Prognostic Molecular Biomarkers in Breast Cancer Lesions with Non-Mass Enhancement on MR
Abstract
1. Introduction
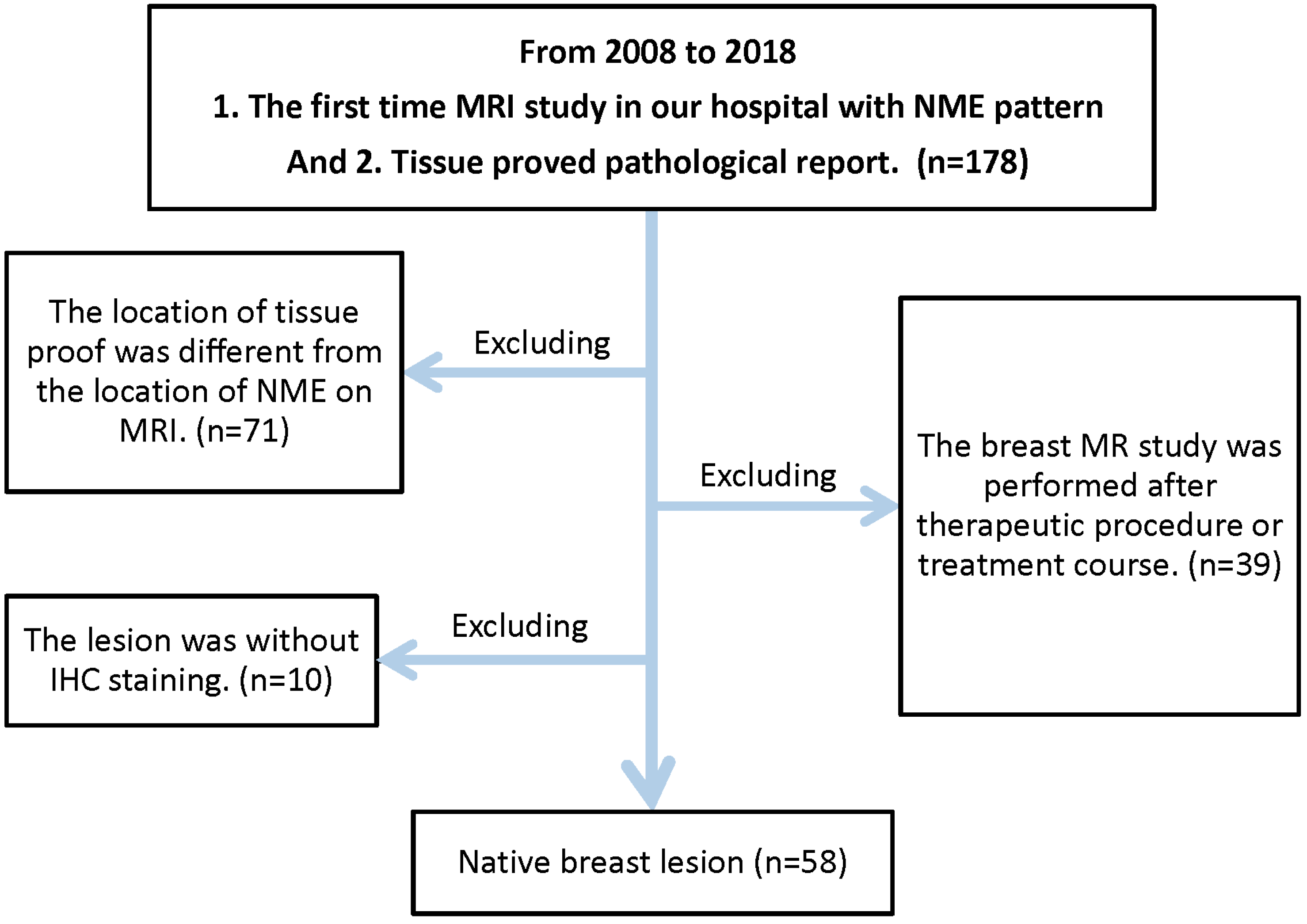
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. MRI Protocol
2.3. Image Interpretation
2.4. Pathological Results
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics of the Study Population and MRI Patterns
3.2. Histological Types
3.3. Age and Demographics
3.3.1. IHC and CRE
3.3.2. Association between Ki-67 and CRE
3.3.3. Association between HER2 and CRE
4. Discussion
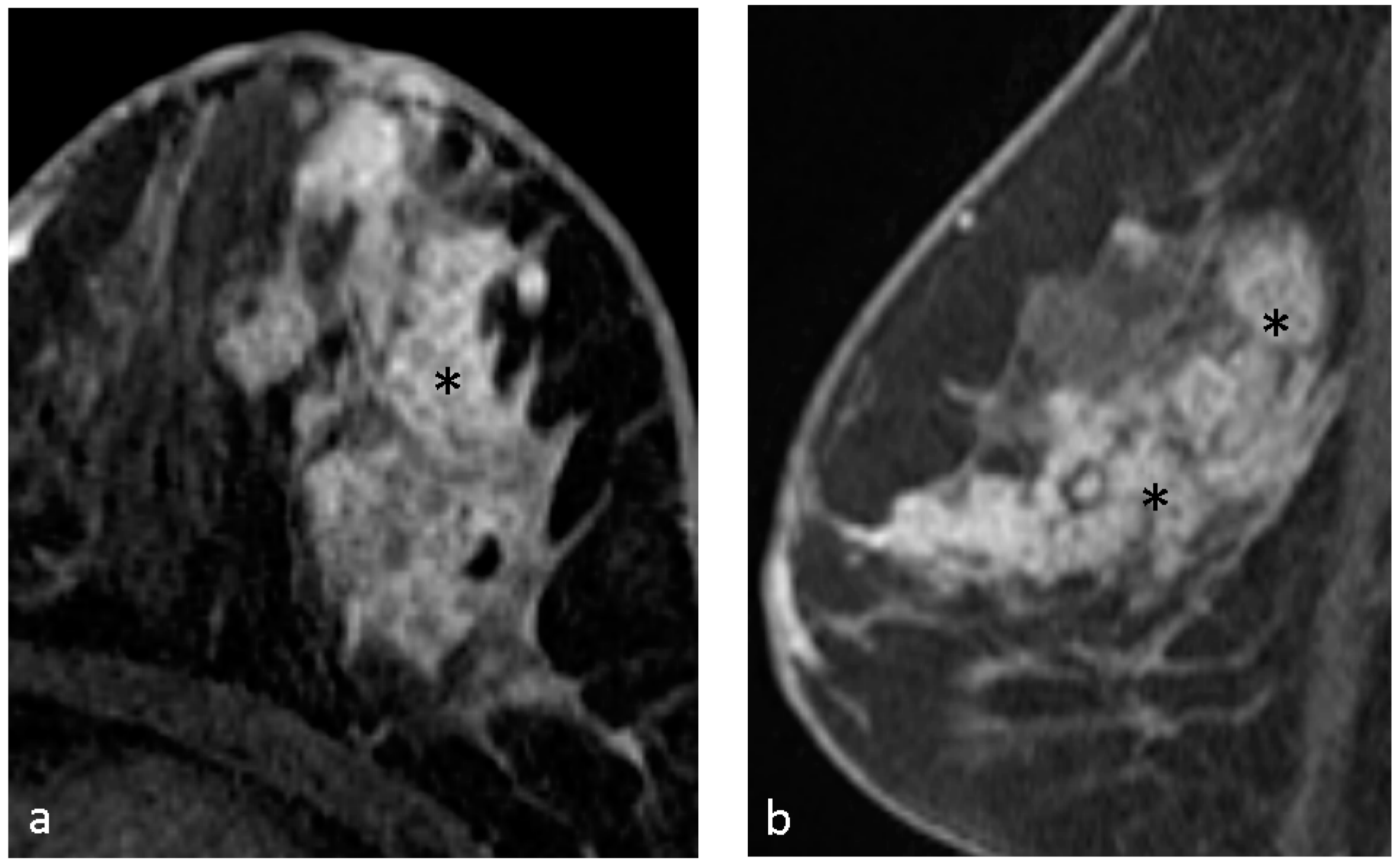
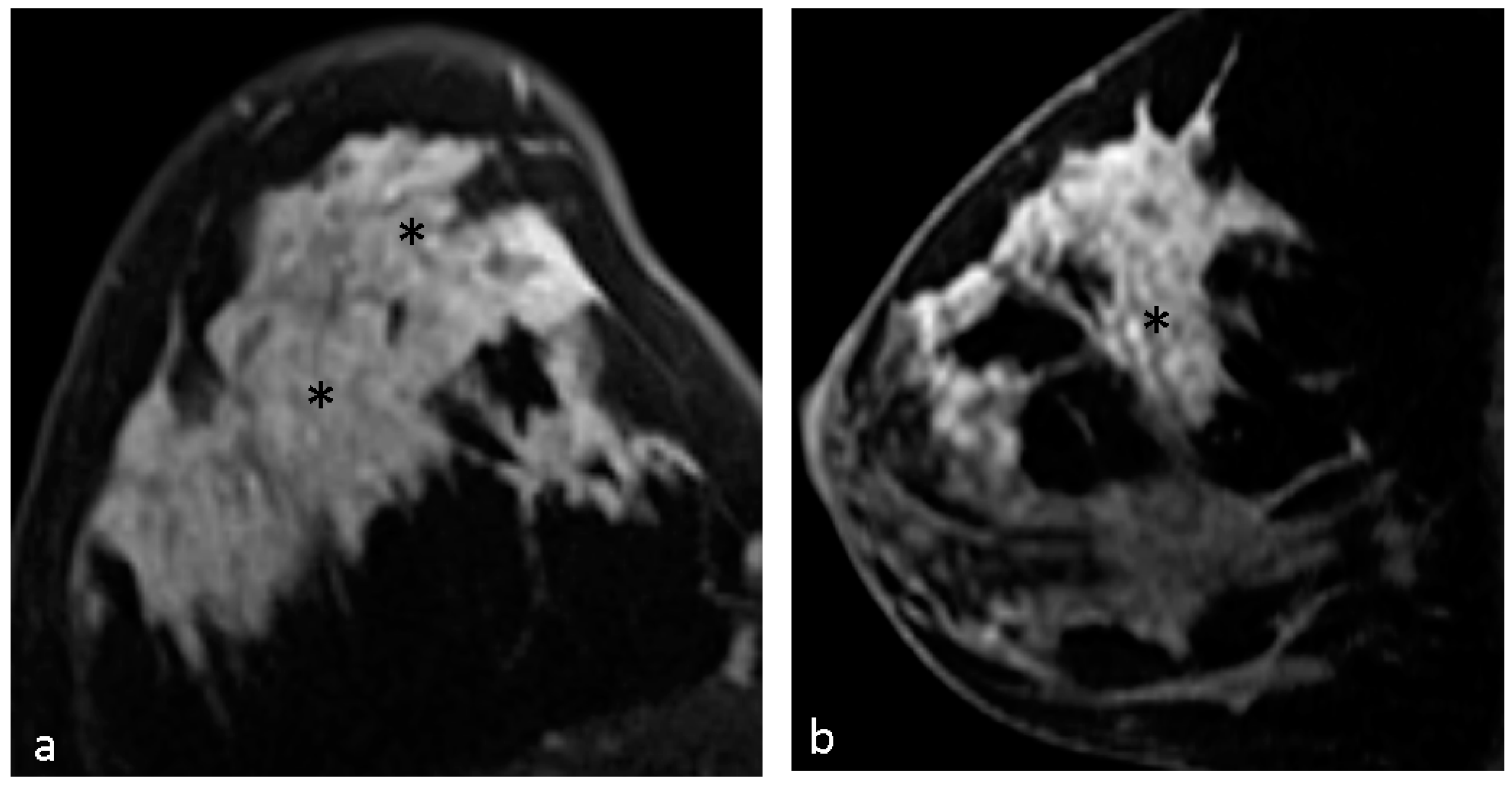
4.1. Malignant Features of NME
4.2. Hypothesis of Formation of CRE
4.3. Pathological Diagnosis in NME
4.4. Pathological Diagnosis in CRE Lesions
4.5. CRE and Biomarkers of ER, PR
4.6. CRE and Biomarkers of Ki67
5. Limitation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NME | Non-mass enhancement |
| CRE | Clustered ring enhancement |
| ER | Estrogen receptor |
| PR | Progesterone receptor |
| HER2 | Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 |
| IHC staining | Immunohistochemical staining |
References
- Harbeck, N.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Cortes, J.; Gnant, M.; Houssami, N.; Poortmans, P.; Ruddy, K.; Tsang, J.; Cardoso, F. Breast cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Health Promotion Administration MoHaW: Cancer Registry Annual Report, 2022; Health Promotion Administration of Ministry of Health and Welfare: Taipei, Taiwan, 2022.
- Bureau of Health Promotion DoHtEY: Cancer Registry Annual Report, 2006; Health Promotion Administration of Ministry of Health and Welfare: Taipei, Taiwan, 2009.
- Mann, R.M.; Kuhl, C.K.; Moy, L. Contrast-enhanced MRI for breast cancer screening. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 50, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tozaki, M.; Igarashi, T.; Fukuda, K. Breast MRI using the VIBE sequence: Clustered ring enhancement in the differential diagnosis of lesions showing non-masslike enhancement. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2006, 187, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asada, T.; Yamada, T.; Kanemaki, Y.; Fujiwara, K.; Okamoto, S.; Nakajima, Y. Grading system to categorize breast MRI using BI-RADS 5th edition: A statistical study of non-mass enhancement descriptors in terms of probability of malignancy. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2018, 36, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirada, N.; Aujero, M.; Khorjekar, G.; Richards, S.; Chopra, J.; Dromi, S.; Ioffe, O. Breast Cancer Tissue Markers, Genomic Profiling, and Other Prognostic Factors: A Primer for Radiologists. Radiographics 2018, 38, 1902–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffa, G.; Galati, F.; Collalunga, E.; Rizzo, V.; Kripa, E.; D’Amati, G.; Pediconi, F. Can MRI Biomarkers Predict Triple-Negative Breast Cancer? Diagnostics 2020, 10, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, G.A.; Danilova, N.V.; Andreeva, I.; Nefedova, N.A. WHO classification of tumors of the breast, 2012. Arkh. Patol. 2013, 75, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Petrelli, F.; Viale, G.; Cabiddu, M.; Barni, S. Prognostic value of different cut-off levels of Ki-67 in breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 64,196 patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 153, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chikarmane, S.A.; Michaels, A.Y.; Giess, C.S. Revisiting Nonmass Enhancement in Breast MRI: Analysis of Outcomes and Follow-Up Using the Updated BI-RADS Atlas. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 209, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunkiewicz, M.; Forte, S.; Freiwald, B.; Singer, G.; Leo, C.; Kubik-Huch, R.A. Interobserver variability and likelihood of malignancy for fifth edition BI-RADS MRI descriptors in non-mass breast lesions. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.X.; Ji, X.; Feng, L.L.; Zheng, L.; Zhou, X.Q.; Wu, Q.; Chen, X. Significant MRI indicators of malignancy for breast non-mass enhancement. J. X-ray Sci. Technol. 2017, 25, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, N.; Tozaki, M.; Higa, K.; Tsunoda, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Abe, S.; Ozaki, S.; Sakamoto, M.; Tsuruhara, T.; Kawano, N.; et al. Categorization of non-mass-like breast lesions detected by MRI. Breast Cancer 2008, 15, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machida, Y.; Shimauchi, A.; Tozaki, M.; Kuroki, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Fukuma, E. Descriptors of Malignant Non-mass Enhancement of Breast MRI: Their Correlation to the Presence of Invasion. Acad. Radiol. 2016, 23, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Ba, Z.; Gao, Y.; Wang, L. Subcategorization of suspicious non-mass-like enhancement lesions(BI-RADS-MRI Category4). BMC Med. Imaging 2023, 23, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwood, H.I.; Heller, S.L.; Kim, S.; Sigmund, E.E.; Shaylor, S.D.; Moy, L. Ductal carcinoma in situ of the breasts: Review of MR imaging features. Radiographics 2013, 33, 1569–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amornsiripanitch, N.; Lam, D.L.; Rahbar, H. Advances in Breast MRI in the Setting of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ. Semin. Roentgenol. 2018, 53, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartels, A.K.; Fadare, O.; Hasteh, F.; Zare, S.Y. Nonmass enhancement lesions of the breast on core needle biopsy: Outcomes, frequency of malignancy, and pathologic findings. Hum. Pathol. 2021, 111, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uematsu, T.; Kasami, M. High-spatial-resolution 3-T breast MRI of nonmasslike enhancement lesions: An analysis of their features as significant predictors of malignancy. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2012, 198, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.M.; Nam, K.J.; Choo, K.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Jeong, D.W.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, J.Y. Patterns of malignant non-mass enhancement on 3-T breast MRI help predict invasiveness: Using the BI-RADS lexicon fifth edition. Acta Radiol. 2018, 59, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.B.; Gao, H.Y.; Wei, L.; Zhang, A.Q.; Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.D.; Zhang, Y. Expression of estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, and Ki-67 in ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and DCIS with microinvasion. Medicine 2018, 97, e13055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, C.A.; Vanzulli, S.I.; Lanari, C. Hormone receptors in breast cancer: More than estrogen receptors. Medicina 2019, 79, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Uematsu, T.; Kasami, M.; Yuen, S. Triple-negative breast cancer: Correlation between MR imaging and pathologic findings. Radiology 2009, 250, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M.; Belli, P.; Distefano, D.; Bufi, E.; Matteo, M.D.; Rinaldi, P.; Giuliani, M.; Petrone, G.; Magno, S.; Bonomo, L. Magnetic resonance imaging features in triple-negative breast cancer: Comparison with luminal and HER2-overexpressing tumors. Clin. Breast Cancer 2012, 12, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boisserie-Lacroix, M.; Macgrogan, G.; Debled, M.; Ferron, S.; Asad-Syed, M.; McKelvie-Sebileau, P.; Mathoulin-Pélissier, S.; Brouste, V.; Hurtevent-Labrot, G. Triple-negative breast cancers: Associations between imaging and pathological findings for triple-negative tumors compared with hormone receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative breast cancers. Oncologist 2013, 18, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, J.S.; Jochelson, M.S.; Brennan, S.; Joo, S.; Wen, Y.H.; Moskowitz, C.; Zheng, J.; Dershaw, D.D.; Morris, E.A. MR imaging features of triple-negative breast cancers. Breast J. 2013, 19, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, M.S.; Moon, H.G.; Han, W.; Noh, D.Y.; Ryu, H.S.; Park, I.A.; Chang, J.M.; Cho, N.; Moon, W.K. Early Stage Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Imaging and Clinical-Pathologic Factors Associated with Recurrence. Radiology 2016, 278, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogan, B.E.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Gilcrease, M.; Dryden, M.J.; Yang, W.T. Multimodality imaging of triple receptor-negative tumors with mammography, ultrasound, and MRI. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 194, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adrada, B.E.; Moseley, T.W.; Kapoor, M.M.; Scoggins, M.E.; Patel, M.M.; Perez, F.; Nia, E.S.; Khazai, L.; Arribas, E.; Rauch, G.M.; et al. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Histopathologic Features, Genomics, and Treatment. Radiographics 2023, 43, e230034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inwald, E.C.; Klinkhammer-Schalke, M.; Hofstadter, F.; Zeman, F.; Koller, M.; Gerstenhauer, M.; Ortmann, O. Ki-67 is a prognostic parameter in breast cancer patients: Results of a large population-based cohort of a cancer registry. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 139, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Patient No. | 56 * |
|---|---|
| Mean age | 48.6 years (29–75 years) |
| Health exam | 1 |
| Clinics | 55 |
| Biopsy | 35 |
| Operation | 23 |
| NME No. | 58 * |
| Immunohistochemical staining No. | |
| ER | 58 |
| PR | 58 |
| Ki67 | 38 |
| HER2 | 39 |
| NME Pattern | No. (%) |
|---|---|
| Clustered ring enhancement | 31 (53.4%) |
| Clump enhancement | 17 (29.3%) |
| Heterogeneous enhancement | 8 (13.8%) |
| Homogeneous enhancement | 2 (3.4%) |
| NME Distribution | |
| Focal | 6 (10.3%) |
| Linear | 2 (3.4%) |
| Segmental | 19 (32.8%) |
| Regional | 10 (17.2%) |
| Multiple regions | 17 (29.3%) |
| Diffuse | 4 (6.9%) |
| Pathological Diagnosis | |
| IDC | 19 (32.8%) |
| DCIS | 23 (39.7%) |
| both DCIS with IDC | 10 (17.2%) |
| LCIS with or without ILC | 4 (6.9%) |
| DCIS (with or without IDC) with lobular cancerization | 2 (3.4%) |
| Parameters | With CRE | Without CRE | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| ER | |||
| Positive | 19 (32.8%) | 24 (41.4%) | |
| Negative | 12 (20.7%) | 3 (5.2%) | 0.017 * |
| PR | |||
| Positive | 16 (27.6%) | 22 (37.9%) | |
| Negative | 15 (25.9%) | 5 (8.6%) | 0.017 * |
| Ki-67 | |||
| ≥25% | 12 (31.6%) | 5 (13.2%) | |
| <25% | 8 (21.1%) | 13 (34.2%) | 0.046 * |
| HER2 | |||
| Positive | 5 (12.8%) | 4 (10.3%) | |
| Negative | 16 (41.0%) | 14 (35.9%) | 0.907 |
| Parameters | NME Features | No./Total | Mean ± SD(%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ER | With CRE | 31/58 | 50.71 ± 45.39 | |
| Without CRE | 27/58 | 74.26 ± 33.59 | 0.028 * | |
| PR | With CRE | 31/58 | 26.61 ± 34.65 | |
| Without CRE | 27/58 | 45.74 ± 41.87 | 0.066 | |
| Ki67 | With CRE | 20/38 | 33.90 ± 22.41 | |
| Without CRE | 18/38 | 24.33 ± 23.27 | 0.205 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.-L.; Chang, Y.-P.; Wu, C.-H.; Chen, C.-H.; Gueng, M.-K.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Chai, J.-W. Prognostic Molecular Biomarkers in Breast Cancer Lesions with Non-Mass Enhancement on MR. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14070747
Wang M-L, Chang Y-P, Wu C-H, Chen C-H, Gueng M-K, Wu Y-Y, Chai J-W. Prognostic Molecular Biomarkers in Breast Cancer Lesions with Non-Mass Enhancement on MR. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(7):747. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14070747
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Mei-Lin, Yu-Pin Chang, Chen-Hao Wu, Chuan-Han Chen, Mein-Kai Gueng, Yi-Ying Wu, and Jyh-Wen Chai. 2024. "Prognostic Molecular Biomarkers in Breast Cancer Lesions with Non-Mass Enhancement on MR" Diagnostics 14, no. 7: 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14070747
APA StyleWang, M.-L., Chang, Y.-P., Wu, C.-H., Chen, C.-H., Gueng, M.-K., Wu, Y.-Y., & Chai, J.-W. (2024). Prognostic Molecular Biomarkers in Breast Cancer Lesions with Non-Mass Enhancement on MR. Diagnostics, 14(7), 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14070747






