Hematopathological Patterns in Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Complications of Overt Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Overt DIC Score Comparison
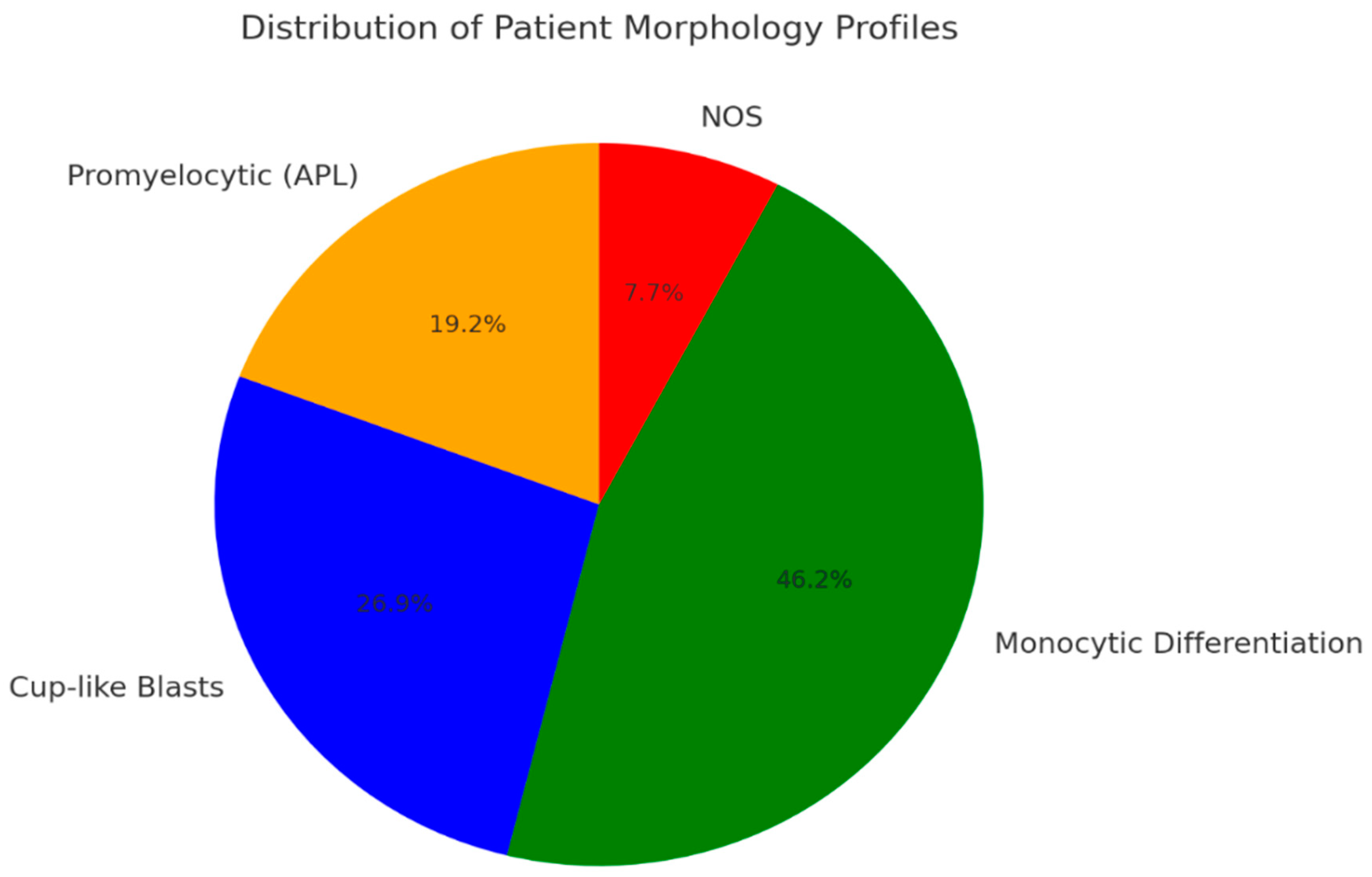
3.2. Key Genetic Drivers and Cellular Characteristics in AML with DIC
- Patients with promyelocytic neoplastic cells (APL);
- Patients with a dominance of cup-like blasts;
- Patients with predominant monocytic differentiation.
3.3. Hematopathological Patterns of AML with Overt DIC
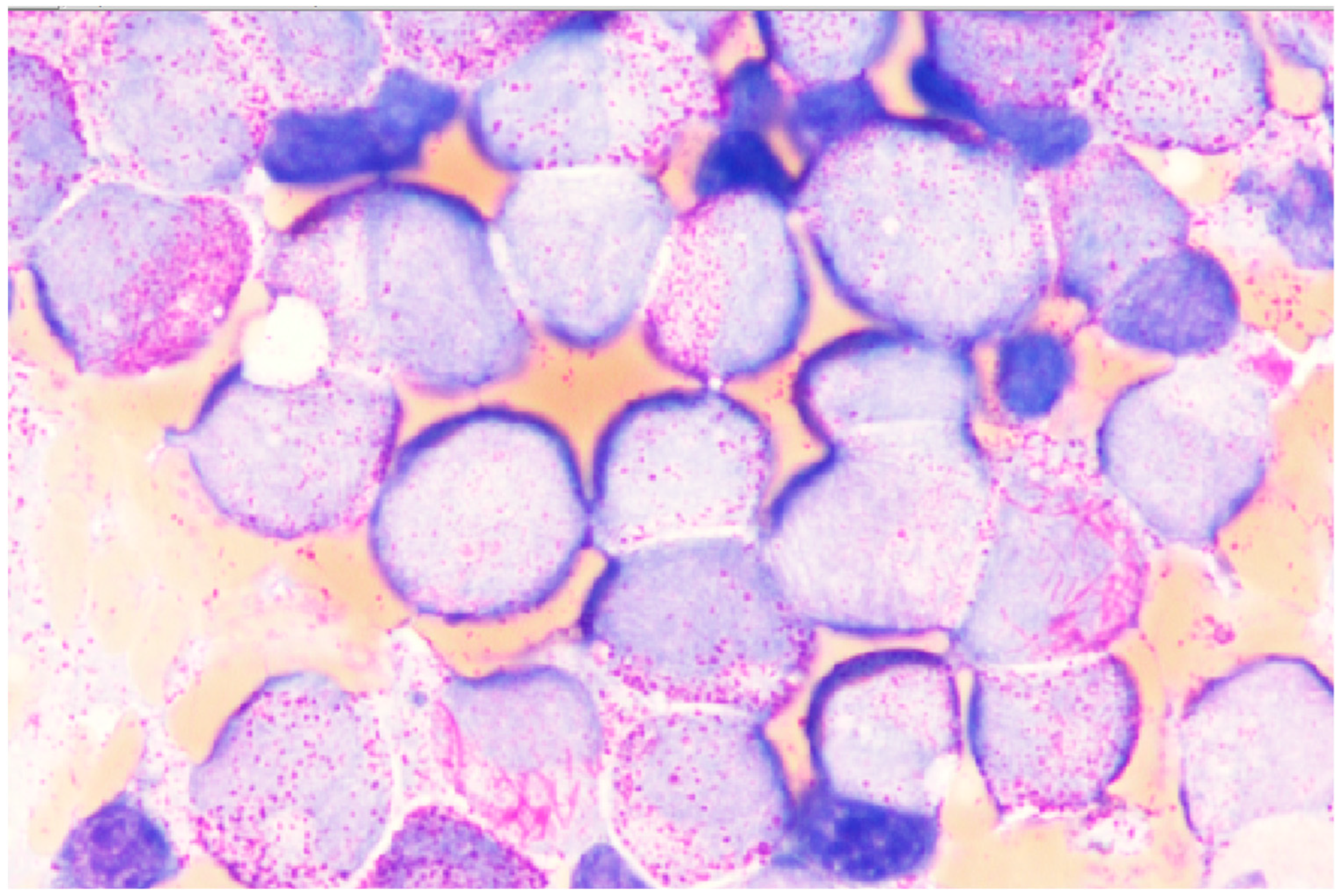
3.3.1. APL
3.3.2. AML with Cup-Like Blast Dominance
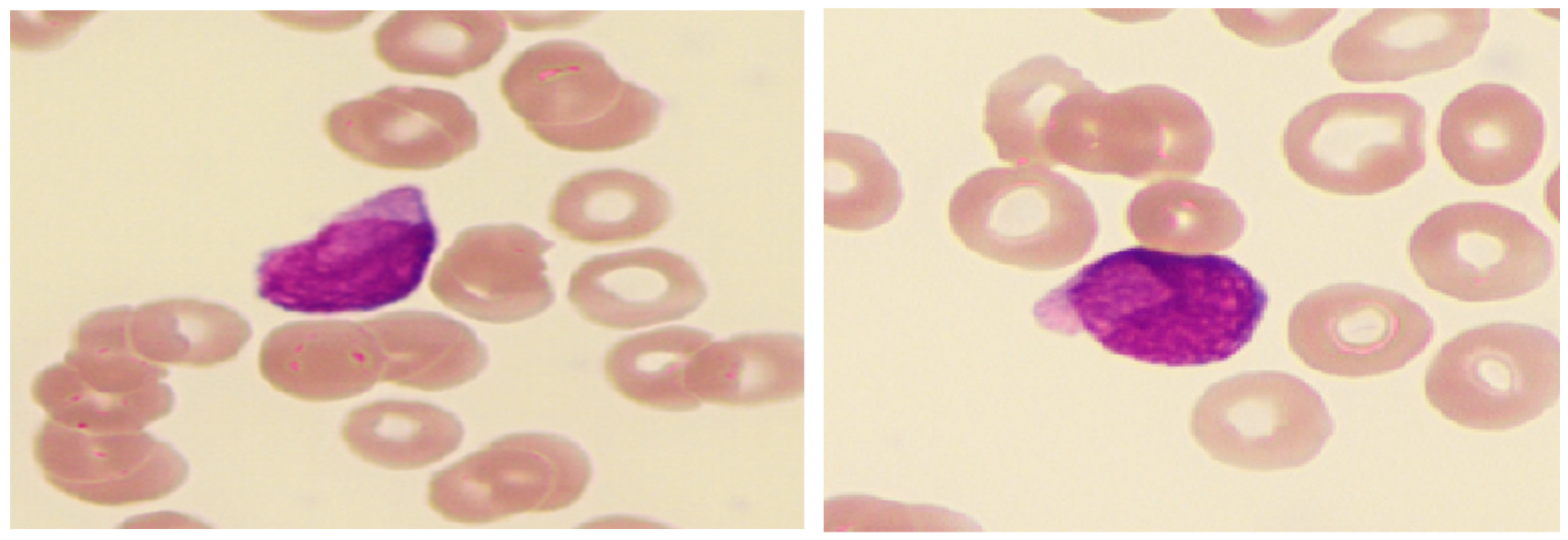
3.3.3. AML with Monocytic Differentiation
3.3.4. Not Otherwise Specified (NOS) Profile
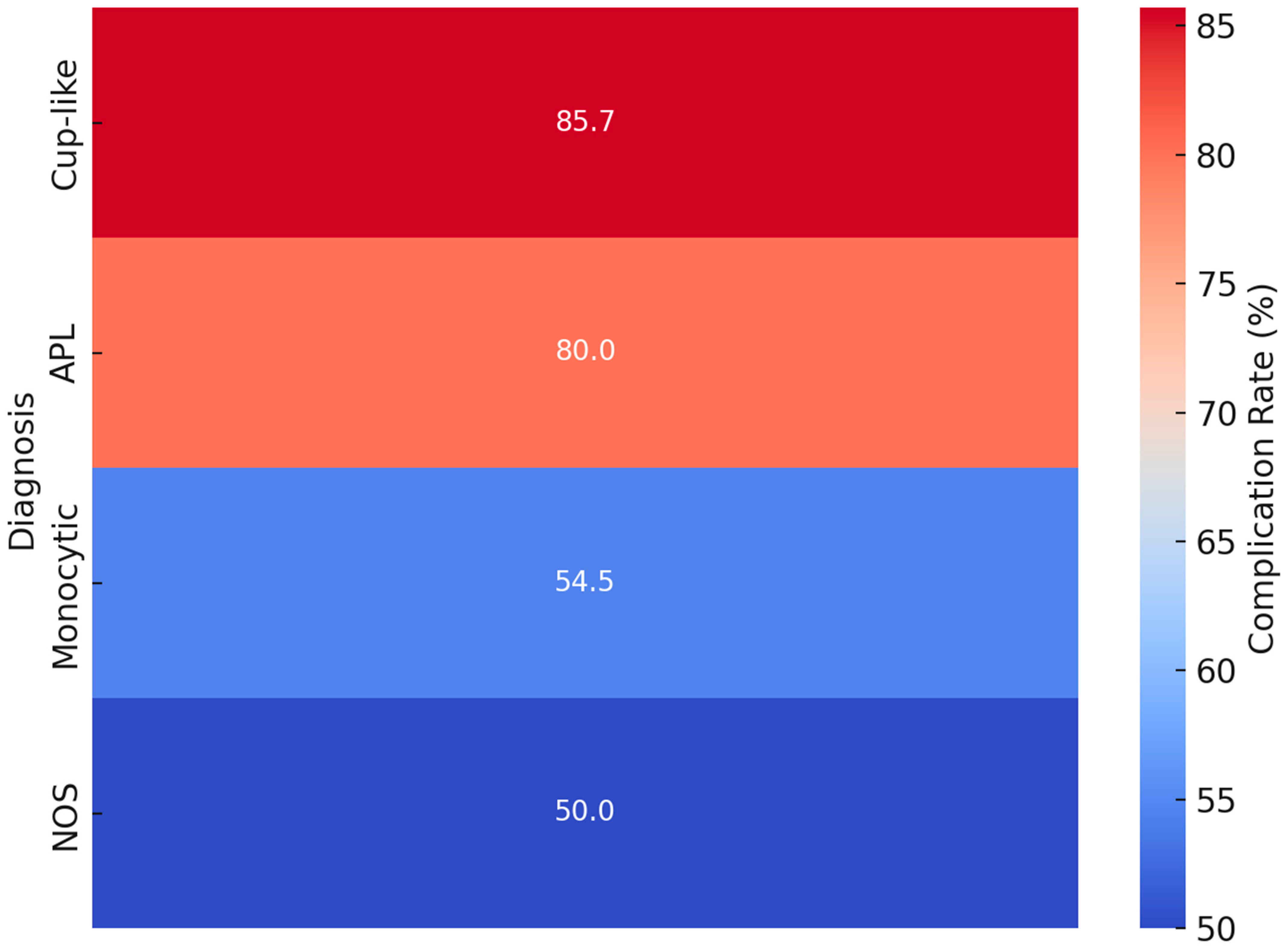
3.4. Complication Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ten Cate, H.; Leader, A. Management of Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation in Acute Leukemias. Hamostaseologie 2021, 41, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grafeneder, J.; Krychtiuk, K.A.; Buchtele, N.; Schoergenhofer, C.; Gelbenegger, G.; Lenz, M.; Wojta, J.; Heinz, G.; Huber, K.; Hengstenberg, C.; et al. The ISTH DIC score predicts outcome in non-septic patients admitted to a cardiovascular intensive care unit. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 79, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Wada, H.; Imai, H.; Iba, T.; Thachil, J.; Toh, C.H.; Subcommittee on Disseminated Intravascular, C. A re-evaluation of the D-dimer cut-off value for making a diagnosis according to the ISTH overt-DIC diagnostic criteria: Communication from the SSC of the ISTH. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 1442–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Short, N.J.; Qiao, W.; Ning, J.; Cuglievan, B.; Daver, N.G.; DiNardo, C.D.; Jabbour, E.J.; Kadia, T.M.; et al. Early mortality in acute myeloid leukemia with KMT2A rearrangement is associated with high risk of bleeding and disseminated intravascular coagulation. Cancer 2023, 129, 1856–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, N.; Chen, P.; Liu, Y. An End-to-End Pipeline for Early Diagnosis of Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia Based on a Compact CNN Model. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.; Gurnari, C.; Scalzulli, E.; Cicconi, L.; Guarnera, L.; Carmosino, I.; Cerretti, R.; Bisegna, M.L.; Capria, S.; Minotti, C.; et al. Response Rates and Transplantation Impact in Patients with Relapsed Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia. Cancers 2024, 16, 3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollig, C.; Kramer, M.; Schliemann, C.; Mikesch, J.H.; Steffen, B.; Kramer, A.; Noppeney, R.; Schafer-Eckart, K.; Krause, S.W.; Hanel, M.; et al. Does time from diagnosis to treatment affect the prognosis of patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia? Blood 2020, 136, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premnath, N.; Madanat, Y.F. Paradigm Shift in the Management of Acute Myeloid Leukemia-Approved Options in 2023. Cancers 2023, 15, 3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capria, S.; Trisolini, S.M.; Torrieri, L.; Amabile, E.; Marsili, G.; Piciocchi, A.; Barberi, W.; Iori, A.P.; Diverio, D.; Carmini, D.; et al. Real-Life Management of FLT3-Mutated AML: Single-Centre Experience over 24 Years. Cancers 2024, 16, 2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martella, F.; Cerrano, M.; Di Cuonzo, D.; Secreto, C.; Olivi, M.; Apolito, V.; D’Ardia, S.; Frairia, C.; Giai, V.; Lanzarone, G.; et al. Frequency and risk factors for thrombosis in acute myeloid leukemia and high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes treated with intensive chemotherapy: A two centers observational study. Ann. Hematol. 2022, 101, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ookura, M.; Hosono, N.; Tasaki, T.; Oiwa, K.; Fujita, K.; Ito, K.; Lee, S.; Matsuda, Y.; Morita, M.; Tai, K.; et al. Successful treatment of disseminated intravascular coagulation by recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Medicine 2018, 97, e12981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, P.; Jasdanwala, S.S.; Wang, Y.; Bhatia, K.; Bhatt, S. Decoding Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Clinician’s Guide to Functional Profiling. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.; Wang, S.A.; Hu, S.; Konoplev, S.N.; Mo, H.; Liu, W.; Zuo, Z.; Xu, J.; Jorgensen, J.L.; Yin, C.C.; et al. Acute promyelocytic leukemia: Immunophenotype and differential diagnosis by flow cytometry. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2022, 102, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, H.; Takahashi, N.; Katsuoka, Y.; Inomata, M.; Ito, T.; Meguro, K.; Kameoka, Y.; Tsumanuma, R.; Murai, K.; Noji, H.; et al. Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of recombinant soluble thrombomodulin for patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation associated with acute leukemia: Multicenter prospective study by the Tohoku Hematology Forum. Int. J. Hematol. 2017, 105, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takezako, N.; Sekiguchi, N.; Nagata, A.; Homma, C.; Takezako, Y.; Noto, S.; Natori, K.; Miwa, A. Recombinant human thrombomodulin in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia patients complicated by disseminated intravascular coagulation: Retrospective analysis of outcomes between patients treated with heparin and recombinant human thrombomodulin therapy. Thromb. Res. 2015, 136, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versluis, J.; Pandey, M.; Flamand, Y.; Haydu, J.E.; Belizaire, R.; Faber, M.; Vedula, R.S.; Charles, A.; Copson, K.M.; Shimony, S.; et al. Prediction of life-threatening and disabling bleeding in patients with AML receiving intensive induction chemotherapy. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 2835–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterno, G.; Palmieri, R.; Tesei, C.; Nunzi, A.; Ranucci, G.; Mallegni, F.; Moretti, F.; Meddi, E.; Tiravanti, I.; Marinoni, M.; et al. The ISTH DIC-score predicts early mortality in patients with non-promyelocitic acute myeloid leukemia. Thromb. Res. 2024, 236, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.Y.; Kashanian, S.M.; Hambley, B.C.; Zacholski, K.; Duong, V.H.; El Chaer, F.; Holtzman, N.G.; Gojo, I.; Webster, J.A.; Norsworthy, K.J.; et al. FLT3-ITD Allelic Burden and Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia Risk Stratification. Biology 2021, 10, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante, J.; Esteves, G.; Raposo, J.; de Lacerda, J.F. Predictors of very early death in acute promyelocytic leukemia: A retrospective real-world cohort study. Ann. Hematol. 2023, 102, 3031–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, S.; Taylor, J. Trying to outRun-DIC in KMT2Ar AML: It’s tricky. Cancer 2023, 129, 1797–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.D.; Vodyanik, M.; Slukvin, I.I. Hematopoietic differentiation and production of mature myeloid cells from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 296–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, D.; Shah, H.P.; Malu, K.; Berliner, N.; Gaines, P. Differentiation and characterization of myeloid cells. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2014, 104, 22F.25.21–22F.25.28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Park, H.J.; Kim, H.W.; Park, S.G. Comparison of laboratory characteristics between acute promyelocytic leukemia and other subtypes of acute myeloid leukemia with disseminated intravascular coagulation. Blood Res. 2013, 48, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| platelets/µL | ≥100 | 50–99 | <50 | |
| fibrinogen (mg/dL) | ≥100 | <100 | ||
| prothrombin time% | >70 | 40–70 | <40 | |
| D-dimer µg/mL | <3 | 3–7 | >7 |
| L/µL | Hb (g/dL) | T/µL | PT (%) | Fib (mg/dL) | D-Dimer (µg/mL) | DIC Score (≥4) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference Range | 4.0–10.0 | >12.0 (F), >13.6 (M) | 150–400 | 70–130 | 180–350 | <0.5 | ||
| non-APL AML | mean | 46.00 | 8.72 | 45.25 | 68.75 | 360.65 | 52.82 | 5.25 |
| 20 patients | std | 53.50 | 1.66 | 27.42 | 21.98 | 190.72 | 68.90 | 0.97 |
| med | 16.45 | 8.35 | 39.50 | 68.00 | 398.50 | 17.08 | 5.50 | |
| APL 5 patients | mean | 36.74 | 11.06 | 30.80 | 64.40 | 136.20 | 33.60 | 5.40 |
| std | 45.83 | 2.29 | 16.15 | 15.98 | 28.05 | 25.97 | 0.89 | |
| med | 12.00 | 11.90 | 27.00 | 62.00 | 130.00 | 22.01 | 6.00 | |
| Comparison | p | 0.61 | 0.08 | 0.15 | 0.62 | 0.09 | 0.72 | 0.76 |
| APL | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnosis | NGS | Cytogenetics | Blast/Promyelocytes | Cytomorphology | Immuncytolology |
| APL | CALR | t(15;17) | 82% | promyelocytes | CD34dim, HLA-DR dim |
| FLT3 | Auer rods | MPO+, CD13+, CD33+, CD117+ | |||
| Faggot bundles | CD4dim, CD15+, CD14dim, CD64+ | ||||
| CD22dim | |||||
| APL | FLT3 | t(15;17) | 78% | promyelocytes | CD34-, HLA-DR- |
| WT1 | Auer rods | MPO+,CD13dim, CD33++, CD117+ | |||
| WT1 | CD15+, CD64+ | ||||
| WT1 | CD22dim | ||||
| APL-V | FLT3 | t(15;17) | 92% | bi-nucleated | CD34dim, HLA-DRdim |
| reniform | MPOdim, CD13dim, CD33+, CD117- | ||||
| hypogranulation | CD64+ | ||||
| Auer rods | CD2+ | ||||
| Faggot bundles | |||||
| APL | no mut | t(15;17) | 85% | promyelocytes | not carried out |
| Auer rods | punctio sicca like aspirate | ||||
| Faggot bundles | |||||
| APL-V | DNMT3A | t(15;17) | 93% | bi-nucleated | CD34-, HLA-DR dim |
| FLT3 | reniform | MPO+,CD13dim, CD33+, CD117+ | |||
| hypogranulation | CD64+ | ||||
| Auer rods | CD2+,CD19+ | ||||
| AML FLT3 with Cup-Like Blast Dominance | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | NGS | Cytogenetics | Blast Count | Blastmorphology | Immuncytolology |
| 1 | DNMT3A | 46,XX | 95% | pseudopods | CD34+, HLA-DR+ |
| FLT3 | cup-like | MPO+, CD13dim, CD33+, CD117+ | |||
| NPM1 | hypogranulation | CD14+,CD64+ | |||
| FLT3 | |||||
| 2 | DNMT3A | 46,XX | 86% | pseudopods | CD34-, HLA-DR+ |
| FLT3 | cup-like | MPO+, CD13+, CD33+, CD117+ | |||
| NPM1 | hypogranulation | ||||
| FLT3 | |||||
| 3 | FLT3 | 46,XX | 84% | Auer rods | CD34+, HLA-DR+ |
| NPM1 | pseudopods | MPO+, CD13+, CD33+, CD117+ | |||
| WT1 | cup-like | CD2+ | |||
| hypogranulation | subpopulation: CD4+, CD14+,CD15+,CD64+ | ||||
| 4 | NPM1 | 46,XY | 87% | cup-like | CD34-,HLA-DR- |
| DNMT3A | hypogranulation | MPO+, CD13+, CD33+, CD117+ | |||
| IDH1 | CD15+, CD64+ | ||||
| 5 | FLT3 | t(8;21) | 90% | Auer rods | CD34+, HLA-DR+ |
| RUNX1 | MPO+, CD13+, CD33+, CD117+ | ||||
| ASXL1 | CD64+ | ||||
| CD19+, CD79dim | |||||
| 6 | NPM1 | 46,XY | 96% | hypogranulation | CD34-, HLA-DR+ |
| IDH1 | MPO+, CD13+, CD33+, CD117+ | ||||
| PTPN11 | CD64dim | ||||
| SRSF2 | |||||
| 7 | DNMT3A | 46,XX | 74% | cup-like | 34dim, HLA-DR+ |
| FLT3 | hypogranulation | MPO+, CD13+, CD33+, CD117+ | |||
| NPM1 | vacuoles | CD19+, CD10+ | |||
| WT1 | |||||
| IDH1 | |||||
| Monocytic Differentiation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | NGS | Cytogenetics | Blast Count | Blastmorphology | Immuncytology | |
| 1 | DNMT3A | 11q23 | 89% | monoblasts | CD34+, HLA-DR+ | |
| vaculisation | MPO+, CD13+, CD33+, CD117+ | |||||
| monolobulated, oval | CD4+,CD14+,CD64+ | |||||
| basophil cytoplasm margin | CD7+, CD56+ | |||||
| 2 | DNMT3A | CK | 94% | monoblasts | CD34+, HLA-DR+ | |
| TET2 | vaculisation | MPO+, CD13dim, CD33+, CD117+ | ||||
| TP53 | monolobulated, oval | CD4+, CD14+, CD15+, CD64+ | ||||
| TET2 | basophil cytoplasm margin | CD56+ | ||||
| 3 | FLT3 | 46,XX | 84% | monoblasts | ||
| NPM1 | vacuolisation | CD34-, HLA-DR+ | ||||
| DNMT3A | monolobulated, oval | MPO-, CD13+, CD33+, CD117- | ||||
| basophil cytoplasm margin | CD4+, CD14+, CD15+, CD64+ | |||||
| 4 | DNMT3A | CK | 83% | monoblasts, pomonocytes | CD34-, HLA-DR- | |
| TET2 | vacuolisation | MPO-, CD13+, CD33+, CD117+ | ||||
| NPM1 | monolobulated, convoluted | CD4+, CD14+, CD15+, CD64+ | ||||
| TP53 | ||||||
| 5 | TP53 | no met. | 43% | promonocytes | CD34-, HLA-DR+ | |
| TET2 | vacuolisation | MPO+, CD13+, CD33+, CD117+ | ||||
| basophil cytoplasm margin | CD4dim, CD14-, CD15++, CD64+ | |||||
| CD56 | ||||||
| 6 | DNMT3A | 46,XY | 90% | monoblasts, pomonocytes | CD34+, HLA-DR+ | |
| FLT3 | vacuolisation | MPOdim, CD13+, CD33+ | ||||
| NPM1 | convoluted, oval | CD15++, CD64+ | ||||
| 7 | DNMT3A | 46,XX | 88% | monoblasts, pomonocytes | CD34+, HLA-DR+ | |
| FLT3 | vacuolisation | MPO+, CD13+, CD33+, CD117+ | ||||
| NPM1 | monolobulated, convoluted | CD64++ | ||||
| 3xWT1 | basophil cytoplasm margin | |||||
| 8 | TET2 | CK | 92% | pseudopodes | CD34+, HLA-DR+ | |
| KRAS | monoblasts, pomonocytes | MPO+, CD13+, CD33+, CD117+ | ||||
| vacuolisation | CD4+, CD14+,CD15+, CD64+ | |||||
| monolobulated, convoluted | CD10+, CD56+ | |||||
| basophil cytoplasm margin | ||||||
| promoncytes | ||||||
| 9 | DNMT3A | 46,XY | 44% | monoblasts, pomonocytes | CD34+, HLA-DR+ | |
| NPM1 | vacuolisation | MPO+, CD13+, CD33+, CD117+ | ||||
| NRAS | monolobulated, oval | CD4+, CD14+, CD15+, CD64+ | ||||
| basophil cytoplasm margin | ||||||
| 10 | FLT3 | 11q23 | 92% | monoblasts | CD34-, HLA-DR- | |
| vacuolisation | MPO-, CD13-, CD33+, CD117+ | |||||
| monolobulated, oval | CD15+, CD64++ | |||||
| basophil cytoplasm margin | CD56dim | |||||
| 11 | NPM1 | 46,XX | 56% | monoblasts, pomonocytes | CD34dim, HLA-DR- | |
| vacuolisation | MPO+, CD13+, CD33+, CD117+ | |||||
| monolobulated, convoluted | CD4+, CD14+, CD15+ | |||||
| basophil cytoplasm margin | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Strasser, B.; Mustafa, S.; Seier, J.; Tomasits, J.; Haushofer, A. Hematopathological Patterns in Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Complications of Overt Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15030383
Strasser B, Mustafa S, Seier J, Tomasits J, Haushofer A. Hematopathological Patterns in Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Complications of Overt Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(3):383. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15030383
Chicago/Turabian StyleStrasser, Bernhard, Sebastian Mustafa, Josef Seier, Josef Tomasits, and Alexander Haushofer. 2025. "Hematopathological Patterns in Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Complications of Overt Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation" Diagnostics 15, no. 3: 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15030383
APA StyleStrasser, B., Mustafa, S., Seier, J., Tomasits, J., & Haushofer, A. (2025). Hematopathological Patterns in Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Complications of Overt Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation. Diagnostics, 15(3), 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15030383






