Radiologic Evaluation of Portosystemic Shunts in Humans and Small Animals: Review of the Literature with Clinical Case Reports
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Clinical Case Presentations
2.1. Case A (Human)
2.2. Case B (Human)
2.3. Case C (Dog)
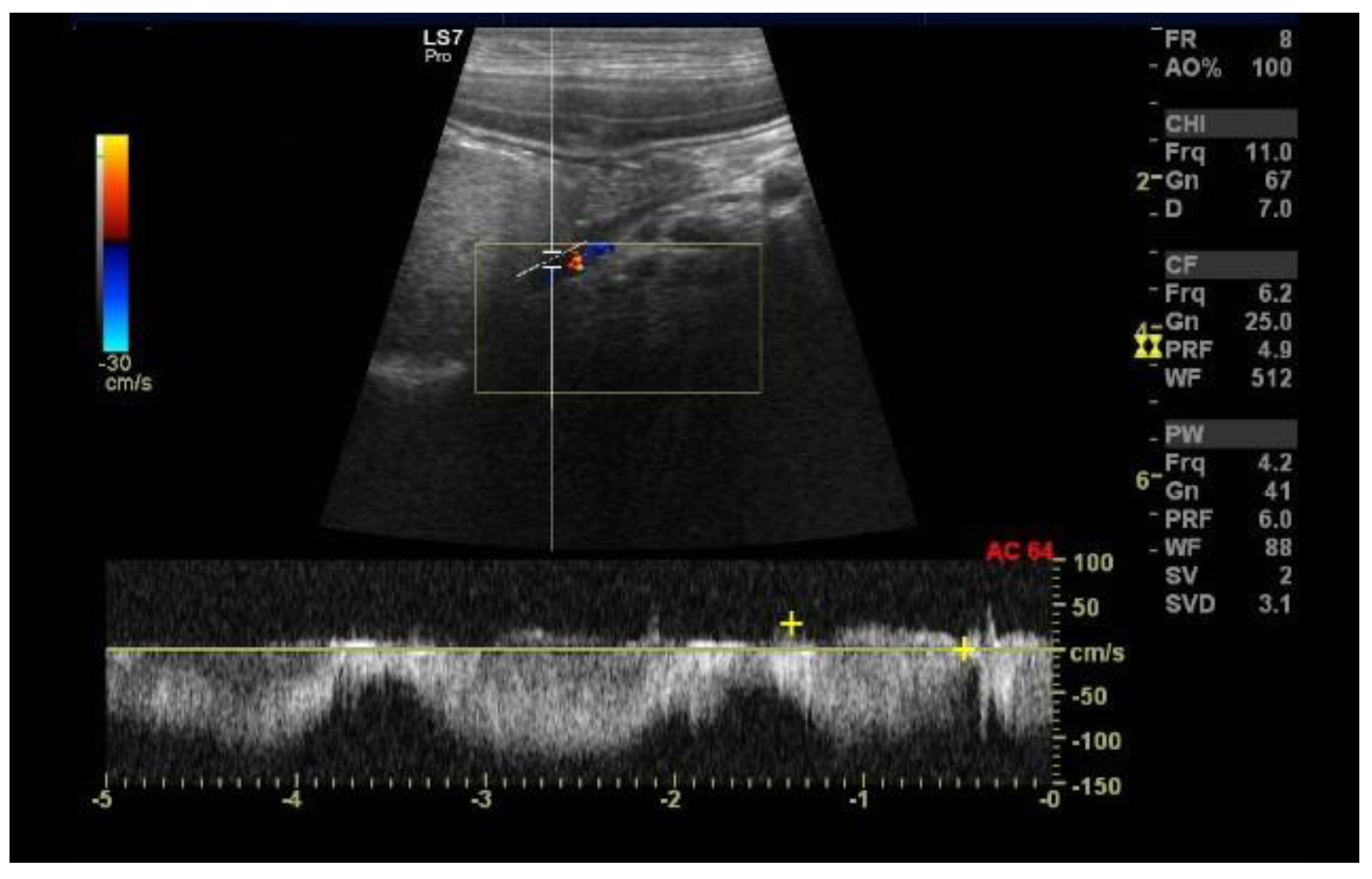
2.4. Case D (Dog)
2.5. Case E (Cat)
3. Anatomy of the Portal Venous System
4. Congenital Portosystemic Shunts
4.1. Embryology of the Portal Venous System
4.2. Congenital Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts
4.3. Congenital Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts
4.4. Aetiology of Congenital Portosystemic Shunts
5. Acquired Portosystemic Shunts
6. Diagnostic Imaging of Portosystemic Shunts
6.1. Signs of Portal Hypertension
6.2. Liver
6.3. Intrahepatic Portal Veins
6.4. Portal Vein Size
6.5. Portal Vein Blood Flow
6.6. Portal Vein Tributaries
6.7. Inferior (Caudal) Vena Cava
6.8. Azygos Vein
6.9. Acquired Portosystemic Shunts
6.10. Kidneys
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Michels, N.A. Newer anatomy of the liver and its variant blood supply and collateral circulation. Am. J. Surg. 1966, 112, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahadori, A.; Kuhlmann, B.; Debray, D.; Franchi-Abella, S.; Wacker, J.; Beghetti, M.; Wildhaber, B.E.; McLin, V.A. Presentation of Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in Children. Children 2022, 9, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolini, G. Anomalies of the portal venous system in dogs and cats as seen on multidetector-row computed tomography: An overview and systematization proposal. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papamichail, M.; Pizanias, M.; Heaton, N. Congenital portosystemic venous shunt. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2018, 177, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, C.R.; White, R.N. Morphology of congenital intrahepatic portacaval shunts in dogs and cats. Vet. Rec. 1998, 142, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, G.; Superina, R. Congenital absence of the portal vein: Two cases and a proposed classification system for portasystemic vascular anomalies. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1994, 29, 1239–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abernethy, J. Account of Two Instances of Uncommon Formation in the Viscera of the Human Body: From the Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Med. Facts Obs. 1797, 7, 100–108. [Google Scholar]
- White, R.N.; Shales, C.; Parry, A.T. New perspectives on the development of extrahepatic portosystemic shunts. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2017, 58, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Steenbeek, F.G.; Van Den Bossche, L.; Leegwater, P.A.J.; Rothuizen, J. Inherited liver shunts in dogs elucidate pathways regulating embryonic development and clinical disorders of the portal vein. Mamm. Genome 2012, 23, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Anjou, M.A. The Sonographic Search for Portosystemic Shunts. Clin. Tech. Small Anim. Pract. 2007, 22, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berent, A.C.; Tobias, K.M. Portosystemic Vascular Anomalies. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2009, 39, 513–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tivers, M.; Lipscomb, V. Congenital portosystemic shunts in cats. Investigation, diagnosis and stabilisation. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2011, 13, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.N.; Parry, A.T. Morphology of congenital portosystemic shunts involving the left colic vein in dogs and cats. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2016, 57, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, J.M.; van den Ingh, T.S.G.A.M.; Bunch, S.E.; Rothuizen, J.; Washabau, R.J.; Desmet, V.J. Morphological classification of circulatory disorders of the canine and feline liver. In WSAVA Standards for Clinical and Histological Diagnosis of Canine and Feline Liver Diseases; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 41–59. ISBN 9780702027918. [Google Scholar]
- Marks, C. Developmental basis of the portal venous system. Am. J. Surg. 1969, 117, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guérin, F.; Blanc, T.; Gauthier, F.; Abella, S.F.; Branchereau, S. Congenital portosystemic vascular malformations. Semin. Pediatr. Surg. 2012, 21, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stringer, M.D. The clinical anatomy of congenital portosystemic venous shunts. Clin. Anat. 2008, 21, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, E.R.; Davenport, M. Congenital extrahepatic portocaval shunts—The Abernethy malformation. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1997, 32, 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, N.C.; Nelson, L.L. Anatomy of extrahepatic portosystemic shunts in dogs as determined by computed tomography angiography. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2011, 52, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, K.; Kanemoto, H.; Ohno, K.; Takahashi, M.; Fujiwara, R.; Nishimura, R.; Tsujimoto, H. Computed tomographic morphology and clinical features of extrahepatic portosystemic shunts in 172 dogs in Japan. Vet. J. 2014, 199, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, J.T.; Bohling, M.W.; Tillson, D.M.; Wright, J.C.; Ballagas, A.J. Portosystemic shunts: Diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of 64, cases (1993–2002). J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2003, 39, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, J.T.; Martin, R.A.; Constantinescu, G.M. The anatomy and embryology of portosystemic shunts in dogs and cats. Semin. Vet. Med. Surg. Small Anim. 1990, 5, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Cha, S.H.; Han, J.K.; Han, M.C. Intrahepatic portosystemic venous shunt. Am. J. Roentgenol 1990, 155, 527–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şenocak, E.; Oǧuz, B.; Edgüer, T.; Cila, A. Congenital intrahepatic portosystemic shunt with variant inferior right hepatic vein. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2008, 14, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tisdall, P.L.C.; Hunt, G.B.; Borg, R.P.; Malik, R. Anatomy of the ductus venosus in neonatal dogs (Canis familiaris). Anat. Histol. Embryol. 1997, 26, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, O.; Franchi-Abella, S.; Branchereau, S.; Pariente, D.; Gauthier, F.; Jacquemin, E. Congenital portosystemic shunts in children: Recognition, evaluation, and management. Semin. Liver Dis. 2012, 32, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganelli, M.; Lipsich, J.E.; Sciveres, M.; Alvarez, F. Predisposing Factors for Spontaneous Closure of Congenital Portosystemic Shunts. J. Pediatr. 2015, 167, 931–935.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plut, D.; Gorjanc, T. A case of a newborn with an intrahepatic congenital portosystemic venous shunt with concurrent congenital duodenal web. Acta Radiol. Open 2019, 8, 205846011985417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahvis, G.P.; Lindell, S.L.; Thomas, R.S.; McCuskey, R.S.; Murphy, C.; Glover, E.; Bentz, M.; Southard, J.; Bradfield, C.A. Portosystemic shunting and persistent fetal vascular structures in aryl hydrocarbon receptor-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10442–10447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baragatti, B.; Ciofini, E.; Scebba, F.; Angeloni, D.; Sodini, D.; Luin, S.; Ratto, G.M.; Ottaviano, V.; Pagni, E.; Paolicchi, A.; et al. Cytochrome P-450 3A13 and endothelin jointly mediate ductus arteriosus constriction to oxygen in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Hear. Circ. Physiol. 2011, 300, H892–H901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Mitchell, D.G.; Ito, K. Portosystemic collaterals of the upper abdomen: Review of anatomy and demonstration on MR imaging. Abdom. Imaging 2000, 25, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, C.; Velasco, M.; Marcuello, P.; Tejedor, D.; De Campo, L.; Friera, A. Congenital and acquired anomalies of the portal venous system. Radiographics 2002, 22, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, G. Acquired portal collateral circulation in the dog and cat. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2010, 51, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, S.; Kemp, W.; Lubel, J. Portal hypertension: Pathophysiology, diagnosis and management. Intern. Med. J. 2015, 45, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sereda, C.W.; Adin, C.A. Methods of gradual vascular occlusion and their applications in treatment of congenital portosystemic shunts in dogs: A review. Vet. Surg. 2005, 34, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiemessen, I.; Rothuizen, J.; Voorhout, G. Ultrasonography in the diagnosis of congenital portosystemic shunts in dogs. Vet. Q. 1995, 17, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, C.R.; Forster-van Hijfte, M.A.; White, R.N.; McEvoy, F.J.; Rutgers, H.C. Ultrasonographic diagnosis of congenital portosystemic shunt in 14 cats. J. Small Anim. Pract. 1996, 37, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyles, A.E.; Hardie, E.M.; Mehl, M.; Gregory, C.R. Evaluation of ameroid ring constrictors for the management of single extrahepatic portosystemic shunts in cats: 23 cases (1996–2001). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2002, 220, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Anjou, M.A.; Penninck, D.; Cornejo, L.; Pibarot, P. Ultrasonographic diagnosis of portosystemic shunting in dogs and cats. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2004, 45, 424–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmári, V.; Rothuizen, J.; Van Den Ingh, T.S.G.A.M.; Van Sluijs, F.J.; Voorhout, G. Ultrasonographic findings in dogs with hyperammonemia: 90 Cases (2000–2002). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2004, 224, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolondi, L.; Mazziotti, A.; Arienti, V.; Casanova, P.; Gasbarrini, G.; Cavallari, A.; Bellusci, R.; Gozzetti, G.; Possati, L.; Labò, G. Ultrasonographic study of portal venous system in portal hypertension and after portosystemic shunt operations. Surgery 1984, 95, 261–269. [Google Scholar]
- Lamb, C.R. Pancreatic edema in dogs with hypoalbuminemia or portal hypertension. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 1999, 13, 498–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, C.R. Ultrasonographic diagnosis of congenital portosystemic shunts in dogs: Results of a prospective study. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 1996, 37, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, C.R. Ultrasonography of portosystemic shunts in dogs and cats. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 1998, 28, 725–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konuş, Ö.L.; Özdemir, A.; Akkaya, A.; Erbaş, G.; Çelik, H.; Işik, S. Normal liver, spleen, and kidney dimensions in neonates, infants, and children: Evaluation with sonography. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1998, 171, 1693–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrigley, R.H.; Konde, L.J.; Park, R.D.; Lebel, J.L. Ultrasonographic diagnosis of portacaval shunts in young dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1987, 191, 421–424. [Google Scholar]
- Szatmári, V.; Sótonyi, P.; Vörös, K. Normal duplex Doppler waveforms of major abdominal blood vessels in dogs: A review. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2001, 42, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.K.; Chang, S.D.; Duddalwar, V.A.; Comin, J.M.; Perera, W.; Lau, W.F.E.; Bekhit, E.K.; Hennessy, O.F. Imaging assessment of congenital and acquired abnormalities of the portal venous system. Radiographics 2011, 31, 905–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Anjou, M.A.; Huneault, L. Imaging diagnosis–Complex intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in a dog. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2008, 49, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gaetano, A.M.; Rinaldi, P.; Barbaro, B.; Mirk, P.; Di Stasi, C.; Gui, B.; Maresca, G.; Bonomo, L. Intrahepatic portosystemic venous shunts: Color Doppler sonography. Abdom. Imaging 2007, 32, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micol, C.; Marsot, J.; Boublay, N.; Pilleul, F.; Berthezene, Y.; Rode, A. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound: A new method for TIPS follow-up. Abdom. Imaging 2012, 37, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patriquin, H.B.; Perreault, G.; Grignon, A.; Boisvert, J.; Filiatrault, D.; Garel, L.; Blanchard, H. Normal portal venous diameter in children. Pediatr. Radiol. 1990, 20, 451–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Demartines, N.; Soler, L.; Schnyder, P.; Denys, A. Portal vein normal anatomy and variants: Implication for liver surgery and portal vein embolization. Semin. Intervent. Radiol. 2008, 25, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, D.E.; Schelling, C.G.; Saunders, H.M.; Orsher, R.J. Correlation of ultrasonographic findings with surgical, portographic, and necropsy findings in dogs and cats with portosystemic shunts: 63 cases (1987–1993). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1995, 207, 1190–1193. [Google Scholar]
- Lamb, C.R.; Mahoney, P.N. Comparison of three methods for calculating portal blood flow velocity in dogs using duplex-doppler ultrasonography. Vet. Radiol. 1994, 35, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyland, T.G.; Fisher, P.E. Evaluation of experimentally induced canine hepatic cirrhosis using duplex doppler ultrasound. Vet. Radiol. 1990, 31, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranpour, P.; Lall, C.; Houshyar, R.; Helmy, M.; Yang, A.; Choi, J., II; Ward, G.; Goodwin, S.C. Altered Doppler flow patterns in cirrhosis patients: An overview. Ultrasonography 2015, 35, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmári, V.; van den Ingh, T.S.G.A.M.; Fenyves, B.; Sótonyi, P.; Kótai, I.; Petrási, Z.; Vörös, K. Portal hypertension in a dog due to circumscribed fibrosis of the wall of the extrahepatic portal vein. Vet. Rec. 2002, 150, 602–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.N.; Parry, A.T. Morphology of congenital portosystemic shunts emanating from the left gastric vein in dogsand cats. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2013, 54, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.N.; Parry, A.T. Morphology of splenocaval congenital portosystemic shunts in dogs and cats. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2016, 57, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suter, P.F. Portal Vein Anomalies in the Dog: Their Angiographic Diagnosis. Vet. Radiol. 1975, 16, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwingenberger, A.L.; McLear, R.C.; Weisse, C. Diagnosis of arterioportal fistulae in four dogs using computed tomographic angiography. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2005, 46, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deppe, T.A.; Center, S.A.; Simpson, K.W.; Erb, H.N.; Randolph, J.F.; Dykes, N.L.; Yeager, A.E.; Reynolds, A.J. Glomerular filtration rate and renal volume in dogs with congenital portosystemic vascular anomalies before and after surgical ligation. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 1999, 13, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Umek, N.; Plut, D.; Krofič Žel, M.; Domanjko Petrič, A. Radiologic Evaluation of Portosystemic Shunts in Humans and Small Animals: Review of the Literature with Clinical Case Reports. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13030482
Umek N, Plut D, Krofič Žel M, Domanjko Petrič A. Radiologic Evaluation of Portosystemic Shunts in Humans and Small Animals: Review of the Literature with Clinical Case Reports. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(3):482. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13030482
Chicago/Turabian StyleUmek, Nejc, Domen Plut, Martina Krofič Žel, and Aleksandra Domanjko Petrič. 2023. "Radiologic Evaluation of Portosystemic Shunts in Humans and Small Animals: Review of the Literature with Clinical Case Reports" Diagnostics 13, no. 3: 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13030482
APA StyleUmek, N., Plut, D., Krofič Žel, M., & Domanjko Petrič, A. (2023). Radiologic Evaluation of Portosystemic Shunts in Humans and Small Animals: Review of the Literature with Clinical Case Reports. Diagnostics, 13(3), 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13030482







