Abstract
In this paper, a new medium entropy alloy with nominal composition of Gd33Co33Al34 was designed and fabricated into microfibers by a melt-extraction method. The microstructure, thermophysical parameters, and magnetocaloric properties of the obtained fibers were systematically analyzed. The results showed that the as-cast fibers show an amorphous matrix with embedded in situ nano crystals. The fibers show a good magnetocaloric effect with the maximum magnetic entropy change of ~6 J/kg·K for a field change of 5 T. Notably, the fibers show excellent cooling efficiencies with an RCP and RC of ~611.72 and ~487.38 J/kg, respectively. Though the as-cast fibers possess an amorphous/nanocrystal bi-phase structure, they still exhibit a second-order transition near a Curie temperature of ~96 K. Our findings provide a promising pathway towards developing new magnetocaloric materials with good magnetocaloric performances.
1. Introduction
Magnetic refrigeration based on the magnetocaloric effect (MCE) provides a feasible and promising alternative to traditional gas compression refrigerators for its energy saving, environmental protection, and high efficiency [,]. Distinct from conventional gas compression refrigeration technology, magnetic refrigeration technology employs a solid substance as the refrigerant, with water often utilized as the heat transfer medium in its circulation loop. This innovative approach mitigates environmental concerns associated with traditional refrigerating materials like Freon, hydrocarbons, and ammonia, thereby averting issues such as ozone layer depletion and the risk of flammable gas leakage. Moreover, magnetic refrigeration boasts an impressive efficiency, reaching between 30% and 60% of the Carnot cycle, surpassing the efficiency of gas compression refrigeration by approximately 20% [,]. This remarkable efficiency contributes significantly to reducing carbon emissions, aligning with the emerging environmental principles of “carbon peak” and “carbon neutrality”. Consequently, magnetic refrigeration garners increasing attention due to its promising application prospects and alignment with sustainability goals [,].
As promising magnetic refrigerants with second-order transition, the pure rare earth element Gd exhibits an excellent magnetocaloric response near room temperature (294 K) with its maximum magnetic entropy change (−ΔSMmax) of ~10.2 J/kg·K and refrigerant capacity (RC) of ~410 J/kg at 5 T, resulting from its large magnetic moment [,,]. However, the application of Gd has been constrained by its high costs; therefore, alloying emerges as one of the most economical choices. In recent years, significant advancements have been made in developing Gd-based materials with excellent magnetocaloric effects (MCEs) through alloying, aimed at reducing costs and optimizing performance. In 2009, Zhang et al. [] obtained an amorphous band of GdCo with the same composition but different proportions using melt rapid quenching technology, and found that the MCE increased with increasing Gd content. Another study [] has shown that Gd55Co20Al25 amorphous bulk alloy has an excellent magnetothermal property with −ΔSMmax of 11.2 J/kg·K for a field change of 7 T, which is almost equivalent to that of pure metal Gd. The addition of Al enhances the glass-forming ability, resulting in an amorphous structure that promotes enhanced atomic interaction, thereby increasing the MCE []. The nanocrystals within the amorphous matrix lead to a distribution of Curie temperatures []. In 2011, Fu et al. [] found that by decreasing the content of Al and increasing the content of Co, the Curie temperature of the amorphous alloy gradually increased while preserving the large −ΔSMmax. Huo et al. [] firstly developed a high entropy amorphous alloy of Gd20Tb20Dy20Al20TM20 (M = Co, Ni and Fe), which broadened the working temperature range by introducing high mixing entropy. Furthermore, studies have reported that the random distribution of elements, along with complex magnetic structures and exchange coupling among multiple principal elements, contribute to prolonging the magnetic phase transition process. This phenomenon results in a sluggish magnetic transition across a wide temperature range, ultimately leading to exceptional cooling efficiency []. Alloy materials composed of multiple principal elements in equimolar or near-equimolar ratios exhibit high entropy of mixing, representing a novel approach to component design for achieving high performance. Medium-entropy alloys based on rare elements have demonstrated excellent magnetocaloric performance while reducing the number of alloy components. Additionally, rare elements with large magnetic moments are typically used in magnetocaloric materials, forming amorphous structures through alloying with magnetic transition and main group elements. To minimize the number of elements while preserving the effects of mixing entropy, Bao et al. [] developed a range of medium entropy amorphous fibers. Among these, the HoErCo alloy exhibits the most outstanding MCE performance, with −ΔSMmax of ~15 J/kg K for a field change of 5 T. However, its Curie temperature is relatively low, around 16 K. In addition, Yin et al. [] noted that the presence of nanocrystals within the amorphous matrix enhances magnetic performance due to interactions within the biphasic structure.
In this work, a new type of medium entropy amorphous fibers of Gd33Co33Al34 composition was designed and fabricated by a melt-extraction method. The microstructure, magnetic transition, and magnetocaloric performances were systematically investigated. The results indicate that Gd33Co33Al34 fibers exhibit favorable MCE properties along with a high Curie temperature. Our study offers a novel approach for developing magnetic refrigerants suitable for cooling systems.
2. Materials and Methods
High-purity raw materials (99.95%Gd, 99.99%Co and 99.99%Al) were selected and alloyed by vacuum non-consumable tungsten arc furnace. The Gd33Co33Al34 alloy ingot with a weight of 70 g was obtained and then an alloy bar with a diameter of 9 mm was formed by suction casting. The prefabricated alloy rod was put into a boron nitride crucible and re-melt by induction heating in a home-made melt-extraction device. The melt was fed to connect with a high-rotating Cu wheel and then was dipped and quenched into microfibers. The detailed process parameters can be found in our previous report []. X-ray diffraction (XRD) (Japan Science D/MAX-γB) with Cu target Kα ray and graphite filter were used to analyze the phase composition of the fiber. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) (Pyris 1 of P-E Company, Netzsch, Gemany) was applied to obtain the thermal physical parameters of the fiber. The surface morphology and element distribution of the fibers were characterized by scanning electron microscope (Zeiss Merlin Compact, Jena, Germany) and EDS energy spectrometer. Transmission electron microscopy (Talos F200x and Tecnai G2 T20) was employed to analyze the microstructure of the as-cast fibers. Thermomagnetic curves (M-T) and isothermal magnetization curves (M-H) were measured using a physical property measurement system (PPMS-9T from Quantum Design Company, San Diego, CA, USA). A bunch of fibers were used and put into a sample holder for ensuring the accuracy of mass weighing. All the fibers were arranged in parallel along the direction of the applied magnetic field. A schematic diagram of the fiber test sample is illustrated in Figure 1c.
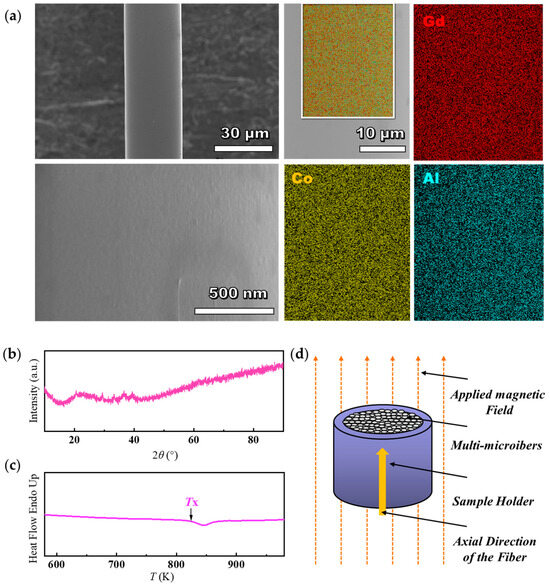
Figure 1.
(a) Morphology and element distribution of the Gd33Co33Al34 fiber surface. (b) XRD and (c) DSC results of the Gd33Co33Al34 microfibers. (d) Diagram illustrating the magneto-thermal performance testing setup for fiber samples.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phase Composition and Microstructure
Figure 1a shows the surface morphology and element distribution of Gd33Co33Al34 fibers. The fibers show a uniform diameter of ~30 μm without obvious groove defects or Rayleigh wave defects. The fibers possess a smooth surface without typical crystal characteristics such as grain and grain boundary. The experimental composition determined by EDS is Gd33.18Co33.32Al33.50, which closely matches the nominal composition. Furthermore, EDS mapping reveals that the elements were evenly distributed without visible fluctuations.
Figure 1b,c shows the XRD and DSC curves of the as-cast Gd33Co33Al34 microfibers, respectively. The XRD pattern of the fibers at room temperature shows that the diffraction peak intensity is low without obvious high-intensity crystalline diffraction peaks and the diffuse scattering peak appears at 2θ of ~22°. However, the presence of a few sharp peaks with low intensity appearing at ~37° indicates that most of the fibers obtained by the rotary dipping process are amorphous with a few crystalline structures distributed in the amorphous matrix. The DSC result (Figure 1d) shows that a crystallization peak appeared clearly, indicating the proper thermophysical characters of an amorphous alloy for the fabricated microfibers. The initial crystallization temperature (Tx) of the fibers was determined to be ~819 K.
The TEM analysis was applied to further confirm the microstructure of the as-cast fibers. Figure 2a shows the high-resolution image of the fiber and the illustration is a selected area electron diffraction diagram. It can be seen that most areas are featureless with a long-range disorder structure such as region 1 in Figure 2a, which exhibits a matrix possessing a typical amorphous structure. It is worth noting that there are also a small number of micro-regions with clear ordered structures with stripe characteristics, such as regions 2 and 3, which are identified as nano-crystalline structures. Simultaneously, two distinct diffraction rings appeared in the SAED image, indicating the presence of nanocrystals distributed within the amorphous matrix. To assess the degree of structural order in the as-cast fibers, Figure 2a was divided into 64 equally sized sub-images. The corresponding autocorrelation transformed images are presented in Figure 2b. A sub-image with clear crystal-like diffraction spots after its fast Fourier transformation (not shown) was selected as a reference in this work. The sub-image shows crystal-like diffraction spots taken as ordered, otherwise as disordered. The degree of structural order (ψ) is defined as follows:
where ζ and κ are the numbers of ordered and total sub-images, respectively. The order degree of the high-resolution image was calculated to be ~14%. In addition, Fourier Function Transform and Inverse Fourier Function Transform (FFT and IFFT) were carried out on the micro-regions 1 and 2 for comparing the atomic arrangement rules of amorphous and nano-crystalline parts, and the corresponding images are shown in the sub-images 1 and 2 of Figure 2c. There are two kinds of nanocrystals with different organizational structures in the diagram, which are consistent with the SAED results. Through the FFT and IFFT of regions 2 and 3 (sub-images 3 and 4 of Figure 2c), the interplanar spacings of the nanocrystals in these two regions were found to be different, and Figure 2d shows the average fringe spacing calculated for each type of nanocrystal. The interplanar spacings of regions 2 and 3 were determined to be D2 = 0.214 nm and D3 = 0.192 nm, corresponding to the Co3Gd and Co2Al5 phases based on the PDF card.
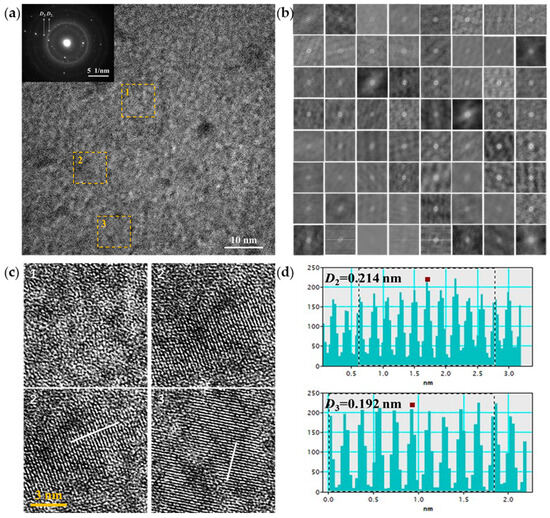
Figure 2.
Gd33Co33Al34 fiber treated by high-resolution transmission electron microscope. (a) Selected area electron diffraction map and high-resolution image; (b) the corresponding autocorrelation transformed image; (c) amorphous matrix and nanocrystalline after forward and inverse Fourier transform; (d) the interplanar spacing of nanocrystalline structures.
3.2. Magnetothermal Properties of Gd33Co33Al34 Fibers
Figure 3 shows the thermo-magnetic curve (M-T) and its corresponding H/M-T curve for the Gd33Co33Al34 fibers over a temperature range of 10–250 K and in an applied field of 0.02 T. Clearly, the sample is ferromagnetic at low temperature and paramagnetic at high temperature, which indicates a transition from the ferromagnetic to paramagnetic state on increasing the temperature. The transition is of the second-order type for the amorphous structure of the as-cast fibers. The Curie temperature TC of the sample is defined as the lowest point of the derivative of the M-T curve (dM/dT-T), which has been determined to be ~95.58 K. This Curie temperature represents the average value between nanocrystals and the amorphous matrix, indicating a distribution of Curie temperatures. This distribution leads to a relatively broad peak in dM/dT []. This value is much higher than those of HoEr-based medium amorphous fibers []. Considering the Curie–Weiss law, the H/M-T or χ−1 (T) curve was constructed and displayed in Figure 3b, according to the following equation:
where χ is the magnetic susceptibility and described as M/H, and the Curie–Weiss temperature θp of the fiber is calculated to be ~106 K, which is about 10 K higher than the Curie temperature TC. The Curie constant C is ~2.56 emu∙K/mol and the effective atomic magnetic moment μeff is ~4.53 μB. The effective magnetic moment of the fiber is lower than that of pure Gd, primarily due to the lower Gd content in the alloy, the presence of Co with lower magnetic properties, and Al, which does not contribute a magnetic moment to the alloy.
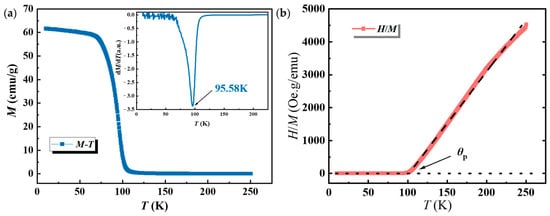
Figure 3.
(a) Thermomagnetic (M-T) curve and its derivative with respect to temperature (the inset (a)); (b) the corresponding H/M-T curve of the Gd33Co33Al34 fibers.
Figure 4a shows the isothermal magnetization curves measured in magnetic fields of up to 5 T over a temperature range of 20–200 K with temperature intervals of 10 K and 5 K far and near to the Curie temperature. The isothermal magnetic entropy change, ΔSM, as a function of magnetic field and temperature is calculated by Maxwell’s equation:
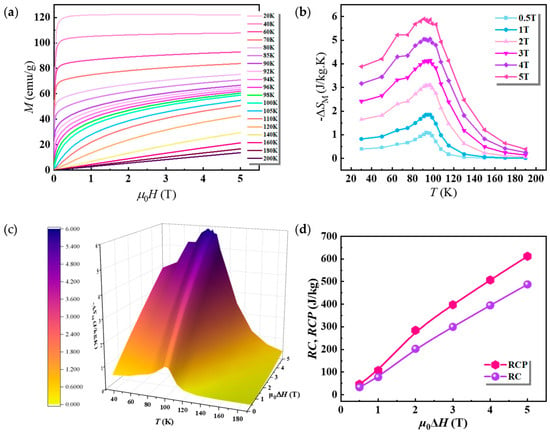
Figure 4.
(a) The isothermal M-H curves, (b) the magnetic field and temperature dependent magnetic entropy change −ΔSM (T, H) curves, (c) the three-dimensional plot of the magnetic entropy change with respect to magnetic field and temperature, (d) RC and RCP as functions of magnetic field for the Gd33Co33Al34 microfibers.
Figure 4b,c shows the −ΔSM (T, H) curves and their three-dimensional plots, respectively. Obviously, the −ΔSM (T, H) curves show a typical broad trigonal peak, and the maximum magnetic entropy change (−ΔSMmax) is determined to be ~6 J/kg K for a field change in (µ0ΔH) of 5 T. This value is relatively lower compared to other Gd-based amorphous fibers [], and lower than that of other medium-entropy amorphous microwires, as indicated in Table 3. This is attributed to the lower effective atomic magnetic moment (~4.53 μB). However, the present research component comprises only 33% of rare earth Gd by atom fraction. The values of −ΔSMmax for different magnetic field changes are also listed in Table 1. Notably, the presently prepared Gd33Co33Al34 fibers exhibit a large working temperature range, highlighting excellent cooling efficiency. Generally, the cooling efficiency can be assessed using refrigerant capacity (RC) or relative cooling power (RCP), which are, respectively, calculated as follows:
where T1 and T2 are the onset and offset temperatures of the full width at half-maximum (δTFWHM), respectively.

Table 1.
The maximum magnetic entropy change values of Gd33Co33Al34 fibers for different external field changes.
Table 2 shows the RC and RCP values at different field changes for the Gd33Co33Al34 fibers, and the corresponding curves are shown in Figure 4d. It can be seen that the magnetic-field-dependent RC and RCP values of the Gd33Co33Al34 fibers follow a nearly linear relationship. At a field of 5 T, the RCP and RC values are calculated to be ~612 J/kg and ~487 J/kg, which are comparable with those of other medium entropy microwires, as seen in Table 3. These good cooling efficiencies are desirable for active magnetic refrigeration. This phenomenon can be attributed to the magnetic interactions among the nanocrystals and between the nanocrystalline and amorphous phases [,]. The interaction between the 4f layer electrons of Gd and the 3d layer electrons of Co is also expected to expand the phase transition range of the fibers [,], thus improving the overall cooling efficiency of the as-cast fibers.

Table 2.
RC and RCP values of the Gd33Co33Al34 fibers (J·kg−1).

Table 3.
The magnetocaloric performances of rare-based medium entropy alloys for a field change of 5 T.
3.3. Analysis of Phase Transition
To confirm the nature of the phase transition in the present fibers, the Arrott plots of the corresponding M-H curves are analyzed and shown in Figure 5a. All the curves show a positive slope and the intercepts with the vertical axis are positive when T < TC; they are negative when T > TC, indicating the characteristics of a second order transition according to Banerjee criterion []. In addition, the normalized curves of −∆SM-T are another approach based on a scaling equation for determining the phase transition []:
where Tr1 and Tr2 are the two reference temperatures above and below the TC, respectively. Usually, the two values are defined by:
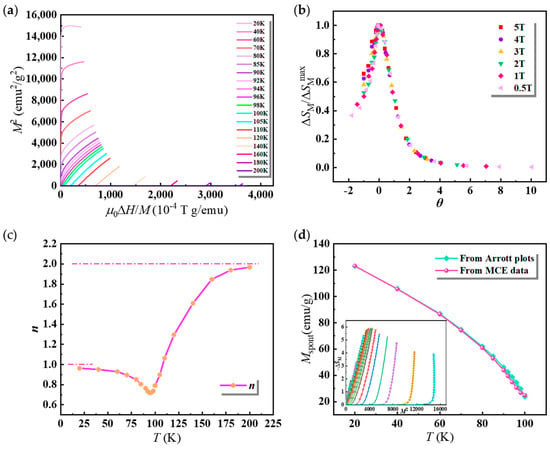
Figure 5.
(a) Arrott plots of the corresponding M-H curves, (b) the normalized magnetic entropy change curves, (c) temperature dependence of n for a field change of 5 T for the Gd33Co33Al34 microfibers. (d) The temperature dependence of spontaneous magnetization Mspont of the Gd33Co33Al34 fibers calculated from the Arrott curves of the mean field theory, and the −∆SM-M2 curve is shown in its inset.
Here, the value of f is set as 0.5. The normalized −∆SM-T curves for different magnetic changes are shown in Figure 5b. The good overlapping signifies that the as-cast fibers undergo a second order transition near the TC. However, the small deviations that appeared at low temperature could be attributed to the presence of the nanocrystals embedded in the amorphous matrix.
The relation between the magnetic entropy changes and the applied field change at different temperatures is another method for evaluating the phase transition state, which can be described by:
As shown in Figure 5c, the local critical exponent n is close to 2 at temperatures much higher than the TC but close to 1 below the TC. This is a typical characteristic of second-order magnetic materials. It is noteworthy that n is equal to 0.721 at the TC, surpassing the mean field theory’s 0.67. This deviation could also be associated with the presence of the nanocrystalline phase. Despite the presence of nanocrystals embedded within the amorphous matrix of the as-cast GdCoAl microwires, the parameter n remains below 1 when T < TC. This suggests that the amorphous fraction predominates within the wires. []. Therefore, the spontaneous magnetization (Mspont) of the as-cast Gd33Co33Al34 fibers in the ferromagnetic state was analyzed through the Arrott plots and magnetic entropy changes based on the mean field theory. The magnetic entropy S(σ) and applied H can be described as follows []:
where N, kB J and BJ are the number of spins, Boltzmann constant, spin value and Brillouin function for a given J value, respectively. σ is the reduced magnetization:
σ = M/(gμBJN).
From a power expansion of Equation (10), ∆SM is proportional to M2. For small values of M, it can be deduced as follows:
If we consider only the first term of the expansion, it can be rewritten as follows:
Mspont can be obtained by constructing the relationship between −∆SM and M2, and the results for the Gd33Co33Al34 fibers are displayed in an inset of Figure 5d.
In the mean field theory, all curves in the inset are expected to exhibit equal slopes in their straight segments under the ferromagnetic state. Although the slopes of the straight-line segments of the present sample in the ferromagnetic state are similar, there are still slight differences near the TC. This discrepancy suggests that the phase transition behavior of the prepared sample deviates from the mean field theory. Furthermore, the spontaneous magnetization (Mspont) can be calculated based on the Arrott–Noakes state equation and mean field theory using Arrott plots. However, the values of Mspont calculated from the Arrott plots and those derived from the constructed −∆SM-M2 curves exhibit deviations, especially near the TC. This phenomenon indicates that the mean field theory is not entirely applicable to describe the magnetic behavior near the FM-PM transition for the as-cast Gd33Co33Al34 fibers.
4. Conclusions
In summary, a new type of medium entropy Gd33Co33Al34 fibers with nanocrystals embedded in an amorphous matrix was prepared by the melt-extraction method. The Curie temperature TC of the fibers was determined to be ~96 K and the effective atomic magnetic moment is ~4.53 μB. The maximum magnetic entropy change −∆SMmax of the sample for a field change of 5 T is ~6 J/kg K. The large RCP and RC values achieved are ~612 J/kg and 487 J/kg, respectively, which are desirable for active magnetic refrigeration. A detailed analysis of the magnetic behavior near the ferromagnetic to paramagnetic phase transition reveals some deviation from the mean field theory, arising from the nonuniform distribution of nanocrystals in the amorphous matrix. Our study provides a new method for developing novel magnetocaloric materials for magnetic refrigeration in the liquid nitrogen temperature regime.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.Z. and H.S.; methodology, N.Z., H.S., L.L., J.L. and Z.Z.; validation, H.S., L.Z., J.S. and M.-H.P.; formal analysis, N.Z., H.S., L.L., Z.Z. and J.L.; investigation, N.Z., H.S., L.L. and Z.Z.; resources, H.S., L.Z., J.S. and M.-H.P.; data curation, N.Z., H.S., L.L., J.L., Z.Z., J.S. and M.-H.P.; writing—original draft preparation, N.Z. and H.S.; writing—review and editing, N.Z., H.S., L.L. and M.-H.P.; visualization, N.Z. and L.L.; supervision, H.S., J.L., J.S. and M.-H.P.; project administration, H.S., J.L. and M.-H.P.; funding acquisition, H.S., J.L. and M.-H.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under grant No. 52061035, Key Project of Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (No. 2024ZD07), Young Leading Talent of “Grassland Talents” Project of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (No. QNLJ012010), and the Program for Innovative Research Team in Universities of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (No. NMGIRT2211).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
N.Z. acknowledges Shu Guo for the TEM analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Smith, A.; Bahl, C.R.H.; Bjørk, R.; Engelbrecht, K.; Nielsen, K.K.; Pryds, N. Materials challenges for high performance magnetocaloric refrigeration devices. Adv. Energy Mater. 2012, 2, 1288–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, N.T.M.; Hung, C.; Huong, N.T.; Phan, M. Magnetic Interactions and Magnetocaloric Effect in (La0.5Pr0.5)0.6Ba0.4MnO3: Effect of A-Site Co doping. J. Electron. Mater. 2020, 49, 2596–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüzüak, E.; Yüzüak, G.D.; Dinçer, İ.; Elerman, Y. 4.13 Magnetic Energy Conversion. In Comprehensive Energy Systems; Dincer, I., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 4, pp. 573–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.Y.; Franco, V.; Keblinski, P.; Ramanujan, R.V. Active transient cooling by magnetocaloric materials. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 52, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitanovski, A. Energy Applications of Magnetocaloric Materials. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 1903741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gombi, S.M.; Sahu, D. A Review on Magneto-Caloric Materials for Room Temperature Refrigeration. Int. J. Automot. Mech. Eng. 2020, 17, 7805–7815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utaka, Y.; Hu, K.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y. Application of simple and effective thermal switch for solid-state magnetic refrigeration at room temperature. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 155, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuarnoz, D.; Kawanami, T. Numerical analysis of a reciprocating active magnetic regenerator made of gadolinium wires. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2012, 37, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprea, C.; Maiorino, A. A flexible numerical model to study an active magnetic refrigerator for near room temperature applications. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 2690–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; Wang, D.H.; Han, Z.D.; Xuan, H.C.; Gu, B.X.; Du, Y.W. Large magnetic entropy changes in Gd-Co amorphous ribbons. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 13912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zheng, Q.; Li, Y.B.; Zhang, Q.; Li, D.; Zhang, Z.D. Large magnetocaloric effect and enhanced magnetic refrigeration in ternary Gd-based bulk metallic glasses. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 23918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.X.; Bingham, N.S.; Wang, H.; Peng, H.X.; Sun, J.F.; Franco, V.; Yu, S.C.; Srikanth, H.; Phan, M.H. Mechanical and magnetocaloric properties of Gd-based amorphous microwires fabricated by melt-extraction. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 1284–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchón-Gordón, A.F.; Ipus, J.J.; Blázquez, J.S.; Conde, C.F.; Conde, A. Influence of milling time on the homogeneity and magnetism of a Fe70Zr30 partially amorphous alloy: Distribution of Curie temperatures. Materials 2020, 13, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Zou, M. Magnetic and magnetocaloric properties of ternary Gd–Co–Al bulk metallic glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 4613–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.; Huo, L.; Men, H.; Wang, X.; Inoue, A.; Wang, J.; Chang, C.; Li, R. The magnetocaloric effect of Gd-Tb-Dy-Al-M (M = Fe, Co and Ni) high-entropy bulk metallic glasses. Intermetallics 2015, 58, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Tong, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.J.; Ma, L.; Suo, H.L.; Lu, Z.P. Rare-earth high-entropy alloys with giant magnetocaloric effect. Acta Mater. 2017, 125, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Shen, H.; Liang, J.; Yin, H.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Sun, J. Manufacture and characterization of HoErCo medium-entropy alloy microwires with excellent magnetic entropy change. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2021, 556, 120570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Law, J.Y.; Huang, Y.; Shen, H.; Jiang, S.; Guo, S.; Franco, V.; Sun, J. Enhancing the magnetocaloric response of high-entropy metallic-glass by microstructural control. Sci. China Mater. 2022, 65, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Xing, D.; Qin, F.; Cao, F.; Chen, D.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J. Enhanced magnetocaloric and mechanical properties of melt-extracted Gd55Al25Co20 micro-fibers. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 603, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.X.; Duc, N.T.M.; Belliveau, H.; Luo, L.; Wang, Y.F.; Sun, J.F.; Qin, F.X.; Phan, M.H. Advanced magnetocaloric microwires: What does the future hold? Vietnam. J. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2023, 65, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.X.; Xing, D.W.; Llamazares, J.L.S.N.; Snchez-Valds, C.F.; Belliveau, H.; Wang, H.; Qin, F.X.; Liu, Y.F.; Sun, J.F.; Srikanth, H.; et al. Enhanced refrigerant capacity in Gd-Al-Co microwires with a biphase nanocrystalline/amorphous structure. App. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 092403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belliveau, H.F.; Yu, Y.Y.; Luo, Y.; Qin, F.X.; Wang, H.; Shen, H.X.; Sun, J.F.; Yu, S.C.; Srikanth, H.; Phan, M.H. Improving mechanical and magnetocaloric responses of amorphous melt-extracted Gd-based microwires via nanocrystallization. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 692, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Wang, H.; Jingshun, L.; Cao, F.; Qin, F.; Xing, D.; Chen, D.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J. Enhanced magnetocaloric properties of melt-extracted GdAlCo metallic glass microwires. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 372, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Shen, H.X.; Liu, J.S.; Yin, H.; Gao, S.Y.; Liang, J.R.; Bahl, C.R.H.; Sun, J.F.; Engelbrecht, K. Magnetocaloric effect and microstructure of amorphous/nanocrystalline HoErFe melt-extracted microwires. Intermetallics 2020, 127, 106974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.X.; Luo, L.; Bao, Y.; Yin, H.; Jiang, S.D.; Zhang, L.Y.; Huang, Y.J.; Feng, S.J.; Xing, D.W.; Liu, J.S.; et al. New DyHoCo medium entropy amorphous microwires of large magnetic entropy change. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 837, 155431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.G.; Tan, Z.C.; Yu, H.Y.; Zhang, J.L.; Zeng, D.C.; Franco, V. Structural, magnetic properties and magnetocaloric effect of Mn1.2Fe0.8P1−xSixB0.03 compounds. Mater. Res. Bull. 2016, 77, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchon-Gord, A.F.; Ipus, J.J.; Moreno-Ramírez, L.M.; Blázquez, J.S.; Conde, C.F.; Franco, V.; Conde, A. Correction of the shape effect on magnetic entropy change in ball milled Fe70Zr30 alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 765, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, J.S.; Silva, N.J.O.; Amaral, V.S. Estimating spontaneous magnetization from a mean field analysis of the magnetic entropy change. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 1569–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).