Orofacial Manifestation of Systemic Sclerosis: A Cross-Sectional Study and Future Prospects of Oral Capillaroscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Group A (cases) included all patients diagnosed with SSc;
- Group B (controls) consisted of all subjects without SSc diagnosis.
- PCR plaque index (Plaque Control Record) to evaluate the presence of plaque deposits on the tooth surfaces.
- Periodontal screening PSR (Periodontal Screening and Recording) to record the maximum probing depth for each sextant.
- DMFT (Decayed Missing and Filled Permanent Teeth) score to calculate the number of decayed, missing, and filled teeth.
- Salivary flow quantification was conducted by collecting a saliva sample and determining the buffering power (pH) using reactive strips with a colorimetric change.
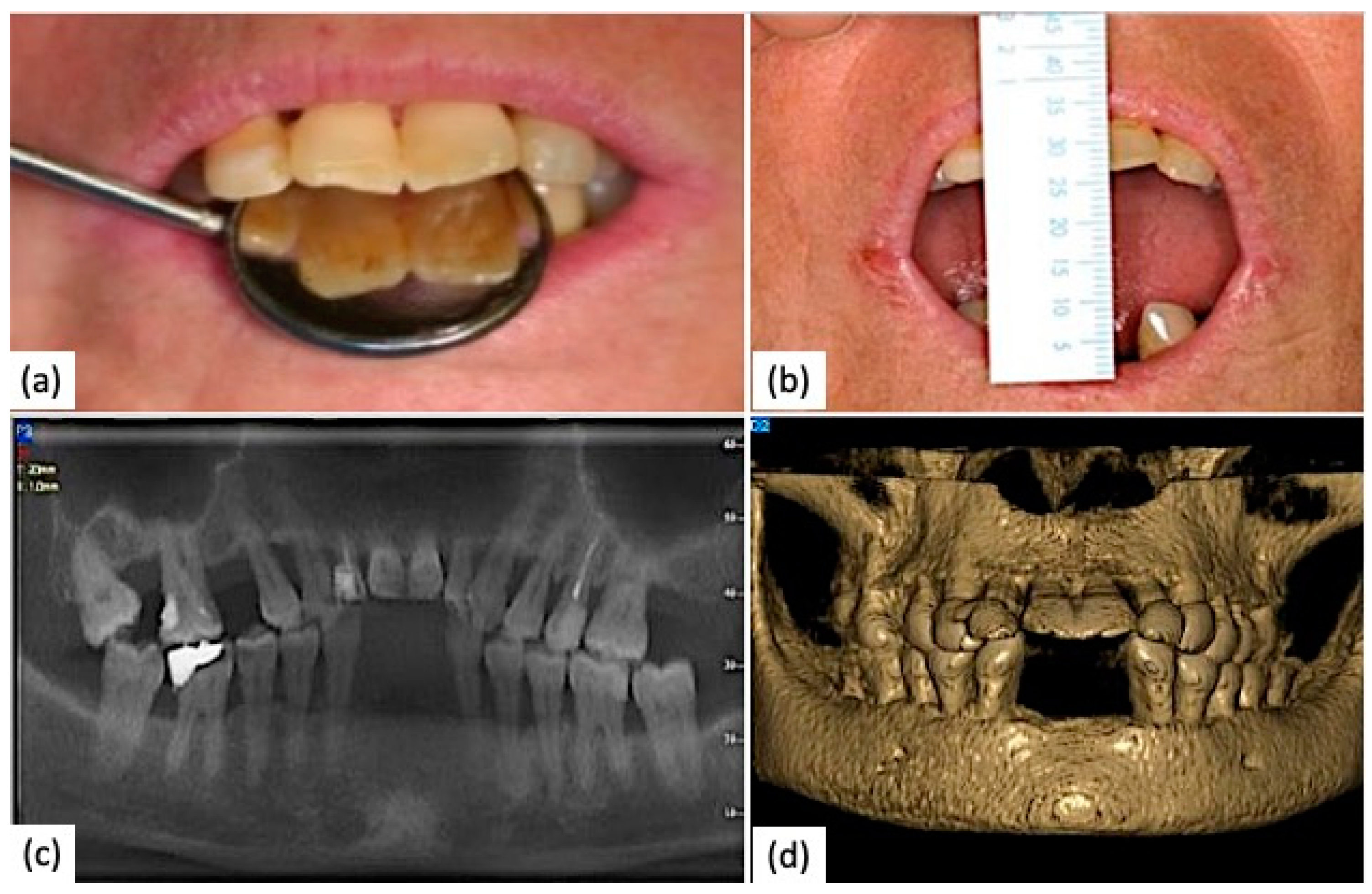
- The degree of microstomia was measured by determining the distance between the incisal margins of the lower central tooth and the upper central tooth during the maximum oral opening.
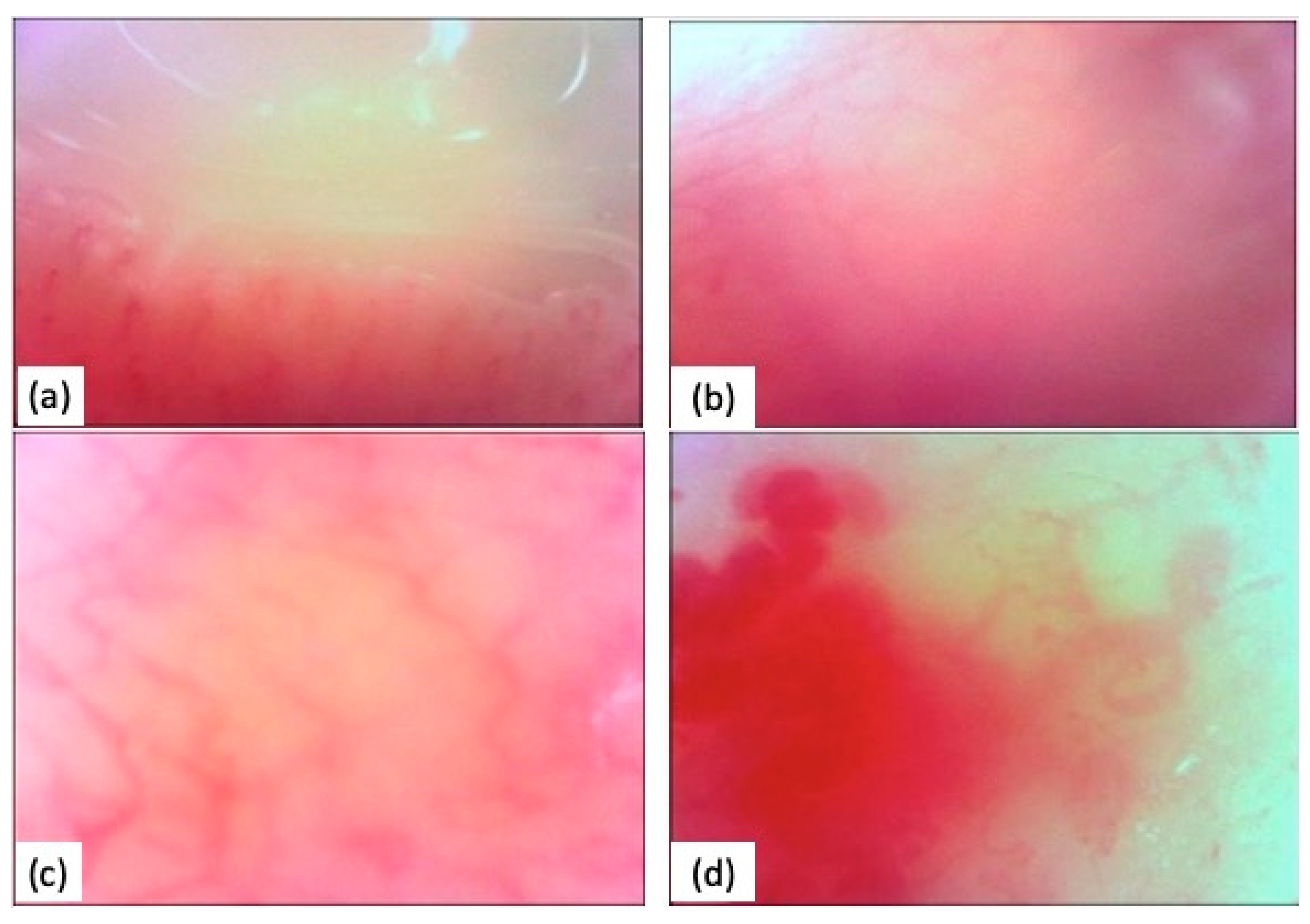
- Visibility of the loops: difficulty in focusing (score from 0 to 4).
- Orientation related to surface (score A, B, or AB). (A) pattern parallel to the surface; (B) pattern perpendicular; (AB) pattern both parallel and perpendicular.
- Microhaemorrhages: (Score 0 or 1). (0) absence; (1) presence.
- Characteristics of capillary loops (e.g., tissue thickening, ectasias, megacapillaries, and reticulum rarefaction): (score 0 or 1). (0) absence; (1) presence.
- Capillary density: the number of loops per surface unit (in a square millimeter, there are typically 12 to 16 loops present);
- Capillary tortuosity, measured on a scale from 0 to 1.
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Clinical Case
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Varga, J.; Abraham, D. Systemic Sclerosis: A Prototypic Multisystem Fibrotic Disorder. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branch, N.S.C.; Scleroderma, O. Available online: https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/scleroderma (accessed on 23 September 2023).
- Careta, M.F.; Romiti, R. Localized Scleroderma: Clinical Spectrum and Therapeutic Update. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2015, 90, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snarskaya, E.S.; Vasileva, K.D. Localized Scleroderma: Actual Insights and New Biomarkers. Int. J. Dermatol. 2022, 61, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vona, R.; Giovannetti, A.; Gambardella, L.; Malorni, W.; Pietraforte, D.; Straface, E. Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Scleroderma: An Overview. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 3308–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourji, K.; Meyer, A.; Chatelus, E.; Pincemail, J.; Pigatto, E.; Defraigne, J.-O.; Singh, F.; Charlier, C.; Geny, B.; Gottenberg, J.-E.; et al. High Reactive Oxygen Species in Fibrotic and Nonfibrotic Skin of Patients with Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 87, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerjen, R.; Nikpour, M.; Krieg, T.; Denton, C.P.; Saracino, A.M. Systemic Sclerosis in Adults. Part I: Clinical Features and Pathogenesis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 87, 937–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.; Almeida, I.; Vasconcelos, C. Quality of Life in Systemic Sclerosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, K.; Baulig, C.; Knippschild, S.; Strietzel, F.P.; Hunzelmann, N.; Jackowski, J. Prevalence of Oral and Maxillofacial Disorders in Patients with Systemic Scleroderma—A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Hoogen, F.; Khanna, D.; Fransen, J.; Johnson, S.R.; Baron, M.; Tyndall, A.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Naden, R.P.; Medsger, T.A.; Carreira, P.E.; et al. 2013 Classification Criteria for Systemic Sclerosis: An American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism Collaborative Initiative. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dima, A.; Berza, I.; Popescu, D.N.; Parvu, M.I. Nailfold Capillaroscopy in Systemic Diseases: Short Overview for Internal Medicine. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 59, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, V.; Herrick, A.L.; Ingegnoli, F.; Damjanov, N.; De Angelis, R.; Denton, C.P.; Distler, O.; Espejo, K.; Foeldvari, I.; Frech, T.; et al. Standardisation of Nailfold Capillaroscopy for the Assessment of Patients with Raynaud’s Phenomenon and Systemic Sclerosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, A.; Sebastiani, M.; Campomori, F.; Pipitone, N.; Giuggioli, D.; Colaci, M.; Praino, E.; Ferri, C. Nailfold Videocapillaroscopy Alterations in Dermatomyositis and Systemic Sclerosis: Toward Identification of a Specific Pattern. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 43, 1575–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbaş, A.; Elmas, Ö.F.; Demirbaş, G.U.; Atasoy, M.; Türsen, Ü.; Lotti, T. Potential Utility of Oral Mucosal Capillaroscopy as an Indicator of Microvascular Damage in Behçet Disease: A Preliminary Study. Dermatol. Pract. Concept. 2021, 11, e2021116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firth, D. Bias Reduction of Maximum Likelihood Estimates. Biometrika 1993, 80, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, V.K.; Valentini, G.; Hachulla, E.; Cozzi, F.; Distler, O.; Airó, P.; Czirják, L.; Allanore, Y.; Siegert, E.; Rosato, E.; et al. Brief Report: Smoking in Systemic Sclerosis: A Longitudinal European Scleroderma Trials and Research Group Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 1829–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, A.D.; Andréasson, K.; McMahan, Z.H.; Bukiri, H.; Howlett, N.; Lagishetty, V.; Lee, S.M.; Jacobs, J.P.; Volkmann, E.R. Gastrointestinal Tract Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis: The Roles of Diet and the Microbiome. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2023, 60, 152185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isola, G.; Williams, R.C.; Lo Gullo, A.; Ramaglia, L.; Matarese, M.; Iorio-Siciliano, V.; Cosio, C.; Matarese, G. Risk Association between Scleroderma Disease Characteristics, Periodontitis, and Tooth Loss. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 36, 2733–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schouffoer, A.A.; van der Giesen, F.J.; Beaart-van de Voorde, L.J.J.; Wolterbeek, R.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Vliet Vlieland, T.P.M. Validity and Responsiveness of the Michigan Hand Questionnaire in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 1386–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, H.K.; Hant, F.N.; Hatfield, C.; Summerlin, L.M.; Smith, E.A.; Silver, R.M. Factors Associated with Oral Hygiene Practices among Adults with Systemic Sclerosis. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 2014, 12, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes da Silva, G.S.; Maymone de Melo, M.L.; Leão, J.C.; Carvalho, A.T.; Porter, S.; Duarte, A.L.B.P.; Dantas, A.T.; Gueiros, L.A. Oral Features of Systemic Sclerosis: A Case-Control Study. Oral Dis. 2019, 25, 1995–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laforgia, A.; Corsalini, M.; Stefanachi, G.; Tafuri, S.; Ballini, A.; Pettini, F.; Di Venere, D. Non-Surgical Periodontal Management in Scleroderma Disease Patients. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2016, 30, 847–851. [Google Scholar]
- Forcella, L.; Filippi, C.; Waltimo, T.; Filippi, A. Measurement of Unstimulated Salivary Flow Rate in Healthy Children Aged 6 to 15 Years. Swiss. Dent. J. 2018, 128, 962–967. [Google Scholar]
- Hadj Said, M.; Foletti, J.M.; Graillon, N.; Guyot, L.; Chossegros, C. Orofacial Manifestations of Scleroderma. A Literature Review. Rev. Stomatol. Chir. Maxillofac. Chir. Orale. 2016, 117, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couderc, M.; Tournadre, A.; Mathieu, S.; Pereira, B.; Soubrier, M.; Dubost, J.J. Do the Salivary Glands of Patients with Systemic Sclerosis Show Ultrasonographic Modifications Suggestive of Sjögren’s Syndrome? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, e137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crincoli, V.; Fatone, L.; Fanelli, M.; Rotolo, R.P.; Chialà, A.; Favia, G.; Lapadula, G. Orofacial Manifestations and Temporomandibular Disorders of Systemic Scleroderma: An Observational Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parat, K.; Radić, M.; Perković, D.; Lukenda, D.B.; Kaliterna, D.M. Reduced Salivary Flow and Caries Status Are Correlated with Disease Activity and Severity in Patients with Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 0300060520941375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parat, K.; Radić, M.; Perković, D.; Biočina Lukenda, D.; Martinović Kaliterna, D. Sjögren’s Syndrome: An Important Confounder in Evaluation of Oral Features in Systemic Sclerosis. Oral Dis. 2020, 26, 1592–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, M.; Hudson, M.; Tatibouet, S.; Steele, R.; Lo, E.; Gravel, S.; Gyger, G.; El Sayegh, T.; Pope, J.; Fontaine, A.; et al. Relationship between Disease Characteristics and Orofacial Manifestations in Systemic Sclerosis: Canadian Systemic Sclerosis Oral Health Study III. Arthritis Care Res. 2015, 67, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirani, R.; Poursac, N.; Naveau, A.; Schaeverbeke, T.; Devillard, R.; Truchetet, M.-E. Orofacial Consequences of Systemic Sclerosis: A Systematic Review. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2018, 3, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, C.; Agard, C.; Barbarot, S.; N’guyen, J.-M.; Planchon, B.; Durant, C.; Pistorius, M.-A.; Dreno, B.; Ponge, T.; Stalder, J.-F.; et al. Orofacial manifestations of systemic sclerosis: A study of 30 consecutive patients. Rev. Stomatol. Chir. Maxillofac. 2010, 111, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, E.L.A.; Christmann, R.B.; Borba, E.F.; Borges, C.T.L.; Siqueira, J.T.T.; Bonfa, E. Mandibular Function Is Severely Impaired in Systemic Sclerosis Patients. J. Orofac. Pain 2010, 24, 197–202. [Google Scholar]
- Puzio, A.; Przywara-Chowaniec, B.; Postek-Stefańska, L.; Mrówka-Kata, K.; Trzaska, K. Systemic Sclerosis and Its Oral Health Implications. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2019, 28, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadakuntla, A.; Juneja, A.; Sattler, S.; Agarwal, A.; Panse, D.; Zakhary, N.; Pasumarthi, A.; Shapiro, L.; Tadros, M. Dysphagia, Reflux and Related Sequelae Due to Altered Physiology in Scleroderma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 5201–5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Xiao, Q.; Fei, Y. A Glimpse Into the Microbiome of Sjögren’s Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 918619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, C.-T.; Huang, S.-L.; Yang, H.-W.; Kao, C.-C.; Wei, C.-C.; Huang, Y.-F. Oral Microbiota in Xerostomia Patients—A Preliminary Study. J. Dent. Sci. 2022, 17, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamont, R.J.; Koo, H.; Hajishengallis, G. The Oral Microbiota: Dynamic Communities and Host Interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 745–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costalonga, M.; Herzberg, M.C. The Oral Microbiome and the Immunobiology of Periodontal Disease and Caries. Immunol. Lett. 2014, 162, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pischon, N.; Hoedke, D.; Kurth, S.; Lee, P.; Dommisch, H.; Steinbrecher, A.; Pischon, T.; Burmester, G.R.; Buttgereit, F.; Detert, J.; et al. Increased Periodontal Attachment Loss in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. J. Periodontol. 2016, 87, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elimelech, R.; Mayer, Y.; Braun-Moscovici, Y.; Machtei, E.E.; Balbir-Gurman, A. Periodontal Conditions and Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Level in Gingival Crevicular Fluid of Scleroderma Patients. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2015, 17, 549–553. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, R.; Li, S.; Su, Y. Oral Manifestations of Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: A Meta-Analysis for Case-Controlled Studies. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rams, T.E.; Loesche, W.J. Relationship between Periodontal Screening and Recording Index Scores and Need for Periodontal Access Surgery. J. Periodontol. 2017, 88, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matarese, G.; Isola, G.; Anastasi, G.P.; Favaloro, A.; Milardi, D.; Vermiglio, G.; Vita, G.; Cordasco, G.; Cutroneo, G. Immunohistochemical Analysis of TGF-Β1 and VEGF in Gingival and Periodontal Tissues: A Role of These Biomarkers in the Pathogenesis of Scleroderma and Periodontal Disease. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 30, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiani, L.; Mosca, G.; Giannini, D.; Giuliani, A.R.; Farello, G.; Marci, M.C.; Ballatori, E. Dental Caries and Bone Mineral Density: A Cross Sectional Study. Eur. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2006, 7, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poole, J.; Conte, C.; Brewer, C.; Good, C.C.; Perella, D.; Rossie, K.M.; Steen, V. Oral Hygiene in Scleroderma: The Effectiveness of a Multi-Disciplinary Intervention Program. Disabil. Rehabil. 2010, 32, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaty, K.L.; Gurenlian, J.R.; Rogo, E.J. Oral Health Experiences of the Limited Scleroderma Patient. J. Dent. Hyg. 2021, 95, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sierakowska, M.; Doroszkiewicz, H.; Sierakowska, J.; Olesińska, M.; Grabowska-Jodkowska, A.; Brzosko, M.; Leszczyński, P.; Pawlak-Buś, K.; Batko, B.; Wiland, P.; et al. Factors Associated with Quality of Life in Systemic Sclerosis: A Cross-Sectional Study. Qual. Life Res. 2019, 28, 3347–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garaiman, A.; Mihai, C.; Dobrota, R.; Jordan, S.; Maurer, B.; Flemming, J.; Distler, O.; Becker, M.O. The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: A Psychometric and Factor Analysis in a Monocentric Cohort. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 39 (Suppl. S131), 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, X.; Thumboo, J.; Low, A.H.L. Validation of the Scleroderma Health Assessment Questionnaire and Quality of Life in English and Chinese-Speaking Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 15, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, S.; Meier, A.; Malcarne, V.L. Measuring and Managing Appearance Anxiety in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, N.M.; Ciaffi, J.; Liem, S.I.E.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; de Vries-Bouwstra, J.K. Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: Evolution over Time and Main Determinants. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 3646–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastiani, M.; Manfredi, A.; Lo Monaco, A.; Praino, E.; Riccieri, V.; Grattagliano, V.; Bortoluzzi, A.; Stefanantoni, K.; D’Amico, R.; Giuggioli, D.; et al. Capillaroscopic Skin Ulcers Risk Index (CSURI) Calculated with Different Videocapillaroscopy Devices: How Its Predictive Values Change. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2013, 31, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sebastiani, M.; Manfredi, A.; Cestelli, V.; Praino, E.; Cannarile, F.; Giuggioli, D.; Colaci, M.; Ferri, C. Validation Study of Predictive Value of Capillaroscopic Skin Ulcer Risk Index (CSURI) in Scleroderma Patients Treated with Bosentan. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33, S196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfredi, A.; Sebastiani, M.; Carraro, V.; Iudici, M.; Bocci, M.; Vukatana, G.; Gerli, R.; De Angelis, R.; Del Medico, P.; Praino, E.; et al. Prediction Risk Chart for Scleroderma Digital Ulcers: A Composite Predictive Model Based on Capillaroscopic, Demographic and Clinico-Serological Parameters. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2015, 59, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassi, W.; Core, P.; Carlino, G.; Blasetti, P.; Cervini, M. Labial Capillary Microscopy in Systemic Sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1993, 52, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scardina, G.A.; Carini, F.; Messina, P. Oral capillaroscopy: A new diagnostic method. Reumatismo 2005, 57, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mathura, K.R.; Vollebregt, K.C.; Boer, K.; De Graaff, J.C.; Ubbink, D.T.; Ince, C. Comparison of OPS Imaging and Conventional Capillary Microscopy to Study the Human Microcirculation. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001, 91, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Scardina, G.A.; Ruggieri, A.; Messina, P. Evaluation of Labial Microvessels in Sjogren Syndrome: A Videocapillaroscopic Study. Ann. Anat. 2009, 191, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scardina, G.A.; Guercio, G.; Valenti, C.F.; Tegolo, D.; Messina, P. Videocapillaroscopy of the Oral Mucosa in Patients with Diabetic Foot: Possible Diagnostic Role of Microangiopathic Damage? J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquaro, A.; Brusca, G.; Casella, S.; Cumbo, E.M.; Valle, A.D.; Karobari, M.I.; Marino, G.; Marya, A.; Messina, P.; Scardina, G.A.; et al. Evaluation of the Oral Microcirculation in Patients Undergoing Anti COVID-19 Vaccination: A Preliminary Study. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scardina, G.A.; Messina, P. Oral Microcirculation in Post-Menopause: A Possible Correlation with Periodontitis. Gerodontology 2012, 29, e1045–e1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutolo, M.; Soldano, S.; Smith, V. Pathophysiology of Systemic Sclerosis: Current Understanding and New Insights. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, M.; Griffin, M.; Denton, C.P.; Butler, P.E. Sidestream Dark Field (SDF) Imaging of Oral Microcirculation in the Assessment of Systemic Sclerosis. Microvasc. Res. 2019, 126, 103890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frech, T.M. Imaging Techniques for Assessment of Vascular Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2022, 34, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameters | Total (n = 59) | SSc (n = 25) | Controls (n = 34) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 50.3 ± 12.7 | 54.7 ± 12 | 47.1 ± 12.4 | 0.021 |
| Smoke | 12 (20.3) | 4 (16) | 8 (23.5) | 0.702 |
| Sport | 15 (25.4) | 4 (16) | 11 (32.6) | 0.262 |
| Snacks | 53 (89.8) | 25 (100) | 28 (82.4) | 0.034 |
| Manual toothbrush | 45 (76.3) | 23 (92) | 22 (64.7) | 0.034 |
| Electric toothbrush | 14 (23.7) | 2 (8) | 12 (35.3) | 0.034 |
| Dental floss | 13 (22) | 2 (8) | 11 (32.4) | 0.056 |
| Tongue cleaner | 4 (6.8) | 1 (4) | 3 (8.8) | 0.603 |
| Mouthwashes | 31 (52.5) | 13 (52) | 18 (52.9) | 0.943 |
| Parameters | Total (n = 59) | SSc (n = 25) | Controls (n = 34) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salivary Flow | ||||
| Xerostomia | 15 (25.4) | 15 (60) | 0 (0) | <0.001 |
| Reduced Flow | 6 (10.2) | 6 (24) | 0 (0) | 0.004 |
| Standard Flow | 27 (45.8) | 4 (16) | 23 (67.7) | <0.001 |
| Halitosis | 15 (25.4) | 10 (40) | 5 (14.7) | 0.057 |
| Microstomia | <0.001 | |||
| Severe | 3 (5.1) | 3 (12) | 0 (0) | |
| Moderate | 31 (52.5) | 12 (48) | 19 (55.9) | |
| Mild | 10 (17) | 10 (40) | 0 (0) | |
| Absent | 15 (25.4) | 0 (0) | 15 (44.1) | |
| Lip retraction | 20 (33.9) | 20 (80) | 0 (0) | <0.001 |
| Oral breathing | 17 (28.8) | 15 (60) | 2 (5.9) | 0.007 |
| Gingival/periodontal diseases | ||||
| Gingivitis | 29 (49.2) | 15 (60) | 14 (41.2) | 0.153 |
| Periodontitis | 22 (37.3) | 15 (60) | 7 (20.6) | 0.002 |
| Parameters | Total (n = 59) | SSc (n = 25) | Controls (n = 34) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCR | 39.5 ± 19.5 | 52.7 ± 21.2 | 32.1 ± 14.2 | 0.001 |
| DMFT | 5 [4–7] | 8 [6–11] | 4.5 [3–6] | <0.001 |
| PSR Score | <0.001 | |||
| 0 | 6 (11.5) | 0 (0) | 6 (17.7) | |
| 1 | 12 (23.1) | 0 (0) | 12 (35.3) | |
| 2 | 10 (19.2) | 2 (11.1) | 8 (23.5) | |
| 3 | 16 (30.8) | 9 (50) | 7 (20.6) | |
| 4 | 8 (15.4) | 7 (38.9) | 1 (2.9) |
| Parameters | Total (n = 59) | SSc (n = 25) | Controls (n = 34) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| s-HAQ test | <0.001 | |||
| Severe | 5 (8.5) | 5 (20) | 0 (0) | |
| Moderate | 6 (10.2) | 6 (24) | 0 (0) | |
| Mild | 14 (23.7) | 14 (56) | 0 (0) | |
| Absent | 34 (57.6) | 0 (0) | 34 (100) | |
| Anxiety degree | <0.001 | |||
| Severe | 4 (6.8) | 4 (16) | 0 (0) | |
| Moderate | 11 (18.6) | 11 (44) | 0 (0) | |
| Mild | 8 (13.6) | 0 (0) | 8 (23.5) | |
| Very Low | 10 (17) | 10 (40) | 0 (0) | |
| Absent | 26 (44) | 0 (0) | 26 (76,5) | |
| Depression degree | <0.001 | |||
| Severe | 4 (6.8) | 4 (16) | 0 (0) | |
| Moderate | 14 (23.7) | 14 (56) | 0 (0) | |
| Mild | 7 (11.9) | 7 (28) | 0 (0) | |
| Absent | 34 (57.6) | 0 (0) | 34 (100) | |
| Physical health | 67 [34–78] | 33 [31–36] | 76.5 [71–84] | <0.001 |
| Psychological state | 67 [42–77] | 42 [39–46] | 75.5 [68–80] | <0.001 |
| Social relations | 67 [33–78] | 32 [31–34] | 76.5 [71–80] | <0.001 |
| Environmental conditions | 70 [33–81] | 32 [30–34] | 79.5 [76–86] | <0.001 |
| Parameters | Total (n = 40) | SSc (n = 25) | Controls (n = 15) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GINGIVAL CAPILLAROSCOPY | ||||
| Loops visibility | <0.001 | |||
| Minimal | 11 (27.5) | 11 (44) | (0) | |
| Medium | 7 (17.5) | 7 (28) | (0) | |
| Standard | 22 (55) | 7 (28) | 15 (100) | |
| Gingival microhemorrhages | 5 (12.5) | 5 (20) | (0) | 0.137 |
| Thickening of the gum tissue | 11 (27.5) | 11 (44) | (0) | 0.002 |
| Tortuosity of the gingival loops | 14 (35) | 14 (56) | (0) | <0.001 |
| Reduced gingival density | 12 (30) | 12 (48) | (0) | 0.001 |
| LABIAL CAPILLAROSCOPY | ||||
| Loops visibility | <0.001 | |||
| Minimal | 9 (22.5) | 9 (36) | (0) | |
| Medium | 9 (22.5) | 9 (36) | (0) | |
| Standard | 22 (55) | 7 (28) | 15 (100) | |
| Lip microhemorrhages | 4 (10) | 4 (16) | (0) | 0.278 |
| Thickening of the lip tissue | 6 (15) | 6 (24) | (0) | 0.067 |
| Lip ectasia | 7 (17.5) | 7 (28) | (0) | 0.033 |
| Labial megacapillaries | 6 (15) | 6 (24) | (0) | 0.067 |
| Rarefaction of the labial reticulum | 5 (12.5) | 5 (20) | (0) | 0.137 |
| Tortuosity labial loops | 16 (40) | 16 (64) | (0) | <0.001 |
| Periodontal/Carious Lesions Prevention | Hyposalivation/Xerostomia Treatment | Microstomia |
|---|---|---|
| Periodic checks, scheduled professional oral hygiene sessions | Topical and systemic salivary substitutes/stimulants, use of alcohol-free chlorhexidine 0.12% mouthwashes, polyenzymatic systems in the form of gels, mouthwashes, and toothpaste | Oral stretching |
| Reduction in the frequency of intake of cariogenic/acidic foods, meticulous oral hygiene | Frequent intake of water, use of chewing gum without added sugar with enzymes, xylitol | |
| Manual toothbrush with medium/soft filaments (ergonomic handle or with ball), electric toothbrush | Using petroleum jelly or lip balm to moisturize lips |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antonacci, A.; Praino, E.; Abbinante, A.; Favia, G.; Rotondo, C.; Bartolomeo, N.; Giotta, M.; Iannone, F.; Orrù, G.; Agneta, M.T.; et al. Orofacial Manifestation of Systemic Sclerosis: A Cross-Sectional Study and Future Prospects of Oral Capillaroscopy. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14040437
Antonacci A, Praino E, Abbinante A, Favia G, Rotondo C, Bartolomeo N, Giotta M, Iannone F, Orrù G, Agneta MT, et al. Orofacial Manifestation of Systemic Sclerosis: A Cross-Sectional Study and Future Prospects of Oral Capillaroscopy. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(4):437. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14040437
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntonacci, Anna, Emanuela Praino, Antonia Abbinante, Gianfranco Favia, Cinzia Rotondo, Nicola Bartolomeo, Massimo Giotta, Florenzo Iannone, Germano Orrù, Maria Teresa Agneta, and et al. 2024. "Orofacial Manifestation of Systemic Sclerosis: A Cross-Sectional Study and Future Prospects of Oral Capillaroscopy" Diagnostics 14, no. 4: 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14040437
APA StyleAntonacci, A., Praino, E., Abbinante, A., Favia, G., Rotondo, C., Bartolomeo, N., Giotta, M., Iannone, F., Orrù, G., Agneta, M. T., Capodiferro, S., Barile, G., & Corsalini, M. (2024). Orofacial Manifestation of Systemic Sclerosis: A Cross-Sectional Study and Future Prospects of Oral Capillaroscopy. Diagnostics, 14(4), 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14040437












