Dynamic Quantitative Imaging of the Masseter Muscles in Bruxism Patients with Myofascial Pain: Could It Be an Objective Biomarker?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Consideration
2.2. Study Design
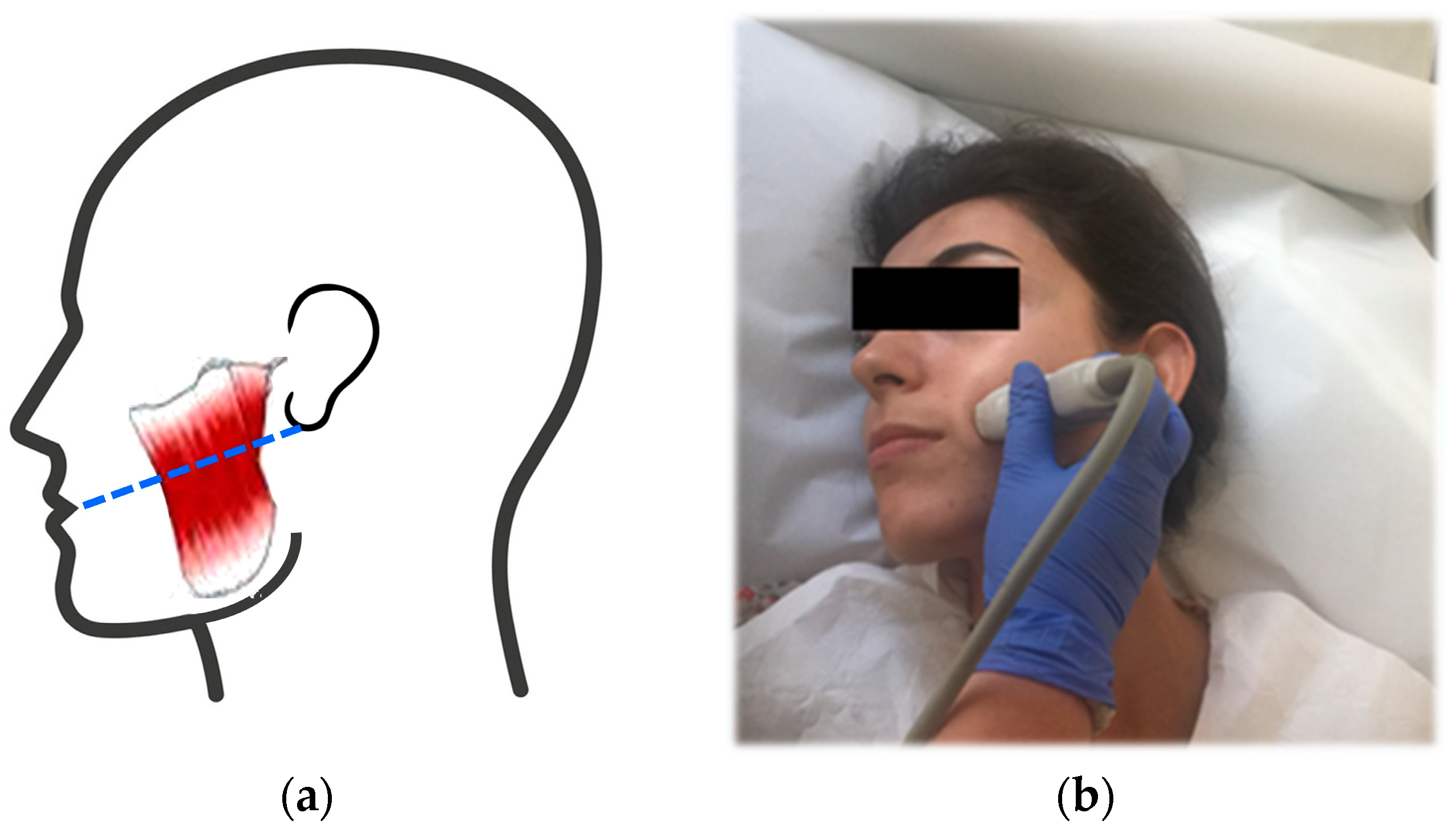
2.3. Imaging and Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Library of Medicine. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=bruxism&filter=datesearch.y_10 (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- Lobbezoo, F.; Ahlberg, J.; Glaros, A.G.; Kato, T.; Koyano, K.; Lavigne, G.J.; de Leeuw, R.; Manfredini, D.; Svensson, P.; Winocur, E. Bruxism defined and graded: An international consensus. J. Oral Rehabil. 2013, 40, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavigne, G.J.; Khoury, S.; Abe, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Raphael, K. Bruxism physiology and pathology: An overview for clinicians. J. Oral Rehabil. 2008, 35, 476–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, N.; Tabatabaei, A.H.; Mohammadi, M.; Rajabi, A. Is bruxism associated with temporomandibular joint disorders? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid. Based Dent. 2023, 24, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffman, E.; Ohrbach, R.; Truelove, E.; Look, J.; Anderson, G.; Goulet, J.-P.; List, T.; Svensson, P.; Gonzalez, Y.; Lobbezoo, F.; et al. Orofacial Pain Special Interest Group, International Association for the Study of Pain. Diagnostic Criteria for Temporomandibular Disorders (DC/TMD) for Clinical and Research Applications: Recommendations of the International RDC/TMD Consortium Network* and Orofacial Pain Special Interest Group. J. Oral Facial Pain Headache 2014, 28, 6–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobbezoo, F.; Ahlberg, J.; Raphael, K.G.; Wetselaar, P.; Glaros, A.G.; Kato, T.; Santiago, V.; Winocur, E.; De Laat, A.; De Leeuw, R.; et al. International consensus on the assessment of bruxism: Report of a work in progress. J. Oral Rehabil. 2018, 45, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredini, D.; Ahlberg, J.; Aarab, G.; Bender, S.; Bracci, A.; Cistulli, P.A.; Conti, P.C.; De Leeuw, R.; Durham, J.; Emodi-Perlman, A.; et al. Standardised Tool for the Assessment of Bruxism. J. Oral Rehabil. 2023. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klauser, A.S.; Miyamoto, H.; Bellmann-Weiler, R.; Feuchtner, G.M.; Wick, M.C.; Jaschke, W.R. Sonoelastography: Musculoskeletal applications. Radiology 2014, 272, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chino, K.; Akagi, R.; Dohi, M.; Fukashiro, S.; Takahashi, H. Reliability and validity of quantifying absolute muscle hardness using ultrasound elastography. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, C.F.; Barr, R.G.; Farrokh, A.; Dighe, M.; Hocke, M.; Jenssen, C.; Dong, Y.; Saftoiu, A.; Havre, R.F. Strain Elastography-How to Do It? Ultrasound Int. Open 2017, 3, E137–E149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfredini, D.; Winocur, E.; Guarda-Nardini, L.; Paesani, D.; Lobbezoo, F. Epidemiology of bruxism in adults: A systematic review of the literature. J. Orofac. Pain 2013, 27, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fluerasu, M.I.; Bocsan, I.C.; Tig, I.A.; Iacob, S.M.; Popa, D.; Buduru, S. The Epidemiology of Bruxism in Relation to Psychological Factors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olchowy, A.; Wieckiewicz, M.; Winocur, E.; Dominiak, M.; Dekkers, I.; Łasecki, M.; Olchowy, C. Great potential of ultrasound elastography for the assessment of the masseter muscle in patients with temporomandibular disorders. A systematic review. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2020, 49, 20200024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Chang, K.V.; Wu, W.T.; Ozcakar, L. Ultrasound measurements of superficial and deep masticatory muscles in various postures: Reliability and influencers. Sci. Rep. 2020, 1, 14357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, M.; Ghasemi, M.; Dehghan Manshdi, F.; Akbarzadeh Baghban, A. A Comparison of Ultrasonic Thickness of Masseter Muscle between Patients with Bruxism and Healthy People. J. Babol Univ. Med. Sci. 2017, 19, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Tetsuka, M.; Saga, T.; Nakamura, M.; Tabira, Y.; Kusukawa, J.; Yamaki, K. Relationship between masseter muscle form and occlusal supports of remaining teeth. Kurume Med. J. 2012, 59, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toker, C.; Marquetand, J.; Symmank, J.; Wahl, E.; Huettig, F.; Grimm, A.; Kleiser, B.; Jacobs, C.; Hennig, C.-L. Shear wave elastography in bruxism-not yet ready for clinical routine. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takashima, M.; Arai, Y.; Kawamura, A.; Hayashi, T.; Takagi, R. Quantitative evaluation of masseter muscle stiffness in patients with temporomandibular disorders using shear wave elastography. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2017, 61, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariji, Y.; Nakayama, M.; Nishiyama, W.; Nozawa, M.; Ariji, E. Shear-wave sonoelastography for assessing masseter muscle hardness in comparison with strain sonoelastography: Study with phantoms and healthy volunteers. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2016, 45, 20150251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arda, K.; Ciledag, N.; Aktas, E.; Arıbas, B.K.; Kose, K. Quantitative assessment of normal soft-tissue elasticity using shear-wave ultrasound elastography. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 197, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, J.; Sedlackova, Z.; Vachutka, J.; Furst, T.; Salzman, R.; Vomacka, J. Shear wave elastography parameters of normal soft tissues of the neck. Biomed. Pap. 2017, 161, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariji, Y.; Gotoh, A.; Hiraiwa, Y.; Kise, Y.; Nakayama, M.; Nishiyama, W.; Sakuma, S.; Kurita, K.; Ariji, E. Sonographic elastography for evaluation of masseter muscle hardness. Oral Radiol. 2013, 29, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, Y.M.; Ariji, Y.; Ferreira, D.M.A.O.; Bonjardim, L.R.; Conti, P.C.R.; Ariji, E.; Svensson, P. Muscle hardness and masticatory myofascial pain: Assessment and clinical relevance. J. Oral Rehabil. 2018, 45, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Chon, S. Assessments of muscle thickness and tonicity of the masseter and sternocleidomastoid muscles and maximum mouth opening in patients with temporomandibular disorder. Healthcare 2021, 9, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, S.J.; Weber, K.K. Bruxism Management; StatPearls Publishing: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482466/ (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- Garrigós-Pedrón, M.; La Touche, R.; Navarro-Desentre, P.; Gracia-Naya, M.; Segura-Ortí, E. Effects of a Physical Therapy Protocol in Patients with Chronic Migraine and Temporomandibular Disorders: A Randomized, Single-Blinded, Clinical Trial. J. Oral Facial Pain Headache 2018, 32, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marotta, N.; Ferrillo, M.; Demeco, A.; Ferrante, V.D.; Inzitari, M.T.; Pellegrino, R.; Pino, I.; Russo, I.; de Sire, A.; Ammendolia, A. Effects of Radial Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy in Reducing Pain in Patients with Temporomandibular Disorders: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, A.; Ahrari, F.; Fallahrastegar, A.; Daghestani, N. A randomized clinical trial comparing the efficacy of low-level laser therapy (LLLT) and laser acupuncture therapy (LAT) in patients with temporomandibular disorders. Lasers Med. Sci. 2020, 35, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcio, K.-H.-L.; Neto, C.-L.d.M.-M.; Pirovani, B.-O.; Dos Santos, D.-M.; Guiotti, A.-M.; Bertoz, A.-P.d.M. Relationship of bruxism with oral health-related quality of life and facial muscle pain in dentate individuals. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2022, 14, e385–e389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, S.; Rudisch, A.; Bodner, G.; Emshoff, R. The short-term effect of stabilization-type splints on the local asymmetry of masseter muscle sites. J. Oral Rehabil. 2001, 28, 1139–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ispirgil, E.; Erdoğan, S.B.; Akın, A.; Sakar, O. The hemodynamic effects of occlusal splint therapy on the masseter muscle of patients with myofascial pain accompanied by bruxism. Cranio J. Craniomandib. Pract. 2020, 38, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deregibus, A.; Ferrillo, M.; Piancino, M.G.; Domini, M.C.; de Sire, A.; Castroflorio, T. Are occlusal splints effective in reducing myofascial pain in patients with muscle-related temporomandibular disorders? A randomized-controlled trial. Turk. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 67, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olchowy, A.; Seweryn, P.; Olchowy, C.; Wieckiewicz, M. Assessment of the masseter stiffness in patients during conservative therapy for masticatory muscle disorders with shear wave elastography. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Measurement (mm) | MM | Relaxation (Mean ± SD) | Contraction (Mean ± SD) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness | Right | 10.16 ± 1.49 | 11.61 ± 1.85 | 0.000 * |
| (AP diameter) | Left | 9.86 ± 1.89 | 11.73 ± 2.02 | 0.000 * |
| Width | Right | 48.29 ± 1.45 | 44.15 ± 1.43 | 0.000 * |
| (TR diameter) | Left | 48.84 ± 1.63 | 43.58 ± 1.52 | 0.000 * |
| Masseter Muscle | Thickness (mm) | Width (mm) | Stiffness (kPa) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Status | Relaxation (Mean ± SD) | Contraction (Mean ± SD) | Relaxation (Mean ± SD) | Contraction (Mean ± SD) | Relaxation (Mean ± SD) | Contraction (Mean ± SD) | |
| Group A (n = 26) | 9.17 ± 0.40 | 10.97 ± 0.44 | 44.08 ± 1.24 | 43.57 ± 1.52 | 39.13 ± 4.52 | 44.04 ± 4.99 | |
| Group B (n = 26) | 10.38 ± 0.27 | 11.98 ± 0.32 | 50.55 ± 1.35 | 48.83 ± 1.64 | 27.73 ± 1.92 | 35.52 ± 2.64 | |
| Group A vs. Group B | Difference | 1.21 | 1.01 | 6.47 | 5.26 | 11.40 | 8.52 |
| CI | 0.23–2.18 | 0.13–2.14 | 2.78–10.17 | 0.77–9.76 | 3.07–19.75 | 1.84–18.87 | |
| p-value | 0.016 * | 0.081 ** | 0.001 * | 0.023 * | 0.008 * | 0.105 ** | |
| Masseter Muscle | Thickness (mm) | Width (mm) | Stiffness (kPa) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Status | Relaxation (Mean ± SD) | Contraction (Mean ± SD) | Relaxation (Mean ± SD) | Contraction (Mean ± SD) | Relaxation (Mean ± SD) | Contraction (Mean ± SD) | |
| Group AI (n = 14) | 9.73 ± 1.41 | 11.28 ± 1.52 | 49.60 ± 8.13 | 44.81 ± 7.44 | 26.91± 2.13 | 37.21 ± 3.06 | |
| Group AII (n = 12) | 10.45 ± 2.03 | 12.28 ± 0.52 | 46.90 ± 7.18 | 42.34 ± 7.48 | 38.16 ± 3.61 | 39.64 ± 4.03 | |
| Group AI vs. Group AII | Difference | 0.72 | 1.0 | 2.70 | 2.48 | 11.25 | 2.43 |
| CI | 0.34–1.78 | 0.21–2.2 | −1.76–7.15 | −1.79–6.75 | 3.40–19.12 | 7.63–12.50 | |
| p-value | 0.173 ** | 0.101 ** | 0.23 ** | 0.25 ** | 0.006 * | 0.629 ** | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aydin Aksu, S.; Kursoglu, P.; Turker, I.; Baskak, F.; Ozen Sutuven, E.; Meric, K.; Cabbar, F. Dynamic Quantitative Imaging of the Masseter Muscles in Bruxism Patients with Myofascial Pain: Could It Be an Objective Biomarker? J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13101467
Aydin Aksu S, Kursoglu P, Turker I, Baskak F, Ozen Sutuven E, Meric K, Cabbar F. Dynamic Quantitative Imaging of the Masseter Muscles in Bruxism Patients with Myofascial Pain: Could It Be an Objective Biomarker? Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2023; 13(10):1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13101467
Chicago/Turabian StyleAydin Aksu, Sibel, Pinar Kursoglu, Izim Turker, Fulya Baskak, Elifnaz Ozen Sutuven, Kaan Meric, and Fatih Cabbar. 2023. "Dynamic Quantitative Imaging of the Masseter Muscles in Bruxism Patients with Myofascial Pain: Could It Be an Objective Biomarker?" Journal of Personalized Medicine 13, no. 10: 1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13101467






