Impact of HIF-1α, LOX and ITGA5 Synergistic Interaction in the Tumor Microenvironment on Colorectal Cancer Prognosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Cases and Tissue Microarray Creation
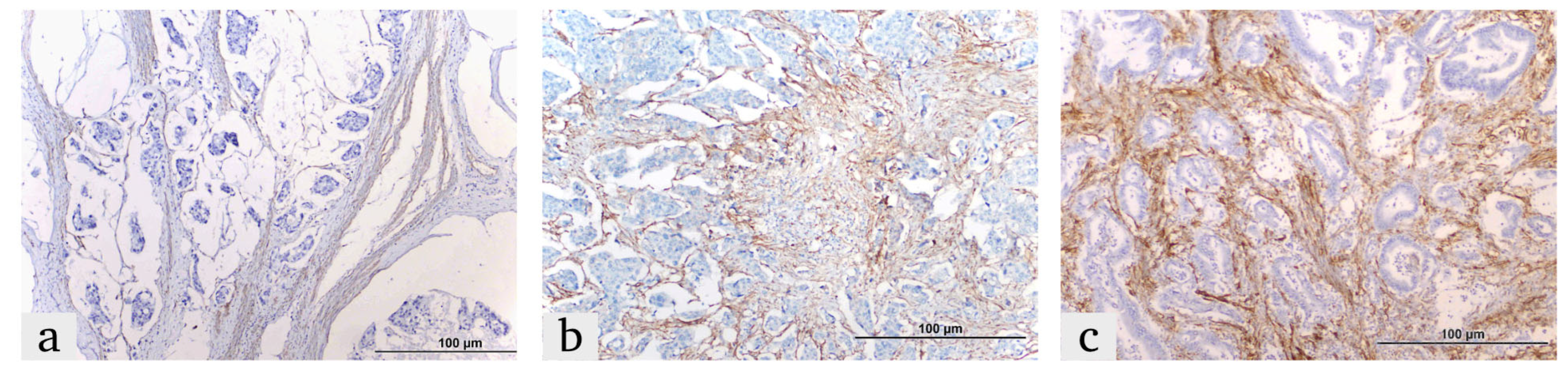
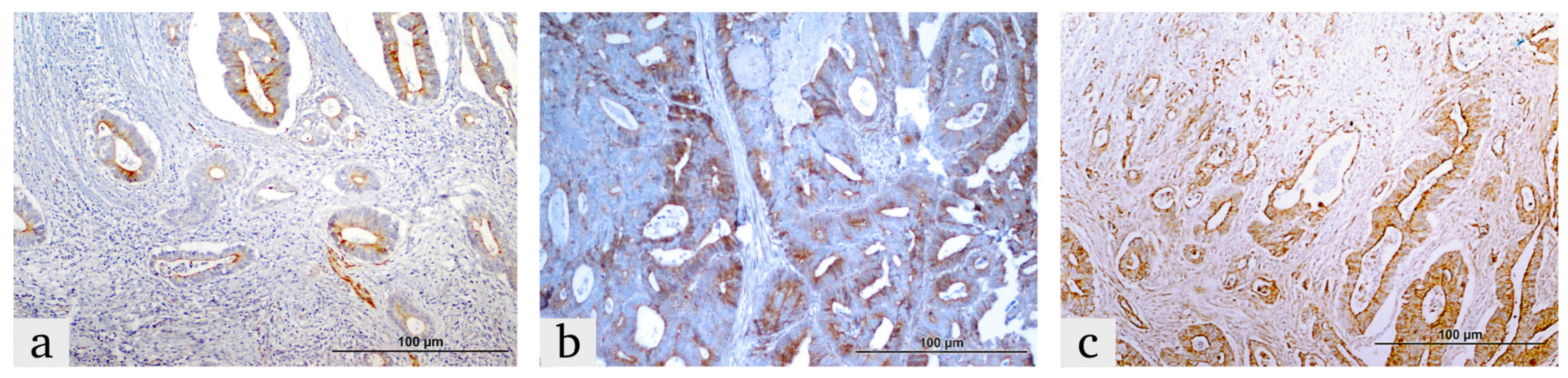
2.2. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Procedure
2.3. IHC Score
- 0 (0%), 1 (0–25%), 2 (25–50%), 3 (50–75%) and 4 (75–100%).
2.4. Single Gene Real-Time PCR Tests for KRAS, NRAS and BRAF
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Patient and Tumor Characteristics
4.2. Overall Survival Analysis and Correlation with Clinicopathological Findings
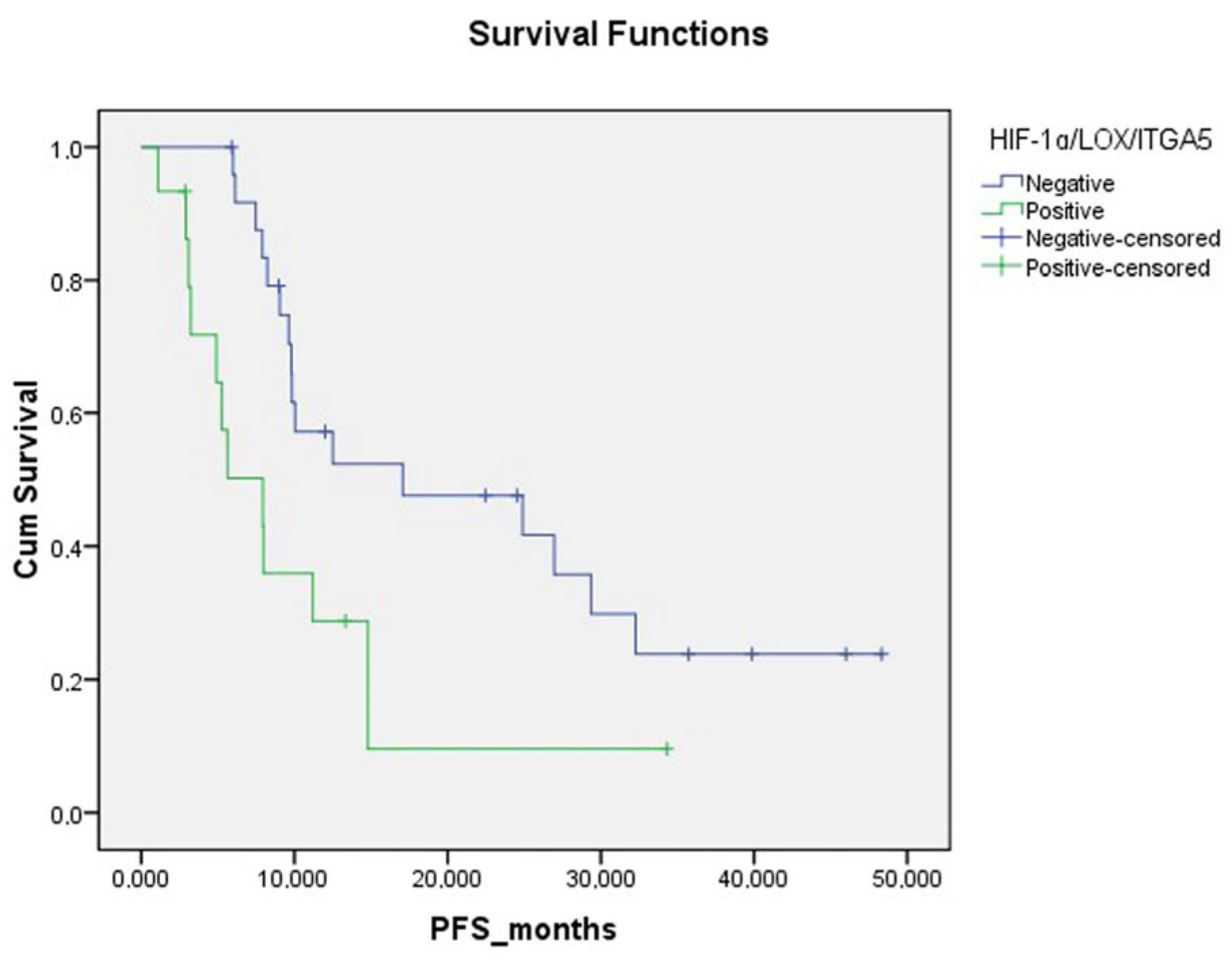
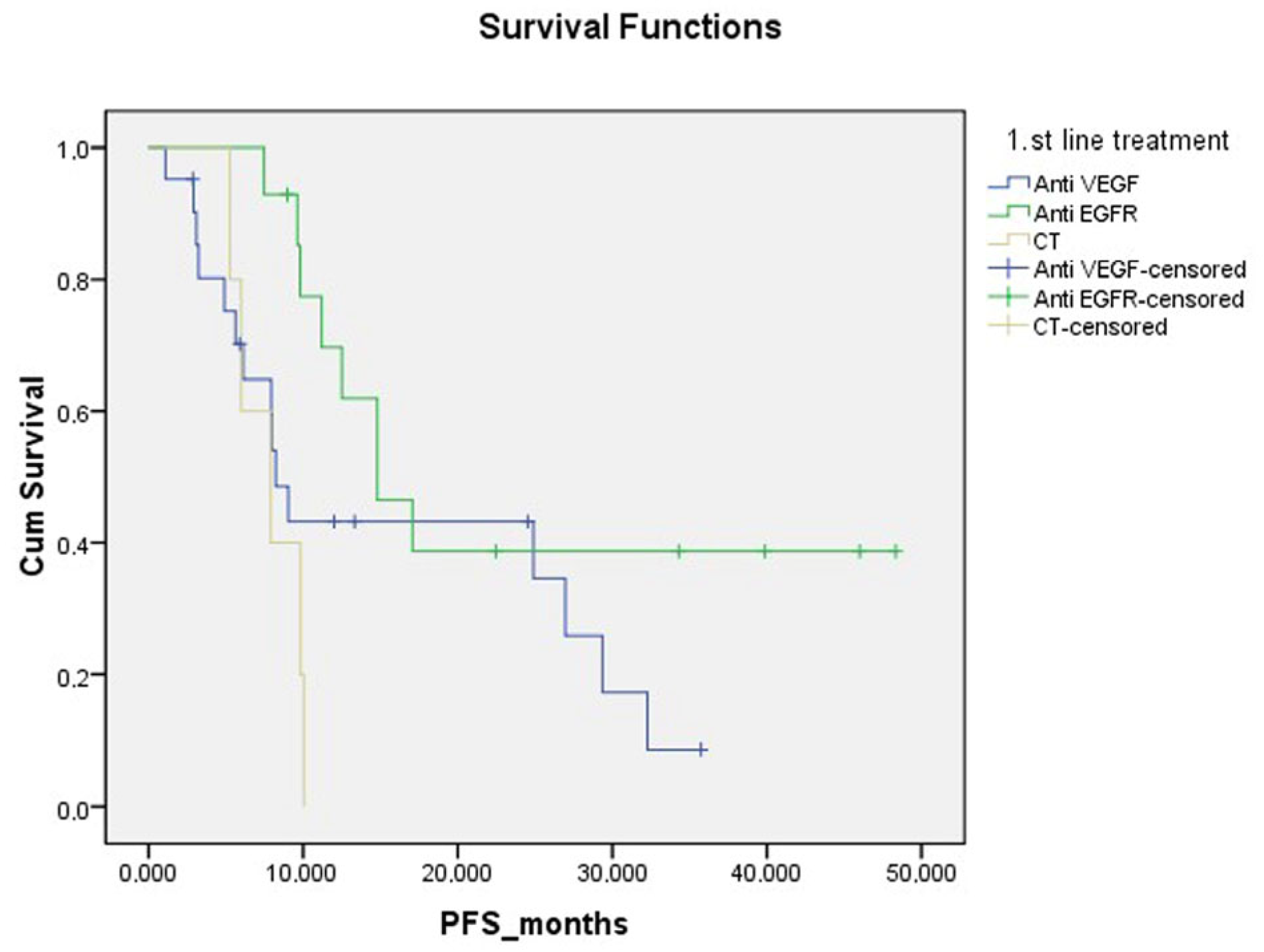
4.3. Progression-Free Survival Analysis and Correlation with Clinicopathological Findings
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fedewa, S.A.; Ahnen, D.J.; Meester, R.G.S.; Barzi, A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Väyrynen, V.; Wirta, E.V.; Seppälä, T.; Sihvo, E.; Mecklin, J.P.; Vasala, K.; Kellokumpu, I. Incidence and Management of Patients with Colorectal Cancer and Synchronous and Metachronous Colorectal Metastases: A Population-Based Study. BJS Open 2020, 4, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhne, C.H. Successes and Limitations of Targeted Cancer Therapy in Colon Cancer. Target. Cancer Ther. 2014, 41, 36–50. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.S.; Heo, J.S.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, M.Y.; Lim, S.H.; Lee, W.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Park, Y.A.; Cho, Y.B.; et al. The Impact of KRAS Mutations on Prognosis in Surgically Resected Colorectal Cancer Patients with Liver and Lung Metastases: A Retrospective Analysis. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koncina, E.; Haan, S.; Rauh, S.; Letellier, E. Prognostic and Predictive Molecular Biomarkers for Colorectal Cancer: Updates and Challenges. Cancers 2020, 12, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Huang, Y.; Sadee, W. Growth Factor Signaling and Resistance to Cancer Chemotherapy. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2005, 4, 1345–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, G.; He, L.; Suo, J. Detection of KRAS Mutations and Their Associations with Clinicopathological Features and Survival in Chinese Colorectal Cancer Patients. J. Int. Med. Res. 2012, 40, 1589–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Pei, L.; Xia, H.; Tang, Q.; Bi, F. Role of Oncogenic KRAS in the Prognosis, Diagnosis and Treatment of Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, N.M.; Simon, M.C. The Tumor Microenvironment. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, R921–R925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnans, C.; Chou, J.; Werb, Z. Remodelling the Extracellular Matrix in Development and Disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 786–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannucci, L. Stroma as an Active Player in the Development of the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Microenviron. 2015, 8, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthebane, D.A.; Rowe, A.; Thomford, N.E.; Shipanga, H.; Munro, D.; Al Mazeedi, M.A.M.; Almazyadi, H.A.M.; Kallmeyer, K.; Dandara, C.; Pepper, M.S.; et al. The Role of Tumor Microenvironment in Chemoresistance: To Survive, Keep Your Enemies Closer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netti, P.A.; Berk, D.A.; Swartz, M.A.; Grodzinsky, A.J.; Jain, R.K. Role of Extracellular Matrix Assembly in Interstitial Transport in Solid Tumors. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 2497–2503. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.F.; Chen, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.W.; Zhao, K.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.C.; Yu, Z.; Li, B.P.; Wang, Z.; et al. ITGA5 Promotes Tumor Progression through the Activation of the FAK/AKT Signaling Pathway in Human Gastric Cancer. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wan, Q.; Yan, W. Integrin A5/Itga5 Promotes the Proliferation, Migration, Invasion and Progression of Oral Squamous Carcinoma by Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 9609–9620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Chu, S.; Fei, B.; Fang, X.; Liu, Z. O-GlcNAcylation of ITGA5 Facilitates the Occurrence and Development of Colorectal Cancer. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 382, 111464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, B.P.; Nguyen, P.L.; Lee, K.; Cho, J. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1: A Novel Therapeutic Target for the Management of Cancer, Drug Resistance, and Cancer-Related Pain. Cancers 2022, 14, 6054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Wang, F.; Yang, H.; Wang, Z. Action Sites and Clinical Application of HIF-1α Inhibitors. Molecules 2022, 27, 3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohwer, N.; Jumpertz, S.; Erdem, M.; Egners, A.; Warzecha, K.T.; Fragoulis, A.; Kühl, A.A.; Kramann, R.; Neuss, S.; Rudolph, I.; et al. Non-Canonical HIF-1 Stabilization Contributes to Intestinal Tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2019, 38, 5670–5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pez, F.; Dayan, F.; Durivault, J.; Kaniewski, B.; Aimond, G.; Le Provost, G.S.; Deux, B.; Clézardin, P.; Sommer, P.; Pouysségur, J.; et al. The HIF-1-Inducible Lysyl Oxidase Activates HIF-1 via the Akt Pathway in a Positive Regulation Loop and Synergizes with HIF-1 in Promoting Tumor Cell Growth. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1647–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saatci, O.; Kaymak, A.; Raza, U.; Ersan, P.G.; Akbulut, O.; Banister, C.E.; Sikirzhytski, V.; Tokat, U.M.; Aykut, G.; Ansari, S.A.; et al. Targeting Lysyl Oxidase (LOX) Overcomes Chemotherapy Resistance in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lei, F.; Rong, W.; Zeng, Q.; Sun, W. Positive Feedback between Oncogenic KRAS and HIF-1α Confers Drug Resistance in Colorectal Cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2015, 8, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, Y.; Takano, O.; Kato, I.; Takahashi, Y.; Shima, F.; Kataoka, T. Ras Inhibitors Display an Anti-Metastatic Effect by Downregulation of Lysyl Oxidase through Inhibition of the Ras-PI3K-Akt-HIF-1α Pathway. Cancer Lett. 2017, 410, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakih, M.G.; Salvatore, L.; Esaki, T.; Modest, D.P.; Lopez-Bravo, D.P.; Taieb, J.; Karamouzis, M.V.; Ruiz-Garcia, E.; Kim, T.-W.; Kuboki, Y.; et al. Sotorasib plus Panitumumab in Refractory Colorectal Cancer with Mutated KRAS G12C. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 2125–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicero, G.; De Luca, R.; Dieli, F. Progression-Free Survival as a Surrogate Endpoint of Overall Survival in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 3059–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raica, M.; Cimpean, A.M.; Anghel, A. Immunohistochemical Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Does Not Correlate with Microvessel Density in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Neoplasma 2007, 54, 278–284. [Google Scholar]
- DeRycke, M.S.; Andersen, J.D.; Harrington, K.M.; Pambuccian, S.E.; Kalloger, S.E.; Boylan, K.L.M.; Argenta, P.A.; Skubitz, A.P.N. S100A1 Expression in Ovarian and Endometrial Endometrioid Carcinomas Is a Prognostic Indicator of Relapse-Free Survival. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 132, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira-Costa, J.P.; Zanetti, J.S.; Silveira, G.G.; Soave, D.F.; Oliveira, L.R.; Zorgetto, V.A.; Soares, F.A.; Zucoloto, S.; Ribeiro-Silva, A. Differential Expression of HIF-1α in CD44+CD24-/Lowbreast Ductal Carcinomas. Diagn. Pathol. 2011, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, M.; Vignaud, J.M.; Hennequin, V.; Toussaint, B.; Bresler, L.; Plénat, F.; Leclère, J.; Duprez, A.; Weryha, G. Increased Expression of the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Is a Pejorative Prognosis Marker in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 656–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wouters, B.G.; Koritzinsky, M. Hypoxia Signalling through MTOR and the Unfolded Protein Response in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasawa, H. Pathophysiological Response to Hypoxia—From the Molecular Mechanisms of Malady to Drug Discovery: Drug Discovery for Targeting the Tumor Microenvironment. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 115, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, Y.; Nosho, K.; Shima, K.; Irahara, N.; Chan, A.T.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Chung, D.C.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Fuchs, C.S.; Ogino, S. HIF1A Overexpression Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in a Cohort of 731 Colorectal Cancers. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 2292–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleven, A.H.G.; Van Engeland, M.; Wouters, B.G.; De Bruïne, A.P. Stromal Expression of Hypoxia Regulated Proteins Is an Adverse Prognostic Factor in Colorectal Carcinomas. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2007, 29, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, H.; Dhar, D.K.; Kohno, H.; Kubota, H.; Fujii, T.; Ueda, S.; Kinugasa, S.; Tachibana, M.; Nagasue, N. Prognostic Impact of Hypoxia-Inducible Factors 1α and 2α in Colorectal Cancer Patients: Correlation with Tumor Angiogenesis and Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 8554–8560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, T.; Rossignol, F.; Matthay, M.A.; Mounier, R.; Couette, S.; Clottes, E.; Clerici, C. Prolonged Hypoxia Differentially Regulates Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF)-1α and HIF-2α Expression in Lung Epithelial Cells: Implication of Natural Antisense HIF-1α. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 14871–14878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, H.; Pino, M.S.; Min, Z.; Shirasawa, S.; Chung, D.C. Oncogenic KRAS and BRAF Differentially Regulate Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α and -2α in Colon Cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8499–8506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.M.; Cox, T.R.; Bird, D.; Lang, G.; Murray, G.I.; Sun, X.F.; Southall, S.M.; Wilson, J.R.; Erler, J.T. The Role of Lysyl Oxidase in SRC-Dependent Proliferation and Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, J.; Giancotti, F.G. Integrin Signaling in Cancer: Mechanotransduction, Stemness, Epithelial Plasticity, and Therapeutic Resistance. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 347–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Yao, F.; Huang, C. Lysyl Oxidase Family Proteins: Prospective Therapeutic Targets in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, G.; Zhu, H.; Xu, A. ITGA5 Is a Prognostic Biomarker and Correlated with Immune Infiltration in Gastrointestinal Tumors. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Shen, Y.; Wei, Z.; Shen, Z.; Tang, M.; Shen, Y.; Deng, H. ITGA5 Is an Independent Prognostic Biomarker and Potential Therapeutic Target for Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Wu, M.; Liu, Y.; Hu, L.; Wu, H.; Xie, L.; Liu, Z.; Wu, A.; Chen, L.; Xu, C. ITGA5 Predicts Dual-Drug Resistance to Temozolomide and Bevacizumab in Glioma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 769592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, N.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X. ITGA5 Is a Novel Oncogenic Biomarker and Correlates With Tumor Immune Microenvironment in Gliomas. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 844144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, E.; Santos, N.; Liu, Y.; Havre, P.; Dang, N.H.; Luesch, H.; Dang, L.H. Targeting HIF-1α and HIF-2α to Overcome Treatment Resistance Mediated by Oncogenic KRAS in Colorectal Cancer. J. Cancer Ther. 2013, 4, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infantino, V.; Santarsiero, A.; Convertini, P.; Todisco, S.; Iacobazzi, V. Cancer Cell Metabolism in Hypoxia: Role of HIF-1 as Key Regulator and Therapeutic Target. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors: Mediators of Cancer Progression and Targets for Cancer Therapy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 33, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, N.B.; Quirt, I.; Hotte, S.; McWhirter, E.; Polintan, R.; Litwin, S.; Adams, P.D.; McBryan, T.; Wang, L.; Martin, L.P.; et al. Phase II Trial of Vorinostat in Advanced Melanoma. Invest. New Drugs 2014, 32, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, T.W.; Bai, G.H.; Wang, T.L.; Shih, I.M.; Chuang, C.M.; Lo, C.L.; Tsai, M.C.; Chiu, L.Y.; Lin, C.C.; Shen, Y.A. Novel Cancer Treatment Paradigm Targeting Hypoxia-Induced Factor in Conjunction with Current Therapies to Overcome Resistance. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Yang, J.; Mao, J.; Zhu, L.; Luo, X.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, L. ITGA5 Inhibition in Pancreatic Stellate Cells Re-Educates the in Vitro Tumor-Stromal Crosstalk. Med. Oncol. 2023, 40, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitty, J.L.; Yam, M.; Perryman, L.; Parker, A.L.; Skhinas, J.N.; Setargew, Y.F.I.; Mok, E.T.Y.; Tran, E.; Grant, R.D.; Latham, S.L.; et al. A First-in-Class Pan-Lysyl Oxidase Inhibitor Impairs Stromal Remodeling and Enhances Gemcitabine Response and Survival in Pancreatic Cancer. Nat. Cancer 2023, 4, 1326–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cetin, M.; Saatci, O.; Rezaeian, A.-H.; Rao, C.N.; Beneker, C.; Sreenivas, K.; Taylor, H.; Pederson, B.; Chatzistamou, I.; Buckley, B.; et al. A Highly Potent Bi-Thiazole Inhibitor of LOX Rewires Collagen Architecture and Enhances Chemoresponse in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cell Chem. Biol. 2024, 31, 1926–1941.E11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Mutation (KRAS/NRAS/BRAF) | Frequency n (%) |
|---|---|
| WILD | 55 (% 55.0) |
| KRAS | 30 (% 30.0) |
| NRAS | 4 (% 4.0) |
| BRAF | 11 (% 11.0) |
| Mutation | |
| WILD | 55 (% 55.0) |
| KRAS A146X | 5 (% 5.0) |
| KRAS A59T | 1 (% 1.0) |
| KRAS G12X | 17 (% 17.0) |
| KRAS G13D | 7 (% 7.0) |
| NRAS G12X | 1 (% 1.0) |
| NRAS Q61K | 3 (% 3.0) |
| BRAF V600E/Ec | 11 (% 11.0) |
| MMR (mismatch repair) | |
| proficient | 87 (% 87.0) |
| deficient | 13 (% 13.0) |
| Variables | N | Progression | Median Survival (Range) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | 40 | 28 | 11.07 (8.4–14.09) | |
| Gender | ||||
| Female | 19 | 17 | 12.30 (7.76–16.84) | 0.016 |
| Male | 21 | 11 | 25.95 (17.29–34.60) | |
| N stage | ||||
| N0 | 12 | 7 | 26.43 (16.58–6.28) | 0.070 |
| N1–N2 | 28 | 21 | 15.39 (9.62–21.15) | |
| KRAS mutation | ||||
| Negative | 26 | 17 | 19.88 (12.70–27.05) | 0.591 |
| Positive | 14 | 11 | 16.90 (10.33–23.46) | |
| BRAF mutation | ||||
| Negative | 36 | 24 | 20.74 (14.91–26.58) | 0.001 |
| Positive | 4 | 4 | 5.70 (3.74–7.67) | |
| HIF-1α tumor | ||||
| Negative | 36 | 24 | 20.70 (14.84–26.56) | 0.030 |
| Positive | 4 | 4 | 6.75 (0.72–12.79) | |
| HIF-1α microenvironment | ||||
| Weak | 17 | 10 | 26.20 (17.59–34.79) | 0.013 |
| Moderate/strong | 23 | 18 | 12.41 (8.05–16.76) | |
| ITGA5 microenvironment | ||||
| Weak | 19 | 11 | 25.12 (16.76–33.54) | 0.018 |
| Moderate/strong | 21 | 17 | 12.22 (7.75–16.69) | |
| LOX microenvironment | ||||
| Weak | 20 | 13 | 23.57 (16.24–30.90) | 0.05 |
| Moderate/strong | 20 | 15 | 11.99 (6.75–17.24) | |
| LOX tumor | ||||
| Low | 22 | 16 | 20.51 (13.31–27.71) | 0.572 |
| High | 18 | 12 | 14.71 (9.14–20.28) | |
| All IHC positive | ||||
| No | 25 | 16 | 23.29 (16.44–30.14) | 0.014 |
| Yes | 15 | 12 | 9.93 (4.95–14.9) | |
| Metastatic first-line treatment | ||||
| CT + Anti-VEGF | 21 | 15 | 16.05 (10.42–21.68) | 0.023 |
| CT + Anti-EGFR | 14 | 8 | 26.18 (16.53–35.83) | |
| CT | 5 | 5 | 7.80 (5.90–9.70) |
| Clinicopathologic Feature | HR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||
| Female vs. male | 0.35 (0.14–0.84) | 0.020 |
| Mutation Positive | ||
| Any of KRAS, NRAS, or BRAF | 0.86 (0.22–3.35) | 0.838 |
| BRAF Mutation | ||
| Negative vs. positive | 1.74 (0.36–8.32) | 0.487 |
| All IHC-Positive | ||
| Triple positive (HIF-1α/LOX/ITGA5) with moderate to strong intensity vs. all others | 4.32 (1.29–14.48) | 0.018 |
| Treatment | ||
| CT + anti-VEGF | 0.021 | |
| CT + anti-EGFR | 0.32 (0.66–1.64) | 0.175 |
| CT | 3.40 (1.01–11.48) | 0.048 |
| Variables | Mutation and IHC Positivity | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No (n = 85) | Yes (n = 15) | ||
| Gender | |||
| Female | 30 (% 35.3) | 5 (% 33.3) | 0.883 |
| Male | 55 (% 64.7) | 10 (% 66.7) | |
| Tumor size | 4.5 (0.2–15) | 5 (1.9–9) | 0.361 * |
| Metastatic lymph node number (median) | 1 | 3 | 0.033 * |
| Differentiation | |||
| Well | 20 (% 23.5) | 0 (% 0.0) | 0.026 |
| Moderate–poor | 65(% 76.5) | 15 (% 100) | |
| T stage | |||
| T2–3 | 60 (% 70.6) | 7 (% 46.7) | 0.069 |
| T4 | 25 (% 29.4) | 8(% 53.3) | |
| N stage | |||
| N0 | 36 (% 42.4) | 2 (% 13.3) | 0.028 |
| N1–2 | 49 (% 57.6) | 13 (% 86.7) | |
| Stage | |||
| Stage I–III | 46 (% 54.1) | 5 (% 33.5) | 0.138 |
| Stage IV | 39 (% 45.9) | 10 (% 66.7) | |
| LVI | |||
| Negative | 30 (% 35.3) | 1 (% 6.7) | 0.021 |
| Positive | 55 (% 64.7) | 14(% 93.3) | |
| PNI | |||
| Negative | 54 (% 63.5) | 3 (% 33.3) | 0.151 |
| Positive | 31 (% 36.5) | 6 (% 66.7) | |
| MMR | |||
| Proficient | 75 (% 88.2) | 12 (% 80) | 0.303 |
| Deficient | 10 (% 11.8) | 3 (% 20) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tatlı Doğan, H.; Doğan, M.; Kahraman, S.; Çanakçı, D.; Şendur, M.A.N.; Tahtacı, M.; Erdoğan, F. Impact of HIF-1α, LOX and ITGA5 Synergistic Interaction in the Tumor Microenvironment on Colorectal Cancer Prognosis. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15020184
Tatlı Doğan H, Doğan M, Kahraman S, Çanakçı D, Şendur MAN, Tahtacı M, Erdoğan F. Impact of HIF-1α, LOX and ITGA5 Synergistic Interaction in the Tumor Microenvironment on Colorectal Cancer Prognosis. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(2):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15020184
Chicago/Turabian StyleTatlı Doğan, Hayriye, Mehmet Doğan, Seda Kahraman, Doğukan Çanakçı, Mehmet Ali Nahit Şendur, Mustafa Tahtacı, and Fazlı Erdoğan. 2025. "Impact of HIF-1α, LOX and ITGA5 Synergistic Interaction in the Tumor Microenvironment on Colorectal Cancer Prognosis" Diagnostics 15, no. 2: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15020184
APA StyleTatlı Doğan, H., Doğan, M., Kahraman, S., Çanakçı, D., Şendur, M. A. N., Tahtacı, M., & Erdoğan, F. (2025). Impact of HIF-1α, LOX and ITGA5 Synergistic Interaction in the Tumor Microenvironment on Colorectal Cancer Prognosis. Diagnostics, 15(2), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15020184






