Ultrasound-Guided Sciatic Nerve Hydrodissection Can Improve the Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Deep Gluteal Syndrome: A Case-Series Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
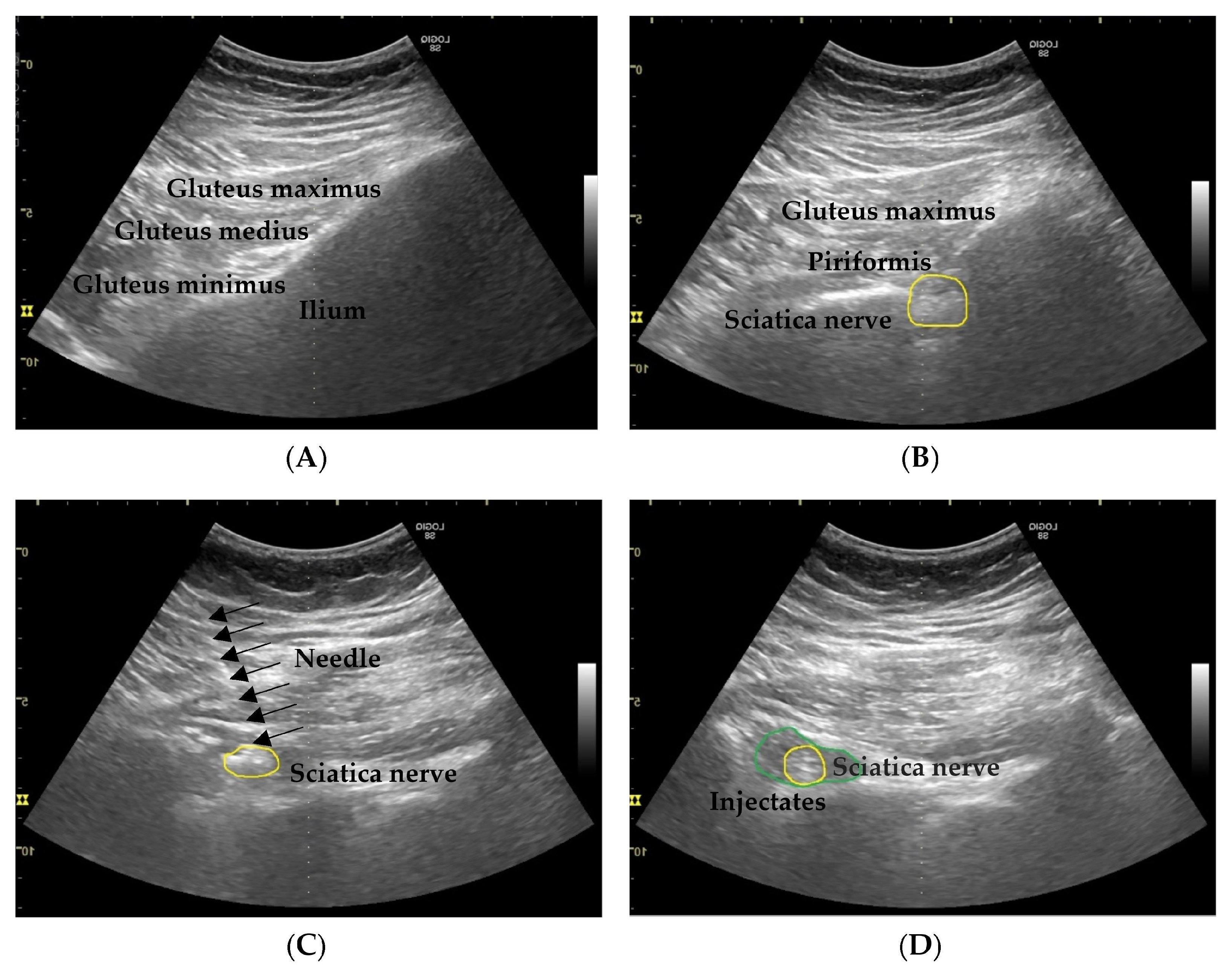
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Outcome Evaluation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, A.; March, L.; Zheng, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Blyth, F.M.; Smith, E.; Buchbinder, R.; Hoy, D. Global low back pain prevalence and years lived with disability from 1990 to 2017: Estimates from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirvanci, M.; Kara, B.; Duran, C.; Ozturk, E.; Karatoprak, O.; Onat, L.; Ulusoy, O.L.; Mutlu, A. Value of perineural edema/inflammation detected by fat saturation sequences in lumbar magnetic resonance imaging of patients with unilateral sciatica. Acta Radiol. 2009, 50, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando, M.F.; Cerezal, L.; Pérez-Carro, L.; Abascal, F.; Canga, A. Deep gluteal syndrome: Anatomy, imaging, and management of sciatic nerve entrapments in the subgluteal space. Skelet. Radiol. 2015, 44, 919–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kizaki, K.; Uchida, S.; Shanmugaraj, A.; Aquino, C.C.; Duong, A.; Simunovic, N.; Martin, H.D.; Ayeni, O.R. Deep gluteal syndrome is defined as a non-discogenic sciatic nerve disorder with entrapment in the deep gluteal space: A systematic review. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. Off. J. ESSKA 2020, 28, 3354–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.E.; Ho, G.W.K.; Tortland, P.D. Deep Gluteal Syndrome: A Pain in the Buttock. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2021, 20, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vij, N.; Kiernan, H.; Bisht, R.; Singleton, I.; Cornett, E.M.; Kaye, A.D.; Imani, F.; Varrassi, G.; Pourbahri, M.; Viswanath, O.; et al. Surgical and Non-surgical Treatment Options for Piriformis Syndrome: A Literature Review. Anesthesiol. Pain Med. 2021, 11, e112825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishman, L.M.; Wilkins, A.N.; Rosner, B. Electrophysiologically identified piriformis syndrome is successfully treated with incobotulinum toxin a and physical therapy. Muscle Nerve 2017, 56, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dere, K.; Akbaş, M.; Sen, H.; Teksöz, E.; Yeǧin, A.; Özkan, S.; Dağlı, G. Comparing the Effectiveness of Thiocolchicoside and Triamcinolone in Piriformis Syndrome Treatment. Turk. Klin. J. Med. Sci. 2009, 29, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar]
- Misirlioglu, T.O.; Akgun, K.; Palamar, D.; Erden, M.G.; Erbilir, T. Piriformis syndrome: Comparison of the effectiveness of local anesthetic and corticosteroid injections: A double-blinded, randomized controlled study. Pain Physician 2015, 18, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naja, Z.; Al-Tannir, M.; El-Rajab, M.; Ziade, F.; Daher, Y.; Khatib, H.; Tayara, K. The effectiveness of clonidine-bupivacaine repeated nerve stimulator-guided injection in piriformis syndrome. Clin. J. Pain 2009, 25, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecco, A.; Pirri, C.; Stecco, C. Fascial entrapment neuropathy. Clin. Anat. 2019, 32, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cass, S.P. Ultrasound-Guided Nerve Hydrodissection: What is it? A Review of the Literature. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2016, 15, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.T.; Ke, M.J.; Ho, T.Y.; Li, T.Y.; Shen, Y.P.; Chen, L.C. Randomized double-blinded clinical trial of 5% dextrose versus triamcinolone injection for carpal tunnel syndrome patients. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 84, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.T.; Ho, T.Y.; Chou, Y.C.; Ke, M.J.; Li, T.Y.; Huang, G.S.; Chen, L.C. Six-month efficacy of platelet-rich plasma for carpal tunnel syndrome: A prospective randomized, single-blind controlled trial. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.T.; Ho, T.Y.; Chou, Y.C.; Ke, M.J.; Li, T.Y.; Tsai, C.K.; Chen, L.C. Six-month Efficacy of Perineural Dextrose for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Trial. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2017, 92, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malahias, M.A.; Nikolaou, V.S.; Johnson, E.O.; Kaseta, M.K.; Kazas, S.T.; Babis, G.C. Platelet-rich plasma ultrasound-guided injection in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome: A placebo-controlled clinical study. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 12, e1480–e1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salman Roghani, R.; Holisaz, M.T.; Tarkashvand, M.; Delbari, A.; Gohari, F.; Boon, A.J.; Lokk, J. Different doses of steroid injection in elderly patients with carpal tunnel syndrome: A triple-blind, randomized, controlled trial. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaeid, M.A. Dexamethasone versus Hyaluronidase as an Adjuvant to Local Anesthetics in the Ultrasound-guided Hydrodissection of the Median Nerve for the Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Patients. Anesth. Essays Res. 2019, 13, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güven, S.C.; Özçakar, L.; Kaymak, B.; Kara, M.; Akıncı, A. Short-term effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma in carpal tunnel syndrome: A controlled study. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2019, 13, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senna, M.K.; Shaat, R.M.; Ali, A.A.A. Platelet-rich plasma in treatment of patients with idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 3643–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.P.; Li, T.Y.; Chou, Y.C.; Ho, T.Y.; Ke, M.J.; Chen, L.C.; Wu, Y.T. Comparison of perineural platelet-rich plasma and dextrose injections for moderate carpal tunnel syndrome: A prospective randomized, single-blind, head-to-head comparative trial. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2019, 13, 2009–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- vanVeen, K.E.; Alblas, K.C.; Alons, I.M.; Kerklaan, J.P.; Siegersma, M.C.; Wesstein, M.; Visser, L.H.; Vankasteel, V.; Jellema, K. Corticosteroid injection in patients with ulnar neuropathy at the elbow: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Muscle Nerve 2015, 52, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, C.J.; Walter, W.R.; Adler, R.S. Targeted Ultrasound-Guided Perineural Hydrodissection of the Sciatic Nerve for the Treatment of Piriformis Syndrome. Ultrasound Q. 2019, 35, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosales, J.; García, N.; Rafols, C.; Pérez, M.; Verdugo, M.A. Perisciatic Ultrasound-Guided Infiltration for Treatment of Deep Gluteal Syndrome: Description of Technique and Preliminary Results. J. Ultrasound Med. Off. J. Am. Inst. Ultrasound Med. 2015, 34, 2093–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reus, M.; de Dios Berná, J.; Vázquez, V.; Redondo, M.V.; Alonso, J. Piriformis syndrome: A simple technique for US-guided infiltration of the perisciatic nerve. Preliminary results. Eur. Radiol. 2008, 18, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.T.; Wu, C.H.; Lin, J.A.; Su, D.C.; Hung, C.Y.; Lam, S.K.H. Efficacy of 5% Dextrose Water Injection for Peripheral Entrapment Neuropathy: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, S.K.H.; Reeves, K.D.; Cheng, A.L. Transition from Deep Regional Blocks toward Deep Nerve Hydrodissection in the Upper Body and Torso: Method Description and Results from a Retrospective Chart Review of the Analgesic Effect of 5% Dextrose Water as the Primary Hydrodissection Injectate to Enhance Safety. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 7920438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Yukawa, Y.; Machino, M.; Inoue, T.; Ouchida, J.; Tomita, K.; Kato, F. Treatment outcomes of intradiscal steroid injection/selective nerve root block for 161 patients with cervical radiculopathy. Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 2015, 77, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huston, C.W.; Slipman, C.W.; Garvin, C. Complications and side effects of cervical and lumbosacral selective nerve root injections. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshrif, A.; Elwan, M. The Effect of Addition of Buffered Dextrose 5% Solution on Pain Occurring During Local Steroid Injection for Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2019, 9, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.C.; Hsu, P.C.; Wang, K.A.; Chang, K.V. Ultrasound-Guided Triamcinolone Acetonide Hydrodissection for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 742724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.H. Can repeat injection provide clinical benefit in patients with cervical disc herniation and stenosis when the first epidural injection results only in partial response? Medicine 2016, 95, e4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| n. of Patients | 53 |
|---|---|
| Male | 19 (35.8%) |
| Female | 34 (64.2%) |
| Age (years) | |
| Mean ± sd | 58.2 ± 15.1 |
| Median (IQR) | 59.0 (22.0) |
| n. of injections | |
| 1 | 20 (37.7%) |
| 2 | 15 (28.3%) |
| 3 and above | 18 (34.0%) |
| Length of follow-up (months) | |
| Mean ± sd | 5.4 ± 4.0 |
| Median (IQR) | 3.0 (3.5) |
| Min–Max | 3–19 |
| Parameters | Values | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NRS of pain (0–10) | |||
| Pretreatment | Mean ± sd: | 6.4 ± 1.6 | Ref. |
| Median (IQR): | 6 (2.5) | ||
| 1 week | Mean ± sd: | 3.1 ± 1.8 | <0.001 * |
| Median (IQR): | 2.5 (3) | ||
| 1 month | Mean ± sd: | 3.0 ± 1.8 | <0.001 * |
| Median (IQR): | 2.5 (2.5) | ||
| 3 months | Mean ± sd: | 3.1 ± 2.0 | <0.001 * |
| Median (IQR): | 2.5 (3.25) | ||
| Final follow-up | Mean ± sd: | 3.0 ± 2.1 | <0.001 * |
| Median (IQR): | 2.5 (3.25) | ||
| Pain reduction ≥ 50% (n, %) | |||
| Post-procedure | 49 (92.5%) | ||
| 1 week | 39 (73.6%) | ||
| 1 month | 38 (71.7%) | ||
| 3 months | 34 (64.2%) | ||
| Final follow-up | 33 (62.3%) | ||
| Unfavorable | Favorable | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 33 | ||
| Age | |||
| Mean ± sd | 58.6 ± 17.4 | 58.0 ± 13.8 | 0.899 |
| Median (IQR) | 58.5 (26.5) | 60 (18.5) | |
| Pain at pretreatment (0–10) | |||
| Mean ± sd | 6.3 ± 1.5 | 6.5 ± 1.6 | 0.651 |
| Median (IQR) | 5.25 (2.5) | 6 (2.5) | |
| n. of injections during the follow-up period | |||
| 1 | 11 (55.0%) | 8 (24.2%) | 0.008 |
| 2 | 7 (35.0%) | 8 (24.2%) | |
| 3 and above | 2 (10.0%) | 17 (51.6%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yen, Y.-S.; Lin, C.-H.; Chiang, C.-H.; Wu, C.-Y. Ultrasound-Guided Sciatic Nerve Hydrodissection Can Improve the Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Deep Gluteal Syndrome: A Case-Series Study. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14070757
Yen Y-S, Lin C-H, Chiang C-H, Wu C-Y. Ultrasound-Guided Sciatic Nerve Hydrodissection Can Improve the Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Deep Gluteal Syndrome: A Case-Series Study. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(7):757. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14070757
Chicago/Turabian StyleYen, Yun-Shan, Chang-Hao Lin, Chen-Hao Chiang, and Cheng-Yi Wu. 2024. "Ultrasound-Guided Sciatic Nerve Hydrodissection Can Improve the Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Deep Gluteal Syndrome: A Case-Series Study" Diagnostics 14, no. 7: 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14070757
APA StyleYen, Y.-S., Lin, C.-H., Chiang, C.-H., & Wu, C.-Y. (2024). Ultrasound-Guided Sciatic Nerve Hydrodissection Can Improve the Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Deep Gluteal Syndrome: A Case-Series Study. Diagnostics, 14(7), 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14070757





