Liquid Biopsies Based on Cell-Free DNA Integrity as a Biomarker for Cancer Diagnosis: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Search Strategy and Study Selection
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Ethical Statement
2.5. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.6. Assessment of Risk Bias
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
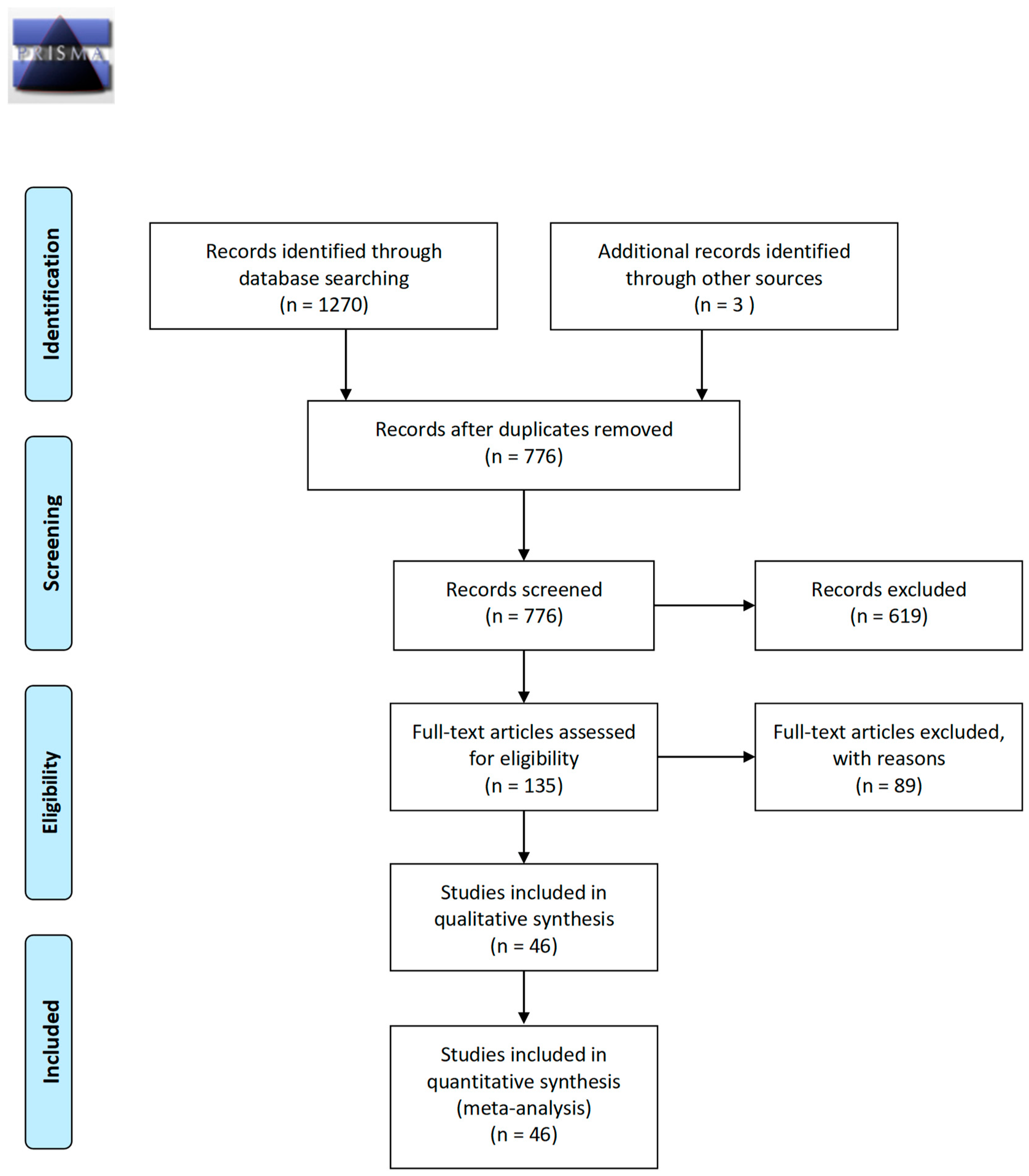
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Characteristics of Included Studies
3.3. Quality Assessment of the Included Studies
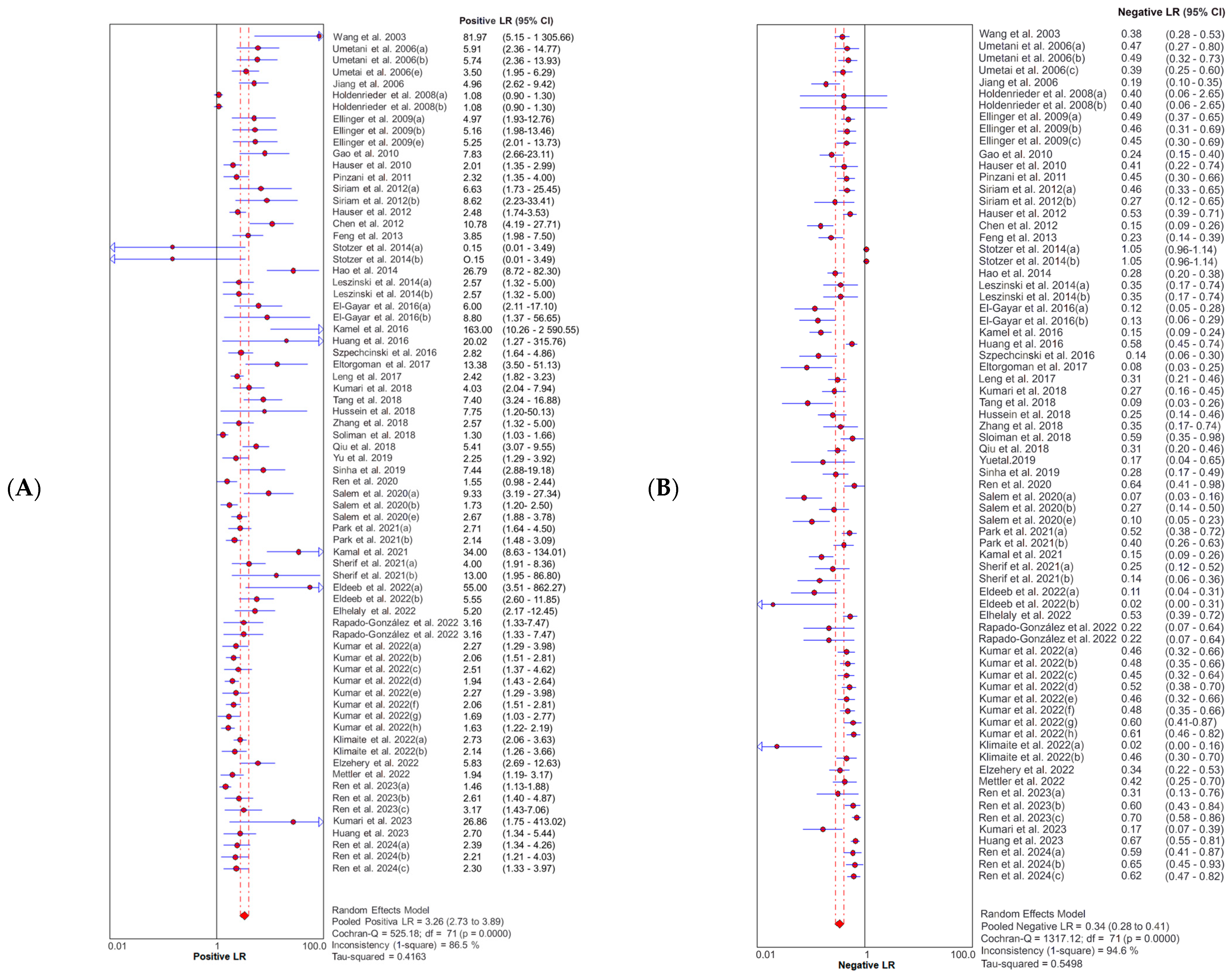
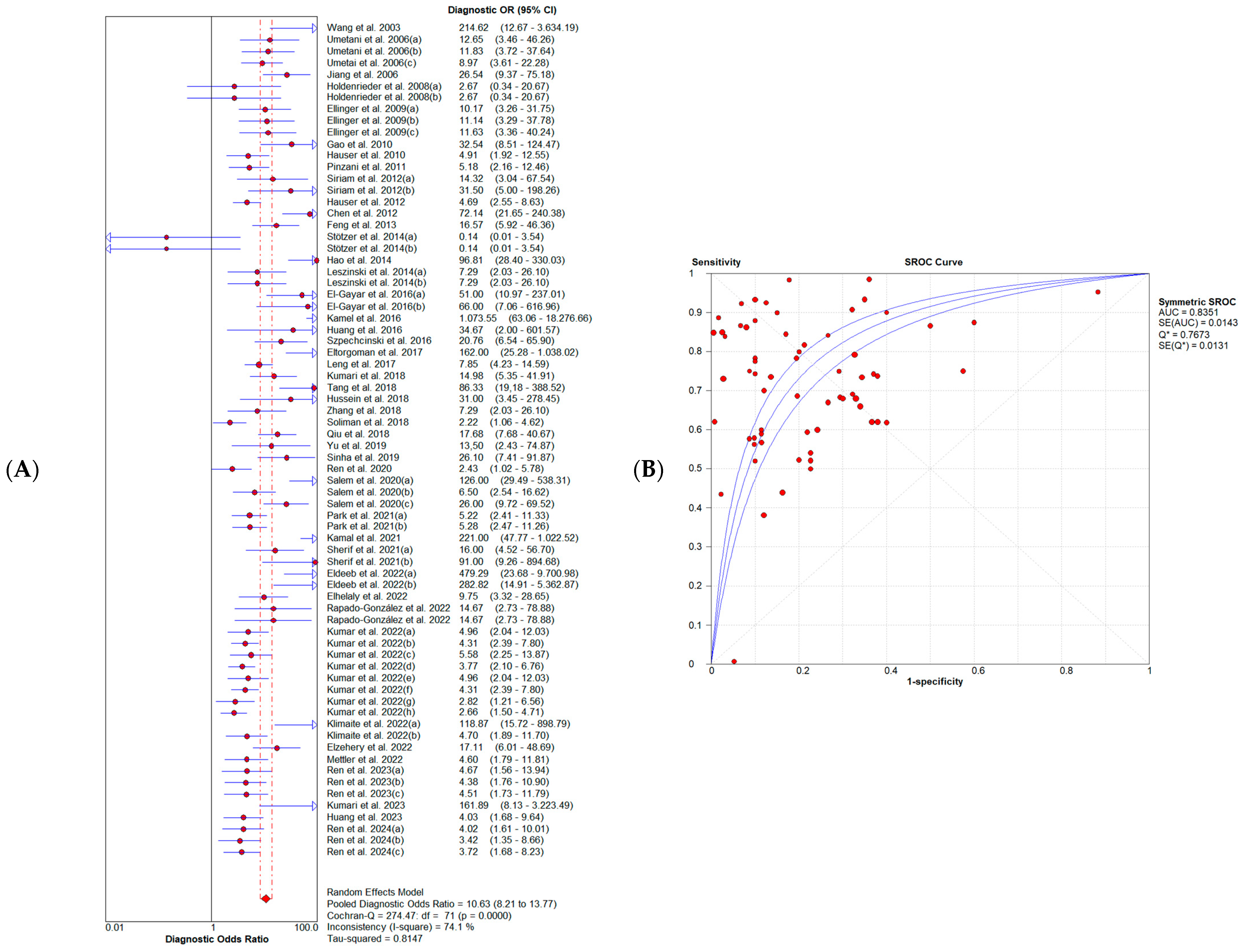
3.4. Diagnostic Accuracy of Cell-Free DNA Integrity Index
3.5. Publication Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naghavi, M.; Ong, K.L.; Aali, A.; Ababneh, H.S.; Abate, Y.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abbasgholizadeh, R.; Abbasian, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abbastanbar, H.; et al. GBD 2021 Causes of Death Collaborators. Global Burden of 288 Causes of Death and Life Expectancy Decomposition in 204 Countries and Territories and 811 Subnational Locations, 1990–2021: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2024, 403, 2100–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, J. It Is Time to Close the Gap in Cancer Care. JCO Glob. Oncol. 2023, 9, e2200429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, I.R.; Fuchs, O.; Hansen, G.; von Mutius, E.; Kopp, M.V. What Is Precision Medicine? Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malone, E.R.; Oliva, M.; Sabatini, P.J.B.; Stockley, T.L.; Siu, L.L. Molecular Profiling for Precision Cancer Therapies. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashley, E.A. Towards Precision Medicine. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Dey, M.K.; Devireddy, R.; Gartia, M.R. Biomarkers in Cancer Detection, Diagnosis, and Prognosis. Sensors 2023, 24, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Zhao, H. Next-Generation Sequencing in Liquid Biopsy: Cancer Screening and Early Detection. Hum. Genom. 2019, 13, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, T.K.Y.; Tan, P.H. Liquid Biopsy in Breast Cancer: A Focused Review. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2021, 145, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulet, G.; Massias, J.; Taly, V. Liquid Biopsy: General Concepts. Acta Cytol. 2019, 63, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, Y.R.; Tsui, D.W.Y.; Diaz, L.A.; Wan, J.C.M. Next-Generation Liquid Biopsies: Embracing Data Science in Oncology. Trends Cancer 2021, 7, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shegekar, T.; Vodithala, S.; Juganavar, A. The Emerging Role of Liquid Biopsies in Revolutionising Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy. Cureus 2023, 15, e43650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisodiya, S.; Kasherwal, V.; Khan, A.; Roy, B.; Goel, A.; Kumar, S.; Arif, N.; Tanwar, P.; Hussain, S. Liquid Biopsies: Emerging Role and Clinical Applications in Solid Tumours. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 35, 101716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Hu, S.; Zhang, L.; Xin, J.; Sun, C.; Wang, L.; Ding, K.; Wang, B. Tumor Circulome in the Liquid Biopsies for Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis. Theranostics 2020, 10, 4544–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, Y.M.D.; Han, D.S.C.; Jiang, P.; Chiu, R.W.K. Epigenetics, Fragmentomics, and Topology of Cell-Free DNA in Liquid Biopsies. Science 2021, 372, eaaw3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitzer, E.; Haque, I.S.; Roberts, C.E.S.; Speicher, M.R. Current and Future Perspectives of Liquid Biopsies in Genomics-Driven Oncology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, T.; Pan, M.; Shi, H.; Wang, L.; Bai, Y.; Ge, Q. Cell-Free DNA Fragmentomics: The Novel Promising Biomarker. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lousada-Fernandez, F.; Rapado-Gonzalez, O.; Lopez-Cedrun, J.-L.; Lopez-Lopez, R.; Muinelo-Romay, L.; Suarez-Cunqueiro, M.M. Liquid Biopsy in Oral Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapado-González, Ó.; Rodríguez-Ces, A.M.; López-López, R.; Suárez-Cunqueiro, M.M. Liquid Biopsies Based on Cell-Free DNA as a Potential Biomarker in Head and Neck Cancer. Jpn. Dent. Sci. Rev. 2023, 59, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, P.S.; Shiang, A.; Alahi, I.; Sundby, R.T.; Feng, W.; Gungoren, B.; Nawaf, C.; Chen, K.; Babbra, R.K.; Harris, P.K.; et al. Urine Cell-Free DNA Multi-Omics to Detect MRD and Predict Survival in Bladder Cancer Patients. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2023, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bruin, E.C.; Medema, J.P. Apoptosis and Non-Apoptotic Deaths in Cancer Development and Treatment Response. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2008, 34, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronkhorst, A.J.; Ungerer, V.; Holdenrieder, S. The Emerging Role of Cell-Free DNA as a Molecular Marker for Cancer Management. Biomol. Detect. Quantif. 2019, 17, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kustanovich, A.; Schwartz, R.; Peretz, T.; Grinshpun, A. Life and Death of Circulating Cell-Free DNA. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoran, R.B.; Chabner, B.A. Application of Cell-Free DNA Analysis to Cancer Treatment. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1754–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thierry, A.R. Circulating DNA Fragmentomics and Cancer Screening. Cell Genom. 2023, 3, 100242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Messaoudi, S.; Rolet, F.; Mouliere, F.; Thierry, A.R. Circulating Cell Free DNA: Preanalytical Considerations. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 424, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdenrieder, S.; Nagel, D.; Schalhorn, A.; Heinemann, V.; Wilkowski, R.; von Pawel, J.; Raith, H.; Feldmann, K.; Kremer, A.E.; Müller, S.; et al. Clinical Relevance of Circulating Nucleosomes in Cancer. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1137, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, H.; Wu, W.; Geng, S.; Zhong, G.; Li, Y.; Guo, H.; Long, G.; Ren, Q.; Luan, Y.; et al. Circulating Cell-Free DNA Fragmentation Is a Stepwise and Conserved Process Linked to Apoptosis. BMC Biol. 2023, 21, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.G.; Huang, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Bristow, R.E.; Kassauei, K.; Cheng, C.-C.; Roden, R.; Sokoll, L.J.; Chan, D.W.; Shih, I.-M. Increased Plasma DNA Integrity in Cancer Patients. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 3966–3968. [Google Scholar]
- Umetani, N.; Giuliano, A.E.; Hiramatsu, S.H.; Amersi, F.; Nakagawa, T.; Martino, S.; Hoon, D.S.B. Prediction of Breast Tumor Progression by Integrity of Free Circulating DNA in Serum. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 4270–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, M.D.F.; Moher, D.; Thombs, B.D.; McGrath, T.A.; Bossuyt, P.M.; the PRISMA-DTA Group; Clifford, T.; Cohen, J.F.; Deeks, J.J.; Gatsonis, C.; et al. Preferred Reporting Items for a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Studies: The PRISMA-DTA Statement. JAMA 2018, 319, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiting, P.F. QUADAS-2: A Revised Tool for the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora, J.; Abraira, V.; Muriel, A.; Khan, K.; Coomarasamy, A. Meta-DiSc: A Software for Meta-Analysis of Test Accuracy Data. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2006, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umetani, N.; Kim, J.; Hiramatsu, S.; Reber, H.A.; Hines, O.J.; Bilchik, A.J.; Hoon, D.S.B. Increased Integrity of Free Circulating DNA in Sera of Patients with Colorectal or Periampullary Cancer: Direct Quantitative PCR for ALU Repeats. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.-W.; Zahurak, M.; Goldenberg, D.; Milman, Y.; Park, H.L.; Westra, W.H.; Koch, W.; Sidransky, D.; Califano, J. Increased Plasma DNA Integrity Index in Head and Neck Cancer Patients. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 2673–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdenrieder, S.; Burges, A.; Reich, O.; Spelsberg, F.W.; Stieber, P. DNA Integrity in Plasma and Serum of Patients with Malignant and Benign Diseases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1137, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellinger, J.; Bastian, P.J.; Ellinger, N.; Kahl, P.; Perabo, F.G.; Buettner, R.; Mueller, S.C.; von Ruecker, A. Apoptotic DNA Fragments in Serum of Patients with Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: A Prognostic Entity. Cancer Lett. 2008, 264, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.-J.; He, Y.-J.; Yang, Z.-L.; Shao, H.-Y.; Zuo, Y.; Bai, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.-C.; Qin, F.-X.; Tan, S.; et al. Increased Integrity of Circulating Cell-Free DNA in Plasma of Patients with Acute Leukemia. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2010, 48, 1651–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, S.; Zahalka, T.; Ellinger, J.; Fechner, G.; Heukamp, L.C.; Von Ruecker, A.; Müller, S.C.; Bastian, P.J. Cell-Free Circulating DNA: Diagnostic Value in Patients with Renal Cell Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 2785–2789. [Google Scholar]
- Pinzani, P.; Salvianti, F.; Zaccara, S.; Massi, D.; De Giorgi, V.; Pazzagli, M.; Orlando, C. Circulating Cell-Free DNA in Plasma of Melanoma Patients: Qualitative and Quantitative Considerations. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 2141–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, K.B.; Relan, V.; Clarke, B.E.; Duhig, E.E.; Windsor, M.N.; Matar, K.S.; Naidoo, R.; Passmore, L.; McCaul, E.; Courtney, D.; et al. Pleural Fluid Cell-Free DNA Integrity Index to Identify Cytologically Negative Malignant Pleural Effusions Including Mesotheliomas. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, S.; Kogej, M.; Fechner, G.; Von Ruecker, A.; Bastian, P.J.; Von Pezold, J.; Vorreuther, R.; Lümmen, G.; Müller, S.C.; Ellinger, J. Cell-Free Serum DNA in Patients with Bladder Cancer: Results of a Prospective Multicenter Study. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 3119–3124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Sun, L.-Y.; Zheng, H.-Q.; Zhang, Q.-F.; Jin, X.-M. Total Serum DNA and DNA Integrity: Diagnostic Value in Patients with Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Pathology 2012, 44, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Gang, F.; Li, X.; Jin, T.; Houbao, H.; Yu, C.; Guorong, L. Plasma Cell-Free DNA and Its DNA Integrity as Biomarker to Distinguish Prostate Cancer from Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Patients with Increased Serum Prostate-Specific Antigen. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2013, 45, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoetzer, O.J.; Lehner, J.; Fersching-Gierlich, D.; Nagel, D.; Holdenrieder, S. Diagnostic Relevance of Plasma DNA and DNA Integrity for Breast Cancer. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, T.B.; Shi, W.; Shen, X.J.; Qi, J.; Wu, X.H.; Wu, Y.; Tang, Y.Y.; Ju, S.Q. Circulating Cell-Free DNA in Serum as a Biomarker for Diagnosis and Prognostic Prediction of Colorectal Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1482–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leszinski, G.; Lehner, J.; Gezer, U.; Holdenrieder, S. Increased DNA Integrity in Colorectal Cancer. In Vivo 2014, 28, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El-Gayar, D.; El-Abd, N.; Hassan, N.; Ali, R. Increased Free Circulating DNA Integrity Index as a Serum Biomarker in Patients with Colorectal Carcinoma. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 17, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, A.M.; Teama, S.; Fawzy, A.; El Deftar, M. Plasma DNA Integrity Index as a Potential Molecular Diagnostic Marker for Breast Cancer. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 7565–7572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, S.-L.; Cao, Y.; Huang, X.-W.; Fan, J.; Yang, X.-R.; Zhou, J. Plasma Circulating Cell-Free DNA Integrity as a Promising Biomarker for Diagnosis and Surveillance in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 1798–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpechcinski, A.; Rudzinski, P.; Kupis, W.; Langfort, R.; Orlowski, T.; Chorostowska-Wynimko, J. Plasma Cell-Free DNA Levels and Integrity in Patients with Chest Radiological Findings: NSCLC versus Benign Lung Nodules. Cancer Lett. 2016, 374, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eltorgoman, A.E.; Badr, E.A.E.; Kombr, Y.F.A.E.; Yousif, M. Pleural Fluid DNA Integrity Index as a Diagnostic Marker of Malignant Pleural Effusion. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 74, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, S.; Zheng, J.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, P. Plasma Cell-Free DNA Level and Its Integrity as Biomarkers to Distinguish Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer from Tuberculosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 477, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, S.; Husain, N.; Agarwal, A.; Neyaz, A.; Gupta, S.; Chaturvedi, A.; Lohani, M.; Sonkar, A.A. Diagnostic Value of Circulating Free DNA Integrity and Global Methylation Status in Gall Bladder Carcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2019, 25, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Li, L.; Shen, L.; Shen, X.; Ju, S.; Cong, H. Diagnostic Value of Serum Concentration and Integrity of Circulating Cell-Free DNA in Breast Cancer: A Comparative Study with CEA and CA15-3. Lab. Med. 2018, 49, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, N.A.; Mohamed, S.N.; Ahmed, M.A. Plasma ALU-247, ALU-115, and CfDNA Integrity as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers for Breast Cancer. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 187, 1028–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Pu, W.; Zhang, S.; Chen, L.; Zhu, W.; Xiao, L.; Xing, C.; Li, K. Clinical Value of ALU Concentration and Integrity Index for the Early Diagnosis of Ovarian Cancer: A Retrospective Cohort Trial. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, S.E.-S.; Alhanafy, A.M.; Habib, M.S.E.; Hagag, M.; Ibrahem, R.A.L. Serum Circulating Cell Free DNA as Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Non Small Cell Lung Cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2018, 15, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.W.; Shen, X.J.; Jin, C.J.; Cao, X.J.; Ju, S.Q. Value of the Concentration and Integrity of Serum Cell-Free DNA for the Clinical Diagnosis of Esophageal Carcinoma. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 2018, 40, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Qin, S.; Wang, H. Alter Circulating Cell-Free DNA Variables in Plasma of Ovarian Cancer Patients. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2019, 45, 2237–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.K.; Brown, H.; Fang, Z.; Couetoux, M.; Gambaro, K.; Batist, G. A Multiplexed RE-QPCR Cell-Free DNA Assay to Assess Response and Resistance to Cancer Therapy. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Ren, X.-D.; Guo, L.-F.; Qu, X.-M.; Shang, M.-Y.; Dai, X.-T.; Huang, Q. Urine Cell-Free DNA as a Promising Biomarker for Early Detection of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, R.; Ahmed, R.; Shaheen, K.; Abdalmegeed, M.; Hassan, H. DNA Integrity Index as a Potential Molecular Biomarker in Colorectal Cancer. Egypt. J. Med. Hum. Genet. 2020, 21, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.-K.; Lee, J.-C.; Lee, J.-W.; Hwang, S.-J. Alu Cell-Free DNA Concentration, Alu Index, and LINE-1 Hypomethylation as a Cancer Predictor. Clin. Biochem. 2021, 94, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal, M.M.; Abdelaziz, A.O.; El-Baz, H.N.; Mohamed, G.M.; Saleh, S.S.; Nabeel, M.M.; Elbaz, T.M.; Lithy, R.; Shousha, H.I. Plasma Cell-Free DNA Integrity Index and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated or Not with Direct-Acting Antivirals: A Case-Control Study. Arab. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 23, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherif, F.F.; El Desouky, M.A.; Gebril, M.; Azmy, O.M. Association of Plasma DNA Integrity and Long Fragment ALU247 in the Diagnosis of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Asia Pac. J. Mol. Biol. Biotechnol. 2021, 29, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldeeb, S.; Afandy, A.; Ahmed, O.; Khodeer, S.; Younes, F.; Hosny, D. Plasma Circulating Cell-Free DNA Integrity as a Noninvasive Diagnostic Tool in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Menoufia Med. J. 2021, 34, 1244–1248. [Google Scholar]
- Elhelaly, R.; Effat, N.; Hegazy, M.A.E.-F.; Abdelwahab, K.; Hamdy, O.; Hashem, E.M.A.; Elzehery, R.R. Circulating Cell Free DNA and DNA Integrity Index as Discriminating Tools between Breast Cancer and Benign Breast Disease. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2022, 23, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapado-Gonzalez, O.; Lopez-Cedrun, J.L.; Lago-Leston, R.M.; Abalo, A.; Rubin-Roger, G.; Salgado-Barreira, A.; Lopez-Lopez, R.; Muinelo-Romay, L.; Suarez-Cunqueiro, M.M. Integrity and Quantity of Salivary Cell-Free DNA as a Potential Molecular Biomarker in Oral Cancer: A Preliminary Study. J. Oral. Pathol. Med. 2022, 51, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Nadda, N.; Paul, S.; Gamanagatti, S.; Dash, N.R.; Vanamail, P.; Saraya, A.; Shalimar; Nayak, B. Evaluation of the Cell-Free DNA Integrity Index as a Liquid Biopsy Marker to Differentiate Hepatocellular Carcinoma from Chronic Liver Disease. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 1024193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimaite, R.; Kazokaite, M.; Kondrotiene, A.; Dauksiene, D.; Verkauskiene, R.; Zilaitiene, B.; Dauksa, A. Diagnostic Value of Circulating Cell-Free DNA in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2022, 42, 2289–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elzehery, R.; Effat, N.; El Farahaty, R.; Elsayed Farag, R.; Abo-Hashem, E.M.; Elhelaly, R. Circulating Cell-Free DNA and DNA Integrity as Molecular Diagnostic Tools in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2022, 158, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mettler, E.; Fottner, C.; Bakhshandeh, N.; Trenkler, A.; Kuchen, R.; Weber, M.M. Quantitative Analysis of Plasma Cell-Free DNA and Its DNA Integrity and Hypomethylation Status as Biomarkers for Tumor Burden and Disease Progression in Patients with Metastatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasias. Cancers 2022, 14, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Zeng, G.; Yi, Y.; Liu, L.; Tu, H.; Chai, T.; Hu, L. Combinations of Plasma CfDNA Concentration, Integrity and Tumor Markers Are Promising Biomarkers for Early Diagnosis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, S.; Mishra, S.; Anand, N.; Hadi, R.; Rastogi, M.; Husain, N. Circulating Free DNA Integrity Index and Promoter Methylation of Tumor Suppressor Gene P16, DAPK and RASSF1A as a Biomarker for Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2023, 246, 154489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Ji, M.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Hsueh, C.; Zhou, L. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Plasma Cell-Free DNA Combined with VEGF-C in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Mol. Cell Probes 2023, 67, 101895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; Yu, C.; Huang, Q. Diagnostic Value of Combined Detection of Plasma CfDNA Concentration and Integrity in NSCLC. Lung Cancer Manag. 2024, 13, LMT64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Li, X.; Xie, K.-P. Coupled Liquid Biopsy and Bioinformatics for Pancreatic Cancer Early Detection and Precision Prognostication. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaher, E.R.; Anwar, M.M.; Kohail, H.M.A.; El-Zoghby, S.M.; Abo-El-Eneen, M.S. Cell-Free DNA Concentration and Integrity as a Screening Tool for Cancer. Indian J. Cancer 2013, 50, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Sun, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.; Yao, J.; Cheng, Y. Feasibility Analysis of Cell-Free DNA Derived from Plasma of Lung Cancer Patients for Next-Generation Sequencing. Biopreserv. Biobank. 2020, 18, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schou, J.V.; Larsen, F.O.; Sørensen, B.S.; Abrantes, R.; Boysen, A.K.; Johansen, J.S.; Jensen, B.V.; Nielsen, D.L.; Spindler, K.L. Circulating Cell-Free DNA as Predictor of Treatment Failure after Neoadjuvant Chemo-Radiotherapy before Surgery in Patients with Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandel, P.; Metais, P. Nuclear Acids In Human Blood Plasma. C. R. Seances Soc. Biol. Fil. 1948, 142, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leon, S.A.; Shapiro, B.; Sklaroff, D.M.; Yaros, M.J. Free DNA in the Serum of Cancer Patients and the Effect of Therapy. Cancer Res. 1977, 37, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Breitbach, S.; Tug, S.; Simon, P. Circulating Cell-Free DNA. Sports Med. 2012, 42, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreatta, M.V.; Curty, V.M.; Coutinho, J.V.S.; Santos, M.Â.A.; Vassallo, P.F.; de Sousa, N.F.; Barauna, V.G. Cell-Free DNA as an Earlier Predictor of Exercise-Induced Performance Decrement Related to Muscle Damage. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2018, 13, 953–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oellerich, M.; Kanzow, P.; Walson, P.D. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring - Key to Personalized Pharmacotherapy. Clin. Biochem. 2017, 50, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urosevic, N.; Merritt, A.J.; Inglis, T.J.J. Plasma CfDNA Predictors of Established Bacteraemic Infection. Access Microbiol. 2022, 4, 000373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Meng, X.-Y.; Zhou, X. Systematically Evaluating Cell-Free DNA Fragmentation Patterns for Cancer Diagnosis and Enhanced Cancer Detection via Integrating Multiple Fragmentation Patterns. Adv. Sci. 2024, e2308243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristiano, S.; Leal, A.; Phallen, J.; Fiksel, J.; Adleff, V.; Bruhm, D.C.; Jensen, S.Ø.; Medina, J.E.; Hruban, C.; White, J.R.; et al. Genome-Wide Cell-Free DNA Fragmentation in Patients with Cancer. Nature 2019, 570, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, A.I.C.; Mathios, D.; Jakubowski, D.; Johansen, J.S.; Lau, A.; Wu, T.; Cristiano, S.; Medina, J.E.; Phallen, J.; Bruhm, D.C.; et al. Cell-Free DNA Fragmentomes in the Diagnostic Evaluation of Patients with Symptoms Suggestive of Lung Cancer. Chest 2023, 164, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarmuzek, P.; Wawrzyniak-Gramacka, E.; Morawin, B.; Tylutka, A.; Zembron-Lacny, A. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Circulating DNA Fragments in Glioblastoma Multiforme Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.H.T.; Jiang, P.; Tam, J.C.W.; Sun, X.; Lee, W.-S.; Yu, S.C.Y.; Teoh, J.Y.C.; Chiu, P.K.F.; Ng, C.-F.; Chow, K.-M.; et al. Genomewide Bisulfite Sequencing Reveals the Origin and Time-Dependent Fragmentation of Urinary CfDNA. Clin. Biochem. 2017, 50, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadano, D.; Yasuda, T.; Kishi, K. Measurement of Deoxyribonuclease I Activity in Human Tissues and Body Fluids by a Single Radial Enzyme-Diffusion Method. Clin. Chem. 1993, 39, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, N.B.Y.; Jiang, P.; Chow, K.C.K.; Su, X.; Leung, T.Y.; Sun, H.; Chan, K.C.A.; Chiu, R.W.K.; Lo, Y.M.D. High Resolution Size Analysis of Fetal DNA in the Urine of Pregnant Women by Paired-End Massively Parallel Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnham, P.; Dadhania, D.; Heyang, M.; Chen, F.; Westblade, L.F.; Suthanthiran, M.; Lee, J.R.; De Vlaminck, I. Urinary Cell-Free DNA Is a Versatile Analyte for Monitoring Infections of the Urinary Tract. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouliere, F.; Chandrananda, D.; Piskorz, A.M.; Moore, E.K.; Morris, J.; Ahlborn, L.B.; Mair, R.; Goranova, T.; Marass, F.; Heider, K.; et al. Enhanced Detection of Circulating Tumor DNA by Fragment Size Analysis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaat4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| First Author | Country | Type of Biofluid | N Case | Type of Cancer | N Control | Type of Control | Repetitive Sequence | Ratio | Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wang et al. (2003) [29] | EE.UU. | Plasma | 61 | Gynecological and BC | 65 | Benign | β-actin (ACTB) | 400/100 | qPCR |
| Umetani et al. (2006) [34] | EE.UU. | Serum | 19 | PACs | 51 | Healthy | ALU | 275/115 | qPCR |
| Serum | 32 | CRC | 51 | Healthy | ALU | 275/115 | qPCR | ||
| Umetai et al. (2006) [30] | EE.UU. | Serum | 51 | BC | 51 | Healthy | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR |
| Jiang et al. (2006) [35] | EE.UU. | Plasma | 58 | HNSCC | 47 | Healthy | β-actin (ACTB) | 400/100 | qPCR |
| Holdenrieder et al. (2008) [36] | Germany | Serum | 42 | Cancer * | 17 | Benign | ERV gene | 347/137 | qPCR |
| Plasma | 42 | 17 | Benign | ERV gene | 347/137 | qPCR | |||
| Ellinger et al. (2009 [37]) | Germany | Serum | 74 | Testicular | 35 | Healthy | β-actin (ACTB) | 384/106 | qPCR |
| Serum | 39 | 35 | Healthy | β-actin (ACTB) | 384/106 | qPCR | |||
| Serum | 35 | 35 | Healthy | β-actin (ACTB) | 384/106 | qPCR | |||
| Gao et al. (2010) [38] | China | Plasma | 60 | Leukemia | 30 | Healthy | β-actin (ACTB) | 384/106 | qPCR |
| Hauser et al. (2010) [39] | Germany | Serum | 35 | RCC | 54 | Healthy | β-actin (ACTB) | 384/106 | qPCR |
| Pinzani et al. (2011) [40] | Italy | Plasma | 79 | Melanoma | 34 | Healthy | APP gene | 180/67 | qPCR |
| Sriram et al. (2012) [41] | Australia | Pleural Fluid | 52 | MPES | 23 | Benign | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR |
| Pleural Fluid | 16 | Mesothelioma | 23 | Benign | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR | ||
| Hauser et al. (2012 [42]) | Germany | Serum | 75 | BCA | 132 | Non-Cancer Control *** | β-actin (ACTB) | 384/106 | qPCR |
| Chen et al. (2012 [43]) | China | Serum | 80 | HCC | 50 | Healthy | β-actin (ACTB) | 400/100 | qPCR |
| Feng et al. (2013) [44] | China | Plasma | 71 | PC | 33 | Benign | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR |
| Stötzer et al. (2014) [45] | Germany | Plasma | 65 | BC | 28 | Healthy | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR |
| Plasma | 65 | 28 | Healthy | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR | |||
| Hao et al. (2014) [46] | China | Serum | 104 | CRC | 110 | Healhty | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR |
| Leszinski et al. (2014) [47] | Germany | Serum | 24 | CRC | 24 | Healthy | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR |
| Serum | 24 | 24 | Healthy | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR | |||
| El-Gayar et al. (2016) [48] | Egypt | Serum | 50 | CRC | 20 | Healthy | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR |
| Serum | 50 | 10 | Benign | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR | |||
| Kamel et al. (2016) [49] | Egypt | Plasma | 95 | BC | 95 | Benign | β-actin (ACTB) | 400/100 | qPCR |
| Huang et al. (2016) [50] | China | Plasma | 53 | HCC | 22 | Healthy | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR |
| Szpechcinski et al. (2016) [51] | Polonia | Plasma | 65 | NSCLC | 28 | Benign | β-actin (ACTB) | 400/100 | qPCR |
| Eltorgoman et al. (2017) [52] | Egypt | Pleural Effusions | 39 | Malignant Effusions ** | 29 | Benign | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR |
| Leng et al. (2017) [53] | China | Plasma | 106 | NSCLC | 107 | Healthy | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR |
| Kumari et al. (2018) [54] | India | Serum | 60 | GBC | 36 | Non-Cancer Control | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR |
| Tang et al. (2018) [55] | China | Serum | 40 | BC | 40 | Healthy | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR |
| Hussein et al. (2018) [56] | Egypt | Plasma | 40 | BC | 10 | Healthy | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR |
| Zhang et al. (2018) [57] | China | Plasma | 24 | OC | 24 | Non-Cancer Control | ALU | 219/115 | qPCR |
| Soliman et al. (2018) [58] | Egypt | Serum | 60 | LC | 80 | Non-Cancer Control | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR |
| Qiu et al. (2018) [59] | China | Serum | 68 | EC | 81 | Non-Cancer Control | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR |
| Yu et al. (2019) [60] | China | Plasma | 20 | OC | 20 | Healthy | ALU | 260/111 | qPCR |
| Sinha et al. (2019) [61] | Canada | Plasma | 39 | CRC | 40 | Healthy | ALU | 265/80 | qPCR |
| Ren et al. (2020) [62] | China | Urine | 55 | NSCLC | 35 | Healthy | LINE-1 | 266/97 | qPCR |
| Salem et al. (2020) [63] | Egypt | Serum | 90 | CRC | 30 | Healthy | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR |
| Serum | 90 | 30 | Benign | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR | |||
| Serum | 90 | 60 | Non-Cancer Control | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR | |||
| Park et al. (2021) [64] | Korea | Plasma | 64 | BC | 64 | Healthy | ALU | 263/58 | qPCR |
| Plasma | 64 | LC | 64 | Healthy | ALU | 263/58 | qPCR | ||
| Kamal et al. (2021) [65] | Egypt | Plasma | 80 | HCC | 80 | Benign | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR |
| Sherif et al. (2021) [66] | Egypt | Plasma | 30 | EOC | 30 | Benign | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR |
| Plasma | 30 | 15 | Healthy | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR | |||
| Eldeeb et al. (2022 [67]) | Egypt | Plasma | 30 | HCC | 30 | Healthy | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR |
| Plasma | 30 | 30 | Benign | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR | |||
| Elhelaly et al. (2022) [68] | Egypt | Serum | 50 | BC | 50 | Benign | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR |
| Rapado-González et al. (2022) [69] | Spain | Saliva | 19 | OSCC | 15 | Healthy | ALU | 274/60 | qPCR |
| Saliva | 19 | 15 | Healthy | ALU | 115/60 | qPCR | |||
| Kumar et al. (2022) [70] | Egypt | Serum | 100 | HCC | 30 | Healthy | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR |
| Serum | 100 | 100 | Non-Cancer Control | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR | |||
| Serum | 100 | 30 | Healthy | GAPDH | 205/110 | qPCR | |||
| Serum | 100 | 100 | Non-Cancer Control | GAPDH | 205/110 | qPCR | |||
| Serum | 100 | 30 | Healthy | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR | |||
| Serum | 100 | 100 | Non-Cancer Control | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR | |||
| Serum | 100 | 30 | Healthy | GAPDH | 205/110 | qPCR | |||
| Serum | 100 | 100 | Non-Cancer Control | GAPDH | 205/110 | qPCR | |||
| Klimaite et al. (2022) [71] | Lithuania | Plasma | 68 | PTC | 86 | Healthy | β-actin (ACTB) | 394/99 | qPCR |
| Plasma | 68 | PTC | 31 | Benign | β-actin (ACTB) | 394/99 | qPCR | ||
| Elzehery et al. (2022) [72] | Egypt | Serum | 50 | HCC | 50 | Non-Cancer Control | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR |
| Mettler et al. (2022) [73] | Germany | Plasma | 62 | NEN | 29 | Healthy | LINE-1 | 266/97 | qPCR |
| Ren et al. (2023) [74] | China | Plasma | 40 | NSCLC | 50 | Healthy | ALU | 115/60 | qPCR |
| 44 | 50 | Healthy | ALU | 115/60 | qPCR | ||||
| 84 | 50 | Healthy | ALU | 115/60 | qPCR | ||||
| Kumari et al. (2023) [75] | India | Serum | 27 | OPSCC | 15 | Healthy | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR |
| Huang et al. (2023) [76] | China | Plasma | 148 | LSCC | 43 | Non-Tumor Control | ALU | 247/115 | qPCR |
| Ren et al. (2024) [77] | China | Plasma | 37 | NSCLC | 53 | Healthy | LINE-1 | 266/97 | qPCR |
| 34 | 53 | Healthy | LINE-1 | 266/97 | qPCR | ||||
| 71 | 53 | Healthy | LINE-1 | 266/97 | qPCR |
| Subgroups | No of Study Units | Sensitivity (95% CI) | I2 (%) | Specificity (95% CI) | I2 (%) | PLR (95% CI) | I2 (%) | NLR (95% CI) | I2 (%) | DOR (95% CI) | I2 (%) | AUC (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biofluid | ||||||||||||
| Plasma | 33 | 0.66 (0.64–0.68) | 94.6 | 0.79 (0.77–0.81) | 87.8 | 3.21 (2.4–4.31) | 87.5 | 0.34 (0.24–0.47) | 97.2 | 10.88 (7.15–16.55) | 73.5 | 0.84 (0.8–0.89) |
| Serum | 33 | 0.73 (0.71–0.75) | 81 | 0.75 (0.73–0.77) | 85.8 | 3.26 (2.53–4.13) | 87.2 | 0.36 (0.31–0.42) | 72.5 | 9.99 (7.05–14.16) | 75.9 | 0.82 (0.78–0.86) |
| Others * | 6 | 0.72 (0.65–0.78) | 76.1 | 0.8 (0.72–0.86) | 69.6 | 4.17 (1.96–8.87) | 74.3 | 0.30 (0.17–0.53) | 75 | 16.37 (4.64–57.81) | 76.1 | 0.87 (0.76–0.98) |
| DNA repetitive sequence | ||||||||||||
| ALU | 47 | 0.69 (0.67–0.71) | 92.7 | 0.79 (0.77–0.81) | 84.2 | 3.63 (2.95–4.48) | 79.5 | 0.31 (0.24–0.40) | 96.4 | 12.82 (9.24–17.80) | 72.4 | 0.86 (0.83–0.89) |
| Others ** | 25 | 0.71 (0.69–0.73) | 85.6 | 0.75 (0.72–0.77) | 88.7 | 2.67 (1.99–3.59) | 90.6 | 0.41 (0.34–0.49) | 76 | 7.64 (5.09–11.46) | 74.7 | 0.80 (0.75–0.85) |
| N size | ||||||||||||
| <100 | 39 | 0.69 (0.67–0.71) | 92.6 | 0.78 (0.76–0.80) | 82.5 | 3.44 (2.52–4.68) | 89.2% | 0.31 (0.23–0.43) | 96.4 | 11.62 (7.99–16.89) | 63 | 0.84 (0.81–0.88) |
| >100 | 33 | 0.70 (0.68–0.72) | 88.8 | 0.77 (0.75–0.79) | 89.1 | 3.07 (2.5–3.76) | 81.9 | 0.37 (0.31–0.44) | 85.2 | 9.81 (6.87–14.02) | 80.8 | 0.82 (0.78–0.87) |
| Control | ||||||||||||
| Healthy | 44 | 0.67 (0.65–0.69) | 92.3 | 0.79 (0.77–0.81) | 79.6 | 3.2 (2.66–3.86) | 70.9 | 0.35 (0.27–0.45) | 96 | 10.20 (7.36–14.15) | 70.7 | 0.84 (0.81–0.88) |
| Benign | 16 | 0.81 (0.78–0.83) | 84.4 | 0.84 (0.81–0.87) | 92.2 | 5.25 (2.51–10.97) | 96.7 | 0.25 (0.18–0.35) | 78.5 | 24.02 (11.50–50.14) | 73.5 | 0.90 (0.86–0.94) |
| Non-Cancer Control *** | 12 | 0.67 (0.64–0.70) | 86.3 | 0.70 (0.67–0.73) | 81.9 | 2.40 (1.9–3.05) | 76.4 | 0.43 (0.35–0.54) | 76 | 6.06 (3.98–9.22) | 73 | 0.77 (0.72–0.83) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Ces, A.M.; Rapado-González, Ó.; Salgado-Barreira, Á.; Santos, M.A.; Aroso, C.; Vinhas, A.S.; López-López, R.; Suárez-Cunqueiro, M.M. Liquid Biopsies Based on Cell-Free DNA Integrity as a Biomarker for Cancer Diagnosis: A Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141465
Rodríguez-Ces AM, Rapado-González Ó, Salgado-Barreira Á, Santos MA, Aroso C, Vinhas AS, López-López R, Suárez-Cunqueiro MM. Liquid Biopsies Based on Cell-Free DNA Integrity as a Biomarker for Cancer Diagnosis: A Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(14):1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141465
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Ces, Ana María, Óscar Rapado-González, Ángel Salgado-Barreira, María Arminda Santos, Carlos Aroso, Ana Sofia Vinhas, Rafael López-López, and María Mercedes Suárez-Cunqueiro. 2024. "Liquid Biopsies Based on Cell-Free DNA Integrity as a Biomarker for Cancer Diagnosis: A Meta-Analysis" Diagnostics 14, no. 14: 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141465
APA StyleRodríguez-Ces, A. M., Rapado-González, Ó., Salgado-Barreira, Á., Santos, M. A., Aroso, C., Vinhas, A. S., López-López, R., & Suárez-Cunqueiro, M. M. (2024). Liquid Biopsies Based on Cell-Free DNA Integrity as a Biomarker for Cancer Diagnosis: A Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics, 14(14), 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141465








