PxDorsal Regulates the Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides and Affects the Bt Susceptibility of Plutella xylostella
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Strains and Plasmids
2.2. Test Insects
2.3. Cloning of PxDorsal and PxCactus Genes
2.4. Sequence and Structural Model Analysis of PxDorsal and PxCactus
2.5. Spatio-Temporal Expression Detection of PxDorsal and PxCactus Genes in P. xylostella and the Immune Genes After Bt Infection
2.6. RNAi of PxDorsal Gene and Its Effects on the Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides of P. xylostella
2.7. The Epidermis Melanization of P. xylostella Under the Infection of Bt8010
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of PxDorsal and PxCactus
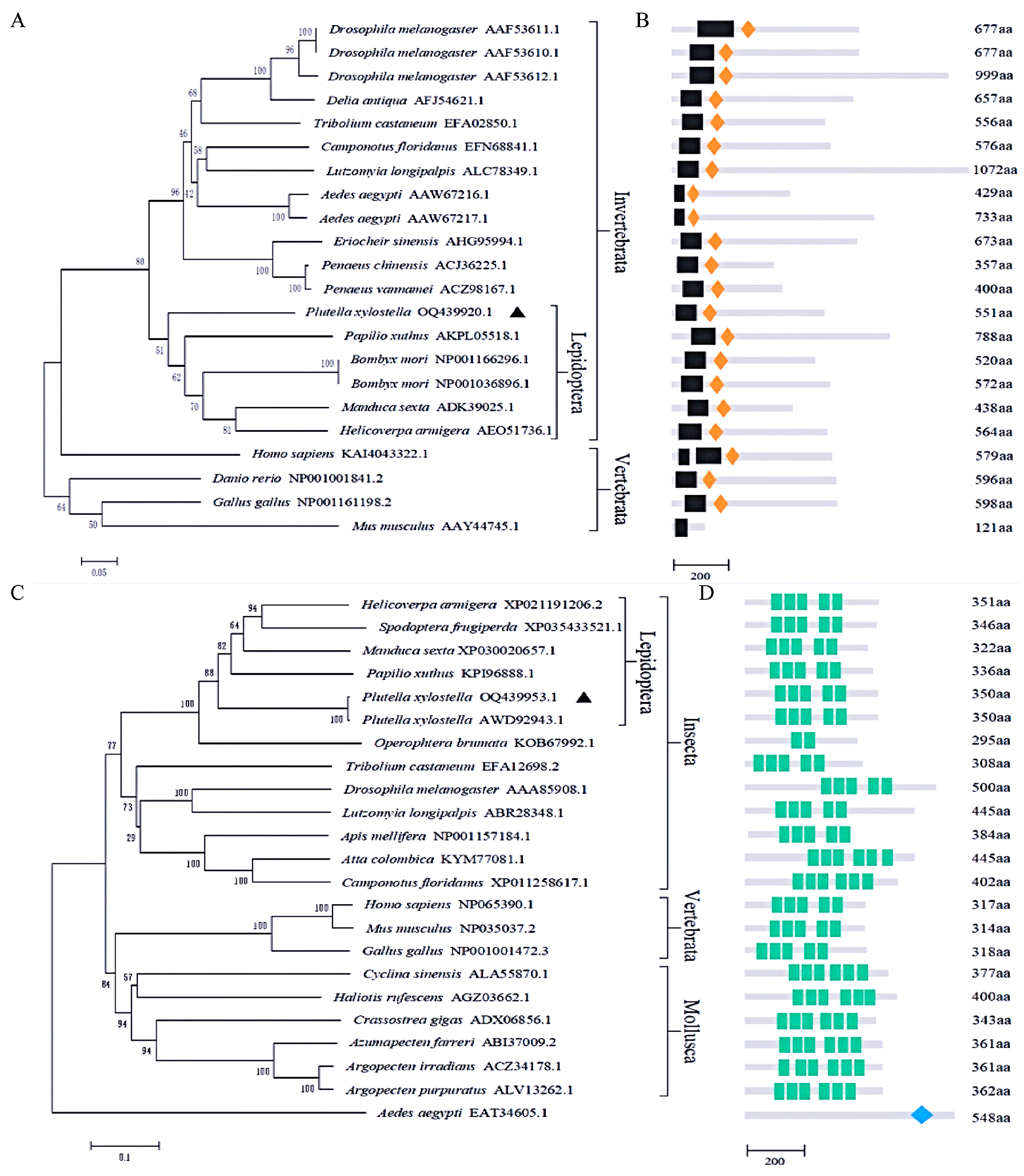
3.2. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis of PxDorsal and PxCactus
3.3. Structural Modeling and PxDorsal–PxCactus Interaction Analysis
3.4. Spatio-Temporal Expression Analysis of PxDorsal and PxCactus
3.5. Bt8010 Regulates the Expression of Immune Genes in P. xylostella
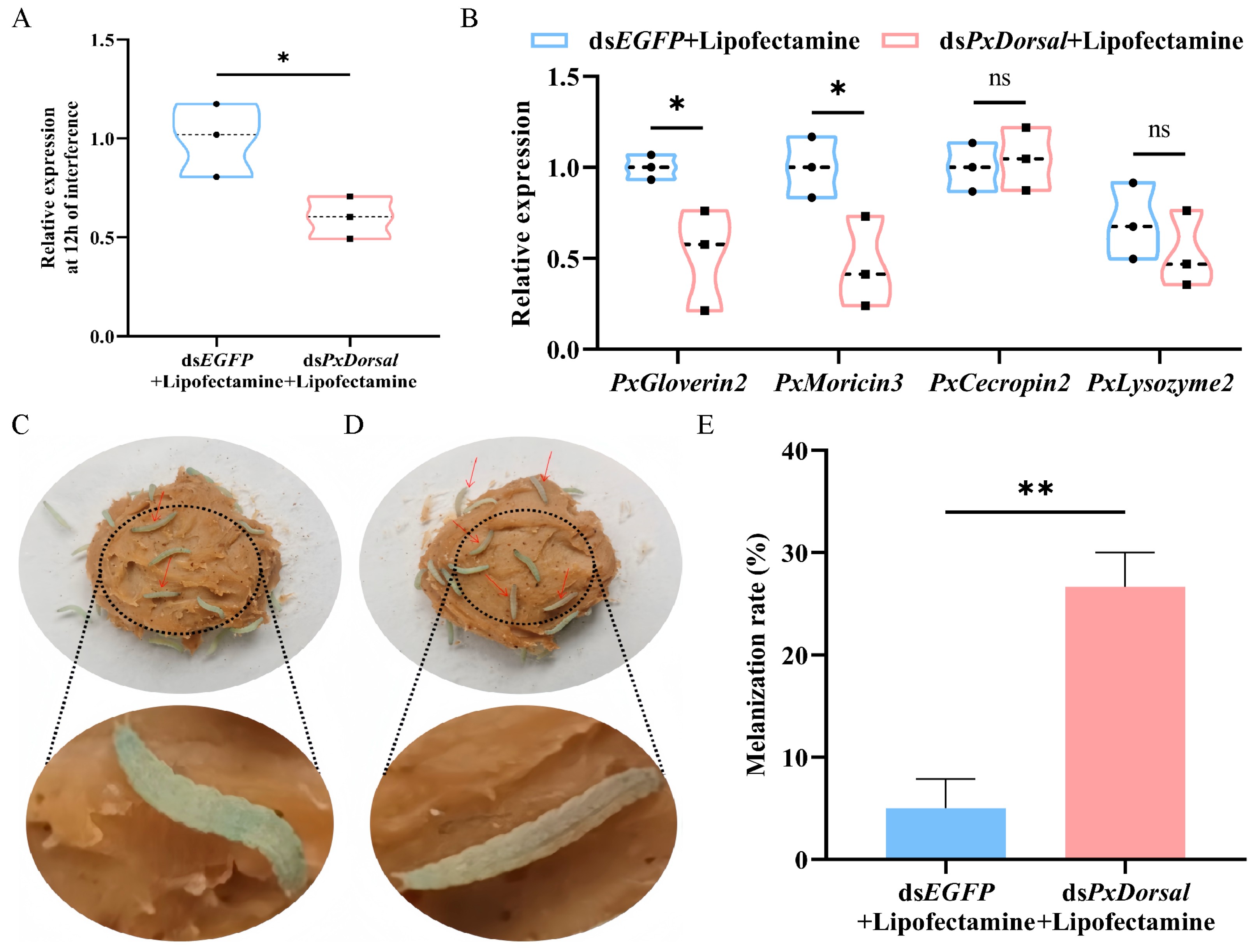
3.6. Knockdown of PxDorsal Inhibited the Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides and Increased the Epidermis Melanization Rate of P. xylostella
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoffmann, J.A. The immune response of Drosophila. Nature 2003, 426, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; May, M.J.; Kopp, E.B. NF-κB and Rel proteins: Evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1998, 16, 225–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetru, C.; Hoffmann, J.A. NF-κB in the immune response of Drosophila. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a000232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.X.; He, Z.; Lu, Y.; Liu, X.S.; Wang, Y.F.; Yu, X.Q. An in vitro study of NF-κB factors cooperatively in regulation of Drosophila melanogaster antimicrobial peptide genes. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 95, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisler, R.; Bergmann, A.; Hiromi, Y.; Nüsslein-Volhard, C. Cactus, a gene involved in dorsoventral pattern formation of Drosophila, is related to the IκB gene family of vertebrates. Cell 1992, 71, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luque, I.; Zong, W.X.; Chen, C.; Gélinas, C. N-terminal determinants of IκBα necessary for the cytoplasmic regulation of c-Rel. Oncogene 2000, 19, 1239–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, S.; Tanaka, H.; Ishibashi, J.; Imanishi, S.; Yamakawa, M. Functional characterization of a cactus homolog from the silkworm Bombyx mori. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 2665–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Li, F.; Li, S.; Chi, Y.; Wen, R.; Feng, N.; Xiang, J. An IκB homologue (FcCactus) in Chinese shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 39, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, Y.X.; Zhang, S.; Lu, L.; Chen, Y.H.; Chai, J.; Weng, S.; Chen, Y.G.; He, J.; Xu, X. Identification, characterization, and function analysis of the Cactus gene from Litopenaeus vannamei. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whalen, A.M.; Steward, R. Dissociation of the dorsal-cactus complex and phosphorylation of the dorsal protein correlate with the nuclear localization of dorsal. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 123, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeuerle, P.A.; Henkel, T. Function and activation of NF-κB in the immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1994, 12, 141–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Rao, X.J.; Yi, H.Y.; Lin, X.Y.; Huang, X.H.; Yu, X.Q. Co-expression of Dorsal and Rel2 negatively regulates antimicrobial peptide expression in the tobacco hornworm Manduca sexta. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Hu, L.; Li, J.; Yan, W.; Song, E.; Kuang, M.; Liu, S.; He, J.; Weng, S. The NF-κB family member dorsal plays a role in immune response against Gram-positive bacterial infection in mud crab (Scylla paramamosain). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 106, 103581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Sun, X.J.; Yan, M.; Chen, Q.; Gao, L.; Kang, C.J. The ECSIT Mediated Toll3-Dorsal-ALFs Pathway Inhibits Bacterial Amplification in Kuruma Shrimp. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 807326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishide, Y.; Nagamine, K.; Kageyama, D.; Moriyama, M.; Futahashi, R.; Fukatsu, T. A new antimicrobial peptide, Pentatomicin, from the stinkbug Plautia stali. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaitre, B.; Reichhart, J.M.; Hoffmann, J.A. Drosophila host defense differential induction of antimicrobial peptide genes after infection by various classes ofmicroorganisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 14614–14619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levashina, E.A.; Ohresser, S.; Lemaitre, B.; Imler, J.L. Two distinct pathways can control expression of the gene encoding the Drosophila antimicrobial peptide metchnikowin. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 278, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfruelli, P.; Reichhart, J.; Steward, R.; Hoffmann, J.A.; Lemaitre, B. A mosaic analysis in Drosophila fat body cells of the control of antimicrobial peptide genes by the Rel proteins Dorsal and DIF. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 3380–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaitre, B.; Kromer-Metzger, E.; Michaut, L.; Nicolas, E.; Meister, M.; Georgel, P.; Reichhart, J.M.; Hoffmann, J.A. A recessive mutation, immune deficiency (imd), defines two distinct control pathways in the Drosophila host defense. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 9465–9469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsay, S.A.; Wasserman, S.A. Conventional and non-conventional Drosophila Toll signaling. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 42, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Yu, L.; Xue, M.; Yu, X.; Vasseur, L.; Gurr, G.M.; Baxter, S.W.; Lin, H.; Lin, J.; You, M. Genome-wide characterization and expression profiling of immune genes in the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (L.). Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Xia, X.; Yu, X.Q.; Shen, J.; Li, Y.; Lin, H.; Tang, S.; Vasseur, L.; You, M. Gene expression profiling provides insights into the immune mechanism of Plutella xylostella midgut to microbial infection. Gene 2018, 647, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furlong, M.J.; Wright, D.J.; Dosdall, L.M. Diamondback moth ecology and management: Problems, progress, and prospects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 517–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Sun, D.; Kang, S.; Zhou, J.; Gong, L.; Qin, J.; Guo, L.; Zhu, L.; Bai, Y.; Luo, L.; et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout of both the PxABCC2 and PxABCC3 genes confers high-level resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac toxin in the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (L.). Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 107, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grizanova, E.V.; Dubovskiy, I.M.; Whitten, M.M.; Glupov, V.V. Contributions of cellular and humoral immunity of Galleria mellonella larvae in defence against oral infection by Bacillus thuringiensis. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2014, 119, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, E.; Benito-Jardon, M.; Lopez-Galiano, M.J.; Real, M.D.; Rausell, C. Tribolium castaneum immune defense genes are differentially expressed in response to Bacillus thuringiensis toxins sharing common receptor molecules and exhibiting disparate toxicity. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 50, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, F.; Chen, C.; Wu, S.; Shao, E.; Li, M.; Guan, X.; Huang, Z. Transcriptional profiling analysis of Spodoptera litura larvae challenged with Vip3Aa toxin and possible involvement of trypsin in the toxin activation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Yi, Y. Transcriptome analysis of differentially expressed genes involved in innate immunity following Bacillus thuringiensis challenge in Bombyx mori larvae. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 103, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovskiy, I.M.; Grizanova, E.V.; Whitten, M.M.; Mukherjee, K.; Greig, C.; Alikina, T.; Kabilov, M.; Vilcinskas, A.; Glupov, V.V.; Butt, T.M. Immuno-physiological adaptations confer wax moth Galleria mellonella resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis. Virulence 2016, 7, 860–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Yang, S.; Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Du, M.; An, S.; Liang, G. Transcriptomic responses to different Cry1Ac selection stresses in Helicoverpa armigera. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Gu, Y.; Liu, X.; Lin, Y.; Yu, X.Q. Possible insecticidal mechanisms mediated by immune response related Cry-binding proteins in the midgut juice of Plutella xylostella and Spodoptera exigua. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 2048–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.X.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Freed, S.; Yu, J.; Gao, Y.F.; Wang, S.; Ouyang, L.N.; Ju, W.Y.; Jin, F.L. An anionic defensin from Plutella xylostella with potential activity against Bacillus thuringiensis. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2016, 106, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.F. Comparative Identification of Immune Related Proteins at Different Development Stages of Plutella xylostella and Functional Study on Cactus Gene. Master’s Thesis, South China Agricultural University, Guangzhou, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Valanne, S.; Wang, J.H.; Ramet, M. The Drosophila Toll signaling pathway. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, B.A.; Yadav, S.; Shokal, U.; Smith, L.C.; Eleftherianos, I. Bacterial and fungal pattern recognition receptors in homologous innate signaling pathways of insects and mammals. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Yu, X.Q.; Wang, Q.; Tao, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Xia, X.; You, M. Immune responses to Bacillus thuringiensis in the midgut of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 107, 103661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyard, S.; Singh, A.D.; Wong, S. Ingested double-stranded RNAs can act as species-specific insecticides. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 39, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatada, E.N.; Nieters, A.; Wulczyn, F.G.; Naumann, M.; Meyer, R.; Nucifora, G.; McKeithan, T.W.; Scheidereit, C. The ankyrin repeat domains of the NF-κB precursor p105 and the protooncogene bc1-3 act as specific inhibitors of NF-κB DNA binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 2489–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yuan, J.; Yang, L.; Weng, S.; He, J.; Zuo, H. The Dorsal/miR-1959/Cactus feedback loop facilitates the infection of WSSV in Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 56, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclerc, V.; Reichhart, J.-M. The immune response of Drosophila melanogaster. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 198, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.M.; Ye, G.Y. NF-κB signaling in insects. Chin. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 28, 561–565. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.J.; Xu, S.; He, Z.H.; Shi, X.Z.; Zhao, X.F.; Wang, J.X. Activation of Toll Pathway Is Different between Kuruma Shrimp and Drosophila. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishide, Y.; Kageyama, D.; Yokoi, K.; Jouraku, A.; Tanaka, H.; Futahashi, R.; Fukatsu, T. Functional crosstalk across IMD and Toll pathways: Insight into the evolution of incomplete immune cascades. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2019, 286, 20182207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, Y.; Kanost, M.R. Pro-phenol oxidase activating proteinase from an insect, Manduca sexta: A bacteria-inducible protein similar to Drosophila easter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 12220–12225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerenius, L.; Söderhäll, K. The prophenoloxidase-activating system in invertebrates. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 198, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barillas-Mury, C. CLIP proteases and Plasmodium melanization in Anopheles gambiae. Trends Parasitol. 2007, 23, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, H.; Kim, C.H.; Kwon, H.M.; Park, J.W.; Roh, K.B.; Lee, H.; Park, B.J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, J.; Soderhall, K.; et al. Molecular control of phenoloxidase-induced melanin synthesis in an insect. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 25316–25323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Wen, H.; Xue, W.; Xia, X. PxDorsal Regulates the Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides and Affects the Bt Susceptibility of Plutella xylostella. Insects 2025, 16, 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16020163
Sun Y, Wen H, Xue W, Xia X. PxDorsal Regulates the Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides and Affects the Bt Susceptibility of Plutella xylostella. Insects. 2025; 16(2):163. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16020163
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yan, Haoqi Wen, Wenrui Xue, and Xiaofeng Xia. 2025. "PxDorsal Regulates the Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides and Affects the Bt Susceptibility of Plutella xylostella" Insects 16, no. 2: 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16020163
APA StyleSun, Y., Wen, H., Xue, W., & Xia, X. (2025). PxDorsal Regulates the Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides and Affects the Bt Susceptibility of Plutella xylostella. Insects, 16(2), 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16020163





