Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound in Diagnosis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
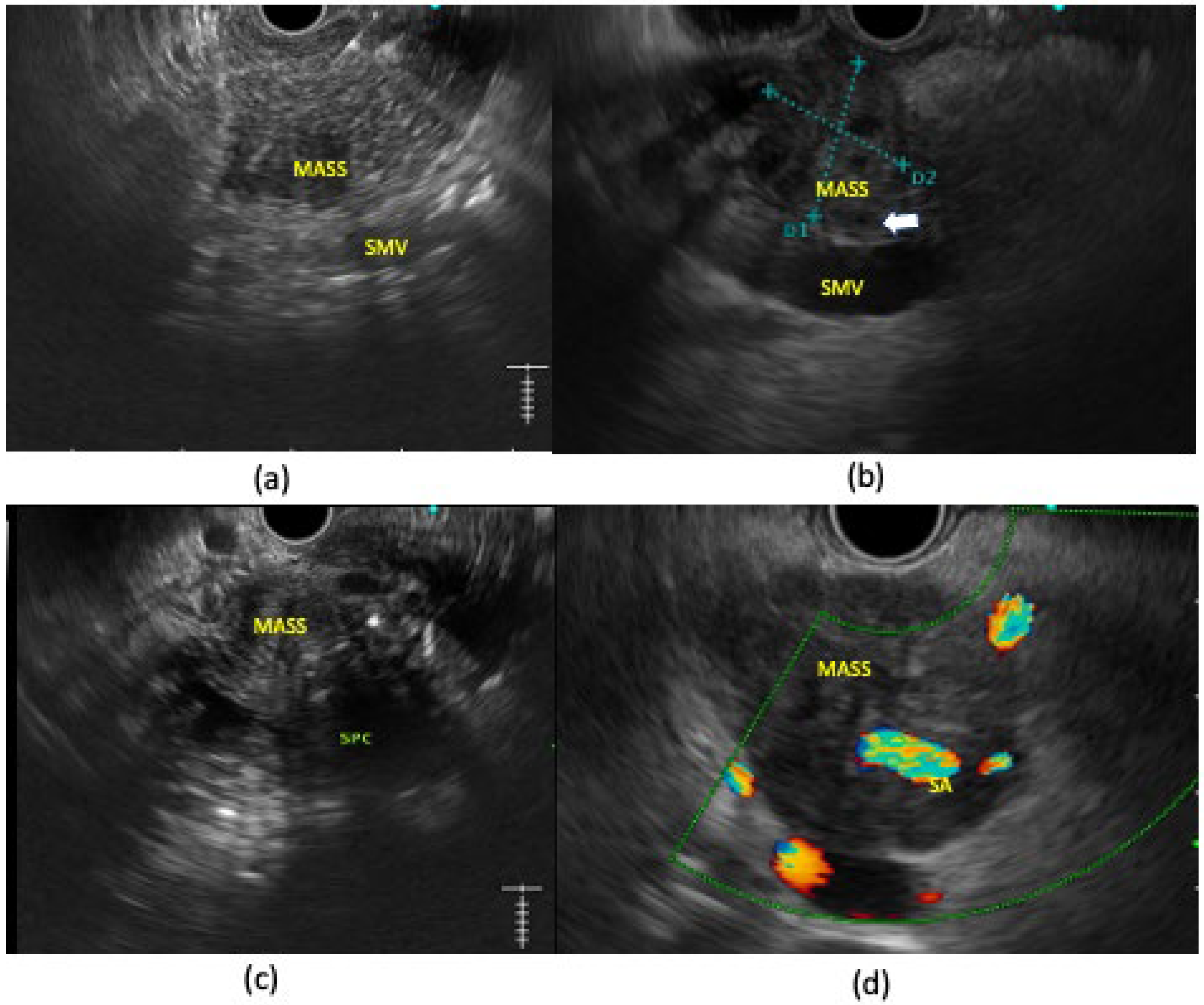
2. EUS in the Detection of Tumors
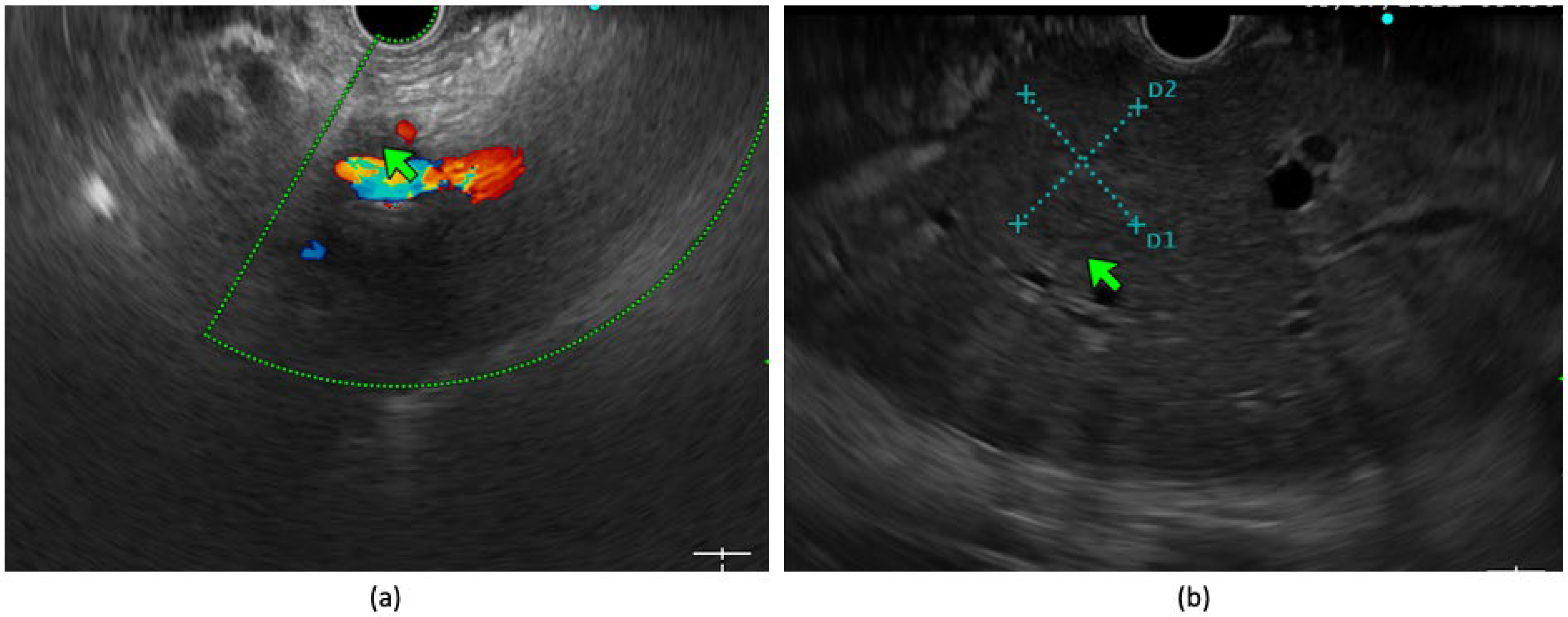
3. Role of EUS in the Staging of Tumors
4. Role of Contrast-Enhanced EUS
5. EUS Elastography
6. EUS-Guided Tissue Acquisition: Techniques and Variations
6.1. EUS FNB and FNB Needles
6.1.1. EUS FNB Needles
6.1.2. EUS FNB Needles
6.2. Technical Aspects in EUS TA
6.3. Role of On-Site Evaluation of the Sample (ROSE and MOSE)
6.3.1. ROSE in EUS TA
6.3.2. MOSE in EUS TA
6.4. Role of Repeat EUS TA
6.5. Effect of Biliary Drainage on EUS TA
6.6. Complications of EUS TA and Risk of Needle Tract Seeding (NTS)
7. Recent Advancement in EUS TA in Pancreatic Carcinoma
7.1. Role of EUS TA in the Era of Precision Medicine
7.2. Role of Artificial Intelligence in EUS for Pancreatic Carcinoma
7.3. Role of Organoid Technology in the Diagnosis of PDAC
7.4. Role of Liquid-Based Cytology
7.5. Automated Needles for EUS TA
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Younan, G. Pancreas Solid Tumors. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 100, 565–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abboud, Y.; Samaan, J.S.; Oh, J.; Jiang, Y.; Randhawa, N.; Lew, D.; Ghaith, J.; Pala, P.; Leyson, C.; Watson, R.; et al. Increasing Pancreatic Cancer Incidence in Young Women in the United States: A Population-Based Time-Trend Analysis, 2001–2018. Gastroenterology 2023, 164, 978–989.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizrahi, J.D.; Surana, R.; Valle, J.W.; Shroff, R.T. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2020, 395, 2008–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, L.D.; Canto, M.I.; Jaffee, E.M.; Simeone, D.M. Pancreatic Cancer: Pathogenesis, Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 386–402.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halbrook, C.J.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; di Magliano, M.P.; Maitra, A. Pancreatic cancer: Advances and challenges. Cell 2023, 186, 1729–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaddam, S.; Abboud, Y.; Oh, J.; Samaan, J.S.; Nissen, N.N.; Lu, S.C.; Lo, S.K. Incidence of Pancreatic Cancer by Age and Sex in the US, 2000–2018. JAMA 2021, 326, 2075–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.; Chawla, A.; O’Reilly, E.M. Pancreatic Cancer: A Review. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2021, 326, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varadarajulu, S.; Bang, J.Y. Role of Endoscopic Ultrasonography and Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography in the Clinical Assessment of Pancreatic Neoplasms. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 25, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, M.N.; Chaudhary, F.S.; Ehsan, A.; Suarez, A.L.; Muniraj, T.; Jamidar, P.; Aslanian, H.R.; Farrell, J.J. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and the management of pancreatic cancer. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2020, 7, e000408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, M.; Yoshida, T.; Itonaga, M.; Tamura, T.; Hatamaru, K.; Yamashita, Y. Impact of endoscopic ultrasonography on diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 54, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.F.; Meyenberger, C.; Bertschinger, P.; Schaer, R.; Marincek, B. Pancreatic tumors: Evaluation with endoscopic US, CT, and MR imaging. Radiology 1994, 190, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, H.; Kitano, M.; Suetomi, Y.; Maekawa, K.; Takeyama, Y.; Kudo, M. Utility of Contrast-Enhanced Endoscopic Ultrasonography for Diagnosis of Small Pancreatic Carcinomas. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2008, 34, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Okusaka, T.; Shimizu, K.; Furuse, J.; Ito, Y.; Hanada, K.; Shimosegawa, T.; Okazaki, K. Clinical practice guidelines for pancreatic cancer 2016 from the Japan pancreas society a synopsis. Pancreas 2017, 46, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, S.G.; Rao, B.B.; Ugbarugba, E.; Shah, Z.K.; Blaszczak, A.; Hinton, A.; Conwell, D.L.; Hart, P.A. Diagnostic performance of endoscopic ultrasound for detection of pancreatic malignancy following an indeterminate multidetector CT scan: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Surg. Endosc. 2017, 31, 4558–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Overbeek, K.; Levink, I.J.M.; Koopmann, B.D.M.; Harinck, F.; Konings, I.C.A.W.; Ausems, M.G.E.M.; Wagner, A.; Fockens, P.; van Eijck, C.H.; Koerkamp, B.G.; et al. Long-term yield of pancreatic cancer surveillance in high-risk individuals. Gut 2022, 71, 1152–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.; Guo, T.; Xu, T.; Zhang, S.; Lai, Y.; Wu, X.; Wu, D.; Feng, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, Q.; et al. The role of EUS in diagnosing focal autoimmune pancreatitis and differentiating it from pancreatic cancer. Endosc. Ultrasound 2021, 10, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izumi, Y.; Hanada, K.; Okazaki, A.; Minami, T.; Hirano, N.; Ikemoto, J.; Kanemitsu, K.; Nakadoi, K.; Shishido, T.; Katamura, Y.; et al. Endoscopic ultrasound findings and pathological features of pancreatic carcinoma in situ. Endosc. Int. Open 2019, 7, E585–E593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.B.; Lu, M.P.; Qian, X.X.; Chen, J.; Li, L.; Wang, J.W.; Zhang, Y. Diagnostic accuracy of EUS and CT of vascular invasion in pancreatic cancer: A systematic review. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 140, 2077–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamata, K.; Nakai, A.; Hyodo, T.; Chikugo, T.; Hara, A.; Otsuka, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Yoshikawa, T.; Ishikawa, R.; Okamoto, A.; et al. Utility of contrast-enhanced harmonic EUS for diagnosis of portal vein invasion by pancreatic cancer. Endosc. Ultrasound 2022, 11, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, M.; Hagi, H.; Atomi, Y.; Saito, M. Diagnosis of portal venous invasion by pancreatobiliary carcinoma: Value of endoscopic ultrasonography. Abdom. Imaging 1997, 22, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Kato, H.; Saragai, Y.; Takada, S.; Mizukawa, S.; Muro, S.; Uchida, D.; Tomoda, T.; Horiguchi, S.; et al. Diagnostic Ability of Convex-Arrayed Endoscopic Ultrasonography for Major Vascular Invasion in Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Endosc. 2019, 52, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bispo, M.; Marques, S.; Rio-Tinto, R.; Fidalgo, P.; Devière, J. The Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound in Pancreatic Cancer Staging in the Era of Neoadjuvant Therapy and Personalised Medicine. GE-Port. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 28, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawaz, H.; Fan, C.Y.; Kloke, J.; Khalid, A.; McGrath, K.; Landsittel, D.; I Papachristou, G. Performance Characteristics of Endoscopic Ultrasound in the Staging of Pancreatic Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. JOP 2013, 14, 484–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurita, A.; Kodama, Y.; Nakamoto, Y.; Isoda, H.; Minamiguchi, S.; Yoshimura, K.; Kuriyama, K.; Sawai, Y.; Uza, N.; Hatano, E.; et al. Impact of EUS-FNA for preoperative para-aortic lymph node staging in patients with pancreatobiliary cancer. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2016, 84, 467–475.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, M.F.; Sivak, M.V.; Rice, T.; Gragg, L.A.; Van Dam, J. Endosonographic features predictive of lymph node metastasis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1994, 40, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okasha, H.; Wifi, M.-N.; Awad, A.; Abdelfatah, Y.; Abdelfatah, D.; El-Sawy, S.; Alzamzamy, A.; Abou-Elenin, S.; Abou-Elmagd, A.; ElHusseiny, R.; et al. Role of EUS in detection of liver metastasis not seen by computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging during staging of pancreatic, gastrointestinal, and thoracic malignancies. Endosc. Ultrasound 2021, 10, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Bhatt, B.; Patel, T.; Kiss, A.; Gupta, R.; Bhat, S.; Erickson, R. Endoscopic Ultrasound Versus CT Scan for Detection of the Metastases to the Liver Results of a Prospective Comparative Study. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2009, 43, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, P.T.; Chang, K.J. EUS in the detection of ascites and EUS-guided paracentesis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2001, 54, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddappa, P.K.; Jain, N.; Agarwal, N.K.; Jain, M.; Lamba, G.S. Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Random Omental Fine Needle Aspiration: A Novel Technique for the Diagnosis of Peritoneal Carcinomatosis. Clin. Endosc. 2020, 53, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustagi, T.; Gleeson, F.C.; Chari, S.T.; Lehrke, H.D.; Takahashi, N.; Malikowski, T.M.; Abu Dayyeh, B.K.; Chandrasekhara, V.; Iyer, P.G.; Kendrick, M.L.; et al. Safety, Diagnostic Accuracy, and Effects of Endoscopic Ultrasound Fine-Needle Aspiration on Detection of Extravascular Migratory Metastases. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 2533–2540.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, P.D.; Meng, Z.W.; Zhang, M.; Belletrutti, P.J.; Mohamed, R.; Ghali, W.; Roberts, D.J.; Martel, G.; Heitman, S.J. The incremental benefit of EUS for identifying unresectable disease among adults with pancreatic adenocarcinoma: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCCN Guidelines Version 2.2023 Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Continue NCCN Guidelines Version 2.2023 Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma - Google Search. Available online: https://www.google.com/search?client=safari&rls=en&q=NCCN+Guidelines+Version+2.2023+Pancreatic+Adenocarcinoma+Continue+NCCN+Guidelines+Version+2.2023+Pancreatic+Adenocarcinoma&ie=UTF-8&oe=UTF-8#ip=1 (accessed on 20 December 2023).
- Conroy, T.; Pfeiffer, P.; Vilgrain, V.; Lamarca, A.; Seufferlein, T.; O’reilly, E.; Hackert, T.; Golan, T.; Prager, G.; Haustermans, K.; et al. Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 987–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saftoiu, A.; Vilmann, P.; Bhutani, M. The role of contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasound in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Endosc. Ultrasound 2016, 5, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, S.; Wang, M.; Sun, L. Contrast-Enhanced EUS for Differential Diagnosis of Pancreatic Masses: A Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2019, 2019, 1670183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Săftoiu, A.; Vilmann, P.; Dietrich, C.F.; Iglesias-Garcia, J.; Hocke, M.; Seicean, A.; Ignee, A.; Hassan, H.; Streba, C.T.; Ioncică, A.M.; et al. Quantitative contrast-enhanced harmonic EUS in differential diagnosis of focal pancreatic masses (with videos). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 82, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, K.; Fan, Z.; Sun, L.; Wu, W.; Yang, W. Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasonography of Pancreatic Carcinoma: Correlation with Pathologic Findings. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2016, 42, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imazu, H.; Uchiyama, Y.; Matsunaga, K.; Ikeda, K.-I.; Kakutani, H.; Sasaki, Y.; Sumiyama, K.; Ang, T.L.; Omar, S.; Tajiri, H. Contrast-enhanced harmonic EUS with novel ultrasonographic contrast (Sonazoid) in the preoperative T-staging for pancreaticobiliary malignancies. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 45, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emori, T.; Nuta, J.; Kawaji, Y.; Tamura, T.; Hatamaru, K.; Itonaga, M.; Yamashita, Y.; Ashida, R.; Shimokawa, T.; Koike, M.; et al. Value of contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasound for diagnosing hepatic metastases of pancreatic cancer: A prospective study. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 3402–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaga, K.; Kitano, M.; Nakai, A.; Omoto, S.; Kamata, K.; Yamao, K.; Takenaka, M.; Tsurusaki, M.; Chikugo, T.; Matsumoto, I.; et al. Improved detection of liver metastasis using Kupffer-phase imaging in contrast-enhanced harmonic EUS in patients with pancreatic cancer (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 93, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, T.; Kitano, M.; Omoto, S.; Kadosaka, K.; Kamata, K.; Imai, H.; Sakamoto, H.; Nisida, N.; Harwani, Y.; Murakami, T.; et al. Contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasonography for assessment of lymph node metastases in pancreatobiliary carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 3381–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facciorusso, A.; Crinò, S.F.; Gkolfakis, P.; Ramai, D.; Mangiavillano, B.; Castillo, J.L.; Chandan, S.; Mohan, B.P.; D’errico, F.; Decembrino, F.; et al. Needle Tract Seeding after Endoscopic Ultrasound Tissue Acquisition of Pancreatic Lesions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.-T.; Chu, Y.-L.; Wong, W.-F.; Han, M.-L.; Chen, C.-C.; Jan, I.-S.; Cheng, W.-C.; Shun, C.-T.; Tsai, M.-C.; Cheng, T.-Y.; et al. Randomized trial of contrast-enhanced harmonic guidance versus fanning technique for EUS-guided fine-needle biopsy sampling of solid pancreatic lesions. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2023, 97, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias-Garcia, J.; de la Iglesia-Garcia, D.; Lariño-Noia, J.; Dominguez-Muñoz, J.E. Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) Guided Elastography. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias–Garcia, J.; Larino–Noia, J.; Abdulkader, I.; Forteza, J.; Dominguez–Munoz, J.E. Quantitative Endoscopic Ultrasound Elastography: An Accurate Method for the Differentiation of Solid Pancreatic Masses. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias-Garcia, J.; Lindkvist, B.; Lariño-Noia, J.; Abdulkader-Nallib, I.; Dominguez-Muñoz, J.E. Differential diagnosis of solid pancreatic masses: Contrast-enhanced harmonic (CEH-EUS), quantitative-elastography (QE-EUS), or both? United Eur. Gastroenterol J. 2017, 5, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, M.; Ni, J.; Liu, D.; Jin, P.; Sun, L. EUS elastography for diagnosis of solid pancreatic masses: A meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2013, 77, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facciorusso, A.; Crinò, S.F.; Ramai, D.; Madhu, D.; Fugazza, A.; Carrara, S.; Spadaccini, M.; Mangiavillano, B.; Gkolfakis, P.; Mohan, B.P.; et al. Comparative diagnostic performance of different techniques for EUS-guided fine-needle biopsy sampling of solid pancreatic masses: A network meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2023, 97, 839–848.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abboud, Y.; Kim, K.; Samaan, J.S.; Chen, C.; Lew, D.; Ghaith, J.; Caldera, W.; El Helou, M.O.; Park, K.H.; Liu, Q.; et al. Endoscopic Ultrasound Guided Shear Wave Elastography Is Safe With High Feasibility and Reproducibility When Used in the Pancreas: Findings From a Prospective Cohort. Pancreas 2023, 52, e115–e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versteijne, E.; van Dam, J.L.; Suker, M.; Janssen, Q.P.; Groothuis, K.; Akkermans-Vogelaar, J.M.; Besselink, M.G.; Bonsing, B.A.; Buijsen, J.; Busch, O.R.; et al. Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy Versus Upfront Surgery for Resectable and Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Cancer: Long-Term Results of the Dutch Randomized PREOPANC Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volmar, K.E.; Vollmer, R.T.; Jowell, P.S.; Nelson, R.C.; Xie, H.B.; Durham, P. Pancreatic FNA in 1000 cases: A comparison of imaging modalities. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2005, 61, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imaoka, H.; Sasaki, M.; Hashimoto, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Ikeda, M. New Era of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Tissue Acquisition: Next-Generation Sequencing by Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Sampling for Pancreatic Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, T.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.S.; Eum, J.B.; Moon, S.H.; Park, D.H.; Seo, D.W.; Lee, S.K.; Jang, S.J.; Yun, S.C.; et al. The Prospective Randomized, Controlled Trial of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration Using 22G and 19G Aspiration Needles for Solid Pancreatic or Peripancreatic Masses. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laquière, A.; Lefort, C.; Maire, F.; Aubert, A.; Gincul, R.; Prat, F.; Grandval, P.; Croizet, O.; Boulant, J.; Vanbiervliet, G.; et al. 19 G nitinol needle versus 22 G needle for transduodenal endoscopic ultrasound-guided sampling of pancreatic solid masses: A randomized study. Endoscopy 2019, 51, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhoun, M.F.; Wani, S.B.; Rastogi, A.; Early, D.; Gaddam, S.; Tierney, W.M.; Maple, J.T. The diagnostic accuracy of 22-gauge and 25-gauge needles in endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration of solid pancreatic lesions: A meta-analysis. Endoscopy 2013, 45, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, H.G.; de Moura, D.T.H.; Duarte, R.B.; Cordero, M.A.C.; dos Santos, M.E.L.; Cheng, S.; Matuguma, S.E.; Chaves, D.M.; Bernardo, W.M.; de Moura, E.G.H. A comparison of the efficiency of 22G versus 25G needles in EUS-FNA for solid pancreatic mass assessment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clinics 2018, 73, e261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Affolter, K.E.; Schmidt, R.L.; Matynia, A.P.; Adler, D.G.; Factor, R.E. Needle Size Has Only a Limited Effect on Outcomes in EUS-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 58, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polkowski, M.; Jenssen, C.C.; Kaye, P.V.; Carrara, S.; Deprez, P.; Ginès, A.; Fernández-Esparrach, G.G.; Eisendrath, P.; Aithal, G.P.; Arcidiacono, P.P.; et al. Technical aspects of endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided sampling in gastroenterology: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Technical Guideline—March 2017. Endoscopy 2017, 49, 989–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, N.; Rana, S.S. Endoscopic Ultrasound Biopsy Needle. J. Dig. Endosc. 2022, 13, 240–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.Y.; Hebert-Magee, S.; Trevino, J.; Ramesh, J.; Varadarajulu, S. Randomized trial comparing the 22-gauge aspiration and 22-gauge biopsy needles for EUS-guided sampling of solid pancreatic mass lesions. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2012, 76, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Sun, B.; Deng, Z.; Shan, H.; Dou, L.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; et al. Analysis of Fine-Needle Biopsy vs Fine-Needle Aspiration in Diagnosis of Pancreatic and Abdominal Masses: A Prospective, Multicenter, Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Riet, P.A.; Erler, N.S.; Bruno, M.J.; Cahen, D.L. Comparison of fine-needle aspiration and fine-needle biopsy devices for endoscopic ultrasound-guided sampling of solid lesions: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy 2021, 53, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renelus, B.D.; Jamorabo, D.S.; Boston, I.; Briggs, W.M.; Poneros, J.M. Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Biopsy Needles Provide Higher Diagnostic Yield Compared to Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Needles When Sampling Solid Pancreatic Lesions: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. Endosc. 2021, 54, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karsenti, D.; Palazzo, L.; Perrot, B.; Zago, J.; Lemaistre, A.-I.; Cros, J.; Napoléon, B. 22G Acquire vs. 20G Procore needle for endoscopic ultrasound-guided biopsy of pancreatic masses: A randomized study comparing histologic sample quantity and diagnostic accuracy. Endoscopy 2020, 52, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurita, A.; Yasukawa, S.; Zen, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Ogura, T.; Ozawa, E.; Okabe, Y.; Asada, M.; Nebiki, H.; Shigekawa, M.; et al. Comparison of a 22-gauge Franseen-tip needle with a 20-gauge forward-bevel needle for the diagnosis of type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis: A prospective, randomized, controlled, multicenter study (COMPAS study). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2019, 91, 373–381.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashat, M.; Klair, J.S.; Rooney, S.L.; Vishal, S.J.; Jensen, C.; Sahar, N.; Murali, A.R.; El-Abiad, R.; Gerke, H. Randomized controlled trial comparing the Franseenneedle with the Fork-tip needle for EUS-guidedfine-needle biopsy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 23, 140–150. [Google Scholar]
- Bang, J.Y.; Hebert-Magee, S.; Navaneethan, U.; Hasan, M.K.; Hawes, R.; Varadarajulu, S. Randomized trial comparing the Franseen and Fork-tip needles for EUS-guided fine-needle biopsy sampling of solid pancreatic mass lesions. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 87, 1432–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, B.P.; Shakhatreh, M.; Garg, R.; Asokkumar, R.; Jayaraj, M.; Ponnada, S.; Navaneethan, U.; Adler, D.G. Comparison of Franseen and fork-tip needles for EUS-guided fine-needle biopsy of solid mass lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Endosc. Ultrasound 2019, 8, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkolfakis, P.; Crinò, S.F.; Tziatzios, G.; Ramai, D.; Papaefthymiou, A.; Papanikolaou, I.S.; Triantafyllou, K.; Arvanitakis, M.; Lisotti, A.; Fusaroli, P.; et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis Comparative diagnostic performance of end-cutting fine-needle biopsy needles for EUS tissue sampling of solid pancreatic masses: A network meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2022, 95, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, T.; Kawakami, H.; Hayashi, T.; Yasuda, I.; Mukai, T.; Inoue, H.; Katanuma, A.; Kawakubo, K.; Ishiwatari, H.; Doi, S.; et al. High and low negative pressure suction techniques in EUS-guided fine-needle tissue acquisition by using 25-gauge needles: A multicenter, prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2014, 80, 1030–1037.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantino, I.; Di Mitri, R.; Fabbri, C.; Pagano, N.; Barresi, L.; Granata, A.; Liotta, R.; Mocciaro, F.; Maimone, A.; Baccarini, P.; et al. Is diagnostic accuracy of fine needle aspiration on solid pancreatic lesions aspiration-related? A multicentre randomised trial. Dig. Liver Dis. 2014, 46, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, K.M.; Shin, J.U.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, K.T.; Jang, K.-T. A prospective, comparative trial to optimize sampling techniques in EUS-guided FNA of solid pancreatic masses. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2013, 77, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attam, R.; Arain, M.A.; Bloechl, S.J.; Trikudanathan, G.; Munigala, S.; Bakman, Y.; Singh, M.; Wallace, T.; Henderson, J.B.; Catalano, M.F.; et al. “Wet suction technique (WEST)”: A novel way to enhance the quality of EUS-FNA aspirate. Results of a prospective, single-blind, randomized, controlled trial using a 22-gauge needle for EUS-FNA of solid lesions. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 81, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, N.A.; Berzosa, M.; Wallace, M.B.; Raijman, I. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration: The wet suction technique. Endosc. Ultrasound 2016, 5, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berzosa, M.; Uthamaraj, S.; Dragomir-Daescu, D.; Raijman, I.; Qumseya, B.J.; Raimondo, M.; Woodward, T.A.; Wallace, M.B. Mo1395 EUS-FNA Wet vs. Dry Suction Techniques; a Proof of Concept Study on How a Column of Water Enhances Tissue Aspiration. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2014, 79, AB421–AB422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, D.; Ramai, D.; Singh, J.; Kani, T.; Barakat, M.; Chandan, S.; Brooks, O.; Ofosu, A.; Khan, S.; Dhindsa, B.; et al. Wet- versus dry-suction techniques for EUS-FNA of solid lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Endosc. Ultrasound 2021, 10, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, P.; El Zein, M.; Stevens, T.; Abdelgelil, A.; Besharati, S.; Messallam, A.; Kumbhari, V.; Azola, A.; Brainard, J.; Shin, E.J.; et al. Stylet slow-pull versus standard suction for endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of solid pancreatic lesions: A multicenter randomized trial. Endoscopy 2018, 50, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kin, T.; Katanuma, A.; Yane, K.; Takahashi, K.; Osanai, M.; Takaki, R.; Matsumoto, K.; Gon, K.; Matsumori, T.; Tomonari, A.; et al. Diagnostic ability of EUS-FNA for pancreatic solid lesions with conventional 22-gauge needle using the slow pull technique: A prospective study. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, Y.; Isayama, H.; Chang, K.J.; Yamamoto, N.; Hamada, T.; Uchino, R.; Mizuno, S.; Miyabayashi, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Kawakubo, K.; et al. Slow Pull Versus Suction in Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration of Pancreatic Solid Masses. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2014, 59, 1578–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, R.K.; Puri, R. EUS-Guided FNA: Tips and Tricks. J. Dig. Endosc. 2020, 11, 099–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.; Afzalpurkar, S.; Angadi, S.; Marikanty, A.; Sundaram, S. Comparison of suction techniques for EUS-guided tissue acquisition: Systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Endosc. Int. Open 2023, 11, E703–E711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.Y.; Magee, S.H.; Ramesh, J.; Trevino, J.M.; Varadarajulu, S. Randomized trial comparing fanning with standard technique for endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of solid pancreatic mass lesions. Endoscopy 2013, 45, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.M.; Lee, H.S.; Hyun, J.J.; Lee, J.M.; Yoo, I.K.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, H.S.; Kim, E.S.; Keum, B.; Seo, Y.S.; et al. Slow-Pull Using a Fanning Technique Is More Useful Than the Standard Suction Technique in EUS-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration in Pancreatic Masses. Gut Liver 2018, 12, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukai, S.; Itoi, T.; Ashida, R.; Tsuchiya, T.; Ikeuchi, N.; Kamada, K.; Tanaka, R.; Umeda, J.; Tonozuka, R.; Fukutake, N.; et al. Multicenter, prospective, crossover trial comparing the door-knocking method with the conventional method for EUS-FNA of solid pancreatic masses (with videos). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2016, 83, 1210–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uehara, H.; Sueyoshi, H.; Takada, R.; Fukutake, N.; Katayama, K.; Ashida, R.; Ioka, T.; Takenaka, A.; Nagata, S.; Tomita, Y. Optimal number of needle passes in endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration for pancreatic lesions. Pancreatology 2015, 15, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, W.H.; Choi, J.H.; Park, Y.; Lee, J.B.; Park, D.H. Optimal Techniques for EUS-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration of Pancreatic Solid Masses at Facilities without On-Site Cytopathology: Results from Two Prospective Randomised Trials. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.-D.; Wang, K.-X.; Zhou, W.; Li, S.-Y.; Jiang, H.; Gao, L.; Li, J.; Kong, X.-Y.; Yang, L.; Fang, A.-Q. Optimal number of needle passes during EUS-guided fine-needle biopsy of solid pancreatic lesions with 22G ProCore needles and different suction techniques: A randomized controlled trial. Endosc. Ultrasound 2021, 10, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Yasuda, I.; Hayashi, N.; Iwashita, T.; Okuno, M.; Mukai, T.; Mabuchi, M.; Adachi, S.; Doi, S.; Imura, J.; et al. EUS-guided fine-needle biopsy sampling of solid pancreatic tumors with 3 versus 12 to-and-fro movements: A multicenter prospective randomized controlled study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2023, 97, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wani, S.; Mullady, D.; Early, D.S.; Rastogi, A.; Collins, B.; Wang, J.F.; Marshall, C.; Sams, S.B.; Yen, R.; Rizeq, M.; et al. The Clinical Impact of Immediate On-Site Cytopathology Evaluation During Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration of Pancreatic Masses: A Prospective Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 110, 1429–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.S.; Nieto, J.; Watson, R.R.; Hwang, A.L.; Muthusamy, V.R.; Walter, L.; Jajoo, K.; Ryou, M.K.; Saltzman, J.R.; Saunders, M.D.; et al. Randomized non-inferiority trial comparing diagnostic yield of cytopathologist-guided versus seven passes for endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of pancreatic masses. Dig. Endosc. 2016, 28, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crinò, S.F.; Di Mitri, R.; Nguyen, N.Q.; Tarantino, I.; de Nucci, G.; Deprez, P.H.; Carrara, S.; Kitano, M.; Shami, V.M.; Fernández-Esparrach, G.; et al. Endoscopic Ultrasound–guided Fine-needle Biopsy With or Without Rapid On-site Evaluation for Diagnosis of Solid Pancreatic Lesions: A Randomized Controlled Non-Inferiority Trial. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 899–909.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.I.; Chatterjee, A.; Berger, R.; Kanber, Y.; Wyse, J.; Lam, E.; Gan, I.; Auger, M.; Kenshil, S.; Telford, J.; et al. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided fine needle biopsy alone vsEUS-guided fine needle aspiration with rapid onsite evaluation in pancreatic lesions: A multicenter randomized trial. Endoscopy. 2022, 54, 4–12. [Google Scholar]
- Iwashita, T.; Yasuda, I.; Mukai, T.; Doi, S.; Nakashima, M.; Uemura, S.; Mabuchi, M.; Shimizu, M.; Hatano, Y.; Hara, A.; et al. Macroscopic on-site quality evaluation of biopsy specimens to improve the diagnostic accuracy during EUS-guided FNA using a 19-gauge needle for solid lesions: A single-center prospective pilot study (MOSE study). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 81, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, J.; Ishiwatari, H.; Sasaki, K.; Yasuda, I.; Takahashi, K.; Imura, J.; Iwashita, T.; Uemura, S.; Hatano, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; et al. Macroscopic visible core length can predict the histological sample quantity in endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition: Multicenter prospective study. Dig. Endosc. 2022, 34, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, C.C.N.; Lakhtakia, S.; Nguyen, N.; Hara, K.; Chan, W.K.; Puri, R.; Almadi, M.A.; Ang, T.L.; Kwek, A.; Yasuda, I.; et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition with or without macroscopic on-site evaluation: Randomized controlled trial. Endoscopy 2020, 52, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaghoobi, M.; Rahman, M.O.; Chan, B.H.; Far, P.; Mbuagbaw, L.; Thabane, L. Endoscopic ultrasound versus computed tomography in determining the resectability of pancreatic cancer: A diagnostic test accuracy meta-analysis. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.Z.; Li, F.; Liu, Y.; Xing, L.X.; Du, L.F. Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound for differential diagnosis of pancreatic mass lesions: A meta-analysis. Med. Ultrason. 2016, 18, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, Y.; Shimokawa, T.; Napoléon, B.; Fusaroli, P.; Gincul, R.; Kudo, M.; Kitano, M. Value of contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasonography with enhancement pattern for diagnosis of pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis. Dig. Endosc. 2019, 31, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, C.M.; Villa, E. The efficiency of contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) combined with EUS elastography for pancreatic cancer diagnosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasonography 2023, 42, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facciorusso, A.; Mohan, B.P.; Crinò, S.F.; Ofosu, A.; Ramai, D.; Lisotti, A.; Chandan, S.; Fusaroli, P. Contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration versus standard fine-needle aspiration in pancreatic masses: A meta-analysis. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 15, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banafea, O.; Mghanga, F.P.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, R.; Zhu, L. Endoscopic ultrasonography with fine-needle aspiration for histological diagnosis of solid pancreatic masses: A meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy studies. BMC Gastroenterol. 2016, 16, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.-M.; Jia, H.-Y.; Yan, L.-L.; Li, S.-S.; Zheng, Y. Comparison of two different size needles in endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for diagnosing solid pancreatic lesions. Medicine 2017, 96, e5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Bao, H.; Li, J.; Jiang, T. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Accuracy of Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA) Using 22-gauge and 25-gauge Needles for Pancreatic Masses. Experiment 2018, 24, 8333–8341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, L.; Qu, C.; Liang, S.; Zeng, B.; Luo, Z. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle core biopsy for the diagnosis of pancreatic malignant lesions: A systematic review and Meta-Analysis. Sci Rep. 2016, 6, 22978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, G.M.; Laporte, L.; Paquin, S.C.; Menard, C.; Sahai, A.V.; Mâsse, B.; Trottier, H. Endoscopic Ultrasound Guided Fine Needle Aspiration versus Endoscopic Ultrasound Guided Fine Needle Biopsy for Pancreatic Cancer Diagnosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, J.Y.; Hawes, R.; Varadarajulu, S. A meta-analysis comparing ProCore and standard fine-needle aspiration needles for endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition. Endoscopy 2015, 48, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.M.; Liu, W.; Xu, X.M.; Li, P.M. A Meta-Analysis Comparing Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided Fine-needle Aspiration With Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided Fine-needle Biopsy. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2022, 56, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facciorusso, A.; Bajwa, H.; Menon, K.; Buccino, V.; Muscatiello, N. Comparison between 22G aspiration and 22G biopsy needles for EUS-guided sampling of pancreatic lesions: A meta-analysis. Endosc. Ultrasound 2020, 9, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facciorusso, A.; Del Prete, V.; Buccino, V.R.; Purohit, P.; Setia, P.; Muscatiello, N. Diagnostic yield of Franseen and Fork-Tip biopsy needles for endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition: A meta-analysis. Endosc. Int. Open 2019, 7, E1221–E1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facciorusso, A.; Gkolfakis, P.; Tziatzios, G.; Ramai, D.; Papanikolaou, I.; Triantafyllou, K.; Lisotti, A.; Fusaroli, P.; Mangiavillano, B.; Chandan, S.; et al. Comparison between EUS-guided fine-needle biopsy with or without rapid on-site evaluation for tissue sampling of solid pancreatic lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Endosc. Ultrasound 2022, 11, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Zhu, J.; Kong, X.; Sun, T.; Deng, X.; Du, Y.; Li, Z. Rapid On-Site Evaluation Does Not Improve Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Adequacy in Pancreatic Masses: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisotti, A.; Frazzoni, L.; Fuccio, L.; Serrani, M.; Cominardi, A.; Bazzoli, F.; Fusaroli, P. Repeat EUS-FNA of pancreatic masses after nondiagnostic or inconclusive results: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 91, 1234–1241.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Bhullar, F.; Alaber, O.; Kamal, A.; Hopson, P.; Kanthasamy, K.; Coughlin, S.; Archibugi, L.; Thiruvengadam, N.; Moreau, C.; et al. Comparative diagnostic accuracy of EUS needles in solid pancreatic masses: A network meta-analysis. Endosc. Int. Open 2021, 9, E853–E862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facciorusso, A.; Chandan, S.; Gkolfakis, P.; Ramai, D.; Mohan, B.P.; Lisotti, A.; Bellocchi, M.C.C.; Papanikolaou, I.S.; Mangiavillano, B.; Triantafyllou, K.; et al. Do Biliary Stents Affect EUS-Guided Tissue Acquisition (EUS-TA) in Solid Pancreatic Lesions Determining Biliary Obstruction? A Literature Review with Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2023, 15, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, S.; Afzalpurkar, S.; Angadi, S.; Varghese, J.; Sundaram, S. Influence of biliary stents on the diagnostic outcome of endoscopic ultrasound–guided tissue acquisition from solid pancreatic lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Endosc. 2023, 56, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandan, S.; Mohan, B.P.; Khan, S.R.; Ofosu, A.; Dhaliwal, A.S.; Shah, A.R.; Bhogal, N.; Mashiana, H.S.; Mashiana, S.S.; Kassab, L.L.; et al. Comparison of EUS-guided conventional smear and liquid-based cytology in pancreatic lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Endosc. Int. Open 2020, 8, E1611–E1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiteerakij, R.; Prasoppokakorn, T.; Tiyarattanachai, T.; Decharatanachart, P.; Mekaroonkamol, P.; Ridtitid, W.; Kongkam, P.; Rerknimitr, R. Application of artificial intelligence for diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by EUS: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Endosc. Ultrasound 2022, 11, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhali, A.; Kipkorir, V.; Srichawla, B.S.; Kumar, H.; Rathna, R.B.; Ongidi, I.; Chaudhry, T.; Morara, G.; Nurani, K.; Cheruto, D.; et al. Artificial intelligence assisted endoscopic ultrasound for detection of pancreatic space-occupying lesion: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2023, 109, 4298–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camus, B.; Pellat, A.; Rouquette, A.; Marchese, U.; Dohan, A.; Belle, A.; Ali, E.A.; Chaussade, S.; Coriat, R.; Barret, M. Diagnostic Yield of Repeat Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Biopsy for Solid Pancreatic Lesions. Cancers 2023, 15, 3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.H.; Kim, J.; Lee, H.S.; Ryu, S.J.; Jang, S.I.; Kim, E.J.; Kang, H.; Lee, S.S.; Song, T.J.; Bang, S. Factors Influencing the Diagnostic Performance of Repeat Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration/Biopsy after the First Inconclusive Diagnosis of Pancreatic Solid Lesions. Gut Liver 2023, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, N.; Wyse, J.; Jayaraman, S.; Ball, C.; Lam, E.; Paquin, S.; Lightfoot, P.; Sahai, A.V. A proposal for the ideal algorithm for the diagnosis, staging, and treatment of pancreas masses suspicious for pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Results of a working group of the Canadian Society for Endoscopic Ultrasound. Endosc Ultrasound. 2020, 9, 154–161. [Google Scholar]
- Nakai, Y.; Isayamam, H.; Wang, H.; Rerknimitr, R.; Khor, C.; Yasuda, I.; Kogure, H.; Moon, J.H.; Lau, J.; Lakhtakia, S.; et al. International consensus statements for endoscopic management of distal biliary stricture. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 35, 967–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, M.E.; Carpenter, S.L.; Elta, G.H.; Nostrant, T.T.; Kochman, M.L.; Ginsberg, G.G.; Stotland, B.; Rosato, E.F.; Morris, J.B.; Eckhauser, F.; et al. EUS compared with CT, magnetic resonance imaging, and angiography and the influence of biliary stenting on staging accuracy of ampullary neoplasms. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1999, 50, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusaroli, P.; Manta, R.; Fedeli, P.; Maltoni, S.; Grillo, A.; Giovannini, E.; Bucchi, L.; Caletti, G. The influence of endoscopic biliary stents on the accuracy of endoscopic ultrasound for pancreatic head cancer staging. Endoscopy 2007, 39, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H.; Tseng, L.-J.; Yang, C.-C.; Yeh, Y.-H. Preoperative evaluation of periampullary tumors by endoscopic sonography, transabdominal sonography, and computed tomography. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2001, 29, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, S.; Rana, A. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition: Techniques and challenges. J. Cytol. 2019, 36, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.S.; Lee, J.H.; Song, T.J.; Lee, J.S.; Jo, S.J.; Oh, D.W.; Song, K.B.; Hwang, D.W.; Park, D.H.; Lee, S.S.; et al. The impact of preoperative EUS-FNA for distal resectable pancreatic cancer: Is it really effective enough to take risks? Surg. Endosc. 2022, 36, 3192–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yane, K.; Kuwatani, M.; Yoshida, M.; Goto, T.; Matsumoto, R.; Ihara, H.; Okuda, T.; Taya, Y.; Ehira, N.; Kudo, T.; et al. Non-negligible rate of needle tract seeding after endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for patients undergoing distal pancreatectomy for pancreatic cancer. Dig. Endosc. 2020, 32, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, S.; Koizumi, K.; Shionoya, K.; Jinushi, R.; Makazu, M.; Nishino, T.; Kimura, K.; Sumida, C.; Kubota, J.; Ichita, C.; et al. Comprehensive review on endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition techniques for solid pancreatic tumor. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 1863–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pishvaian, M.J.; Blais, E.M.; Brody, J.R.; Lyons, E.; DeArbeloa, P.; Hendifar, A.; Mikhail, S.; Chung, V.; Sahai, V.; Sohal, D.P.S.; et al. Overall survival in patients with pancreatic cancer receiving matched therapies following molecular profiling: A retrospective analysis of the Know Your Tumor registry trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imaoka, H.; Sasaki, M.; Hashimoto, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Miyazawa, S.; Shibuki, T.; Mitsunaga, S.; Ikeda, M. Impact of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Tissue Acquisition on Decision-Making in Precision Medicine for Pancreatic Cancer: Beyond Diagnosis. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.Y.; Hebert-Magee, S.; Navaneethan, U.; Hasan, M.K.; Hawes, R.; Varadarajulu, S. EUS-guided fine needle biopsy of pancreatic masses can yield true histology. Gut 2018, 67, 2081–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, M.; Irie, H.; Takagi, T.; Suzuki, R.; Konno, N.; Asama, H.; Sato, Y.; Nakamura, J.; Takasumi, M.; Hashimoto, M.; et al. Efficacy of EUS-guided FNB using a Franseen needle for tissue acquisition and microsatellite instability evaluation in unresectable pancreatic lesions. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.Y.; Jhala, N.; Seth, A.; Krall, K.; Navaneethan, U.; Hawes, R.; Wilcox, C.M.; Varadarajulu, S. Standardisation of EUS-guided FNB technique for molecular profiling in pancreatic cancer: Results of a randomised trial. Gut 2023, 72, 1255–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.-M.; Yang, H.; Jin, Z.-D.; Yu, J.-G.; Cai, Z.-Y.; Li, Z.-S. Differential diagnosis of pancreatic cancer from normal tissue with digital imaging processing and pattern recognition based on a support vector machine of EUS images. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2010, 72, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurt, M.; Ozkan, M.; Cakiroglu, M.; Kocaman, O.; Yilmaz, B.; Can, G.; Korkmaz, U.; Dandil, E.; Eksi, Z. Age-based computer-aided diagnosis approach for pancreatic cancer on endoscopic ultrasound images. Endosc. Ultrasound 2016, 5, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, H.; Sherazi, S.A.A.; Gupta, S.; Perisetti, A.; Achebe, I.; Ali, A.; Tharian, B.; Thosani, N.; Sharma, N.R. Application of artificial intelligence in diagnosis of pancreatic malignancies by endoscopic ultrasound: A systemic review. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2022, 15, 17562848221093873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Săftoiu, A.; Vilmann, P.; Gorunescu, F.; Janssen, J.; Hocke, M.; Larsen, M.; Iglesias–Garcia, J.; Arcidiacono, P.; Will, U.; Giovannini, M.; et al. Efficacy of an Artificial Neural Network–Based Approach to Endoscopic Ultrasound Elastography in Diagnosis of Focal Pancreatic Masses. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 84–90.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yin, H.; Yang, X.; Sun, L.; Pan, P.; Peng, L.; Li, K.; Zhang, D.; Cui, F.; Xia, C.; et al. The value of artificial intelligence techniques in predicting pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with EUS images: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Endosc. Ultrasound 2023, 12, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumitrescu, E.A.; Ungureanu, B.S.; Cazacu, I.M.; Florescu, L.M.; Streba, L.; Croitoru, V.M.; Sur, D.; Croitoru, A.; Turcu-Stiolica, A.; Lungulescu, C.V. Diagnostic Value of Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Endoscopic Ultrasound for Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahiya, D.S.; Al-Haddad, M.; Chandan, S.; Gangwani, M.K.; Aziz, M.; Mohan, B.P.; Ramai, D.; Canakis, A.; Bapaye, J.; Sharma, N. Artificial Intelligence in Endoscopic Ultrasound for Pancreatic Cancer: Where Are We Now and What Does the Future Entail? J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, T.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Deng, M.; Wang, X. Preclinical models derived from endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition for individualized treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Front. Med. 2023, 9, 934974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peschke, K.; Jakubowsky, H.; Schäfer, A.; Maurer, C.; Lange, S.; Orben, F.; Bernad, R.; Harder, F.N.; Eiber, M.; Öllinger, R.; et al. Identification of treatment-induced vulnerabilities in pancreatic cancer patients using functional model systems. EMBO Mol. Med. 2022, 14, e14876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demyan, L.; Habowski, A.N.; Plenker, D.; King, D.A.; Standring, O.J.; Tsang, C.B.; Surin, L.S.; Rishi, A.; Crawford, J.M.; Boyd, J.; et al. Pancreatic Cancer Patient-derived Organoids Can Predict Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Ann. Surg. 2022, 276, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogenson, T.L.; Xie, H.; Phillips, W.J.; Toruner, M.D.; Li, J.J.; Horn, I.P.; Kennedy, D.J.; Almada, L.L.; Marks, D.L.; Carr, R.M.; et al. Culture media composition influences patient-derived organoid ability to predict therapeutic responses in gastrointestinal cancers. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 7, e158060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grützmeier, S.E.; Kovacevic, B.; Vilmann, P.; Rift, C.V.; Melchior, L.C.; Holmström, M.O.; Brink, L.; Hassan, H.; Karstensen, J.G.; Grossjohann, H.; et al. Validation of a Novel EUS-FNB-Derived Organoid Co-Culture System for Drug Screening in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornblaser, D.W.; Khamaysi, I.; Gross, S.A. Pilot study comparing a novel EUS-guided motorized biopsy needle technique with traditional sampling. iGIE 2023, 2, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Type of Needle, Needle Design | Proprietary Name, Needle Diameter | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|
| EUS FNA needle | ||
| Menghini type | Beacon EUS Delivery system with BNX FNA preloaded needle | Beacon Endoscopic, Newton, MA, USA |
| BNX FNA needle (without sheath) | Beacon Endoscopic, Newton, MA, USA | |
| Expect 19, 22, 25G | Boston Scientific, Marlborough, MA, USA | |
| Expect Flex 19G | Boston Scientific, Marlborough, MA, USA | |
| Expect Slimline 19, 22, 25G | Boston Scientific, Marlborough, MA, USA | |
| Expect Slimline Flex 19G | Boston Scientific, Marlborough, MA, USA | |
| ClearView 19, 22, 25G | Conmed, Billercia, MA, USA | |
| ClearView Sheath Stabilizer 22, 25G | Conmed, Billercia, MA, USA | |
| ClearView Extended Bevel 22G | Conmed, Billercia, MA, USA | |
| SonoTip Pro Control 19, 22, 25G | MediGlobe GmbH, Achenmühle, Germany | |
| EchoTip Ultra 19, 22, 25G | Cook Medical, Bloomington, IN, USA | |
| EchoTip Ultra coil sheath 22G | Cook Medical, Bloomington, IN, USA | |
| EchoTip Ultra HD Access 19G | Cook Medical, Bloomington, IN, USA | |
| EZ shot 2 19, 22, 25G | Olympus America, Center Valley, PA, USA | |
| EZ shot 2 sideport 22G | Olympus America, Center Valley, PA, USA | |
| EZ shot 3 plus 19, 22G | Olympus America, Center Valley, PA, USA | |
| EUS Sonopsy CY™ 21G | Hakko Co., Tokyo, Japan | |
| EUS FNB needles | ||
| Forward-bevel | Echotip Procore 20G | Cook Medical, Bloomington, IN, USA |
| Reverse-bevel | Echotip Procore 19, 22, 25G | Cook Medical, Bloomington, IN, USA |
| Fork-tip | SharkCore 19, 22, 25G | Medtronic, Dublin, Ireland |
| Beacon EUS delivery system with SharkCore preloaded FNB needle 19, 22, 25G | Medtronic, Dublin, Ireland | |
| Franseen | Acquire 19, 22, 25G | Boston Scientific, Marlborough, MA, USA |
| Sonotip Topgain 19, 22, 25G | Mediglobe, Achenmühle, Germany | |
| SRMA (Author, year) | Number of Studies and Total Number of Patients (n) | Modality/Comparison | Type of Lesion | Main Outcome Measure | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | PPV | NPV | Adequacy (%) | Accuracy (%) | Contamination (%) | Other Parameters (%) | Adverse Events (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Role of Diagnostic EUS | |||||||||||||
| Rahman MIO et al., 2020 [96] | 2 studies, n = 77 | EUS vs. CECT in pancreatic protocol | Neoplastic pancreatic lesions | Diagnostic accuracy for pancreatic cancer resectability | 87 | 63 | - | - | - | - | - | Similar diagnostic OR (p > 0.05) | - |
| Krishna SG et al., 2017 [14] | 4 studies | EUS after an indeterminate MDCT | Suspected pancreatic malignancies | Diagnostic performance for detection of pancreatic malignancies | 85 | 58 | 77 | 66 | - | 75 | - | - | - |
| Li Y et al., 2019 [97] | 16 studies, n = 1325 | CE EUS for pancreatic masses | Pancreatic masses | Diagnostic performance of CE EUS for the differentiation of pancreatic masses | 93 | 84 | - | - | - | - | - | LR+ 5.58 LR− 0.09 DOR 72.5% | - |
| Yamashita Y et al., 2019 [98] | 9 studies, n = 887 | CE EUS | Pancreatic cancer | Diagnostic performance for diagnosing pancreatic cancer | 93 | 80 | - | - | - | - | - | LR+ 4.56 LR− 0.09 DOR 59.89 | - |
| Shin CM et al., 2023 [99] | 6 studies, n = 430 | Combined CE EUS and EUS elastography in solid pancreatic lesions | Solid pancreatic lesions | Diagnostic performance in detecting pancreatic malignancies | 84 | 85 | - | - | - | - | - | LR+ 5.31 LR− 0.15 DOR 67.72 | - |
| Facciorusso A et al., 2021 [100] | 6 studies, n = 701 | CE EUS-guided vs. standard EUS FNA in pancreatic masses | Solid pancreatic lesions | Diagnostic outcome | 84.6 vs. 75.3 (p < 0.001) | 100% both | - | - | 95.1 vs. 89.4 (p = 0.02) | 88.8 vs. 83.6 (p = 0.05) | - | Histological core procurement p = 0.08, number of needle passes p = 0.29 | - |
| EUS tissue acquisition (EUS TA) | |||||||||||||
| Banafea O et al., 2016 [101] | 20 studies, n = 2761 | EUS FNB | Pancreatic mass | Diagnsotic accuracy | 90.8 | 96.5 | - | - | - | 91 | - | LR+ 14.8 LR− 0.12 DOR 142.47 | 35 of 1760 patients in 15 studies |
| Guedes HG et al., 2018 [56] | 4 studies, n = 504 | 22G versus 25G needles in EUS FNB for solid pancreatic mass | Solid pancreatic masses | Diagnostic performance | 91 vs. 93 p>0.05 | 83 vs. 87 p>0.05 | - | - | - | - | - | LR+ 4.26 vs. 4.57 LR− 0.13 vs. 0.08 p > 0.05 | - |
| Xu MM et al. [102] | 11 studies, n = 837 | 22G vs. 25G EUS FNA needle | Solid pancreatic lesions | Diagnostic performance | 88 vs. 92 p = 0.046 | 100 vs. 100 p = 0.842 | - | - | - | - | - | LR+ 12.61 vs. 8.44 LR− 0.16 vs. 0.13 AUSROC 0.97 vs. 0.96 | - |
| Tian G et al., 2018 [103] | 16 studies, n = 1824 | 22G vs. 25G EUS FNA needle | Masses with suspicion of pancreatic cancer | Diagnostic yield for the detection of pancreatic cancer | 89 vs. 90 p = 0.02 | 100 vs. 99 p = 0.15 | - | - | - | - | - | LR+ 485.28 vs. 59.53 LR− 0.11 vs. 0.10 AUROC 0.97 for both | - |
| Yang Y et al., 2016 [104] | 16 studies, n = 828 | EUS FNB | Solid malignant pancreatic lesions | Diagnostic accuracy | 84 | 98 | LR+ 8 LR− 0.17 DOR 64 AUROC 0.96 | - | |||||
| Reneleus et al., 2021 [63] | 11 studies, n = 1365 | EUS FNB vs. FNA | Solid pancreatic lesions | Diagnostic accuracy and safety | - | - | - | - | - | Diagnostic accuracy of 87 vs. 81 (p = 0.005). Cytopathological accuracy of 89 vs. 82 (p = 0.04). Histological accuracy of 81 vs. 74 (p = 0.39) | - | Mean TSR was 99% in both. Mean needle passes required for adequate tissue was 2.3 vs. 1.6 (mean difference was 0.71) (p < 0.0001) | 2.3 vs. 1.8 (p = 0.64) |
| van Riet PA et al., 2021 [62] | 18 RCTs, n = 2695 | EUS FNB vs. FNA for sampling | Solid pancreatic and non-pancreatic lesions | Diagnostic accuracy, adequacy, number of passes, presence of tissue cores, and adverse events | - | - | - | - | 90 vs. 88 (p = 0.76) | 85 vs. 80 (p = 0.03) High-quality studies 82 vs. 74 (p = 0.002) | - | Mean number of passes was lower in FNB (mean difference −0.54) p = 0.03. Presence of tissue cores: 79 vs. 63 (p = 0.11) | 0.8 vs. 1.0 (p = 0.8) |
| Hassan GM et al., 2022 [105] | 9 RCTs, n NA | EUS FNB vs. EUS FNA | Solid pancreatic masses | Diagnostic accuracy for the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer | - | - | - | - | - | FNB had a superior accuracy compared to FNA (OR 1.87) | - | - | - |
| Bang JY et al., 2016 [106] | 9 studies, n = 576 | Procore vs. standard EUS FNA needle in solid lesions | All solid lesions | Diagnostic adequacy, diagnostic accuracy, acquisition of histological core tissue, and mean number of passes | - | - | - | - | 75.2 vs. 89.0; OR 0.39 (p = 0.23) | 85.8 vs. 86.2; OR 0.88 (p = 0.53) | - | Rate of histological core specimen acquisition (77.7% vs. 76.5%; OR 0.94, p = 0.85). Lower mean number of passes required for diagnosis with the ProCore needle (SMD—1.2, p < 0.001). | - |
| Li Z et al., 2022 [107] | 18 studies, n = 2718 | EUS FNB vs. EUS FNB | Pancreatic and non-pancreatic solid lesions (only solid pancreatic lesions are mentioned in the subgroup analysis) | Diagnostic accuracy, number of needle passes, adequacy, presence of tissue cores, and adverse events | - | - | - | - | FNB had a higher adequacy (RR = 0.93) p = 0.004 | Similar pooled accuracy (RR = 0.97) p = 0.13 | - | Fewer number of passes for adequate sampling in FNB group (MD 0.57) p < 0.00001. Presence of tissue core was similar (RR 0.60) p = 0.16 | Similar (RR 1.27) p = 0.97 |
| Facciorusso A et al., 2020 [108] | 11 trials, 833 patients | 22G FNB vs. 22G FNA needle | Solid pancreatic lesions | Diagnostic outcome and tissue adequacy | 93.1 vs. 90.4 | 100 in both | - | - | Slightly in favour of FNB (p = 0.61) | - | - | No difference in histological core procurement (p = 0.86). Similar number of passes in FNB (MD -0.32, p = 0.07) | Six adverse events in FNA group and one in FNB group reported |
| Gkolfakis P et al., 2022 [69] | RCT 16, n = 1934 | Different FNB needles | Solid pancreatic masses | Diagnostic accuracy (network meta-analysis) | 94.6% with Franseen needle, 93.9% with Fork-tip needle, 90.4% with Menghini-tip needle, 82% with reverse-bevel needle, and 87.4% with FNA needle | Pooled specificity 100% with all needles tested | - | - | Franseen needle was better than FNA and reverse-beveled needles. Fork-tip needles were superior to reverse-beveled needle. None was superior when compared to FNA with ROSE. Both 22G and 25G Franseen needles followed by the 22G fork-tip needle showed the highest SUCRA scores concerning sample adequacy | Franseen needle was better than FNA and reverse-beveled needles. Fork-tip needles were superior to reverse-beveled needle. None was superior when compared to FNA with ROSE. The 22G Franseen needle ranked as the best FNB needle in terms of diagnostic accuracy (SUCRA score of 0.81) | - | - | Pooled rate was 2.7% with Franseen needle; 2% with Fork-tip needle; 1.3% with Menghini-tip needle; 0.8% with reverse-bevel needle, and 1.9% with the FNA needle. |
| Facciorusso A et al., 2019 [109] | 24 studies, n = 6641 | Franseen vs. fork-tip EUS FNB needles | Pancreatic and non-pancreatic solid lesions (only solid pancreatic lesions are mentioned in the subgroup analysis) | Sample adequacy | Similar sensitivity (95.3 vs. 93.4) | Similar specificity [100] | - | - | 97 vs. 92.6 (p = 0.006) | 96.8 vs. 95.2 (p = 0.8) | - | Histological core procurement was 94 vs. 93.1 (p = 0.7). Fewer number of passes compared to standard FNA needles (MD for Franseen was -0.44 and for Fork-tip was −1.82) | - |
| Facciorusso A et al., 2022 [110] | 8 studies, n = 2147 | EUS FNB with and without ROSE | Solid pancreatic lesions | Sample adequacy | 94.3 vs. 91.5 | - | - | - | EUS FNB with ROSE is not superior to EUS FNB alone (95.5 vs. 88.9, p = 0.07) especially when end-cutting needles (compared to reverse-bevel needles) are used | Superior in the EUS FNB + ROSE group (OR = 2.49, p = 0.03) | Number of needle passes needed to obtain diagnostic samples was not significantly different (mean difference 0.07; p = 0.62) | - | Only one study reported (Crino et al.) |
| Kong F et al., 2016 [111] | 7 studies, n = 1299 | EUS FNB with ROSE vs. EUS FNB without ROSE | Pancreatic masses | Diagnostic adequacy, yield, number of needle passes, pooled sensitivity, and specificity | 91 vs. 85 | 100 in both | - | - | No significant difference in cytological adequacy | No significant difference in diagnostic yield | - | LR+ 28.15 vs. 29.08 LR− 0.1 vs. 0.16. Fewer needle passes in ROSE group (4 vs. 7, p < 0.0001) | - |
| Lisotti A et al., 2020 [112] | 12 studies, n = 505 | Repeat EUS FNB for the diagnosis of solid pancreatic masses | Solid pancreatic masses | Diagnostic performance of repeat EUS FNB in case of negative or inconclusive first FNA | 77 (83% with ROSE) | 98 | 99 | 61 | - | - | - | LR+ 38.9 LR− 0.23 | - |
| Han S et al., 2021 [113] | 26 studies, n = 3398 (in primary NMA) | Various EUS TA needles | Solid pancreatic masses | Diagnostic accuracy compared to 22G Echotip (Cook) EUS FNA needle (NMA) | - | - | - | - | - | Performance score-wise: 22 G SharkCore FNB needle (Medtronic) > 22G EZ Shot 3 FNB needle (Olympus) > 22G Acquire FNB needle (Boston Scientific) | - | Diagnostic accuracy was not significantly different between needles with or without suction except 20G FNB needle with suction which performed significantly worse than the 22G FNA needle with suction | - |
| Suction Techniques in EUS TA | |||||||||||||
| Facciorusso A et al., 2023 [42] | 9 RCTs, n = 756 | Various EUS FNB techniques | Solid pancreatic masses | Rates of sample adequacy, blood contamination, and tissue integrity (NMA) | Modified wet suction was most sensitive (SUCRA score, 0.85) followed by slow-pull techniques and no stylet technique (SUCRA scores, 0.66 and 0.48, respectively) | - | - | - | Modified wet-suction technique was best for adequacy (SUCRA score of 0.90) followed by dry-suction and slow-pull techniques (SUCRA scores of 0.59 and 0.50, respectively) | - | Higher level of blood contamination seen with dry-suction than slow-pull technique; no-suction technique ranked as the best strategy (SUCRA score of 0.99) followed by the slow-pull technique (SUCRA score of 0.65). Modified wet-suction (SUCRA score of 0.32) and dry-suction (SUCRA score of 0.12) techniques showed poor performance in terms of blood contamination of the sample | Regarding tissue integrity, modified wet-suction technique was ranked as the best strategy (SUCRA score of 0.89) followed by slow-pull (SUCRA score of 0.66) and no-suction (SUCRA score of 0.42) techniques | Uncommon and usually mild, without significant impact on patient outcomes (abdominal pain and bleeding) |
| Ramai D et al., 2021 [76] | 6 studies, n = 418 | Wet vs. dry suction techniques | Solid pancreatic masses | Adequacy, sample contamination, and histological accuracy | - | - | - | - | Wet-suction technique has superior tissue adequacy (pooled adequacy rate of 91.9 vs. 77.32 (OR 3.18, p < 0.001)) | Wet-suction technique is superior in histological diagnosis (OR of 3.68, pooled rate of 84.06 vs. 68.87, p < 0.001). Wet suction has superior sample quality, and accuracy | Wet-suction technique has comparable blood contamination (OR of 1.18, contamination rate of 58.33 and 54.6, p = 0.256) | - | - |
| Giri S et al., 2023 [81] | 7 studies, n = 2048 | Various suction techniques in EUS TA | Solid pancreatic and non-pancreatic lesions | Compare the diagnostic yields during EUS TA (NMA) | - | - | - | - | There was no difference between the various modalities. For the SUCRA analysis, WS > SSP > DS > NS | No significant difference in ORs of adequacy when adjusted for either of the needle types. For the SUCRA analysis, WS > NS > DS > SSP | When adjusting for FNA needle, there was no difference between the interventions | No significant difference between the studies with respect to moderate-to-high cellularity of samples | - |
| EUS TA in Presence of Biliary Stents | |||||||||||||
| Facciorusso A et al., 2023 [114] | 7 studies, n = 2458 | EUS TA in presence and absence of biliary stent | Solid pancreatic head masses | Diagnostic accuracy before and after biliary stenting in jaundiced patients with pancreatic head masses | Overall diagnostic sensitivity lower in biliary stent group (82.9 vs. 87.5; OR 0.59; p < 0.001); in SEMS subgroup (p = 0.006) but not in plastic stent group (p = 0.12) | - | - | - | No significant difference in adequacy (p = 0.81) | No overall significant difference 85.4 vs. 88.1 (p = 0.07). No significant difference in plastic stent vs. no stent (p = 0.67). Significant difference in SEMS vs. no SEMS (p = 0.05) | - | No significant difference in number of needle passes (p = 0.38) | No significant difference (p = 0.75) |
| Giri S et al., 2023 [115] | 9 studies, n = 3257 | EUS TA in presence and absence of biliary stent | Pancreatic masses undergoing EUS TA | Diagnostic accuracy of EUS TA in presence and absence of biliary stent | 79 vs. 88; Using non-strict criteria in patients with stents, the sensitivity was lower with metal stents than with plastic stents (83% vs. 90%) | - | - | - | Comparable in stent vs. non-stent groups and in plastic and SEMS group | Lower accuracy with stent (OR of 0.58) using non-strict criteria and comparable sensitivity between metal stents and plastic stents | - | Patients with stents required greater number of passes (MD = 0.31) | - |
| Advances of EUS | |||||||||||||
| Chandan S et al., 2020 [116] | 9 studies, n = 1308 | EUS-guided precipitation-based LBC conventional smear | Solid pancreatic masses | Diagnostic yield of EUS-guided conventional smear vs. LBC | Precipitation based LBC higher sensitivity (85.2 vs. 79.7) | Precipitation based LBC comparable specificity (99.5 vs. 99.4) | Precipitation based LBC comparable PPV (99.5 in both) | NPV was found to be higher with filtration-based LBC technique (50.9%) as compared with CS (46.2%) and precipitation-based LBC techniques (35.4%). | - | Precipitation-based LBC had a higher accuracy | - | - | - |
| Prasoppokakorn T et al., 2021 [117] | 8 studies, n = 870 | AI-assisted diagnosis of PDAC by EUS | Pancreatic mass | AI-assisted B-mode EUS sensitivity and specificity 90%, 91% respectively. AI-assisted CE EUS sensitivity and specificity 95%, 95% respectively. AI-assisted EUS elastography sensitivity and specificity 88%, 83% respectively. | AI-assisted EUS 91% AI-assisted B-mode EUS 91% | AI-assisted EUS 90% AI-assisted B-mode EUS 90% | AI-assisted B-mode EUS 94% | AI-assisted B-mode EUS 84% | - | - | - | - | - |
| Dhali A et al., 2023 [118] | 21 studies | AI-assisted vs. conventional EUS for detection of pancreatic SoLs | Diagnostic performance | Higher accuracy of AI-assisted EUS for detection and differentiation | 93.9 | 93.1 | 91.6 | 93.6 | - | 93.6 | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chatterjee, A.; Shah, J. Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound in Diagnosis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14010078
Chatterjee A, Shah J. Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound in Diagnosis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(1):78. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14010078
Chicago/Turabian StyleChatterjee, Abhirup, and Jimil Shah. 2024. "Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound in Diagnosis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma" Diagnostics 14, no. 1: 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14010078
APA StyleChatterjee, A., & Shah, J. (2024). Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound in Diagnosis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Diagnostics, 14(1), 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14010078





