Concentration- and Time-Dependent Dietary Exposure to Graphene Oxide and Silver Nanoparticles: Effects on Food Consumption and Assimilation, Digestive Enzyme Activities, and Body Mass in Acheta domesticus
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. NP Characteristics
2.2. Acheta Domesticus
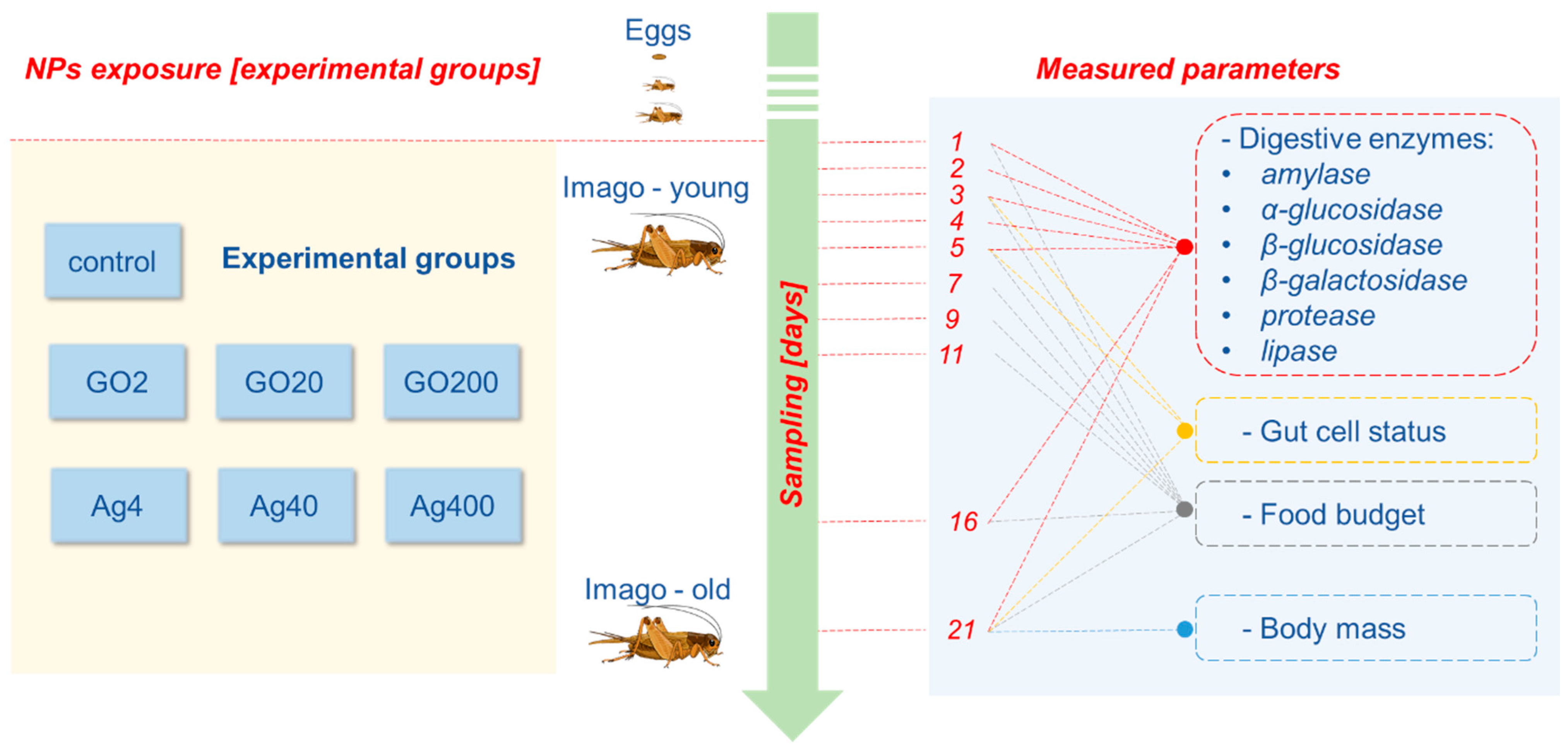
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Food Consumption and Assimilation
2.5. Gut Cell Status
2.6. Digestive Enzyme Measurements
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
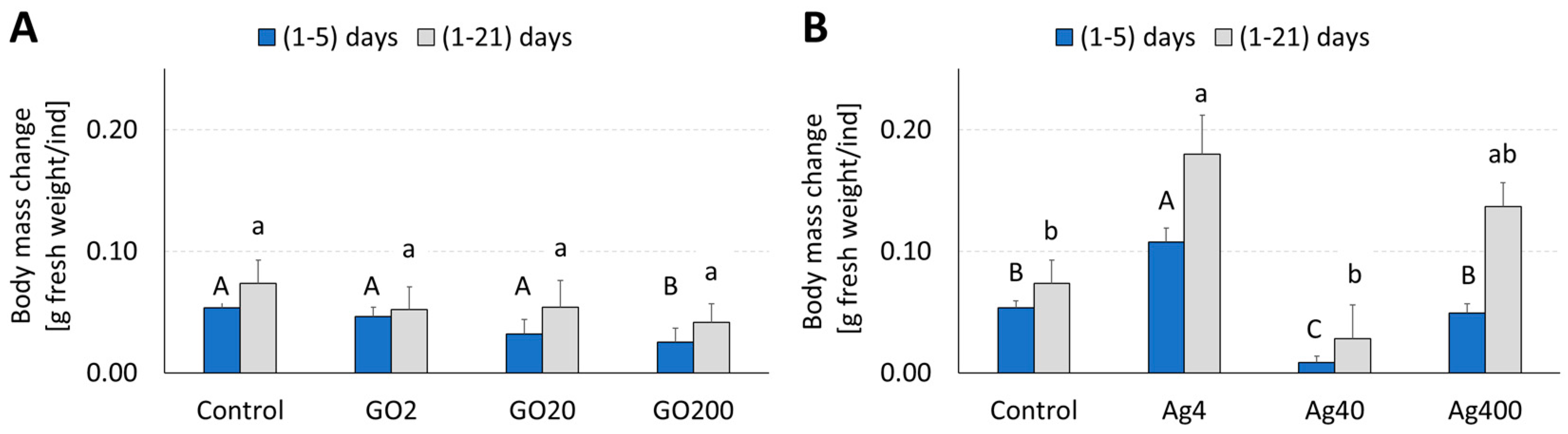
3.1. Body Mass and Food Budget—Consumption and Assimilation
3.2. Gut Cell Status
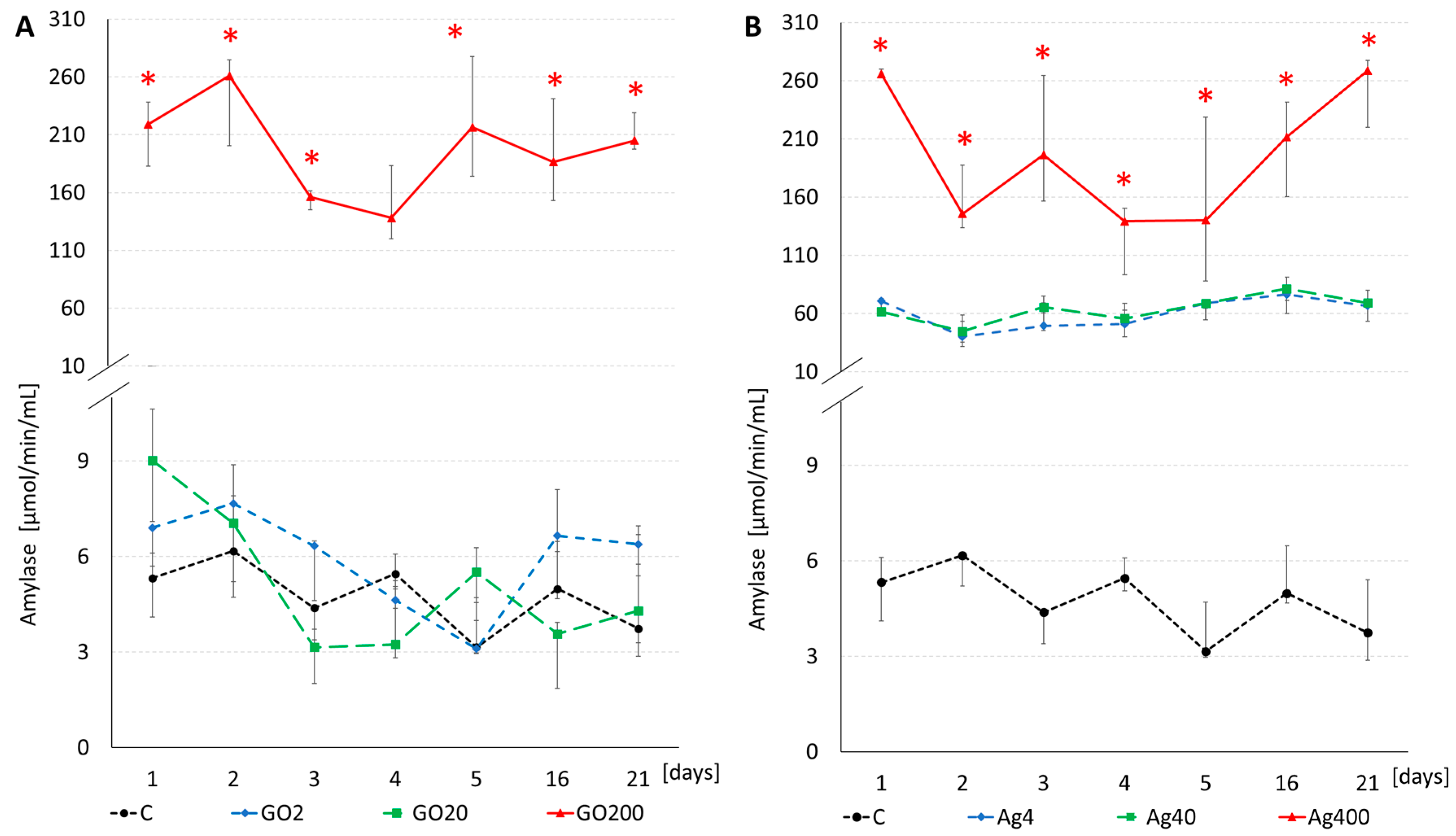
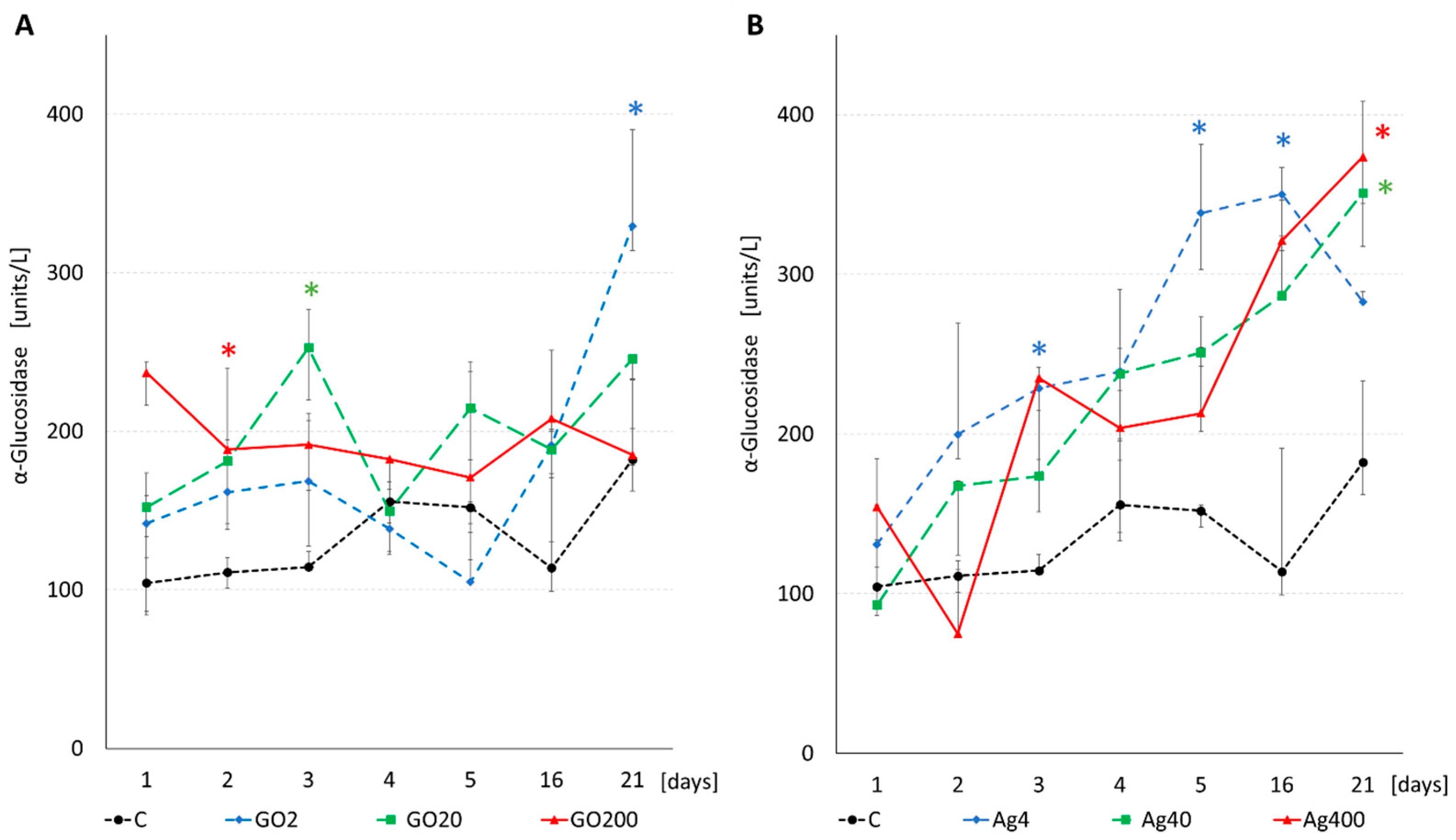
3.3. Enzyme Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pulit-Prociak, J.; Banach, M. Silver Nanoparticles—A Material of the Future...? Open Chem. 2016, 14, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inshakova, E.; Inshakov, O. World Market for Nanomaterials: Structure and Trends. In Proceedings of the MATEC Web of Conferences, EDP Sciences, Sevastopol, Ukraine, 7 November 2017; Volume 129. [Google Scholar]
- McGillicuddy, E.; Murray, I.; Kavanagh, S.; Morrison, L.; Fogarty, A.; Cormican, M.; Dockery, P.; Prendergast, M.; Rowan, N.; Morris, D. Silver Nanoparticles in the Environment: Sources, Detection and Ecotoxicology. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malakar, A.; Kanel, S.R.; Ray, C.; Snow, D.D.; Nadagouda, M.N. Nanomaterials in the Environment, Human Exposure Pathway, and Health Effects: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, S.P.; Patil, S.M.; Mullani, S.B.; Delekar, S.D. Silver Nanoparticles as an Effective Disinfectant: A Review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 97, 954–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.S.; Yousuf, O.; Islam, R.U.; Younis, K. Silver Nanoparticles as an Active Packaging Ingredient and Its Toxicity. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2021, 34, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istiqola, A.; Syafiuddin, A. A Review of Silver Nanoparticles in Food Packaging Technologies: Regulation, Methods, Properties, Migration, and Future Challenges. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2020, 67, 1942–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, N.; Abdullah, S.; Yusoh, K. Graphene Nanomaterials in the Food Industries: Quality Control in Promising Food Safety to Consumers. Graphene 2D Mater. 2022, 7, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossa, V.; Monteiro Ferreira, L.E.; da Costa Vasconcelos, S.; Tai Shimabukuro, E.T.; Gomes da Costa Madriaga, V.; Carvalho, A.P.; Castellã Pergher, S.B.; de Carvalho da Silva, F.; Ferreira, V.F.; Conte Junior, C.A.; et al. Nanocomposites Based on the Graphene Family for Food Packaging: Historical Perspective, Preparation Methods, and Properties. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 14084–14111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, M.; Sarkar, S. Involuntary Graphene Intake with Food and Medicine. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 30162–30167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebadero-Domínguez, Ó.; Jos, A.; Cameán, A.M.; Cătunescu, G.M. Hazard Characterization of Graphene Nanomaterials in the Frame of Their Food Risk Assessment: A Review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 164, 113014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Zhu, Z.; Sun, D.W. Novel Graphene Oxide/Polymer Composite Membranes for the Food Industry: Structures, Mechanisms and Recent Applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Andnutrition 2022, 62, 3705–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasur, J.; Usha Rani, P. Lepidopteran Insect Susceptibility to Silver Nanoparticles and Measurement of Changes in Their Growth, Development and Physiology. Chemosphere 2015, 124, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Xiao, H. Is Nano Safe in Foods? Establishing the Factors Impacting the Gastrointestinal Fate and Toxicity of Organic and Inorganic Food-Grade Nanoparticles. NPJ Sci. Food 2017, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, A.; He, J.; Yu, T.; Sun, C.; Shi, D.; Jiang, Y.; Xianyu, Y.; Shao, Y. Dietary Exposure of Copper and Zinc Oxides Nanoparticles Affect the Fitness, Enzyme Activity, and Microbial Community of the Model Insect, Silkworm Bombyx Mori. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 152608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; McClements, D.J. Recent Advances in the Gastrointestinal Fate of Organic and Inorganic Nanoparticles in Foods. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaszewski, M.; Kawalski, K.; Wiechetek, W.; Szudrowicz, H.; Martynow, J.; Adamek-Urbańska, D.; Łosiewicz, B.; Szczepański, A.; Bujarski, P.; Frankowska-Łukawska, J.; et al. The Effect of Silver Nanoparticles on the Digestive System, Gonad Morphology, and Physiology of Butterfly Splitfin (Ameca Splendens). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, P.A. Energetic Efficiency under Stress Underlies Positive Genetic Correlations between Longevity and Other Fitness Traits in Natural Populations. Biogerontology 2007, 8, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyed Alian, R.; Dziewięcka, M.; Kędziorski, A.; Majchrzycki, Ł.; Augustyniak, M. Do Nanoparticles Cause Hormesis? Early Physiological Compensatory Response in House Crickets to a Dietary Admixture of GO, Ag, and GOAg Composite. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Long, X.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yan, S. A Comparison Effect of Copper Nanoparticles versus Copper Sulphate on Juvenile Epinephelus Coioides: Growth Parameters, Digestive Enzymes, Body Composition, and Histology as Biomarkers. Int. J. Genom. 2015, 2015, 783021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvind Bharani, R.; Karthick Raja Namasivayam, S. Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles Mediated Stress on Developmental Period and Gut Physiology of Major Lepidopteran Pest Spodoptera Litura (Fab.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae)-An Eco-Friendly Approach of Insect Pest Control. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantrao, S.; Ravindra, M.A.; Akbar, S.M.D.; Kamala Jayanthi, P.D.; Venkataraman, A. Effect of Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles on Growth and Development of Helicoverpa Armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae): Interaction with Midgut Protease. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2017, 20, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Wang, R.; Qin, D.; Yang, L.; Lin, S.; Cheng, D.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Z. Insecticidal Efficacy and Mechanism of Nanoparticles Synthesized from Chitosan and Carboxymethyl Chitosan against Solenopsis Invicta (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 260, 117839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Badawy, A.M.; Silva, R.G.; Morris, B.; Scheckel, K.G.; Suidan, M.T.; Tolaymat, T.M. Surface Charge-Dependent Toxicity of Silver Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortella, G.R.; Rubilar, O.; Durán, N.; Diez, M.C.; Martínez, M.; Parada, J.; Seabra, A.B. Silver Nanoparticles: Toxicity in Model Organisms as an Overview of Its Hazard for Human Health and the Environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 121974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, F.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Xing, B. Transfer and Toxicity of Silver Nanoparticles in the Food Chain. Environ. Sci. Nano 2021, 8, 1519–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodaparast, Z.; van Gestel, C.A.M.; Papadiamantis, A.G.; Gonçalves, S.F.; Lynch, I.; Loureiro, S. Toxicokinetics of Silver Nanoparticles in the Mealworm Tenebrio Molitor Exposed via Soil or Food. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Samad, L.M.; El-Ashram, S.; Hussein, H.K.; Abdul-Aziz, K.K.; Radwan, E.H.; Bakr, N.R.; El Wakil, A.; Augustyniak, M. Time-Delayed Effects of a Single Application of AgNPs on Structure of Testes and Functions in Blaps Polychresta Forskal, 1775 (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziewięcka, M.; Pawlyta, M.; Majchrzycki, Ł.; Balin, K.; Barteczko, S.; Czerkawska, M.; Augustyniak, M. The Structure–Properties–Cytotoxicity Interplay: A Crucial Pathway to Determining Graphene Oxide Biocompatibility. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Singh Raman, A.P.; Meena, H.; Goswami, A.G.; Bhawna; Kumar, V.; Jain, P.; Kumar, G.; Sagar, M.; Rana, D.K.; et al. An Update on Graphene Oxide: Applications and Toxicity. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 35387–35445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghulam, A.N.; Dos Santos, O.A.L.; Hazeem, L.; Backx, B.P.; Bououdina, M.; Bellucci, S. Graphene Oxide (GO) Materials—Applications and Toxicity on Living Organisms and Environment. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowski, B.; Żuchowska, A.; Brzózka, Z. Graphene Oxide Internalization into Mammalian Cells—A Review. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 221, 112998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horch, H.W.; Mito, T.; Popadi, A.; Ohuchi, H.; Noji, S. The Cricket as a Model Organism Development, Regeneration, and Behavior; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Clifford, C.W.; Roe, R.M.; Woodring, J.P. Rearing Methods for Obtaining House Crickets, Acheta Domesticus, of Known Age, Sex, and Instar. Annnals Entomol. Soc. Am. 1977, 70, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szelei, J.; Woodring, J.; Goettel, M.S.; Duke, G.; Jousset, F.X.; Liu, K.Y.; Zadori, Z.; Li, Y.; Styer, E.; Boucias, D.G.; et al. Susceptibility of North-American and European Crickets to Acheta Domesticus Densovirus (AdDNV) and Associated Epizootics. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2011, 106, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Cassi, X.; Supeanu, A.; Vaga, M.; Jansson, A.; Boqvist, S.; Vagsholm, I. The House Cricket (Acheta Domesticus) as a Novel Food: A Risk Profile. J. Insects Food Feed 2019, 5, 137–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordoñez-Araque, R.; Egas-Montenegro, E. Edible Insects: A Food Alternative for the Sustainable Development of the Planet. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2021, 23, 100304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Toalá, J.E.; Cruz-Monterrosa, R.G.; Liceaga, A.M. Beyond Human Nutrition of Edible Insects: Health Benefits and Safety Aspects. Insects 2022, 13, 1007. [Google Scholar]
- Ververis, E.; Boué, G.; Poulsen, M.; Pires, S.M.; Niforou, A.; Thomsen, S.T.; Tesson, V.; Federighi, M.; Naska, A. A Systematic Review of the Nutrient Composition, Microbiological and Toxicological Profile of Acheta Domesticus (House Cricket). J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 114, 104859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flasz, B.; Dziewięcka, M.; Kędziorski, A.; Tarnawska, M.; Augustyniak, M. Vitellogenin Expression, DNA Damage, Health Status of Cells and Catalase Activity in Acheta Domesticus Selected According to Their Longevity after Graphene Oxide Treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 140274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flasz, B.; Dziewięcka, M.; Ajay, A.K.; Tarnawska, M.; Babczyńska, A.; Kędziorski, A.; Napora-Rutkowski, Ł.; Ziętara, P.; Świerczek, E.; Augustyniak, M. Age- and Lifespan-Dependent Differences in GO Caused DNA Damage in Acheta Domesticus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziewięcka, M.; Karpeta-Kaczmarek, J.; Augustyniak, M.; Rost-Roszkowska, M. Short-Term in Vivo Exposure to Graphene Oxide Can Cause Damage to the Gut and Testis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 328, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, A.; Shah, P.; Agrawal, N. Sedentary Behavior and Altered Metabolic Activity by AgNPs Ingestion in Drosophila Melanogaster. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nebol’sin, V.A.; Galstyan, V.; Silina, Y.E. Graphene Oxide and Its Chemical Nature: Multi-Stage Interactions between the Oxygen and Graphene. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 21, 100763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhazouani, A.; Gamrani, H.; El Achaby, M.; Aziz, K.; Gebrati, L.; Uddin, M.S.; Aziz, F. Synthesis and Toxicity of Graphene Oxide Nanoparticles: A Literature Review of in Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Biomed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 5518999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agathokleous, E.; Brown, P.H.; Calabrese, E.J. A Gift from Parent to Offspring: Transgenerational Hormesis. Trends Plant Sci. 2021, 26, 1098–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, D.; Yu, Z.; Huang, S.; Zhang, J. Hormone-Mediated Multi- and Trans-Generational Reproductive Toxicities of 1-Ethyl-3-Methylimidazolium Hexafluorophosphate on Caenorhabditis Elegans. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 160958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, W.; Mo, L.; Zhang, J. Reproductive Toxicities of 1-Ethyl-3-Methylimidazolium Bromide on Caenorhabditis Elegans with Oscillation between Inhibition and Stimulation over Generations. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 144334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorshidi, Z.; Moghanlou, K.S.; Imani, A.; Behrouzi, S.; Policar, T.; Rahimnejad, S. Interactive Effects of Curcumin and Silver Nanoparticles on Growth, Hemato-Biochemical Parameters, Digestive Enzymes Activity and Histology of Common Carp (Cyprinus Carpio). Res. Squ. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralisankar, T.; Bhavan, P.S.; Radhakrishnan, S.; Seenivasan, C.; Manickam, N.; Srinivasan, V. Dietary Supplementation of Zinc Nanoparticles and Its Influence on Biology, Physiology and Immune Responses of the Freshwater Prawn, Macrobrachium Rosenbergii. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2014, 160, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, J.L.; Kanaras, A.G.; Nativo, P.; Tshikhudo, T.R.; Rees, C.; Fernandez, L.C.; Dirvianskyte, N.; Razumas, V.; Skjøt, M.; Svendsen, A.; et al. Enzymatic Activity of Lipase-Nanoparticle Conjugates and the Digestion of Lipid Liquid Crystalline Assemblies. Langmuir 2010, 26, 13590–13599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, J.; Paul, A.; Chattopadhyay, A. Modulating Enzymatic Activity in the Presence of Gold Nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 4736–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saware, K.; Aurade, R.M.; Kamala Jayanthi, P.D.; Abbaraju, V. Modulatory Effect of Citrate Reduced Gold and Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles on α-Amylase Activity. J. Nanoparticles 2015, 2015, 829718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gole, A.; Dash, C.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Sainkar, S.R.; Mandale, A.B.; Rao, M.; Sastry, M. Pepsin-Gold Colloid Conjugates: Preparation, Characterization, and Enzymatic Activity. Langmuir 2001, 17, 1674–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Zhu, E.; Su, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, Q. Trypsin-Gold Nanoparticle Conjugates: Binding, Enzymatic Activity, and Stability. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2009, 39, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Effect | 5th and 21st Day | 5th Day | 21st Day | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | df1 | df2 | p | F | df1 | df2 | p | F | df1 | df2 | p | |
| NP type [1] | 4.973 | 2 | 37 | 0.012 | 6.065 | 1 | 40 | 0.018 | 9.823 | 1 | 38 | 0.003 |
| Concentration [2] | 6.564 | 6 | 74 | <0.001 | 15.135 | 3 | 40 | <0.001 | 3.710 | 3 | 38 | 0.020 |
| [1] × [2] | 4.111 | 6 | 74 | 0.001 | 8.381 | 3 | 40 | <0.001 | 5.393 | 3 | 38 | 0.003 |
| Effect | Food Consumption | Food Assimilation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | df1 | df2 | p | F | df1 | df2 | p | |
| NP type [1] | 2.383 | 1 | 37 | 0.131 | 7.882 | 1 | 33 | 0.008 |
| Concentration [2] | 5.235 | 3 | 37 | 0.004 | 7.819 | 3 | 33 | <0.001 |
| [1] × [2] | 1.952 | 3 | 37 | 0.138 | 5.697 | 3 | 33 | 0.003 |
| Time [3] | 69.177 | 6 | 32 | <0.001 | 36.632 | 6 | 28 | <0.001 |
| [3] × [1] | 5.453 | 6 | 32 | <0.001 | 4.350 | 6 | 28 | <0.001 |
| [3] × [2] | 2.461 | 18 | 91 | 0.001 | 1.933 | 18 | 80 | 0.015 |
| [3] × [1] × [2] | 1.499 | 18 | 91 | 0.092 | 1.428 | 18 | 80 | 0.121 |
| Effect | CFC | CFA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | df1 | df2 | p | F | df1 | df2 | p | |
| NP type [1] | 2.555 | 1 | 40 | 0.118 | 12.366 | 1 | 40 | 0.001 |
| Concentration [2] | 4.451 | 3 | 40 | 0.009 | 8.002 | 3 | 40 | <0.001 |
| [1] × [2] | 2.541 | 3 | 40 | 0.070 | 9.471 | 3 | 40 | <0.001 |
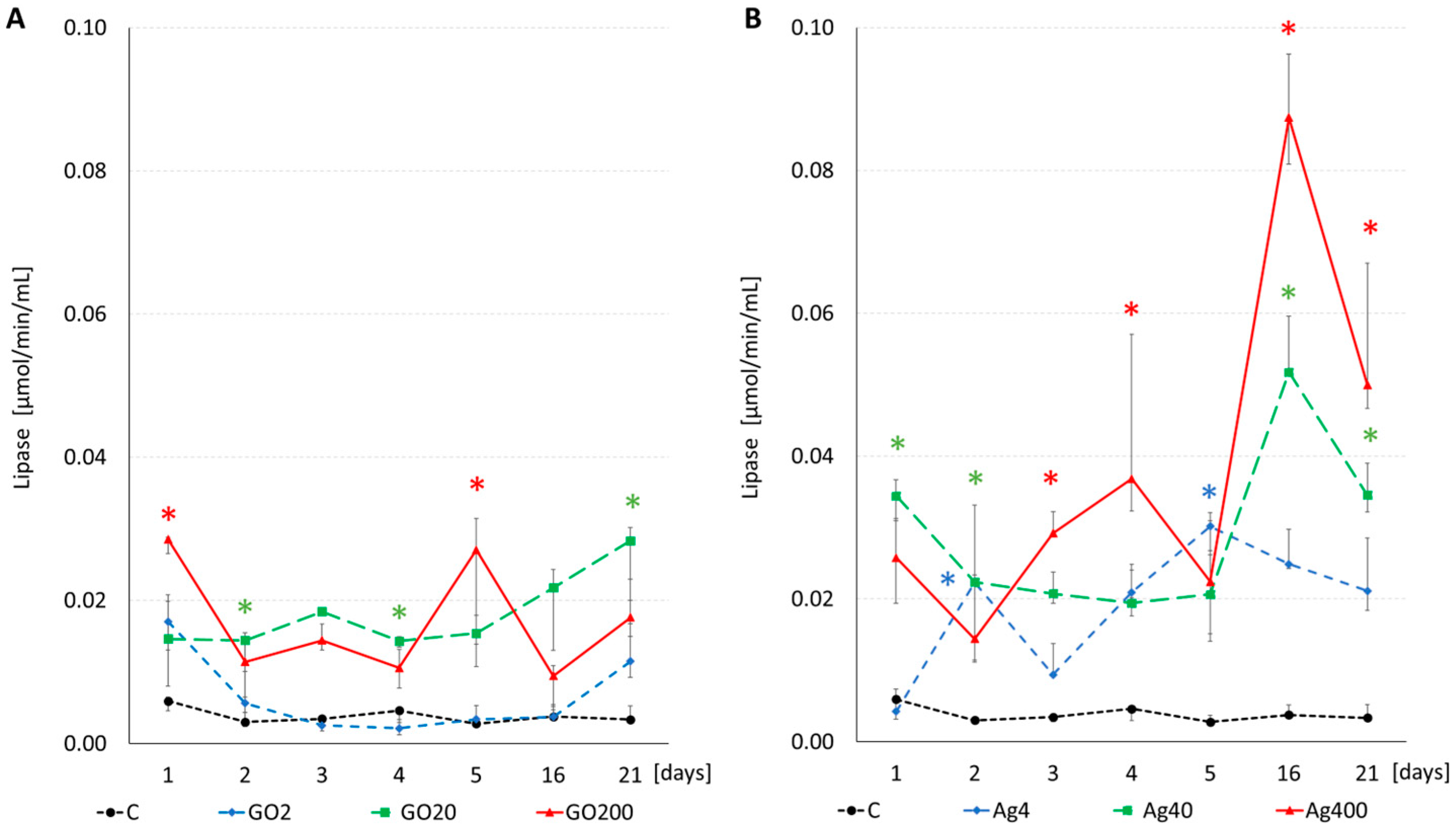
| Effect | All Parameters | Amylase | Protease | Lipase | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | df | p | F | df | p | F | df | p | F | df | p | |
| NP type [1] | 62.015 | 1 | 0.001 | 413.564 | 1 | 0.001 | 15.880 | 1 | 0.001 | 61.463 | 1 | 0.001 |
| Concentration [2] | 133.090 | 3 | 0.001 | 455.196 | 3 | 0.001 | 24.528 | 3 | 0.001 | 106.993 | 3 | 0.001 |
| Time [3] | 14.300 | 6 | 0.001 | 4.727 | 6 | 0.001 | 54.354 | 6 | 0.001 | 4.270 | 6 | 0.001 |
| [1] × [2] | 21.819 | 3 | 0.001 | 144.079 | 3 | 0.001 | 3.811 | 3 | 0.006 | 15.371 | 3 | 0.001 |
| [1] × [3] | 3.412 | 6 | 0.001 | 2.409 | 6 | 0.009 | 11.015 | 6 | 0.001 | 4.897 | 6 | 0.001 |
| [2] × [3] | 2.604 | 18 | 0.001 | 2.540 | 18 | 0.001 | 6.107 | 18 | 0.001 | 3.084 | 18 | 0.001 |
| [1] × [2] × [3] | 1.738 | 18 | 0.008 | 1.725 | 18 | 0.019 | 9.762 | 18 | 0.001 | 4.037 | 18 | 0.001 |
| Residual | 211 | 211 | 211 | 211 | ||||||||
| Total | 266 | 266 | 266 | 266 | ||||||||
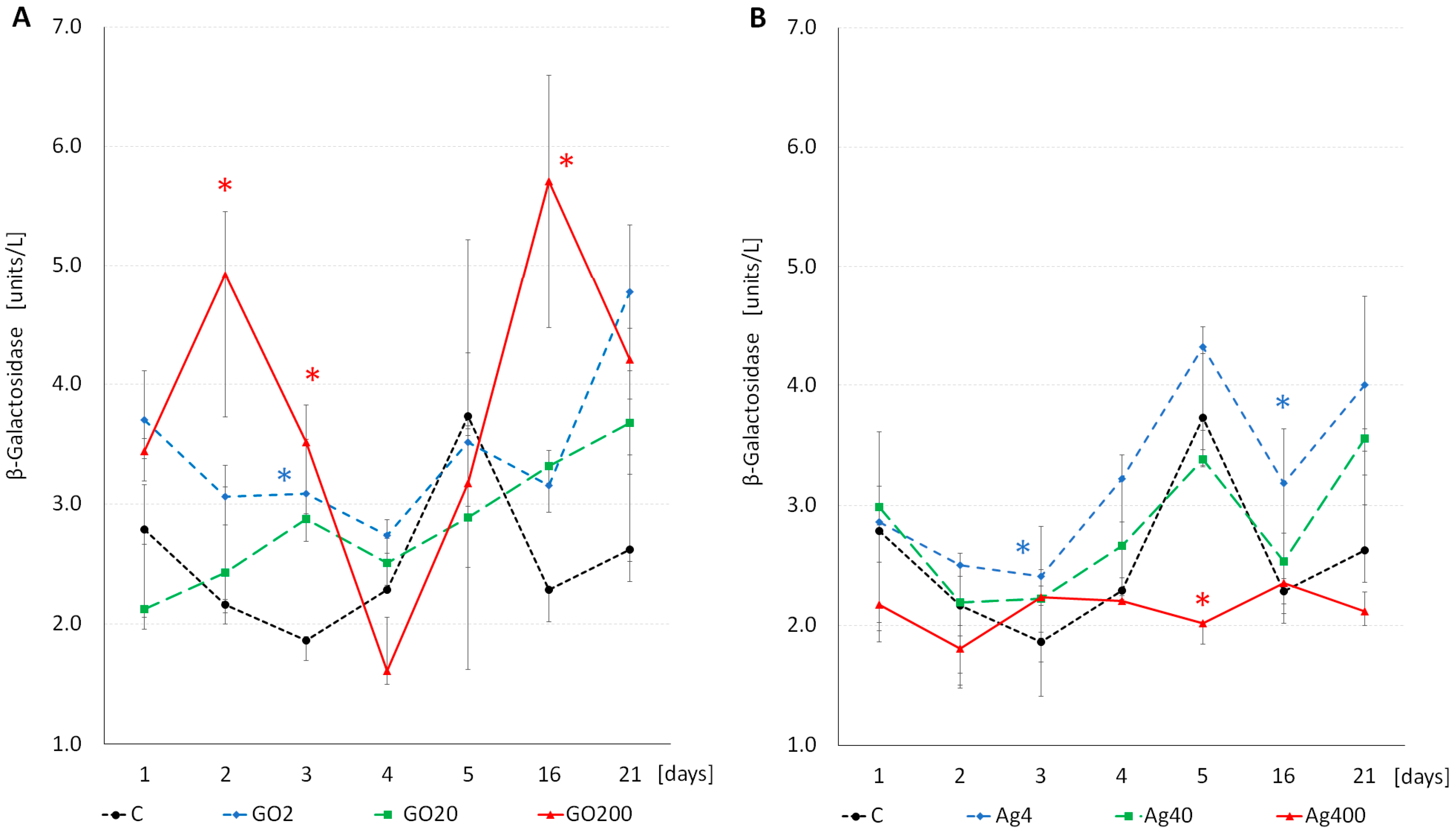
| Effect | α-Glu | β-Glu | β-Gal | |||||||||
| F | df | p | F | df | p | F | df | p | ||||
| NP type [1] | 15.728 | 1 | 0.001 | 47.961 | 1 | 0.001 | 27.483 | 1 | 0.001 | |||
| Concentration [2] | 24.852 | 3 | 0.001 | 13.239 | 3 | 0.001 | 16.973 | 3 | 0.001 | |||
| Time [3] | 17.558 | 6 | 0.001 | 3.111 | 6 | 0.003 | 14.541 | 6 | 0.001 | |||
| [1] × [2] | 4.453 | 3 | 0.004 | 32.356 | 3 | 0.001 | 18.742 | 3 | 0.001 | |||
| [1] × [3] | 5.181 | 6 | 0.001 | 2.681 | 6 | 0.010 | 5.717 | 6 | 0.001 | |||
| [2] × [3] | 2.625 | 18 | 0.001 | 3.147 | 18 | 0.001 | 4.732 | 18 | 0.001 | |||
| [1] × [2] × [3] | 2.231 | 18 | 0.003 | 2.100 | 18 | 0.004 | 2.502 | 18 | 0.001 | |||
| Residual | 211 | 211 | 211 | |||||||||
| Total | 266 | 266 | 266 | |||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seyed Alian, R.; Flasz, B.; Kędziorski, A.; Majchrzycki, Ł.; Augustyniak, M. Concentration- and Time-Dependent Dietary Exposure to Graphene Oxide and Silver Nanoparticles: Effects on Food Consumption and Assimilation, Digestive Enzyme Activities, and Body Mass in Acheta domesticus. Insects 2024, 15, 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15020089
Seyed Alian R, Flasz B, Kędziorski A, Majchrzycki Ł, Augustyniak M. Concentration- and Time-Dependent Dietary Exposure to Graphene Oxide and Silver Nanoparticles: Effects on Food Consumption and Assimilation, Digestive Enzyme Activities, and Body Mass in Acheta domesticus. Insects. 2024; 15(2):89. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15020089
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeyed Alian, Reyhaneh, Barbara Flasz, Andrzej Kędziorski, Łukasz Majchrzycki, and Maria Augustyniak. 2024. "Concentration- and Time-Dependent Dietary Exposure to Graphene Oxide and Silver Nanoparticles: Effects on Food Consumption and Assimilation, Digestive Enzyme Activities, and Body Mass in Acheta domesticus" Insects 15, no. 2: 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15020089
APA StyleSeyed Alian, R., Flasz, B., Kędziorski, A., Majchrzycki, Ł., & Augustyniak, M. (2024). Concentration- and Time-Dependent Dietary Exposure to Graphene Oxide and Silver Nanoparticles: Effects on Food Consumption and Assimilation, Digestive Enzyme Activities, and Body Mass in Acheta domesticus. Insects, 15(2), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15020089







