Abstract
Background: Hyponatremia and hypokalemia are common electrolyte imbalances in trauma patients and have been identified to be risk factors for a fall. In addition, hyponatremia was reported to be related to osteoporosis and fragility fractures, while the association between hypokalemia and osteoporosis has only been reported in rare case reports. This study investigated the impact of hyponatremia and hypokalemia on the incidence of fractures in various body regions of adult trauma patients, using the propensity score-matched patient cohort to reduce the influence of patients’ baseline characteristics. Methods: The study analyzed data from 11,173 hospitalized adult trauma patients treated from 1 January 1998, to 31 December 2022. The study included 1968 patients with hyponatremia and 9205 without, and 1986 with hypokalemia and 9187 without. Different 1:1 propensity score-matched cohorts were generated to create the 1903 pairings of patients with or without hyponatremia, 1977 pairings of patients with or without hypokalemia, and 380 pairing of patients with both hyponatremia and hypokalemia vs. normal control patients. Analysis was conducted on the incidence of fracture in various anatomic regions. Results: Hyponatremic patients had increased odds of thoracic vertebral fracture [odds ratio (95% confidence interval) 1.63 (1.10–2.42), p = 0.014], pelvic fracture [2.29 (1.12–4.67), p = 0.019], and femoral fracture [1.28 (1.13–1.45), p < 0.001] but decreased odds of radial and patella fractures. Hypokalemic patients showed no significant differences in fracture risk except for a decreased likelihood of radial fractures. The patients with both hyponatremia and hypokalemia showed a decreased likelihood of radial fractures and patella fractures. Conclusion: Hyponatremia may have a greater impact on the occurrence of bone fractures than hypokalemia in trauma patients who have suffered a fall. Electrolyte abnormalities should be taken into account while assessing the risk of fractures in trauma patients.
1. Introduction
Chronic hyponatremia has been linked to an increase in the incidence of falls and fractures [1]. Studies have shown that even mild hyponatremia can lead to gait disturbances, decreased mentation, and falls, especially from walking height or less than one meter [2,3]. Hyponatremia appears to contribute to falls and fractures through two mechanisms [4]. Initially, it induces a state of moderate cognitive impairment, leading to instability in walking and an increased likelihood of experiencing falls. This can likely be attributed to the depletion of glutamate, a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in the regulation of gait function, as a consequence of the brain’s adaptation to prolonged hyponatremia [4]. This association is further supported by findings from De Giorgi et al. [5] and Tolouian et al. [6], who noted that mild hyponatremia is linked to unsteadiness and attention deficits, which are risk factors for falls. Even modest chronic hyponatremia has been shown to impair cognitive performance and increase the risk of falling [7,8]. Second, hyponatremia increases the risk of osteoporosis and bone fragility by increasing bone resorption to mobilize salt reserves in bone.
A significant relationship between hyponatremia and osteoporosis has been established. Kruse, Eiken, and Vestergaard [9] discovered that hyponatremia is linked to reduced bone mineralization in the hip as well as an increased risk of osteoporosis. A significant odds ratio for fractures, in addition to a substantial correlation between hyponatremia, osteoporosis, and fractures, has been observed in previous research [10,11]. Multivariate conditional logistic regression models demonstrated that hyponatremia was associated with osteoporosis and fragility fractures [12]. Additionally, hyponatremia is linked to disordered osteoclast and osteoblast activity, affecting bone health [12]. Low levels of circulating sodium directly boost osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption activity by lowering the uptake of ascorbic acid by cells and increasing oxidative stress. These effects depend on the amount of sodium present [4]. Therefore, chronic hyponatremia leads to increased osteoclast numbers and resorptive activity, resulting in resorptive osteoporosis [13].
Hypokalemia, a condition characterized by low potassium levels in the blood, has been identified as a risk factor for falls, particularly in the elderly and in situations involving falls from walking height or less than one meter. The condition can lead to muscle weakness, fatigue, and dizziness, which are all factors that can increase the likelihood of falls. Additionally, hypokalemia has been associated with various cardiovascular complications, such as arrhythmias [14] or electrolyte disturbances [15], can further contribute to the risk of falls. Contrastingly, reports for hyponatremia, the relationship between hyperkalemia and osteoporosis is not established in the literature and is only seen in a few case reports. A case report has shown that hypokalemia is secondary to hypomagnesium, which is also associated with hypoparathyroidism with the suppression of bone remodeling [16]. The hypokalemia associated with a significant prevalence of osteoporosis had been reported in the patients with chronic pancreatitis [17]. In these chronic pancreatitis patients, the chronic relapsing nature of the disease process in the pancreas result in maldigestion with malabsorption of vitamin D and calcium and thus lead to hypokalemia [17]. Gitelman syndrome is an autosomal recessive hereditary illness that is characterized by several clinical manifestations, including hypokalemia, metabolic alkalosis, hypomagnesemia, and hypocalciuria. Notably, it has been observed that individuals with Gitelman syndrome also have high bone mineral density, thus highlighting the association between hypokalemia and this particular skeletal characteristic [18]. In individuals presenting with incomplete Sjogren’s syndrome, the presence of hypokalemia has been seen to be correlated with persistent metabolic acidosis. This condition leads to enhanced release of alkaline substances from the skeletal system, hence fostering the progression of osteoporosis [19].
The correlation between hyponatremia or hypokalemia and an elevated risk of fractures might be confounded by some factors, such as age [20]. The increased risk of falls among patients with hyponatremia or hypokalemia is especially concerning in the elderly, who are already at an increased risk of falls due to other age-related factors, according to Tachi et al. [21]. Additionally, certain authors have suggested that hyponatremia and hypokalemia should be regarded as indicators of compromised health rather than as isolated risk factors for fractures [20]. Furthermore, although hip fractures are consistently identified as the most prevalent among patients with hyponatremia [4,22,23,24,25], no distinct order is established regarding the ranking of other fracture sites. Furthermore, there are also no published reports concerning the location of fractures associated with hypokalemia. As a result, this study aimed to assess the frequency of fractures in various body regions in hospitalized adult trauma patients with hyponatremia or hypokalemia using a propensity score-matched patient cohort to decrease inequalities in baseline factors such as age, sex, and comorbidities.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Declaration of Ethics
The study employed a retrospective cross-sectional analytic approach, utilizing data from the trauma registry system at Chang Gung Memorial Hospital. This research has been granted permission by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the hospital, with the authorization number 202100761BAS. According to the regulation of IRB, the research was given an exemption from the informed consent procedure.
2.2. Criteria for Selection of Patients wih Hyponatremia or Hypokalemia
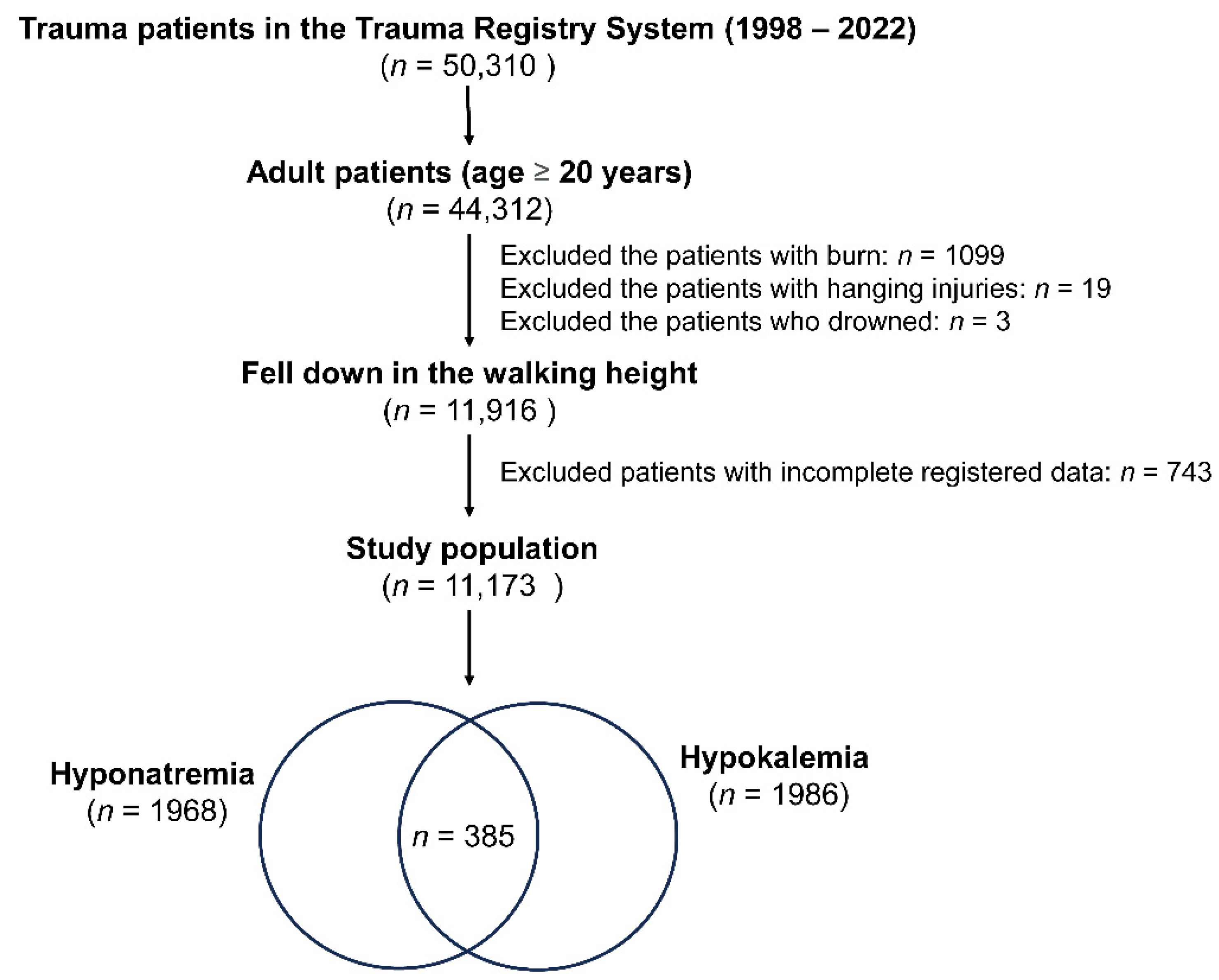
In this research, as shown in Figure 1, of a total of 50,310 trauma patients in the Trauma Registry System (1998–2022), only adult patients aged 20 years or older were included, amounting to 44,312 individuals. Only those people who fell down while walking were considered for this study (a total of 11,916 patients). Exclusions were made based on specific injury types and health conditions: 1099 patients with burn injuries, 19 with hanging injuries, and 3 who drowned. Additionally, 743 patients with incomplete registered data were excluded. The blood collected for detecting the electrolyte level of these fall patients was performed at the time of arrival to the emergency room. Hyponatremia is characterized by a serum sodium concentration below the threshold of 135 mEq/L [26], whereas hypokalemia is defined as a potassium level lower than or equal to 3.5 mEq/L [27]. After applying these criteria, the final study population comprised 11,173 patients, including 1968 cases of hyponatremia, 1986 cases of hypokalemia, and 385 cases with both hyponatremia and hypokalemia.
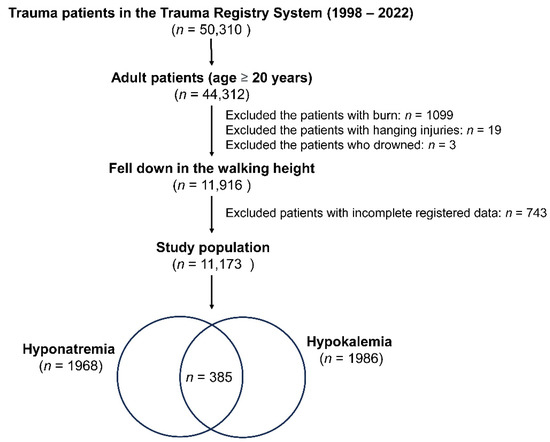
Figure 1.
A flowchart depicting the process of selection of hospitalized adult trauma patients with hyponatremia and/or hypokalemia from the trauma registered database.
2.3. Gathering of Clinical Information
The trauma registry system was utilized to gather a multitude of medical details. The information included in this document comprised patient demographics, including age and sex, as well as a record of any pre-existing medical conditions the patient had, such as diabetes mellitus (DM), hypertension (HTN), cerebrovascular accident (CVA), coronary artery disease (CAD), congestive heart failure (CHF), and end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Injury severity was evaluated using the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) and the Injury Severity Scores (ISS). The location of patients’ fractures was documented. The length of each patient’s hospitalization, expressed in days, was documented, along with any instances of mortality that occurred within the facility.
2.4. Statistical Analyses
The analytical assessments were performed using the SPSS 23.0 program, developed by IBM Corp. (Armonk, NY, USA) and tailored for the Windows operating system. The Kolmogorov–Smirnov test was used to evaluate the normalization of scattered data relevant to continuous variables. The correlation between continuous variables was initially examined using a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Subsequently, Games–Howell post-hoc tests were employed to further investigate any significant differences identified in the ANOVA. The test findings are reported in the form of a mean value accompanied by its matching standard deviation. The examination of categorical variables entailed the utilization of either Fisher’s exact tests or Pearson’s chi-squared (χ2) tests. The researchers computed odds ratios (ORs) and their accompanying 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
In order to effectively account for any initial differences in baseline characteristics among different patient groups, especially when evaluating the incidence of fractures in different anatomical regions, a cohort with a 1:1 propensity score matching was created using the NCSS software version 10 (NCSS LLC, Kaysville, UT, USA), which was developed by the NCSS Statistical program located in Kaysville, Utah. The approach utilized in this investigation was the implementation of the Greedy strategy, with a caliper width of 0.2. The propensity scores that were utilized in this study were obtained by the implementation of a logistic regression model, which considered several parameters such as gender, age, and pre-existing medical conditions. To identify statistically significant differences between groups, a predetermined threshold for the p-value was established at a level below 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Patients with Hyponatremia
For hyponatremia, the study involved 1968 and 9205 patients with and without hyponatremia. As shown in the Table 1, the statistics demonstrate that these groups differ significantly in terms of sex, age, and various comorbidities. Males made up a lower proportion of the hyponatremia group (40.5%) compared with 35.4% of the patients without hyponatremia. The average age in the hyponatremia group was substantially greater (74.2 years) than in the non-hyponatremia group (68.0 years). Comorbidities like cerebrovascular accident (CVA), hypertension (HTN), coronary artery disease (CAD), congestive heart failure (CHF), diabetes mellitus (DM), and end-stage renal disease (ESRD) were more prevalent in the hyponatremia group, with ORs ranging from 1.47 for CVA to 2.58 for ESRD. Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) scores and Injury Severity Score (ISS) also differed significantly, indicating a more severe injured status in the hyponatremia group. Mortality rates were higher in patients with hyponatremia than those without (4.9% vs. 2.0%, respectively, p < 0.001). The hospital stay was significantly longer in those patients with hyponatremia than those without (10.1 days vs. 7.1 days, respectively, p < 0.001).

Table 1.
Demographic and injury characteristics of adult trauma patients admitted to the hospital—a comparison with and without hyponatremia.
3.2. The Fracture Risks of Location in Patients with Hyponatremia
For patients with and without hyponatremia, a propensity score-matched patient cohort of 1:1 was established to reduce the influence of confounding factors related to the patients’ baseline characteristics on outcome assessments. The propensity score-matched patient populations, comprising 1903 pairings, exhibited no statistically significant variations in terms of age, comorbidities, or sex (Table 2). Hyponatremia greatly increased the risk of sustaining a thoracic vertebral fracture [OR (95% CI) 1.63 (1.10–2.42), p = 0.014], pelvic fracture [2.29 (1.12–4.67), p = 0.019], and femoral fracture [1.28 (1.13–1.45), p < 0.001] compared with those without hyponatremia (Table 3). However, they had lower odds of sustaining a radial fracture [0.63 (0.51–0.79), p < 0.001] and a patella fracture [0.43–0.92), p = 0.017] than patients without hyponatremia.

Table 2.
The developed propensity scores-matched patient cohort of the research population in terms of the presence or absence of hyponatremia.

Table 3.
The incidences of fracture in body location in propensity scores-matched patient cohort in terms of the presence or absence of hyponatremia.
3.3. Characteristics of the Patients with Hypokalemia
In the case of hypokalemia, the study involved 1986 and 9187 patients with and without hypokalemia (Table 4). The results show no significant differences in sex and age. Comorbidities like CVA and HTN were more prevalent in the hypokalemia group, with ORs ranging from 1.22 for CVA to 1.30 for HTN. However, the DM and ESRD were less prevalent in the patients with hypokalemia than those without, with ORs ranging from 0.73 for DM to 0.70 for ESRD. A significantly lower GCS score but higher ISS indicated a higher injury severity in the hypokalemia group. In patients with hypokalemia, the mortality rate was significantly higher at 4.2% compared with 2.2% in the absence of hypokalemia (p < 0.001). Patients with hypokalemia had a substantially longer hospital stay (8.7 days vs. 7.4 days, respectively, p < 0.001) than those without hypokalemia.

Table 4.
Demographic and injury characteristics of adult trauma patients admitted to the hospital—a comparison with and without hypokalemia.
3.4. The Fracture Risks of Location in Patients with Hypokalemia
A cohort of 1977 patient pairings, including those with and without hypokalemia, was chosen in accordance with a propensity score match ratio of 1:1. There were no significant statistical differences identified with regard to age, sex, or comorbidities (Table 5). The likelihood of developing a radial fracture was found to be significantly reduced in patients with hypokalemia [0.66 (0.55–0.80), p < 0.001] compared with those without hypokalemia (Table 6). Regarding the incidence of fractures in other body regions, no significant statistical distinction was observed between patients who had hypokalemia and those who did not.

Table 5.
The developed propensity scores-matched patient cohort of the research population in terms of the presence or absence of hypokalemia.

Table 6.
The incidences of fracture in body location in propensity scores-matched patient cohort in terms of the presence or absence of hypokalemia.
3.5. Characteristics of the Patients with Both Hyponatremia and Hypokalemia
This study comprised 385 patients who presented with both hyponatremia and hypokalemia. In contrast, 7601 patients were included as the normal control group for subsequent analysis, devoid of either hyponatremia or hypokalemia (Table 7). In addition to age and sex, the results indicate that these groups differ substantially with regard to a variety of comorbidities, such as HTN, CAD, DM, and ESRD, all of which were more prevalent among patients who presented with hyponatremia and hypokalemia. In patients with both hyponatremia and hypokalemia, a substantially lower GCS score but a higher ISS score indicated a more severe injury. Mortality was significantly higher at 7.3% in patients with both hyponatremia and hypokalemia compared with 1.7% in normal patients (p < 0.001), and hospital stays were substantially longer (11.6 days vs. 6.9 days, respectively, p < 0.001).

Table 7.
Demographic and injury characteristics of adult trauma patients admitted to the hospital—a comparison with and without both hyponatremia and hypokalemia.
3.6. The Fracture Risks of Location in Patients with Both Hyponatremia and Hypokalemia
A cohort of 380 patient pairings, including those with both hyponatremia and hypokalemia vs. those normal patients, was chosen in a propensity score match ratio of 1:1. There were no significant statistical differences identified with regard to age, sex, or comorbidities. (Table 8). The likelihood of developing a radial fracture was found to be significantly reduced in patients with both hyponatremia and hypokalemia [0.50 (0.31–0.80), p = 0.004] compared with those normal patients (Table 9). Regarding the incidence of fractures in other body regions, no significant statistical distinction was observed.

Table 8.
The developed propensity scores-matched patient cohort of the research population in terms of the presence or absence of both hyponatremia and hypokalemia.

Table 9.
The incidences of fracture in body location in propensity scores-matched patient cohort in terms of the presence or absence of both hyponatremia and hypokalemia.
4. Discussion
Following propensity score matching to account for differences in baseline characteristics, this research demonstrated that individuals with hyponatremia have an increased risk of sustaining a thoracic vertebral fracture, pelvic fracture, and femoral fracture in comparison with those without hyponatremia. However, hypokalemia did not show a similar association. In addition, hyponatremia is correlated with a decreased likelihood of developing a radial fracture and a patella fracture, whereas hypokalemia is associated with decreased likelihood of developing a radial fracture. A summary of the risk of bone fractures in adult trauma patients who are hospitalized and have hyponatremia and/or hypokalemia was provided in Table 10.

Table 10.
A summary of the risk of bone fractures in adult trauma patients who are hospitalized and have hyponatremia and/or hypokalemia.
This study’s results indicated that hyponatremia was linked to thoracic vertebral, pelvic, and femoral fractures when someone falls. The study results are in accordance with those reports describing the patients with hyponatremia who have experienced a fall had the pelvis and femur as the most common sites of fracture [2,6]. In addition to an elevated risk of hip fracture, hyponatremia is also linked to a higher incidence of morphometric spine fractures and incident morphometric spine fractures [28,29]. Chronic hyponatremia increases the prevalence of vertebral fractures after low-energy trauma due to decreased bone quality [30]. Additional research suggests that individuals with central fractures demonstrate reduced bone mineral density, a poorer trabecular bone score, and a greater incidence of vertebral fractures in comparison with individuals with peripheral fractures [31]. A complex and varied relationship between fractures in different parts of the skeleton after a fall might be influenced by factors not only like osteoporosis or bone mineral density, but also the specific bones involved. A study using cadaveric specimens to directly measure experimental bone strength at L4 vertebra and proximal femur sites as the reference standard and to determine the correlations with strength at the radius and tibia [32], indicating that the increased fractures in central and large bones are related to osteoporosis, while fractures in peripheral bones are not [33]. And this is the reason why a peripheral bone mineral densitometry strategy using forearm bone mineral density alone will miss many individuals with osteoporosis [34]. Although the electrolytes imbalance might cast influence on the bone mineral density; however, in this study, the incidences of radial fracture were decreased in the patients with either hyponatremia or hypokalemia. Notably, although these patients might be more prone to certain types of injuries (like vertebral fractures) due to their overall health status, while being less exposed to the mechanisms that commonly cause bony fractures. Patients with hyponatremia often have accompanying symptoms such as muscle weakness, fatigue, or neurological changes. These symptoms can lead to a decrease in physical activity levels, leading to a different type of fracture during the fall that typically result in radial fractures.
Gender differences significantly influence fracture patterns and locations resulting from falls. Females, especially those who have reached the postmenopausal stage, have a greater susceptibility to hip fractures as a result of a heightened incidence of osteoporosis and diminished bone mineral density in comparison with males [35]. This is further exacerbated by age-related changes in body composition and hormonal changes [36,37]. Men, on the other hand, are more likely to experience upper limb fractures, such as those of the humerus and clavicle, attributed to differences in fall mechanics and protective responses during falls [38]. These gender-specific fracture patterns underscore the importance of targeted prevention strategies, considering the distinct anatomical and physiological differences between men and women. It has been found that the incidence of vertebral fracture increases with age in both men and women, however, the increase is greater in women than in men [39]. Differential bone microstructure is linked to vertebral fractures in both men and women, but the particular causes differ: trabecular bone density at the tibia in women and femoral neck areal bone mineral density in males are linked to vertebral fractures separately [40]. Although peripheral bone strength can predict axial bone quality, the association is not as strong in women as it is in males [41].
In addition, comorbidities can significantly influence fracture patterns and locations in falls. For example, individuals with DM often have a higher risk of lower limb fractures, particularly of the foot and ankle, due to diabetic neuropathy and vascular complications affecting bone quality [42]. Patients with HTN and CAD may experience falls due to dizziness or weakness, leading to a higher incidence of hip and upper extremity fractures [43]. ESRD patients, often with altered bone metabolism, are more susceptible to hip and vertebral fractures [44]. CHF patients, due to their reduced physical activity and associated osteoporosis, are at an increased risk of vertebral and hip fractures [45]. Lastly, individuals with a history of CVA have a predisposition to falls and fractures, particularly on the affected side, due to hemiparesis and balance issues [46].
By utilizing a propensity score-matched patient cohort, this research aims to analyze fracture incidents while mitigating the influence of confounding factors including age, sex, and comorbidities. This study reported that hyponatremia is associated with increased incidences of fractures of thoracic vertebral fracture, pelvic fracture, and femoral fracture, which may be caused by hyponatremia’s influence on reducing bone mineralization, which has been linked with an elevated risk of osteoporosis. While such adverse effects were not observed in hypokalemic individuals, further research is required to examine the long-term effects of hyponatremia and hypokalemia, as well as to investigate the underlying mechanisms that contribute to these conditions affecting bone health and fracture risk. It is also recommended that this research be expanded to encompass diverse patient populations and geographic regions to ascertain whether the observed associations between hyponatremia, hypokalemia, and fracture risk are consistent in different demographic and environmental contexts.
This study has substantial limitations. First, the retrospective approach, in combination with the removal of missing data, may cause selection bias. Second, the usage of drugs and nutritional state in this study population are unclear, which may contribute to bias in the interpretation of the data. Third, some diseases, such as hypophosphatemia or metabolic alkalosis [47], syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH) [11,25], primary hyperaldosteronism [48,49], Cushing syndrome [50,51,52], and Bartter syndrome [53], may be strongly linked to hyponatremia or hypokalemia and fracture incidence but were not excluded or analyzed in this study. Finally, the study is confined to a single trauma center, potentially limiting the generalizability of its findings to broader populations. Therefore, caution should be exercised when attempting to apply our results to different geographical contexts.
5. Conclusions
This study revealed a correlation between hyponatremia and a higher occurrence of fractures in the thoracic vertebra, pelvic, and femoral bones, while a lower occurrence of fractures was observed in the radial and patella bones. However, patients with hypokalemia were found to be merely related with a decreased risk of radial fracture. The hyponatremia may exert a more significant influence on the occurrence of bone fractures compared with the hypokalemia observed in trauma patients who have had a fall. Electrolyte abnormalities should be taken into account while evaluating the risk of fractures in trauma patients. Furthermore, it is advisable to regularly monitor the levels of electrolytes, namely sodium, in those patients who are at risk of falling.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, S.-Y.H.; writing—review and editing, C.-S.R.; formal analysis, S.-Y.H.; funding acquisition, S.-Y.H.; validation, C.-H.T., S.-E.C. and W.-T.S.; methodology, C.-H.H.; supervision, C.-H.H.; conceptualization, C.-H.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, grant number CMRPG8M1511.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (protocol code 202301724B0 and date of approval 4 December 2023).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived due to retrospective study.
Data Availability Statement
De-identification data available on request.
Acknowledgments
We appreciated the Biostatistics Center, Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital for statistics work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ganguli, A.; Mascarenhas, R.C.; Jamshed, N.; Tefera, E.; Veis, J.H. Hyponatremia: Incidence, risk factors, and consequences in the elderly in a home-based primary care program. Clin. Nephrol. 2015, 84, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandhu, H.S.; Gilles, E.; DeVita, M.V.; Panagopoulos, G.; Michelis, M.F. Hyponatremia associated with large-bone fracture in elderly patients. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2009, 41, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.C.H.; Kuo, P.J.; Rau, C.S.; Wu, S.C.; Hsu, S.Y.; Hsieh, C.H. Hyponatremia Is Associated with Worse Outcomes from Fall Injuries in the Elderly. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, A.L.; Ayus, J.C. Hyponatremia and bone disease. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2017, 18, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Giorgi, A.; Caranti, A.; Moro, F.; Parisi, C.; Molino, C.; Fabbian, F.; Manfredini, R. Spontaneous Resolution of Gallstone Ileus with Giant Stone: A Case Report and Literature Review. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2015, 63, 1964–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolouian, R.; Alhamad, T.; Farazmand, M.; Mulla, Z.D. The correlation of hip fracture and hyponatremia in the elderly. J. Nephrol. 2012, 25, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.R.; Baghitabar, N.; Mirzapour, A.; Oliaei, F.; Nooreddini, H.; Bijani, A.; Mouodi, S. Hyponatremia, bone mineral density and falls in the elderly; Results from AHAP study. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 56, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, S.; Gayot, C.; Bimou, C.; Mergans, T.; Kajeu, P.; Castelli, M.; Dantoine, T.; Tchalla, A. Prevalence of mild hyponatremia and its association with falls in older adults admitted to an emergency geriatric medicine unit (the MUPA unit). BMC Geriatr. 2019, 19, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, C.; Eiken, P.; Vestergaard, P. Hyponatremia and osteoporosis: Insights from the Danish National Patient Registry. Osteoporos. Int. 2015, 26, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upala, S.; Sanguankeo, A. Association Between Hyponatremia, Osteoporosis, and Fracture: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 1880–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, K.; Ondrey, G.J.; Malkani, N.; Raman, G.; Hodge, M.B.; Marcantonio, A.J.; Verbalis, J.G. The effects of hyponatremia on bone density and fractures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocr. Pract. 2019, 25, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usala, R.L.; Fernandez, S.J.; Mete, M.; Cowen, L.; Shara, N.M.; Barsony, J.; Verbalis, J.G. Hyponatremia Is Associated with Increased Osteoporosis and Bone Fractures in a Large US Health System Population. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 3021–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsony, J.; Sugimura, Y.; Verbalis, J.G. Osteoclast response to low extracellular sodium and the mechanism of hyponatremia-induced bone loss. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 10864–10875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfant, R.H. Hypokalemia and arrhythmias. Am. J. Med. 1986, 80, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, M.R.; Espaillat, R. Clinical perspectives on the rationale for potassium supplementation. Postgrad. Med. 2015, 127, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, I.; Yamamoto, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Yamauchi, M.; Yano, S.; Sugimoto, T. A case of magnesium deficiency associated with insufficient parathyroid hormone action and severe osteoporosis. Endocr. J. 2007, 54, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasiyeshvili, L.M. Chronic pancreatitis as a predictor of osteoporosis formation. Eksp. Klin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 10, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Ea, H.K.; Blanchard, A.; Dougados, M.; Roux, C. Chondrocalcinosis secondary to hypomagnesemia in Gitelman’s syndrome. J. Rheumatol. 2005, 32, 1840–1842. [Google Scholar]
- Furqan, S.; Banu, S.; Ram, N. Osteoporosis Complicating Renal Tubular Acidosis in Association With Sjogren’s Syndrome. Cureus 2021, 13, e18373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiara, L.A.M.; Moirano, G.; Grosso, E.; Richiardi, L.; Tibaldi, M.; Spertino, E.; Vezza, C.; Isaia, G.C.; Massaia, M.; D’Amelio, P. Hyponatremia, Hypokalemia, and Fragility Fractures in Old Patients: More than an Association? Calcif. Tissue Int. 2020, 106, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachi, T.; Yokoi, T.; Goto, C.; Umeda, M.; Noguchi, Y.; Yasuda, M.; Minamitani, M.; Mizui, T.; Tsuchiya, T.; Teramachi, H. Hyponatremia and hypokalemia as risk factors for falls. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 69, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPherson, E.; Dunsmuir, R.A. Hyponatraemia in hip fracture patients. Scott. Med. J. 2002, 47, 115–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayus, J.C.; Negri, A.L.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Moritz, M.L. Is chronic hyponatremia a novel risk factor for hip fracture in the elderly? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 3725–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corona, G.; Norello, D.; Parenti, G.; Sforza, A.; Maggi, M.; Peri, A. Hyponatremia, falls and bone fractures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Endocrinol. 2018, 89, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzoulis, P.; Yavropoulou, M.P. Association of hyponatremia with bone mineral density and fractures: A narrative review. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 14, 20420188231197921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M. Hyponatremia and arginine vasopressin dysregulation: Mechanisms, clinical consequences, and management. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2006, 54, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardak, S.; Turgutalp, K.; Koyuncu, M.B.; Harı, H.; Helvacı, I.; Ovla, D.; Horoz, M.; Demir, S.; Kıykım, A. Community-acquired hypokalemia in elderly patients: Related factors and clinical outcomes. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2017, 49, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, S.A.; Arampatzis, S.; Harrison, S.L.; Bucur, R.C.; Ensrud, K.; Orwoll, E.S.; Bauer, D.C. Hyponatremia and Fractures: Findings From the MrOS Study. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2015, 30, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoorn, E.J.; Liamis, G.; Zietse, R.; Zillikens, M.C. Hyponatremia and bone: An emerging relationship. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 8, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäckle, K.; Klockner, F.; Hoffmann, D.B.; Roch, P.J.; Reinhold, M.; Lehmann, W.; Weiser, L. Influence of Hyponatremia on Spinal Bone Quality and Fractures Due to Low-Energy Trauma. Medicina 2021, 57, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnard, V.; Baleanu, F.; Iconaru, L.; Moreau, M.; Paesmans, M.; Body, J.J.; Bergmann, P. Postfracture Risk Assessment: Target the Centrally Sited Fractures First! A Substudy of NoFRACT. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2020, 35, 827–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroker, A.; Plett, R.; Nishiyama, K.K.; McErlain, D.D.; Sandino, C.; Boyd, S.K. Distal skeletal tibia assessed by HR-pQCT is highly correlated with femoral and lumbar vertebra failure loads. J. Biomech. 2017, 59, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloia, J.F. The gain and loss of bone in the human life cycle. Adv. Nutr. Res. 1994, 9, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, P.J. Bone densitometry in the management of Colles’ fractures: Which site to measure? Br. J. Radiol. 2001, 74, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, S.R.; Melton, L.J. Epidemiology and outcomes of osteoporotic fractures. Lancet 2002, 359, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullberg, B.; Johnell, O.; Kanis, J.A. World-wide projections for hip fracture. Osteoporos. Int. 1997, 7, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.P.; Fu, T.S.; Lin, Y.C.; Fan, C.M. Risk factors and quality of life for the occurrence of hip fracture in postmenopausal women. Biomed. J. 2018, 41, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Court-Brown, C.M.; Caesar, B. Epidemiology of adult fractures: A review. Injury 2006, 37, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnick, S.L. Osteoporosis in men and women. Clin. Cornerstone 2006, 8, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, G.H.F.; Guzman, L.F.E.; Alvarenga, J.C.; Lopes, N.H.M.; Pereira, R.M.R. Association of moderate/severe vertebral fractures with reduced trabecular volumetric bone density in older women and reduced areal femoral neck bone density in older men from the community: A cross-sectional study (SPAH). Maturitas 2019, 120, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarenga, J.C.; Boyd, S.K.; Pereira, R.M.R. The relationship between estimated bone strength by finite element analysis at the peripheral skeleton to areal BMD and trabecular bone score at lumbar spine. Bone 2018, 117, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, A.V. Diabetes Mellitus: Does it Affect Bone? Calcif. Tissue Int. 2003, 73, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivers, R.Q.; Cumming, R.G.; Mitchell, P.; Peduto, A.J. The accuracy of self-reported fractures in older people. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2002, 55, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alem, A.M.; Sherrard, D.J.; Gillen, D.L.; Weiss, N.S.; Beresford, S.A.; Heckbert, S.R.; Wong, C.; Stehman-Breen, C. Increased risk of hip fracture among patients with end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. 2000, 58, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, L.; Buzková, P.; Fink, H.A.; Lee, J.S.; Chen, Z.; Ahmed, A.; Parashar, S.; Robbins, J.R. Hip fractures and heart failure: Findings from the Cardiovascular Health Study. Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramnemark, A.; Nyberg, L.; Borssén, B.; Olsson, T.; Gustafson, Y. Fractures after stroke. Osteoporos. Int. 1998, 8, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berl, T.; Rastegar, A. A patient with severe hyponatremia and hypokalemia: Osmotic demyelination following potassium repletion. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2010, 55, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Lu, C.; Tian, H.; Ren, Y.; Chen, T. Primary Aldosteronism and Bone Metabolism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 574151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Hu, X.; Li, J.; Xu, H.; Nie, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lyu, Z. Bone and mineral metabolism in patients with primary aldosteronism: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1027841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frara, S.; Allora, A.; di Filippo, L.; Formenti, A.M.; Loli, P.; Polizzi, E.; Tradati, D.; Ulivieri, F.M.; Giustina, A. Osteopathy in mild adrenal Cushing’s syndrome and Cushing disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 35, 101515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianferotti, L.; Cipriani, C.; Corbetta, S.; Corona, G.; Defeudis, G.; Lania, A.G.; Messina, C.; Napoli, N.; Mazziotti, G. Bone quality in endocrine diseases: Determinants and clinical relevance. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2023, 46, 1283–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skjødt, M.K.; Abrahamsen, B. New Insights in the Pathophysiology, Epidemiology, and Response to Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 108, e1175–e1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, R.N.; Saba, F. Osteomalacia in a Case of Adult-Onset Bartter Syndrome. Eur. J. Case Rep. Intern. Med. 2018, 5, 000764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).