Long-Term HBsAg Titer Kinetics with Entecavir/Tenofovir: Implications for Predicting Functional Cure and Low Levels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Clinical and Laboratory Data
2.3. Follow-Up
2.4. Outcome Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
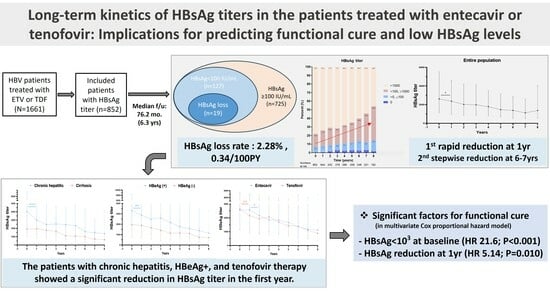
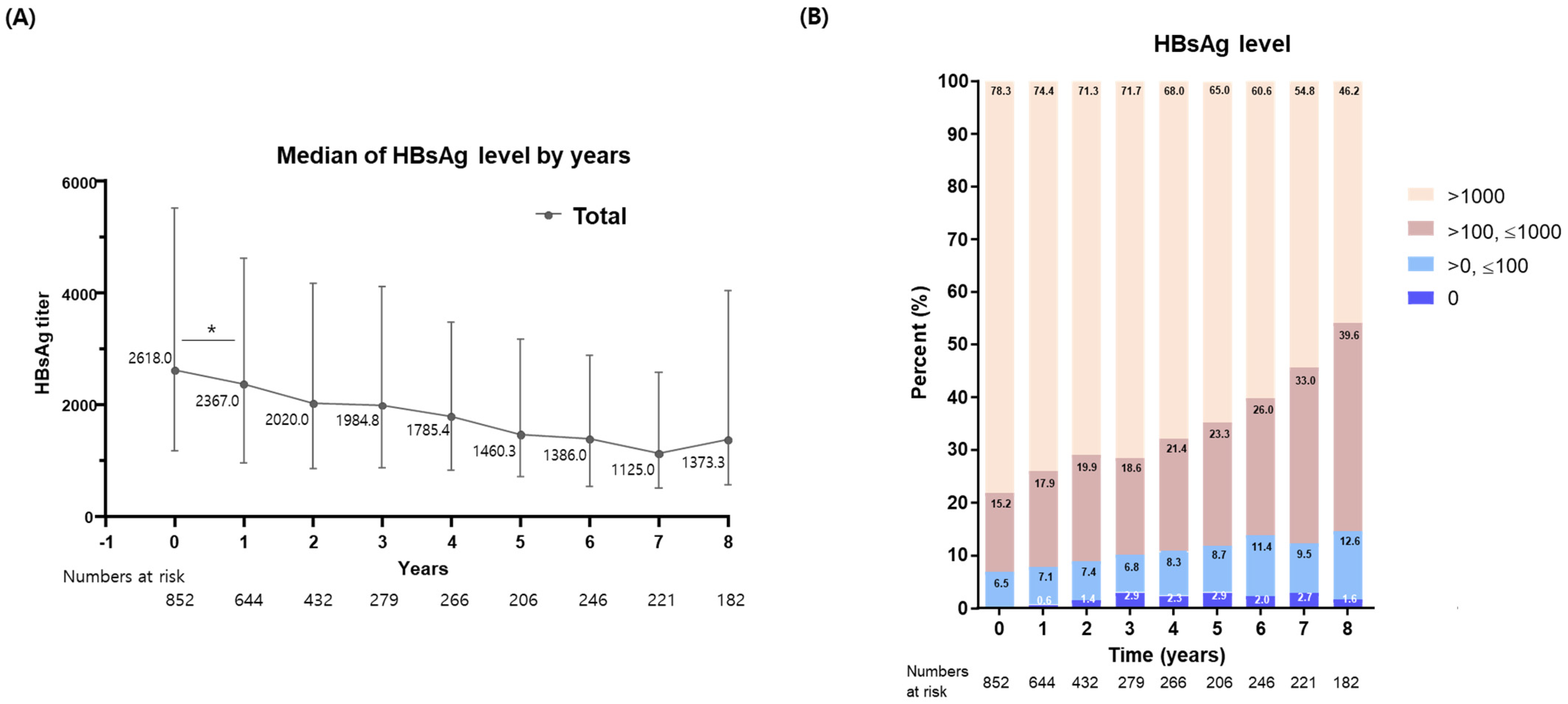
3.2. Long-Term Kinetics in HBsAg Levels following NA Therapy
3.3. Achievement of Functional Cure and Low HBsAg Levels
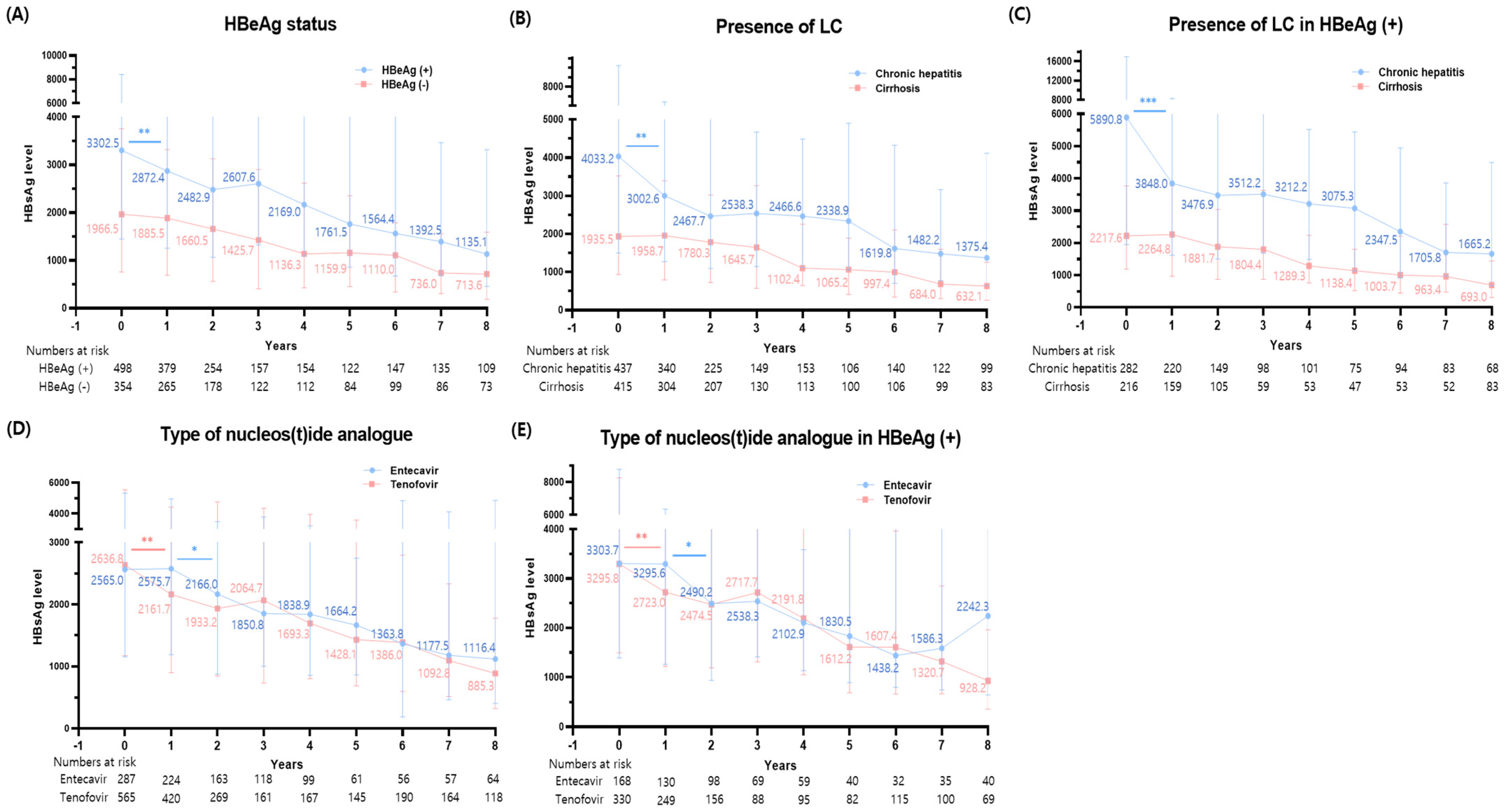
3.4. Changes in HBsAg Levels Based on Various Disease Status
3.5. Changes in HBsAg Levels among HBeAg (+) Patients
3.6. Comparison of HBsAg Level Changes between Tenofovir and Entecavir
3.7. Factors Associated with Functional Cure and Low HBsAg Levels
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Hepatitis B. Available online: https://www.who.int/newsroom/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b (accessed on 18 July 2023).
- Yoo, S.H.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, S.G.; Kwon, J.H.; Lee, H.A.; Seo, Y.S.; Jung, Y.K.; Yim, H.J.; Song, D.S.; Kang, S.H.; et al. Current status of ultrasonography in national cancer surveillance program for hepatocellular carcinoma in South Korea: A large-scale multicenter study. J. Liver Cancer 2023, 23, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korean Association for the Study of the Liver (KASL). KASL clinical practice guidelines for management of chronic hepatitis B. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2019, 25, 93–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, N.; Kagawa, T.; Hirose, S.; Arase, Y.; Tsuruya, K.; Anzai, K.; Shiraishi, K.; Mine, T. Off-treatment durability of antiviral response to nucleoside analogues in patients with chronic hepatitis B. BMC Gastroenterol. 2016, 16, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.M.; Liaw, Y.F. Hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance during chronic HBV infection. Antivir. Ther. 2010, 15, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoutendijk, R.; Hansen, B.E.; van Vuuren, A.J.; Boucher, C.A.B.; Janssen, H.L.A. Serum HBsAg Decline During Long-term Potent Nucleos(t)ide Analogue Therapy for Chronic Hepatitis B and Prediction of HBsAg Loss. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 204, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Korean Association for the Study of the Liver (KASL). KASL clinical practice guidelines for management of chronic hepatitis B. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2022, 28, 276–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrault, N.A.; Lok, A.S.F.; McMahon, B.J.; Chang, K.M.; Hwang, J.P.; Jonas, M.M.; Brown, R.S., Jr.; Bzowej, N.H.; Wong, J.B. Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1560–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, Y.F. Clinical utility of HBV surface antigen quantification in HBV e antigen-negative chronic HBV infection. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striki, A.; Manolakopoulos, S.; Deutsch, M.; Kourikou, A.; Kontos, G.; Kranidioti, H.; Hadziyannis, E.; Papatheodoridis, G. Hepatitis B s antigen kinetics during treatment with nucleos(t)ides analogues in patients with hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 1642–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.F.; Chen, C.F.; Lai, H.C.; Su, W.P.; Lin, C.H.; Chuang, P.H.; Chen, S.H.; Chen, C.H.; Wang, H.W.; Huang, G.T.; et al. Trajectories of serum hepatitis B surface antigen kinetics in patients with chronic hepatitis B receiving long-term nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reijnders, J.G.; Rijckborst, V.; Sonneveld, M.J.; Scherbeijn, S.M.; Boucher, C.A.; Hansen, B.E.; Janssen, H.L. Kinetics of hepatitis B surface antigen differ between treatment with peginterferon and entecavir. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.H.; Jang, J.W.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.; Chung, K.W.; Lee, Y.S.; Choi, J.Y. Pretreatment HBeAg level and an early decrease in HBeAg level predict virologic response to entecavir treatment for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. J. Viral Hepat. 2012, 19, e41–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korean Liver Cancer Association (KLCA) and National Cancer Center (NCC) Korea. 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2022, 28, 583–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.C.; Chiu, Y.C.; Chiu, H.C.; Liu, W.C.; Cheng, P.N.; Chen, C.Y.; Chang, T.T.; Wu, I.C. Clinical utility of hepatitis B surface antigen kinetics in treatment-naïve chronic hepatitis B patients during long-term entecavir therapy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcellin, P.; Buti, M.; Krastev, Z.; de Man, R.A.; Zeuzem, S.; Lou, L.; Gaggar, A.; Flaherty, J.F.; Massetto, B.; Lin, L.; et al. Kinetics of hepatitis B surface antigen loss in patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B treated with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 1228–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papatheodoridis, G.; Goulis, J.; Manolakopoulos, S.; Margariti, A.; Exarchos, X.; Kokkonis, G.; Hadziyiannis, E.; Papaioannou, C.; Manesis, E.; Pectasides, D.; et al. Changes of HBsAg and interferon-inducible protein 10 serum levels in naive HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B patients under 4-year entecavir therapy. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papatheodoridis, G.; Triantos, C.; Hadziyannis, E.; Zisimopoulos, K.; Georgiou, A.; Voulgaris, T.; Vlachogiannakos, I.; Nikolopoulou, V.; Manolakopoulos, S. Serum HBsAg kinetics and usefulness of interferon-inducible protein 10 serum in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B patients treated with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. J. Viral Hepat. 2015, 22, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, Y.F.; Chu, C.M. Hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet 2009, 373, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaw, Y.F. Clinical utility of hepatitis B surface antigen quantitation in patients with chronic hepatitis B: A review. Hepatology 2011, 53, 2121–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.H.; Yoon, S.K.; Jang, J.W.; Kim, C.W.; Nam, S.W.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, B.S.; Park, Y.M.; Suzuki, S.; Sugauchi, F.; et al. Hepatitis B virus genotype C prevails among chronic carriers of the virus in Korea. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2005, 20, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.L.; Kao, J.H. Natural history of acute and chronic hepatitis B: The role of HBV genotypes and mutants. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 31, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.A.; Lim, Y.S.; An, J.; Lee, D.; Shim, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; Lee, H.C.; Chung, Y.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Suh, D.J. HBsAg seroclearance after nucleoside analogue therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B: Clinical outcomes and durability. Gut 2014, 63, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, T.C.; Liu, C.J.; Su, T.H.; Wang, C.C.; Chen, C.L.; Chen, P.J.; Chen, D.S.; Kao, J.H. Serum hepatitis B surface antigen levels predict surface antigen loss in hepatitis B e antigen seroconverters. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 517–525, 525.e511–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ding, X.; Liao, G.; Xia, M.; Ren, Z.; Fan, R.; Peng, J. Hepatitis B surface antigen kinetics after discontinuation of and retreatment with oral antivirals in non-cirrhotic HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. J. Viral Hepat. 2021, 28, 1121–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, J.; Lai, C.L.; Young, J.; Wong, D.K.; Yuen, J.; Seto, W.K.; Yuen, M.F. Quantitative hepatitis B surface antigen levels in patients with chronic hepatitis B after 2 years of entecavir treatment. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 1766–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, T.C.; Kao, J.H. Clinical utility of quantitative HBsAg in natural history and nucleos(t)ide analogue treatment of chronic hepatitis B: New trick of old dog. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, K.; Mizokami, M. Possible biological mechanisms of entecavir versus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate on reducing the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 38, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.W.; Kim, S.M.; Hur, W.; Kang, B.Y.; Lee, H.L.; Nam, H.; Yoo, S.H.; Sung, P.S.; Kwon, J.H.; Jang, J.W.; et al. Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate directly ameliorates liver fibrosis by inducing hepatic stellate cell apoptosis via downregulation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0261067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, K.; Tsukuda, S.; Suizu, F.; Kimura, A.; Sugiyama, M.; Watashi, K.; Noguchi, M.; Mizokami, M. Immunomodulatory Mechanism of Acyclic Nucleoside Phosphates in Treatment of Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Hepatology 2020, 71, 1533–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.C.; Jun, D.W.; Peng, C.Y.; Yeh, M.L.; Trinh, H.; Wong, G.L.; Kim, S.E.; Chen, C.H.; Oh, H.; Lin, C.H.; et al. Effectiveness of entecavir vs tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for functional cure of chronic hepatitis B in an international cohort. Hepatol. Int. 2022, 16, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Carey, I.; Bruce, M.; Montague, S.; Dusheiko, G.; Agarwal, K. HBsAg and HBcrAg as predictors of HBeAg seroconversion in HBeAg-positive patients treated with nucleos(t)ide analogues. J. Viral Hepat. 2018, 25, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variables | Total (N = 852) | Achievement of Functional Cure | Achievement of Low HBsAg Titer (≤100 IU/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Functional Cure | Functional Cure | p-Value | High HBsAg (>100) | Low HBsAg (≤100) | p-Value | ||
| (n = 833) | (n = 19) | (n = 725) | (n = 127) | ||||
| Age, years | 51.0 [43.5; 58.0] | 51.0 [43.0; 58.0] | 55.0 [47.0; 63.0] | 0.216 | 49.7 ± 11.4 | 55.7 ± 12.3 | <0.001 |
| Male | 517 (60.7%) | 504 (60.5%) | 13 (68.4%) | 0.645 | 427 (58.9%) | 90 (70.9%) | 0.014 |
| Cirrhosis | 415 (48.7%) | 407 (48.9%) | 8 (42.1%) | 0.726 | 347 (47.9%) | 68 (53.5%) | 0.278 |
| HBeAg positivity | 498 (58.5%) | 488 (58.6%) | 10 (52.6%) | 0.776 | 441 (60.8%) | 57 (44.9%) | 0.001 |
| HBVDNA, log IU/mL | 6.6 [5.5; 7.5] | 6.6 [5.5; 7.5] | 6.3 [5.4; 6.8] | 0.126 | 6.7 [5.6; 7.6] | 6.1 [5.1; 7.1] | <0.001 |
| AST, IU/mL | 76.0 [49.0; 140.5] | 76.0 [49.0; 139.0] | 94.0 [43.0; 270.0] | 0.644 | 152.8 ± 288.6 | 199.2 ± 346.5 | 0.156 |
| ALT, IU/mL | 83.0 [44.5; 178.5] | 83.0 [44.0; 175.0] | 153.0 [60.5; 449.5] | 0.108 | 177.5 ± 295.1 | 241.0 ± 473.2 | 0.145 |
| Tbil, mg/dL | 1.0 [0.7; 1.4] | 1.0 [0.7; 1.4] | 1.2 [0.8; 2.1] | 0.321 | 1.6 ± 2.7 | 2.0 ± 2.6 | 0.099 |
| Alb, g/dL | 4.0 [3.6; 4.3] | 4.0 [3.6; 4.3] | 4.3 [4.0; 4.5] | 0.009 | 3.9 ± 0.6 | 3.8 ± 0.7 | 0.062 |
| Cr, mg/dL | 0.8 [0.7; 0.9] | 0.8 [0.7; 0.9] | 0.8 [0.8; 0.9] | 0.201 | 0.9 ± 0.9 | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 0.270 |
| INR | 1.1 [1.1; 1.2] | 1.1 [1.1; 1.2] | 1.1 [1.1; 1.1] | 0.251 | 1.2 ± 0.3 | 1.2 ± 0.3 | 0.096 |
| Plt, 103/μL | 149.0 [107.0; 191.0] | 149.0 [107.0; 191.0] | 159.0 [141.5; 191.5] | 0.405 | 156.4 ± 62.6 | 140.3 ± 64.6 | 0.008 |
| WBC, μL | 5190.0 [4100.0; 6425.0] | 5190.0 [4100.0; 6420.0] | 5220.0 [4500.0; 6800.0] | 0.496 | 5504.4 ± 2173.9 | 5585.5 ± 2170.0 | 0.698 |
| CTP score | 5.0 [5.0; 6.0] | 5.0 [5.0; 6.0] | 5.0 [5.0; 5.0] | 0.659 | 5.7 ± 1.5 | 5.9 ± 1.7 | 0.183 |
| MELD score | 6.0 [6.0; 8.0] | 6.0 [6.0; 8.0] | 6.0 [6.0; 9.0] | 0.536 | 7.7 ± 3.8 | 8.5 ± 4.2 | 0.030 |
| HBsAg, IU/mL | 2618.0 [1167.0; 5523.4] | 2650.4 [1209.5; 5636.1] | 71.7 [22.9; 246.6] | <0.001 | 24,832.4 ± 366,366.3 | 1711.6 ± 4953.7 | 0.090 |
| Functional Cure | Low HBsAg Level (<2 log IU/mL) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Univariate Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | Variables | Univariate Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | ||||||||
| HR | 95% CI | p-Value | HR | 95% CI | p-Value | HR | 95% CI | p-Value | HR | 95% CI | p-Value | ||
| Age | 1.03 | 0.99, 1.07 | 0.2 | Age | 1.02 | 1.00, 1.05 | 0.041 | 1.01 | 0.99, 1.04 | 0.4 | |||
| Male | 1.48 | 0.56, 3.90 | 0.4 | Male | 2.13 | 1.25, 3.63 | 0.006 | 1.85 | 1.01, 3.40 | 0.048 | |||
| HBeAg (+) | 0.73 | 0.30, 1.80 | 0.5 | HBeAg (+) | 0.67 | 0.42, 1.06 | 0.087 | 0.88 | 0.50, 1.55 | 0.7 | |||
| HBVDNA | 1.00 | 1.00, 1.00 | 0.15 | HBVDNA | 1.00 | 1.00, 1.00 | 0.020 | 1.00 | 1.00, 1.00 | 0.10 | |||
| Alb | 4.01 | 1.26, 12.7 | 0.018 | 6.08 | 1.59, 23.3 | 0.008 | Alb | 0.66 | 0.47, 0.94 | 0.021 | 0.67 | 0.41, 1.08 | 0.10 |
| Plt | 1.00 | 1.00, 1.01 | 0.6 | Plt | 1.00 | 0.99, 1.00 | 0.11 | ||||||
| AST | 1.00 | 1.00, 1.00 | <0.001 | 1.00 | 1.00, 1.00 | 0.8 | AST | 1.00 | 1.00, 1.00 | 0.030 | 1.00 | 1.00, 1.00 | >0.9 |
| ALT | 1.00 | 1.00, 1.00 | <0.001 | 1.00 | 1.00, 1.00 | 0.079 | ALT | 1.00 | 1.00, 1.00 | 0.046 | 1.00 | 1.00, 1.00 | 0.3 |
| Tbil | 1.06 | 0.97, 1.16 | 0.2 | Tbil | 1.05 | 1.00, 1.11 | 0.064 | 0.99 | 0.87, 1.12 | 0.8 | |||
| INR | 0.44 | 0.03, 6.55 | 0.6 | INR | 1.16 | 0.81, 1.68 | 0.4 | ||||||
| Cr | 0.97 | 0.40, 2.35 | >0.9 | Cr | 0.98 | 0.66, 1.46 | >0.9 | ||||||
| MELD | 1.03 | 0.96, 1.11 | 0.4 | MELD | 1.03 | 1.00, 1.07 | 0.060 | 0.98 | 0.88, 1.10 | 0.8 | |||
| Antiviral | 0.71 | 0.28, 1.80 | 0.5 | Antiviral | 1.51 | 0.90, 2.54 | 0.12 | ||||||
| Cirrhosis | 0.84 | 0.34, 2.09 | 0.7 | Cirrhosis | 1.03 | 0.65, 1.64 | 0.9 | ||||||
| HBsAg ≤ 103 at baseline | 15.5 | 5.15, 46.8 | <0.001 | 21.6 | 7.00, 66.7 | <0.001 | HBsAg ≤ 103 at baseline * | 5.94 | 3.74, 9.44 | <0.001 | 6.37 | 3.70, 10.9 | <0.001 |
| HBsAg reduction at 1 yr | 3.17 | 0.92, 10.9 | 0.066 | 5.14 | 1.47, 18.0 | 0.010 | HBsAg reduction at 1 yr | 1.86 | 1.04, 3.33 | 0.036 | 2.82 | 1.54, 5.17 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.K.; Nam, S.W.; Jang, J.W.; Kwon, J.H. Long-Term HBsAg Titer Kinetics with Entecavir/Tenofovir: Implications for Predicting Functional Cure and Low Levels. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14050495
Lee SK, Nam SW, Jang JW, Kwon JH. Long-Term HBsAg Titer Kinetics with Entecavir/Tenofovir: Implications for Predicting Functional Cure and Low Levels. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(5):495. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14050495
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Soon Kyu, Soon Woo Nam, Jeong Won Jang, and Jung Hyun Kwon. 2024. "Long-Term HBsAg Titer Kinetics with Entecavir/Tenofovir: Implications for Predicting Functional Cure and Low Levels" Diagnostics 14, no. 5: 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14050495
APA StyleLee, S. K., Nam, S. W., Jang, J. W., & Kwon, J. H. (2024). Long-Term HBsAg Titer Kinetics with Entecavir/Tenofovir: Implications for Predicting Functional Cure and Low Levels. Diagnostics, 14(5), 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14050495