A Critical Review on the Removal and Recovery of Hazardous Cd from Cd-Containing Secondary Resources in Cu-Pb-Zn Smelting Processes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
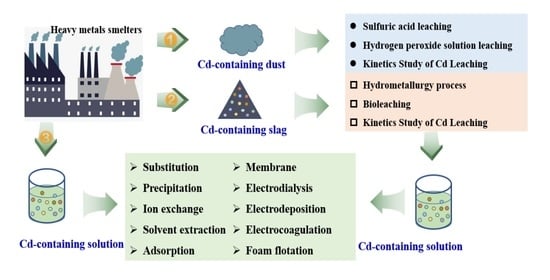
2. Cd Resources and Cd-Containing Secondary Resources
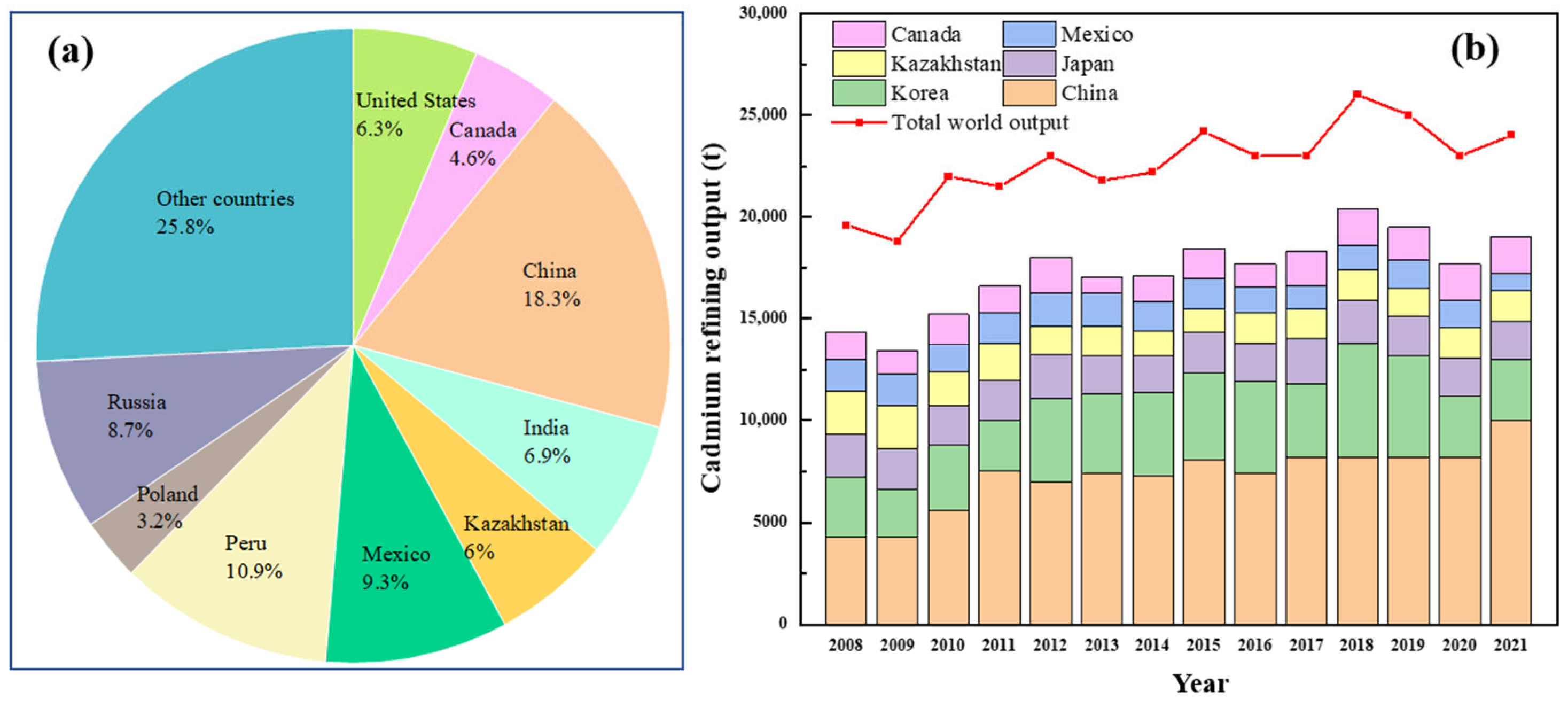
2.1. Cd Resources and Products
2.2. Cd-Containing Secondary Resources in Cu-Pb-Zn Smelting Process
3. Cd Recovery Principles and Technologies
3.1. Recovery of Cd from Dust
3.1.1. Sulfuric Acid Leaching
3.1.2. Hydrogen Peroxide Solution Leaching
3.1.3. Kinetics Study of Cd Leaching
3.2. Recovery of Cd from slag
3.2.1. Hydrometallurgical Process
3.2.2. Bioleaching
3.2.3. Kinetics Study of Cd Leaching
3.3. Removal and Recovery of Cd from Waste Solutions
3.3.1. Cementation
3.3.2. Precipitation
3.3.3. Ion Exchange
3.3.4. Solvent Extraction
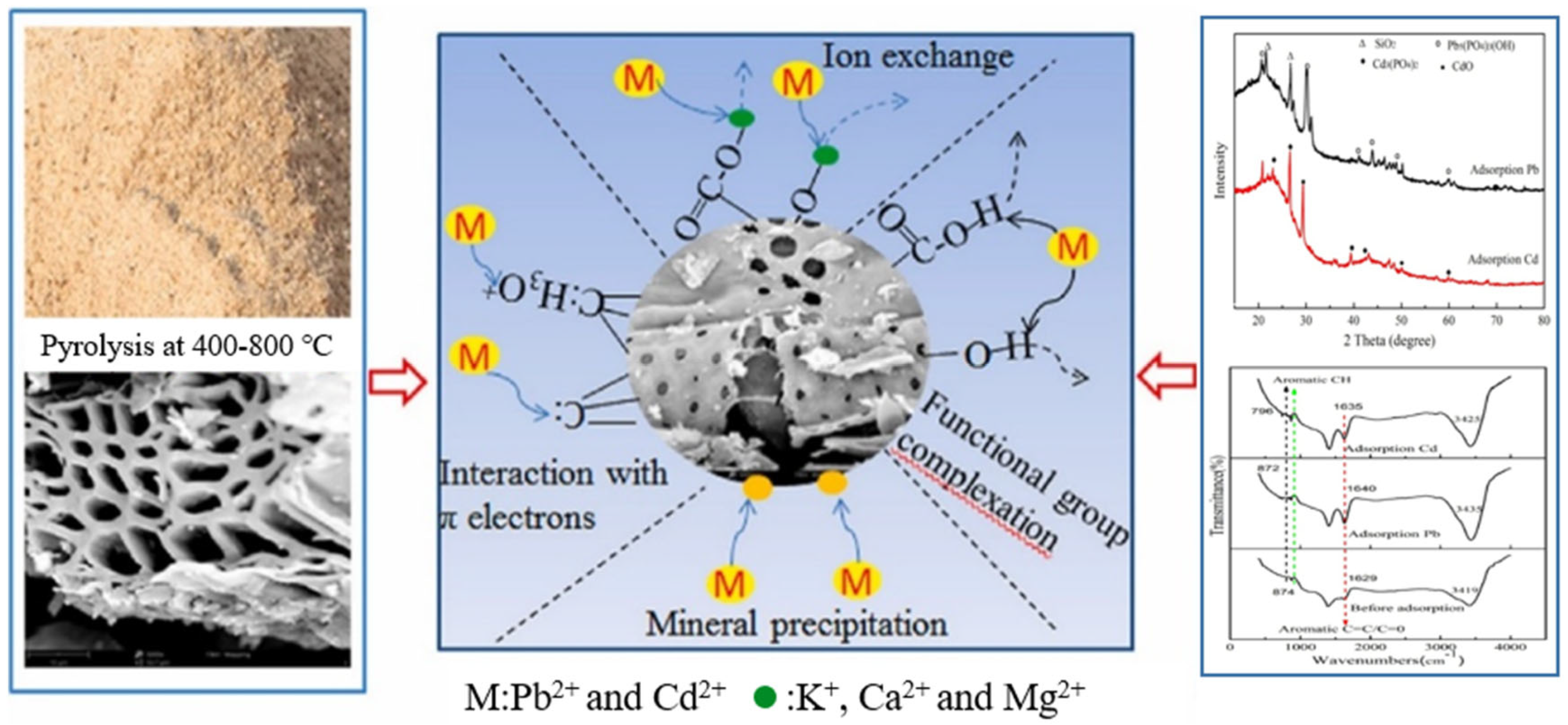
3.3.5. Adsorption
3.3.6. Membrane Separation
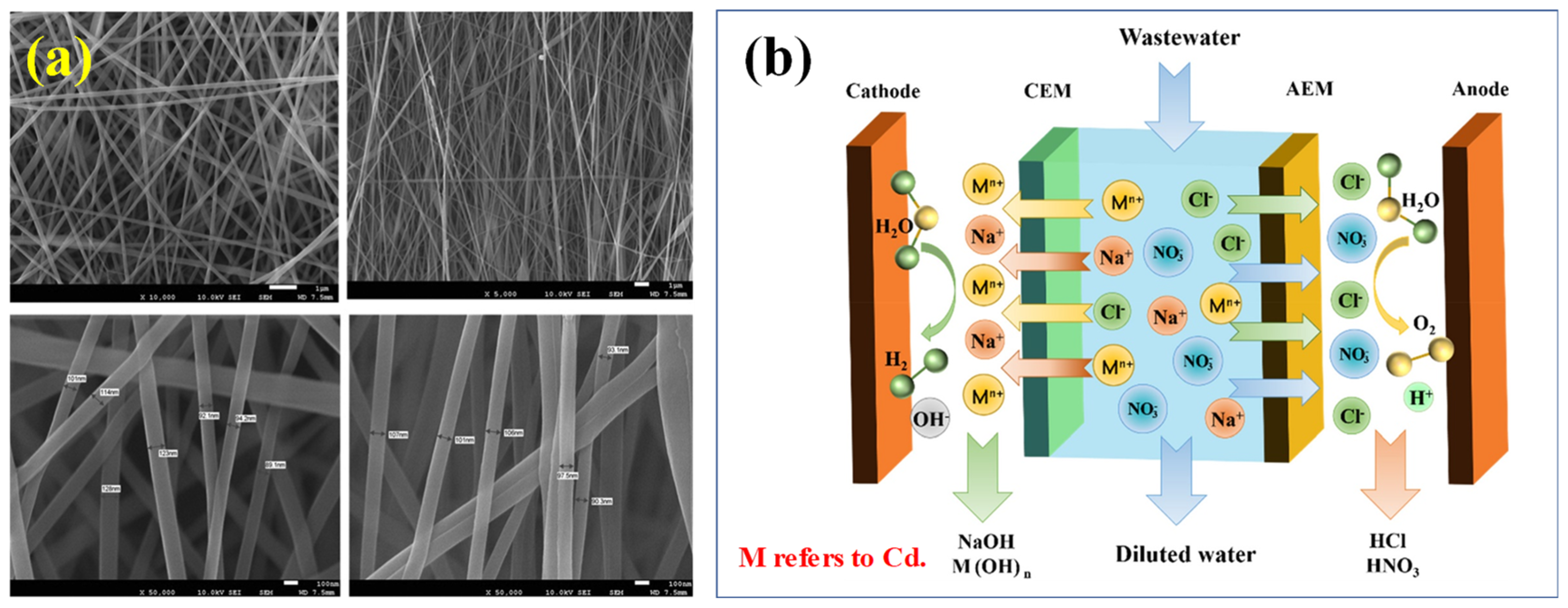
3.3.7. Electrodialysis
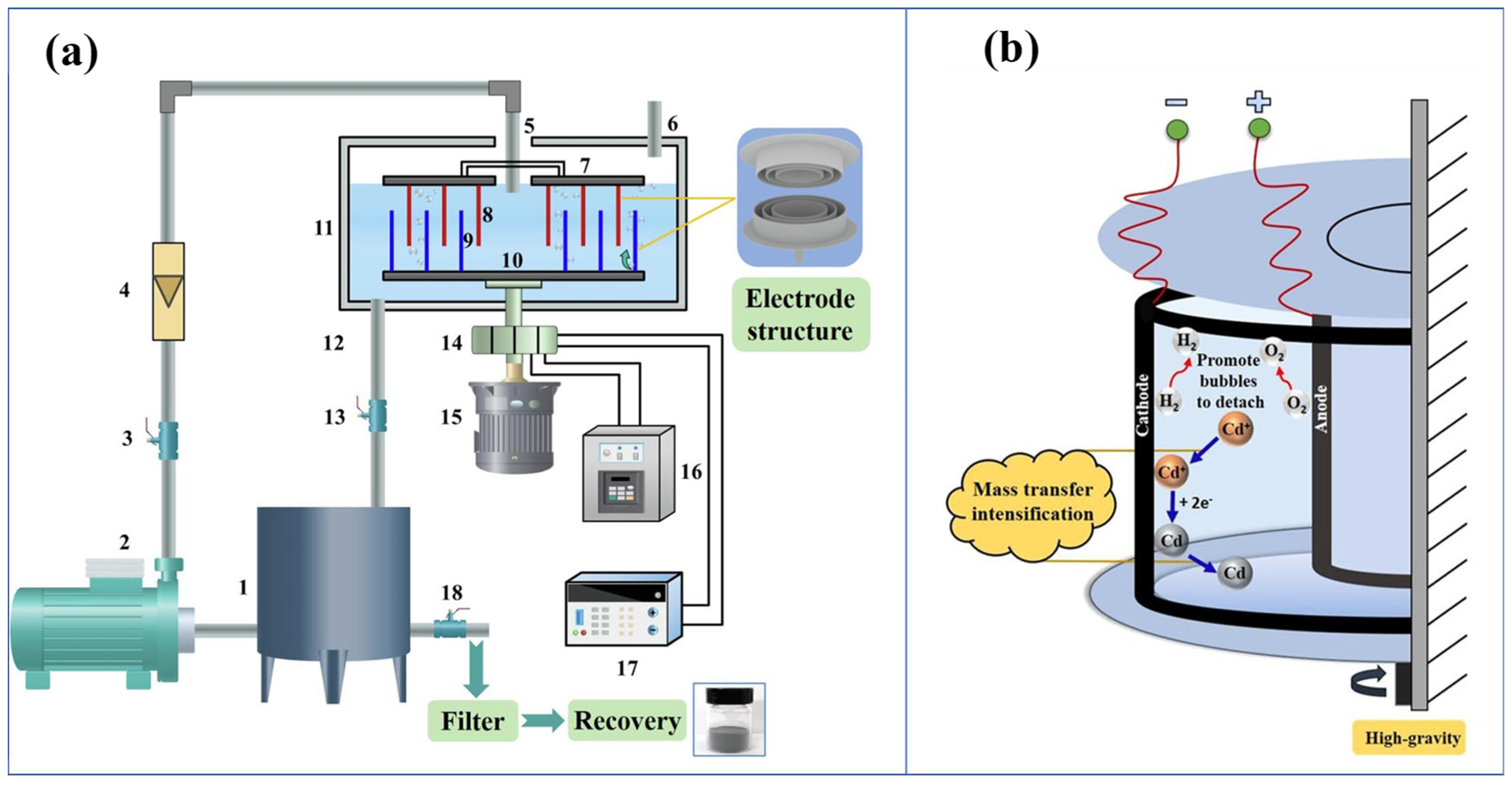
3.3.8. Electrodeposition
3.3.9. Electrocoagulation

3.3.10. Foam Extraction
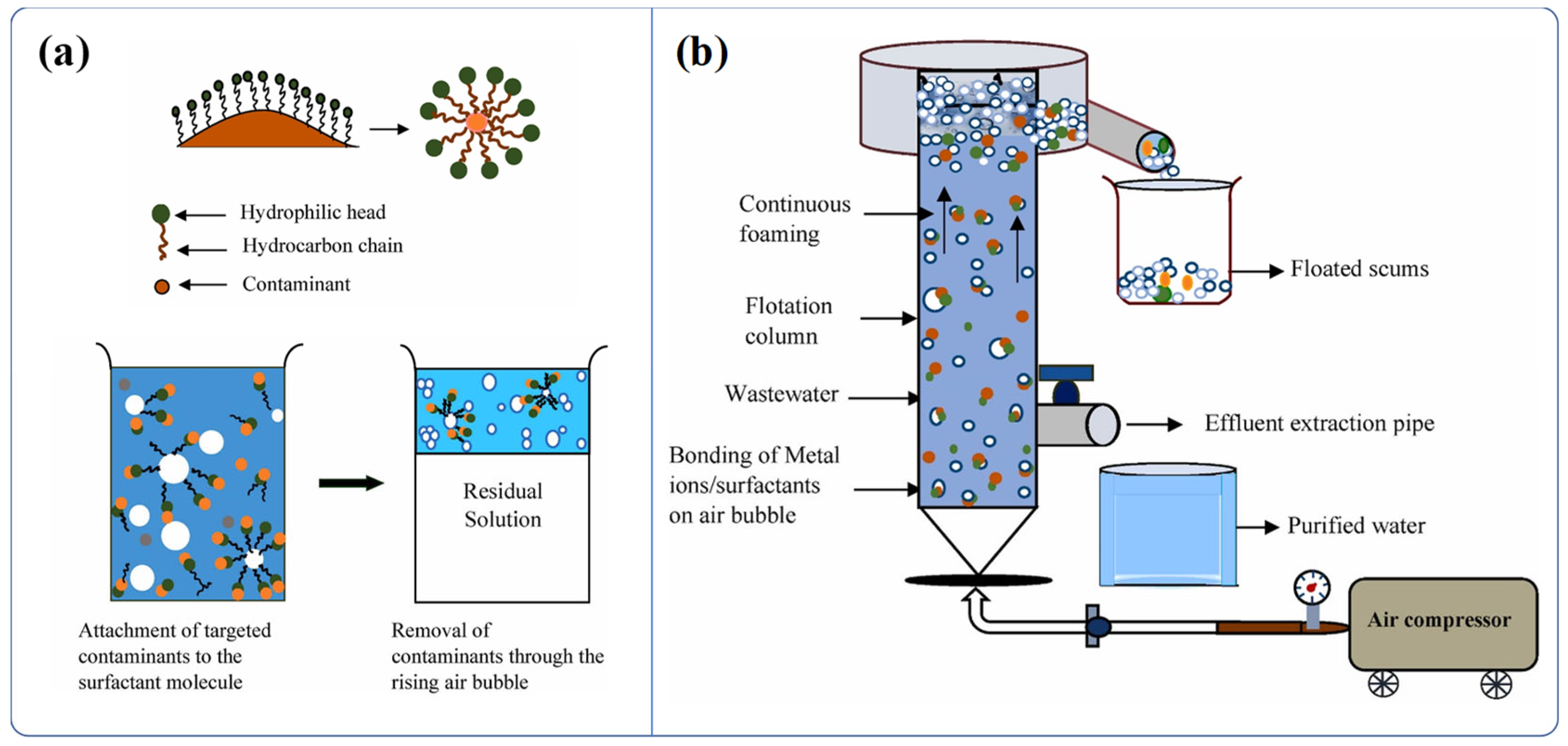
3.3.11. Comparison of Different Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhong, Q.; Yin, M.; Zhang, Q.; Beiyuan, J.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Xiao, T.; et al. Cadmium isotopic fractionation in lead-zinc smelting process and signatures in fluvial sediments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 125015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, J.; She, J.; Yin, M.; Fang, F.; Xiao, T.; Song, G.; Liu, J. Geochemical transfer of cadmium in river sediments near a lead-zinc smelter. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 196, 110529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Luo, T.; Liu, X.; Hua, H.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, W.; Ren, J. Tracing anthropogenic cadmium emissions: From sources to pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 676, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, T.; Perkins, R.B.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Ning, Z. Geogenic cadmium pollution and potential health risks, with emphasis on black shale. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 176, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, M.; Kushwaha, A.; Goswami, L.; Singh, A.K.; Sikandar, M. A review on advances and mechanism for the phycoremediation of cadmium contaminated wastewater. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2021, 5, 100288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, T.; Ning, Z.; Li, H.; Tang, J.; Zhou, G. High cadmium concentration in soil in the Three Gorges region: Geogenic source and potential bioavailability. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 37, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Shen, F.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, H.; Li, R.; Liu, T.; Guo, D.; Du, J.; Guo, Z.; et al. Sustainable biochar effects on the remediation of contaminated soil: A 2-crop season site practice near a lead-zinc smelter in Feng County, China. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 302, 119095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satarug, S.; Baker, J.R.; Urbenjapol, S.; Haswell-Elkins, M.; Reilly, P.E.B.; Williams, D.J.; Moore, M.R. A global perspective on cadmium pollution and toxicity in non-occupationally exposed population. Toxicol. Lett. 2003, 137, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Ning, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Chen, H.; Xiao, E.; Xiao, T. Geochemical distribution, fractionation, and sources of heavy metals in dammed-river sediments: The Longjiang River, Southern China. Acta Geochim. 2019, 38, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.-M.; Fu, R.-B.; Tong, Y.-H.; Shen, D.-L.; Guo, X.-P. The potential environmental risk implications of heavy metals based on their geochemical and mineralogical characteristics in the size-segregated zinc smelting slags. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 128199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Luo, X.; Cheng, Y.; Ke, W.; Hartley, W.; Li, C.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, F.; Xue, S. Spatial distribution of toxic metal(loid)s at an abandoned zinc smelting site, Southern China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, H.; Meng, W.; Liu, N.; Wu, P. Accumulation and source apportionment of heavy metal(loid)s in agricultural soils based on GIS, SOM and PMF: A case study in superposition areas of geochemical anomalies and zinc smelting, Southwest China. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 159, 964–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Xiao, T.; Chen, Y.; Beiyuan, J.; She, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, M.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. Legacy of multiple heavy metal(loid)s contamination and ecological risks in farmland soils from a historical artisanal zinc smelting area. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.; Hou, H.; Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Jeyakumar, P.; Lu, Y.; Cao, L.; Zhao, L.; Han, D. Comparison of Pb and Cd in wheat grains under air-soil-wheat system near lead-zinc smelters and total suspended particulate introduced modeling attempt. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Işıklı, B.; Demir, T.A.; Akar, T.; Berber, A.; Ürer, S.M.; Kalyoncu, C.; Canbek, M. Cadmium exposure from the cement dust emissions: A field study in a rural residence. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 1546–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đukić-Ćosić, D.; Baralić, K.; Javorac, D.; Djordjevic, A.B.; Bulat, Z. An overview of molecular mechanisms in cadmium toxicity. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2020, 19, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroyer, A.; Gomajee, H.; Leroy, R.; Mazzuca, M.; Leleu, B.; Nisse, C. Cancer mortality and chemical exposure in a retrospective zinc and lead smelter cohort: A 48-year follow-up. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2022, 242, 113955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhani, I.; Sahab, S.; Srivastava, V.; Singh, R.P. Impact of cadmium pollution on food safety and human health. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2021, 27, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Hendry, M.J.; Essilfie-Dughan, J.; Day, S.; Villeneuve, S.A.; Barbour, S.L. Geochemistry of zinc and cadmium in coal waste rock, Elk Valley, British Columbia, Canada. Appl. Geochem. 2022, 136, 105148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Pan, Z.; Li, C.; Liu, T.; Xia, B. Current status and prospects of geochemical studies on cadmium. Acta Petrol. Mineral. 2005, 4, 339–348. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, S.; Xiao, X.; Guo, Z. Regional distribution of cadmium mines and risk analysis of soil cadmium pollution in China. Environ. Pollut. Control 2012, 34, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Du, P.; Luo, H.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, M.; Xu, G.; Gao, H. Soil contamination with cadmium and potential risk around various mines in China during 2000–2020. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 310, 114509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyszka, R.; Pietranik, A.; Kierczak, J.; Zieliński, G.; Darling, J. Cadmium distribution in Pb-Zn slags from Upper Silesia, Poland: Implications for cadmium mobility from slag phases to the environment. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 186, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ke, W.; Zeng, J.; Zhu, F.; Luo, X.; Feng, J.; He, J.; Xue, S. Geochemical partitioning and spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils contaminated by lead smelting. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 307, 119486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.X.; Wang, X.D.; Lei, J.; Ran, Q.Q.; Ren, Y.X.; Zhou, J.H. Spatial distribution and source identification of heavy metals in a typical Pb/Zn smelter in an arid area of northwest China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2019, 25, 1661–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Li, D. Analysis of the current situation of cadmium resources in China and suggestions for sustainable development. China Min. Mag. 2015, 24, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, H.; Zhu, C.; Du, S.; Fan, Y.; Luo, C. China Gallium Germanium Thallium Cadmium Resources. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 3688–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Xia, T. Cadmium: Supply continues to be loose prices hovering at low levels. China Nonferr. Met. 2019, 15, 42–43. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Tian, Y.; Ye, J. China’s supply and demand status of cadmium and control countermeasures for cadmium. Mod. Chem. Ind. 2019, 39, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.; Yu, P.; Wei, N. Analysis of the development status of domestic and international CdTe power generation glass industry. Glass 2021, 48, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Fu, G.; Guan, M.; Yu, T.; Xie, L.; Qian, X.; Cheng, H.; Chu, J. Progress on CdTe thin film solar cells. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 50, 2305–2312. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.; Xie, S.; Lei, Y.; Gan, T.; Wu, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y. Betavoltaic battery prepared by using polycrystalline CdTe as absorption layer. Opt. Mater. 2022, 127, 112265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.-Y.; Jiang, S.-Y.; Su, H.-M.; Duan, Z.-P. In situ geochemical analysis of multiple generations of sphalerite from the Weilasituo Sn-Li-Rb-Cu-Zn ore field (Inner Mongolia, northeastern China): Implication for critical metal enrichment and ore-forming process. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 139, 104473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Khan, S.; Khan, A.; Alam, M. Soil contamination with cadmium, consequences and remediation using organic amendments. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 1591–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, M.; Mickus, K.; Camacho, L.M. Abandoned PbZn mining wastes and their mobility as proxy to toxicity: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wu, L.; Zhou, J.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, T.; Li, Z.; Hu, P.; Christie, P. Potential environmental risk of natural particulate cadmium and zinc in sphalerite- and smithsonite-spiked soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 429, 128313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Liu, T. Exploration of cadmium distribution and fugacity in cadmium-rich zinc deposits in Niujotang, Duyun, Guizhou. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2001, 1, 115–118. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, T.; Chen, Q.; Yu, W. Global Zinc Consumption and Demand Forecast and China Zinc Industry Development. Resour. Sci. 2015, 37, 951–960. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, J.; Jin, B. China’s Lead Demand Forecast Based on “Incomplete S-Shape” Model. China Min. Mag. 2019, 28, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Yang, S.; Luo, T.; Chen, Y. Removal of halogens from Pb-bearing dust by alkaline washing. Hydrometallurgy 2022, 209, 105838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Song, Y. Technology Innovation and Application Practice in China’s Lead Smelting Industry. China Nonferr. Metall. 2021, 50, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, L.; Zhang, W.; Ma, B.; Wang, C. Patterns of electrowinning behavior of cadmium in lead smelting fume leach solution. Nonferr. Met. Sci. Eng. 2022, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Nikkhou, F.; Xia, F.; Deditius, A.P. Variable surface passivation during direct leaching of sphalerite by ferric sulfate, ferric chloride, and ferric nitrate in a citrate medium. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 188, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Gao, L. Current status and outlook of zinc sulfate solution purification technology. Non-Ferr. Min. Metall. 2006, 1, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Q.; Du, X.; Wang, L.; Lan, Y. Status of recycling of copper and cadmium slag. Hydrometall. China 2003, 2, 66–68. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D. Analysis on distribution and control technology of metal cadmium in copper smelting process. Copp. Eng. 2022, 1, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, L.; Yang, X. Analysis of water pollution sources in copper smelting industry. China Min. Mag. 2020, 29, 551–553. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, W.; Sun, Z. New technology of high purity Cd powder prepared from roasting dust of zinc smelting. Chin. J. Nonferr. Met. 2014, 24, 1070–1075. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Xu, B.; Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, B.; Liu, G.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, T. Comprehensive recovery of valuable metals from copper smelting open-circuit dust with a clean and economical hydrometallurgical process. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 424, 130411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Liu, J.; Zou, W.; Zhang, T.; Mu, X.; Zhai, Z.; Xie, T.; Wang, K. Experimental of oxidative acid leaching of high cadmium dust. Nonferr. Met. 2021, 11, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Luo, T.; Chen, Y. Removal of cadmium and arsenic from Cd-As-Pb-bearing dust based on peroxide leaching and coprecipitation. Hydrometallurgy 2022, 209, 105839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yu, C.; Fu, X.; Yang, W.; Ma, B.; Wang, C.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Q. Quantitative characterization of secondary copper flue dust and guidance for separating valuable and toxic elements via low-temperature roasting and selective leaching. Miner. Eng. 2022, 189, 107871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Sun, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, R.; Han, H.; Hu, Y.; Yang, Y. Recovery of cobalt and zinc from the leaching solution of zinc smelting slag. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Min, X.-B.; Zhang, J.-Q.; Wang, M.; Zhou, B.-S.; Shen, C. Reductive acid leaching of cadmium from zinc neutral leaching residue using hydrazine sulfate. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 4175–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhang, C.; Liu, B.; Wang, L.; Peng, W.; Cao, Y.; Song, X.; Zhu, X. A novel method for the separation of zinc and cobalt from hazardous zinc–cobalt slag via an alkaline glycine solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 273, 119009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yan, W.; Shi, A.; Gao, F. Research on leaching process of copper, zinc and cadmium from copper-cadmium slag. J. Jishou Univ. 2010, 31, 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Fu, L.; Zhang, G.; Zuo, Y.; Zhang, L. Mechanism and kinetics analysis of valuable metals leaching from copper-cadmium slag assisted by ultrasound cavitation. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 379, 134775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, H. Copper slag: The leaching behavior of heavy metals and its applicability as a supplementary cementitious material. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.-J.; Sun, Z.-M. Preparation of high purity cadmium with micro-spherical architecture from zinc flue dust. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 2073–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tang, X.; Rong, Z.; Wu, L.; Deng, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, L.; Dang, W. A green strategy toward extraction of cadmium(II) during the transformation from arsenic-rich flue dust to scorodite. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 197, 105489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Pan, D.; Liu, G.; Yang, F.; Pan, J. Leaching Br from high bromine containing circuit board smelting flue dust by sodium hydroxide solution: Thermodynamics and kinetics study. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 8675–8684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Bao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, J. Mechanism and kinetics study on ultrasound assisted leaching of gallium and zinc from corundum flue dust. Miner. Eng. 2022, 183, 107624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Brahim, J.; Ait Hak, S.; Achiou, B.; Boulif, R.; Beniazza, R.; Benhida, R. Kinetics and mechanisms of leaching of rare earth elements from secondary resources. Miner. Eng. 2022, 177, 107351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Le, H.; Fang, X. Kinetics of sulfuric acid leaching of cadmium from zinc suboxide dust. Energy Environ. 2009, 5, 14–15. [Google Scholar]
- Król, A.; Mizerna, K.; Bożym, M. An assessment of pH-dependent release and mobility of heavy metals from metallurgical slag. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Zhou, G.; Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Cheng, W. Fugacity pattern and environmental risk assessment of heavy metals in Pb-Zn slag in Shihai. Earth Environ. 2016, 44, 478–483. [Google Scholar]
- Silwamba, M.; Ito, M.; Hiroyoshi, N.; Tabelin, C.B.; Fukushima, T.; Park, I.; Jeon, S.; Igarashi, T.; Sato, T.; Nyambe, I.; et al. Detoxification of lead-bearing zinc plant leach residues from Kabwe, Zambia by coupled extraction-cementation method. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollmann, K.; Kutschke, S.; Matys, S.; Raff, J.; Hlawacek, G.; Lederer, F.L. Bio-recycling of metals: Recycling of technical products using biological applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1048–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhong, Z.; Xu, Y. Investigation on bio-leaching of Cd from Cu/Cd smelting slag. Environ. Chem. 2013, 32, 259–266. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Huang, Q.; Li, T.; Xin, B.; Chen, S.; Guo, X.; Liu, C.; Li, Y. Bioleaching mechanism of Zn, Pb, In, Ag, Cd and As from Pb/Zn smelting slag by autotrophic bacteria. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 159, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zheng, S.; Liu, B.; Du, H.; Dreisinger, D.B.; Tafaghodi, L.; Zhang, Y. The leaching kinetics of cadmium from hazardous Cu-Cd zinc plant residues. Waste Manag. 2017, 65, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safarzadeh, M.S.; Moradkhani, D.; Ojaghi-Ilkhchi, M. Kinetics of sulfuric acid leaching of cadmium from Cd–Ni zinc plant residues. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Min, X.; Wang, M.; Zhou, B.; Shen, C. Kinetics of Reductive Acid Leaching of Cadmium-Bearing Zinc Ferrite Mixture Using Hydrazine Sulfate. J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. 2015, 67, 2028–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousif, S.A.; Al-Mosawi, S. Adsorptive separation of dissolved cadmium from aqueous solution using (Ziziphus Spina-Christi) leaves as an adsorbent. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 42, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manwani, S.; Bhoot, N.; Pandey, H.; Awasthi, G. Mitigation of lead and Cadmium from vegetable crops through different biochemical adsorbent treatments at Sanganer industrial area, Jaipur. Mater. Today Proc. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Dreisinger, D.; Rees, K. Simultaneous removal of Co, Cu, Cd and Ni from zinc sulfate solution by zinc dust cementation. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 197, 105479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lei, Y.; Zhu, C.; Sun, C.; Xu, Q.; Cheng, H.; Zou, X.; Lu, X. Morphology and distribution of cemented product formed via cementation over Zn in zinc sulfate solution relevant to roast-leach-electrowin process. Hydrometallurgy 2022, 210, 105847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouvea, L.R.; Morais, C.A. Recovery of zinc and cadmium from industrial waste by leaching/cementation. Miner. Eng. 2007, 20, 956–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, T.-X.; Yang, J.-G.; Wang, W.-C.; Li, L.-C.; Yang, J.-Y. Process and anodic reaction mechanism of cadmium electrically enhanced cementation on zinc plate under an ultrasonic field in ammoniacal system. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2019, 29, 1967–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, D.C.A.; Majuste, D.; Ciminelli, V.S.T. Improvements in the selective cementation of Cd and Ni/Co from zinc industrial electrolyte. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 201, 105572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarzadeh, M.S.; Moradkhani, D.; Ilkhchi, M.O. Determination of the optimum conditions for the cementation of cadmium with zinc powder in sulfate medium. Chem. Eng. Processing Process Intensif. 2007, 46, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, T.; Cao, Y.; Colombus, Y.; Steenari, B.-M. Investigation of the kinetics and the morphology of cementation products formed during purification of a synthetic zinc sulfate electrolyte. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 181, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Yang, J.; Nan, T.; Xie, X.; Ye, Y. Study on the electrically enhanced process for cadmium removal by a pulse in a sulfuric acid system. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 159, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.D.; Meshram, A.; Verma, H.R.; Singh, K.K.; Mankhand, T.R. Study to enhance cementation of impurities from zinc leach liquor by modifying the shape and size of zinc dust. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 195, 105352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashhadikhan, S.; Ebadi Amooghin, A.; Sanaeepur, H.; Shirazi, M.M.A. A critical review on cadmium recovery from wastewater towards environmental sustainability. Desalination 2022, 535, 115815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Qi, S.; Chen, G.; Wang, X.; Zhao, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Xin, B. Efficient removal of As, Cu and Cd and synthesis of photo-catalyst from Cu-smelting waste acid through sulfide precipitation by biogenic gaseous H2S produced by anaerobic membrane bioreactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 138096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Huang, R.; Zheng, L. Chemical precipitation method for the treatment of cadmium-containing wastewater from Huludao zinc plant. Environ. Prot. Circ. Econ. 2010, 30, 44–46. [Google Scholar]
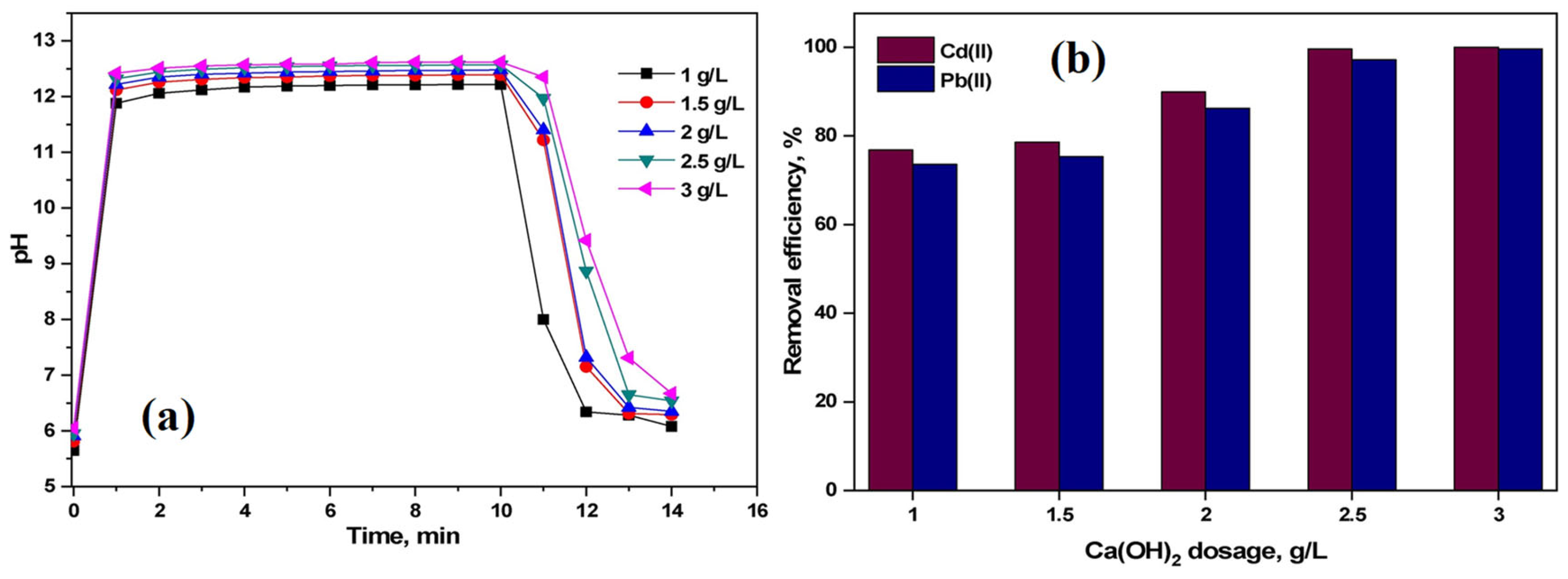
- Habte, L.; Shiferaw, N.; Thriveni, T.; Mulatu, D.; Lee, M.-H.; Jung, S.-H.; Ahn, J.W. Removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II) from wastewater via carbonation of aqueous Ca(OH)2 derived from eggshell. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 141, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.-W.; Barford, J.P.; Chen, G.; McKay, G. Kinetics and equilibrium studies for the removal of cadmium ions by ion exchange resin. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Elfeghe, S.; Tang, Z. Mechanism study of Cd(II) ion adsorption onto resins with sulfonic/phosphonic groups using electronic structure methods. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 358, 119199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Wen, J.; Hua, Y.; Ruan, R. Selective separation of Cu(II), Zn(II), and Cd(II) by solvent extraction. Rare Met. 2008, 27, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, K.; Watanabe, K.; Nakano, Y.; Watanabe, M. Solvent extraction separation of Cd(II) and Zn(II) with the organophosphorus extractant D2EHPA and the aqueous nitrogen-donor ligand TPEN. Hydrometallurgy 2003, 70, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, T.; Yang, Y.; Tang, K. Simultaneously enhanced ELM selectivity and stability by difunctional additives for batch and continuous separation of Cd(II)/Cu(II). Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 140, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghshenas Fatmehsari, D.; Darvishi, D.; Etemadi, S.; Eivazi Hollagh, A.R.; Keshavarz Alamdari, E.; Salardini, A.A. Interaction between TBP and D2EHPA during Zn, Cd, Mn, Cu, Co and Ni solvent extraction: A thermodynamic and empirical approach. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 98, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Xing, H.; Wu, H.; Lv, Y.; Wu, L.; Mi, S.; Yang, L. Preparation of magnetic Levextrel resin for cadmium(II) removal. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.R.; Neela Priya, D.; Venkateswara Rao, S.; Radhika, P. Solvent extraction and separation of Cd(II), Ni(II) and Co(II) from chloride leach liquors of spent Ni–Cd batteries using commercial organo-phosphorus extractants. Hydrometallurgy 2005, 77, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balesini Aghdam, A.A.; Yoozbashizadeh, H.; Moghaddam, J. Simple separation method of Zn(II) and Cd(II) from brine solution of zinc plant residue and synthetic chloride media using solvent extraction. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 28, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, H.; Abdollahi, H.; Gharabaghi, M.; Balesini, A.A. Solvent extraction of zinc from synthetic Zn-Cd-Mn chloride solution using D2EHPA: Optimization and thermodynamic studies. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 197, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, A.; Rahbar-Kelishami, A.; Shayesteh, H. Microfluidic solvent extraction of Cd(II) in parallel flow pattern: Optimization, ion exchange, and mass transfer study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 258, 118031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kumar, M.; Jha, M.K.; Jeong, J.; Lee, J.-C. Solvent extraction of cadmium from sulfate solution with di-(2-ethylhexyl) phosphoric acid diluted in kerosene. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 96, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwikima, M.M.; Mateso, S.; Chebude, Y. Potentials of agricultural wastes as the ultimate alternative adsorbent for cadmium removal from wastewater. A review. Sci. Afr. 2021, 13, e00934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praneeth, S.; Zameer, A.; Zhang, N.; Dubey, B.K.; Sarmah, A.K. Biochar admixture cement mortar fines for adsorptive removal of heavy metals in single and multimetal solution: Insights into the sorption mechanisms and environmental significance. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 155992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buema, G.; Lupu, N.; Chiriac, H.; Ciobanu, G.; Bucur, R.-D.; Bucur, D.; Favier, L.; Harja, M. Performance assessment of five adsorbents based on fly ash for removal of cadmium ions. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 333, 115932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, M.; Hu, X. Removal of heavy metals from soil with biochar composite: A critical review of the mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameen Hezam Saeed, A.; Yub Harun, N.; Mahmoud Nasef, M.; Al-Fakih, A.; Abdulhakim Saeed Ghaleb, A.; Kolawole Afolabi, H. Removal of cadmium from aqueous solution by optimized rice husk biochar using response surface methodology. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2022, 13, 101516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Liu, Y.; Xing, B.; Qin, X.; Zhang, C.; Xia, H. Lead and cadmium clean removal from wastewater by sustainable biochar derived from poplar saw dust. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 128074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Q.; Li, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Peng, Q.; Yuan, S.; Li, H.; Huang, R.; et al. An integrated method to produce fermented liquid feed and biologically modified biochar as cadmium adsorbents using corn stalks. Waste Manag. 2021, 127, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Guo, H.; Bian, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, F. Magnetic graphene oxide−based covalent organic frameworks as novel adsorbent for extraction and separation of triazine herbicides from fruit and vegetable samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1219, 339984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Ye, Q.; Wang, L.; Meng, F.; Dai, H. Graphene oxide-doped stearate-intercalated layered double oxide nanocomposites as high-performance CO2 adsorbents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 288, 120686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yin, J.; Ma, Q.; Baihetiyaer, B.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yin, X. Montmorillonite-reduced graphene oxide composite aerogel (M−rGO): A green adsorbent for the dynamic removal of cadmium and methylene blue from wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 296, 121416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahat, M.M.; Abdel Khalek, M.A.; Sanad, M.M.S. Affordable and reliable cationic-anionic magnetic adsorbent: Processing, characterization, and heavy metals removal. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 360, 132178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, E.; Azizkhani, S.; Mohammad, A.W.; Ng, L.Y.; Benamor, A.; Ang, W.L.; Ba-Abbad, M. Simultaneous removal of Congo red and cadmium(II) from aqueous solutions using graphene oxide–silica composite as a multifunctional adsorbent. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 98, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Calderón, L.; Basualto-Flores, C.; Paredes-García, V.; Venegas-Yazigi, D. Advances of magnetic nanohydrometallurgy using superparamagnetic nanomaterials as rare earth ions adsorbents: A grand opportunity for sustainable rare earth recovery. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 299, 121708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, N.; Tian, K.; Qing, T.; Hao, Y.; Liang, P.; Li, M. Nitrilotriacetic acid modified magnetic Prussian blue for efficient removal of cadmium from wastewater. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 600, 154102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, S.; Ahmad, Z.; Asma, M.; Ahmad, M.; Rehan, K.; Munir, M.; Bazmi, A.A.; Ali, H.M.; Mazroua, Y.; Salem, M.A.; et al. Effective adsorption of cadmium and lead using SO3H-functionalized Zr-MOFs in aqueous medium. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragheb, E.; Shamsipur, M.; Jalali, F.; Mousavi, F. Modified magnetic-metal organic framework as a green and efficient adsorbent for removal of heavy metals. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kaushal, S.; Kaur, J.; Kaur, G.; Mittal, S.K.; Singh, P.P. CaFu MOF as an efficient adsorbent for simultaneous removal of imidacloprid pesticide and cadmium ions from wastewater. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, M. Research Status and Prospects of Membrane Separation Technology for Treatment of Oilfield Wastewater. Chem. Eng. 2022, 36, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Bhowmick, K.; Roy, S.; Mukherjee, M.; Sahoo, G.C.; Majumdar, S.; Mondal, P. Removal of cadmium by in-situ Cu nanoparticle enhanced ceramic-supported-polymeric composite NF membrane. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 1496–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Xiao, L. Manganese-doped ferrihydrite/cellulose/polyvinyl alcohol composite membrane: Easily recyclable adsorbent for simultaneous removal of arsenic and cadmium from soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, M.R.; Aijaz, M.O.; Alharth, N.H.; Alharbi, H.F.; Al-Mubaddel, F.S.; Awual, M.R. Composite nanofibers membranes of poly(vinyl alcohol)/chitosan for selective lead(II) and cadmium(II) ions removal from wastewater. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Min, X.; Tang, C.-J.; Sillanpää, M.; Zhao, F. Recent advances in membrane filtration for heavy metal removal from wastewater: A mini review. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 103023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, N.; Bicer, Y. Integration of electrodialysis with renewable energy sources for sustainable freshwater production: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 289, 112496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arana Juve, J.-M.; Christensen, F.M.S.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Z. Electrodialysis for metal removal and recovery: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dai, L.; Ke, X.; Ding, J.; Wu, X.; Chen, R.; Ding, R.; Van der Bruggen, B. Arsenic and cation metal removal from copper slag using a bipolar membrane electrodialysis system. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 338, 130662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frioui, S.; Oumeddour, R.; Lacour, S. Highly selective extraction of metal ions from dilute solutions by hybrid electrodialysis technology. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 174, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liang, B.; Cao, M.; Yang, Y.; Wang, D.; Yang, Q.; Han, Z.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; et al. Simulation of aluminium electrodeposition on complex geometry: Influence of input parameters and electrodeposition conditions. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 33, 102208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Gao, J.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, W.; Su, G.; Zheng, R.; Zhong, H. High-gravity intensified electrodeposition for efficient removal of Cd2+ from heavy metal wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 289, 120809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanong, K.; Tran, L.-H.; Mercier, G.; Blais, J.-F. Recovery of Zn (II), Mn (II), Cd (II) and Ni (II) from the unsorted spent batteries using solvent extraction, electrodeposition and precipitation methods. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 148, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gautam, P.; Kumar, S.; Vishwakarma, S.; Gautam, A. Synergistic optimization of electrocoagulation process parameters using response surface methodology for treatment of hazardous waste landfill leachate. Chemosphere 2022, 290, 133255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhou, C. Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation strategy for operating state of electrocoagulation purification process based on sliding window. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 165, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xu, X.; Wu, D. Initial dissolved oxygen-adjusted electrochemical generation of sulfate green rust for cadmium removal using a closed-atmosphere Fe–electrocoagulation system. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 1411–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlJaberi, F.Y.; Alardhi, S.M.; Ahmed, S.A.; Salman, A.D.; Juzsakova, T.; Cretescu, I.; Le, P.-C.; Chung, W.J.; Chang, S.W.; Nguyen, D.D. Can electrocoagulation technology be integrated with wastewater treatment systems to improve treatment efficiency? Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasudevan, S.; Lakshmi, J. Effects of alternating and direct current in electrocoagulation process on the removal of cadmium from water—A novel approach. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 80, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stylianou, M.; Montel, E.; Zissimos, A.; Christoforou, I.; Dermentzis, K.; Agapiou, A. Removal of toxic metals and anions from acid mine drainage (AMD) by electrocoagulation: The case of North Mathiatis open cast mine. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 29, 100737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, B.; Huang, Y.; Yang, S.; Wu, H.; Han, G.; Cao, Y. Enhancing surface interactions between humic surfactants and cupric ion: DFT computations coupled with MD simulations study. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 324, 114781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Huang, Y.; Han, G.; Yang, S.; Su, S.; Sana, H.; Peng, W.; Cao, Y.; Liu, J. Comprehensive evaluation on a prospective precipitation-flotation process for metal-ions removal from wastewater simulants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 371, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Chang, L.; Li, P.; Han, G.; Huang, Y.; Cao, Y. An overview on the surfactants used in ion flotation. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 286, 110955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Han, G.; Cao, Y.; Sun, K.; Song, S. Efficiently removing Pb(II) from wastewater by graphene oxide using foam flotation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 556, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Du, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, W.; Su, S.; Liu, B. Study on the removal of hazardous Congo red from aqueous solutions by chelation flocculation and precipitation flotation process. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 133109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, G.; Du, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, W.; Su, S.; Liu, B. Efficient removal of hazardous benzohydroxamic acid (BHA) contaminants from the industrial beneficiation wastewaters by facile precipitation flotation process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 279, 119718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Wu, H.; Huang, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, W.; Yang, S.; Su, S. Research on the treatment of non-ferrous industrial wastewater by ion flotation process: A review. J. Guizhou Univ. 2020, 37, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Huang, Y.; Liu, B.; Han, G.; Su, S.; Wang, W.; Yang, S.; Xue, Y.; Li, S. An efficient separation for metal-ions from wastewater by ion precipitate flotation: Probing formation and growth evolution of metal-reagent flocs. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooja, G.; Kumar, P.S.; Prasannamedha, G.; Varjani, S.; Vo, D.-V.N. Sustainable approach on removal of toxic metals from electroplating industrial wastewater using dissolved air flotation. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 295, 113147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.R.; Lazaridis, N.K.; Matis, K.A. Study of flotation conditions for cadmium(II) removal from aqueous solutions. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2015, 94, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooja, G.; Kumar, P.S.; Indraganti, S. Recent advancements in the removal/recovery of toxic metals from aquatic system using flotation techniques. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Types | Concentration (%) | Mineralogy | Ref. | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Zn | Pb | Cu | S | As | K | Cl | Co | Mn | ||||
| Dust | Zn roasting dust | 18.32 | 0.2 | 42.45 | 0.09 | - | 0.51 | 0.99 | - | - | - | PbSO4, CdO | [48] |
| Cu smelting open-circuit dust | 1.2 | 2.3 | 21 | 8.6 | 12 | 11.2 | 0.4 | - | - | - | PbSO4, As2O3 | [49] | |
| Pb-Zn smelting Isaar furnace dust | 16.86 | 2.84 | 45.84 | - | 8.67 | 1.4 | - | 1.15 | - | - | PbSO4, CdO, CdS, ZnO | [50] | |
| Secondary Pb materials smelting dust | 13 | 0.42 | 18.5 | - | 3.35 | 6.63 | 5.53 | 11.7 | - | - | KCdCl3, As2O3, CdS, PbClF | [51] | |
| Secondary copper flue dust | 1.27 | 23.4 | 21.8 | 4.67 | 3.32 | 0.16 | 1.8 | 6.21 | - | - | ZnO, PbCl2, Cd2SnO4 | [52] | |
| Pb smelting dust | 18.5 | 3.01 | 18.5 | 3.35 | 14.1 | 5.53 | 11.7 | - | - | KCdCl3, K4CdCl6, Pb5(AsO3)3Cl | [40] | ||
| Slag | Zn smelter slag | 4.77 | 44.24 | - | 0.74 | 9.71 | - | - | - | 0.38 | 0.33 | PbSO4, CdO | [53] |
| Zn neutral leaching residue | 0.26 | 35.99 | 1.73 | 0.52 | 10.05 | 0.41 | - | - | - | 0.74 | ZnFe2O4, ZnO, ZnS | [54] | |
| Zn-Co slag from Zn smelting | 2.57 | 4.9 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 27.8 | 21.47 | ZnO, CdO | [55] | |
| Cu-Cd slag from Zn smelting | 6.43 | 40.9 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 3.35 | 6.63 | - | - | - | - | Zn, ZnO, ZnSO4, Cd, CdO | [56] | |
| Cu-Cd slag from Zn smelting | 21.43 | 28.58 | 1.58 | 1.03 | 8.21 | - | - | 0.03 | - | 0.11 | ZnO, ZnSO4, CdO | [57] | |
| Cu slag from Cu smelting | 0.16 | 4.97 | 0.26 | 1.09 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.09 | FeOx, SiO2, CaO | [58] | |
| Method | Advantages | Limitations | Specific Application | Initial Content (mg/L) | Removal Rate/Adsorption Capacity | Residual Content (mg/L) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cementation |
|
| Graded addition of Zn powder | 640–740 | 99.9% | - | [80] |
| Reduce the size of Zn powder | 400 | - | 1 | [83] | |||
| Electrical enhancement | 20,000 | 99.21% | - | [79] | |||
| Precipitation |
|
| Cd(OH)2 precipitation | 1200 | - | 0.086 | [87] |
| CdCO3 precipitation | 100 | 99.9% | - | [51] | |||
| CdS precipitation | 70.9 | - | 0.08 | [88] | |||
| Cd5H2(AsO4)4·4H2O Coprecipitation | 22,000 | 99.7% | - | [86] | |||
| Ion exchange |
|
| Chelating resin D-401 | 675 | 245 mg/g | - | [90] |
| G-26 | - | 99.68% | - | [91] | |||
| MTS9570 | - | 98.95% | - | [91] | |||
| Solvent extraction |
|
| D2EHPA | 5000 | 3% | - | [99] |
| MDEHPA | 100 | 90.9% | - | [100] | |||
| Adsorption |
|
| Poplar sawdust | 180 | 49.32 mg/g | - | [107] |
| BCB24 | 100 | 47.39 mg/g | - | [108] | |||
| M−rGO | 35 | 262.79 mg/g | - | [111] | |||
| Ternary magnetic ABI composite | 250 | 219.2 mg/g | - | [112] | |||
| SGO | 80 | 43.45 mg/g | - | [113] | |||
| Fe3O4@PB@NTA | 25 | 310.56 mg/g | - | [115] | |||
| ZrMOF@GSH | 200 | 393 mg/g | - | [117] | |||
| CaFuMOF | 21.24 | 781.2 mg/g | - | [118] | |||
| Membrane separation |
|
| Ceramic-supported-polymeric composite NF membrane | 5 | 95.5% | - | [120] |
| Mn-Fh/Cell/PVA composite membrane | 50 | 11.11 mg/g | - | [121] | |||
| Poly(vinyl alcohol)/chitosan nanofiber | 400 | 148 mg/g | - | [122] | |||
| Electrodialysis |
|
| BMED | - | 75.8% | - | [126] |
| Complexation electrodialysis | 5.63 | - | 0.3 | [127] | |||
| Electrodeposition |
|
| Provide high gravity field | 800 | 99.4% | - | [129] |
| Selective electrodeposition | 2207 | - | 4.6 | [130] | |||
| Electrocoagulation |
|
| Green rust floc | 25 | - | 0.02 | [133] |
| Alternating current | 50 | - | 0.005 | [135] | |||
| Existence system of multiple heavy metal ions | 0.042 | 96% | - | [136] | |||
| Foam extraction |
|
| SDS surfactant | 63 | Over 98% | 1.13 | [145] |
| Cd-KEtX and HDTMA | 0.113 | 99% | - | [146] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, G.; Wang, J.; Sun, H.; Liu, B.; Huang, Y. A Critical Review on the Removal and Recovery of Hazardous Cd from Cd-Containing Secondary Resources in Cu-Pb-Zn Smelting Processes. Metals 2022, 12, 1846. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12111846
Han G, Wang J, Sun H, Liu B, Huang Y. A Critical Review on the Removal and Recovery of Hazardous Cd from Cd-Containing Secondary Resources in Cu-Pb-Zn Smelting Processes. Metals. 2022; 12(11):1846. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12111846
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Guihong, Jingwen Wang, Hu Sun, Bingbing Liu, and Yanfang Huang. 2022. "A Critical Review on the Removal and Recovery of Hazardous Cd from Cd-Containing Secondary Resources in Cu-Pb-Zn Smelting Processes" Metals 12, no. 11: 1846. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12111846
APA StyleHan, G., Wang, J., Sun, H., Liu, B., & Huang, Y. (2022). A Critical Review on the Removal and Recovery of Hazardous Cd from Cd-Containing Secondary Resources in Cu-Pb-Zn Smelting Processes. Metals, 12(11), 1846. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12111846