Choroidal Changes in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
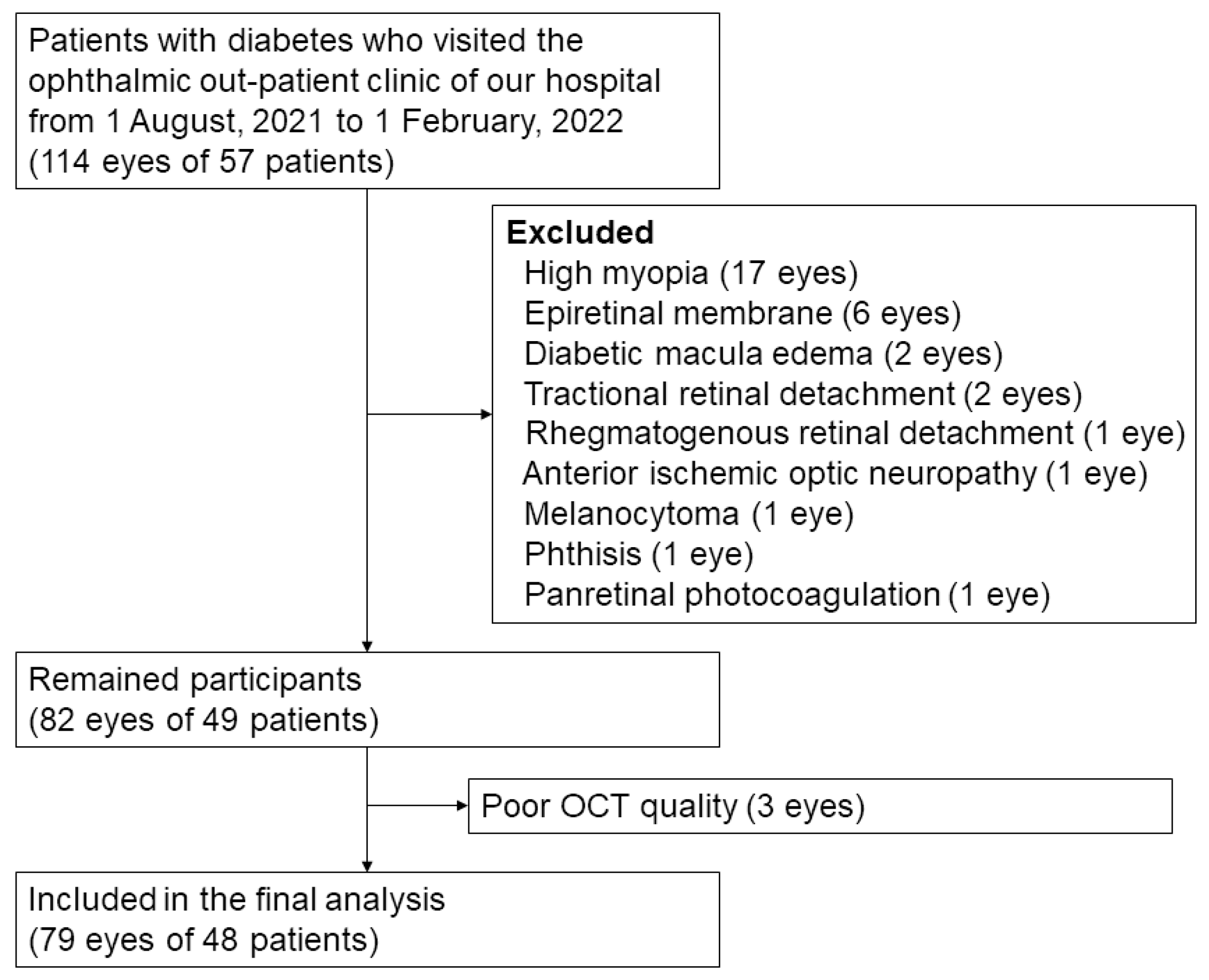
2.1. Participants
2.2. General Information and Laboratory Tests
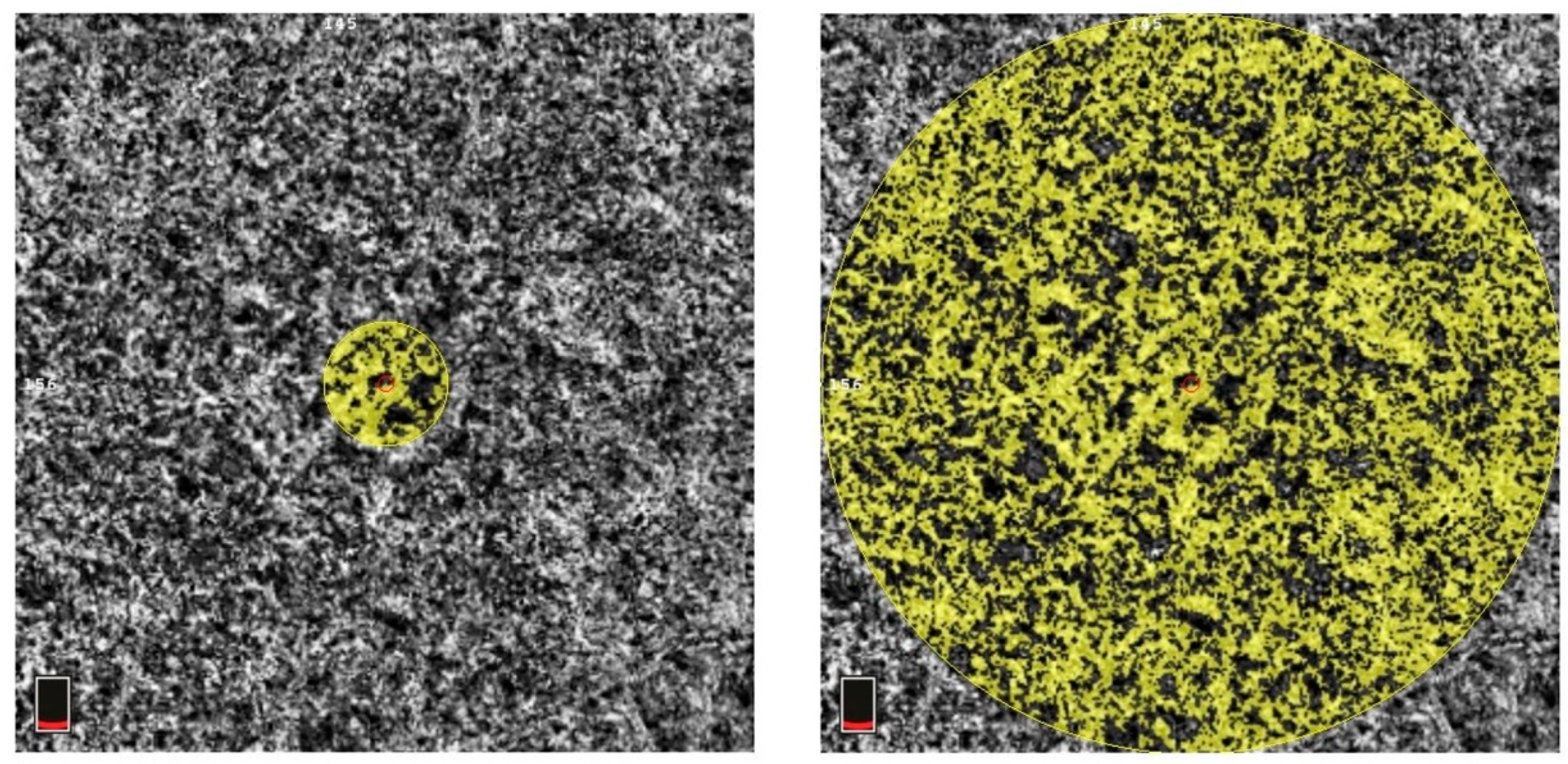
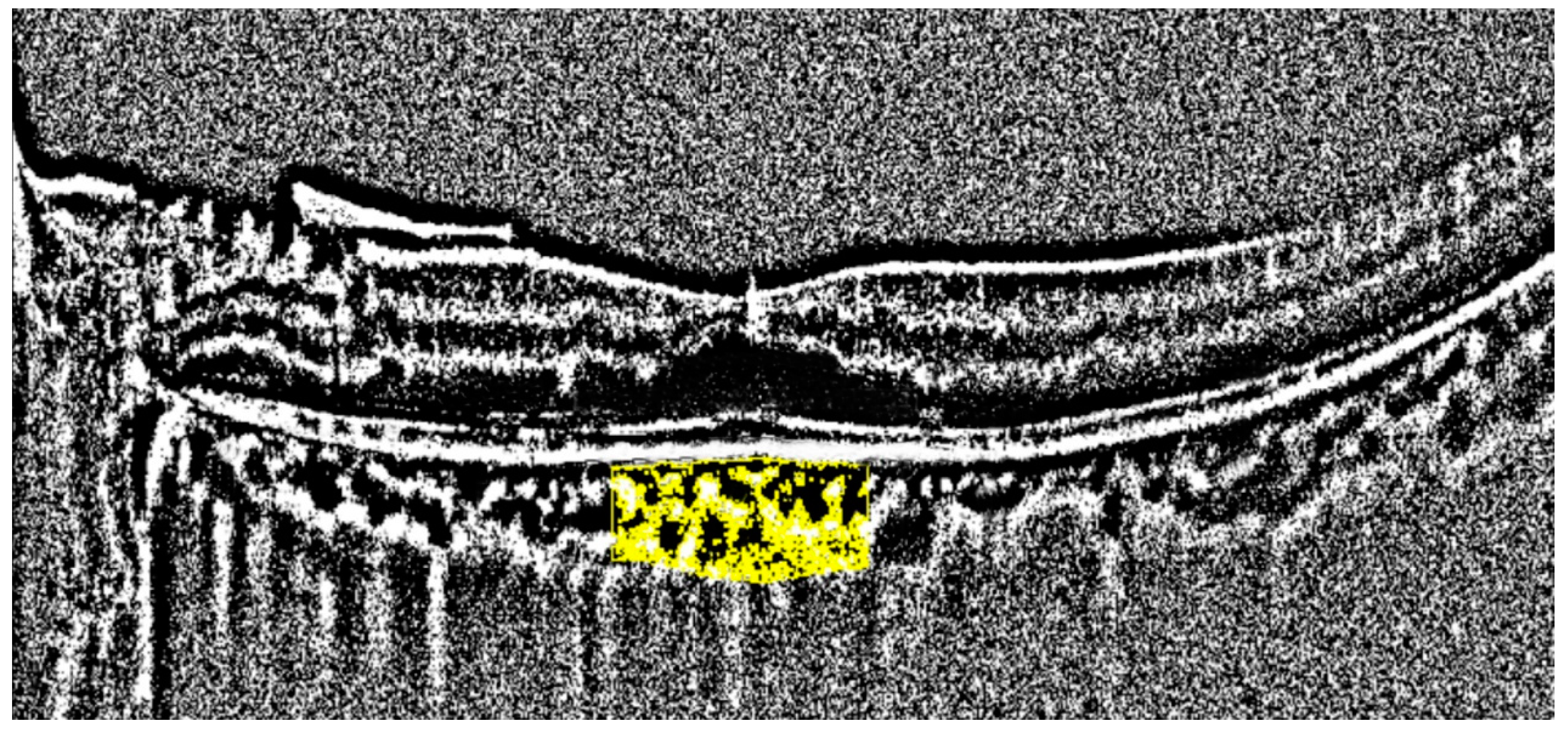
2.3. OCT Imaging
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of DR of Different Severities
3.2. Choroidal Thickness (CTh)
3.3. Choroidal Vascular Index (CVI)
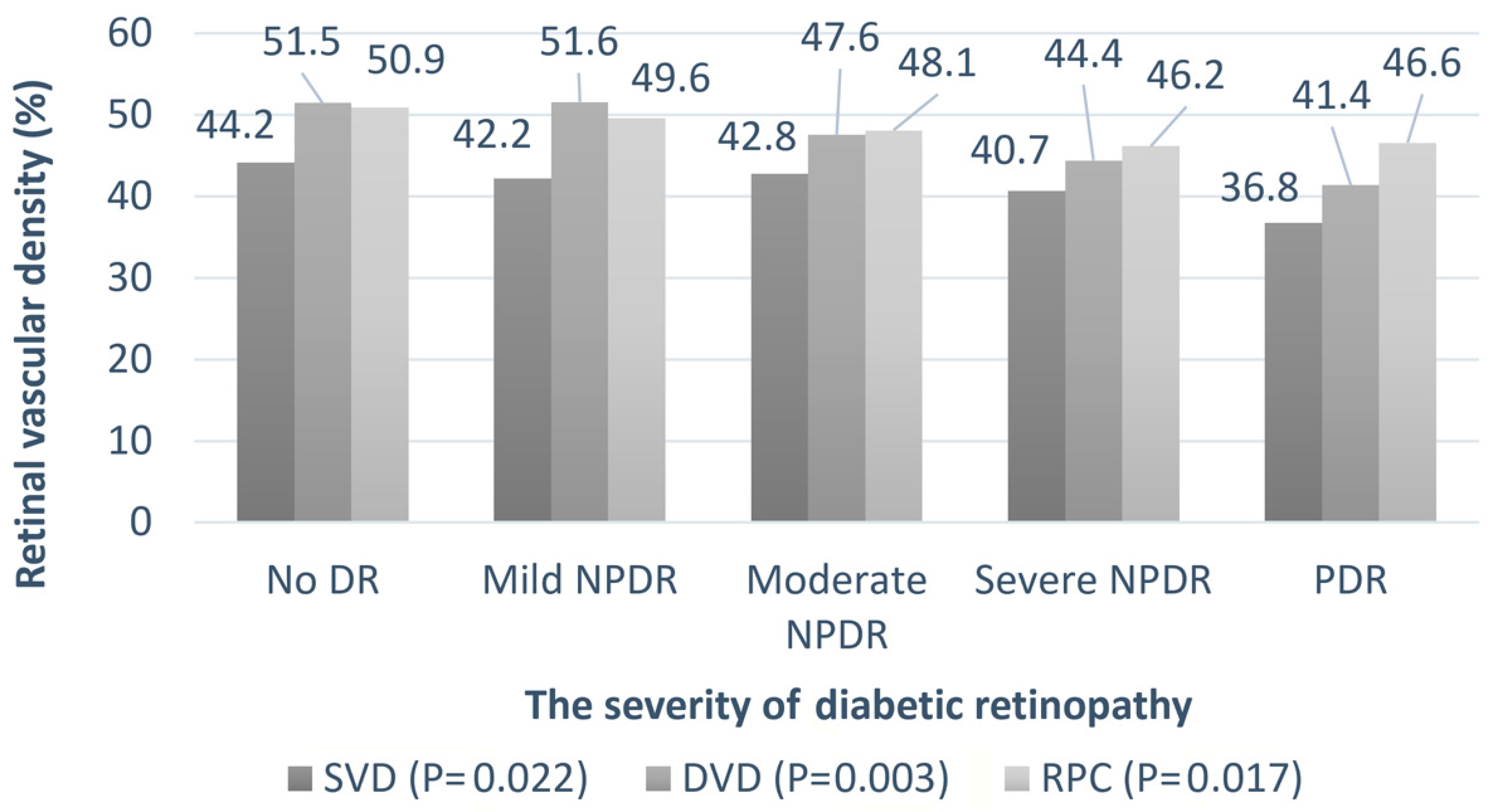
3.4. Choriocapillaris Flow
3.4.1. All DR Patients
3.4.2. Low-Grade DR Patients
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mrejen, S.; Spaide, R.F. Optical coherence tomography: Imaging of the choroid and beyond. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2013, 58, 387–429. [Google Scholar]
- Hidayat, A.A.; Fine, B.S. Diabetic choroidopathy: Light and electron microscopic observations of seven cases. Ophthalmology 1985, 92, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiragami, C.; Shiraga, F.; Matsuo, T.; Tsuchida, Y.; Ohtsuki, H. Risk factors for diabetic choroidopathy in patients with diabetic retinopathy. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2002, 240, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamadneh, T.; Aftab, S.; Sherali, N.; Vetrivel Suresh, R.; Tsouklidis, N.; An, M. Choroidal changes in diabetic patients with different stages of diabetic retinopathy. Cureus 2020, 12, e10871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, H.; Kovacs, I.; Sandor, G.L.; Czako, C.; Mallar, K.; Recsan, Z.; Somogyi, A.; Nagy, Z.Z.; Ecsedy, M. Choroidal thickness changes in non-treated eyes of patients with diabetes: Swept-source optical coherence tomography study. Acta Diabetol. 2018, 55, 927–934. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, X. Higher choroidal thickness and lower choriocapillaris blood flow signal density based on optical coherence tomography angiography in diabetics. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5799. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Liu, S.; Qiu, Z.; He, M.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Huang, W. Choroidal thickness in diabetes and diabetic retinopathy: A swept source OCT study. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Endo, H.; Kase, S.; Takahashi, M.; Yokoi, M.; Isozaki, C.; Katsuta, S.; Ishida, S.; Kase, M. Alteration of layer thickness in the choroid of diabetic patients. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2018, 46, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ra, H.; Kang, N.Y.; Song, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, I.; Baek, J. Discordance in retinal and choroidal vascular densities in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on optical coherence tomography angiography. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 2021, 8871602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlatanović, M.; Đorđević Jocić, J.; Jakšić, V.; Zlatanović, N.; Golubović, M.; Živković, M. The determination of type 2 diabetes mellitus’s impact on the density of retinal blood vessels and the choriocapillaris: Optical coherence tomography angiography study. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 2021, 7043251. [Google Scholar]
- Lupidi, M.; Cerquaglia, A.; Gujar, R.; Fruttini, D.; Cardillo Piccolino, F.; Fiore, T.; Coscas, F.; Coscas, G.; Chhablani, J.; Cagini, C. Functional correlation between choroidal and retinal vascularity in low-grade diabetic retinopathy. Acta Diabetol. 2020, 57, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, R.; Salman, M.; Tan, K.A.; Karampelas, M.; Sim, D.A.; Keane, P.A.; Pavesio, C. Choroidal Vascularity Index (CVI)—A novel optical coherence tomography parameter for monitoring patients with panuveitis? PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146344. [Google Scholar]
- Papathanasiou, K.A.; Kazantzis, D.; Vrachatis, D.A.; Giotaki, S.G.; Papaconstantinou, E.; Kanakis, M.; Avramides, D.; Deftereos, S.; Chatziralli, I.; Georgalas, I. Choroidal thickness in patients with systemic arterial hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ther. Adv. Ophthalmol. 2022, 14, 25158414221132825. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zha, Y.; Zhuang, J.; Feng, W.; Zheng, H.; Cai, J. Evaluation of choroidal thickness in amblyopia using optical coherence tomography. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 30, 629–634. [Google Scholar]
- Foo, V.H.X.; Gupta, P.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Chong, C.C.Y.; Agrawal, R.; Cheng, C.Y.; Yanagi, Y. Decrease in choroidal vascularity index of Haller’s layer in diabetic eyes precedes retinopathy. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e001295. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Choi, S.Y.; Park, Y.H. Quantitative analysis of retinal and choroidal microvascular changes in patients with diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tao, Y. Choroidal structural changes correlate with severity of diabetic retinopathy in diabetes mellitus. BMC Ophthalmol. 2019, 19, 186. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, K.A.; Laude, A.; Yip, V.; Loo, E.; Wong, E.P.; Agrawal, R. Choroidal vascularity index—A novel optical coherence tomography parameter for disease monitoring in diabetes mellitus? Acta Ophthalmol. 2016, 94, e612–e616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laviers, H.; Zambarakji, H. Enhanced depth imaging-OCT of the choroid: A review of the current literature. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2014, 252, 1871–1883. [Google Scholar]
- Cougnard-Gregoire, A.; Gattoussi, S.; Korobelnik, J.-F.; Rougier, M.B.; Delyfer, M.-N.; Schweitzer, C.; Le Goff, M.; Merle, B.M.J.; Dartigues, J.-F.; Delcourt, C. Associations of choroidal thickness with vascular risk factors: The ALIENOR study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 2186. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.B.; Xu, L.; Jonas, J.B.; Shao, L.; Du, K.F.; Wang, S.; Chen, C.X.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhou, J.Q.; et al. Subfoveal choroidal thickness: The Beijing Eye Study. Ophthalmology 2013, 120, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazgan, S.; Arpaci, D.; Celik, H.U.; Dogan, M.; Isik, I. Macular choroidal thickness may be the earliest determiner to detect the onset of diabetic retinopathy in patients with prediabetes: A prospective and comparative study. Curr. Eye Res. 2017, 42, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, I.Y.; Wong, R.L.; Zhao, P.; Lai, W.W. Choroidal thickness in relation to hypercholesterolemia on enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography. Retina 2013, 33, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, J.J.; Ramírez, A.I.; de Hoz, R.; Rojas, B.; Ruiz, E.; Tejerina, T.; Triviño, A.; Ramírez, J.M. Alterations in the choroid in hypercholesterolemic rabbits: Reversibility after normalization of cholesterol levels. Exp. Eye Res. 2007, 84, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Goyal, T.; Mehta, J.L.; Oxidized, L.D.L. LOX-1 and atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2011, 25, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoads, J.P.; Major, A.S. How oxidized low-density lipoprotein activates inflammatory responses. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 38, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Ha, M.J.; Choi, S.Y.; Park, Y.H. Choroidal vascularity index in type-2 diabetes analyzed by swept-source optical coherence tomography. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.T.; Lee, I.G. Correlation of renal profiles with choroidal vascularity index in eyes with diabetic retinopathy. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, R.-Y.; Kim, J.-Y.; Park, Y.-H. Correlation of systemic arterial stiffness with changes in retinal and choroidal microvasculature in type 2 diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, F.F.; Qin, V.L.; Rodrigues, E.B.; Sharma, S.; Rachitskaya, A.V.; Ehlers, J.P.; Singh, R.P. Choriocapillaris and retinal vascular plexus density of diabetic eyes using split-spectrum amplitude decorrelation spectral-domain optical coherence tomography angiography. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 103, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coscas, G.; Lupidi, M.; Coscas, F.; Chhablani, J.; Cagini, C. Optical coherence tomography angiography in healthy subjects and diabetic patients. Ophthalmologica 2018, 239, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, G.; Kim, I.; Sagong, M. Topographic analysis of retinal and choroidal microvasculature according to diabetic retinopathy severity using optical coherence tomography angiography. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2021, 259, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Number |
|---|---|
| Patients (no.) | 48 |
| Eyes (no.) | 79 |
| Age (years) (mean ± SD) | 66.7 ± 10.8 |
| Sex (male/female) | 23:25 |
| Side (right/left) | 40:39 |
| AXL (mm) | 23.8 ± 1.1 (excluded > 26 mm) |
| BCVA a (LogMAR) | 0.32 ± 0.33 |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.7 ± 1.9 |
| Diabetic retinopathy classification (no. of eyes) | |
| No DR | 23 |
| Mild NPDR | 21 |
| Moderate NPDR | 15 |
| Severe NDPR | 12 |
| PDR | 8 |
| Parameter | No DR | Mild NPDR | Moderate NPDR | Severe NPDR | PDR | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eyes (no.) | 23 | 21 | 15 | 12 | 8 | - |
| Age (years) (mean ± SD) | 69.2 ± 11.7 | 66.5 ± 11.5 | 66.9 ± 8.1 | 64.6 ± 6.1 | 54.9 ± 15.9 | 0.076 |
| AXL (mm) | 23.7 ± 0.87 | 23.5 ± 1.3 | 23.4 ± 0.89 | 24.4 ± 1.1 | 25.48 | 0.562 |
| BCVA (LogMAR) | 0.26 ± 0.26 | 0.17 ± 0.16 | 0.24 ± 0.17 | 0.69 ± 0.52 | 0.47 ± 0.36 | 0.017 |
| Lab data | ||||||
| HbA1c (%) | 6.8 ± 0.94 | 7.3 ± 0.42 | 7.3 ± 0.83 | 8.1 ± 1.9 | 10.85 ± 3.1 | <0.001 |
| Cre (mg/dL) | 1.4 ± 1.7 | 0.93 ± 0.29 | 2.1 ± 2.8 | 1.2 ± 0.67 | 1.4 ± 1.0 | 0.684 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 35.6 ± 15.7 | 20.2 ± 1.8 | 32.4 ± 29.5 | 22.4 ± 5.4 | 26.3 | 0.438 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 73.2 ± 28.0 | 80.4 ± 19.6 | 67.8 ± 34.8 | 69.9 ± 33.3 | 69.6 ± 37.5 | 0.675 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 116.1 ± 42.5 | 96.2 ± 39.5 | 94.2 ± 25.5 | 139.6 ± 67.5 | 150.3 ± 90.6 | 0.439 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 59.7 ± 14.9 | 61.4 ± 14.6 | 66 | 64 | 72 | 0.099 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 91.1 ± 20.5 | 107.1 ± 29.4 | 76.6 ± 2.9 | 88.9 ± 23.6 | 153.3 ± 23.7 | 0.334 |
| T-CHO (mg/dL) | 161.2 ± 34.4 | 182.7 ± 27.7 | 150.0 ± 3.5 | 157.4 ± 22.5 | 251 | 0.367 |
| GCC a (average) (μm) | 93.7 ± 9.2 | 89.1 ± 20.6 | 93.6 ± 14.8 | 120.8 ± 15.1 | 123 ± 32.3 | <0.001 |
| RNFL b (average) (μm) | 101.2 ± 23.2 | 103.4 ± 13.3 | 91.4 ± 15.3 | 110.8 ± 23.9 | 122.1 ± 21.3 | 0.076 |
| Location of CTh | No DR n = 23 | Mild NPDR n = 21 | Moderate NPDR n = 15 | Severe NPDR n = 12 | PDR n = 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subfoveal | 215.4 ± 95.2 | 234.1 ± 99.2 | 193.9 ± 70.5 | 253.9 ± 81.8 | 297.7 ± 81.0 |
| p-value | - | 0.406 | 0.406 | 0.052 | 0.076 |
| 1000 μm (average) | 199.0 ± 85.3 | 223.3 ± 94.8 | 180.0 ± 65.0 | 235.0 ± 71.1 | 260.0 ± 66.5 |
| p-value | - | 0.285 | 0.525 | 0.052 | 0.085 |
| 1500 μm (average) | 192.9 ± 78.5 | 209.7 ± 84.5 | 174.6 ± 61.0 | 226.3 ± 64.1 | 247.3 ± 65.9 |
| p-value | - | 0.428 | 0.489 | 0.050 | 0.085 |
| 3000 μm (average) | 169.7 ± 67.8 | 182.1 ± 60.5 | 160.2 ± 48.5 | 196.9 ± 46.4 | 235.0 ± 40.8 |
| p-value | - | 0.285 | 0.765 | 0.014 | 0.024 |
| Parameter | CTh Location (Average) * | Beta Estimations | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | Subfoveal | −4.054 | 0.003 |
| 1000 μm | −3.454 | 0.004 | |
| 3000 μm | −2.307 | 0.007 | |
| Sex (male, female) | Subfoveal | −12.359 | 0.597 |
| 1000 μm | −12.330 | 0.544 | |
| 3000 μm | −14.588 | 0.384 | |
| AXL (mm) | Subfoveal | −0.287 | 0.797 |
| 1000 μm | −0.658 | 0.568 | |
| 3000 μm | −0.318 | 0.699 | |
| LDL (mg/dL) | Subfoveal | 1.210 | <0.001 |
| 1000 μm | 0.996 | <0.001 | |
| 3000 μm | 0.618 | 0.003 | |
| CVI (%) | Subfoveal | −13.247 | 0.007 |
| 1000 μm | −13.296 | 0.007 | |
| 3000 μm | −8.297 | 0.019 |
| Parameter | Beta Estimations | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) * | −0.315 | 0.003 |
| AXL (mm) * | 0.094 | 0.057 |
| DR severity * | −1.525 | 0.010 |
| BUN (mg/dL) * | 0.026 | 0.320 |
| Choroid thickness (average) | ||
| Subfoveal | −0.009 | 0.038 |
| 1000 μm # | −0.009 | 0.050 |
| 1500 μm # | −0.012 | 0.035 |
| 3000 μm # | −0.019 | 0.020 |
| Parameter | Choroid Flow Area (Diameter) * | Beta Estimations | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 500 μm | 9.06 × 10−5 | 0.640 |
| 3000 μm | −0.006 | 0.467 | |
| HbA1 (%) | 500 μm | −3.73 × 10−4 | 0.893 |
| 3000 μm | −0.148 | <0.001 | |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 500 μm | 2.23 × 10−4 | 0.011 |
| 3000 μm | 0.001 | 0.755 | |
| SVD (average) (%) | 500 μm | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| 3000 μm | −0.009 | 0.314 | |
| DVD (average) (%) | 500 μm | −4.16 × 10−4 | 0.433 |
| 3000 μm | 0.008 | 0.105 |
| Parameter | Choroid Flow Area (Diameter) * | Beta Estimations | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 500 μm | −1.80 × 10−4 | 0.441 |
| 3000 μm | −0.013 | 0.060 | |
| HbA1 (%) | 500 μm | −0.005 | 0.095 |
| 3000 μm | −0.189 | 0.023 | |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 500 μm | −1.38 × 10−4 | 0.385 |
| 3000 μm | −0.008 | 0.001 | |
| Cre (mg/dL) | 500 μm | −0.008 | 0.003 |
| 3000 μm | −0.167 | <0.001 | |
| SVD (average) (%) | 500 μm | 0.001 | 0.051 (Trend) |
| 3000 μm | −0.033 | 0.001 | |
| DVD (average) (%) | 500 μm | −0.002 | 0.018 |
| 3000 μm | −0.004 | 0.462 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, S.-Y.; Chen, T.-C.; Hsieh, Y.-T.; Ho, T.-C.; Yang, C.-M.; Yang, C.-H. Choroidal Changes in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy: A Retrospective Study. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14050537
Peng S-Y, Chen T-C, Hsieh Y-T, Ho T-C, Yang C-M, Yang C-H. Choroidal Changes in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy: A Retrospective Study. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(5):537. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14050537
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Shu-Yu, Ta-Ching Chen, Yi-Ting Hsieh, Tzyy-Chang Ho, Chung-May Yang, and Chang-Hao Yang. 2024. "Choroidal Changes in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy: A Retrospective Study" Diagnostics 14, no. 5: 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14050537
APA StylePeng, S.-Y., Chen, T.-C., Hsieh, Y.-T., Ho, T.-C., Yang, C.-M., & Yang, C.-H. (2024). Choroidal Changes in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy: A Retrospective Study. Diagnostics, 14(5), 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14050537






