, J.; Zschaebitz, J.V.; Lake, D.E.; Clark, M.T. Predictive Analytics in the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit for Early Identification of Sepsis: Capturing the Context of Age. Pediatr. Res. 2019, 86, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dix, A.; Hünniger, K.; Weber, M.; Guthke, R.; Kurzai, O.; Linde, J. Biomarker-Based Classification of Bacterial and Fungal Whole-Blood Infections in a Genome-Wide Expression Study. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Li, B.; Jia, L.; Li, Y. Identification of Core Genes and Pathways in Melanoma Metastasis Via Bioinformatics Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. Wgcna: An R Package for Weighted Correlation Network Analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Horvath, S. A General Framework for Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2005, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Robust Enumeration of Cell Subsets from Tissue Expression Profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Khodadoust, M.S.; Liu, C.L.; Newman, A.M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Profiling Tumor Infiltrating Immune Cells with Cibersort. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1711, 243–259. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, W.; Zheng, P.; Luo, D.; Xie, Q.; Liu, F.; Shao, Q.; Zhao, N.; Qian, K. Lpin1 Is a Regulatory Factor Associated with Immune Response and Inflammation in Sepsis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 820164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentles, A.J.; Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Bratman, S.V.; Feng, W.; Kim, D.; Nair, V.S.; Xu, Y.; Khuong, A.; Hoang, C.D.; et al. The Prognostic Landscape of Genes and Infiltrating Immune Cells across Human Cancers. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angus, D.C.; van der Poll, T. Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, T.; Yamakawa, K.; Ogura, H.; Kushimoto, S.; Saitoh, D.; Fujishima, S.; Otomo, Y.; Kotani, J.; Umemura, Y.; Sakamoto, Y.; et al. Epidemiology of Sepsis and Septic Shock in Intensive Care Units between Sepsis-2 and Sepsis-3 Populations: Sepsis Prognostication in Intensive Care Unit and Emergency Room (Spice-Icu). J. Intensive Care 2020, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivers, E.; Nguyen, B.; Havstad, S.; Ressler, J.; Muzzin, A.; Knoblich, B.; Peterson, E.; Tomlanovich, M. Early Goal-Directed Therapy in the Treatment of Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonsen, K.A.; Anderson-Berry, A.L.; Delair, S.F.; Davies, H.D. Early-Onset Neonatal Sepsis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 21–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doenhardt, M.; Seipolt, B.; Mense, L.; Winkler, J.L.; Thürmer, A.; Rüdiger, M.; Berner, R.; Armann, J. Neonatal and Young Infant Sepsis by Group B Streptococci and Escherichia Coli: A Single-Center Retrospective Analysis in Germany-Gbs Screening Implementation Gaps and Reduction in Antibiotic Resistance. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2020, 179, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, A.; Adhikari, P.; Shenoy, S.; Saralaya, V. Genomic Analysis and Clinical Importance of Escherichia Coli Isolate from Patients with Sepsis. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2015, 58, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKinnon, M.C.; McEwen, S.A.; Pearl, D.L.; Lyytikäinen, O.; Jacobsson, G.; Collignon, P.; Gregson, D.B.; Valiquette, L.; Laupland, K.B. Increasing Incidence and Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli Bloodstream Infections: A Multinational Population-Based Cohort Study. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2021, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chan PH, Y.; Lau HY, S.; Tsoi, K.; Lam, H.S. Epidemiologic Changes of Neonatal Early-Onset Sepsis after the Implementation of Universal Maternal Screening for Group B Streptococcus in Hong Kong. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2023, 42, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.K.; Trotta, E.; Simeonov, D.R.; Marson, A.; Bluestone, J.A. Revisiting Il-2: Biology and Therapeutic Prospects. Sci. Immunol. 2018, 3, eaat1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, R.T.; Araújo, O.R.; Brunialti MK, C.; Assunção MS, C.; Azevedo LC, P.; Freitas, F.; Salomão, R. T Helper Type Cytokines in Sepsis: Time-Shared Variance and Correlation with Organ Dysfunction and Hospital Mortality. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 23, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, T.; Mitoma, H.; Harashima, S.; Tsukamoto, H.; Shimoda, T. Transmembrane Tnf-Alpha: Structure, Function and Interaction with Anti-Tnf Agents. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 1215–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtmann, M.H.; Neurath, M.F. Differential Tnf-Signaling in Chronic Inflammatory Disorders. Curr. Mol. Med. 2004, 4, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Huang, X.; Yang, Y.; Lei, Z.; Chen, Q.; Guo, X.; Tian, J.; Gao, X. Clinical Analysis of An69st Membrane Continuous Venous Hemofiltration in the Treatment of Severe Sepsis. Open Med. (Wars) 2023, 18, 20230784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, G.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Chen, K.; Liu, P.; Ling, B.; Yang, Y. Role of Serum Inflammatory Cytokines in Sepsis Rats Following Bmscs Transplantation: Protein Microarray Analysis. Cell Transplant. 2023, 32, 9636897231198175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, R.; Nillegoda, N.B.; Mayer, M.P.; Bukau, B. The Hsp70 Chaperone Network. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2019, 20, 665–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radons, J. The Human Hsp70 Family of Chaperones: Where Do We Stand? Cell Stress Chaperones 2016, 21, 379–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, M.P. Hsp70 Chaperone Dynamics and Molecular Mechanism. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2013, 38, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temple, S.E.; Cheong, K.Y.; Ardlie, K.G.; Sayer, D.; Waterer, G.W. The Septic Shock Associated Hspa1b1267 Polymorphism Influences Production of Hspa1a and Hspa1b. Intensive Care Med. 2004, 30, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asea, A.; Kraeft, S.K.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Stevenson, M.A.; Chen, L.B.; Finberg, R.W.; Koo, G.C.; Calderwood, S.K. Hsp70 Stimulates Cytokine Production through a Cd14-Dependant Pathway, Demonstrating Its Dual Role as a Chaperone and Cytokine. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Xiong, H.; Li, W.; Peng, L.; Zheng, Y.; Liao, W.; Zhou, M.; Xu, Y. T Cell Activation Profiles Can Distinguish Gram Negative/Positive Bacterial Sepsis and Are Associated with Icu Discharge. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1058606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Tu, H.; Bai, X.; Qin, S.; Li, Z. Intrinsic/Extrinsic Apoptosis and Pyroptosis Contribute to the Selective Depletion of B Cell Subsets in Septic Shock Patients. Shock 2023, 60, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

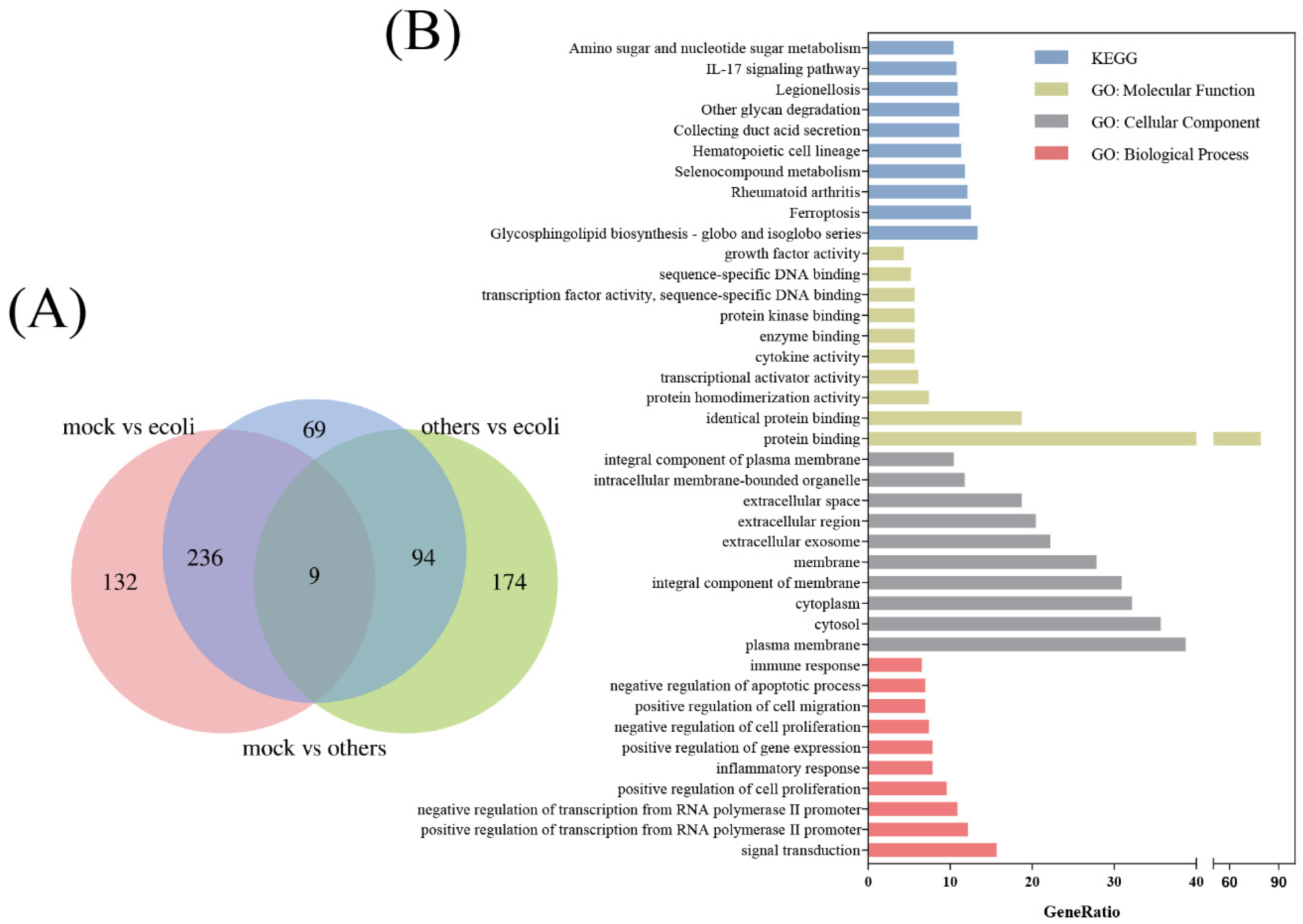
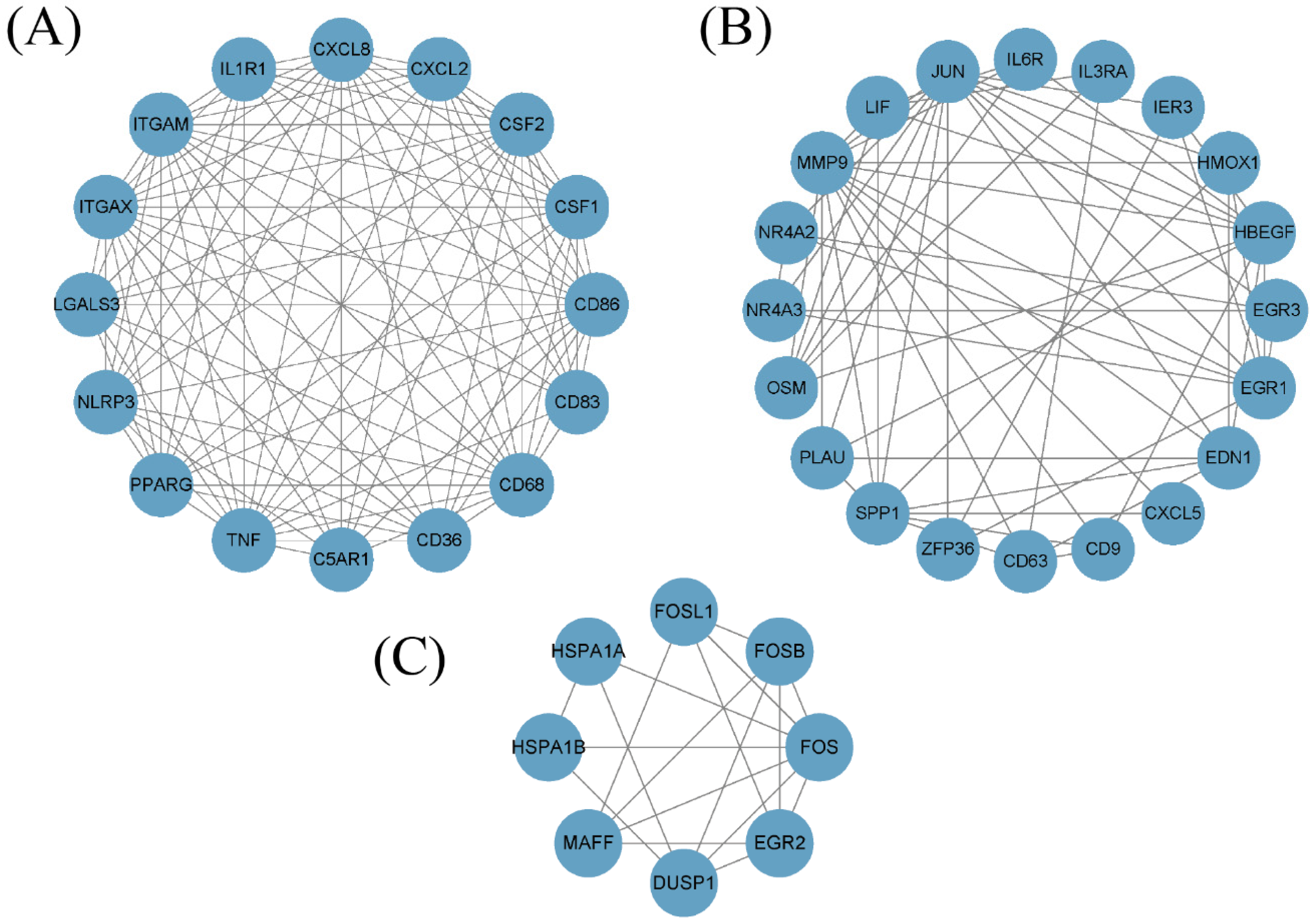
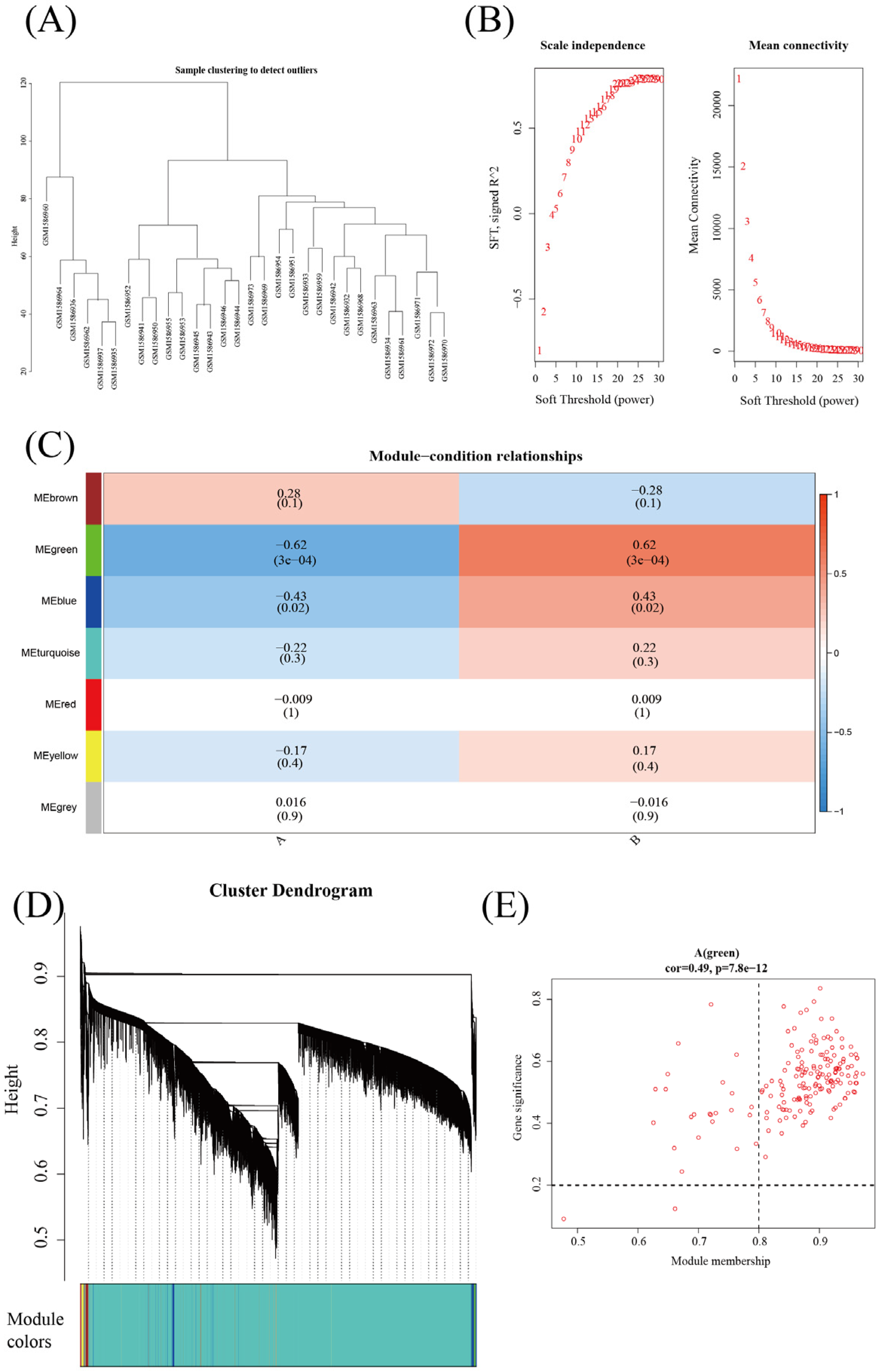
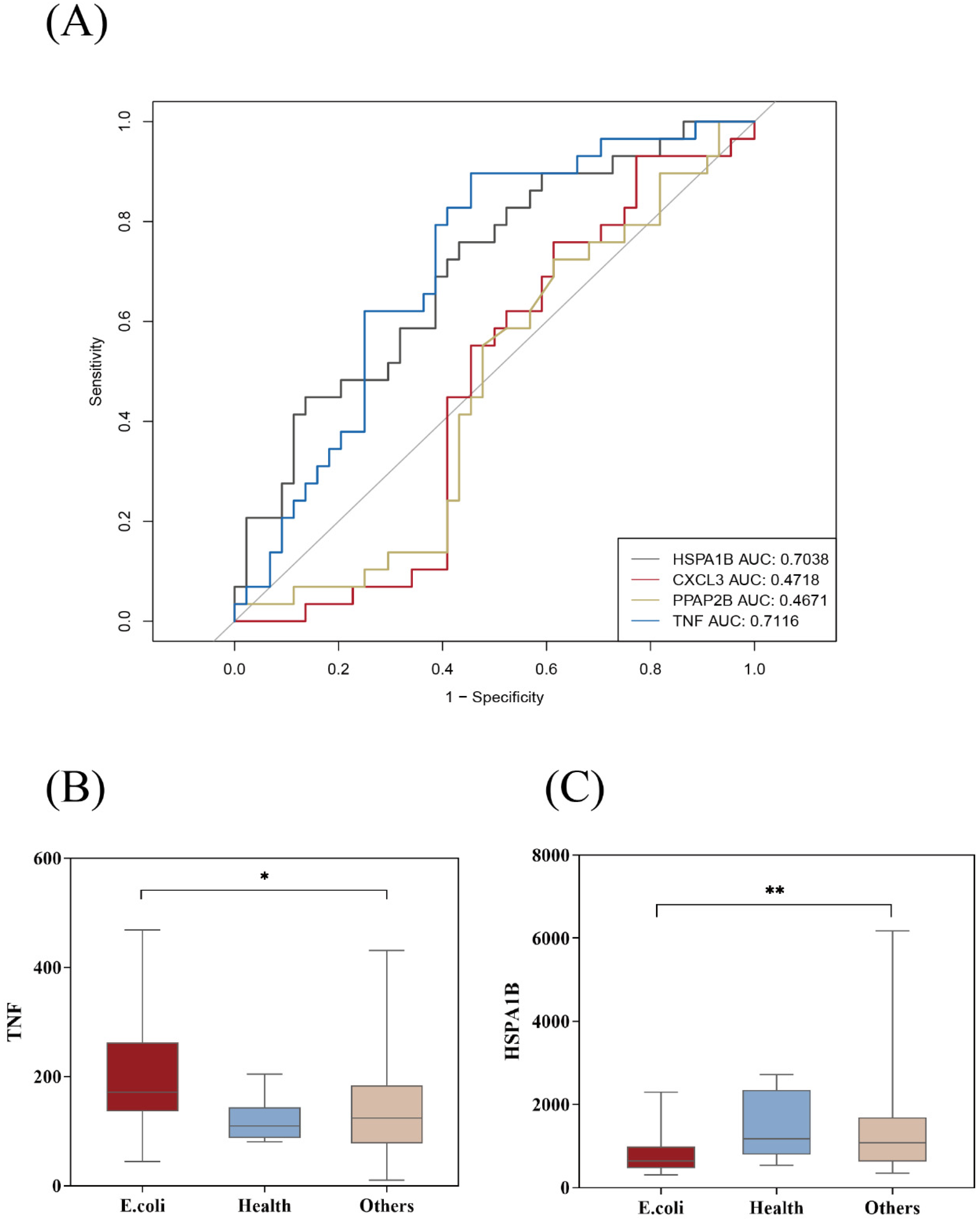

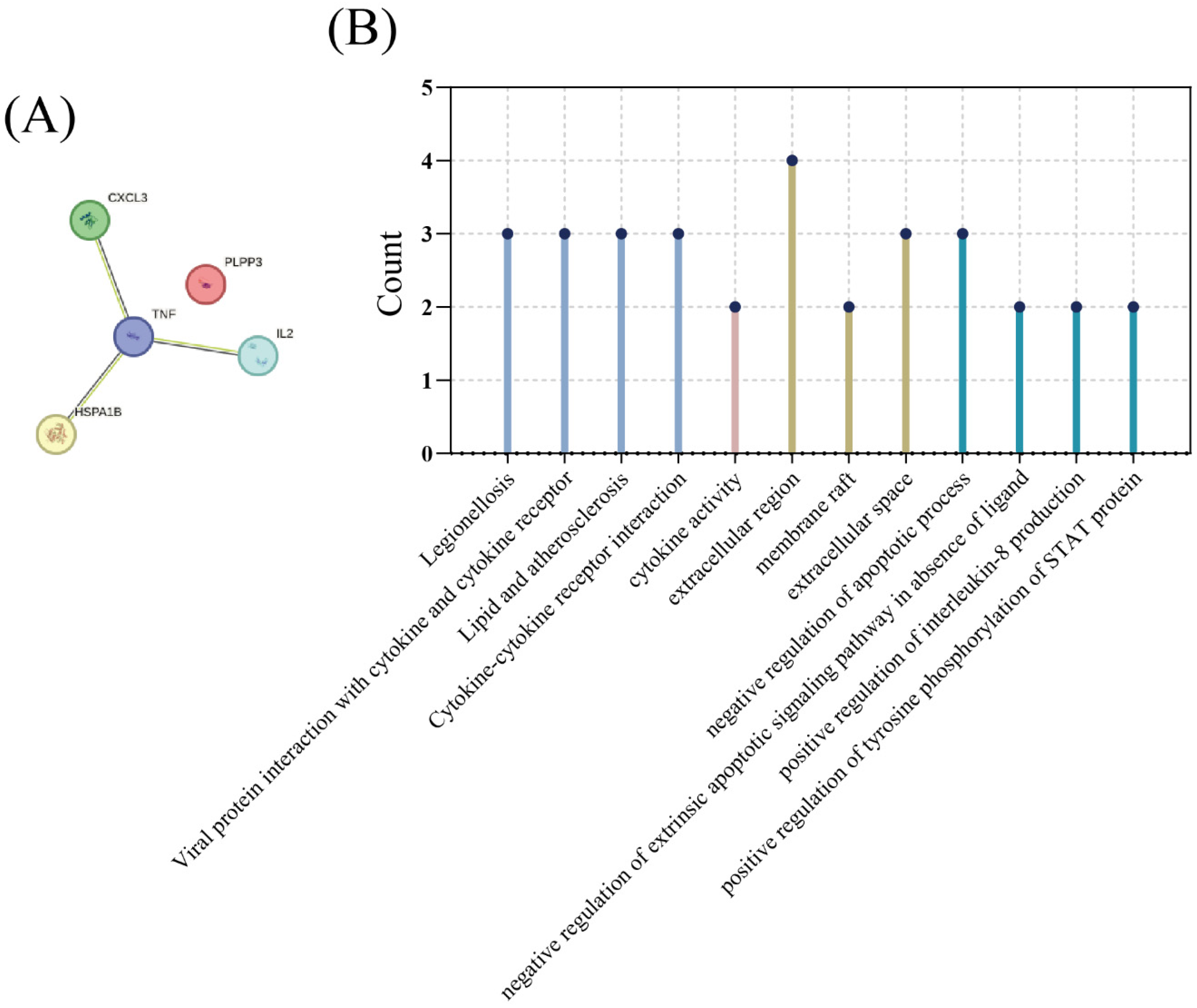
| Nine Genes in Figure 2A | WGCNA | MCODE |
|---|---|---|
| LOC728830 | HSPA1B | HSPA1B |
| EDN1 | PPAP2B | TNF |
| HSPA1B | CXCL2 | |
| PPAP2B | TNF | |
| CXCL2 | ||
| TNF | ||
| LOC643930 | ||
| LOC387763 | ||
| LOC642093 |
| Characteristics | E. coli (n = 26) | G+ (n = 72) | P E. coli vs. G+ | G− (n = 11) | P E. coli vs. G− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, F, n (%) | 9 (34.6) | 32 (40.5) | 0.263 | 7 (58.3) | 0.206 |
| Age (month) median (IQR) | 2 (0, 11) | 24 (4, 72) | 0.000 | 10.5 (2.3, 4.5) | 0.3680 |
| Laboratory parameters median (IQR) | |||||
| Albumin (g/L) | 36.4 (33.1, 37.2) | 39.5 (35.7, 43.3) | 0.002 | 36.5 (33.8, 38.5) | 0.370 |
| Globulin (g/L) | 18.3 (16.6, 20.5) | 23.3 (17.4, 27.3) | 0.004 | 20.0 (18.3, 23.6) | 0.342 |
| Total bilirubin (mol/L) | 22.8 (8.7, 137.8) | 8.6 (5.1, 14.6) | 0.033 | 9.2 (5.5, 75.0) | 0.071 |
| Indirect bilirubin (mol/L) | 14.1 (7.0, 122.9) | 6.7 (3.8, 11.1) | 0.031 | 7.3 (4.3, 28.5) | 0.019 |
| Adenosine deaminase (U/L) | 10.1 (5.5, 13.6) | 13.95 (9.5, 18.8) | 0.033 | 13.7 (6.3, 22.4) | 0.173 |
| Prealbumin (g/L) | 100.3 (61.2, 118.4) | 139.1 (108.1, 188.6) | 0.000 | 110.9 (91.3, 132.7) | 0.063 |
| Creatine kinase (U/L) | 77.4 (50.0, 131.5) | 123.5 (60.3, 271.8) | 0.023 | 72.0 (59.0, 84.0) | 0.447 |
| Neutrophil (%) | 46.8 (37.4, 61.5) | 61.5 (41.8, 77.1) | 0.037 | 61.0 (21.3, 90.4) | 0.578 |
| Monocyte (%) | 9.1 (6.8, 11.9) | 4.8 (6.7, 8.4) | 0.006 | 5.6 (3.0, 8.6) | 0.043 |
| TNFα (ng/mL) | 2.4 (1.9, 6.0) | 2.1 (1.4, 4.1) | 0.332 | 1.8 (1.6, 2.1) | 0.619 |
| IL2 (pg/mL) | 2.1 (1.2, 3.1) | 2.8 (2.4, 4.2) | 0.023 | 2.8 (2.0, 4.85) | 0.115 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, Q.; Chen, D.; Chen, S.; Ru, X.; Ye, Q. Escherichia coli Infection Sepsis: An Analysis of Specifically Expressed Genes and Clinical Indicators. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3542. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13233542
Shao Q, Chen D, Chen S, Ru X, Ye Q. Escherichia coli Infection Sepsis: An Analysis of Specifically Expressed Genes and Clinical Indicators. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(23):3542. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13233542
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Qingyi, Danlei Chen, Simiao Chen, Xuanwen Ru, and Qing Ye. 2023. "Escherichia coli Infection Sepsis: An Analysis of Specifically Expressed Genes and Clinical Indicators" Diagnostics 13, no. 23: 3542. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13233542
APA StyleShao, Q., Chen, D., Chen, S., Ru, X., & Ye, Q. (2023). Escherichia coli Infection Sepsis: An Analysis of Specifically Expressed Genes and Clinical Indicators. Diagnostics, 13(23), 3542. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13233542





