Changes in the Relationship Between Gray Matter, Functional Parameters, and Quality of Life in Patients with a Post-Stroke Spastic Upper Limb After Single-Event Multilevel Surgery: Six-Month Results from a Randomized Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
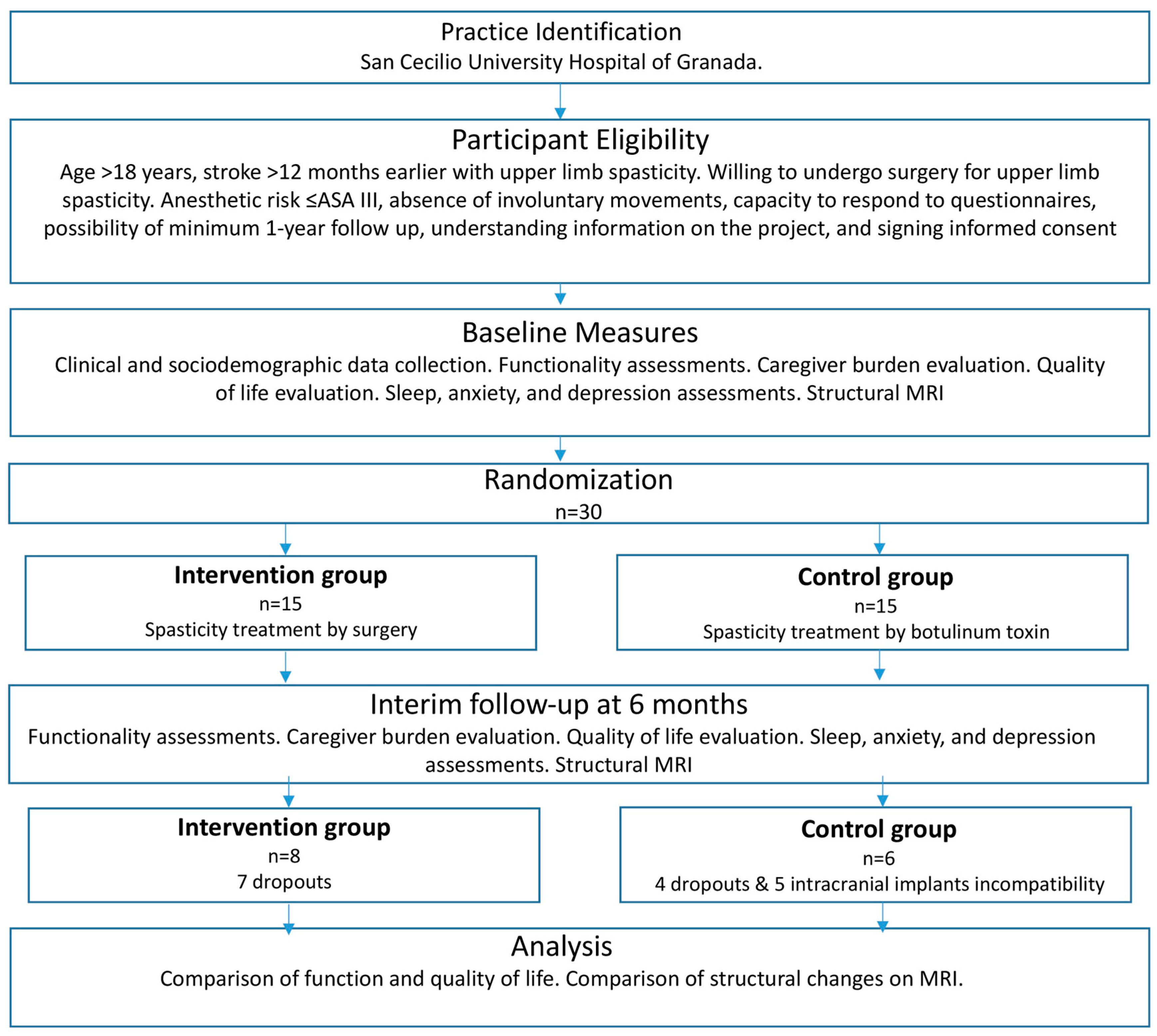
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Patients
2.3. Experimental Group
2.4. Control Group
2.5. Data Collection
2.6. Clinical Evaluation
2.6.1. Evaluation of Upper Limb Functionality
- Modified Ashworth scale for spasticity [28]. The score ranges from 0 to 5. The result is positive when significant improvement is achieved in at least one of the five sites evaluated (elbow, forearm, wrist, thumb, fingers).
- Nine-point hand function scale by House [29].
- Fugl-Meyer post-stroke recovery scale for shoulder, elbow, wrist, and hand domains with 33 items scored on a three-point scale (0–2), with a total score ranging from 0 to 66 [30].
2.6.2. Evaluation of Hygienic/Nonfunctional Outcomes
2.6.3. Evaluation of Quality of Life
2.6.4. Evaluation of Quality of Sleep, Anxiety, and Depression
2.7. MRI Assessment and Segmentation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feigin, V.L.; Stark, B.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Roth, G.A.; Bisignano, C.; Abady, G.G.; Abbasifard, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abedi, V.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Stroke and Its Risk Factors, 1990–2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 795–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjellström, T.; Norrving, B.; Shatchkute, A. Helsingborg Declaration 2006 on European Stroke Strategies. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2007, 23, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angulo-Parker, F.J.; Adkinson, J.M. Common Etiologies of Upper Extremity Spasticity. Hand Clin. 2018, 34, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carod-Artal, J.; Egido, J.A.; González, J.L.; Varela De Seijas, E. Quality of Life Among Stroke Survivors Evaluated 1 Year After Stroke: Experience of a Stroke Unit. Stroke 2000, 31, 2995–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nudo, R.J.; Plautz, E.J.; Frost, S.B. Role of Adaptive Plasticity in Recovery of Function after Damage to Motor Cortex. Muscle Nerve 2001, 24, 1000–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Liu, X.; Bao, C.; Wei, F.; Gong, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, J. Advanced Non-Invasive MRI of Neuroplasticity in Ischemic Stroke: Techniques and Applications. Life Sci. 2020, 261, 118365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleim, J.A.; Jones, T.A. Principles of Experience-Dependent Neural Plasticity: Implications for Rehabilitation After Brain Damage. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2008, 51, S225–S239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradke, F. Mechanisms of Axon Growth and Regeneration: Moving between Development and Disease. J. Neurosci. 2022, 42, 8393–8405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Deng, W.; Gage, F.H. Mechanisms and Functional Implications of Adult Neurogenesis. Cell 2008, 132, 645–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Dong, R.; Wang, X.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhao, L. Neuroimaging of Motor Recovery after Ischemic Stroke—Functional Reorganization of Motor Network. NeuroImage Clin. 2024, 43, 103636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen-Berg, H.; Dawes, H.; Guy, C.; Smith, S.M.; Wade, D.T.; Matthews, P.M. Correlation between Motor Improvements and Altered fMRI Activity after Rehabilitative Therapy. Brain 2002, 125, 2731–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, T.; Wissel, J. Treatment of spasticity after stroke. Neurol. Rehabil. 2013, 19, 285–309. [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzler, A.; Ruet, A.; Baron, S.; Buzzi, J.-C.; Genet, F. Botulinum Toxin A for Treating Spasticity in Adults: Costly for French Hospitals? Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2015, 58, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morone, G.; Baricich, A.; Paolucci, S.; Bentivoglio, A.R.; De Blasiis, P.; Carlucci, M.; Violi, F.; Levato, G.; Pani, M.; Carpagnano, L.F.; et al. Long-Term Spasticity Management in Post-Stroke Patients: Issues and Possible Actions—A Systematic Review with an Italian Expert Opinion. Healthcare 2023, 11, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diserens, K.; Ruegg, D.; Kleiser, R.; Hyde, S.; Perret, N.; Vuadens, P.; Fornari, E.; Vingerhoets, F.; Seitz, R.J. Effect of Repetitive Arm Cycling Following Botulinum Toxin Injection for Poststroke Spasticity: Evidence From fMRI. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2010, 24, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomášová, Z.; Hluštík, P.; Král, M.; Otruba, P.; Herzig, R.; Krobot, A.; Kaňovský, P. Cortical Activation Changes in Patients Suffering from Post-Stroke Arm Spasticity and Treated with Botulinum Toxin A. J. Neuroimaging 2013, 23, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veverka, T.; Hluštík, P.; Hok, P.; Otruba, P.; Tüdös, Z.; Zapletalová, J.; Krobot, A.; Kaňovský, P. Cortical Activity Modulation by Botulinum Toxin Type A in Patients with Post-Stroke Arm Spasticity: Real and Imagined Hand Movement. J. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 346, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, M.J.; Gardner, A.J.; Wojtowicz, M.; Williams, W.H.; Iverson, G.L.; Stanwell, P. Task-Related Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Activations in Patients with Acute and Subacute Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: A Coordinate-Based Meta-Analysis. NeuroImage Clin. 2020, 25, 102129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergfeldt, U.; Jonsson, T.; Bergfeldt, L.; Julin, P. Cortical Activation Changes and Improved Motor Function in Stroke Patients after Focal Spasticity Therapy–an Interventional Study Applying Repeated fMRI. BMC Neurol. 2015, 15, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinehout, K.; Tynes, K.; Sotelo, M.R.; Hyngstrom, A.S.; McGuire, J.R.; Schmit, B.D. Changes in Cortical Activity in Stroke Survivors Undergoing Botulinum Neurotoxin Therapy for Treatment of Focal Spasticity. Front. Rehabilit. Sci. 2021, 2, 735819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, P.C. Surgical Management of Upper Extremity Deformities in Patients With Upper Motor Neuron Syndrome. J. Hand Surg. 2019, 44, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gschwind, C.R.; Yeomans, J.L.; Smith, B.J. Upper Limb Surgery for Severe Spasticity after Acquired Brain Injury Improves Ease of Care. J. Hand Surg. Eur. Vol. 2019, 44, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holden, M.K.; Gill, K.M.; Magliozzi, M.R. Gait Assessment for Neurologically Impaired Patients. Phys. Ther. 1986, 66, 1530–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; McHugh, P.R. “Mini-Mental State”. A Practical Method for Grading the Cognitive State of Patients for the Clinician. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1975, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohoney, F.; Barthel, D. Functional evaluation: The Barthel Index. Md State Med. 1965, 14, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Dripps, R.D. American Society of Anesthesiologists. New classification of physical status. Anesthesiology 1963, 24, 111. [Google Scholar]
- Keenan, M.A.E.; Abrams, R.A.; Garland, D.E.; Waters, R.L. Results of Fractional Lengthening of the Finger Flexors in Adults with Upper Extremity Spasticity. J. Hand Surg. 1987, 12, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohannon, R.W.; Smith, M.B. Interrater Reliability of a Modified Ashworth Scale of Muscle Spasticity. Phys. Ther. 1987, 67, 206–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, J.; Gwathmey, F.; Fidler, M. A dynamic approach to the thumb-in palm deformity in cerebral palsy. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1981, 63, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugl-Meyer, A.; Jääskö, L.; Leyman, I.; Olsson, S.; Steglind, S. The post-stroke hemiplegic patient. 1. a method for evaluation of physical performance. Scand. J. Rehabil. Med. 1975, 7, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasny-Pacini, A.; Hiebel, J.; Pauly, F.; Godon, S.; Chevignard, M. Goal Attainment Scaling in Rehabilitation: A Literature-Based Update. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2013, 56, 212–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijur, P.E.; Silver, W.; Gallagher, E.J. Reliability of the Visual Analog Scale for Measurement of Acute Pain. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2001, 8, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, J.; Prieto, L.; Antó, J.M. La versión española del SF-36 Health Survey (Cuestionario de Salud SF-36): Un instrumento para la medida de los resultados clínicos. Med. Clín. 1995, 104, 771–776. [Google Scholar]
- Buck, D.; Jacoby, A.; Massey, A.; Steen, N.; Sharma, A.; Ford, G.A. Development and Validation of NEWSQOL®, the Newcastle Stroke-Specific Quality of Life Measure. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2004, 17, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buysse, D.J. Sleep Health: Can We Define It? Does It Matter? Sleep 2014, 37, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero, M.J.; Blanch, J.; Peri, J.M.; De Pablo, J.; Pintor, L.; Bulbena, A. A Validation Study of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) in a Spanish Population. General. Hosp. Psychiatry 2003, 25, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjón, J.V.; Coupé, P. volBrain: An Online MRI Brain Volumetry System. Front. Neuroinformatics 2016, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannoun, S.; Tutunji, R.; El Homsi, M.; Saaybi, S.; Hourani, R. Automatic Thalamus Segmentation on Unenhanced 3D T1 Weighted Images: Comparison of Publicly Available Segmentation Methods in a Pediatric Population. Neuroinformatics 2019, 17, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.K.; Singh, K.K. A Review of Publicly Available Automatic Brain Segmentation Methodologies, Machine Learning Models, Recent Advancements, and Their Comparison. Ann. Neurosci. 2021, 28, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjón, J.V.; Coupé, P.; Martí-Bonmatí, L.; Collins, D.L.; Robles, M. Adaptive Non-local Means Denoising of MR Images with Spatially Varying Noise Levels. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2010, 31, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, S.C.; Riley, J.D. Neuroplasticity and Brain Repair after Stroke. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2008, 21, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lazzaro, V.; Dileone, M.; Pilato, F.; Capone, F.; Musumeci, G.; Ranieri, F.; Ricci, V.; Bria, P.; Di Iorio, R.; De Waure, C.; et al. Modulation of Motor Cortex Neuronal Networks by rTMS: Comparison of Local and Remote Effects of Six Different Protocols of Stimulation. J. Neurophysiol. 2011, 105, 2150–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhardt, J.; Hayward, K.S.; Kwakkel, G.; Ward, N.S.; Wolf, S.L.; Borschmann, K.; Krakauer, J.W.; Boyd, L.A.; Carmichael, S.T.; Corbett, D.; et al. Agreed Definitions and a Shared Vision for New Standards in Stroke Recovery Research: The Stroke Recovery and Rehabilitation Roundtable Taskforce. Int. J. Stroke 2017, 12, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, E.S.; Coshall, C.; Dundas, R.; Stewart, J.; Rudd, A.G.; Howard, R.; Wolfe, C.D.A. Estimates of the Prevalence of Acute Stroke Impairments and Disability in a Multiethnic Population. Stroke 2001, 32, 1279–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, H.; Price, C. Stroke Unit Care, Inpatient Rehabilitation and Early Supported Discharge. Clin. Med. 2017, 17, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, K.; Wang, X.; Sun, C.; Zhu, B.; Xu, Y.; Fan, M.; Tong, S.; Guo, X.; et al. Motor Network Reorganization after Motor Imagery Training in Stroke Patients with Moderate to Severe Upper Limb Impairment. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graef, P.; Dadalt, M.L.R.; Rodrigués, D.A.M.D.S.; Stein, C.; Pagnussat, A.D.S. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Combined with Upper-Limb Training for Improving Function after Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 369, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Chen, R.; Wei, M.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, P.; Zhou, J.; He, P.; Zhan, X.; Xie, J.; Li, R.; et al. Effects of Radial Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Flexor Spasticity of the Upper Limb in Post-Stroke Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2024, 38, 1200–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanas-Valdés, R.; Serra-Llobet, P.; Rodriguez-Rubio, P.R.; López-de–Celis, C.; Llauró-Fores, M.; Calvo-Sanz, J. The Effectiveness of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Improving Upper Limb Spasticity and Functionality in Stroke Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Rehabil. 2020, 34, 1141–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihara, M.; Hattori, N.; Hatakenaka, M.; Yagura, H.; Kawano, T.; Hino, T.; Miyai, I. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy–Mediated Neurofeedback Enhances Efficacy of Motor Imagery–Based Training in Poststroke Victims: A Pilot Study. Stroke 2013, 44, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.M.; Lopez-Larraz, E.; Figueiredo, T.C.; Birbaumer, N.; Ramos-Murguialday, A. Movement-Related Brain Oscillations Vary with Lesion Location in Severely Paralyzed Chronic Stroke Patients. In Proceedings of the 2017 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 11–15 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 1664–1667. [Google Scholar]
- Beutel, B.G.; Marascalchi, B.J.; Melamed, E. Trends in Utilization of Upper Extremity Reconstructive Surgery Following Traumatic Brain Injury and Stroke. Hand 2020, 15, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavazzi, E.; Bergsland, N.; Pirastru, A.; Cazzoli, M.; Blasi, V.; Baglio, F. MRI Markers of Functional Connectivity and Tissue Microstructure in Stroke-Related Motor Rehabilitation: A Systematic Review. NeuroImage Clin. 2022, 33, 102931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veverka, T.; Hluštík, P.; Hok, P.; Otruba, P.; Zapletalová, J.; Tüdös, Z.; Krobot, A.; Kaňovský, P. Sensorimotor Modulation by Botulinum Toxin A in Post-Stroke Arm Spasticity: Passive Hand Movement. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 362, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veverka, T.; Hok, P.; Otruba, P.; Zapletalová, J.; Kukolová, B.; Tüdös, Z.; Krobot, A.; Kaňovský, P.; Hluštík, P. Botulinum Toxin Modulates Posterior Parietal Cortex Activation in Post-Stroke Spasticity of the Upper Limb. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, A.M.; Cacciante, L.; Schuler, A.-L.; Turolla, A.; Pellegrino, G. Cortical Thickness of Brain Areas Beyond Stroke Lesions and Sensory-Motor Recovery: A Systematic Review. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 764671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Ji, Y.-Y.; Yan, L.-F.; Lin, J.-J.; Li, Z.-Y.; Wang, W.; Li, J.-L.; Cui, G.-B. Gray Matter Volume Abnormality in Chronic Pain Patients With Depressive Symptoms: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis of Voxel-Based Morphometry Studies. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 826759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cameron, M.; Sejnowski, T. Predictive sequence learning in the hippocampal formation. Neuron 2024, 112, 2645–2658.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, T.J.; Pasalar, S. Cerebellum Predicts the Future Motor State. Cerebellum 2008, 7, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, D.; Li, M.; Tang, C.; Li, Z.; Xu, R.; Chan, C.C.H. Altered Gray Matter Volumes in Post-Stroke Depressive Patients after Subcortical Stroke. NeuroImage Clin. 2020, 26, 102224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Shuai, Y.; Wang, J.; Yan, J.; Lin, B.; Li, X.; Zhao, Z. Hippocampal Gray Matter Volume Alterations in Patients with First-Episode and Recurrent Major Depressive Disorder and Their Associations with Gene Profiles. BMC Psychiatry 2025, 25, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, S.C. Repairing the Human Brain after Stroke: I. Mechanisms of Spontaneous Recovery. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 63, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantopoulos, K.; Giakoumettis, D. Neuroimaging in Neurogenic Communication Disorders; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Trevarrow, M.P.; Lew, B.J.; Hoffman, R.M.; Taylor, B.K.; Wilson, T.W.; Kurz, M.J. Altered Somatosensory Cortical Activity Is Associated with Cortical Thickness in Adults with Cerebral Palsy: Multimodal Evidence from MEG/sMRI. Cereb. Cortex 2022, 32, 1286–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, B.R.; Williams, V.C.; Leigh, P.N.; Williams, S.C.R.; Blain, C.R.V.; Jarosz, J.M.; Simmons, A. Altered Cortical Activation during a Motor Task in ALS: Evidence for Involvement of Central Pathways. J. Neurol. 2007, 254, 1260–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xiong, F.; Gao, F.; Yu, B.; Tu, Y. Cortical Changes in the Brain of Patients with Hemifacial Spasm. Neurol. Sci. 2024, 45, 3209–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zheng, H.; Ma, Q.; Wang, C.; Fan, L.; Wu, H.; Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhan, Y. Cortical Damage Associated With Cognitive and Motor Impairment in Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia: Evidence of a Novel SPAST Mutation. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.-J.; Xing, X.-X.; Qu, J.; Wu, J.-J.; Hua, X.-Y.; Zheng, M.-X.; Xu, J.-G. Morphological alterations of contralesional hemisphere relate to functional outcomes after stroke. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2023, 58, 3347–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arachchige, P.; Karunarathna, S.; Wataru, U.; Ryo, U.; Median, A.; Yao, D.; Abo, M.; Senoo, A. Changes in brain morphometry after motor rehabilitation in chronic stroke. Somatosens. Motor Res. 2021, 38, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abela, A.R.; Chudasama, Y. Dissociable Contributions of the Ventral Hippocampus and Orbitofrontal Cortex to Decision-making with a Delayed or Uncertain Outcome. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2013, 37, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapaliya, K.; Marshall-Gradisnik, S.; Staines, D.; Su, J.; Barnden, L. Alteration of Cortical Volume and Thickness in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 848730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Gay, L.; Conti Nibali, M.; Sciortino, T.; Ambrogi, F.; Leonetti, A.; Puglisi, G.; Howells, H.; Zito, P.; Villa, F.; et al. Challenging Giant Insular Gliomas With Brain Mapping: Evaluation of Neurosurgical, Neurological, Neuropsychological, and Quality of Life Results in a Large Mono-Institutional Series. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 629166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.-T.; Wu, J.-J.; Ma, J.; Xing, X.-X.; Zhang, J.-P.; Hua, X.-Y.; Zheng, M.-X.; Xu, J.-G. Peripheral Nerve Transfers for Dysfunctions in Central Nervous System Injuries: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Surg. 2024, 110, 3814–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Baseline | Six Months | Rate of Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Control | Experimental | Control | Experimental | Control | Experimental |
| n | 10 | 15 | 6 | 8 | ||
| Male sex | 7 | 6 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Ashworth | 3.9 (±0.38) | 4.93 (±0.23) | 3.83 (±0.60) | 2.63 (±0.38) | −0.02 | −0.47 |
| House | 1.70 (±0.60) | 1.67 (±0.41) | 1.67 (±0.67) | 2.63 (±0.68) | −0.02 | 0.57 |
| Keenan | 4.10 (±0.53) | 4.33 (±0.36) | 2.83 (±0.83) | 1.63 (±0.50) | −0.31 | −0.62 |
| Fugl Mayer | 44.9 (±9.28) | 49.6 (±6.47) | 44.5 (±12.3) | 62.75 (±8.18) | −0.01 | 0.27 |
| Carer Burden | 6.50 (±1.56) | 7.40 (±0.76) | 5.33 (±1.96) | 1.50 (±1.22) | −0.18 | −0.80+ |
| Pain Evaluation | 4.70 (±0.58) | 4.87 (±1.01) | 5.33 (±0.56) | 1.75 (±0.75) | 0.13 | −0.64 ** |
| Newcastle | 8.50 (±0.83) | 7.51 (±0.69) | 8.85 (±1.2) | 5.95 (±0.60) | 0.04 | −0.21 * |
| SF36 | 51.5 (±7.59) | 52.77 (±5.73) | 46.02 (±11) | 51.28 (±7.79) | −0.11 | −0.03 |
| Age | 58.8 (±2.99) | 57.93 (±2.88) | 58.5 (±4.08) | 58.63 (±4.82) | −0.01 | 0.01 |
| Ashworth | House | Keenan | Fugl Mayer | Carer Burden | Pain Evaluation | Newcastle | SF-36 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | −0.058 | −0.048 | −0.267 | 0.136 | −0.048 | −0.056 | −0.026 | 0.025 |
| Experimental | −0.460 | 0.750 | −0.575 | 0.526 | −0.852 | −0.323 | −0.180 | 0.034 |
| p-value | 0.002 | 0.080 | 0.160 | 0.360 | 0.080 | 0.050 | 0.230 | 0.100 |
| (a) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Volumes (cm3) | Control | Experimental | p-Value |
| Cerebellum left | −0.032 | 0.065 | 0.020 |
| Cerebellum WM total | −0.017 | 0.114 | 0.010 |
| Hippocampus total | −0.032 | 0.177 | 0.020 |
| GRe total | −0.052 | 0.237 | 0.010 |
| GRe left | −0.083 | 0.212 | 0.010 |
| MSFG right | −0.021 | 0.465 | 0.020 |
| STG total | −0.015 | 0.789 | 0.020 |
| STG right | −0.020 | 0.463 | 0.010 |
| Cun left | −0.021 | 0.504 | 0.020 |
| OFuG left | −0.017 | 0.273 | 0.020 |
| (b) | |||
| Thickness (mm) | Control | Experimental | p-Value |
| FRP right | −0.055 | 0.354 | 0.005 |
| AOrG total | −0.076 | 0.032 | 0.008 |
| POrG right | −0.041 | 0.232 | 0.008 |
| PP asym | −0.067 | 0.137 | 0.020 |
| ITG asym | −0.067 | 0.212 | 0.008 |
| Calc total | −0.074 | 0.286 | 0.003 |
| Calc left | −0.149 | 4.844 | 0.008 |
| Calc asym | −0.074 | 0.142 | 0.020 |
| LiG asym | −0.034 | 0.113 | 0.020 |
| OFuG right | −0.037 | 0.121 | 0.005 |
| IOG total | −0.036 | 0.304 | 0.020 |
| MOG right | −0.038 | 0.242 | 0.008 |
| MOG asym | −0.055 | 0.077 | 0.013 |
| SOG right | −0.050 | 0.108 | 0.003 |
| Volume (cm3) | Keenan | Fugl-Meyer | Newcastle |
|---|---|---|---|
| TrIFG right | 2.87 (−0.89/0.57) | - | - |
| IOG left | - | −3.26 (−0.76/0.88) | - |
| PIns left | - | −3.25 (−0.32/097) | - |
| Vermis | - | - | −3.01 (−0.96/0.30) |
| AnG total | - | - | 3.30 (0.97/−0.29) |
| Thickness (mm) | Ashworth | House | Keenan | Fugl-Meyer | Carer Burden | SF36 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMC total | −2.9 (−0.95/0.27) | - | - | - | - | - |
| Temporal total | −3.4 (−0.97/0.35) | - | - | - | - | - |
| PCu left | 3.4 (0.90/−0.75) | - | - | - | - | - |
| Occipital left | −2.8 (−0.88/0.55) | - | - | - | - | - |
| Insular total | −2.7 (−0.93/0.31) | - | - | - | - | - |
| OFuG asym | - | −3.2 (−0.98/−0.03) | - | - | - | - |
| TTG left | - | - | 3.5 (0.98/−0.31) | - | - | - |
| Parietal right | - | - | - | 2.7 (0.88/−0.51) | - | - |
| POrG left | - | - | - | - | 3.3 (0.72/−0.90) | −3.62 (−0.78/0.92) |
| PoG asym | - | - | - | - | 2.6 (0.96/0.04) | - |
| MOG left | - | - | - | - | - | −3.59 (−0.93/0.75) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hurtado-Olmo, P.; Hernández-Cortés, P.; González-Santos, Á.; Zuñiga-Gómez, L.; Del Olmo-Iruela, L.; Catena, A. Changes in the Relationship Between Gray Matter, Functional Parameters, and Quality of Life in Patients with a Post-Stroke Spastic Upper Limb After Single-Event Multilevel Surgery: Six-Month Results from a Randomized Trial. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15081020
Hurtado-Olmo P, Hernández-Cortés P, González-Santos Á, Zuñiga-Gómez L, Del Olmo-Iruela L, Catena A. Changes in the Relationship Between Gray Matter, Functional Parameters, and Quality of Life in Patients with a Post-Stroke Spastic Upper Limb After Single-Event Multilevel Surgery: Six-Month Results from a Randomized Trial. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(8):1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15081020
Chicago/Turabian StyleHurtado-Olmo, Patricia, Pedro Hernández-Cortés, Ángela González-Santos, Lourdes Zuñiga-Gómez, Laura Del Olmo-Iruela, and Andrés Catena. 2025. "Changes in the Relationship Between Gray Matter, Functional Parameters, and Quality of Life in Patients with a Post-Stroke Spastic Upper Limb After Single-Event Multilevel Surgery: Six-Month Results from a Randomized Trial" Diagnostics 15, no. 8: 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15081020
APA StyleHurtado-Olmo, P., Hernández-Cortés, P., González-Santos, Á., Zuñiga-Gómez, L., Del Olmo-Iruela, L., & Catena, A. (2025). Changes in the Relationship Between Gray Matter, Functional Parameters, and Quality of Life in Patients with a Post-Stroke Spastic Upper Limb After Single-Event Multilevel Surgery: Six-Month Results from a Randomized Trial. Diagnostics, 15(8), 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15081020








