Combining Molecular and Traditional Prognostic Factors: A Holistic Approach to Breast Cancer Prognostication
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davey, M.G.; Hynes, S.O.; Kerin, M.J.; Miller, N.; Lowery, A.J. Ki-67 as a Prognostic Biomarker in Invasive Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassadonia, A.; Graziano, V.; Iezzi, L.; Vici, P.; Barba, M.; Pizzuti, L.; Cicero, G.; Krasniqi, E.; Mazzotta, M.; Marinelli, D.; et al. Prognostic Relevance of Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) in Luminal Breast Cancer: A Retrospective Analysis in the Neoadjuvant Setting. Cells 2021, 10, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bao, C.; Lu, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, D.; Lou, W.; Ding, B.; Xu, L.; Fan, W. Exploring specific prognostic biomarkers in triple-negative breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fekete, J.T.; Győrffy, B. ROCplot.org: Validating predictive biomarkers of chemotherapy/hormonal therapy/anti-HER2 therapy using transcriptomic data of 3,104 breast cancer patients. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 3140–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieci, M.V.; Guarneri, V.; Tosi, A.; Bisagni, G.; Musolino, A.; Spazzapan, S.; Moretti, G.; Vernaci, G.M.; Griguolo, G.; Giarratano, T.; et al. Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy in Luminal B-like Breast Cancer: Results of the Phase II GIADA Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Guan, X.; Fan, Z.; Ching, L.-M.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Cao, W.-M.; Liu, D.-X. Non-Invasive Biomarkers for Early Detection of Breast Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soerjomataram, I.; Louwman, M.W.J.; Ribot, J.G.; Roukema, J.A.; Coebergh, J.W.W. An overview of prognostic factors for long-term survivors of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2008, 107, 309–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höller, A.; Nguyen-Sträuli, B.D.; Frauchiger-Heuer, H.; Ring, A. Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers of Luminal Breast Cancer: Where are We now? Breast Cancer Targets Ther. 2023, 15, 525–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cserni, G.; Francz, M.; Járay, B.; Kálmán, E.; Kovács, I.; Krenács, T.; Tóth, E.; Udvarhelyi, N.; Vass, L.; Vörös, A.; et al. Pathological Diagnosis, Work-Up and Reporting of Breast Cancer 1st Central-Eastern European Professional Consensus Statement on Breast Cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2022, 28, 1610373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Ma, G.; Deng, Y.; Luo, W.; Zhao, Y.; Li, W.; Zhou, Q. Prognostic Value of Ki-67 in Patients With Resected Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagree, A.; Shiner, A.; Alera, M.A.; Fleshner, L.; Law, E.; Law, B.; Lu, F.-I.; Dodington, D.; Gandhi, S.; Slodkowska, E.A.; et al. Assessment of Digital Pathology Imaging Biomarkers Associated with Breast Cancer Histologic Grade. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 4298–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madigan, L.I.; Dinh, P.; Graham, J.D. Neoadjuvant endocrine therapy in locally advanced estrogen or progesterone receptor-positive breast cancer: Determining the optimal endocrine agent and treatment duration in postmenopausal women—A literature review and proposed guidelines. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocco, S.; Piezzo, M.; Calabrese, A.; Cianniello, D.; Caputo, R.; Di Lauro, V.; Fusco, G.; di Gioia, G.; Licenziato, M.; de Laurentiis, M. Biomarkers in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: State-of-the-Art and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kos, Z.; Roblin, E.; Kim, R.S.; Michiels, S.; Gallas, B.D.; Chen, W.; van de Vijver, K.K.; Goel, S.; Adams, S.; Demaria, S.; et al. Pitfalls in assessing stromal tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (sTILs) in breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2020, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Bairi, K.; Haynes, H.R.; Blackley, E.; Fineberg, S.; Shear, J.; Turner, S.; de Freitas, J.R.; Sur, D.; Amendola, L.C.; Gharib, M.; et al. The tale of TILs in breast cancer: A report from The International Immuno-Oncology Biomarker Working Group. NPJ Breast Cancer 2021, 7, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Torralba, E.; Ramos, M.P.; Rubio, A.I.; Navarro-Manzano, E.; Boluda, N.B.; Barrio, P.d.l.M.; García-Garre, E.; Díaz, F.M.; Chaves-Benito, A.; García-Martínez, E.; et al. Clinical Meaning of Stromal Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes (sTIL) in Early Luminal B Breast Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.-H.; Li, C.-X.; Liu, M.; Jiang, J.-Y. Predictive and prognostic role of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancer patients with different molecular subtypes: A meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tullberg, A.S.; Sjöström, M.; Tran, L.; Niméus, E.; Killander, F.; Kovács, A.; Lundstedt, D.; Holmberg, E.; Karlsson, P. Combining histological grade, TILs, and the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway to identify immunogenic tumors and de-escalate radiotherapy in early breast cancer: A secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e006618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Tsang, J.Y.; Shao, Y.; Poon, I.K.; Tam, F.; Shea, K.-H.; Tse, G.M. Combining Analysis of Tumor-infiltrating Lymphocytes (TIL) and PD-L1 Refined the Prognostication of Breast Cancer Subtypes. Oncologist 2022, 27, e313–e327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmahs, A.; Mohamed, G.; Salem, M.; Omar, D.; Helal, A.M.; Soliman, N. The Impact of Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes Densities and Ki67 Index on Residual Breast Cancer Burden following Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Int. J. Breast Cancer 2022, 2022, 2597889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinterri, C.; Fernandes, B.; Zambelli, A.; Sagona, A.; Barbieri, E.; Grimaldi, S.D.M.; Darwish, S.S.; Jacobs, F.; De Carlo, C.; Iuzzolino, M.; et al. The Impact of Different Patterns of Residual Disease on Long-Term Oncological Outcomes in Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Neo-Adjuvant Chemotherapy. Cancers 2024, 16, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laas, E.; Labrosse, J.; Hamy, A.-S.; Benchimol, G.; de Croze, D.; Feron, J.-G.; Coussy, F.; Balezeau, T.; Guerin, J.; Lae, M.; et al. Determination of breast cancer prognosis after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: Comparison of Residual Cancer Burden (RCB) and Neo-Bioscore. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 1421–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, A.C.; Somerfield, M.R.; Dowsett, M.; Hammond, M.E.H.; Hayes, D.F.; McShane, L.M.; Saphner, T.J.; Spears, P.A.; Allison, K.H. Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Testing in Breast Cancer: ASCO–College of American Pathologists Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 3867–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgibbons, P.L.; Connolly, J.L. Template for Reporting Results of Biomarker Testing of Specimens from Patients with Carcinoma of the Breast, version 1.5.0.1.; College of American Pathologists: Northfield, IL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. WHO Classification of Tumours. Breast Tumours, 5th ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2019; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Petre, I.; Barna, F.; Gurgus, D.; Tomescu, L.C.; Apostol, A.; Petre, I.; Furau, C.; Năchescu, M.L.; Bordianu, A. Analysis of the Healthcare System in Romania: A Brief Review. Healthcare 2023, 11, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, D.P.; Azeredo-Lopes, S.; Antunes, A.; Salvador, R.; Borralho, P.; Assis, B.; Pereira, I.L.; Seabra, Z.; Negreiros, I.; Jacinto, A.; et al. Expression of HLA-DR in Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes: A Validated Predictive Biomarker and a Potential Therapeutic Strategy in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual, T.; Martin, M.; Fernández-Martínez, A.; Paré, L.; Alba, E.; Rodríguez-Lescure, Á.; Perrone, G.; Cortés, J.; Morales, S.; Lluch, A.; et al. A pathology-based combined model to identify PAM50 non-luminal intrinsic disease in hormone receptor-positive HER2-negative breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, H.D.; Posch, F.; Suppan, C.; Bargfrieder, U.; Gumpoldsberger, M.; Hammer, R.; Hauser, H.; Dandachi, N.; Prein, K.; Stoeger, H.; et al. Validation of residual cancer burden as prognostic factor for breast cancer patients after neoadjuvant therapy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 4274–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zhao, W.; Liu, C.; Gao, Y.; Chen, D.; Wu, M.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Song, X.; Yu, J.; et al. The residual cancer burden index as a valid prognostic indicator in breast cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Abubakar, M.; Yuan, P.; Koka, H.; Guo, L.; Li, X.; Yang, X.R.; Ying, J.; Lyu, N. Prognostic significance of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in premenopausal, luminal breast cancer treated with adjuvant endocrine therapy. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 12750. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, S.; Chung, Y.R.; Na Seo, A.; Kim, M.; Woo, J.W.; Park, S.Y. Changes and prognostic values of tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte subsets after primary systemic therapy in breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbeau, I.; Jacot, W.; Guiu, S. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio as Prognostic and Predictive Factor in Breast Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2020, 12, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, A.F.; Schmitt, F. An update on breast cancer multigene prognostic tests—Emergent clinical biomarkers. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marra, A.; Viale, G.; Curigliano, G. Recent advances in triple negative breast cancer: The immunotherapy era. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewelina, N.; Mączyńska, E.; Lewandowska, M.A. Prognostic and predictive biomarkers: Tools in personalized oncology. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2014, 18, 273–284. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Yu, X.; Jin, F. Identification and validation of stemness-related lncRNA prognostic signature for breast cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazzichetto, C.; Conciatori, F.; Pallocca, M.; Falcone, I.; Fanciulli, M.; Cognetti, F.; Milella, M.; Ciuffreda, L. PTEN as a Prognostic/Predictive Biomarker in Cancer: An Unfulfilled Promise? Cancers 2019, 11, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citu, C.; Danciu, C.; Pinzaru, I.; Ghiulai, R.; Vlaia, L.; Vlaia, V.; Borcan, F.; Dumitru, C.; Pavel, I.Z.; Sas, I.; et al. Genistein and its Fatty Acid Esters as New In vitro Antitumor Compounds. Rev. Chim. 2015, 66, 1100–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Goidescu, I.G.; Caracostea, G.; Rotar, I.C.; Eniu, D.T.; Nemeti, G.I.; Cruciat, G.; Stamatian, F.; Muresan, D. The influence of reproductive factors on breast cancer risk in women with pathogenic mutations. JBUON 2019, 24, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar]
- Hamy, A.-S.; Darrigues, L.; Laas, E.; De Croze, D.; Topciu, L.; Lam, G.-T.; Evrevin, C.; Rozette, S.; Laot, L.; Lerebours, F.; et al. Prognostic value of the Residual Cancer Burden index according to breast cancer subtype: Validation on a cohort of BC patients treated by neoadjuvant chemotherapy. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, C.; Osdoit, M.; van der Noordaa, M.; Shad, S.; Wei, J.; de Croze, D.; Hamy, A.-S.; Laé, M.; Reyal, F.; Sonke, G.S.; et al. Residual cancer burden after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and long-term survival outcomes in breast cancer: A multicentre pooled analysis of 5161 patients. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

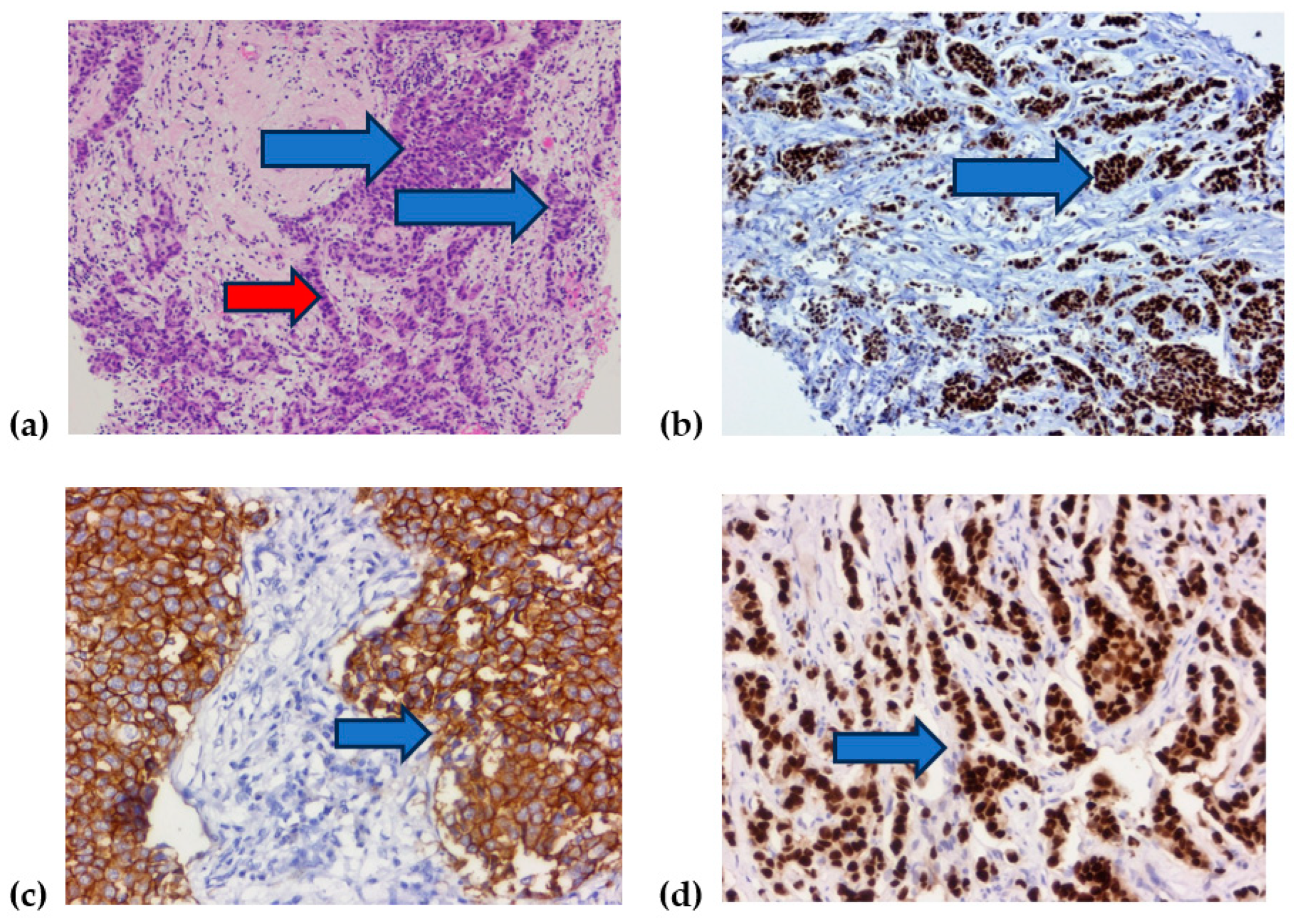
| Variables | Nottingham Grade | Total | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | ||||
| Ki67 (1 means < 14 and has good prognosis) | 1 | 28 (51.9) | 49 (27.1) | 8 (21.1) | 85 (31.1) | 0.0001 Statistically significant |
| 2 | 26 (48.1) | 132 (72.9) | 30 (78.9) | 188 (68.9) | ||
| HER | 0 | 39 (72.2) | 107 (59.1) | 23 (60.5) | 169 (61.9) | p = 0.10 |
| 1 | 11 (20.4) | 38 (21.0) | 4 (10.5) | 53 (19.4) | ||
| 2 | 0 (0.0) | 13 (7.2) | 5 (13.2) | 18 (6.6) | ||
| 3 | 4 (7.4) | 23 (12.7) | 6 (15.8) | 33 (12.1) | ||
| Luminal category | A | 22 (40.7) | 39 (21.5) | 4 (10.5) | 65 (23.8) | p = 0.0001 Statistically significant |
| B | 13 (24.1) | 59 (32.6) | 13 (34.2) | 85 (31.1) | ||
| B (HER2) | 12 (22.2) | 59 (32.6) | 5 (13.2) | 76 (27.8) | ||
| HER2 | 2 (3.7) | 4 (2.2) | 8 (21.1) | 14 (5.1) | ||
| TNBC | 5 (9.3) | 20 (11.0) | 8 (21.2) | 33 (12.1) | ||
| TILs (1 means low prognosis) | 1 | 25 (46.3) | 50 (27.6) | 13 (34.2) | 88 (32.2) | p = 0.032 Statistically significant |
| 2 | 29 (53.7) | 131 (72.4) | 25 (65.8) | 185 (67.8) | ||
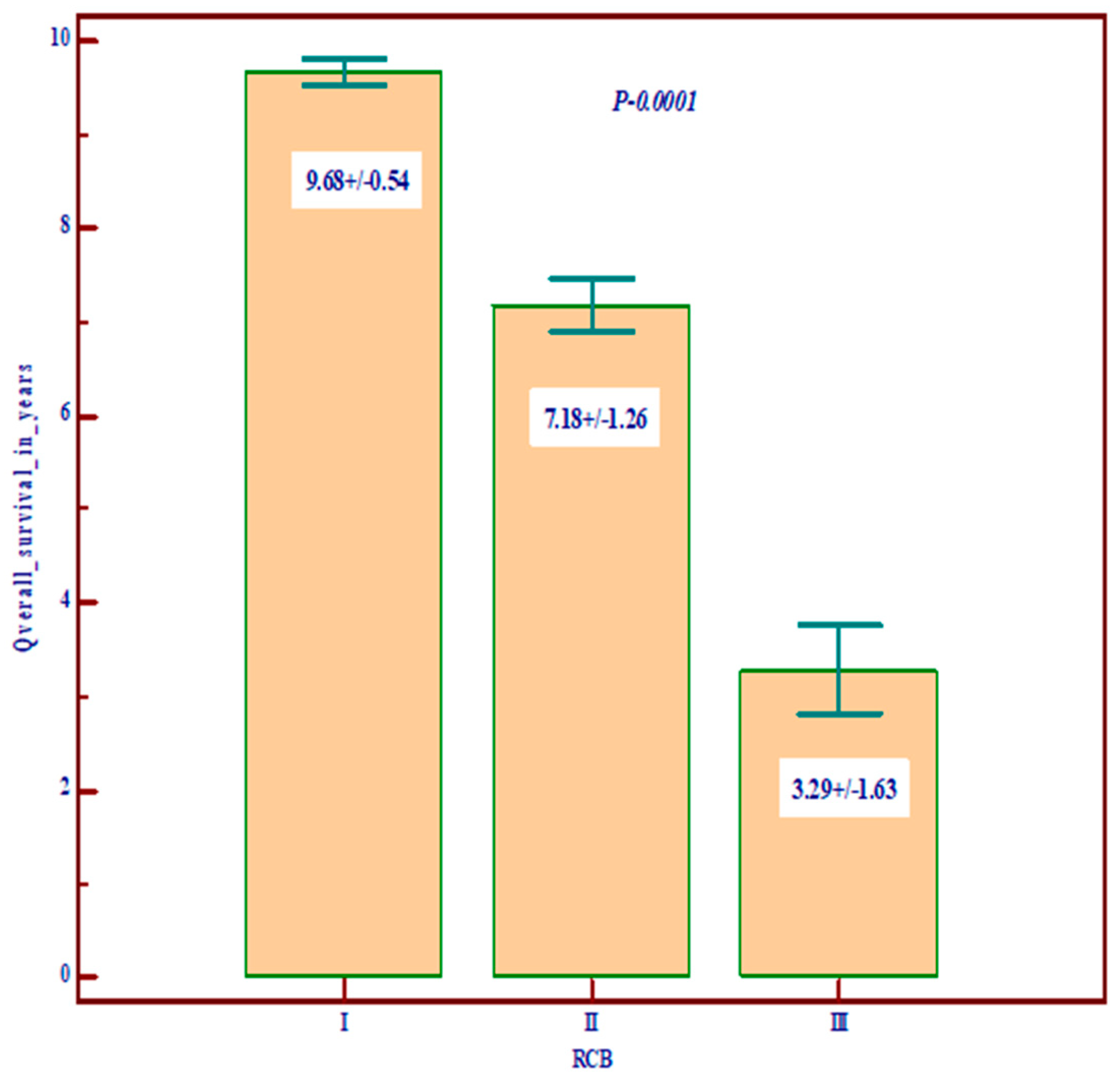
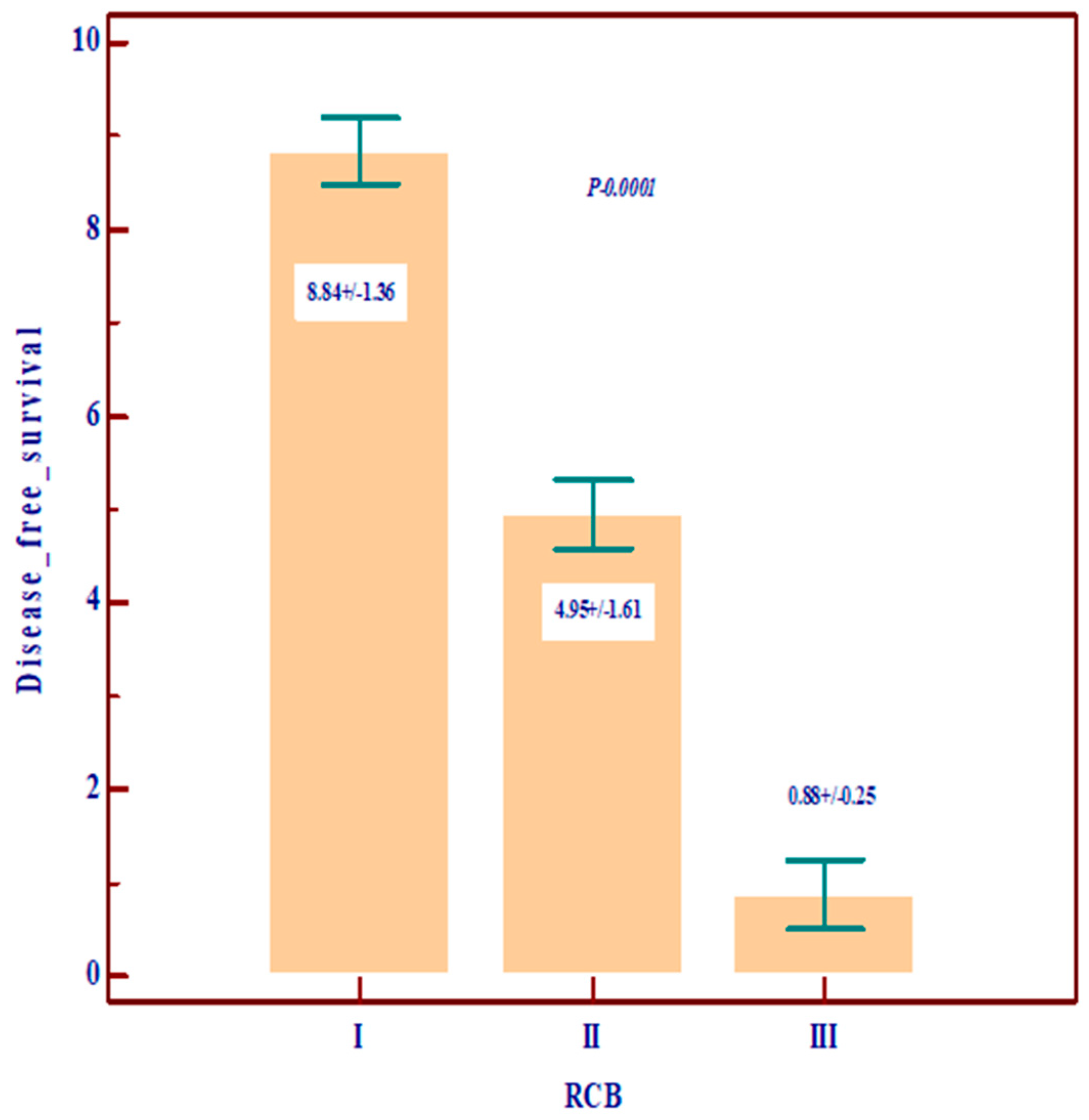
| RCB | 0 | 17 (31.5) | 62 (34.3) | 9 (23.7) | 88 (32.2) | p = 0.10 |
| 1 | 17 (31.5) | 34 (18.8) | 6 (15.8) | 57 (20.9) | ||
| 2 | 14 (25.9) | 54 (29.8) | 11 (28.9) | 79 (28.9) | ||
| 3 | 6 (11.1) | 31 (17.1) | 12 (31.6) | 49 (17.9) | ||
| R estrogen H Score | Mean ± SD | 232.78 ± 73.4 | 221.83 ± 80.3 | 168.0 ± 105.5 | 218.8 ± 83.2 | Statistically significantly lower values in grade III (p = 0.008) |
| R estrogen Allred score | Mean ± SD | 7.43 ± 1.25 | 7.34 ± 1.47 | 6.23 ± 2.13 | 7.25 ± 1.53 | Statistically significantly lower values in grade III (p = 0.007) |
| R progesterone H score | Mean ± SD | 163.2 ± 37.4 | 148.4 ± 38.16 | 90.32 ± 32.58 | 146.23 ± 38.84 | Statistically significantly lower values in grade III (p = 0.021) |
| R progesterone Allred sScore | Mean ± SD | 6.20 ± 1.94 | 6.30 ± 2.01 | 4.42 ± 2.21 | 6.11 ± 2.07 | Statistically significantly lower values in grade III (p = 0.004) |
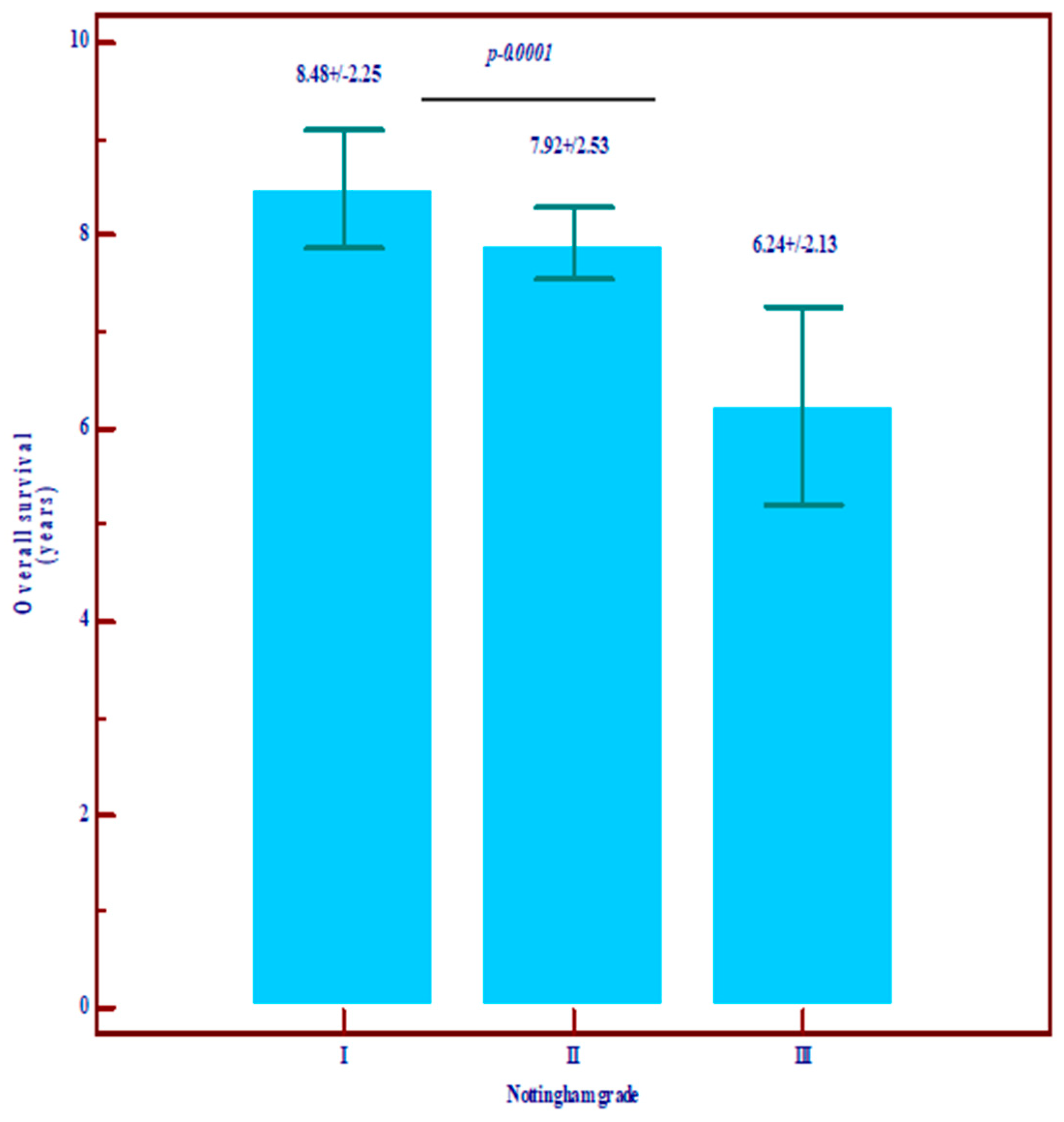
| Overall survival in years | Mean ± SD | 8.48 ± 2.25 | 7.92 ± 2.53 | 6.24 ± 2.13 | 7.79 ± 2.65 | Statistically significantly lower values in grade III (p = 0.0001) |
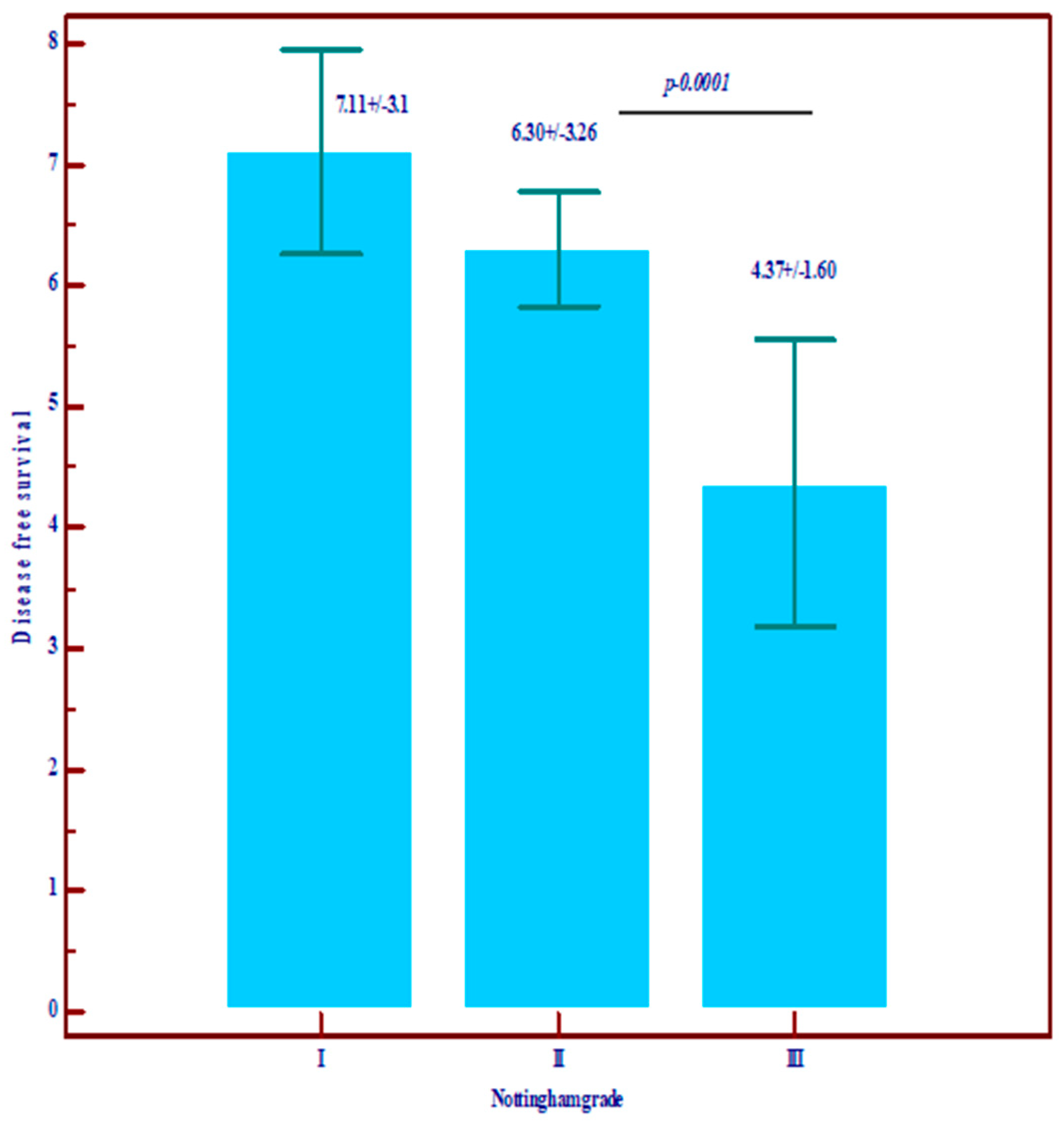
| Disease-free survival (DFS) | Mean ± SD | 7.11 ± 3.10 | 6.30 ± 3.26 | 4.37 ± 1.60 | 3.19 ± 3.36 | Statistically significantly lower values in grade III (p = 0.0001) |
| Variables | Stadium TNM | Total | p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | In Situ | IV | ||||
| Ki67 (1 means < 14 and has good prognosis) | 1 | 49 (36.8) | 25 (26.3) | 7 (25.9) | 3 (33.3) | 1 (11.1) | 85 (31.1) | p = 0.28 |
| 2 | 84 (63.2) | 70 (73.7) | 20 (74.1) | 6 (66.7) | 8 (88.9) | 188 (68.9) | ||
| HER2 | 0 | 84 (63.2) | 59 (62.1) | 14 (51.9) | 6 (66.7) | 6 (66.7) | 169 (61.9) | p = 0.36 |
| 1 | 22 (16.5) | 21 (22.1) | 9 (33.3) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (11.1) | 53 (19.4) | ||
| 2 | 10 (7.5) | 6 (6.3) | 2 (7.4) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 18 (6.6) | ||
| 3 | 17 (12.8) | 9 (9.5) | 2 (7.4) | 3 (33.3) | 2 (22.2) | 33 (12.1) | ||
| Luminal category | A | 37 (27.8) | 20 (21.1) | 5 (18.5) | 2 (22.2) | 1 (11.1) | 65 (23.8) | p = 0.75 |
| B | 40 (30.1) | 32 (33.7) | 6 (22.2) | 2 (22.2) | 5 (55.6) | 85 (31.1) | ||
| B (HER2) | 39 (29.3) | 24 (25.3) | 10 (37.0) | 2 (22.2) | 1 (11.1) | 76 (27.8) | ||
| HER2 | 4 (3.0) | 6 (6.3) | 2 (7.4) | 1 (11.1) | 1 (11.1) | 14 (5.1) | ||
| TNBC | 13 (9.8) | 13 (13.7) | 4 (14.8) | 2 (22.2) | 1 (11.1) | 33 (12.1) | ||
| TILs (1 means low prognosis) | 1 | 47 (35.3) | 22 (23.2) | 9 (33.3) | 7 (77.8) | 3 (33.3) | 88 (32.2) | p = 0.01 Statistically significant |
| 2 | 86 (64.7) | 73 (76.8) | 18 (66.7) | 2 (22.2) | 6 (66.7) | 185 (67.8) | ||
| RCB | 0 | 74 (55.6) | 6 (6.3) | 1 (3.7) | 7 (77.8) | 0 (0.0) | 88 (32.2) | p = 0.0001 Statistically significant |
| 1 | 52 (39.1) | 3 (3.2) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (22.2) | 0 (0.0) | 57 (20.9) | ||
| 2 | 7 (5.3) | 68 (71.6) | 4 (14.8) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 79 (28.9) | ||
| 3 | 0 (0.0) | 18 (18.9) | 22 (81.5) | 0 (0.0) | 9 (100) | 49 (17.9) | ||
| R estrogen H score | Mean ± SD | 217.63 ± 85.7 | 224.05 ± 75.3 | 217.6 ± 88.5 | 180.83 ± 98.92 | 218.57 ± 82.5 | 218.8 ± 83.2 | Statistically insignificant |
| R estrogen Allred score | Mean ± SD | 7.29 ± 1.48 | 7.27 ± 1.46 | 7.14 ± 1.83 | 6.33 ± 2.42 | 7.43 ± 1.51 | 7.25 ± 1.53 | Statistically insignificant |
| R progesterone H score | Mean ± SD | 144.45 ± 54.01 | 141.41 ± 35.26 | 137.11 ± 35.66 | 247.5 ± 59.1 | 188.57 ± 52.8 | 146.23 ± 38.8 | Statistically insignificant |
| R progesterone Allred score | Mean ± SD | 6.28 ± 1.92 | 5.83 ± 2.19 | 5.61 ± 2.38 | 7.75 ± 0.5 | 6.71 ± 2.36 | 6.11 ± 2.07 | Statistically insignificant |
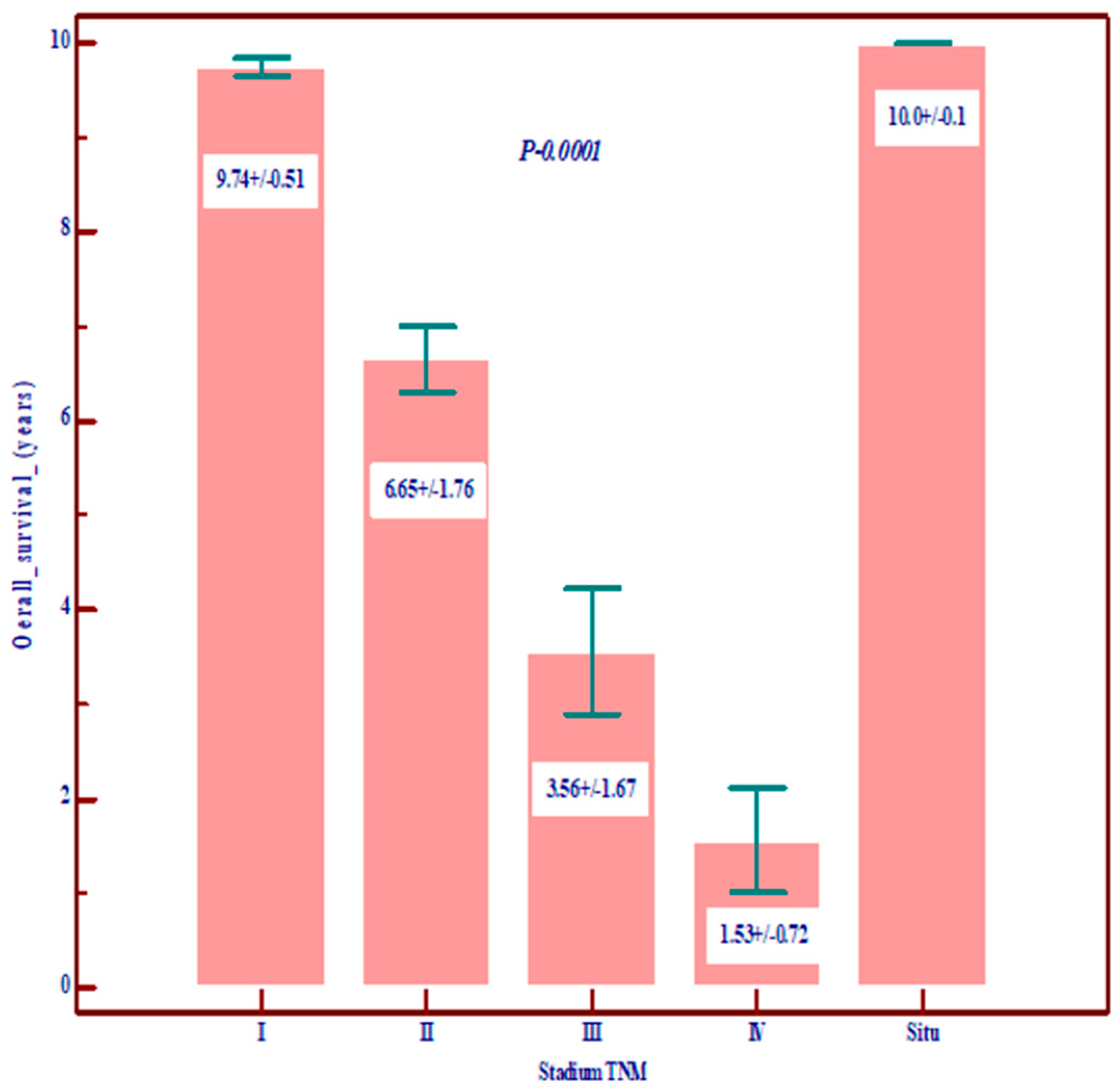
| Overall survival in years | Mean ± SD | 9.74 ± 0.51 | 6.65 ± 1.76 | 3.56 ± 1.67 | 10.0 ± 0.1 | 1.56 ± 0.72 | 7.79 ± 2.65 | 0.0001 Statistically significant lower value in stages III and IV |
| Disease-free survival (DFS) | Mean ± SD | 8.74 ± 1.37 | 4.33 ± 2.06 | 1.04 ± 0.31 | 10.0 ± 0.1 | - | 6.19 ± 2.36 | 0.0001 Statistically significant lower value in stages III and IV |
| RCB | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | p Value | ||||
| Chemotherapy | yes | Count | 36 | 65 | 43 | 144 | 0.0001 |
| % | 63.2% | 82.3% | 87.8% | 77.8% | |||
| Hormontherapy | yes | Count | 24 | 24 | 13 | 61 | 0.19 |
| % | 42.1% | 30.4% | 26.5% | 33.0% | |||
| Herceptin | yes | Count | 9 | 18 | 12 | 39 | 0.49 |
| % | 15.8% | 22.8% | 24.5% | 21.1% | |||
| Radiotherapy | yes | Count | 3 | 2 | 1 | 6 | 0.57 |
| % | 5.3% | 2.5% | 2.0% | 3.2% | |||
| Stadium TNM | Total | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | In Situ | IV | p Value | ||||
| Chemotherapy | yes | Count | 70 | 75 | 25 | 4 | 9 | 183 | 0.0001 |
| % | 52.6% | 78.9% | 92.6% | 44.4% | 100.0% | 67.0% | |||
| Hormontherapy | yes | Count | 41 | 28 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 79 | 0.072 |
| % | 30.8% | 29.5% | 37.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 28.9% | |||
| Herceptin | yes | Count | 22 | 21 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 53 | 0.70 |
| % | 16.5% | 22.1% | 18.5% | 33.3% | 22.2% | 19.4% | |||
| Radiotherapy | yes | Count | 5 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 0.93 |
| % | 3.8% | 2.1% | 3.7% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 2.9% | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moraru, L.; Mitranovici, M.I.; Moraru, R.; Voidazan, S.; Munteanu, M.; Georgescu, R.; Costachescu, D.; Turdean, S.G. Combining Molecular and Traditional Prognostic Factors: A Holistic Approach to Breast Cancer Prognostication. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14131449
Moraru L, Mitranovici MI, Moraru R, Voidazan S, Munteanu M, Georgescu R, Costachescu D, Turdean SG. Combining Molecular and Traditional Prognostic Factors: A Holistic Approach to Breast Cancer Prognostication. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(13):1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14131449
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoraru, Liviu, Melinda Ildiko Mitranovici, Raluca Moraru, Septimiu Voidazan, Mihai Munteanu, Rares Georgescu, Dan Costachescu, and Sabin Gligore Turdean. 2024. "Combining Molecular and Traditional Prognostic Factors: A Holistic Approach to Breast Cancer Prognostication" Diagnostics 14, no. 13: 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14131449
APA StyleMoraru, L., Mitranovici, M. I., Moraru, R., Voidazan, S., Munteanu, M., Georgescu, R., Costachescu, D., & Turdean, S. G. (2024). Combining Molecular and Traditional Prognostic Factors: A Holistic Approach to Breast Cancer Prognostication. Diagnostics, 14(13), 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14131449










