Optimal Design of the Shape of a Non-Ball Mandrel for Thin-Walled Tube Small Radius Cold Bending
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
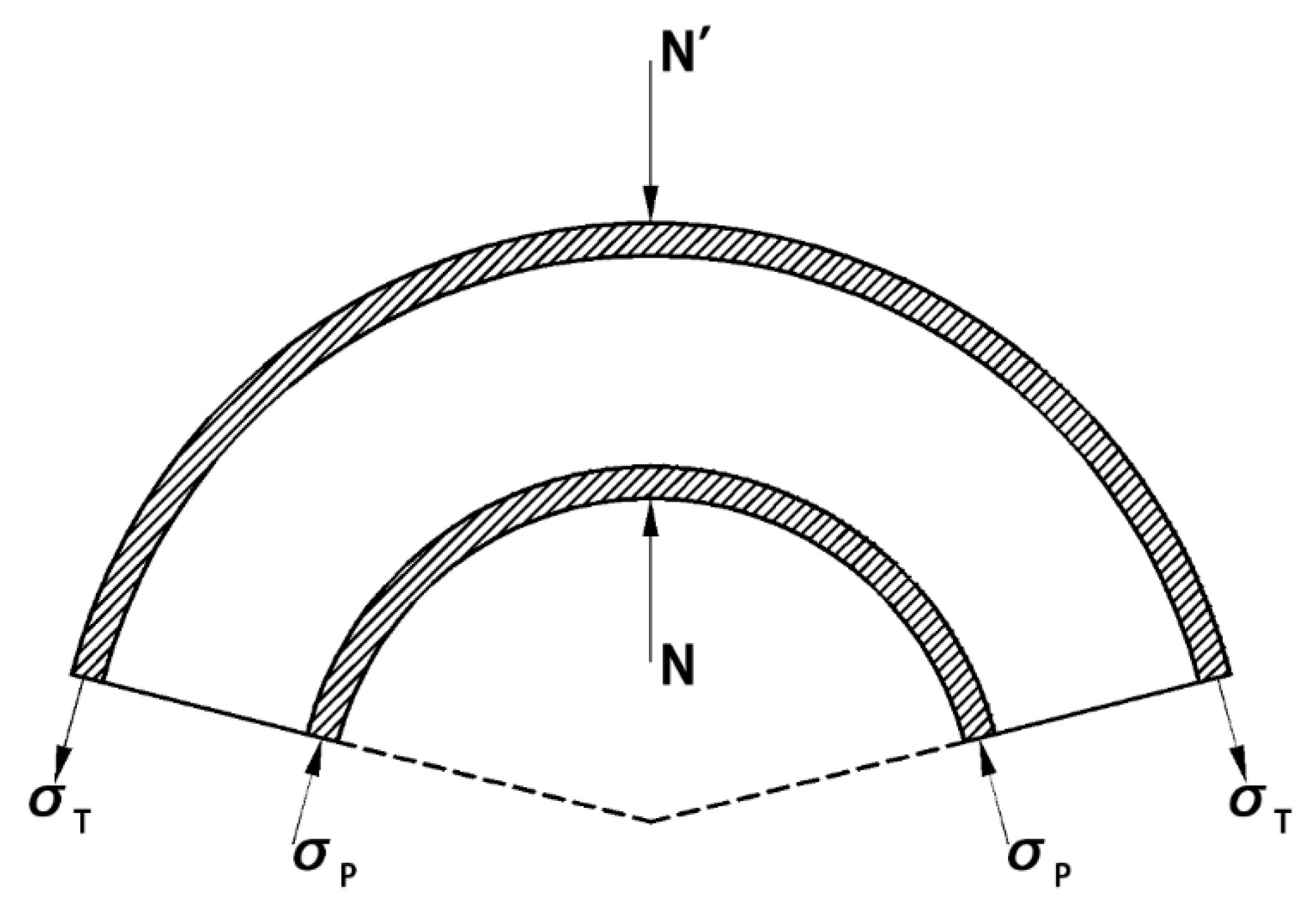
2.1. Modes of Behavior in Cold Bending
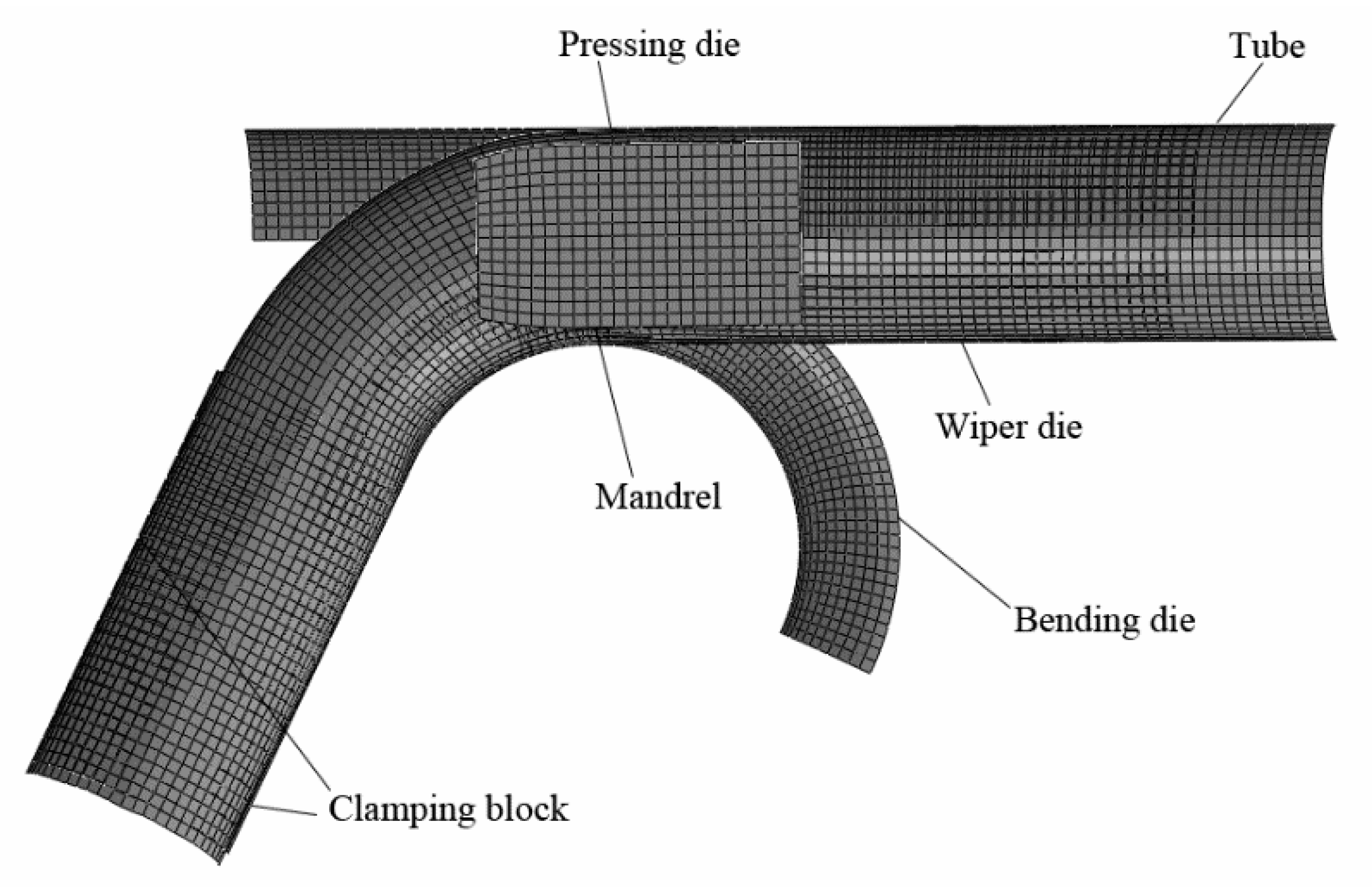
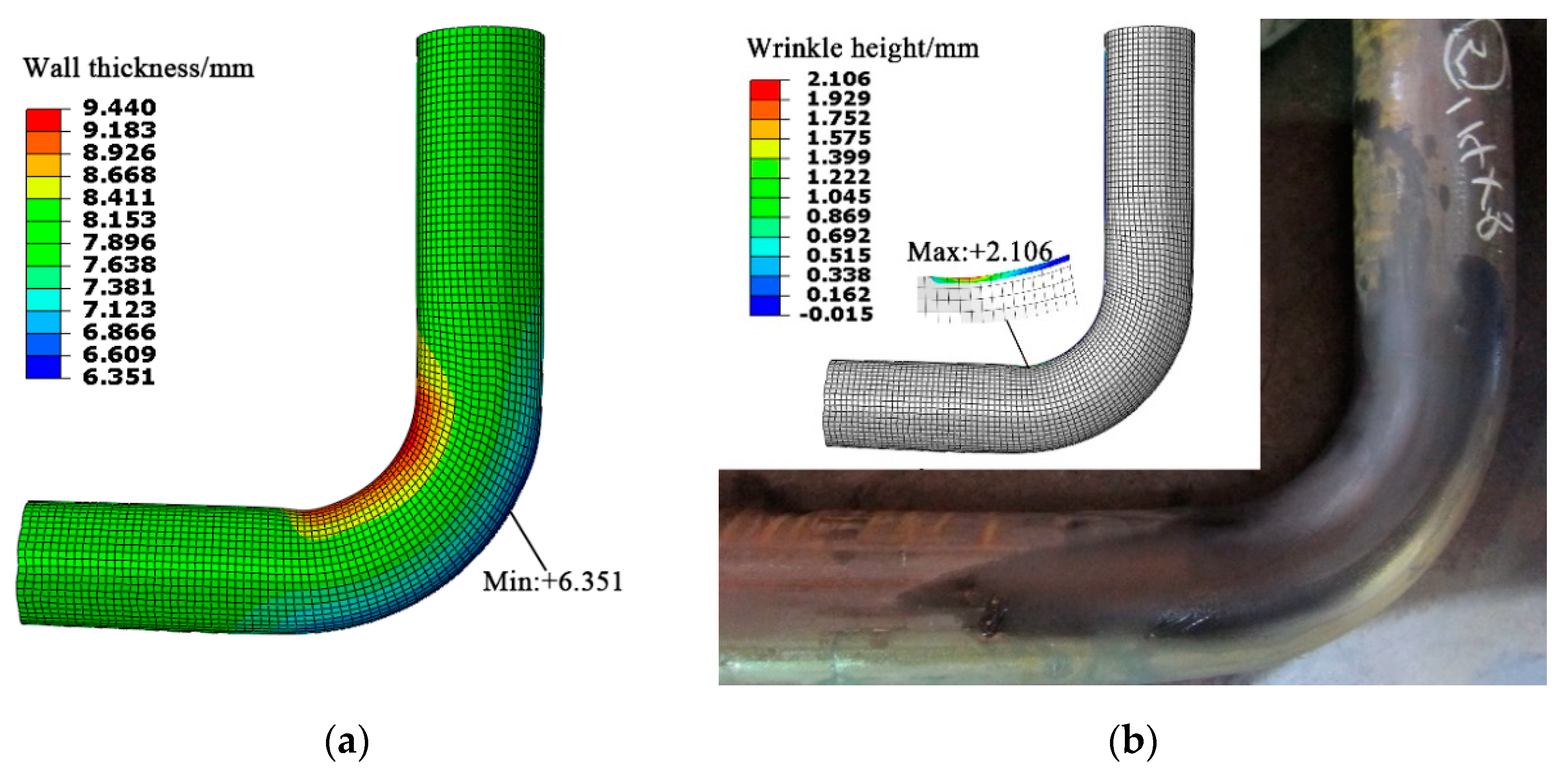
2.2. Numerical Method and Reliability Verification
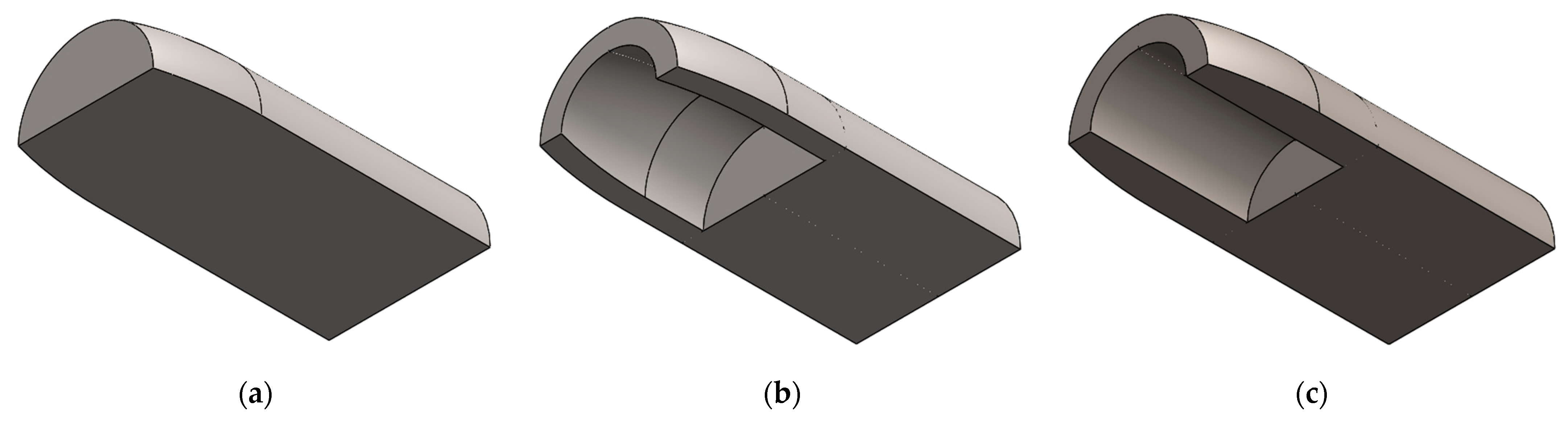
2.3. Hollow Mandrel Shape Design for Thin-Walled Tube Bending
3. Results and Discussion
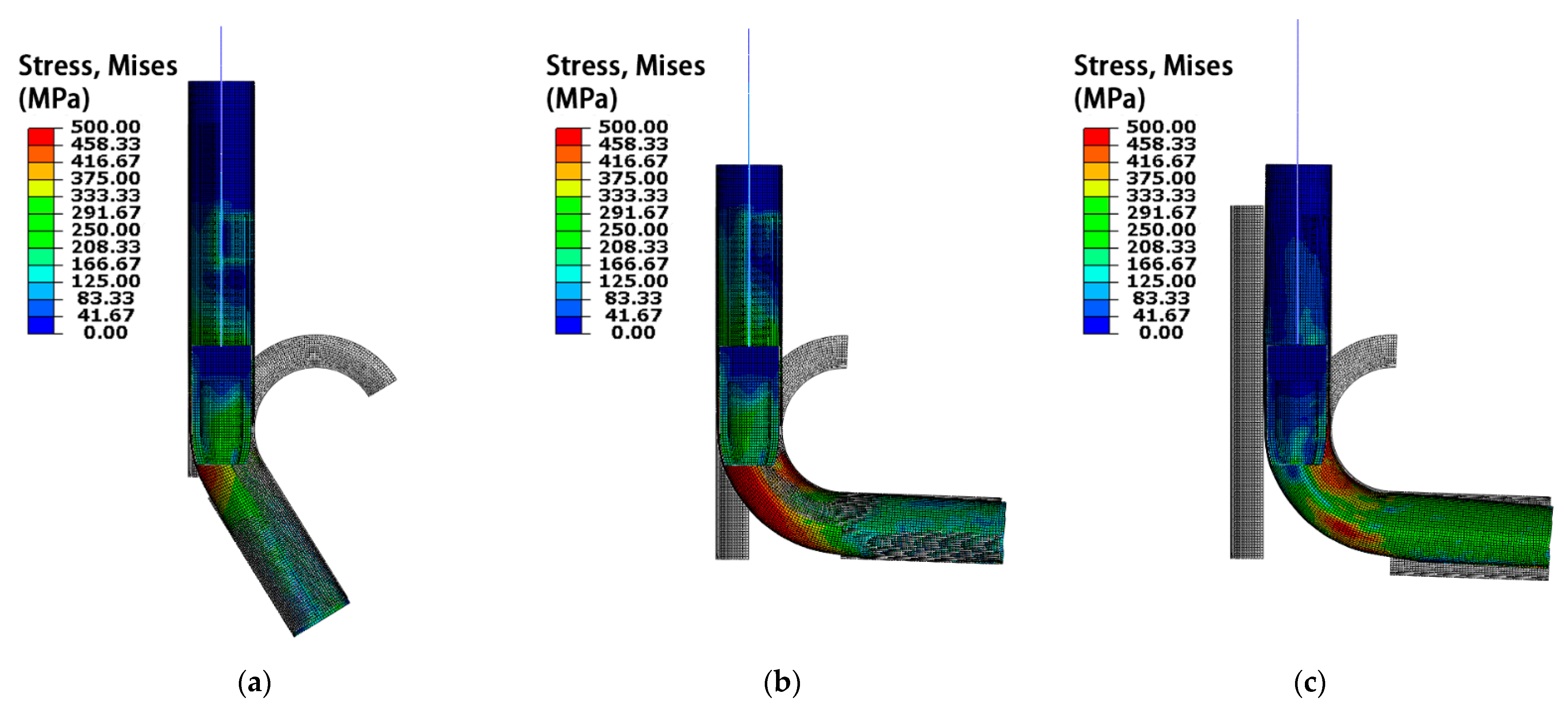
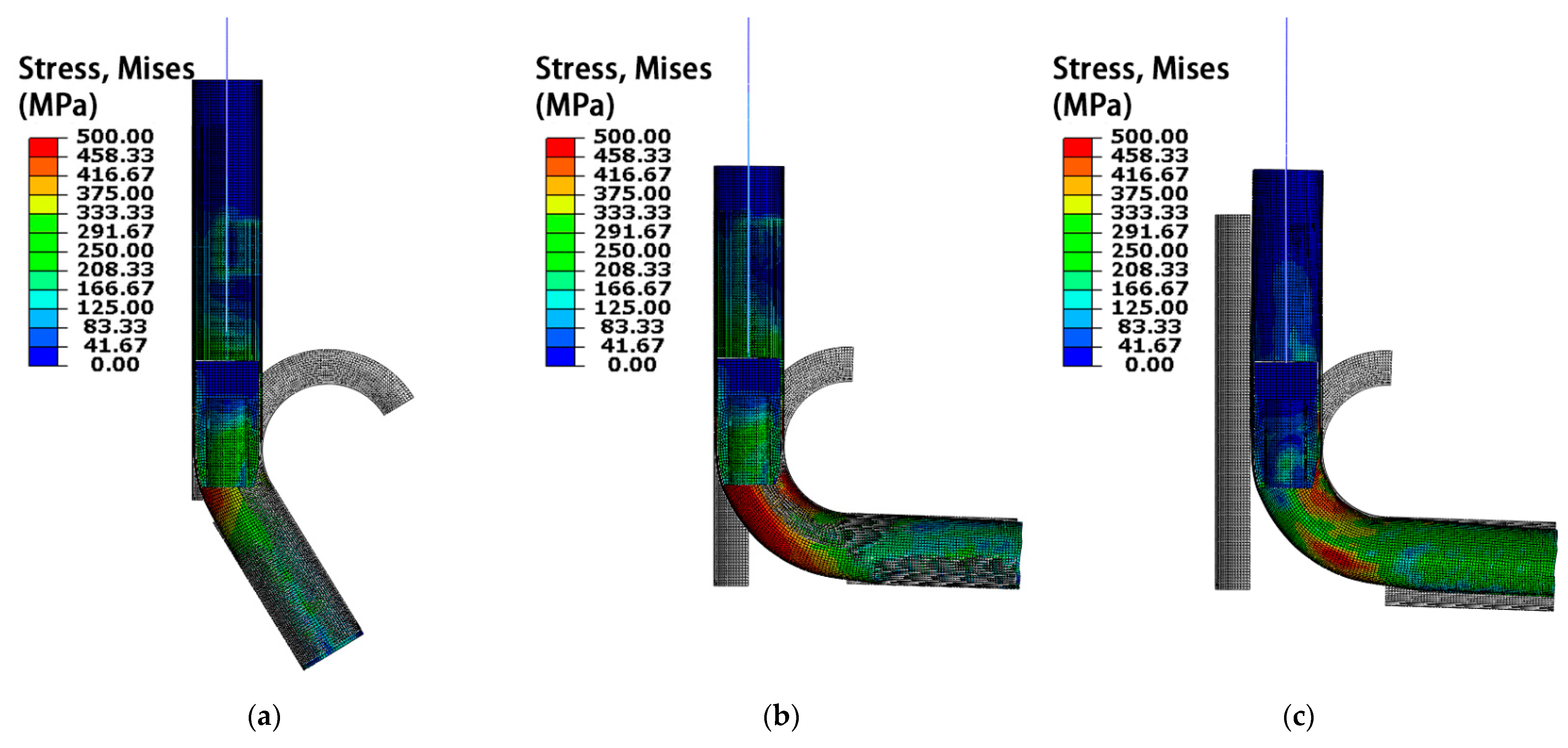
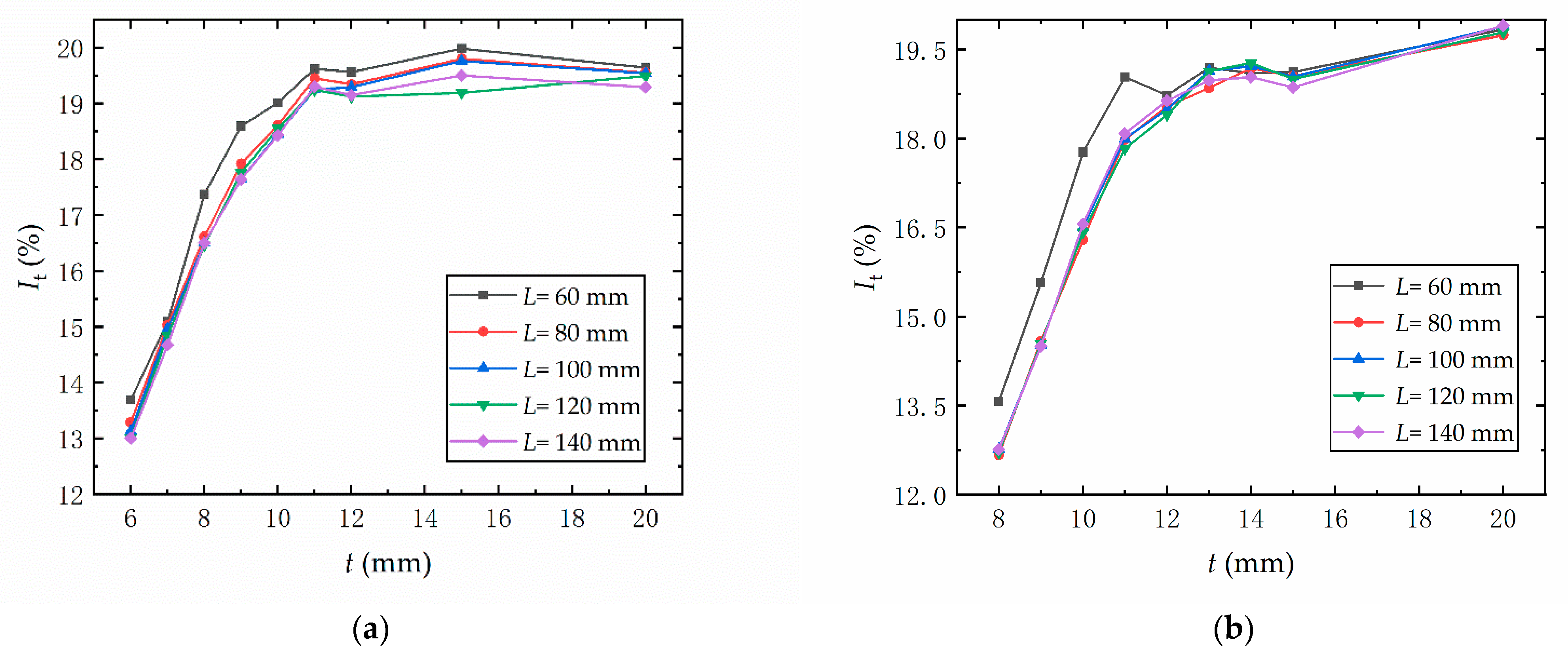
3.1. Simulation Results and Analysis of Hollow Mandrel
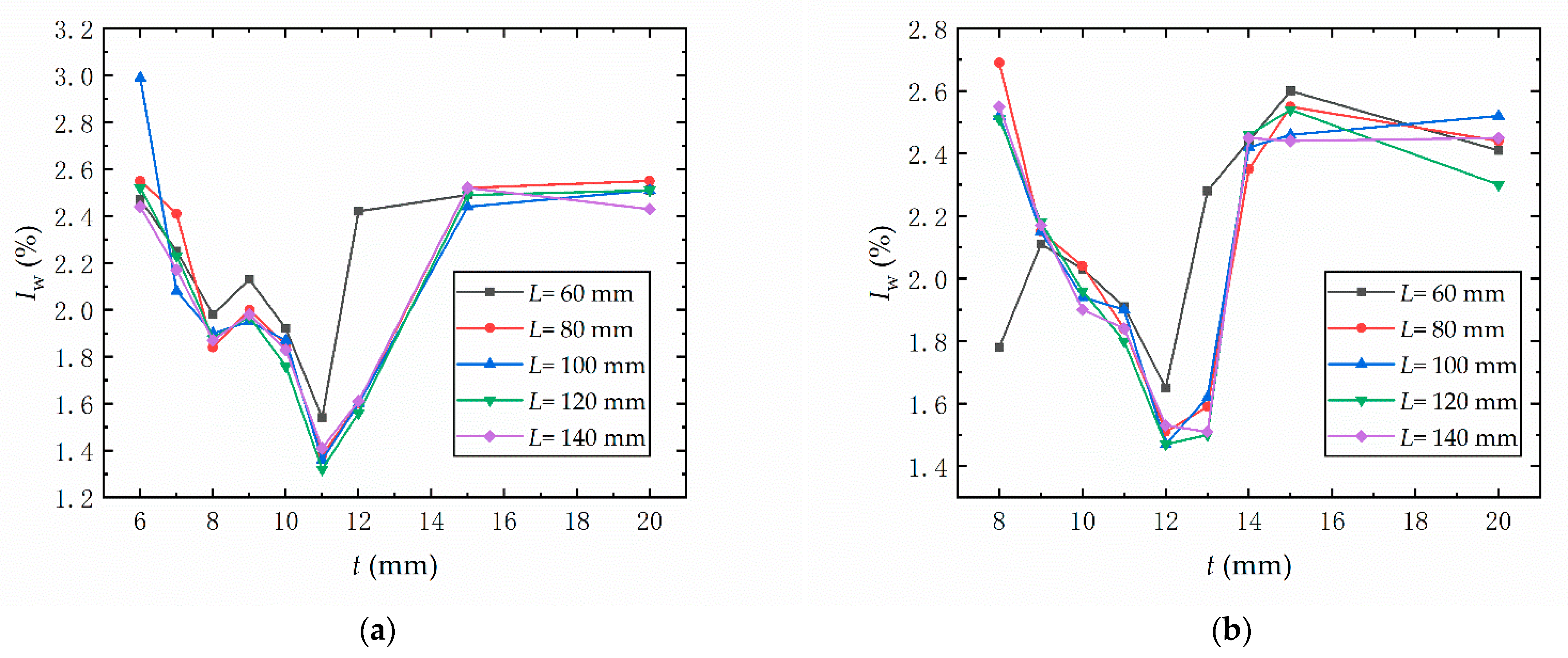
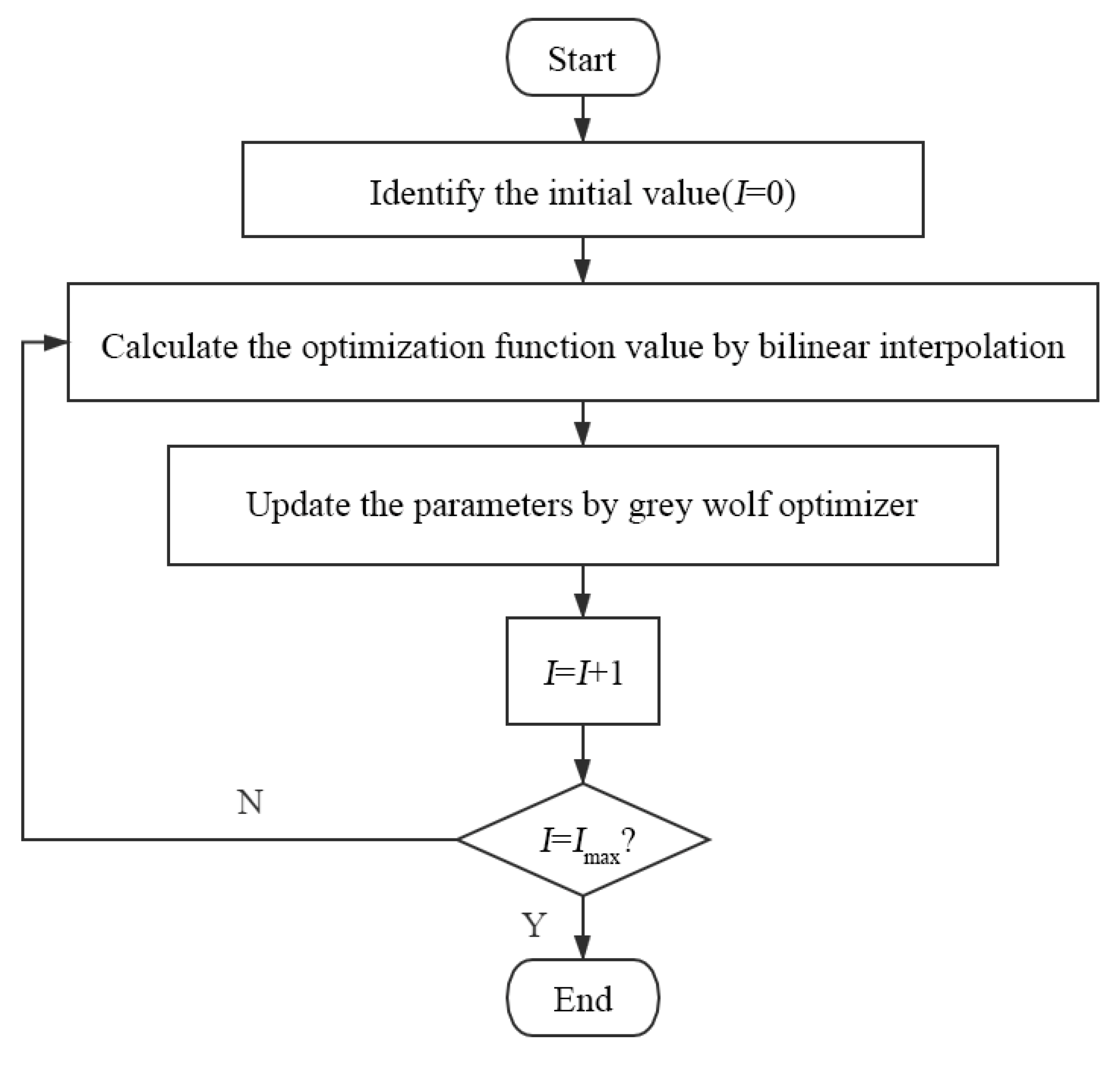
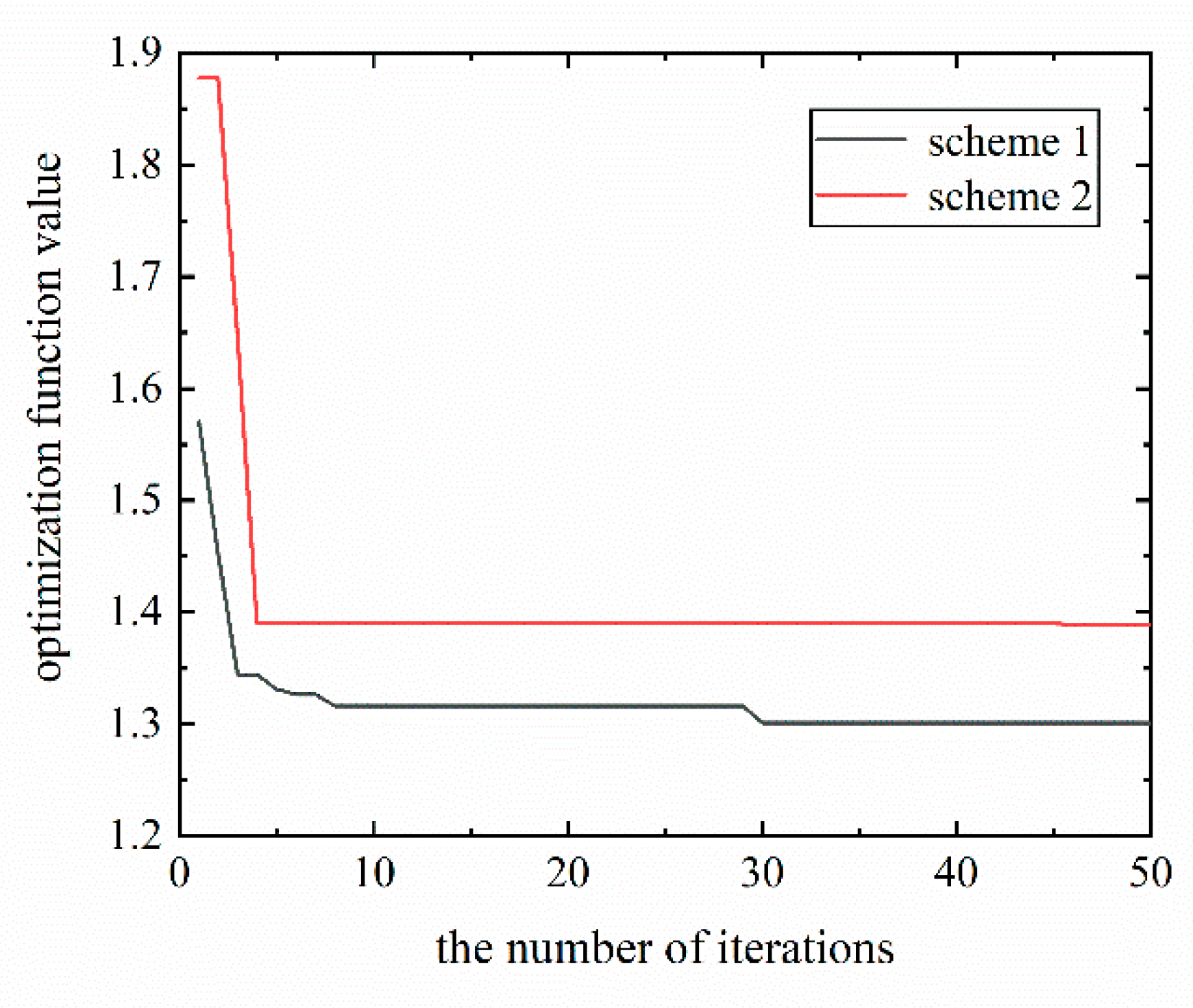
3.2. Multi-Objective Optimization of Hollow Mandrel Parameters
4. Conclusions
- Small radius cold bending of thin-walled tubes using an ordinary non-ball mandrel does not meet the forming requirements. Therefore, two kinds of hollow non-ball mandrel schemes were proposed to obtain satisfactory forming results;
- Comparing the two hollow mandrel schemes, the influence of tested parameters on the forming indices were similar. The hollow section thickness had the greatest influence of the parameters measured. In scheme 1, as the hollow section thickness increased from 6 to 11 mm, the wrinkling rate declined by 45.58%. When the thickness increased from 11 to 15 mm, the wrinkling rate increased by 78.21%. In scheme 2, the wrinkling rate first decreased by 39.41% and then increased by 51.44% as the thickness increased. The wrinkling rate was lowest when the hollow section thickness was 11 mm in scheme 1 and 13 mm in scheme 2. As the hollow section thickness increased, the flattening rate decreased by 60.49% and 63.83% in scheme 1 and scheme 2, respectively. As the hollow section thickness increased, the thinning rate increased by 35.44% and 41.02% in scheme 1 and scheme 2, respectively.
- Improved hollow section parameters were obtained based on the ideal point method and grey wolf optimizer. It was shown that it is feasible to use a hollow non-ball mandrel instead of a ball mandrel for cold bending of thin-walled tube with a small radius;
- Both the hollow mandrel scheme with a cylinder-like hollow section and a regular cylindrical hollow section met the forming requirements for a tube. Considering that the mandrel with a regular cylinder hollow section has the advantages of simple processing and its forming quality is similar to that of the cylinder-like hollow section, we recommend this design for use.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, H.; Sun, Z.C.; Lin, Y. Advanced plastic processing technology and research progress on tube forming. J. Plast. Eng. 2001, 8, 83–85. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.W.; Dong, F.F.; Li, L.X.; Yao, Z.Q. Process Parameters Optimization of Rotary Draw Bending for Large Diameter Thin-walled Steel Tube for Automotive Bumper. Automot. Eng. 2015, 37, 853–860. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, S.J.; Yang, H.; Li, H.; Zhan, M. Experimental study on role of mandrel in thin walled tube NC bending process with small bending radius. J. Plast. Eng. 2007, 14, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima, K.; Utsumi, N.; Saito, Y.; Yoshida, M. Deformation property and suppression of ultra-thin-walled rectangular tube in rotary draw bending. Metals 2020, 10, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utsumi, N.; Sakaki, S. Countermeasures against undesirable phenomena in the draw-bending process for extruded square tubes. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2002, 123, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Różyło, P. Optimization of I-section profile design by the finite element method. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2016, 10, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsumura, K. Hierarchically aggregated optimization algorithm for heterogeneously dispersed utility functions. IFAC Pap. Online 2017, 50, 14442–14446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Sun, Y.J. A new multiplexed optimization with enhanced performance for complex air conditioning systems. Energy Build. 2017, 156, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzampour, A.; Khatibinia, M.; Mansouri, I. Shape optimization of butterfly-shaped shear links using grey wolf algorithm. Ing. Sismica 2019, 36, 27–41. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Yang, H.; Zhan, M.; Sun, Z.C.; Gu, R.J. Role of mandrel in NC precision bending process of thin-walled tube. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2007, 47, 1164–1175. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Li, G.J.; Liu, N.; Welo, T. Multiple instability-constrained tube bending limits. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2014, 214, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z. ‘Size effect’ related bending formability of thin-walled aluminum alloy tube. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2013, 26, 230–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Tang, W.Y.; Zou, S.G. Rapid prediction of small radius bending forming results based on MPSO-BP model. J. Plast. Eng. 2018, 25, 122–128. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.A.; Liu, J. Shape parameter optimization of mandrel for tube bending based on orthogonal experimental design. J. Plast. Eng. 2020, 27, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, C.K. Selection of mandrel for steel tube cold bending forming. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Society of Mechanical Engineering, Henan, China, 1 September 2002; pp. 116–119. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Yan, Y.; Hu, Z.L. Effect of mandrel on the forming quality of thin walled tube. Hydro Mechatron. Eng. 2015, 43, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.Y.; Liu, D.X.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.M.; Tian, X. Analysis on the effects of material models on wall thickness variation of tube bending based on numerical simulation. J. Plast. Eng. 2010, 17, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, X. Study of Small Radius Tube Bending with Numerical Experiment Based on Response Surface Methodology. Master’s Thesis, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, Z.; You, X.C. Finite Element Analysis and Application based on ABAQUS, 1st ed.; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2009; p. 111. [Google Scholar]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Lewis, A. Grey wolf optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

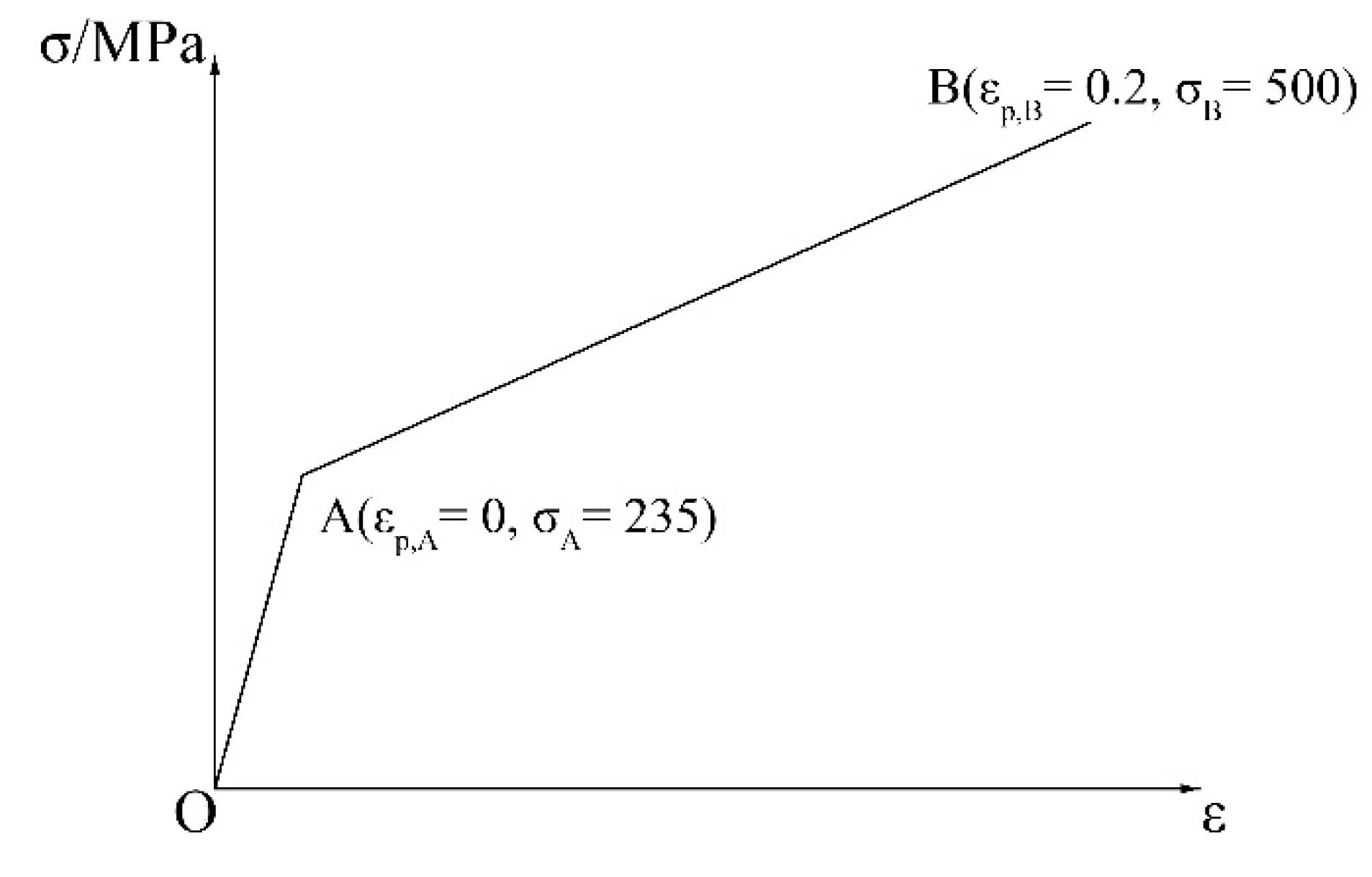


| 7.84 × 103 | 206,000 | 0.3 | 235 | 0 | 500 | 0.2 |
| Contact Surface | Tube-Clamping Block | Tube-Bending Die | Tube-Pressing Die | Tube-Wiper Die | Tube-Mandrel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Friction coefficient | No relative slip | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.05 |
| Clearance between Mandrel and Tube/mm | Radius of Curvature at the Mandrel Head/mm | Curve Segment Length of Mandrel/mm | Mandrel Extension/mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 220 | 50 | 12 |
| Experimental Result | Numerical Result | Error | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum wall thickness/mm | 6.3 | 6.351 | 0.81% |
| Wrinkle | No obvious wrinkle was measured | The maximum wrinkle height was 2.106 mm | <2% of tube diameter |
| Iw/% | If/% | It/% |
| 2.44 | 8.94 | 19.92 |
| No. | L/mm | t/mm | Iw/% | If/% | It/% | No. | L/mm | t/mm | Iw/% | If/% | It/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 60 | 6 | 2.47 | 17.86 | 13.69 | 24 | 100 | 11 | 1.36 | 8.15 | 19.25 |
| 2 | 60 | 7 | 2.25 | 11.48 | 15.09 | 25 | 100 | 12 | 1.60 | 7.53 | 19.29 |
| 3 | 60 | 8 | 1.98 | 10.02 | 17.37 | 26 | 100 | 15 | 2.44 | 8.78 | 19.76 |
| 4 | 60 | 9 | 2.13 | 9.86 | 18.59 | 27 | 100 | 20 | 2.51 | 8.88 | 19.54 |
| 5 | 60 | 10 | 1.92 | 8.39 | 19.01 | 28 | 120 | 6 | 2.52 | 23.44 | 13.01 |
| 6 | 60 | 11 | 1.54 | 8.28 | 19.62 | 29 | 120 | 7 | 2.23 | 15.90 | 14.84 |
| 7 | 60 | 12 | 2.42 | 9.94 | 19.56 | 30 | 120 | 8 | 1.88 | 13.01 | 16.46 |
| 8 | 60 | 15 | 2.49 | 8.88 | 19.98 | 31 | 120 | 9 | 1.97 | 10.66 | 17.76 |
| 9 | 60 | 20 | 2.51 | 8.95 | 19.64 | 32 | 120 | 10 | 1.76 | 8.87 | 18.55 |
| 10 | 80 | 6 | 2.55 | 22.81 | 13.29 | 33 | 120 | 11 | 1.32 | 8.11 | 19.24 |
| 11 | 80 | 7 | 2.41 | 15.15 | 15.03 | 34 | 120 | 12 | 1.56 | 7.63 | 19.12 |
| 12 | 80 | 8 | 1.84 | 11.85 | 16.61 | 35 | 120 | 15 | 2.49 | 9.87 | 19.19 |
| 13 | 80 | 9 | 2.00 | 10.67 | 17.92 | 36 | 120 | 20 | 2.51 | 9.07 | 19.49 |
| 14 | 80 | 10 | 1.85 | 8.24 | 18.61 | 37 | 140 | 6 | 2.44 | 24.33 | 13.00 |
| 15 | 80 | 11 | 1.38 | 7.90 | 19.45 | 38 | 140 | 7 | 2.17 | 16.14 | 14.67 |
| 16 | 80 | 12 | 1.60 | 7.78 | 19.34 | 39 | 140 | 8 | 1.87 | 12.88 | 16.50 |
| 17 | 80 | 15 | 2.52 | 9.25 | 19.80 | 40 | 140 | 9 | 1.98 | 10.86 | 17.64 |
| 18 | 80 | 20 | 2.55 | 9.00 | 19.55 | 41 | 140 | 10 | 1.83 | 9.04 | 18.43 |
| 19 | 100 | 6 | 2.99 | 23.74 | 13.13 | 42 | 140 | 11 | 1.41 | 8.23 | 19.30 |
| 20 | 100 | 7 | 2.08 | 15.28 | 14.96 | 43 | 140 | 12 | 1.61 | 7.89 | 19.15 |
| 21 | 100 | 8 | 1.90 | 12.63 | 16.50 | 44 | 140 | 15 | 2.52 | 9.18 | 19.50 |
| 22 | 100 | 9 | 1.95 | 10.59 | 17.64 | 45 | 140 | 20 | 2.43 | 10.05 | 19.29 |
| 23 | 100 | 10 | 1.87 | 9.36 | 18.45 |
| No. | L/mm | t/mm | Iw/% | If/% | It/% | No. | L/mm | t/mm | Iw/% | If/% | It/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 60 | 8 | 1.78 | 21.08 | 13.57 | 24 | 100 | 13 | 1.62 | 8.86 | 19.14 |
| 2 | 60 | 9 | 2.11 | 19.02 | 15.57 | 25 | 100 | 14 | 2.42 | 9.66 | 19.22 |
| 3 | 60 | 10 | 2.03 | 11.26 | 17.77 | 26 | 100 | 15 | 2.46 | 9.39 | 19.04 |
| 4 | 60 | 11 | 1.91 | 10.23 | 19.03 | 27 | 100 | 20 | 2.52 | 8.68 | 19.89 |
| 5 | 60 | 12 | 1.65 | 9.02 | 18.73 | 28 | 120 | 8 | 2.51 | 27.22 | 12.71 |
| 6 | 60 | 13 | 2.28 | 9.63 | 19.19 | 29 | 120 | 9 | 2.18 | 23.58 | 14.55 |
| 7 | 60 | 14 | 2.44 | 9.23 | 19.10 | 30 | 120 | 10 | 1.96 | 15.03 | 16.42 |
| 8 | 60 | 15 | 2.60 | 9.43 | 19.12 | 31 | 120 | 11 | 1.80 | 10.52 | 17.83 |
| 9 | 60 | 20 | 2.41 | 9.24 | 19.84 | 32 | 120 | 12 | 1.47 | 9.72 | 18.40 |
| 10 | 80 | 8 | 2.69 | 27.02 | 12.67 | 33 | 120 | 13 | 1.50 | 8.26 | 19.13 |
| 11 | 80 | 9 | 2.15 | 22.50 | 14.59 | 34 | 120 | 14 | 2.46 | 9.81 | 19.27 |
| 12 | 80 | 10 | 2.04 | 13.33 | 16.29 | 35 | 120 | 15 | 2.54 | 9.30 | 19.00 |
| 13 | 80 | 11 | 1.84 | 10.68 | 17.98 | 36 | 120 | 20 | 2.30 | 8.35 | 19.79 |
| 14 | 80 | 12 | 1.51 | 8.75 | 18.54 | 37 | 140 | 8 | 2.55 | 27.26 | 12.76 |
| 15 | 80 | 13 | 1.59 | 8.47 | 18.85 | 38 | 140 | 9 | 2.17 | 24.30 | 14.50 |
| 16 | 80 | 14 | 2.35 | 9.81 | 19.18 | 39 | 140 | 10 | 1.90 | 14.03 | 16.56 |
| 17 | 80 | 15 | 2.55 | 9.41 | 19.05 | 40 | 140 | 11 | 1.84 | 10.62 | 18.08 |
| 18 | 80 | 20 | 2.44 | 8.91 | 19.74 | 41 | 140 | 12 | 1.53 | 9.43 | 18.64 |
| 19 | 100 | 8 | 2.52 | 27.23 | 12.77 | 42 | 140 | 13 | 1.51 | 8.41 | 18.98 |
| 20 | 100 | 9 | 2.15 | 24.04 | 14.52 | 43 | 140 | 14 | 2.45 | 9.52 | 19.03 |
| 21 | 100 | 10 | 1.94 | 14.66 | 16.50 | 44 | 140 | 15 | 2.44 | 9.39 | 18.86 |
| 22 | 100 | 11 | 1.90 | 10.96 | 18.00 | 45 | 140 | 20 | 2.45 | 8.77 | 19.90 |
| 23 | 100 | 12 | 1.47 | 9.63 | 18.49 |
| Mandrel Shape | L/mm | t/mm | Iw/% | If/% | It/% | I |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solid mandrel | - | - | 2.44 | 8.94 | 19.92 | 1.7095 |
| Hollow mandrel scheme 1 | 120 | 11 | 1.32 | 8.11 | 19.24 | 1.2983 |
| Hollow mandrel scheme 2 | 120 | 13 | 1.50 | 8.26 | 19.13 | 1.3529 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Zou, S. Optimal Design of the Shape of a Non-Ball Mandrel for Thin-Walled Tube Small Radius Cold Bending. Metals 2021, 11, 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11081221
Bai L, Liu J, Wang Z, Zou S. Optimal Design of the Shape of a Non-Ball Mandrel for Thin-Walled Tube Small Radius Cold Bending. Metals. 2021; 11(8):1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11081221
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Lu, Jun Liu, Ziang Wang, and Shuanggui Zou. 2021. "Optimal Design of the Shape of a Non-Ball Mandrel for Thin-Walled Tube Small Radius Cold Bending" Metals 11, no. 8: 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11081221
APA StyleBai, L., Liu, J., Wang, Z., & Zou, S. (2021). Optimal Design of the Shape of a Non-Ball Mandrel for Thin-Walled Tube Small Radius Cold Bending. Metals, 11(8), 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11081221





