Puncture Accuracy of Robot-Assisted CT-Based Punctures in Interventional Radiology: An Ex Vivo Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
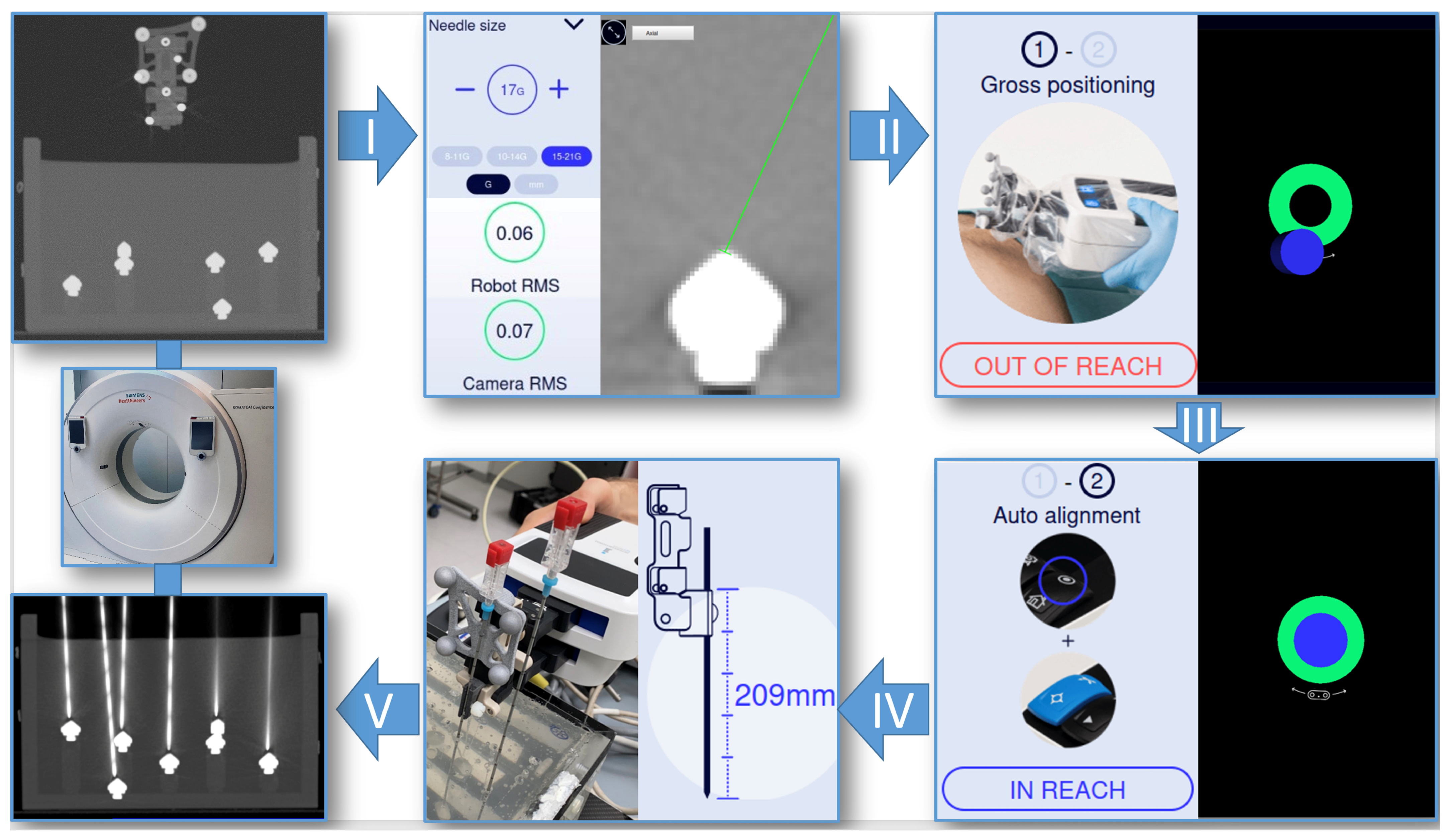
2.1. Phantom
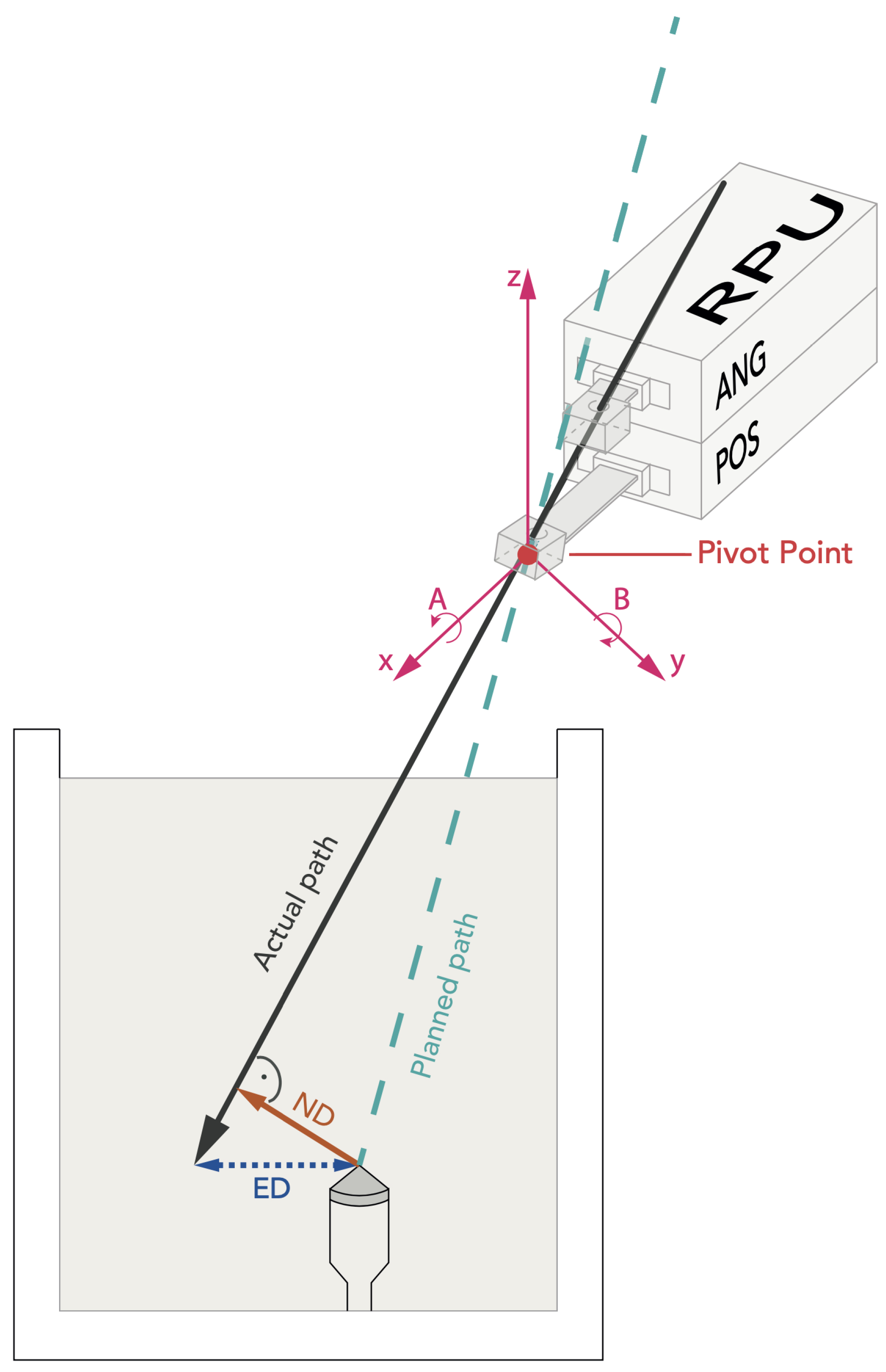
2.2. Micromate Navigation System
2.3. Experimental Setup
2.4. Evaluation
3. Results
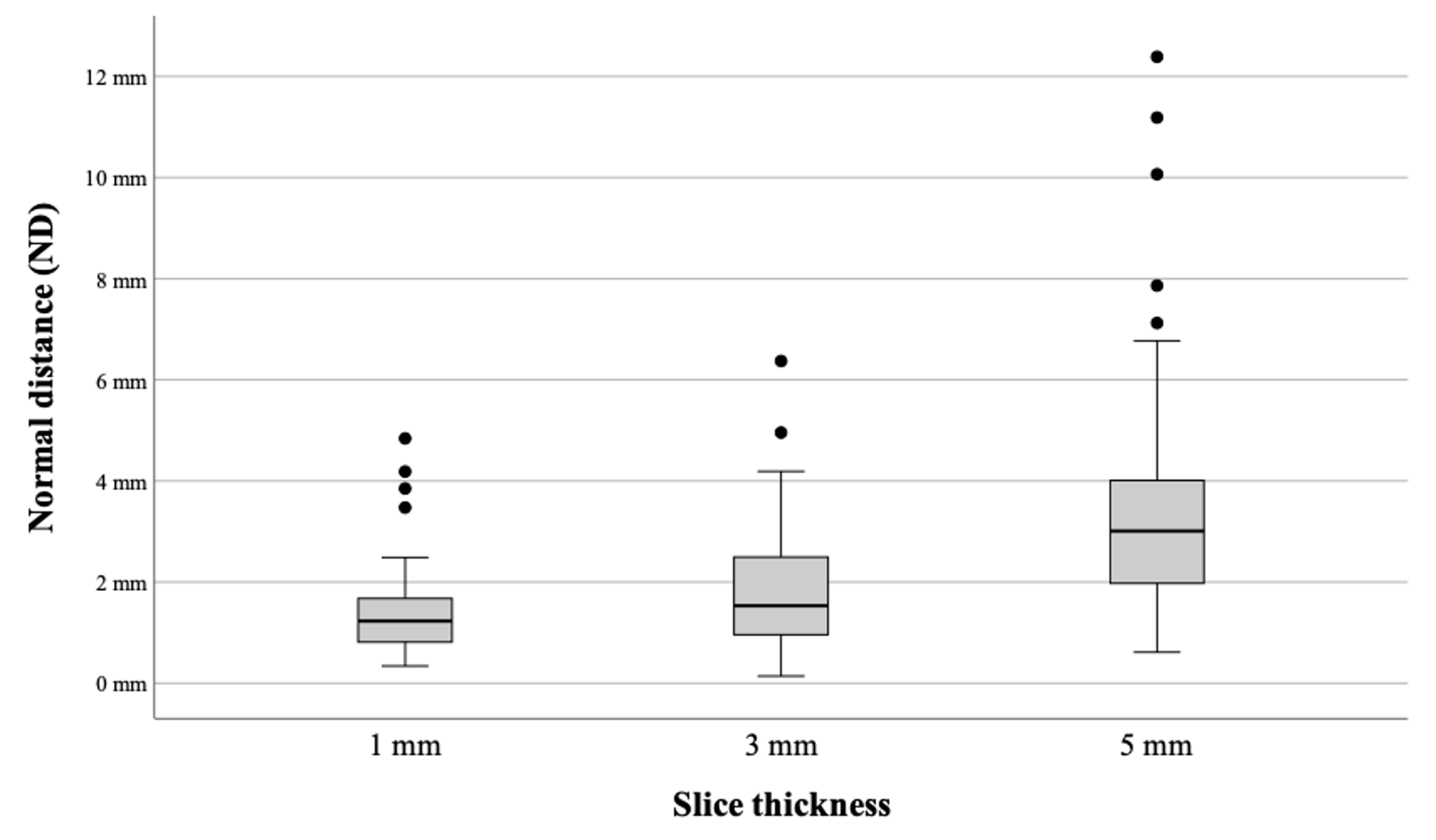
3.1. Accuracy
- ED: 1 mm vs. 3 mm (p = 0.095), 1 mm vs. 5 mm (p < 0.01), and 3 mm vs. 5 mm (p < 0.01)
- ND: 1 mm vs. 3 mm (p = 0.02), 1 mm vs. 5 mm (p < 0.01), and 3 mm vs. 5 mm (p < 0.01)
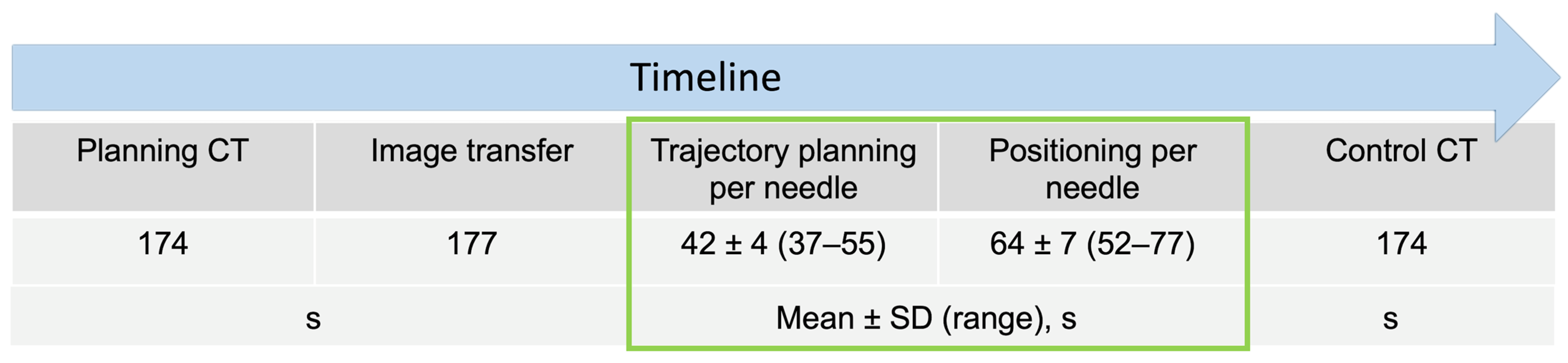
3.2. Procedural Time
4. Discussion
4.1. Targeting Accuracy
4.2. Time Efforts
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Z.; Li, Z.; Guo, M.; Bian, H.; Niu, T.; Wang, J. Application of Three-dimensional Visualization Fused with Ultrasound for Percutaneous Renal Puncture. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bale, R.; Widmann, G. Navigated CT-guided interventions. Minim. Invasive Ther. Allied Technol. 2007, 16, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moche, M.; Heinig, S.; Garnov, N.; Fuchs, J.; Petersen, T.O.; Seider, D.; Brandmaier, P.; Kahn, T.; Busse, H. Navigated MRI-guided liver biopsies in a closed-bore scanner: Experience in 52 patients. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 2462–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, K.; Hamamoto, S.; Okada, A.; Tanaka, Y.; Sugino, T.; Unno, R.; Kato, T.; Ando, R.; Tan, Y.K.; Yasui, T. Robot-Assisted Fluoroscopy Versus Ultrasound-Guided Renal Access for Nephrolithotomy: A Phantom Model Benchtop Study. J. Endourol. 2019, 33, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaikner, M.; Kögl, N.; Gruber, H.; Bale, R.; Ho, W.M.; Skalla-Oberherber, E.; Loizides, A. Ultrasound-guided versus computed tomography-controlled periradicular injections of the first sacral nerve: A prospective randomized clinical trial. Med. Ultrason. 2023, 25, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanza, C.; Carriero, S.; Buijs, E.F.M.; Mortellaro, S.; Pizzi, C.; Sciacqua, L.V.; Biondetti, P.; Angileri, S.A.; Ianniello, A.A.; Ierardi, A.M.; et al. Robotics in Interventional Radiology: Review of Current and Future Applications. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 22, 15330338231152084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spenkelink, I.M.; Heidkamp, J.; Avital, Y.; Fütterer, J.J. Evaluation of the performance of robot assisted CT-guided percutaneous needle insertion: Comparison with freehand insertion in a phantom. Eur. J. Radiol. 2023, 162, 110753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbalisike, E.C.; Vogl, T.J.; Zangos, S.; Eichler, K.; Balakrishnan, P.; Paul, J. Image-guided microwave thermoablation of hepatic tumours using novel robotic guidance: An early experience. Eur. Radiol. 2015, 25, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koethe, Y.; Xu, S.; Velusamy, G.; Wood, B.J.; Venkatesan, A.M. Accuracy and efficacy of percutaneous biopsy and ablation using robotic assistance under computed tomography guidance: A phantom study. Eur. Radiol. 2014, 24, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, K.Y.; Tan, A.S.M.; Bin Sulaiman, M.S.; Leong, S.H.; Ng, K.W.; Too, C.W. Phantom and Animal Study of a Robot-Assisted, CT-Guided Targeting System using Image-Only Navigation for Stereotactic Needle Insertion without Positional Sensors. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2022, 33, 1416–1423.e1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, B.J.; Yeong, C.H.; Goh, K.L.; Yoong, B.K.; Ho, G.F.; Yim, C.C.W.; Kulkarni, A. Robot-assisted radiofrequency ablation of primary and secondary liver tumours: Early experience. Eur. Radiol. 2014, 24, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fichtinger, G.; Troccaz, J.; Haidegger, T. Image-Guided Interventional Robotics: Lost in Translation? Proc. IEEE 2022, 110, 932–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettenbach, J.; Kronreif, G. Robotic systems for percutaneous needle-guided interventions. Minim. Invasive Ther. Allied Technol. 2015, 24, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafi, G.; Kreiser, K.; Abdelaziz, M.E.M.K.; Hamady, M.S. Current State of Robotics in Interventional Radiology. Cardiovasc. Intervent Radiol. 2023, 46, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharll, Y.; Mitteregger, A.; Laimer, G.; Schwabl, C.; Schullian, P.; Bale, R. Comparison of a Robotic and Patient-Mounted Device for CT-Guided Needle Placement: A Phantom Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharll, Y.; Letrari, S.; Laimer, G.; Schullian, P.; Bale, R. Puncture accuracy of an optical tracked robotic aiming device-a phantom study. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 6769–6776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharll, Y.; Böhler, D.; Laimer, G.; Schullian, P.; Bale, R. Laser Target System in Combination with an Aiming Device for Percutaneous CT-Guided Interventions—An Accuracy Study. Acad. Radiol. 2023, 30, 3047–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoffner, R.; Augschöll, C.; Widmann, G.; Böhler, D.; Bale, R. Accuracy and feasibility of frameless stereotactic and robot-assisted CT-based puncture in interventional radiology: A comparative phantom study. Rofo 2009, 181, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putzer, D.; Arco, D.; Schamberger, B.; Schanda, F.; Mahlknecht, J.; Widmann, G.; Schullian, P.; Jaschke, W.; Bale, R. Comparison of Two Electromagnetic Navigation Systems For CT-Guided Punctures: A Phantom Study. Rofo 2016, 188, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venturi, D.; Glossop, N.; Bale, R. Patient-specific templates for image-guided intervention—A phantom study. Minim. Invasive Ther. Allied Technol. 2020, 29, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, H.-J. Taschenbuch Mathematischer Formeln; Fachbuchverlag Leipzig: Leipzig, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Pollock, R.; Mozer, P.; Guzzo, T.J.; Marx, J.; Matlaga, B.; Petrisor, D.; Vigaru, B.; Badaan, S.; Stoianovici, D.; Allaf, M.E. Prospects in percutaneous ablative targeting: Comparison of a computer-assisted navigation system and the AcuBot Robotic System. J. Endourol. 2010, 24, 1269–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, B.; Eichler, K.; Siebenhandl, P.; Gruber-Rouh, T.; Czerny, C.; Vogl, T.J.; Zangos, S. Accuracy and speed of robotic assisted needle interventions using a modern cone beam computed tomography intervention suite: A phantom study. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widmann, G.; Schullian, P.; Haidu, M.; Wiedermann, F.J.; Bale, R. Respiratory motion control for stereotactic and robotic liver interventions. Int. J. Med. Robot. 2010, 6, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yan, Y.; Li, A.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y. Robot-Assisted Needle Insertion for CT-Guided Puncture: Experimental Study with a Phantom and Animals. Cardiovasc. Intervent Radiol. 2023, 46, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoth, F.; Plumhans, C.; Kraemer, N.; Mahnken, A.; Friebe, M.; Günther, R.W.; Krombach, G. Evaluation of an interactive breath-hold control system in CT-guided lung biopsy. Rofo 2010, 182, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haidegger, T.; Kazanzides, P.; Rudas, I.; Benyó, B.; Benyó, Z. The Importance of Accuracy Measurement Standards for Computer-Integrated Interventional Systems. In Proceedings of the 26th IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA2010), Anchorage, AK, USA, 3–7 May 2010. [Google Scholar]

| Slice Thickness | Micromate | iSYS-1 S7 | Innomotion | ArciNav | Stealth Station Treon | AxiEM | PercuNav | PCS | Slice Thickness | Maxio | SimpliCT +Atlas | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scharll et al. [16] | Stoffner et al. [18] | Venturi et al. [20] | Stoffner et al. [18] | Putzer et al. [19] | Putzer et al. [19] | Scharll et al. [15] | Scharll et al. [15] | Scharll et al. [17] | ||||
| 1 mm | 1.25 mm | |||||||||||
| ED mean (mm) | 2.1 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 2.5 | 1.9 | 3.9 | 4.4 | 4.1 | 1.5 | 2.8 | ||
| ED min. (mm) | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0 | 1.1 | 2.4 | 0 | 0 | 1.1 | ||
| ED max. (mm) | 5.3 | 2.5 | 3.3 | 4.6 | 4.8 | 15.8 | 8.7 | 8.0 | 3.3 | 5.4 | ||
| ED SD (mm) | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 2.3 | 1.3 | 1.7 | 0.9 | 0.9 | ||
| ND mean (mm) | 1.3 | 0.9 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 3.3 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 1.3 | 1.8 | ||
| ND min. (mm) | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 1.2 | 0 | 0.3 | 1.3 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | ||
| ND max. (mm) | 4.8 | 2.2 | 3.1 | 2.6 | 4.6 | 9.9 | 8.7 | 7.8 | 3.2 | 5.1 | ||
| ND SD (mm) | 0.8 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 1.5 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 0.8 | 0.9 | ||
| 3 mm | 2.5 mm | |||||||||||
| ED mean (mm) | 2.4 | 2.0 | 1.9 | 2.8 | 2.2 | 3.7 | 4.3 | 4.6 | 1.6 | 3.4 | ||
| ED min. (mm) | 0.4 | 0.7 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 1.1 | 2.1 | 0 | 0 | 2.0 | ||
| ED max. (mm) | 8.5 | 3.0 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 5.5 | 10.3 | 8.0 | 9.9 | 6.7 | 5.7 | ||
| ED SD (mm) | 1.1 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 2.1 | 1.3 | 2.3 | 1.2 | 0.8 | ||
| ND mean (mm) | 1.8 | 0.9 | 1.6 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 3.2 | 3.8 | 4.4 | 1.3 | 2.1 | ||
| ND min. (mm) | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 1.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| ND max. (mm) | 6.4 | 1.7 | 3.7 | 5.2 | 5.1 | 8.4 | 7.7 | 9.3 | 3.4 | 5.4 | ||
| ND SD (mm) | 1.1 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 2.3 | 0.8 | 1.1 | ||
| 5 mm | 5 mm | |||||||||||
| ED mean (mm) | 3.9 | 1.8 | 2.3 | No data | 2.7 | 4.8 | 4.5 | 4.6 | 1.7 | 3.7 | ||
| ED min. (mm) | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.7 | No data | 0.3 | 1.3 | 2.1 | 0 | 0 | 2.3 | ||
| ED max. (mm) | 15.4 | 2.9 | 5.2 | No data | 6.8 | 10.5 | 9.2 | 8.9 | 7.1 | 7.6 | ||
| ED SD (mm) | 2.8 | 0.5 | 0.9 | No data | 1.2 | 2.1 | 1.6 | 2.1 | 1.2 | 1.1 | ||
| ND mean (mm) | 3.4 | 0.7 | 2.0 | No data | 2.5 | 3.9 | 3.8 | 4.4 | 1.4 | 1.9 | ||
| ND min. (mm) | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.5 | No data | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | ||
| ND max. (mm) | 12.4 | 2.2 | 5.2 | No data | 6.6 | 8.8 | 8.1 | 8.8 | 7.0 | 7.5 | ||
| ND SD (mm) | 2.1 | 0.5 | 1.0 | No data | 1.2 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 2.1 | 1.0 | 1.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scharll, Y.; Radojicic, N.; Laimer, G.; Schullian, P.; Bale, R. Puncture Accuracy of Robot-Assisted CT-Based Punctures in Interventional Radiology: An Ex Vivo Study. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14131371
Scharll Y, Radojicic N, Laimer G, Schullian P, Bale R. Puncture Accuracy of Robot-Assisted CT-Based Punctures in Interventional Radiology: An Ex Vivo Study. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(13):1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14131371
Chicago/Turabian StyleScharll, Yannick, Nenad Radojicic, Gregor Laimer, Peter Schullian, and Reto Bale. 2024. "Puncture Accuracy of Robot-Assisted CT-Based Punctures in Interventional Radiology: An Ex Vivo Study" Diagnostics 14, no. 13: 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14131371
APA StyleScharll, Y., Radojicic, N., Laimer, G., Schullian, P., & Bale, R. (2024). Puncture Accuracy of Robot-Assisted CT-Based Punctures in Interventional Radiology: An Ex Vivo Study. Diagnostics, 14(13), 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14131371







