Abstract
In the current study, dynamic strain ageing (DSA) phenomena in 316L austenitic stainless steel was investigated under as-received and as-welded conditions. A tensile test was carried out on as-received and as-welded samples for the temperatures of 25–800 °C at a strain rate of 1 × 10−3 s−1. Microstructure and fracture surfaces were investigated by optic and scanning electron microscopes (SEM). 316L austenitic stainless steel showed different DSA behavior under as-received and as-welded conditions, which are discussed in terms of microstructure and mechanical properties.
1. Introduction
Austenitic stainless steels are the most important types of stainless steels which are known as nonmagnetic, formable and weldable. They are used from cryogenic temperatures to the hot temperatures of furnaces and jet engines. They contain chromium in the weight percentage of 16 and 25, and they can also contain nitrogen in solid solution, both of which contribute to their high corrosion resistance [1]. 316 type austenitic stainless steels contain molibdenium which increases corrosion resistance and strength at high temperatures. Mechanical properties are similar to that of 304 type stainless steel, but this alloy shows higher strength at higher temperatures [2].
In the early 1990s, intergranular cracking was observed in 316 Nuclear Grade (NG) and 304L stainless steel materials. In several reported cases, cracking was observed in the heat-affected zone (HAZ) and as-received metal of the weld joint. Although all parameters affecting the cracking are so far unknown, deformation could be an important parameter [3]. The thermally dramatic act of casting a small amount of metal as in each weld run can severely alter the microstructure and toughness of the parent steel in the HAZ, locally changing the original tough parent steel into a less tough and sometimes brittle material. The thermal contraction accompanying freezing may also produce short and/or long range stresses in the surrounding materials. Then stresses may be sufficient to cause local plastic strain around the weld [4].
The affecting mechanisms may also be dynamic strain ageing (DSA), which occurs at elevated temperatures depending on strain rates. The aging occurs slowly at room temperature and faster at higher temperatures, because diffusion of the solute atoms responsible for the ageing is supported by increasing the temperature. When the ageing occurs in alloys containing solute atoms, which can rapidly move to dislocations and prevent their movement during deformation, the phenomenon is commonly known as DSA [5].
AISI 316 and 316L austenitic stainless steels show DSA behaviour in the temperature range of 200–800 °C [6,7,8]. However, literature investigation indicated that there are inconclusive works related to DSA behaviour of weld joints of austenitic stainless steels. Therefore, an effort is needed to study the effect of DSA on the mechanical properties of austenitic stainless steels which have been used at elevated temperatures. The purpose of the present study is to investigate DSA behavior of 316L austenitic stainless steel under as-received and as-welded conditions. This investigation will provide the metallurgical basis to understand the mechanical behaviour of as-received and as-welded samples of 316L austenitic stainless steel dynamically aged at elevated temperatures.
2. Materials and Methods
316L austenitic stainless steel and AS MIG 316LSi welding wire in diameter of 1.2 mm were used in the present study. The chemical composition of the steel and welding wire used for joining are given in Table 1. Steel was supplied as plates in dimensions of 8 × 150 × 350 mm. The steel plates, except those in the as-received conditions, were welded longitudinally using Fanuc Robotic Lincoln Electric brand MIG welding machine (Cleveland, OH, USA) with a single pass through a V-groove configuration at 30°. Welding was performed under argon gas by using the welding parameters as indicated in Table 2.

Table 1.
Chemical compositions of 316L austenitic stainless steel and welding wire (wt. %).

Table 2.
The welding parameters used in the submerged arc welding (SAW).
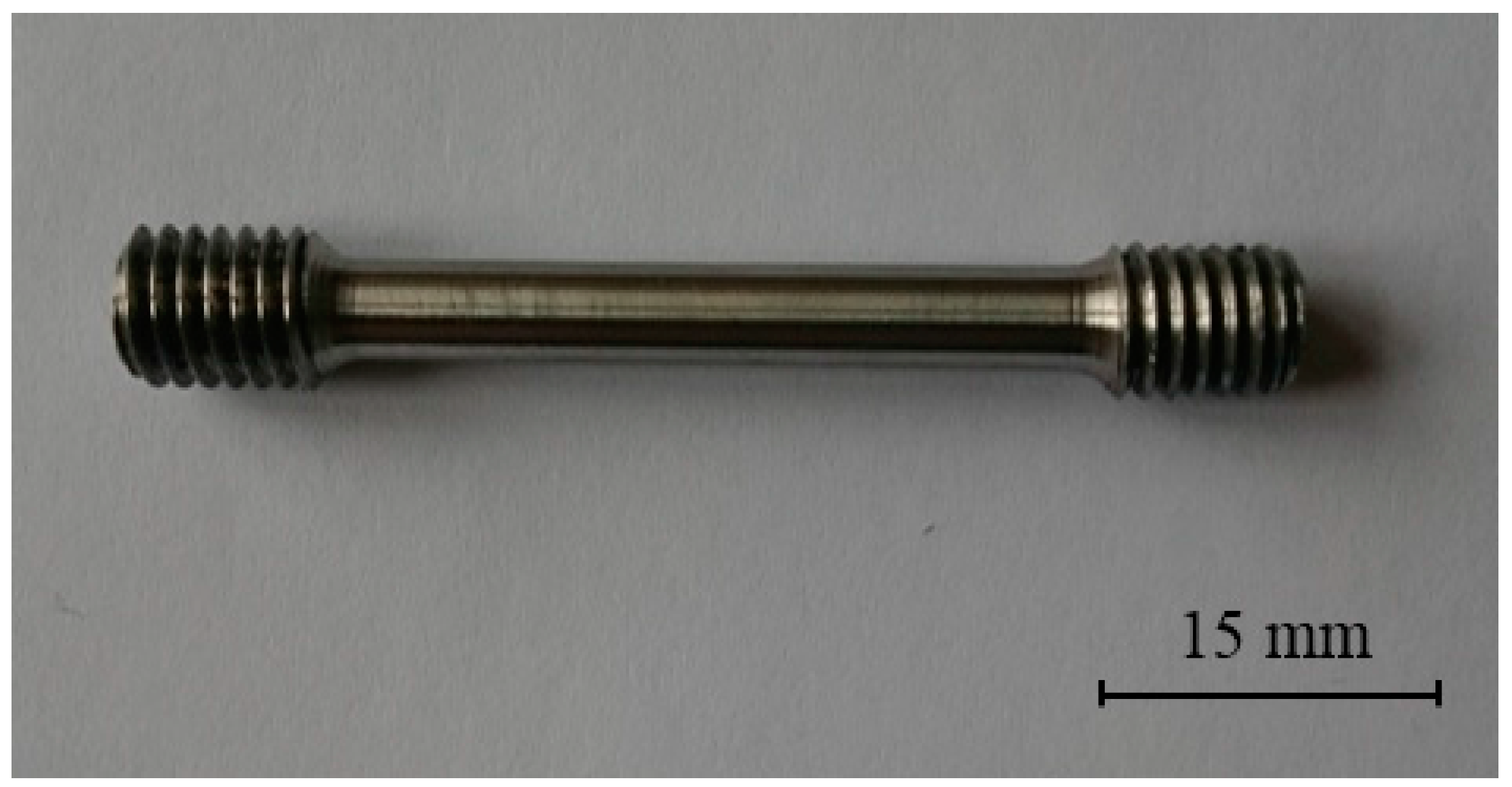
For evaluation of the tensile testing, specimens were cut from the as-received and as-welded blanks. Specimens for tensile test were manufactured according to relevant standard E8 (30 mm gauge length and 5 mm diameter) as shown in Figure 1. The weld zone was at the center of the specimes for welded joints. Tensile tests were done by using a MTS (100kN Servohydraulic Dynamic Tester, Eden Prairie, MN, USA) at temperatures of 25–800 °C and a strain rate of 1 × 10−3 s−1. After each test, stress and strain diagrams were obtained. From these, yield strength (YS, 0.2%) ultimate tensile strength (UTS), elongation (%) and work hardening index (n) were derived. In order to obtain the work hardening index (n), true stress (σ) and true strain (ε) and log true stress and strain were calculated for the homogeneous plastic deformation region up to maximum strength. The slope of the latter relationship defines the work hardening index (n) which gives a quantitative measurement of the work hardening characteristic of as-received and as-welded samples. It can be defined as [9]:
where k is a constant.

Figure 1.
Tensile test specimen used for hot tensile testing.
Microstructure and fracture surface examinations of as-received and as-welded samples were carried out by means of optic and scanning electron microscopes (SEM) with energy dispersive spectrometry (EDS) analyzer. In order to observe the microstructure of the samples, a mixture of 89% distilled water, 10% oxalic acid and 1% nitric acid solution was used for electrolytic etching, which was done at room temperature and a potential of 15–20 V. Vickers hardness measurement of welded joints was also carried out at 500 g load. 13 hardness measurements were made at 1 mm intervals along the width of the welding section.
3. Results and Discussion
Table 3 and Table 4 show DSA behaviour of as-received samples and as-welded samples by giving YS (0.2%), UTS and elongation (%) for the testing temperature in the range of 25–800 °C. It can be seen that both as-received and as-welded samples revealed small variation in YS and UTS values up to 600 °C. YS and UTS values change drastically beyond 600 °C. Elongation (%) showed a continuous decrease as the testing temperature increased to 600 °C. Further increase in testing temperature of 700 °C or 800 °C has increased the elongation (%). This suggests that DSA occurs in 316L austenitic stainless steel up to 600 °C under as-received and as-welded conditions. DSA generally occurs due to interactions between mobile dislocations and diffusing solute atoms in solid solutions [10].

Table 3.
Mechanical properties of as-received blanks tested at temperatures of 200–800 °C.

Table 4.
Mechanical properties of as-welded blanks tested at temperatures of 200–800 °C.
The results also indicated that as-welded samples are more susceptible to DSA than as-received samples. For example, as-welded samples showed higher values in YS and UTS but lower values in elongation (%) compared to the as-received samples for all testing temperatures of 25–800 °C. This is due to the least and greatest amount of free or uncombined interstitial atoms such as C and N. In Table 3 and Table 4, it is seen that the DSA depends on the presence of free interstitial atoms in solid solution. Incomplete precipitation of carbides and nitrides occurs during fast cooling after welding, which resulted in an increase in the amount of uncombined C and N in solid solution in the as-welded condition. Higher dislocation density in the HAZ of the welds can also be seen owing to development of strains during the thermal cycle of welding and in later loading in the DSA temperature range, that is, inside of the crack tip plastic zone [11,12].
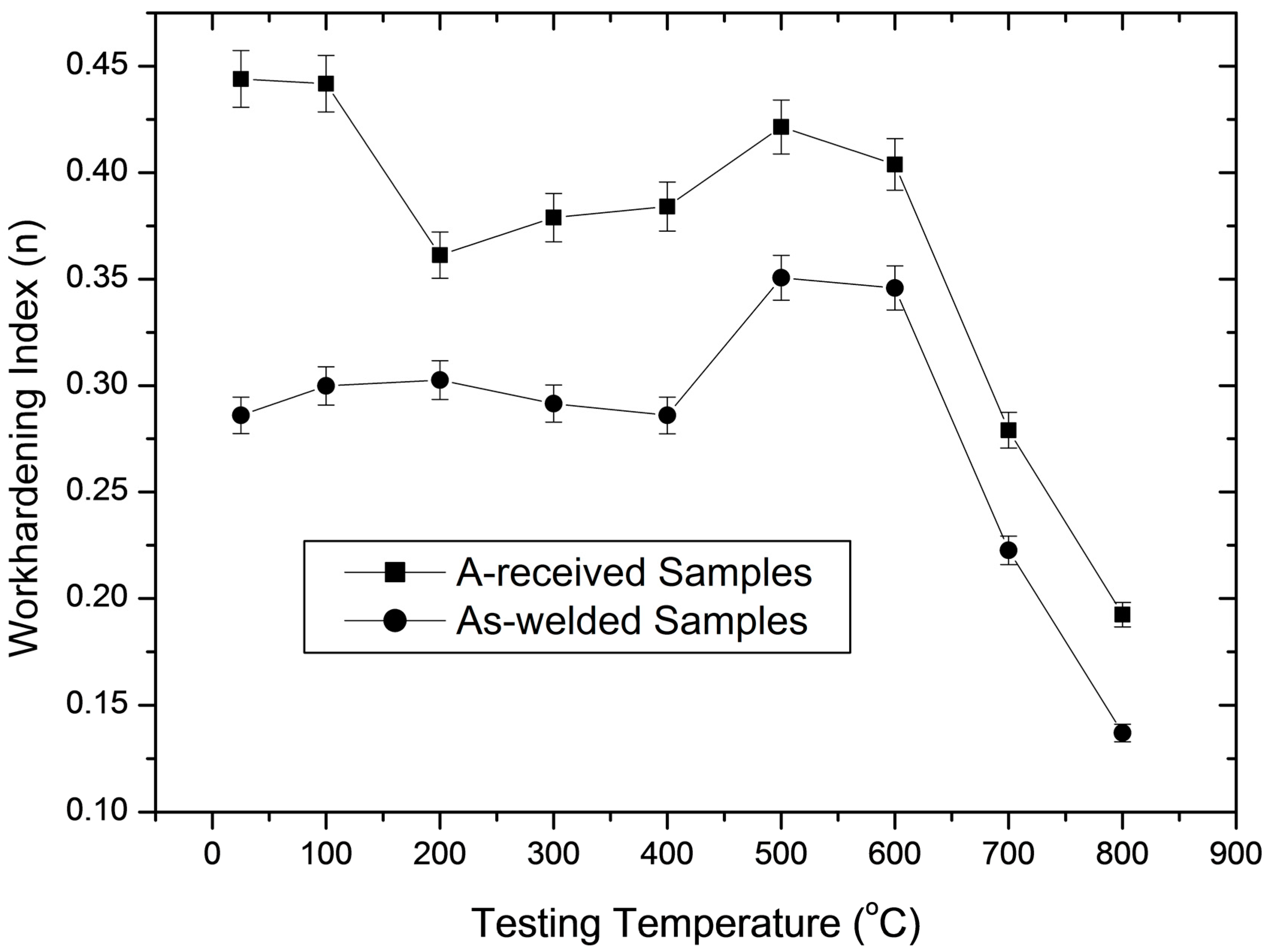
Work hardening index (n) which has generally been taken as criteria for the occurrence of DSA was calculated for as-received and as-welded samples. Figure 2 shows work hardening index n values of as-received and as-welded samples at various testing temperatures. It is noted from Figure 2 that work hardening index showed an increment between 400–600 °C for both as-received and as-welded samples. This indicates the interaction between dislocation and carbon or nitrogen atoms which affects the work hardening behaviour of 316L austenitic steel under as-received and as-welded conditions. The activation energy for strain ageing in AISI 430 stainless steel was calculated as ΔH = 126.7 kJ·mol−1 by Buona et al. [13]. This value is bigger than the activation energy for strain ageing in low carbon steels which is equal to the activation energy for the diffusion of C atoms in ferrite, 84.2 kJ·mol−1. However, it can be said that the affinity of chromium for carbon atoms changes the activation energy for diffusion of the latter in 316L austenitic stainless steel to such an extent. Therefore, as-received and as-welded samples did not show any discontinuous yielding behaviour, because chromium retards the diffusion of carbon to dislocations at lower temperatures in 316L austenitic stainless steel. Figure 2 also shows that the as-received samples achieved higher work hardening index n values than as-welded samples due to good formability. The as-received samples reached a larger reduction in work hardening index (5%) while as-welded samples showed an increase in work hardening index (23%) at the peak ageing temperature of 500 °C, compared to those in the room temperature testing conditions. This indicates that DSA is more pronounced in as-welded samples compared to the as-received samples.
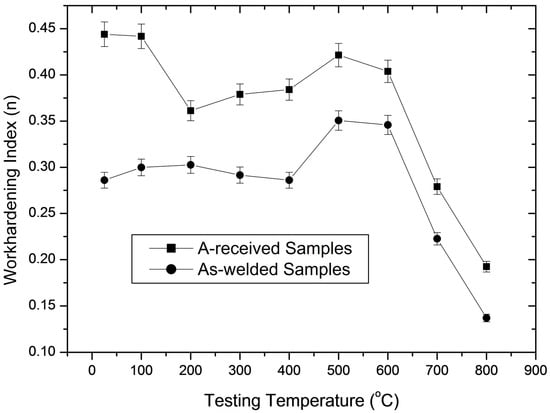
Figure 2.
Work hardening index (n) values of the as-received and as-welded samples tested at different temperatures.
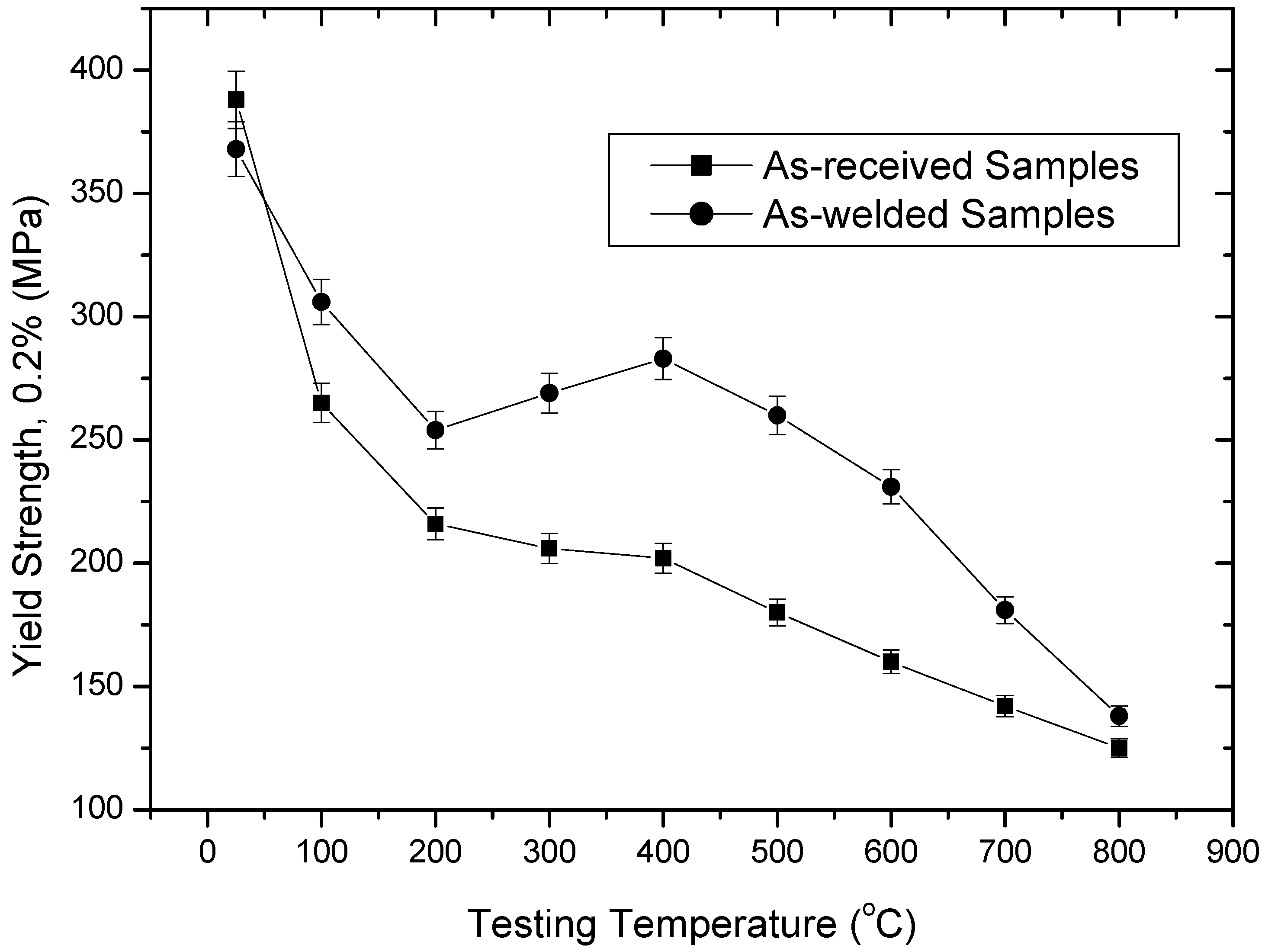
This is also confirmed in Figure 3, where YS is graphed against testing temperature. As seen in Figure 3, there is a decrease in YS values of as-welded samples with increasing temperature, reaching a minimum at 200 °C; it then increased with increasing temperature and reached a maximum at 400 °C. This indicates the presence of C and/or N in solid solution, where they would make dislocation movement more difficult. YS values changed drastically beyond 600 °C. However, as-received samples revealed a decrease in YS value up to 400 °C, after which it decreased too fast. This also suggests that DSA is more operative in as-welded samples than as-received samples at the test temperatures of 25–800 °C.
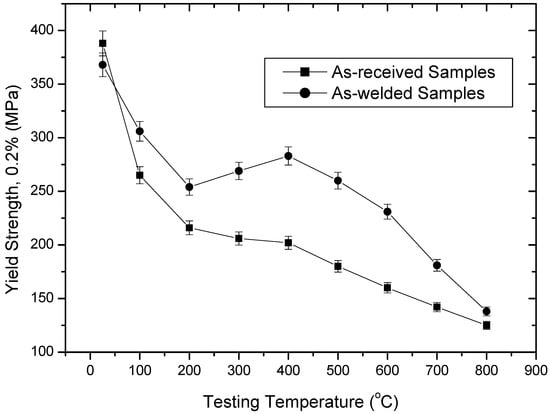
Figure 3.
Yield strength values of the as-received and as-welded samples tested at different temperatures.
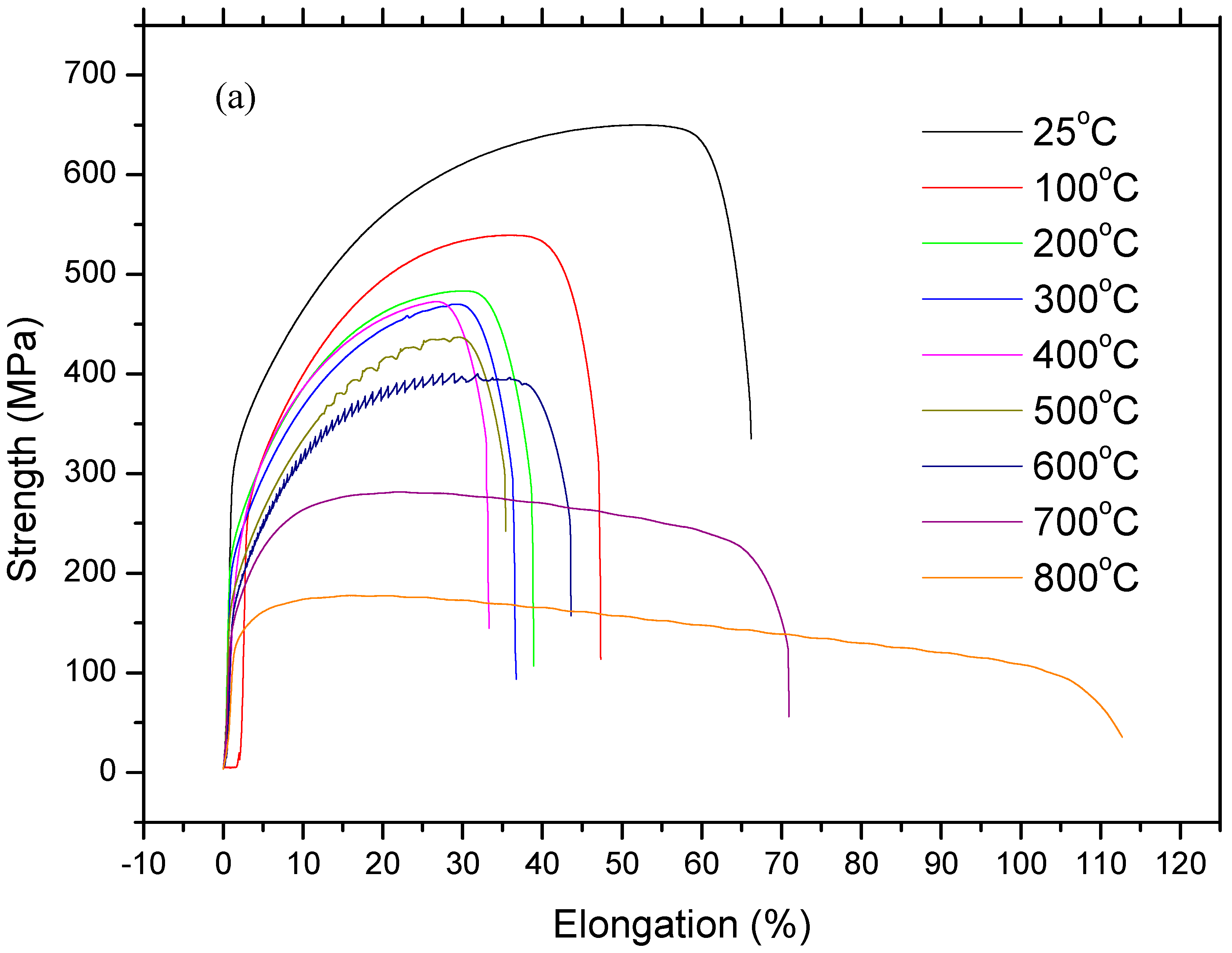
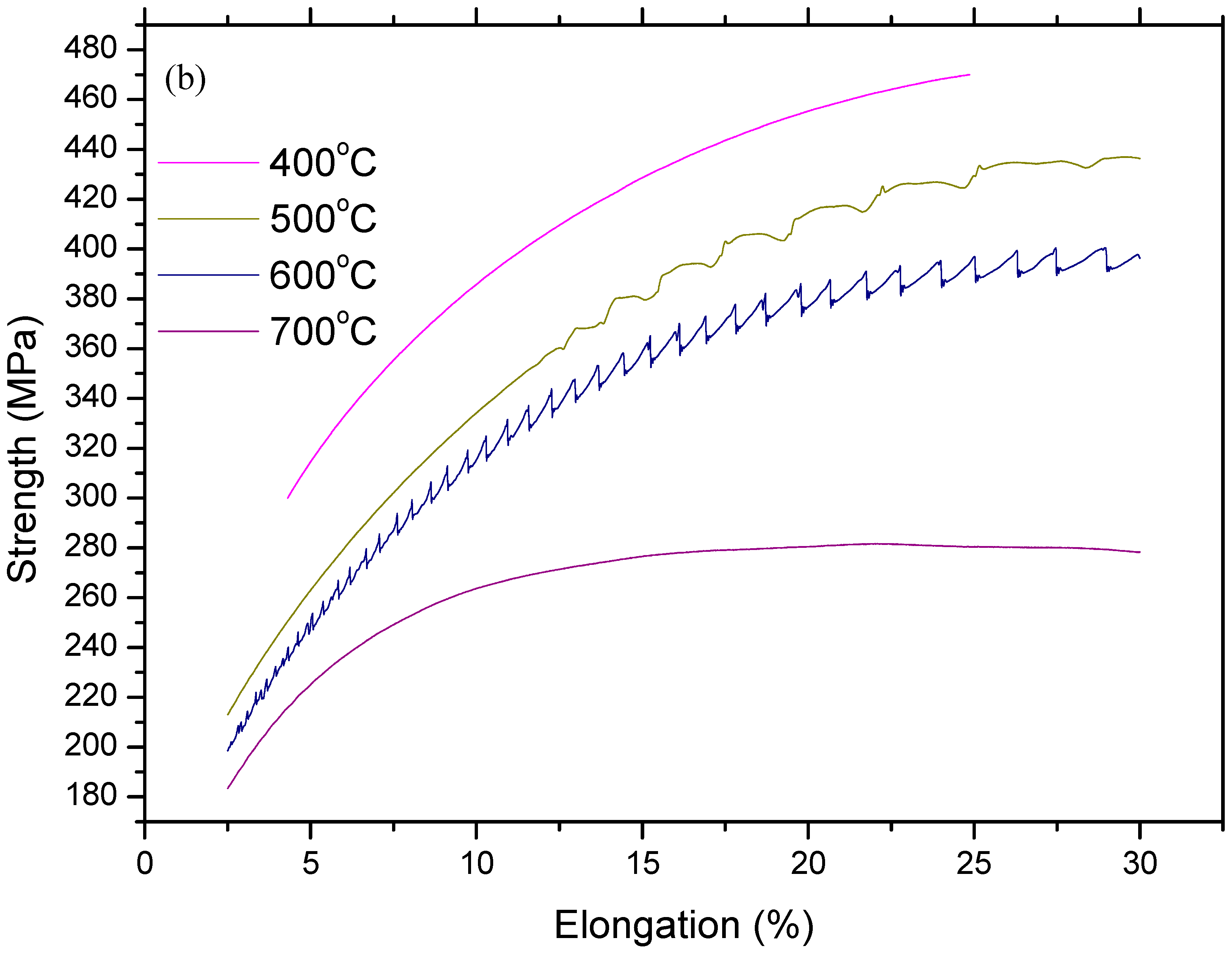
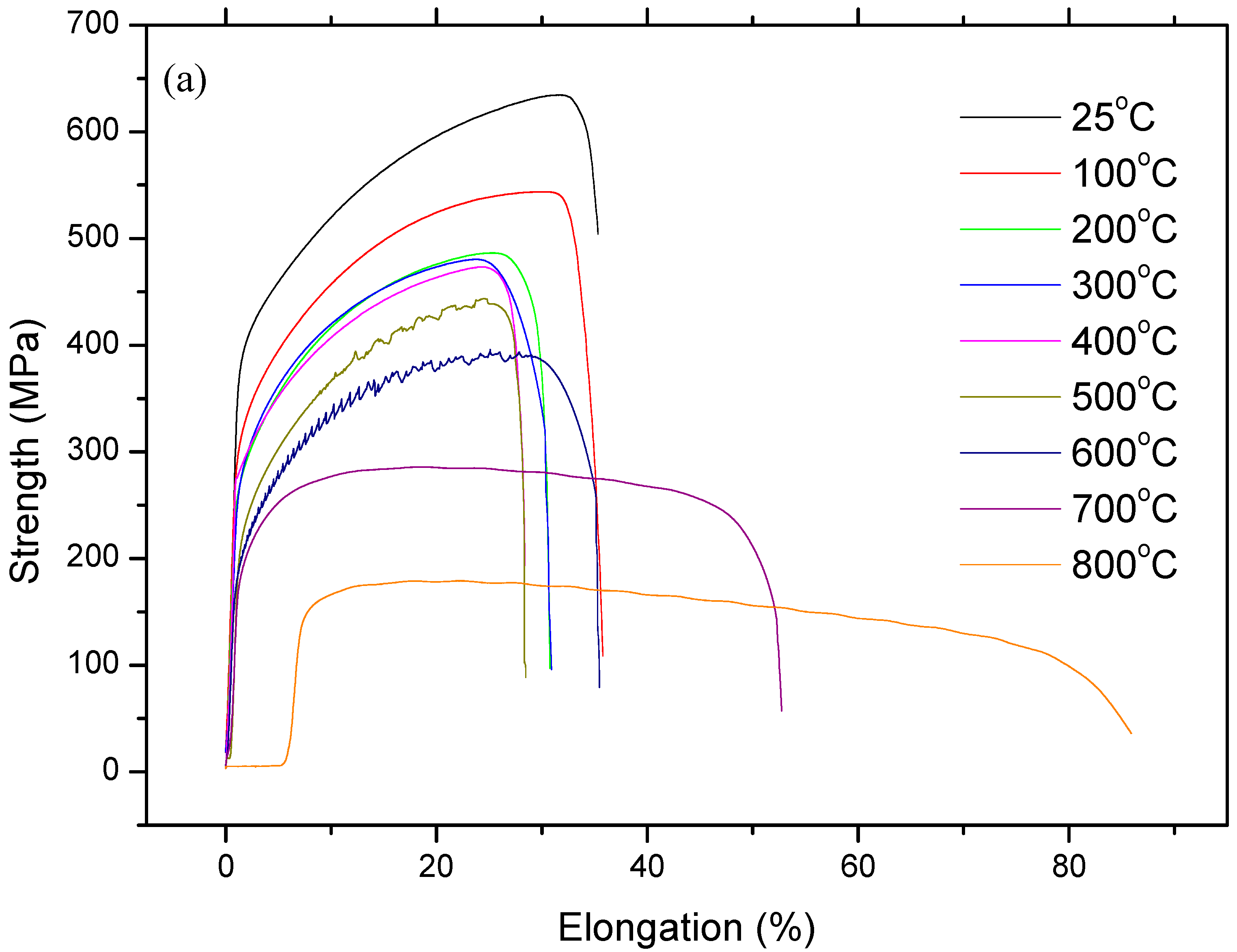
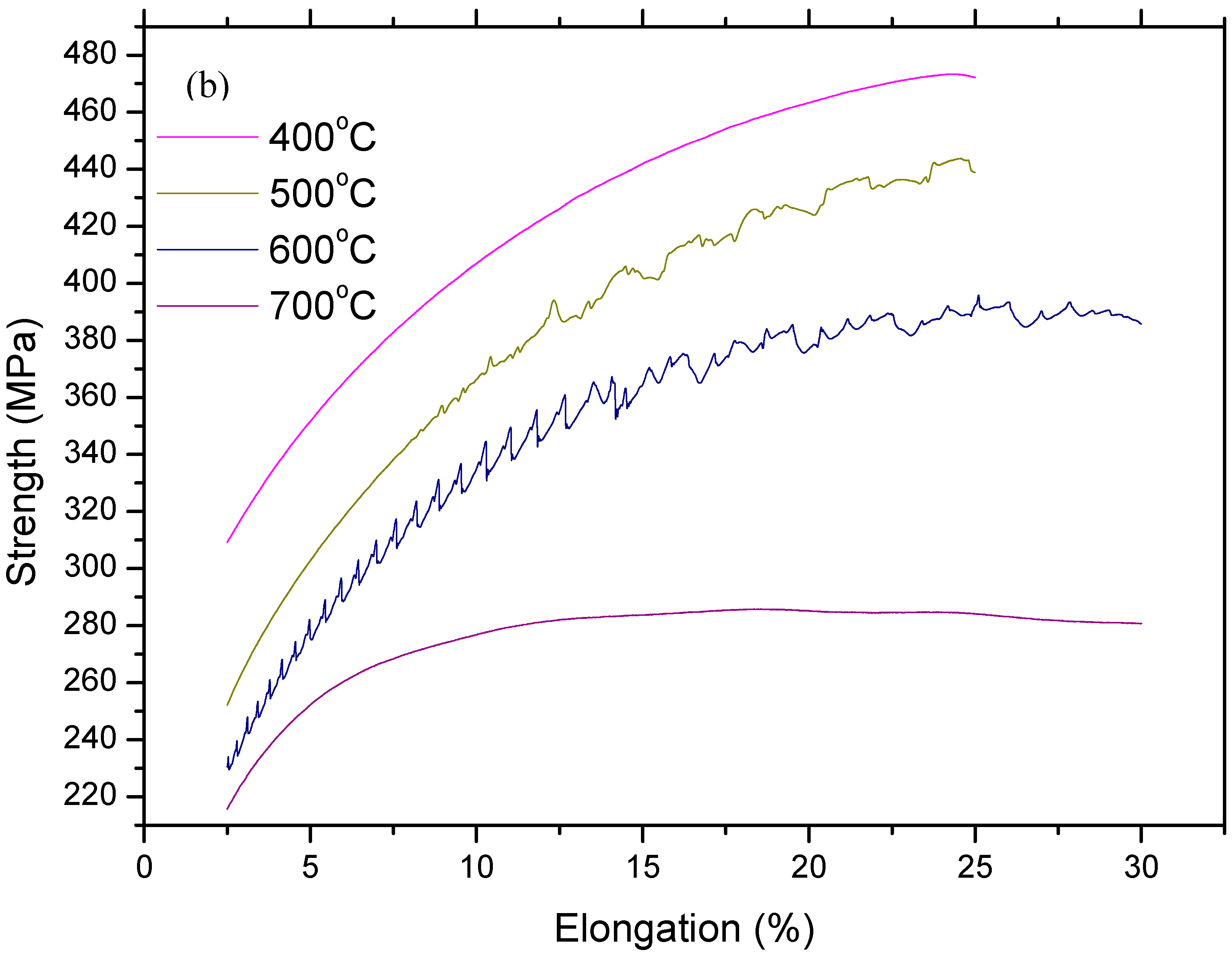
Figure 4 and Figure 5 show stress and strain diagrams for as-received and as-welded samples in the temperature range of 25–800 °C. As can be seen, the stress and strain diagrams showed significant changes in appearance when the testing temperature was increased for the strain rate of 1 × 10–3 sn−1. Serrated yielding, which is a characteristic of DSA, was clearly seen in as-received and as-welded samples at testing temperatures of 500 °C and 600 °C. The serrations disappeared from the curves at higher temperatures of 700 °C and 800 °C. Such serrated behaviour is shown by a plateau in the variation of strength and a minima in the variation of elongation. Deformation rate and temperature, which affect the diffusing solute atoms and the velocity of mobile dislocation, play a very important role for DSA. At a high deformation rate and low temperature, the diffusion of solute atoms is slower than dislocation for the occurrence of strain ageing. However, at a low deformation rate and high temperature, solute atoms can move with the dislocations resulted of DSA disappear. Therefore, DSA can be observed in the temperature range of intermediate strain rates [14,15].
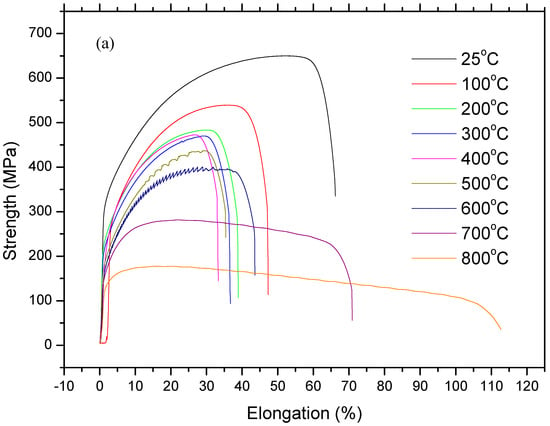
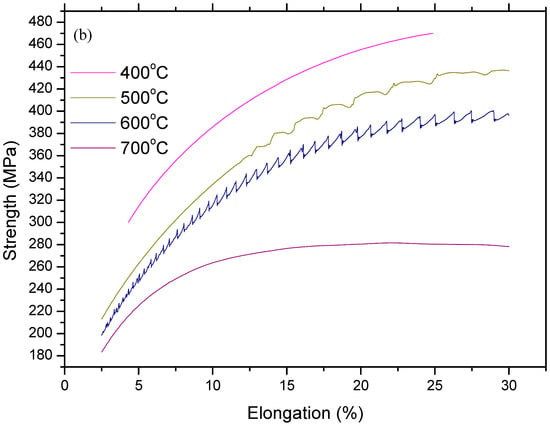
Figure 4.
Stress and strain diagrams of as-received samples: (a) full range profiles and (b) sections in large scala.
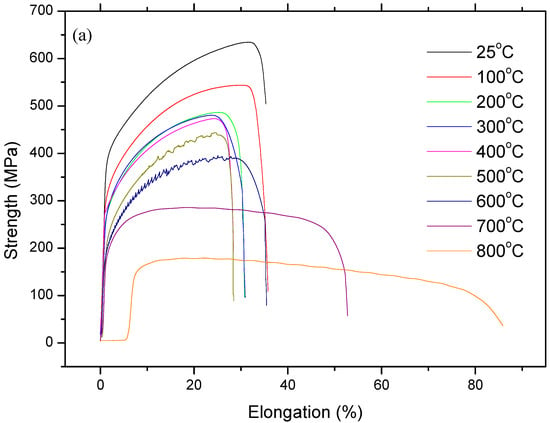
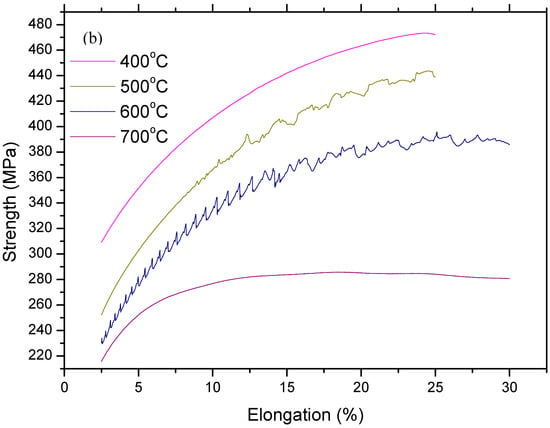
Figure 5.
Stress and strain diagrams of as-welded samples: (a) full range profiles and (b) sections in large scala.
However, as-welded samples showed more pronounced serrations than as-received samples due to the presence of a higher amount of solute atoms in solution. It is generally known that these effects are caused by free C or N moving to dislocations and locking them [16]. Partial dissolution of carbides occurs in the HAZ next to the fusion line during welding. This results in a larger amount of solute atoms in the solid solution which can result in more pronounced serrations in as-welded samples compared to the as-received samples.
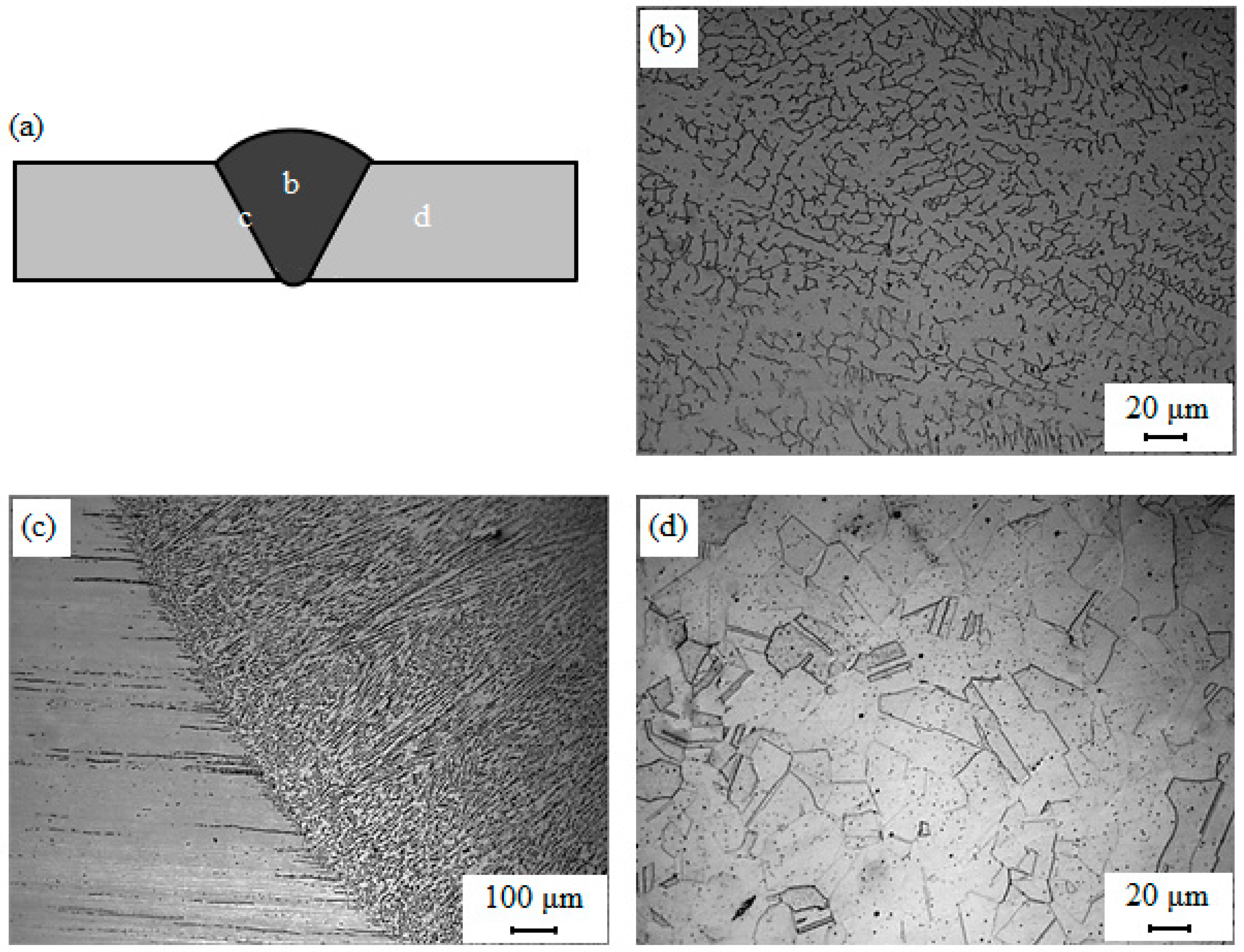
Figure 6a–d shows optic microscopy images of the as-welded samples. Three different zones were observed as indicated in Figure 6a. The weld metal (Figure 6b) showed a solidification microstructure due to the welding thermal cycle [17]. This consisted of skeletal ferrites in an austenitic matrix of large columnar austenite grains. The alignment is along the heat flow direction, which is also the primary dendrite growth direction. The ferrite is located within the cores of the primary and secondary dendrite arms and is the result of the incomplete primary δ → γ transformation [18]. HAZ occurred by the peak temperatures and cooling rates showed slightly coarse austenite grains located beside the fusion lines as seen in Figure 6c. The microstructure of the as-received metal (Figure 6d) was austenitic with a low delta ferrite. Ideally, austenitic stainless steels contain a single phase which is maintained over a wide temperature range. However, a fully austenitic microstructure is more crack sensitive compared to the microstructure containing a small amount of ferrite [19].
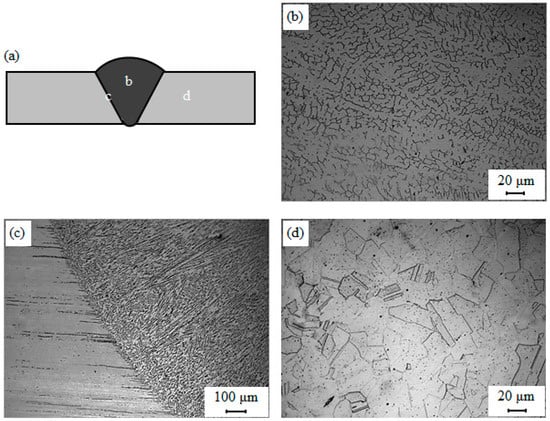
Figure 6.
SEM micrographs of (a) schematic representation of welded joint; (b) weld metal; (c) heat-affected zone (HAZ) and (d) base metal.
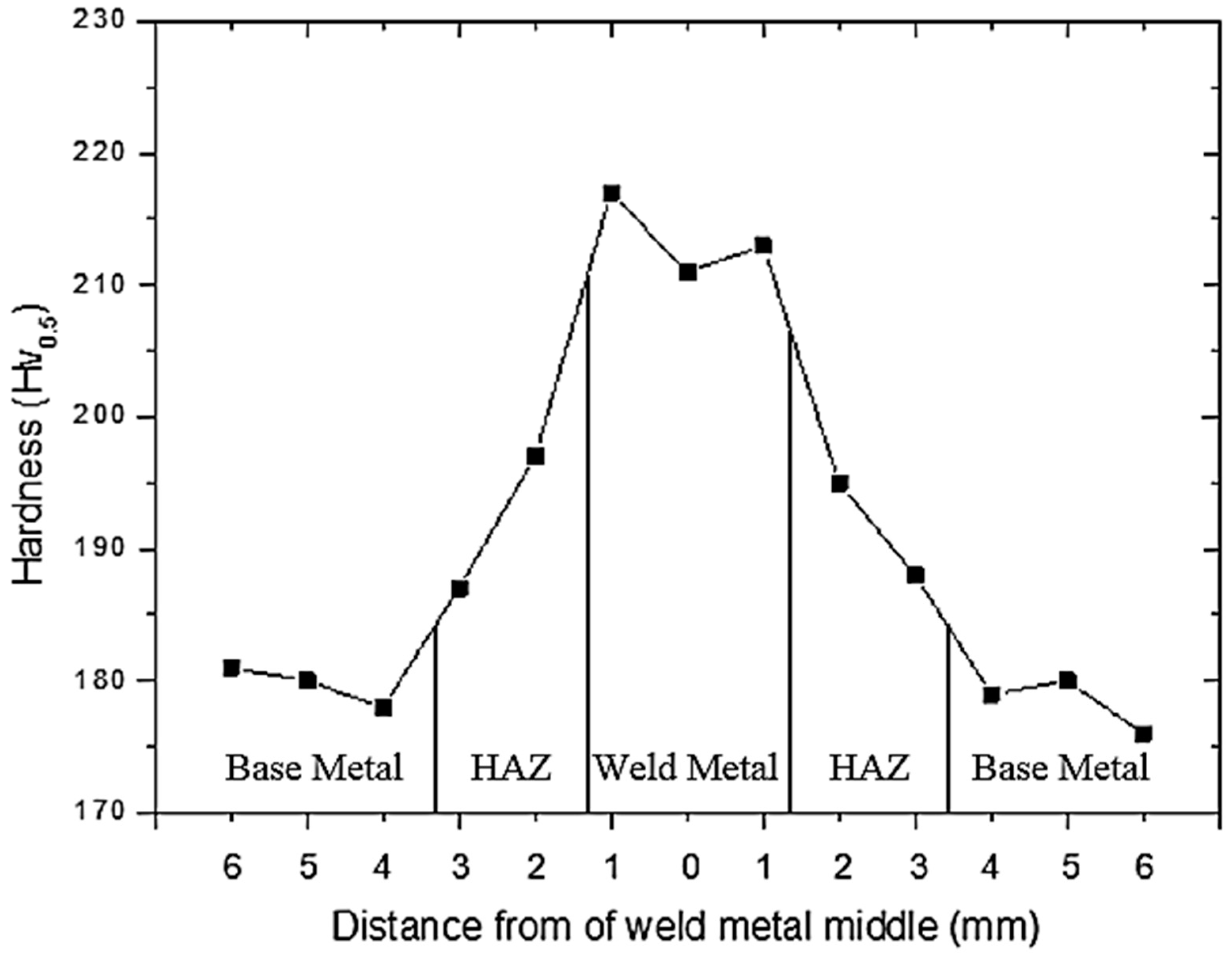
Figure 7 shows Vickers microhardness measurement of the base metal, HAZ and weld metal. It was observed that the highest hardness was obtained in the weld metal. This could be the presence of a higher amount of Cr in solid solution due to welding thermal cycle. It was shown that higher Cr content in the weld metal increases hardenability of steel [2]. This is consistent with the results obtained by Hee-jin and Hae-woo [20] who investigated effects of Cr content on microstructure and mechanical properties of low carbon steel welds. Higher hardness in weld metals may also be owing to melting and solidification of the area during or cooling after welding. Generally, as-welded samples revealed the lowest and highest hardness in the base metal and weld metal respectively. Hardness of HAZ was found to be higher than base metal, but lower than weld metal.
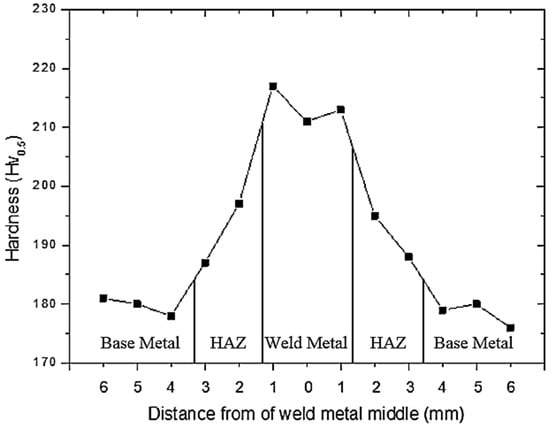
Figure 7.
Vickers hardness (HV0.5) in the welded sections after welding.
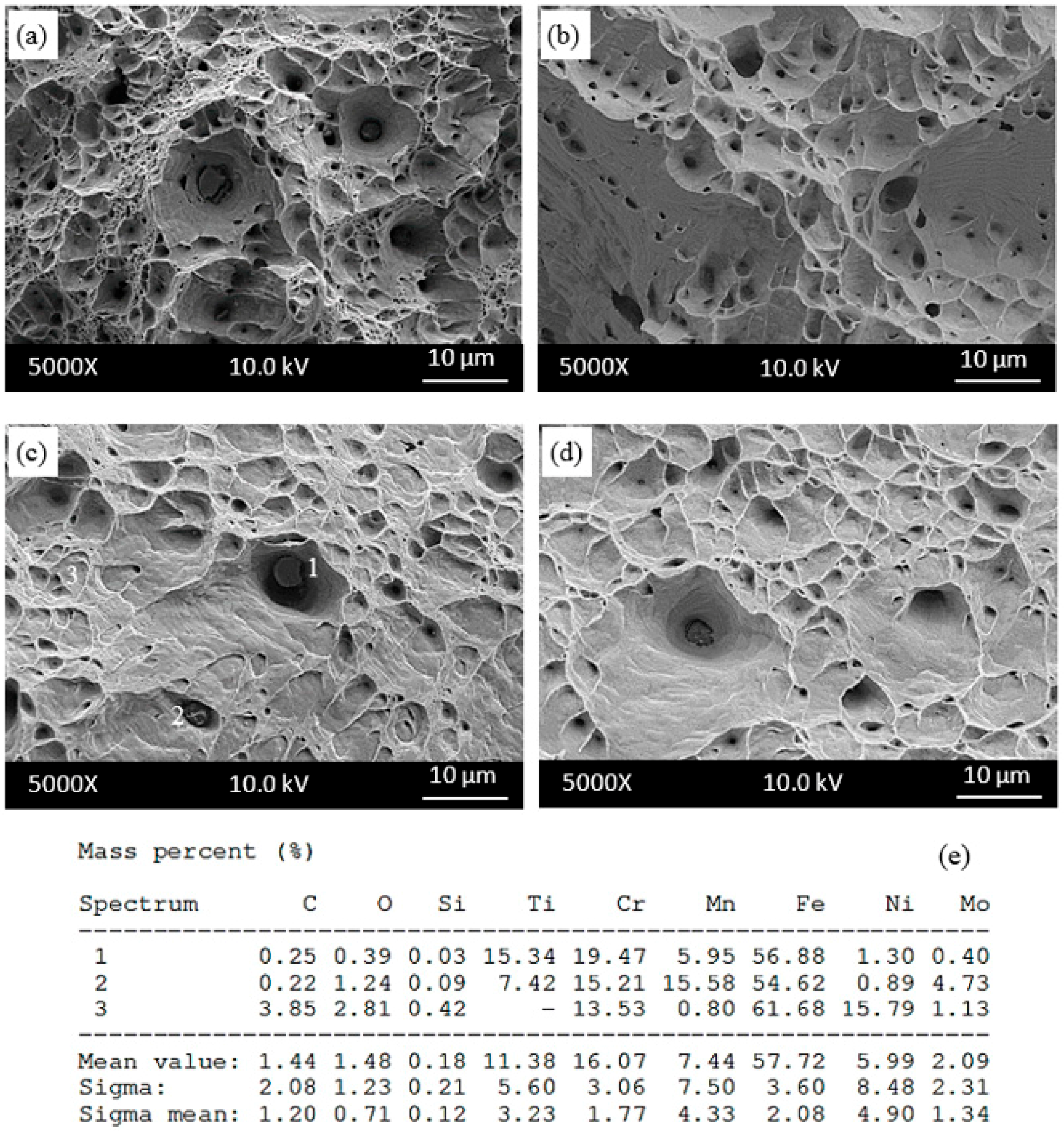
Figure 8 shows the scanning electron micrographs of the as-received samples tensile tested at different temperatures. Figure 8a–d shows the microstructures near fracture surface of the as-received samples tested at 25 °C, 200 °C, 400 °C and 600 °C respectively. Martensite structure was observed in samples tested 25 °C as seen in Figure 8a. Deformation martensite occurs at the deformation twins, grain boundaries and shear bands which have large strain gradients. It was indicated that mechanical twins are the primary nucleation sites for deformation martensite [21]. The occurrence of deformation martensite is related to the austenite instability at temperatures close or below room temperature. The structural transformation susceptibility is correlated to the stacking fault energy (SFE), which is a function not only of the chemical composition, but also of the testing temperature. Austenitic stainless steels have high plasticity and can be easily cold formed. However, the hardening phenomena always occurs during cold processing. Nevertheless, the deformation martensite transformation can increase the work-hardening rate and it may or may not be in favour of further material processing [22].
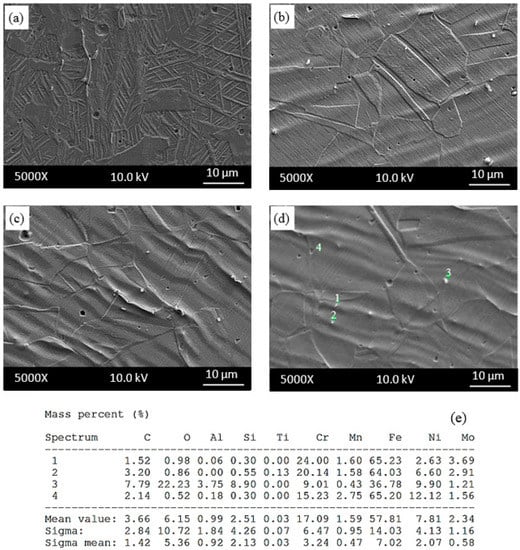

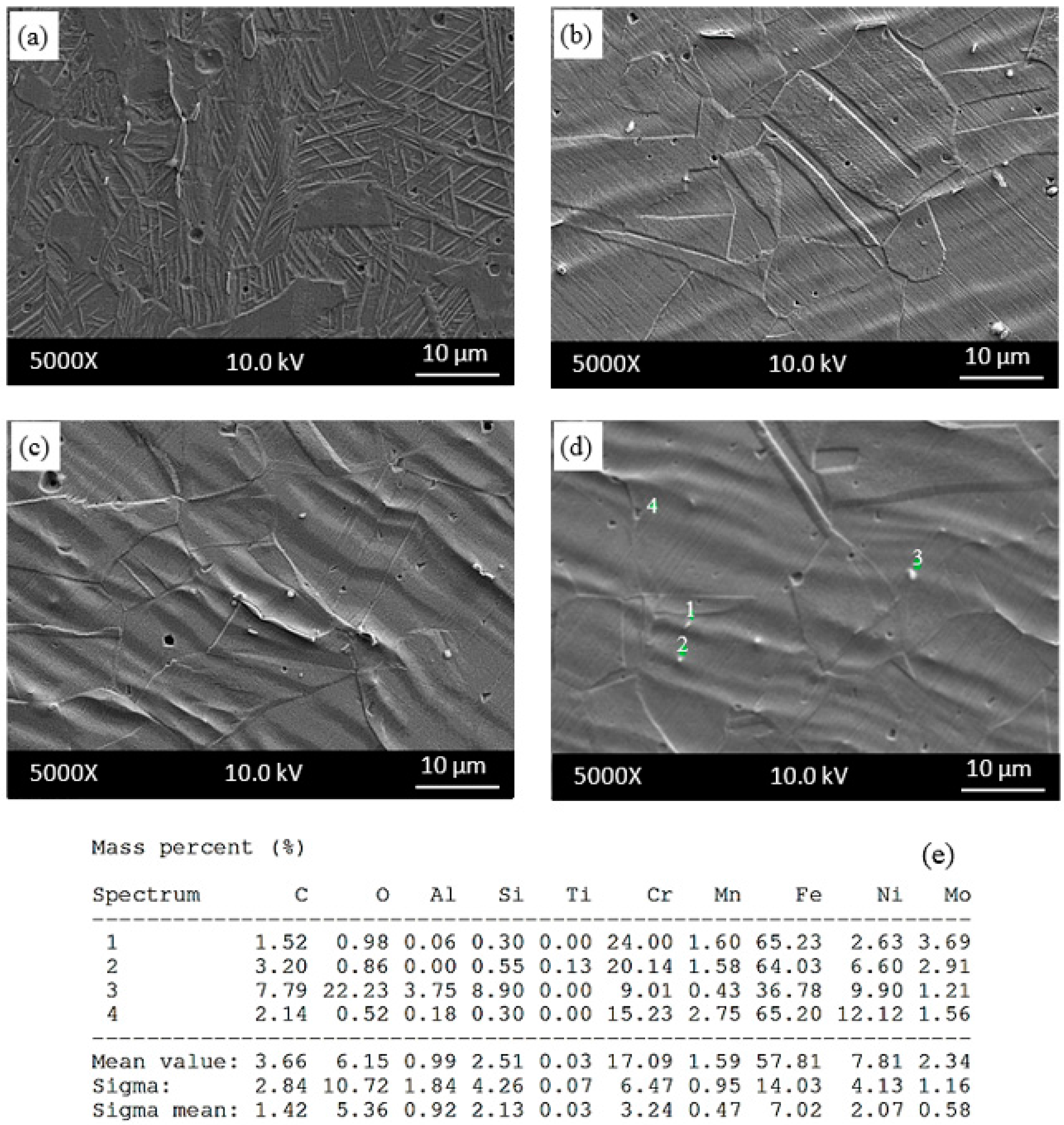
Figure 8.
SEM micrographs near fracture surface of as-received samples tested at (a) 25 °C; (b) 200 °C; (c) 400 °C; (d) 600 °C and (e) corresponding energy dispersive spectrometry (EDS) of the indicated particles in samples tested at 600 °C.
The results obtained from the present study suggest that the martensite develops at the shear bands. Ren-bo et al. [23] indicated that 316L austenitic stainless steel has low stacking fault energy (64 mJ/m2), and a low stacking fault energy is generally related to higher susceptibility to martensite transformation. Many parallel shear bands can be seen in Figure 8b–d for the samples tested at 200 °C, 400 °C and 600 °C. Figure 8 also shows EDS analysis with the spectrum points 1, 2, 3 and 4 marked on the microstructure of samples tested at 600 °C. Points 1 and 2 contain Fe, C, Cr and Mo, but point 3 contains Fe, C, Cr, O and Mo. The presence of these elements indicated that (Cr,Mo)C and CrO occurred during testing or cooling after testing at 600 °C in which the sample showed serration behaviour.
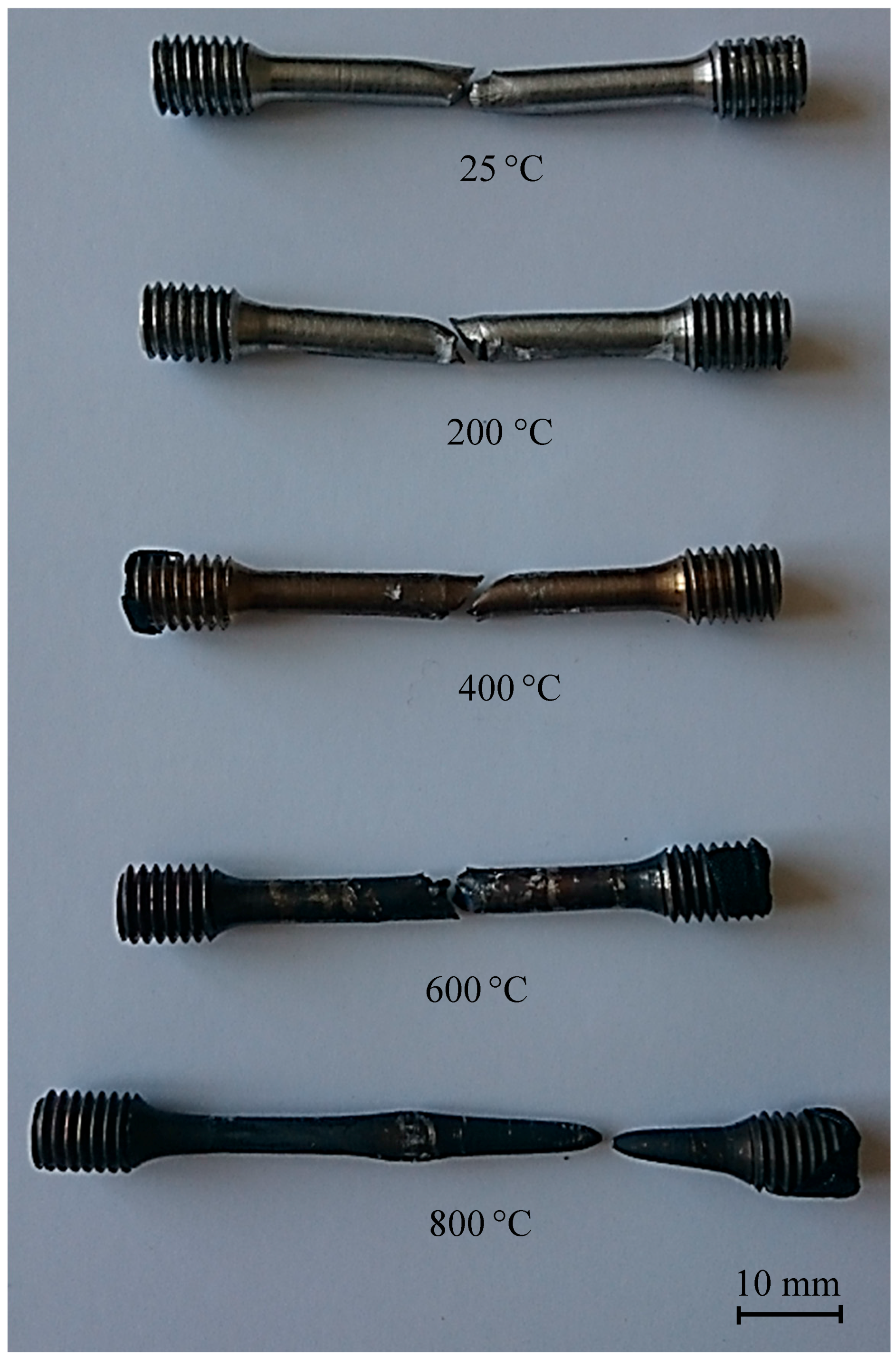
The fracture characteristics of tensile test samples were analyzed in the present experimental work. The macrographs of the as-welded samples are shown in Figure 9. The results revealed that the fracture formed in the HAZ of as-welded samples tested at 25–600 °C. The fracture of the as-welded samples tested at temperatures of 25–600 °C started from adjacent to the fusion zone in the HAZ and continued through into the weld metal. The strains developed during the thermal cycle of welding in the HAZ region is primarily responsible for starting fracture [24]. Due to strains, the grain growth in the HAZ next to fusion line can encourage to the starting failure from this region. However, the fracture in as-welded samples tested at 700 °C and 800 °C occurred in the base metal.

Figure 9.
Failure mode of as-welded samples tensile tested at different temperatures.
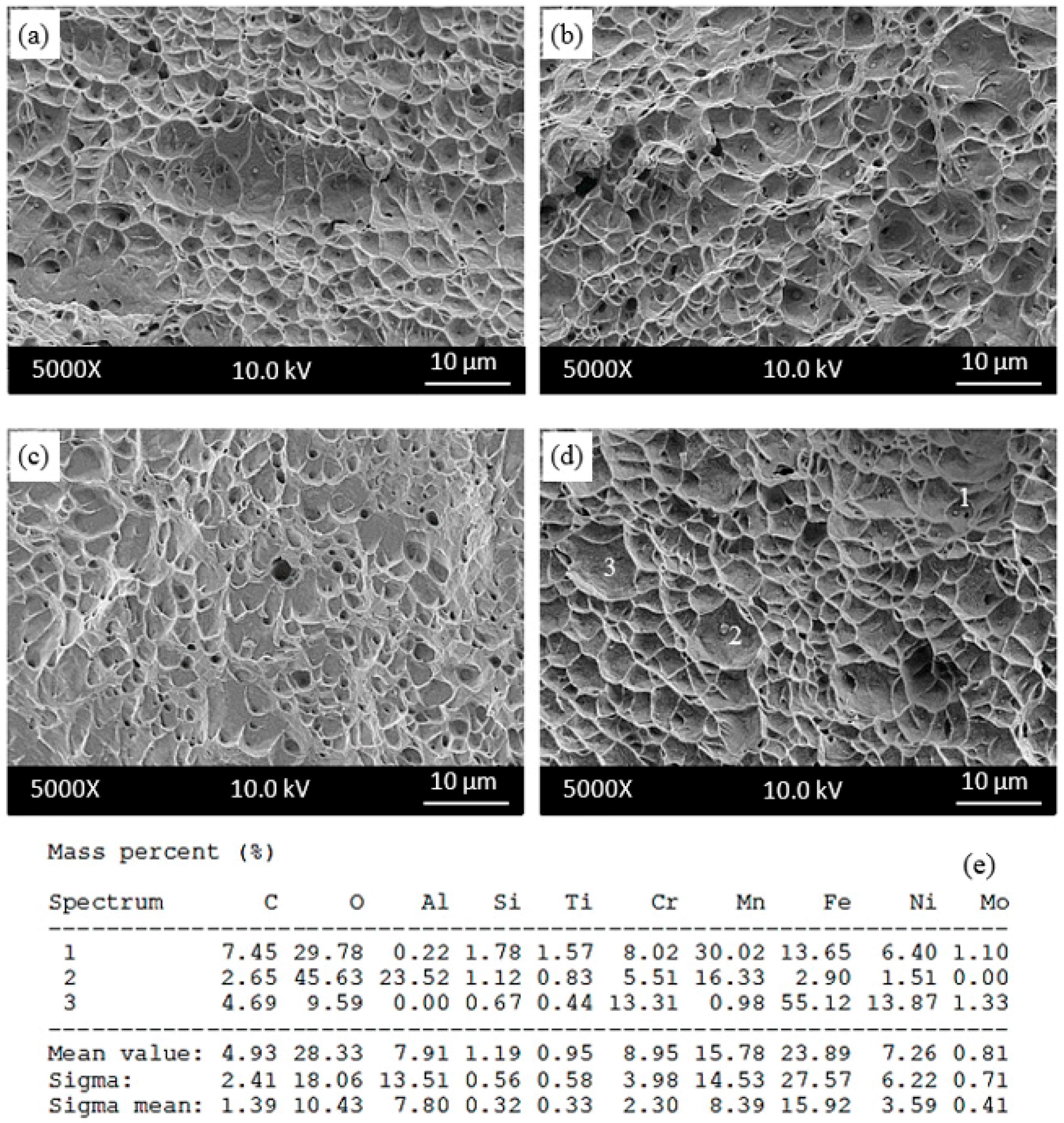
To show the fracture type after the tensile test, the fractured specimens were examined using SEM. Figure 10 and Figure 11 show fracture morphology of the as-received and as-welded samples respectively for the testing temperatures of 25–600 °C. The fracture surface of as-received and as-welded samples tensile tested at 25 and 200 °C showed ductile dimple fracture which is characteristic of ductile fracture. This indicates a ductile fracture mode with microvoid morphology, which is associated with the nucleation, growth and coalescence of microcavities [25]. At 400 °C and 600 °C, as-received and as-welded samples revealed mixed type fracture of cleavage facets and dimples. The reduction in area is also decreased at the same temperatures of 400 °C or 600 °C, which suggests that DSA occurs in the 316L austenitic stainless steel under as-received and as-welded conditions. However, as-welded samples showed lower decrease in area than as-received samples, owing to DSA. On the other hand, ductile dimples were found in as-received and as-welded samples after testing at 800 °C, which led to the increase in elongation and reduction in area. Some inclusions in small holes were seen on the microfractographs of as-received samples (Figure 10c) and as-welded samples (Figure 11d). The EDS analysis showed the presence of complex Mn-Cr-Ti-Al inclusions in both as-received and as-welded samples.
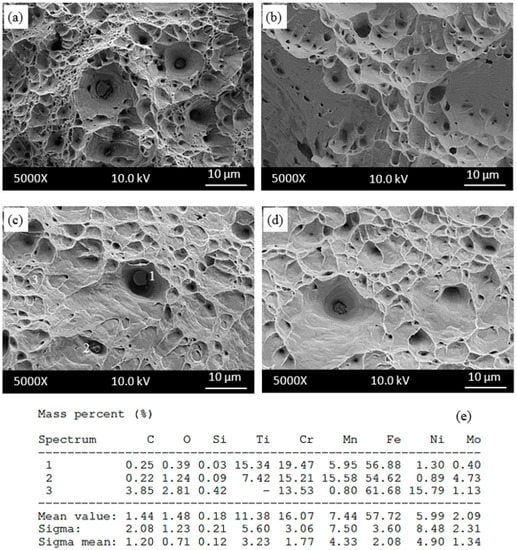
Figure 10.
Fractography of as-received samples tested at (a) 25 °C; (b) 200 °C; (c) 400 °C and (d) 600 °C and (e) corresponding energy dispersive spectrometry (EDS) of the indicated particles in samples tested at 400 °C.
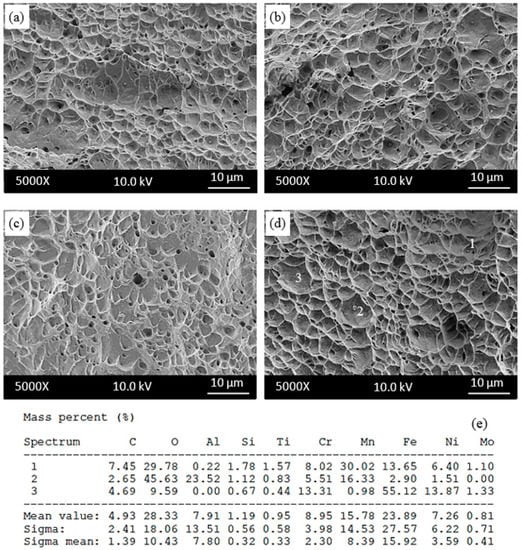
Figure 11.
Fractography of as-welded samples tensile tested at (a) 25 °C; (b) 200 °C; (c) 400 °C and (d) 600 °C and (e) corresponding energy dispersive spectrometry (EDS) of the indicated particles in samples tested at 600 °C.
4. Conclusions
In the present work, the DSA behaviour of AISI 316L grade austenitic stainless steel was investigated under as-received and as-welded conditions. The conclusions obtained from present study can be given as follows:
- DSA occurs in 316L austenitic stainless steel under as-received and as-welded conditions which revealed small variation in YS and UTS values up to 600 °C corresponding to the DSA region.
- As-welded samples are more susceptible to DSA compared to the as-received samples, due to the partial dissolution of carbides in the HAZ next to the fusion line during welding.
- As-received samples of 316L austenitic stainless steel achieved higher work hardening index n values than as-welded samples because of good formability. However, the as-received samples reached a larger reduction in work hardening index (5%) while as-welded samples showed an increase in work hardening index (23%) at the peak ageing temperature of 500 °C, compared to those in the room temperature testing conditions.
- 316L austenitic stainless steel has high susceptibility to deformation induced martensite after testing at 25 °C. The results obtained from present study indicated that the martensite occurred at the shear bands.
- Fracture surface analysis indicated that as-received and as-welded samples showed ductile fracture mode after testing at 25 °C, 200 °C and 800 °C. However, as-received and as-welded samples revealed mixed type fracture of cleavage facets and dimples at 400 °C and 600 °C. The reduction in area is also decreased at the same temperatures of 400 °C or 600 °C, which suggests that fracture occurs more easily under DSA conditions.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit of Karabük University (Karabük, Turkey). Project Number: KBÜBAP-17-DR-169.
Author Contributions
Guma Alnaji Muhamed, Mehmet Akif Erden and Demet Taştemur designed the experiments, performed the experiments, analysed the data and wrote the paper, Süleyman Gündüz directed the research and contributed to the discussion and interpretation of the results.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mcguire, M. Stainless Steel for Design Engineering, 1st ed.; ASM International: Geauga County, OH, USA, 2008; Chapter 6; pp. 69–78. ISBN 978-0-87170-717-8. [Google Scholar]
- Lippold, J.C.; Kotecki, D.J. Welding Metallurgy and Weldability of Stainless Steels, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 20–44. ISBN 978-0-471-47379-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrnsten, U.; Toivonen, A.; Ivanchenko, M.; Nevdacha, V.; Yagozinskyy, Y.; Haenninen, H. Dynamic strain ageing of deformed nitrogen-alloyed AISI 316 stainless steels. In Proceedings of the EUROCORR 2004—European Corrosion Conference: Long Term Prediction and Modeling of Corrosion, Paris, France, 12–16 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.Q.; Zhu, M.L.; Xuan, F.Z. Correlation of local strain with microstructures around fusion zone of a CrNi-Mo-V steel welded joint. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 685, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuenschwander, M.; Knobloch, M.; Fontana, M. Elevated temperature mechanical properties of solid section structural steel. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 149, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanchenko, M. Dynamic Strain Ageing of Austenitic Stainless Steels and Ni-based Alloys. Ph.D. Thesis, Aalto University, Espoo, Finland, 19 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gopinath, K.; Gogia, A.K.; Kamat, S.V.; Ramamurty, U. Dynamic strain ageing in Ni-base superalloy 720Li. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Yu, W.; Chen, G.; Jin, F.; Chen, X. Role of dynamic strain aging in the tensile property, cyclic deformation and fatigue behavior of Z2CND18.12N stainless steel between 293 K and 723 K. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 558, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieter, G.E. Mechanical Metallurgy, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2013; pp. 100–130. ISBN 10: 1-25-906479-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ananthakrishna, G. Current theoretical approaches to collective behavior of dislocations. Phys. Rep. 2007, 440, 113–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Arista, B.; Angeles-Chavez, C.; Albiter, A.; Hallen, J.M. Metallurgical investigation of the aging process on tensile fracture welded joints in pipeline steel. Mater. Charact. 2009, 60, 1561–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, B.; Komenda, J.; Rohrer, G.S.; Beladi, H. Heat affected zone microstructures and their influence on toughness in two microalloyed HSLA steels. Acta Mater. 2015, 97, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buono, V.T.L.; Gonzales, B.M.; Andrade, M.S. Strain aging of AISI 430 ferritic stainless steel. Scr. Mater. 1997, 38, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.G.; Lee, S.B. The tensile and low-cycle fatigue behavior of cold worked 316L stainless steel: influence of dynamic strain aging. Int. J. Fatigue 2004, 26, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gündüz, S. Dynamic strain aging effects in niobium microalloyed steel. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2002, 29, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wagner, D.; Bathias, C. Some metallurgical aspects of Dynamic Strain Aging effect on the Low Cycle Fatigue behavior of C-Mn steels. Int. J. Fatigue 2015, 80, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S. Welding Metallurgy, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 143–147. ISBN 0-471-43491-4. [Google Scholar]
- Kožuh, S.; Gojić, M.; Kosec, L. Mechanical properties and microstructure of austenitic stainless steel after welding and post-weld heat treatment. Kovove Mater. 2007, 47, 253–262. [Google Scholar]
- Kožuh, S.; Gojić, M.; Kosec, L. The effect of annealing on properties of AISI 316L base and weld metals. Mater. Geoenviron. 2007, 54, 331–344. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.J.; Lee, H.W. Effect of Cr content on microstructure and mechanical properties of low carbon steel welds. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10, 8028–8040. [Google Scholar]
- Odnobokova, M.; Kipelova, A.; Belyakov, A.; Kaibyshev, R. Microstructure evolution in a 316L stainless steel subjected to multidirectional forging and unidirectional bar rolling. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 63, 012060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, N.; Solomon, I. Deformation induced martensite in AISI 316 stainless steel. Rev. Metal. 2010, 46, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.B.; Xiang, J.Y.; Hou, D.P. Characteristics of mechanical properties an microstructure for 316L austenitic stainless steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2011, 18, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karcı, F.; Kaçar, R.; Gündüz, S. The effect of process parameter on the properties of spot welded cold deformed AISI304 grade austenitic stainless steel. J. Mater. Proc. Technol. 2009, 209, 4011–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callister, W.D.; Rethwisch, D.G. Materials Science and Engineering, 8th ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 237–250. ISBN 13: 978-0-471-73696-7. [Google Scholar]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).