Differences in Radiosensitivity According to EGFR Mutation Status in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Clinical and In Vitro Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical
2.2. In Vitro
3. Results
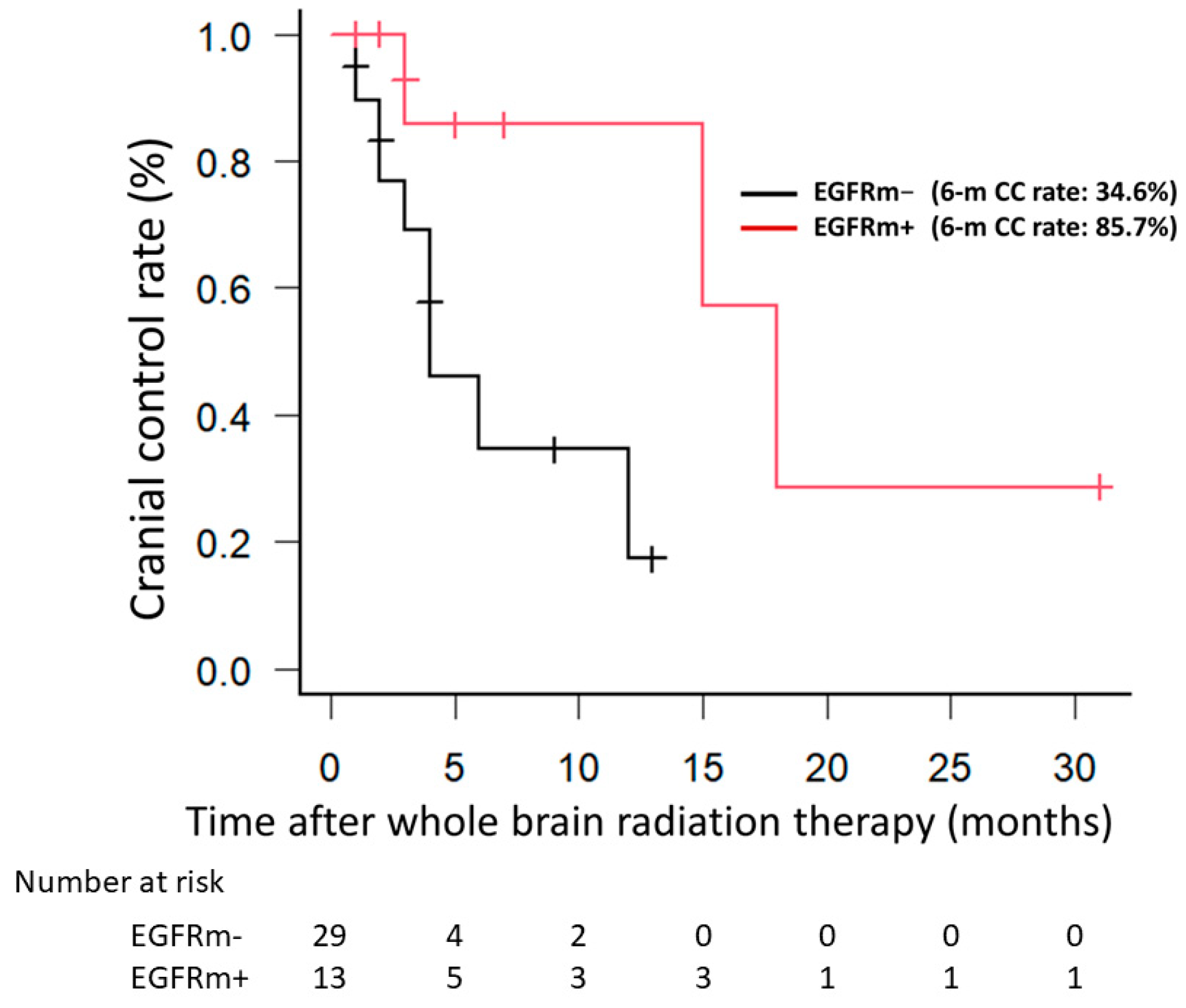
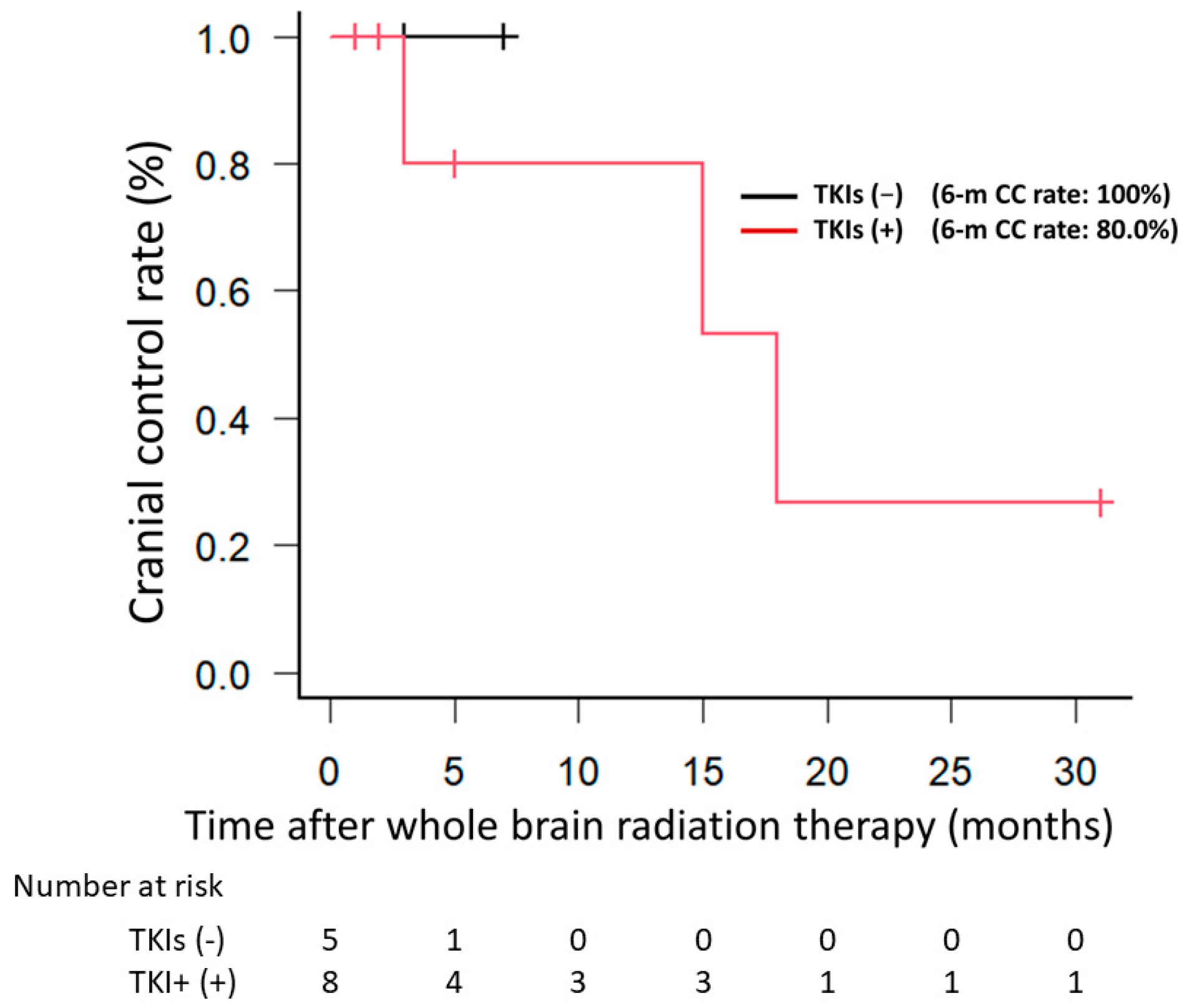
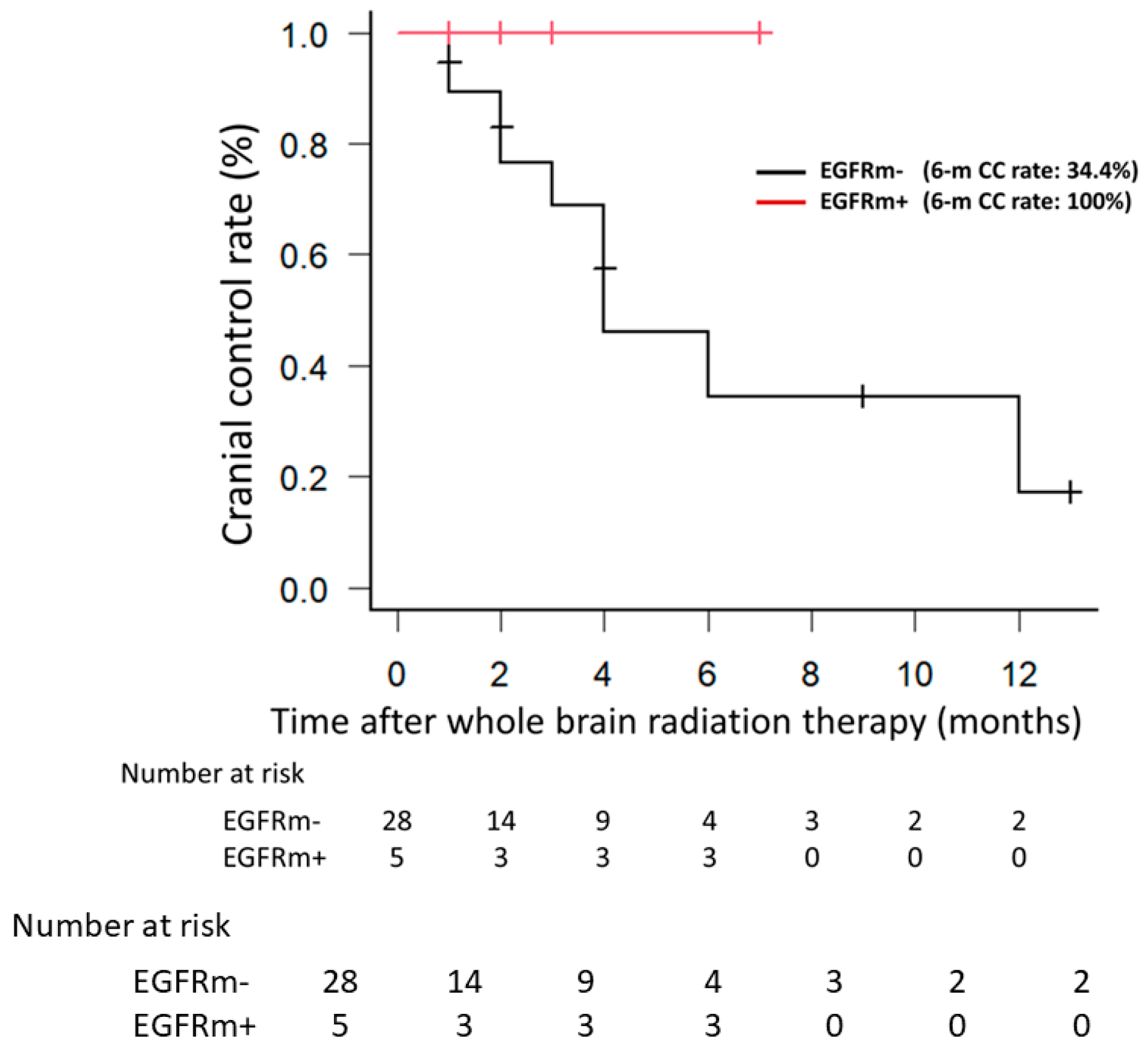
3.1. Clinical
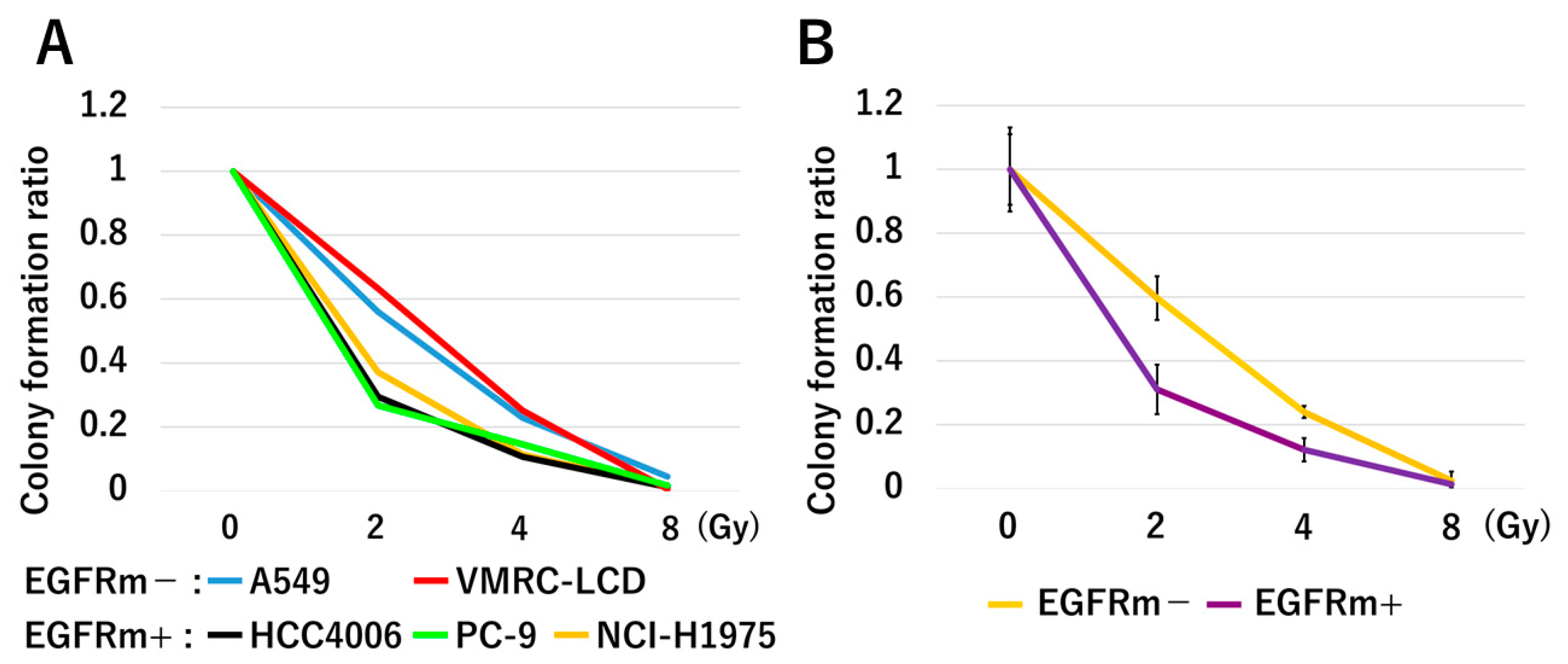
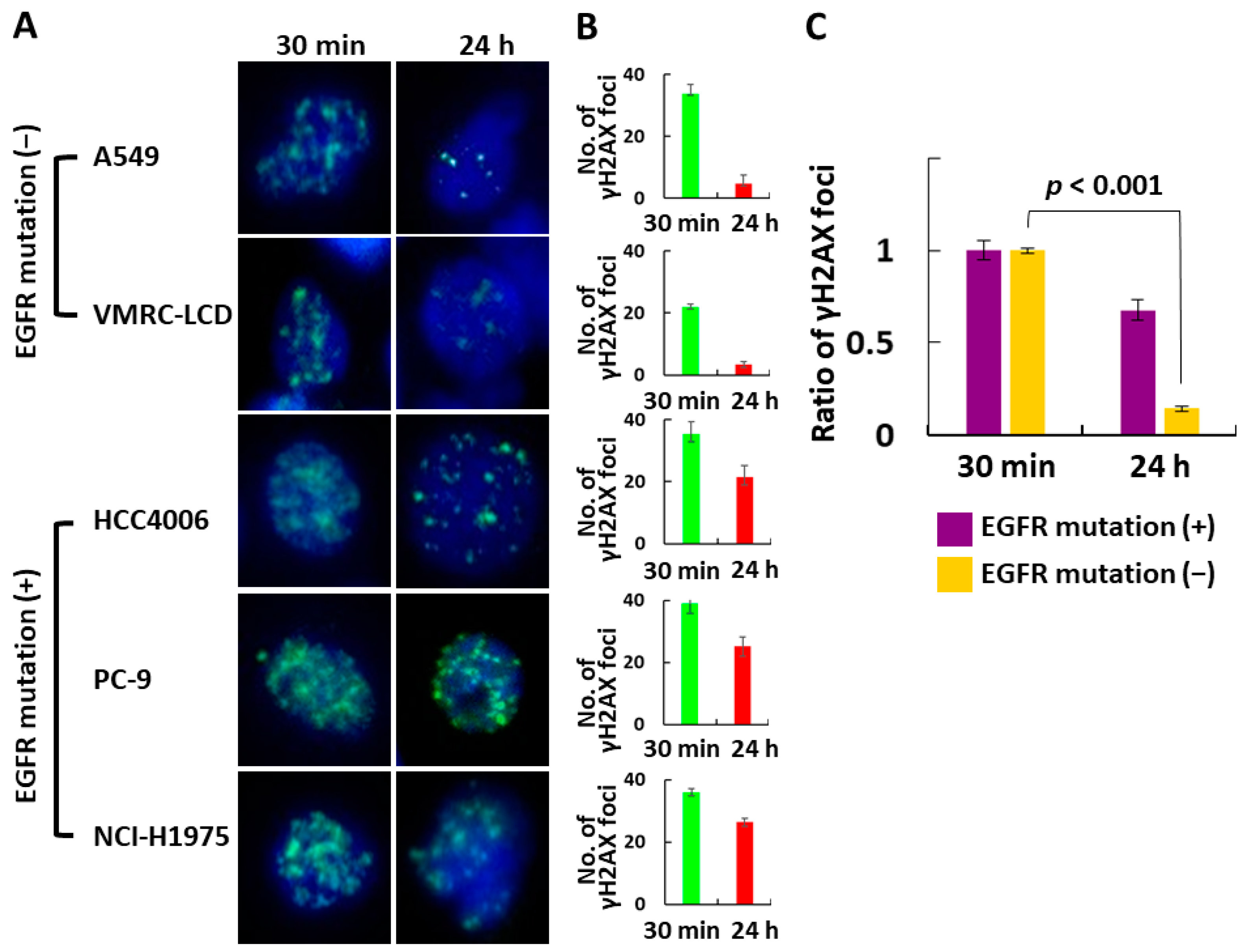
3.2. In Vitro
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Cancer Observatory. Cancer Today. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/home (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Ho, C.; Murray, N.; Laskin, J.; Melosky, B.; Anderson, H.; Bebb, G. Asian ethnicity and adenocarcinoma histology continues to predict response to gefitinib in patients treated for advanced non-small cell carcinoma of the lung in North America. Lung Cancer 2005, 49, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, T.; Mitsudomi, T. Mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor gene and effects of EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors on lung cancers. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2008, 56, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigematsu, H.; Takahashi, T.; Nomura, M.; Majmudar, K.; Suzuki, M.; Lee, H.; Wistuba, I.I.; Fong, K.M.; Toyooka, S.; Shimizu, N.; et al. Somatic mutations of the HER2 kinase domain in lung adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 1642–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pao, W.; Miller, V.; Zakowski, M.; Doherty, J.; Politi, K.; Sarkaria, I.; Singh, B.; Heelan, R.; Rusch, V.; Fulton, L.; et al. EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from “never smokers” and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib and erlotinib. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13306–13311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dearden, S.; Stevens, J.; Wu, Y.L.; Blowers, D. Mutation incidence and coincidence in non-small cell lung cancer: Meta-analyses by ethnicity and hisology (mutMap). Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2371–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midha, A.; Dearden, S.; McCormack, R. EGFR mutation incidence in non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology: A systematic review and global map by ethnicity (mutMAPII). Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 2892–2911. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, T.J.; Bell, D.W.; Sordella, R.; Gurubhagavatula, S.; Okimoto, R.A.; Brannigan, B.W.; Harris, P.L.; Haserlat, S.M.; Supko, J.G.; Haluska, F.G.; et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2129–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paez, J.G.; Jänne, P.A.; Lee, J.C.; Tracy, S.; Greulich, H.; Gabriel, S.; Herman, P.; Kaye, F.J.; Lindeman, N.; Boggon, T.J.; et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 2004, 304, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Version 3.203. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Ninomiya, K.; Teraoka, S.; Zenke, Y.; Kenmotsu, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Okuma, Y.; Tamiya, A.; Nosaki, K.; Morise, M.; Aokage, K.; et al. Japanese Lung Cancer Society Guidelines for Stage IV NSCLC with EGFR Mutations. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2020, 2, 100107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia. Depmap Portal. Available online: https://depmap.org/portal/ (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Kobayashi, Y.; Mitsudomi, T. Not all epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer are created equal: Perspectives for individualized treatment strategy. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, R.H.; Doran, E.; Muzikansky, A.; Kang, J.; Neal, J.W.; Baldini, E.H.; Choi, N.C.; Willers, H.; Jackman, D.M.; Sequist, L.V. Outcomes after combined modality therapy for EGFR-mutant and wild-type locally advanced NSCLC. Oncologist 2011, 16, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagishita, S.; Horinouchi, H.; Taniyama, T.K.; Nakamichi, S.; Kitazono, S.; Mizugaki, H.; Kanda, S.; Fujiwara, Y.; Nokihara, H.; Yamamoto, N.; et al. Epidermal growth factor mutation is associated with longerlocal control after definitive chemoradiotherapy in patients with stage III nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Pnhys 2015, 91, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akamatsu, H.; Kaira, K.; Murakami, H.; Serizawa, M.; Koh, Y.; Ono, A.; Shukuya, T.; Tsuya, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Kenmotsu, H.; et al. The impact of clinical outcomes according to EGFR mutation status in patients with locally advanced lung adenocarcinoma who received concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 37, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gow, C.H.; Chien, C.R.; Chang, Y.L.; Chiu, Y.H.; Kuo, S.H.; Shih, J.Y.; Chang, Y.C.; Yu, C.J.; Yang, C.H.; Yang, P.C. Radiotherapy in lung adenocarcinoma with brain metastases: Effects of activating epidermal growth factor receptor mutations on clinical response. Clin. Cancer Res 2008, 14, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichler, A.F.; Kahle, K.T.; Wang, D.L.; Joshi, V.A.; Willers, H.; Engelman, J.A.; Lynch, T.J.; Sequist, L.V. EGFR mutation status and survival after diagnosis of brain metastasis in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Neuro Oncol. 2010, 12, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johung, K.L.; Yao, X.; Li, F.; Yu, J.B.; Gettinger, S.N.; Goldberg, S.; Decker, R.H.; Hess, J.A.; Chiang, V.L.; Contessa, J.N. A clinical model for identifying radiosensitive tumor genotypes in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5523–5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodburn, J.R. The epidermal growth factor receptor and its inhibition in cancer therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 1999, 82, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Kern, A.M.; Hülskötter, M.; Greninger, P.; Singh, A.; Pan, Y.; Chowdhury, D.; Krause, M.; Baumann, M.; Benes, C.H.; et al. EGFR-mediated chromatin condensation protects KRAS-mutant cancer cells against ionizing radiation. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2825–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyati, M.K.; Morgan, M.A.; Feng, F.Y.; Lawrence, T.S. Integration of EGFR inhibitors with radiochemotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, D.B.; Contessa, J.N.; Mikkelsen, R.B.; Valerie, K.; Amir, C.; Dent, P.; Schmidt-Ullrich, R.K. Dominant negative EGFR-CD533 and inhibition of MAPK modify JNK1 activation and enhance radiation toxicity of human mammary carcinoma cells. Oncogene 1999, 18, 4756–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.; Hagekyriakou, J.; Trivett, M.K.; Stacker, S.A.; McArthur, G.A.; Cullinane, C. EGFR blockade with ZD1839 (“Iressa”) potentiates the antitumor effects of single and multiple fractions of ionizing radiation in human A431 squamous cell carcinoma. Epidermal growth factor receptor. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2003, 55, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheridan, M.T.; O’Dwyer, T.; Seymour, C.B.; Mothersill, C.E. Potential indicators of radiosensitivity in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Radiat. Oncol. Investig. 1997, 5, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimoto, T.; Hunter, N.R.; Buchmiller, L.; Mason, K.; Ang, K.K.; Milas, L. Inverse relationship between epidermal growth factor receptor expression and radiocurability of murine carcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 1999, 5, 2884–2890. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burdak-Rothkamm, S.; Rübe, C.E.; Nguyen, T.P.; Ludwig, D.; Feldmann, K.; Wiegel, T.; Rübe, C. Radiosensitivity of tumor cell lines after pretreatment with the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor ZD1839 (Iressa). Strahlenther. Onkol. 2005, 181, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.K.; Sato, M.; Story, M.D.; Peyton, M.; Graves, R.; Redpath, S.; Girard, L.; Gazdar, A.F.; Shay, J.W.; Minna, J.D.; et al. Non-small-cell lung cancers with kinase domain mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor are sensitive to ionizing radiation. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 9601–9608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anakura, M.; Nachankar, A.; Kobayashi, D.; Amornwichet, N.; Hirota, Y.; Shibata, A.; Oike, T.; Nakano, T. Radiosensitivity Differences between EGFR Mutatn and Wild-Type Lung Cancer Cells are Larger at Lower doses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postow, M.A.; Callahan, M.K.; Barker, C.A.; Yamada, Y.; Yuan, J.; Kitano, S.; Mu, Z.; Rasalan, T.; Adamow, M.; Ritter, E.; et al. Immunologic correlates of the abscopal effect in a patient with melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonia, S.J.; Villegas, A.; Daniel, D.; Vicente, D.; Murakami, S.; Hui, R.; Kurata, T.; Chiappori, A.; Lee, K.H.; de Wit, M.; et al. Overall survival with durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2342–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Luft, A.; Vicente, D.; Tafreshi, A.; Gümüş, M.; Mazières, J.; Hermes, B.; Çay Şenler, F.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy for squamous non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2040–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Ueda, K.; Karita, M.; Ono, T.; Manabe, Y.; Kajima, M.; Fujimoto, K.; Yuasa, Y.; Shiinoki, T. Immune checkpoint inhibitors after radiation therapy improve the overall survival in patients with stage IV lung cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondini, M.; Levy, A.; Meziani, L.; Milliat, F.; Deutsch, E. Radiotherapy-immunotherapy combinations-perspectives and chal-lenges. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 1529–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharabi, A.; Lim, M.; DeWeese, T.; Drake, C.G. Radiation and checkpoint blockade immunotherapy: Radiosensitisation and potential mechanisms of synergy. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e498–e509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Peng, H. STING-cytosolic DNA sensing: The backbone for an effective tumor radiation therapy. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Popp, I.; Grosu, A.L.; Niedermann, G.; Duda, D.G. Immune modulation by hypofractionated stereotactic radiation therapy: Therapeutic implications. Radiother. Oncol. 2016, 120, 158–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracia-Diaz, A.; Shin, D.S.; Moreno, B.H.; Saco, J.; Escuin-Ordinas, H.; Rodriguez, G.A.; Zaretsky, J.M.; Sun, L.; Hugo, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Interferon receptor signaling pathways regulating PD-L1 and PD-L2 expression. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 1189–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, N.U.; Wefel, J.S.; Lee, E.Q.; Schiff, D.; van den Bent, M.J.; Soffietti, R.; Suh, J.H.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; Mehta, M.P.; Dancey, J.; et al. Challenges relating to solid tumour brain metastases in clinical trials, part 2: Neurocognitive, neurological, and quality-of-life outcomes. A report from the RANO group. Lancet 2013, 14, e407–e416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.D.; Gondi, V.; Pugh, S.; Tome, W.A.; Wefel, J.S.; Armstrong, T.S.; Bovi, J.A.; Robinson, C.; Konski, A.; Khuntia, D.; et al. Hippocampal Avoidance During Whole-Brain Radiotherapy Plus Memantine for Patients With Brain Metastases: Phase III Trial NRG Oncology CC001. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vees, H.; Caparrotti, F.; Eboulet, E.I.; Xyrafas, A.; Fuhrer, A.; Meier, U.; Mark, M.; Elicin, O.; Aebersold, D.M.; Zwahlen, D.R.; et al. Impact of Early Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation With Hippocampal Avoidance on Neurocognitive Function in Patients With Limited Disease Small Cell Lung Cancer. A Multicenter Phase 2 Trial (SAKK 15/12). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 107, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelbaum, M.A.; Brown, P.D.; Messersmith, H.; Brastianos, P.K.; Burri, S.; Cahill, D.; Dunn, I.F.; Gaspar, L.E.; Gatson, N.T.N.; Gondi, V.; et al. Treatment for Brain Metastases: ASCO-SNO-ASTRO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 492–516, Erratum in J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondi, V.; Bauman, G.; Bradfield, L.; Burri, S.H.; Cabrera, A.R.; Cunningham, D.A.; Eaton, B.R.; Hattangadi-Gluth, J.A.; Kim, M.M.; Kotecha, R.; et al. Radiation Therapy for Brain Metastases: An ASTRO Clinical Practice Guideline. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 12, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Gantery, M.M.; Abd El Baky, H.M.; El Hossieny, H.A.; Mahmoud, M.; Youssef, O. Management of brain metastases with stereotactic radiosurgery alone versus whole brain irradiation alone versus both. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.D.; Jaeckle, K.; Ballman, K.V.; Farace, E.; Cerhan, J.H.; Anderson, S.K.; Carrero, X.W.; Barker, F.G., 2nd; Deming, R.; Burri, S.H.; et al. Effect of Radiosurgery Alone vs Radiosurgery With Whole Brain Radiation Therapy on Cognitive Function in Patients With 1 to 3 Brain Metastases: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 316, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Description | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male/female | 28 (66.7)/14 (33.3) |
| Age (years) | 68 (33–84) | |
| Pathology | Adenocarcinoma | 34 (81.0) |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 4 (9.5) | |
| Pleomorphic canrcinoma | 1 (2.4) | |
| Large cell carcinoma | 1 (2.4) | |
| NSCLC, NOS | 2 (4.8) | |
| EGFR mutation | Positive/negative | 13 (31.0)/29 (69.0) |
| Performance status | 0 | 5 (11.9) |
| 1 | 20 (47.6) | |
| 2 | 9 (21.4) | |
| 3 | 6 (14.3) | |
| 4 | 2 (4.8) | |
| Irradiated dose | 30 Gy in 10 fractions | 36 (85.7) |
| 40 Gy in 20 fractions | 4 (9.5) | |
| 37.5 Gy in 15 fractions | 2 (4.8) | |
| Primary site | Controlled/uncontrolled | 16 (38.1)/26 (61.9) |
| Extracranial disease | Presence/absence | 39 (92.9)/3 (7.1) |
| Number of BMs | 1 | 2 (4.8) |
| 2 | 2 (4.8) | |
| ≥3 | 38 (90.5) | |
| Maximum size of BM (mm) | 15 (4–55) | |
| Use of TKIs after WBRT | Yes/no | 9 (21.4)/33 (78.6) |
| STI | Before/after WBRT | 9 (21.4)/2 (4.8) |
| Surgery | Before/after WBRT | 2 (4.8)/0 (0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanaka, H.; Karita, M.; Ueda, K.; Ono, T.; Kajima, M.; Manabe, Y.; Fujimoto, K.; Yuasa, Y.; Shiinoki, T. Differences in Radiosensitivity According to EGFR Mutation Status in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Clinical and In Vitro Study. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14010025
Tanaka H, Karita M, Ueda K, Ono T, Kajima M, Manabe Y, Fujimoto K, Yuasa Y, Shiinoki T. Differences in Radiosensitivity According to EGFR Mutation Status in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Clinical and In Vitro Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2024; 14(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanaka, Hidekazu, Masako Karita, Kazushi Ueda, Taiki Ono, Miki Kajima, Yuki Manabe, Koya Fujimoto, Yuki Yuasa, and Takehiro Shiinoki. 2024. "Differences in Radiosensitivity According to EGFR Mutation Status in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Clinical and In Vitro Study" Journal of Personalized Medicine 14, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14010025
APA StyleTanaka, H., Karita, M., Ueda, K., Ono, T., Kajima, M., Manabe, Y., Fujimoto, K., Yuasa, Y., & Shiinoki, T. (2024). Differences in Radiosensitivity According to EGFR Mutation Status in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Clinical and In Vitro Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 14(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14010025






