Metabarcoding in Diet Assessment of Heterotrigona itama Based on trnL Marker towards Domestication Program
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling of the Stingless Bees
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. DNA Sample QC
2.4. Second PCR (Index PCR)
2.5. Next-Generation Sequencing
2.6. Data Analysis
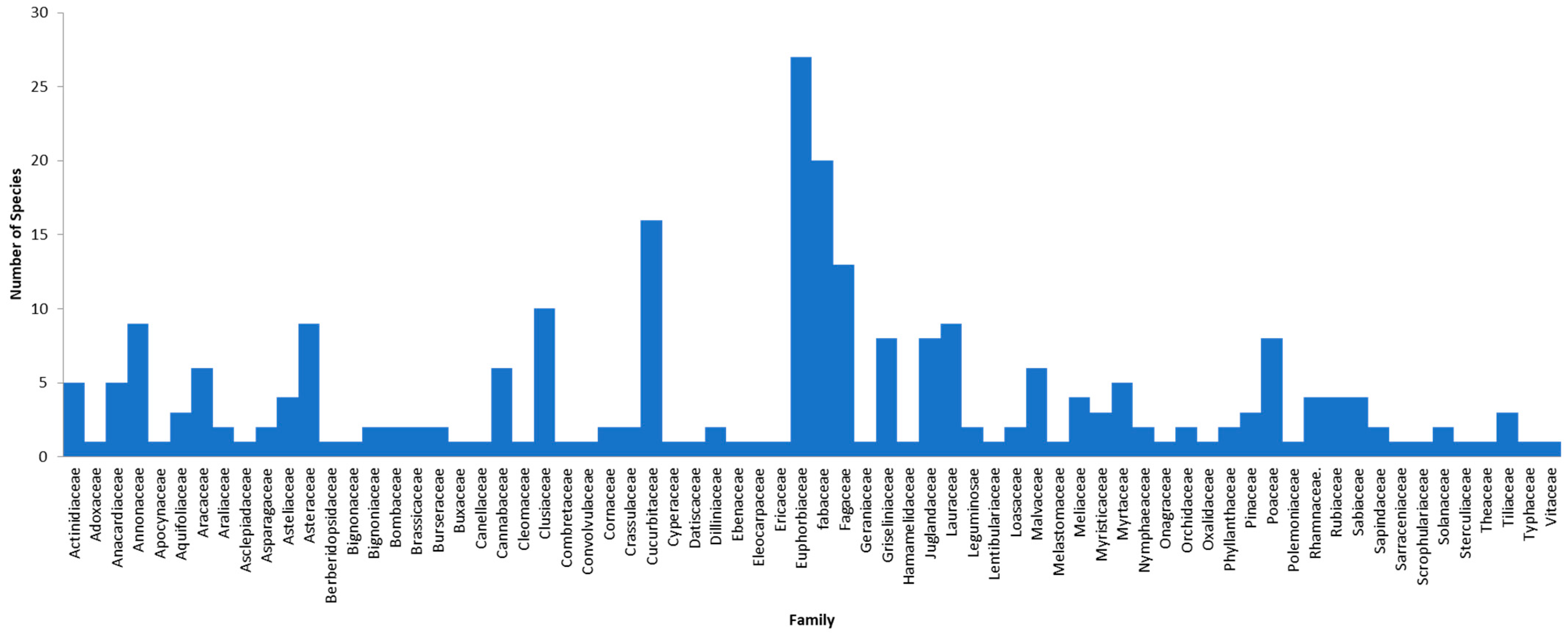
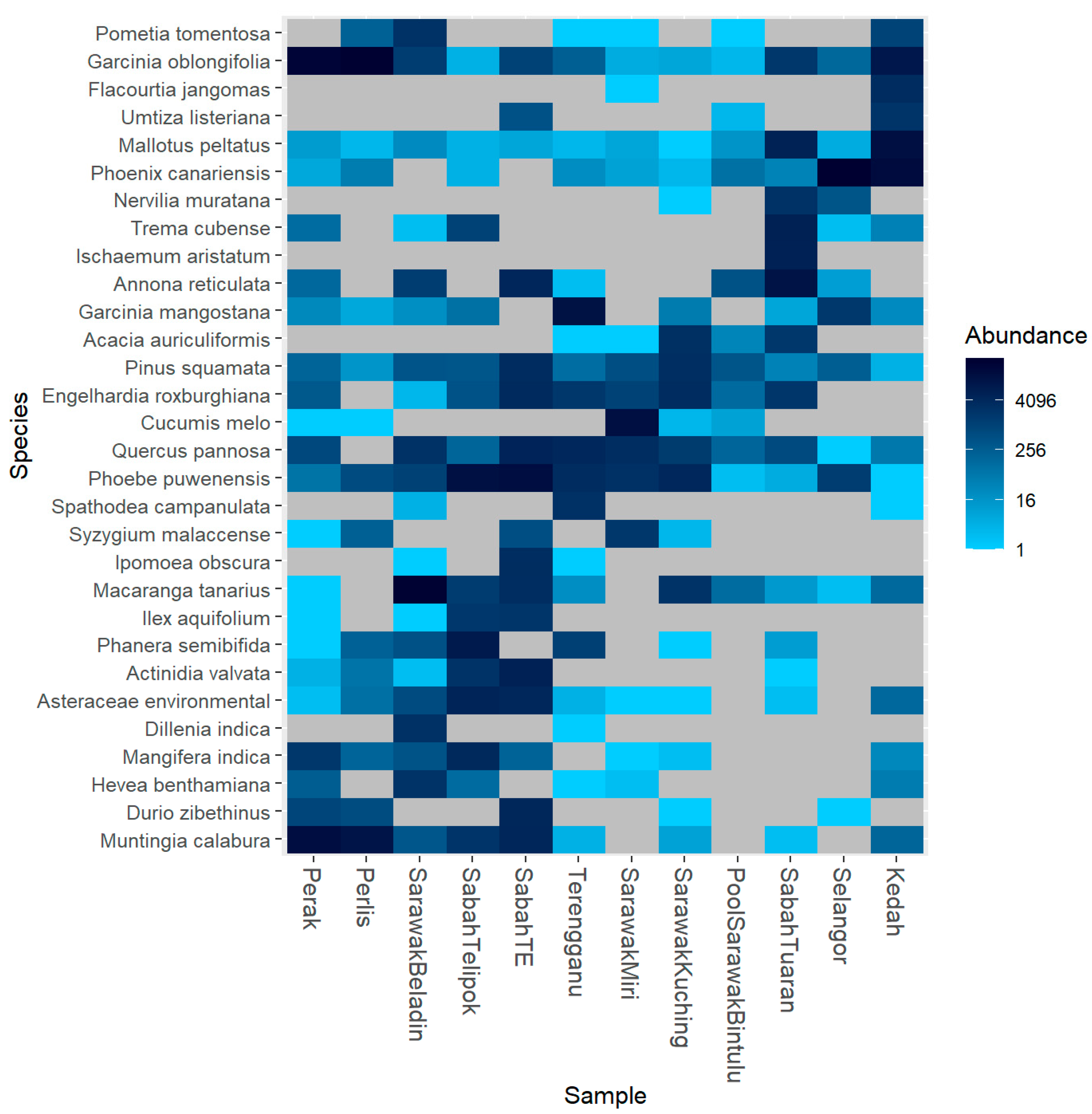
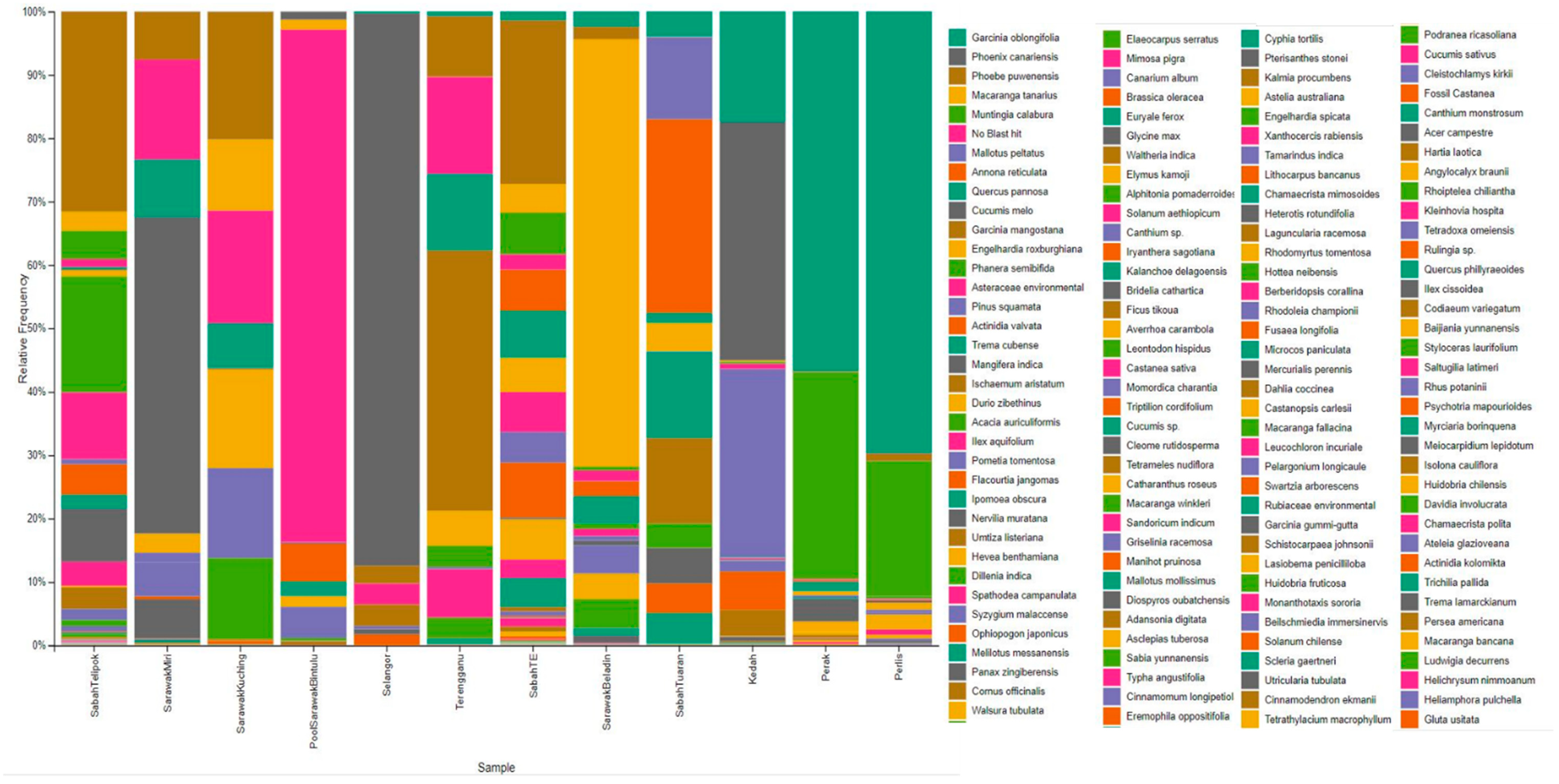
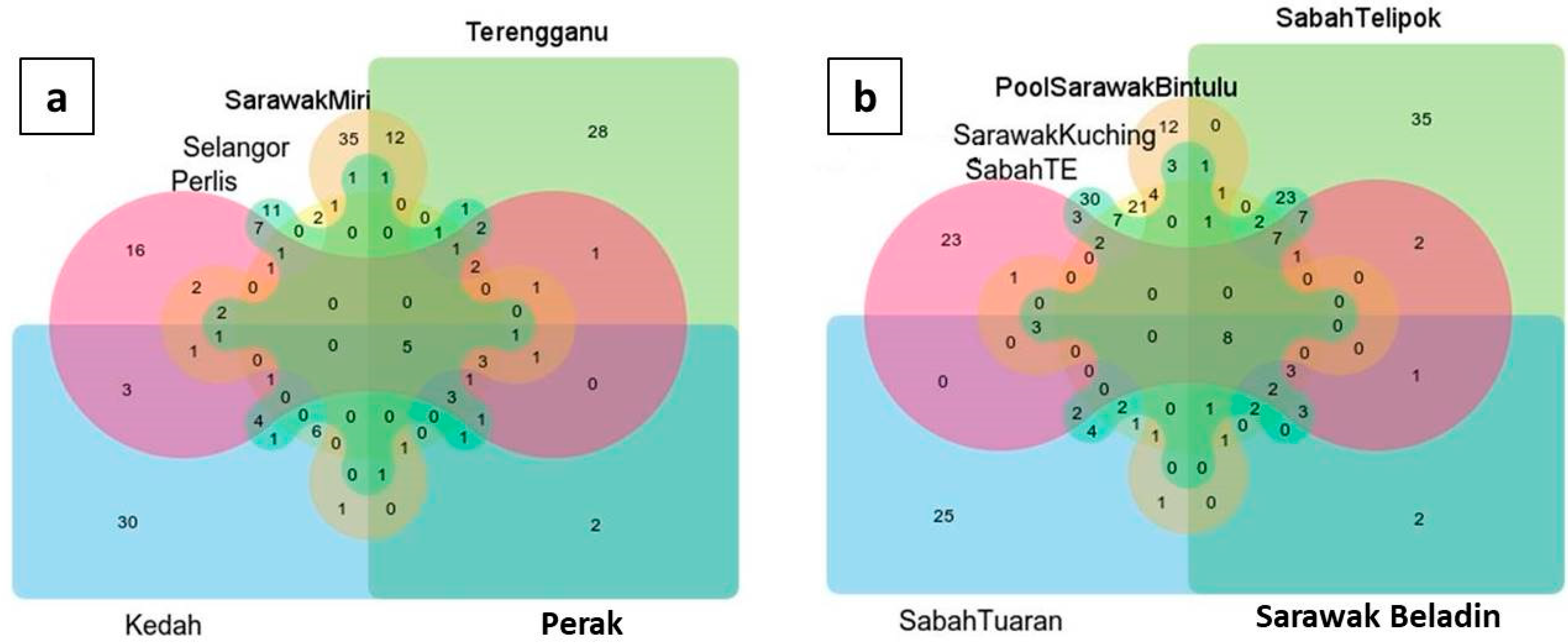
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghazi, R.; Zulqurnain, N.S.; Azmi, W.A. Melittopalynological Studies of Stingless Bees from the East Coast of Peninsular Malaysia. In Pot-Pollen in Stingless Bee Melittology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 77–88. [Google Scholar]
- Michener, C.D. The Bees of the World, 2nd ed.; JHU Press: Baltimore, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jaapar, M.F.; Halim, M.; Mispan, M.R.; Jajuli, R.; Saranum, M.M.; Zainuddin, M.Y.; Ghazi, R.; Abd Ghani, I. The diversity and abundance of stingless bee (Hymenoptera: Meliponini) in Peninsular Malaysia. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2016, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Roubik, D.W.; Momose, K.; Inoue, T.; Nagamitsu, T. Preference in flower visits and partitioning in pollen diets of stingless bees in an Asian tropical rain forest. Popul. Ecol. 1999, 41, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaapar, M.F.; Jajuli, R. Lebah Kelulut Malaysia: Biologi dan Penternakan; Penerbit MARDI: Serdang, Malaysia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rattanawannee, A.; Duangphakdee, O. Southeast Asian meliponiculture for sustainable livelihood. In Modern Beekeeping: Bases for Sustainable Production; Ranz, R.E.R., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Vit, P.; Pedro, S.R.; Roubik, D. (Eds.) Pot-Honey: A Legacy of Stingless Bees; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Badrulhisham, N.S.R.; Ab Hamid, S.N.P.; Ismail, M.A.H.; Yong, Y.K.; Zakuan, N.M.; Harith, H.H.; Saidi, H.I.; Nurdin, A. Harvested locations influence the total phenolic content, antioxidant levels, cytotoxic, and anti-inflammatory activities of stingless bee honey. J. Asia-Pac. Èntomol. 2020, 23, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, U.; Abrol, D.P.; Singh, A.K. Plants for bees Pongamia pinnata (L.). Pierre. J. Palynol. 2017, 53, 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Afik, O.; Delaplane, K.S.; Shafir, S.; Moo-Valle, H.; Javier, J.; Quezada-Euán, J.J. Nectar minerals as regulators of flower vis-itation in stingless bees and nectar hoarding wasps. J. Chem. Ecol. 2014, 40, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Absy, M.L.; Rech, A.R.; Ferreira, M.G. Pollen collected by stingless bees: A contribution to understanding Amazonian bio-diversity. In Pot-Pollen in Stingless Bee Melittology; Vit, P., Pedro, S., Roubik, D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 29–46. [Google Scholar]
- Jaapar, M.F.; Nasarodin, N.S.; Reward, N.F.; Jajuli, R.; Abd Ghani, I. Notes on resin collected by stingless bees in Taman Tropika Tasik Kenyir, Terengganu, Malaysia. Serangga 2019, 24, 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Dos Santos, W.E.; Carneiro, L.T.; Alves, A.C.F.; Creão-Duarte, A.J.; Martins, C.F. Stingless Bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae: Meliponini) Attracted to Animal Carcasses in the Brazilian Dry Forest and Implications for Forensic Entomology. Sociobiology 2014, 61, 490–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Greco, M.K.; Spooner-Hart, R.N.; Beattie, A.G.A.C.; Barchia, I.; Holford, P. Australian stingless bees improve greenhouse Capsicum production. J. Apic. Res. 2011, 50, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffé, R.; Pope, N.; Carvalho, A.T.; Maia, U.M.; Blochtein, B.; De Carvalho, C.A.L.; Carvalho-Zilse, G.A.; Freitas, B.M.; Menezes, C.; Ribeiro, M.D.F.; et al. Bees for Development: Brazilian Survey Reveals How to Optimize Stingless Beekeeping. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; Yao, L.; Ying, X.; Lu, L.; Guardone, L.; Armani, A.; Guidi, A.; Xiong, X. Multiple fish species identified from China’s roasted Xue Yu fillet products using DNA and mini-DNA barcoding: Implications on human health and marine sustainability. Food Control. 2018, 88, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, M.; Talebi, M.; Farkhondeh, T.; Samarghandian, S. Molecular mechanism-based therapeutic properties of honey. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez, S.R.; Nieh, J.C.; Quental, T.B.; Roubik, D.W.; Imperatriz-Fonseca, V.L.; Pierce, N.E. A molecular phylogeny of the stingless bee genus Melipona (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2010, 56, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, S.; Murphy, D.J.; Miller, J.T.; Bhave, M. Application of Molecular Markers for Identification of Potential Salt Tolerant Plant Species for use in Agroforestry and Saline Land Reclamation. APCBEE Procedia 2013, 5, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taberlet, P.; Coissac, E.; Pompanon, F.; Gielly, L.; Miquel, C.; Valentini, A.; Vermat, T.; Corthier, G.; Brochmann, C.; Willerslev, E. Power and limitations of the chloroplast trn L (UAA) intron for plant DNA barcoding. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics. 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Gonzalez, P.A.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods. 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattley, S.; Arthur, J.W. BioManager: The use of a bioinformatics web application as a teaching tool in undergraduate bioinformatics training. Brief Bioinform. 2007, 8, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 2018. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- Hawkins, J.; De Vere, N.; Griffith, A.; Ford, C.R.; Allainguillaume, J.; Hegarty, M.J.; Baillie, L.; Adams-Groom, B. Using DNA metabarcoding to identify the floral composition of honey: A new tool for investigating honey bee foraging preferences. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, K.; Vikram, P.; Soon, J.M.; Krishnan, K.T.; Mohammed, A. Melissopalynological, physicochemical and antioxidant properties of honey from West Coast of Malaysia. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 2508–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazi, R. Melissopalynology and Foraging Activity of the Stingless Bees, Heterotrigona itama (Hymenoptera: Apidae) at Taman Tropika Kenyir, Terengganu. Master’s Thesis, Universiti Malaysia Terengganu, Terengganu, Malaysia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn-Neto, B.; Contrera, F.A.L.; Castro, M.S.; Nieh, J.C. Long distance foraging and recruitment by a stingless bee, Melipona mandacaia. Apidologie 2009, 40, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonhardt, S.D.; Dworschak, K.; Eltz, T.; Blüthgen, N. Foraging loads of stingless bees and utilisation of stored nectar for pollen harvesting. Apidologie 2007, 38, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boongird, S.; Michener, C.D. Pollen and Propolis Collecting by Male Stingless Bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae). J. Kans. Èntomol. Soc. 2010, 83, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Nozaki, A.; Nakadai, H.; Shiwa, Y.; Shimizu-Kadota, M. Using pollen DNA metabarcoding to profile nectar sources of urban beekeeping in Kōtō-ku, Tokyo. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaman, J. Mount Kinabalu: Hotspot of plant diversity in Borneo. In Plant Diversity and Complexity Patterns: Local, Regional and Global Dimensions. Proceedings of an International Symposium Held at the Royal Danish Academy of Sciences and Letters in Copenhagen, Denmark, 25–28 May 2003; Det Kongelige Danske Videnskabernes Selskab: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2005; Volume 55, pp. 103–127. [Google Scholar]
- Saw, L.; Chung, R. The flora of Malaysia projects. Rodriguésia 2015, 66, 947–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pereira, J.T.; Sugau, J.B.; Nilus, R.; Khoo, E.; Tze Lui, S.T.; Leung, L.Y.; Damit, A.; Mustapeng, A.M.A.; Kiat, H.P.; Tanggaraju, S.; et al. Conservation efforts towards contributing to the plant conservation strategies in Sabah, Malaysia. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association of Tropical Biology and Conservation, Antananarivo, MA, USA, 30 July–3 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jaafar, W.S.W.M.; Maulud, K.N.A.; Kamarulzaman, A.M.M.; Raihan, A.; Sah, S.M.; Ahmad, A.; Saad, S.N.M.; Azmi, A.T.M.; Syukri, N.K.A.J.; Khan, W.R. The Influence of Deforestation on Land Surface Temperature—A Case Study of Perak and Kedah, Malaysia. Forests 2020, 11, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenking, C.M.; Boyce, A. Phylum Spermatophyta—Introduction. In The Diversity of Life; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1979; pp. 129–131. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Sluijs, J.P.; Vaage, N. Pollinators and global food security: The need for holistic global stewardship. Food Ethics 2016, 1, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, K.-L.J.; Kingston, J.M.; Albrecht, M.; Holway, D.A.; Kohn, J.R. The worldwide importance of honey bees as pollinators in natural habitats. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2018, 285, 20172140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takhtajan, A. Phylum Magnoliophyta (flowering plants). In Flowering Plants; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Amolin, A.V.; Ogol, I.N. Trophic relations of wasps (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) with flowering plants (Magnoliophyta) in Donbass. Euroasian Èntomol. J. 2019, 18, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucek, K.; Galli, A.; Gurten, S.; Hohmann, N.; Maccagni, A.; Patsiou, T.; Willi, Y. Metabarcoding of honey to assess differences in plant-pollinator interactions between urban and non-urban sites. Apidologie 2019, 50, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dow, R.A.; Ngiam, R.W.J.; Ahmad, R. Odonata of Maludam National Park, Sarawak, Malaysia. J. Threat. Taxa 2015, 7, 6764–6773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J. Status of Peat Swamp Forest of Sarawak; Sarawak Forestry Corporation/Alterra Wageningen UR: Kuching, Malaysia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hazebroek, H.P. National Parks of Sarawak; Natural History Pub. (Borneo): Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sanz, M.; Gonzalez, M.; de Lorenzo, C.; Sanz, J.; Martínez-CastroI, I. A contribution to the differentiation between nectar honey and honeydew honey. Food Chem. 2005, 91, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiala, B.; Maschwitz, U. Extrafloral nectaries in the genus Macaranga (Euphorbiaceae) in Malaysia: Comparative studies of their possible significance as predispositions for myrmecophytism. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1991, 44, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckroth, H.-P.; Fiala, B.; Gullan, P.J.; Idris, A.H.; Maschwitz, U. The soft scale (Coccidae) associates of Malaysian ant-plants. J. Trop. Ecol. 1998, 14, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahri, S. Pollen profile by stingless bee (Heterotrigona itama) reared in rubber smallholding environment at Tepoh, Terengganu. Malays. J. Microsc. 2018, 14, 38–54. [Google Scholar]
- Jaapar, M.F.; Jajuli, R.; Mispan, M.R.; Ghani, I.A. Foraging behavior of stingless bee Heterotrigona itama (Cockerell, 1918) (Hymenoptera: Apidae: Meliponini). AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1940, 020037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asma, S.S.; Adam, N.A.; Najwa, M.Y.S.; Asilah, N.; Syukri, T.S.; Asiah, W.N. Foraging behavior of stingless bee (Geniotrigona thoracica and Heterotrigona itama) on star fruit trees (Averrhoa carambola L.). IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 383, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, H.M.; Lee, D.J. Resin-foraging by colonies of Trigona sapiens and T. hockingsi (Hymenoptera: Apidae, Meliponini) and consequent seed dispersal of Corymbia torelliana (Myrtaceae). Apidologie 2010, 41, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bill, N.M. Palynology of Stingless Bee, Tetragonula laeviceps (Hymenoptera: Meliponinae). Master’s Thesis, Faculty of Agro-Based Industry, Universiti Malaysia Kelantan, Kelantan, Malaysia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi-Shu, X.I.; Yu-Shan, W.A.; Zhi-Bin, Z.H. Seed bank and the factors influencing it for three Fagaceae species in Dujiangyan Region, Sichuan. Biodivers. Sci. 2001, 9, 373–381. [Google Scholar]
- Engel, M.S.; Dingemans-Bakels, F. Nectar and pollen resources for stingless bees (Meliponinae, Hymenoptera) in Surinam (South America). Apidologie 1980, 11, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vongsak, B.; Kongkiatpaiboon, S.; Jaisamut, S.; Machana, S.; Pattarapanich, C. In vitro alpha glucosidase inhibition and free-radical scavenging activity of propolis from Thai stingless bees in mangosteen orchard. Rev. Bras. Farm. 2015, 25, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuan, A.; Maya Izar, K.; Salma, I.; Raziah, M.L. Distribution and diversity of Garcinia species in Malaysia. In Proceedings of the Biodiversity and National Development Achievements, Opportunities and Challenges Conference, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 28–30 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Slaa, E.J.; Tack, A.J.; Sommeijer, M.J. The effect of intrinsic and extrinsic factors on flower constancy in stingless bees. Apidologie 2003, 34, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momose, K.; Yumoto, T.; Nagamitsu, T.; Kato, M.; Nagamasu, H.; Sakai, S.; Harrison, R.D.; Itioka, T.; Hamid, A.A.; Inoue, T. Pollination biology in a lowland dipterocarp forest in Sarawak, Malaysia. I. Characteristics of the plant-pollinator community in a lowland dipterocarp forest. Am. J. Bot. 1998, 85, 1477–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wayo, K.; Phankaew, C.; Stewart, A.B.; Bumrungsri, S. Bees are supplementary pollinators of self-compatible chiropterophilous durian. J. Trop. Ecol. 2018, 34, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
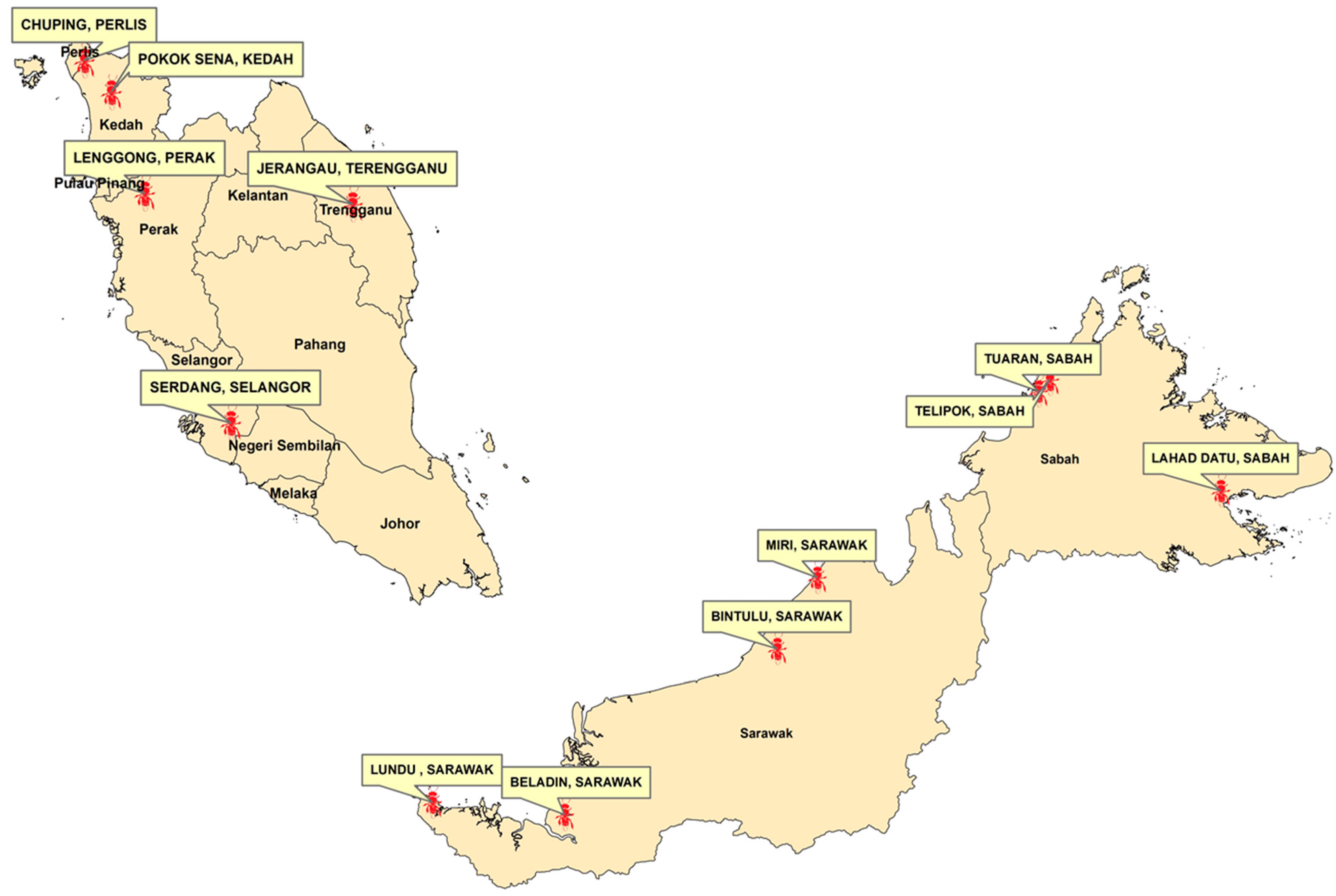

| Sample Code | Location | Grid | Ecosystem |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sabah TE | Borneo. Sabah: Lahad Datu | 5.01248, 118.0970218 | Crop field adjacent to secondary forest |
| Terengganu | Peninsular Malaysia. Terengganu: Jerangau | 5.0655177, 102.8652274 | Crop field adjacent to secondary forest |
| Sabah Telipok | Borneo. Sabah: Telipok | 6.1732126, 116.2984958 | Crop field adjacent to hill forest |
| Perak | Peninsular Malaysia. Perak: Lenggong | 5.1662481, 100.8801384 | Crop field |
| Kedah | Peninsular Malaysia. Kedah: Pokok Sena | 6.126510, 100.559629 | Crop field |
| Sarawak Kuching | Borneo. Sarawak: Lundu | 1.758078, 109.806310 | Crop field adjacent to coastal area |
| Pool Sarawak Bintulu | Borneo. Sarawak: MARDI Bintulu | 3.358613, 113.430816 | Crop field adjacent to oil palm estate |
| Perlis | Peninsular Malaysia. Perlis: Chuping | 6.427755, 100.304074 | Crop field |
| Sarawak Beladin | Borneo. Sarawak: Beladin | 1.6273364, 111.1958089 | Crop field |
| Selangor | Peninsular Malaysia. Selangor: MARDI Serdang | 2.990892, 101.702434 | Crop field |
| Sabah Tuaran | Bornoe. Sabah: Tuaran | 6.0523621, 116.1788793 | Crop field adjacent to river |
| Sarawak Miri | Borneo. Sarawak: Miri | 4.102966, 113.853467 | Crop field adjacent to coastal area |
| Localities | Sequences | OTUs | Chao1 | Shannon–Weiner | Simpson | Evenness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
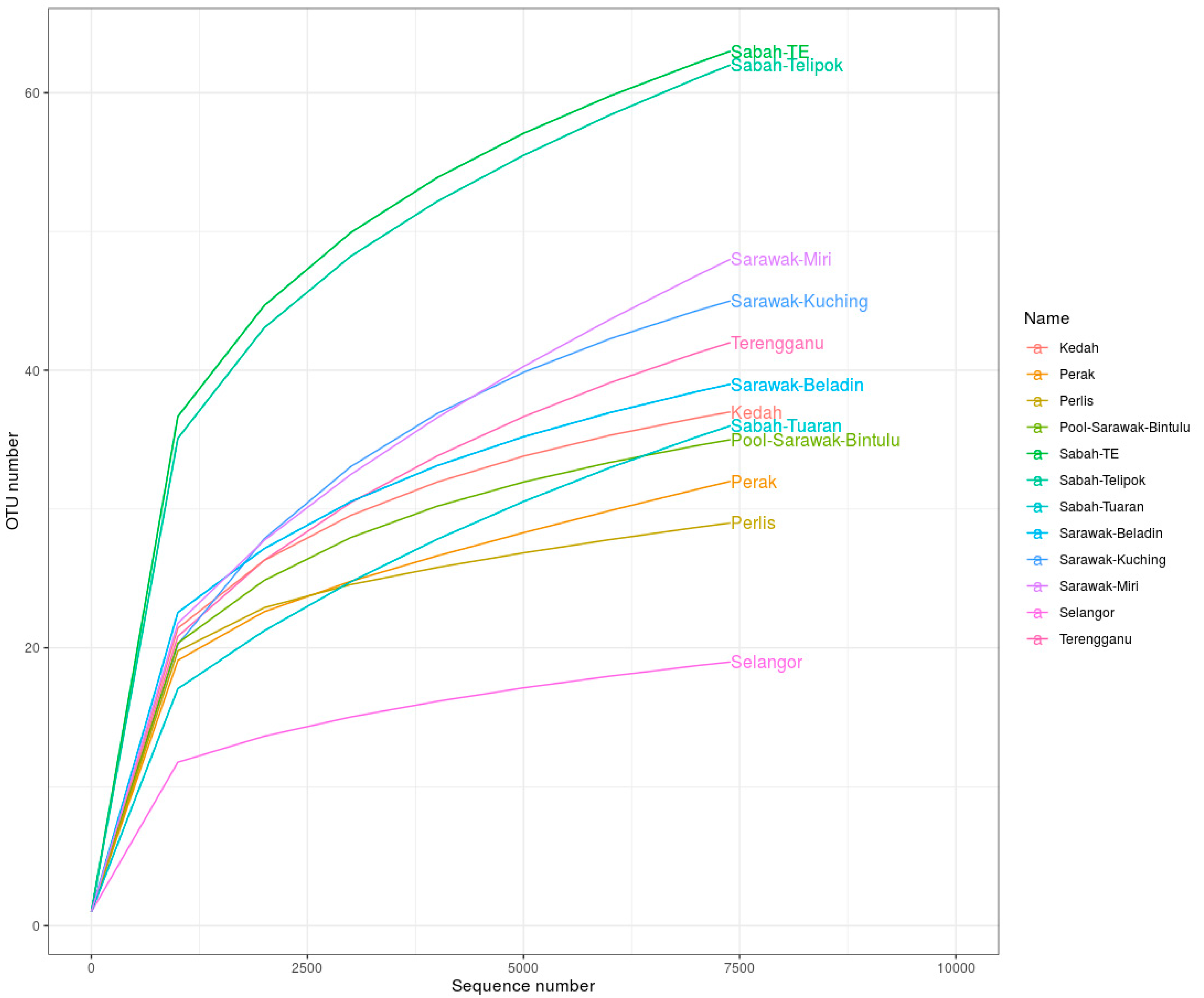
| Sabah TE | 70,068 | 63 | 83.000 | 2.732 | 0.900 | 23.056 |
| Terengganu | 34,210 | 42 | 53.375 | 2.126 | 0.826 | 19.769 |
| Sabah Telipok | 50,173 | 62 | 87.500 | 2.372 | 0.841 | 26.144 |
| Perak | 52,216 | 32 | 59.500 | 1.147 | 0.564 | 27.901 |
| Kedah | 54,937 | 37 | 42.600 | 1.672 | 0.739 | 22.126 |
| Sarawak Kuching | 20,642 | 45 | 54.75 | 2.023 | 0.851 | 22.244 |
| Pool Sarawak Bintulu | 7448 | 35 | 42.000 | 1.939 | 0.794 | 18.047 |
| Perlis | 56,612 | 29 | 34.000 | 1.044 | 0.476 | 27.786 |
| Sarawak Beladin | 55,714 | 39 | 48.000 | 1.494 | 0.541 | 26.098 |
| Selangor | 47,532 | 19 | 22.330 | 0.645 | 0.243 | 29.470 |
| Sabah Tuaran | 44,060 | 36 | 53.500 | 2.130 | 0.840 | 16.899 |
| Sarawak Miri | 33,786 | 48 | 86.500 | 1.857 | 0.715 | 25.844 |
| Total | 527,398 | 487 |
| Phylum | Localities % |
|---|---|
| Tracheophyta | 4.72 |
| Anthophyta | 1.97 |
| Magnoliophyta | 32.39 |
| Spermatophyta | 55.95 |
| Embryophyta | 0.13 |
| Unknown | 4.85 |
| Phylum | Borneo (%) | Peninsular Malaysia (%) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sabah TE | Sabah Telipok | Sabah Tuaran | Sarawak Kuching | Pool Sarawak Bintulu | Sarawak Beladin | Sarawak Miri | Terengganu | Perak | Kedah | Perlis | Selangor | |
| Tracheophyta | 6.66 | 2.81 | 18 | 15.7 | 1.6 | 0.11 | 9.39 | 8.9 | 1.114 | 0.9 | 0.08 | 0 |
| Anthophyta | 6.32 | 10.56 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0 | 1.13 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.3 | 0.17 | 0.05 |
| Magnoliophyta | 41.92 | 57.37 | 38.3 | 39 | 4.09 | 78.7 | 22.4 | 32.5 | 2.9 | 34.7 | 5.6 | 3.6 |
| Spermatophyta | 42.7 | 27.9 | 43.5 | 27.48 | 13.4 | 17.1 | 52.3 | 43.2 | 95.8 | 63.2 | 94.1 | 93 |
| Embryophyta | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Unknown | 2.3 | 1.253 | 0.014 | 17.7 | 80.8 | 1.64 | 15.7 | 15.2 | 0.14 | 0.7 | 0.01 | 3.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fahimee, J.; Badrulisham, A.S.; Zulidzham, M.S.; Reward, N.F.; Muzammil, N.; Jajuli, R.; Md-Zain, B.M.; Yaakop, S. Metabarcoding in Diet Assessment of Heterotrigona itama Based on trnL Marker towards Domestication Program. Insects 2021, 12, 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12030205
Fahimee J, Badrulisham AS, Zulidzham MS, Reward NF, Muzammil N, Jajuli R, Md-Zain BM, Yaakop S. Metabarcoding in Diet Assessment of Heterotrigona itama Based on trnL Marker towards Domestication Program. Insects. 2021; 12(3):205. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12030205
Chicago/Turabian StyleFahimee, Jaapar, Aqilah Sakinah Badrulisham, Mohd Sani Zulidzham, Nurul Farisa Reward, Nizar Muzammil, Rosliza Jajuli, Badrul Munir Md-Zain, and Salmah Yaakop. 2021. "Metabarcoding in Diet Assessment of Heterotrigona itama Based on trnL Marker towards Domestication Program" Insects 12, no. 3: 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12030205
APA StyleFahimee, J., Badrulisham, A. S., Zulidzham, M. S., Reward, N. F., Muzammil, N., Jajuli, R., Md-Zain, B. M., & Yaakop, S. (2021). Metabarcoding in Diet Assessment of Heterotrigona itama Based on trnL Marker towards Domestication Program. Insects, 12(3), 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12030205






