Assessment of Lambda-Cyhalothrin and Spinetoram Toxicity and Their Effects on the Activities of Antioxidant Enzymes and Acetylcholinesterase in Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) Larvae
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. In Vitro Rearing of Honey Bee Larvae
2.3. Assessment of Risk to Honey Bee Larva
2.3.1. Acute Toxicity Test for Honey Bee Larvae (Single Exposure)
2.3.2. Chronic Toxicity Test for Honey Bee Larvae (Repeated Exposure)
2.3.3. Analysis of Mortality, Emergence Rate, and Morphological Abnormality
2.4. Assessment of the Enzyme Activity
2.4.1. SOD Assay
2.4.2. CAT Assay
2.4.3. GST Assay
2.4.4. AChE Assay
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Acute Toxicity of LCY and SPI in Honey Bee Larvae (Survival of Honey Bee Larvae and Endpoint)
3.2. Chronic Toxicity of Lambda-Cyhalothrin and Spinetoram in Honey Bee Larvae
3.2.1. Effect of Chronic Toxicity (Survival of Honey Bee Larvae and Endpoint)
3.2.2. Morphological Abnormality
3.3. Analysis of Enzyme Activity
3.3.1. Survival of Honey Bee Larvae
3.3.2. Physiological Effects of Lambda-Cyhalothrin
3.3.3. Physiological Effects of Spinetoram
4. Discussion
4.1. Acute Toxicity to Bee Larvae (Single Larvae Exposure)
4.2. Chronic Toxicity to Bee Larvae (Repeated Larvae Exposure)
4.3. Analysis of the Enzyme Activity
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kulhanek, K.; Steinhauer, N.; Rennich, K.; Caron, D.M.; Sagili, R.R.; Pettis, J.S.; Ellis, J.D.; Wilson, M.E.; Wilkes, J.T.; Tarpy, D.R. A national survey of managed honey bee 2015–2016 annual colony losses in the USA. J. Apic. Res. 2017, 56, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervez, M.; Manzoor, F. Honey bee losses and pesticides threat: An Asian perspective. J. Apic. Res. 2023, 62, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, P.; Shumkova, R.; Palova, N.; Neov, B. Factors associated with honey bee colony losses: A mini-review. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beekman, M.; Ratnieks, F. Long-range foraging by the honey-bee, Apis mellifera L. Funct. Ecol. 2000, 14, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, K.H.; Jamal, M.; Ahmad, S.; Ghramh, H.A.; Khanum, S.; Khan, K.A.; Ullah, M.A.; Aljedani, D.M.; Zulfiqar, B. Standardization of managed honey bee (Apis mellifera) hives for pollination of Sunflower (Helianthus annuus) crop. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2021, 33, 101608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Bayo, F.; Goka, K. Pesticide residues and bees–a risk assessment. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullin, C.A.; Frazier, M.; Frazier, J.L.; Ashcraft, S.; Simonds, R.; VanEngelsdorp, D.; Pettis, J.S. High levels of miticides and agrochemicals in North American apiaries: Implications for honey bee health. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mužinić, V.; Želježić, D. Non-target toxicity of novel insecticides. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2018, 69, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y.; Anelli, C.M.; Sheppard, W.S. Sub-lethal effects of pesticide residues in brood comb on worker honey bee (Apis mellifera) development and longevity. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e14720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, D.A.; Dussaubat, C.; Kretzschmar, A.; Carvalho, S.M.; Silva-Zacarin, E.C.; Malaspina, O.; Bérail, G.; Brunet, J.-L.; Belzunces, L.P. Exposure of larvae to thiamethoxam affects the survival and physiology of the honey bee at post-embryonic stages. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yordanova, M.; Evison, S.E.; Gill, R.J.; Graystock, P. The threat of pesticide and disease co-exposure to managed and wild bee larvae. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2022, 17, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burr, S.A.; Ray, D.E. Structure-activity and interaction effects of 14 different pyrethroids on voltage-gated chloride ion channels. Toxicol. Sci. 2004, 77, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drew, W.T.; Harper, K.; Parmar, A.; Dow, M. Lambda-Cyhalothrin. Human Health Risk Assessment for the Proposed Food/Feed Uses of the Insecticide on Cucurbit Begetables (Group 9), Tuberous and Corm Vegetables (Subgroup 1C), Grass Forage, Fodder, and Hay (Group 17), Barley, Buckwheat, Oat, Rye, Wild Rice, and Pistachios; Petition Numbers 5F6994, 3E6593, and 6E7077EPA; Office of Prevention, Pesticides, and Toxic Substances Risk Assessment P: 2007. Available online: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&opi=89978449&url=https://www3.epa.gov/pesticides/endanger/litstatus/effects/redleg-frog/2012/lambda-cyha/appendix-j.pdf&ved=2ahUKEwj6g4rnk8uHAxXFnK8BHYaEGbgQFnoECBIQAQ&usg=AOvVaw19rB_WntwTUVV8GcMHjbit (accessed on 4 February 2024).
- Grout, T.A.; Koenig, P.A.; Kapuvari, J.K.; McArt, S.H. Neonicotinoid Insecticides in New York State; Cornell University: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, Z.; Duan, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Q.; He, Q.; Shi, Y.; Yu, L.; Cao, H. A survey of multiple pesticide residues in pollen and beebread collected in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640, 1578–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaila, L.; Ketola, J.; Toivonen, M.; Loukola, O.; Hakala, K.; Raiskio, S.; Hurme, T.; Jalli, M. Pesticide residues in honeybee-collected pollen: Does the EU regulation protect honeybees from pesticides? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 18225–18244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; He, Q.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Yin, F.; Chai, Y.; Yang, Q.; Jiang, X.; Liao, M.; Yu, L. Analysis of honey bee exposure to multiple pesticide residues in the hive environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PPDB: Pesticide Properties DataBase (2022) Lambda-Cyhalothrin (Ref: OMS 3021). Available online: http://sitem.herts.ac.uk/aeru/ppdb/en/Reports/415.htm (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Ingram, E.M.; Augustin, J.; Ellis, M.D.; Siegfried, B.D. Evaluating sub-lethal effects of orchard-applied pyrethroids using video-tracking software to quantify honey bee behaviors. Chemosphere 2015, 135, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel Razik, M.A.R.A.M. Toxicity and side effects of some insecticides applied in cotton fields on Apis mellifera. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 4987–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.-h.; He, X.-j.; Wang, Z.-l.; Barron, A.B.; Zhang, B.; Zeng, Z.-j.; Wu, X.-b. Short-term exposure to lambda-cyhalothrin negatively affects the survival and memory-related characteristics of worker bees Apis mellifera. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 75, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Castro, M.B.A.; Martinez, L.C.; Cossolin, J.F.S.; Serra, R.S.; Serrão, J.E. Cytotoxic effects on the midgut, hypopharyngeal, glands and brain of Apis mellifera honey bee workers exposed to chronic concentrations of lambda-cyhalothrin. Chemosphere 2020, 248, 126075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galm, U.; Sparks, T.C. Natural product derived insecticides: Discovery and development of spinetoram. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 43, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, G.D.; Dutton, R.; Sparks, T.C. Spinosad–a case study: An example from a natural products discovery programme. Pest Manag. Sci. Former. Pestic. Sci. 2000, 56, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dripps, J.; Boucher, R.; Chloridis, A.; Cleveland, C.; DeAmicis, C.; Gomez, L.; Paroonagian, D.; Pavan, L.; Sparks, T.; Watson, G. The spinosyn insecticides. In Green Trends in Insect Control; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2011; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- D’Ambrosio, D.A.; Huseth, A.S.; Kennedy, G.G. Evaluation of alternative mode of action insecticides in managing neonicotinoid-resistant Frankliniella fusca in cotton. Crop Prot. 2018, 113, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostiguy, N.; Drummond, F.A.; Aronstein, K.; Eitzer, B.; Ellis, J.D.; Spivak, M.; Sheppard, W.S. Honey bee exposure to pesticides: A four-year nationwide study. Insects 2019, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PPDB: Pesticide Properties DataBase (2022) Spinetoram (Ref: XDE 175). Available online: http://sitem.herts.ac.uk/aeru/ppdb/en/Reports/1144.htm (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Abdu-Allah, G.A.; Pittendrigh, B.R. Lethal and sub-lethal effects of select macrocyclic lactones insecticides on forager worker honey bees under laboratory experimental conditions. Ecotoxicology 2018, 27, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.-H.; Li, W.-L.; Wang, J.-P.; Li, X.-J.; Li, D.; Cao, Z.; Huang, Q.; Li, J.-L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.-W. Effects of spinetoram and glyphosate on physiological biomarkers and gut microbes in Bombus terrestris. Front. Physiol. 2023, 13, 1054742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, S.M.; Belzunces, L.P.; Carvalho, G.A.; Brunet, J.L.; Badiou-Beneteau, A. Enzymatic biomarkers as tools to assess environmental quality: A case study of exposure of the honeybee Apis mellifera to insecticides. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 2117–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, S.; Zhu, L.; Wang, D.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Xue, X.; Wu, L. Flumethrin at honey-relevant levels induces physiological stresses to honey bee larvae (Apis mellifera L.) in vitro. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murawska, A.; Migdał, P.; Roman, A. Effects of plant protection products on biochemical markers in honey bees. Agriculture 2021, 11, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighodaro, O.; Akinloye, O. First line defence antioxidants-superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX): Their fundamental role in the entire antioxidant defence grid. Alex. J. Med. 2018, 54, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Q.; Yuan, K.; Liang, P.; Gao, X. Tissue distribution and properties of glutathione S-transferases in Apis cerana cerana Fabricius and Apis mellifera ligustica Spinola. J. Apic. Res. 2006, 45, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badiou, A.; Meled, M.; Belzunces, L. Honeybee Apis mellifera acetylcholinesterase—A biomarker to detect deltamethrin exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2008, 69, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmehl, D.R.; Tomé, H.V.; Mortensen, A.N.; Martins, G.F.; Ellis, J.D. Protocol for the in vitro rearing of honey bee (Apis mellifera L.) workers. J. Apic. Res. 2016, 55, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 237: Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) Larval Toxicity Test, Single Exposure. OECD Guidance for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2, No. 237; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Test No. 239: Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) Larval Toxicity Test, Repeated Exposure. OECD Environment, Health and Safety Publications, Series on Testing and Assessment, No.239; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Chon, K.; Kim, B.S.; Oh, J.A.; Yoon, C.Y.; Park, H.H. Assessment of acute and chronic toxicity of cyantraniliprole and sulfoxaflor on honey bee (Apis mellifera) larvae. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 5402–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Chon, K.; Kim, B.-S.; Oh, J.-A.; Yoon, C.-Y.; Park, H.-H.; Choi, Y.-S. Horizontal honey-bee larvae rearing plates can increase the deformation rate of newly emerged adult honey bees. Insects 2021, 12, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, P.; Jack, C.J.; Mortensen, A.N.; Ellis, J.D. Acute toxicity of five pesticides to Apis mellifera larvae reared in vitro. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 2282–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Zhang, S.; Yin, F.; Liu, Q.; Gao, Q.; Xiao, J.; Huang, Y.; Yu, L.; Cao, H. Risk assessment of honeybee larvae exposure to pyrethroid insecticides in beebread and honey. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 267, 115591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, L.D.; Atkins Jr, E.L. Pesticide usage in relation to beekeeping. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1968, 13, 213–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardstone, M.C.; Scott, J.G. Is Apis mellifera more sensitive to insecticides than other insects? Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ma, S.; Liu, F.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Hou, C.; Wu, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. Acute and chronic toxicity of acetamiprid, carbaryl, cypermethrin and deltamethrin to Apis mellifera larvae reared in vitro. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staroň, M.; Sabo, R.; Sobeková, A.; Sabová, L.; Legáth, J.; Lohajová, Ľ.; Javorský, P. Formetanate toxicity and changes in antioxidant enzyme system of Apis mellifera larvae. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 14060–14070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Guo, Y.; Chen, J.; Diao, Q.-Y.; Wang, Q.; Dai, P.-L.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.-M.; Wu, Y.-Y. Acute oral toxicity, apoptosis, and immune response in nurse bees (Apis mellifera) induced by flupyradifurone. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1150340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrese, E.L.; Soulages, J.L. Insect fat body: Energy, metabolism, and regulation. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2010, 55, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jehlík, T.; Kodrík, D.; Krištůfek, V.; Koubová, J.; Sábová, M.; Danihlík, J.; Tomčala, A.; Čapková Frydrychová, R. Effects of Chlorella sp. on biological characteristics of the honey bee Apis mellifera. Apidologie 2019, 50, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farris, S.; Robinson, G.; Davis, R.; Fahrbach, S. Larval and pupal development of the mushroom bodies in the honey bee, Apis mellifera. J. Comp. Neurol. 1999, 414, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.J.; Moffat, C.; Saranzewa, N.; Harvey, J.; Wright, G.A.; Connolly, C.N. Cholinergic pesticides cause mushroom body neuronal inactivation in honeybees. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grillone, G.; Laurino, D.; Manino, A.; Porporato, M. Toxicity of thiametoxam on in vitro reared honey bee brood. Apidologie 2017, 48, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, W.F.; Tomé, H.V.V.; Bernardes, R.C.; Siqueira, M.A.L.; Smagghe, G.; Guedes, R.N.C. Biopesticide-induced behavioral and morphological alterations in the stingless bee Melipona quadrifasciata. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 2149–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, F.C.; Da Cruz-Landim, C.; Malaspina, O. Influence of the insecticide pyriproxyfen on the flight muscle differentiation of Apis mellifera (Hymenoptera, Apidae). Microsc. Res. Tech. 2012, 75, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oertel, E. Metamorphosis in the honeybee. J. Morphol. 1930, 50, 295–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truman, J.; Hiruma, K.; Allee, J.; MacWhinnie, S.; Champlin, D.; Riddiford, L. Juvenile hormone is required to couple imaginal disc formation with nutrition in insects. Science 2006, 312, 1385–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jia, Q.Q.; Li, S. Juvenile hormone signaling—A mini review. Insect Sci. 2019, 26, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-W.; Wu, P.-S.; Yang, E.-C.; Nai, Y.-S.; Huang, Z.Y. The impact of pyriproxyfen on the development of honey bee (Apis mellifera L.) colony in field. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2016, 19, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botina, L.L.; Barbosa, W.F.; Acosta, J.P.L.; Bernardes, R.C.; Cortes, J.E.Q.; Pylro, V.S.; Mendonça, A.C.; Barbosa, R.C.; Lima, M.A.P.; Martins, G.F. The impact of early-life exposure to three agrochemicals on survival, behavior, and gut microbiota of stingless bees (Partamona helleri). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 70143–70158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, D.E.; Latorre-Estivalis, J.M.; Ons, S.; Farina, W.M. Chronic exposure to glyphosate induces transcriptional changes in honey bee larva: A toxicogenomic study. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Diao, Q. Current knowledge of detoxification mechanisms of xenobiotic in honey bees. Ecotoxicology 2017, 26, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shi, T.; Xu, S.; Lu, B.; Qin, H.; Yu, L. Synergistic toxicity and physiological impact of thiamethoxam alone or in binary mixtures with three commonly used insecticides on honeybee. Apidologie 2020, 51, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordberg, J.; Arnér, E.S. Reactive oxygen species, antioxidants, and the mammalian thioredoxin system. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2001, 31, 1287–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weirich, G.F.; Collins, A.M.; Williams, V.P. Antioxidant enzymes in the honey bee, Apis mellifera. Apidologie 2002, 33, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabová, L.; Sobeková, A.; Staroň, M.; Sabo, R.; Legáth, J.; Staroňová, D.; Lohajová, Ľ.; Javorský, P. Toxicity of oxalic acid and impact on some antioxidant enzymes on in vitro–reared honeybee larvae. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 19763–19769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Hu, Z.; Gao, Q.; Dong, Y.; Xiao, J.; Yu, L.; Cao, H. The effects of beta-cypermethrin, chlorbenzuron, chlorothalonil, and pendimethalin on Apis mellifera ligustica and Apis cerana cerana larvae reared in vitro. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenbaum, M.R.; Johnson, R.M. Xenobiotic detoxification pathways in honey bees. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2015, 10, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.A.; Brødsgaard, C.J.; Hansen, H. Effects on detoxification enzymes in different life stages of honey bees (Apis mellifera L., Hymenoptera: Apidae) treated with a synthetic pyrethroid (flumethrin). Altern. Lab. Anim. 2000, 28, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Gao, J.; Wu, T.; Han, B.; Qian, B.; Shi, M.; Yang, S.; Diao, Q.; Bu, C.; Dai, P. Exposure of chlorothalonil and acetamiprid reduce the survival and cause multiple internal disturbances in Apis mellifera larvae reared in vitro. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1114403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, L.; Qi, S.; Zhao, W.; Xue, X.; Wu, L.; Huang, S. Sublethal effects of Isoclast™ Active (50% sulfoxaflor water dispersible granules) on larval and adult worker honey bees (Apis mellifera L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 220, 112379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boily, M.; Sarrasin, B.; DeBlois, C.; Aras, P.; Chagnon, M. Acetylcholinesterase in honey bees (Apis mellifera) exposed to neonicotinoids, atrazine and glyphosate: Laboratory and field experiments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5603–5614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabea, E.I.; Nasr, H.M.; Badawy, M.E. Toxic effect and biochemical study of chlorfluazuron, oxymatrine, and spinosad on honey bees (Apis mellifera). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 58, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, M.E.; Nasr, H.M.; Rabea, E.I. Toxicity and biochemical changes in the honey bee Apis mellifera exposed to four insecticides under laboratory conditions. Apidologie 2015, 46, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colovic, M.B.; Krstic, D.Z.; Lazarevic-Pasti, T.D.; Bondzic, A.M.; Vasic, V.M. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: Pharmacology and toxicology. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2013, 11, 315–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, S.M.; Moffat, C.; Gomersall, M.A.; Saranzewa, N.; Connolly, C.N.; Wright, G.A. Exposure to acetylcholinesterase inhibitors alters the physiology and motor function of honeybees. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.; Wang, C.; Dong, S.; Li, X.; Nieh, J.C. The pesticide flupyradifurone impairs olfactory learning in Asian honey bees (Apis cerana) exposed as larvae or as adults. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Chen, W.; Dong, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Nieh, J.C. A neonicotinoid impairs olfactory learning in Asian honey bees (Apis cerana) exposed as larvae or as adults. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grünewald, B.; Siefert, P. Acetylcholine and its receptors in honeybees: Involvement in development and impairments by neonicotinoids. Insects 2019, 10, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


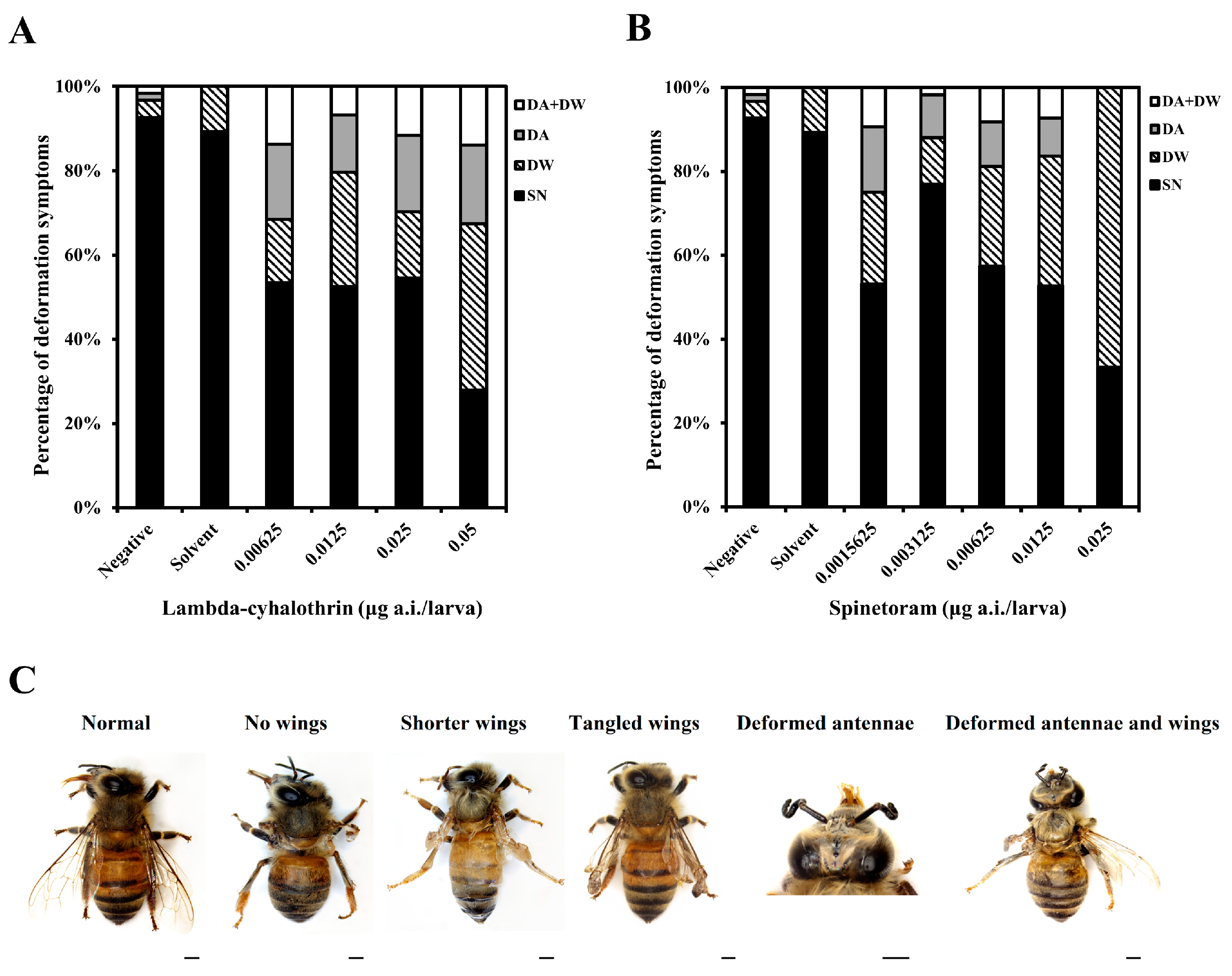
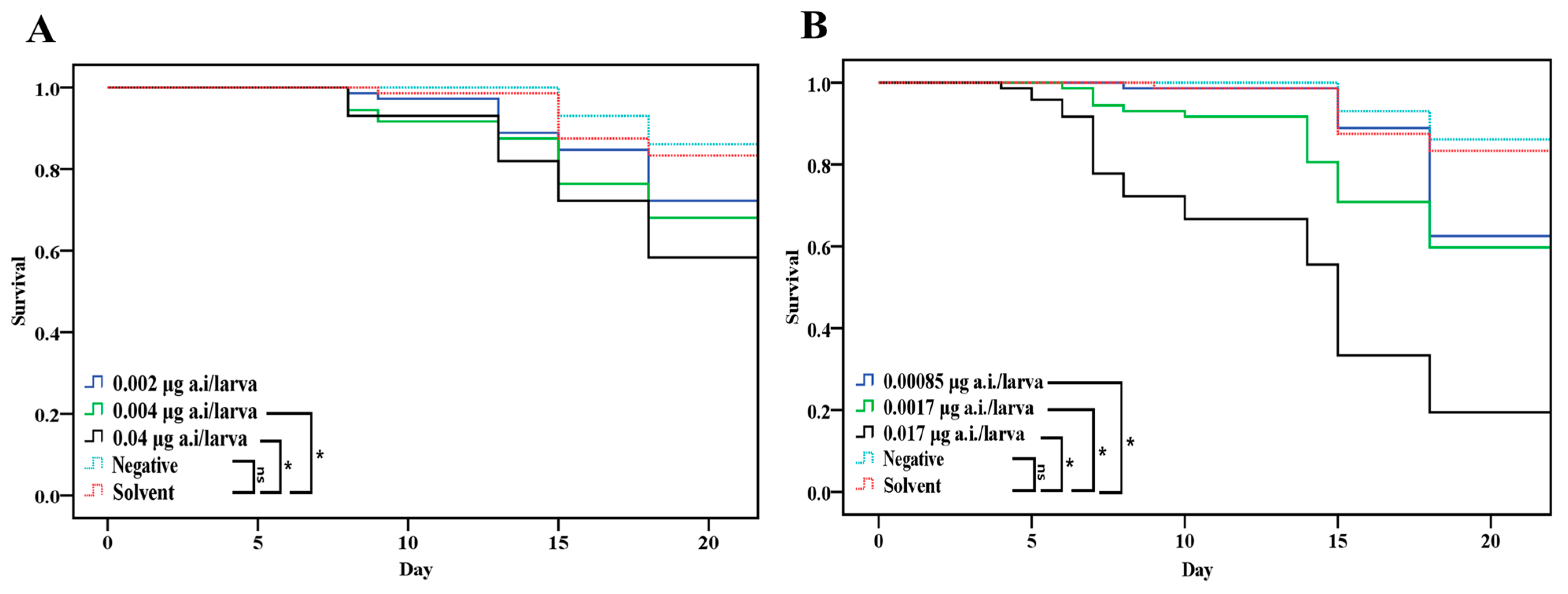
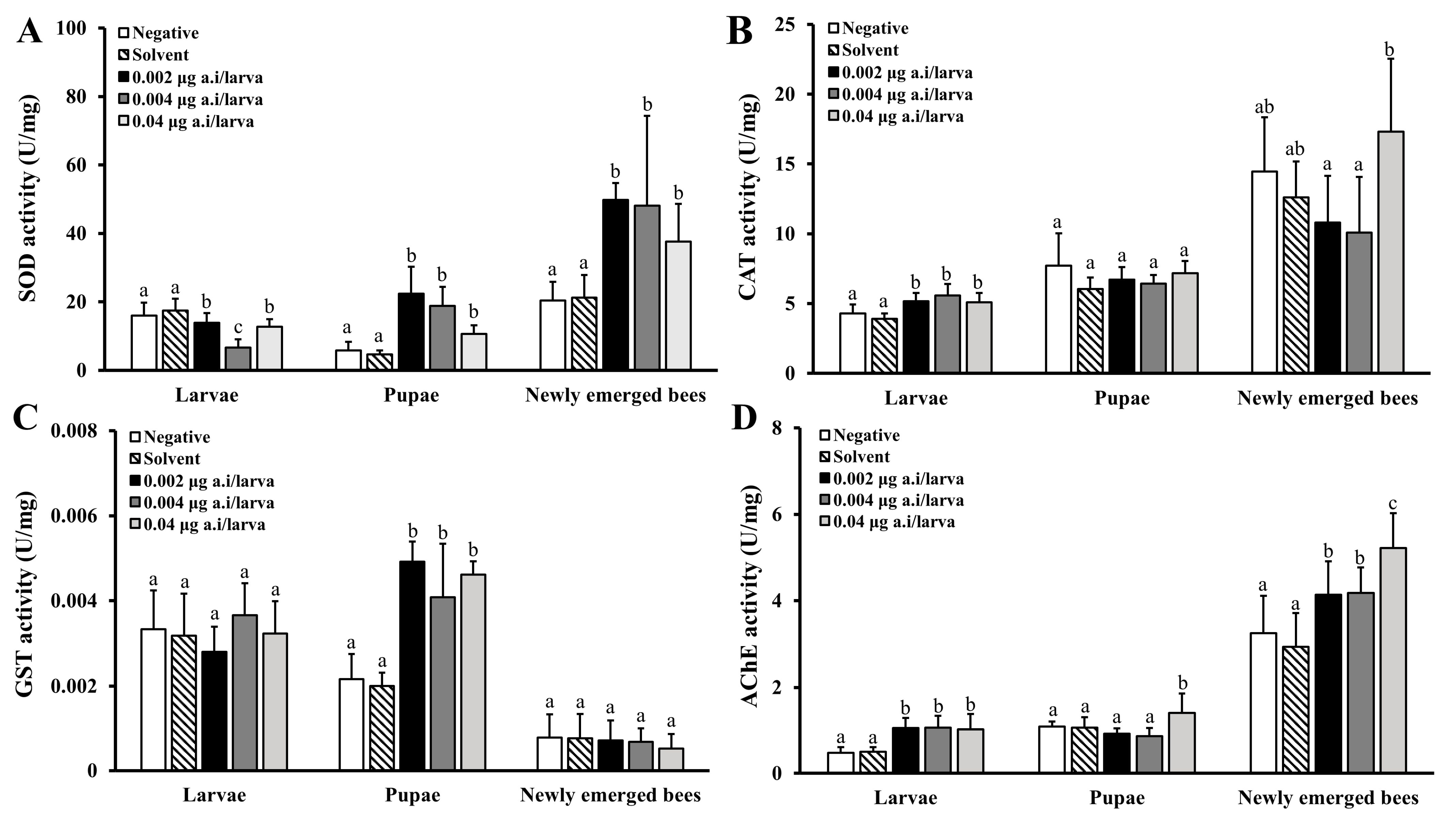

| Bioassay | Pesticide | LC50 (mg/L) | LD50 (μg a.i./larva) | Chronic NOED a (μg a.i./larva) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute toxicity b | Lambda-cyhalothrin | 1.947 (1.706–2.185) | 0.058 (0.051–0.066) | |
| Spinetoram | 0.826 (0.449–1.166) | 0.026 (0.01–0.045) | ||
| Chronic toxicity c | Lambda-cyhalothrin | 0.289 (0.238–0.327) | 0.040 (0.033–0.046) | 0.0125 |
| Spinetoram | 0.119 (0.103–0.133) | 0.017 (0.014–0.019) | 0.0125 |
| Chemical | Treatment Group (μg/larva) | Larval Mortality (%) | Pupal Mortality (%) | Adult Emergence Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative control | 0.0 | 15.3 (±2.6) | 84.7 (±2.8) | |
| Solvent control | 0.0 | 22.2 (±2.8) | 77.8 (±2.8) | |
| Lambda-cyhalothrin | 0.00625 | 2.8 (±1.8) | 15.5 (±2.4) | 81.9 (±1.4) |
| 0.0125 | 1.4 (±1.4) | 25.3 (±5.2) | 73.6 (±5.0) | |
| 0.025 | 2.8 (±1.8) | 28.4 (±5.0) | 69.4 (±4.6) * | |
| 0.05 | 23.6 (±3.3) *** | 71.5 (±4.7) *** | 22.2 (±4.1) *** | |
| 0.1 | 97.2 (±1.8) *** | 100 | - | |
| Spinetoram | 0.0015625 | 2.8 (±1.8) | 18.4 (±4.7) | 79.2 (±4.2) |
| 0.003125 | 1.4 (±1.4) | 18.3 (±5.0) | 80.6 (±5.1) | |
| 0.00625 | 5.6 (±2.8) | 21.1 (±5.0) | 75 (±5.7) | |
| 0.0125 | 18.1 (±3.3) *** | 16.5 (±2.7) | 68.1 (±1.4) | |
| 0.025 | 61.1 (±6.3) *** | 91.3 (±4.1) *** | 8.3 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, J.-Y.; Chon, K.; Kim, J.; Vasamsetti, B.M.K.; Kim, B.-S.; Yoon, C.-Y.; Hwang, S.; Park, K.-H.; Lee, J.-H. Assessment of Lambda-Cyhalothrin and Spinetoram Toxicity and Their Effects on the Activities of Antioxidant Enzymes and Acetylcholinesterase in Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) Larvae. Insects 2024, 15, 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15080587
Choi J-Y, Chon K, Kim J, Vasamsetti BMK, Kim B-S, Yoon C-Y, Hwang S, Park K-H, Lee J-H. Assessment of Lambda-Cyhalothrin and Spinetoram Toxicity and Their Effects on the Activities of Antioxidant Enzymes and Acetylcholinesterase in Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) Larvae. Insects. 2024; 15(8):587. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15080587
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Ji-Yeong, Kyongmi Chon, Juyeong Kim, Bala Murali Krishna Vasamsetti, Bo-Seon Kim, Chang-Young Yoon, Sojeong Hwang, Kyeong-Hun Park, and Ji-Hoon Lee. 2024. "Assessment of Lambda-Cyhalothrin and Spinetoram Toxicity and Their Effects on the Activities of Antioxidant Enzymes and Acetylcholinesterase in Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) Larvae" Insects 15, no. 8: 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15080587
APA StyleChoi, J.-Y., Chon, K., Kim, J., Vasamsetti, B. M. K., Kim, B.-S., Yoon, C.-Y., Hwang, S., Park, K.-H., & Lee, J.-H. (2024). Assessment of Lambda-Cyhalothrin and Spinetoram Toxicity and Their Effects on the Activities of Antioxidant Enzymes and Acetylcholinesterase in Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) Larvae. Insects, 15(8), 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15080587








