Influence of Defoamer on the Properties and Pore Structure of Cementitious Grout for Rebar Sleeve Splicing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation and Testing Methods
2.2.1. Fluidity
2.2.2. Flexural Strength and Compressive Strength
2.2.3. Wet Apparent Density
2.2.4. MIP
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Influence of Defoamer on the Fluidity and Loss Rate of Grouts at 30 min
3.2. Influence of Defoamer on Wet Apparent Density of Grouts
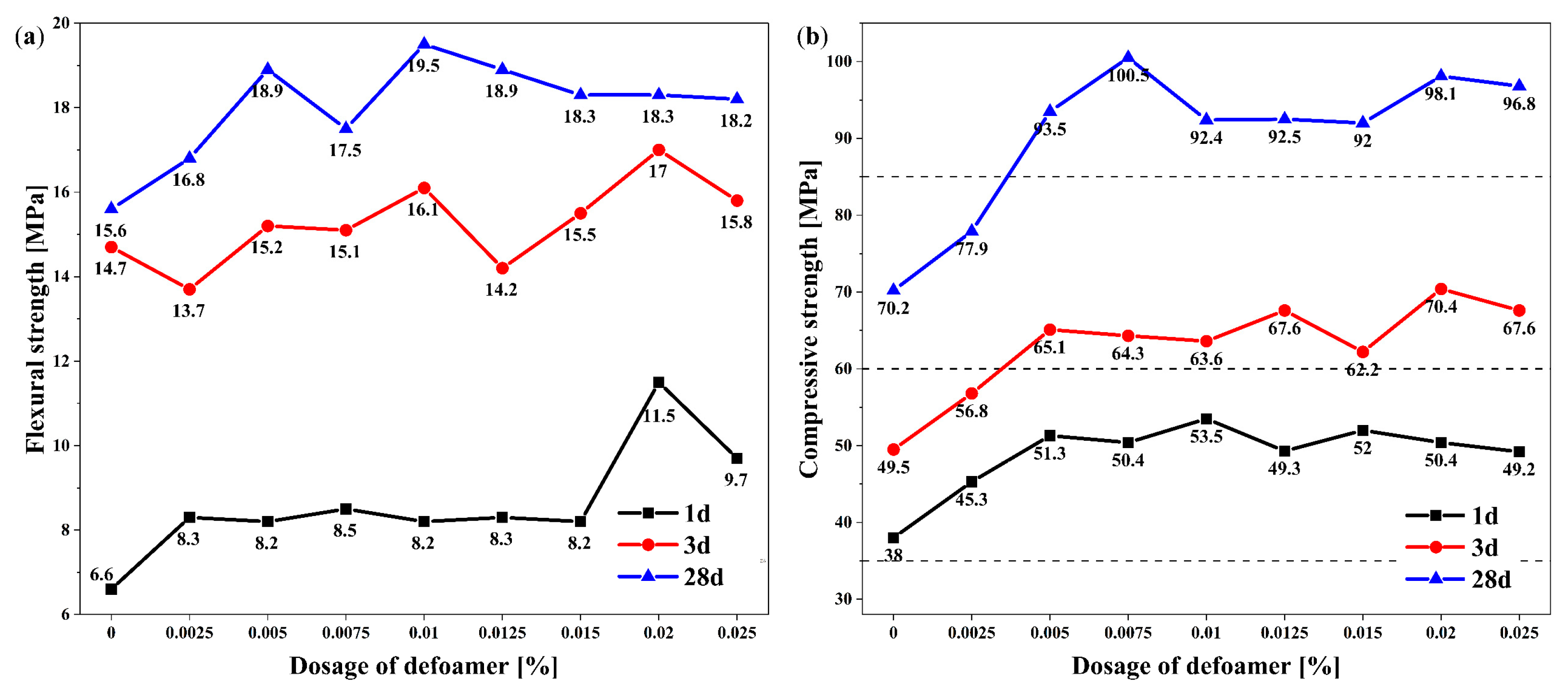
3.3. Influence of Defoamer on Mechanical Properties of Grouts
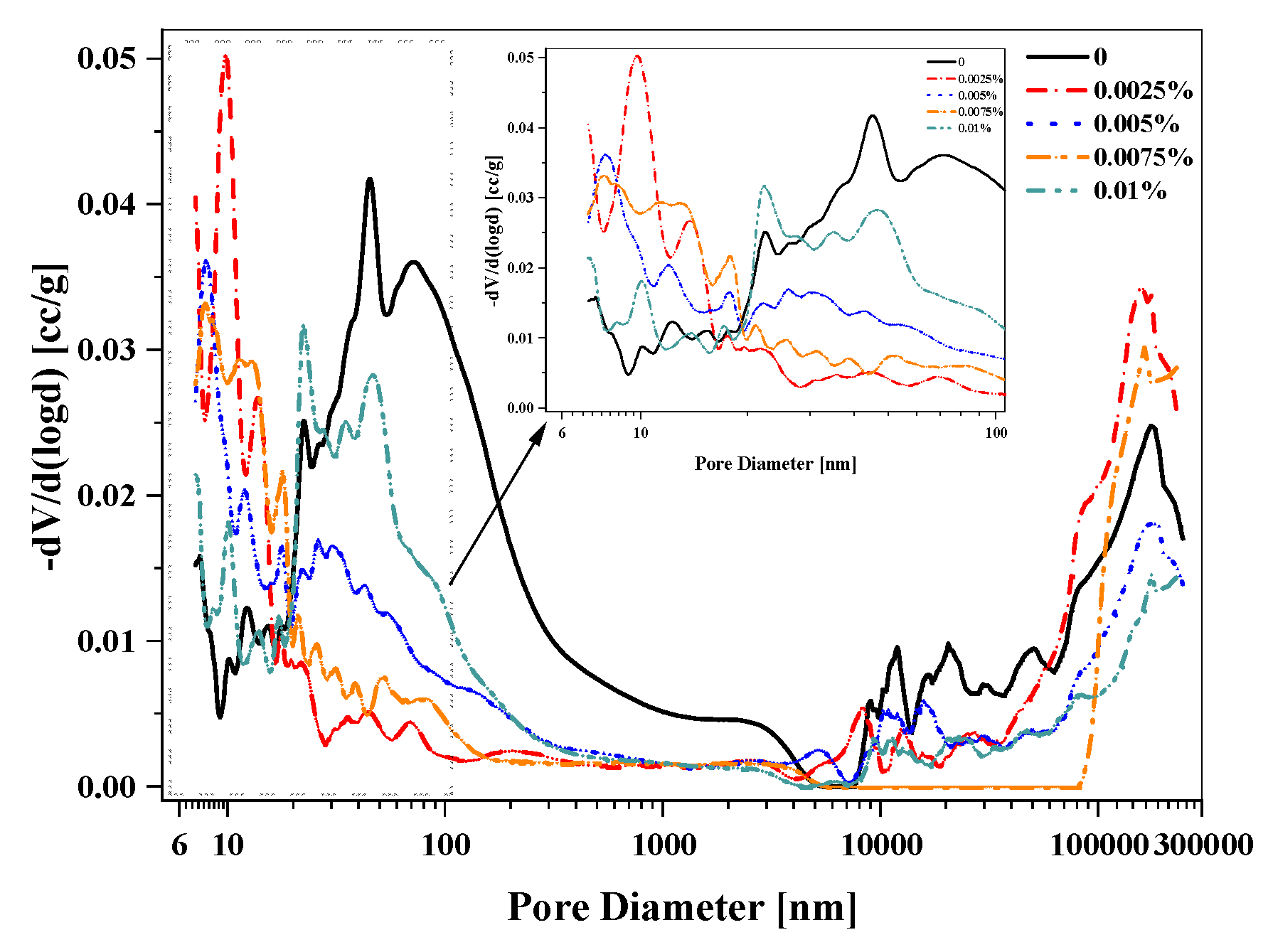
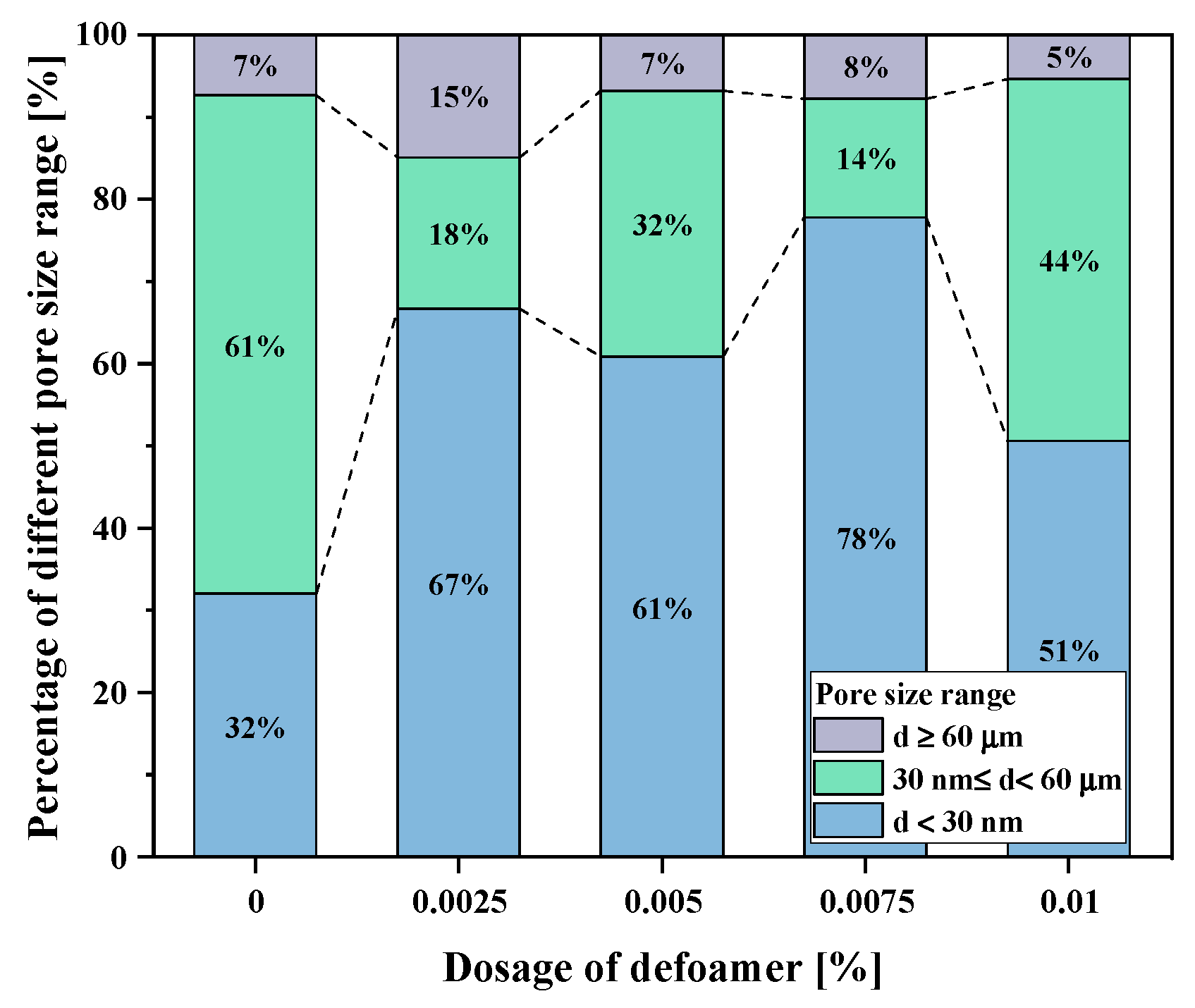
3.4. Influence of Defoamer on Grout Pore Structure
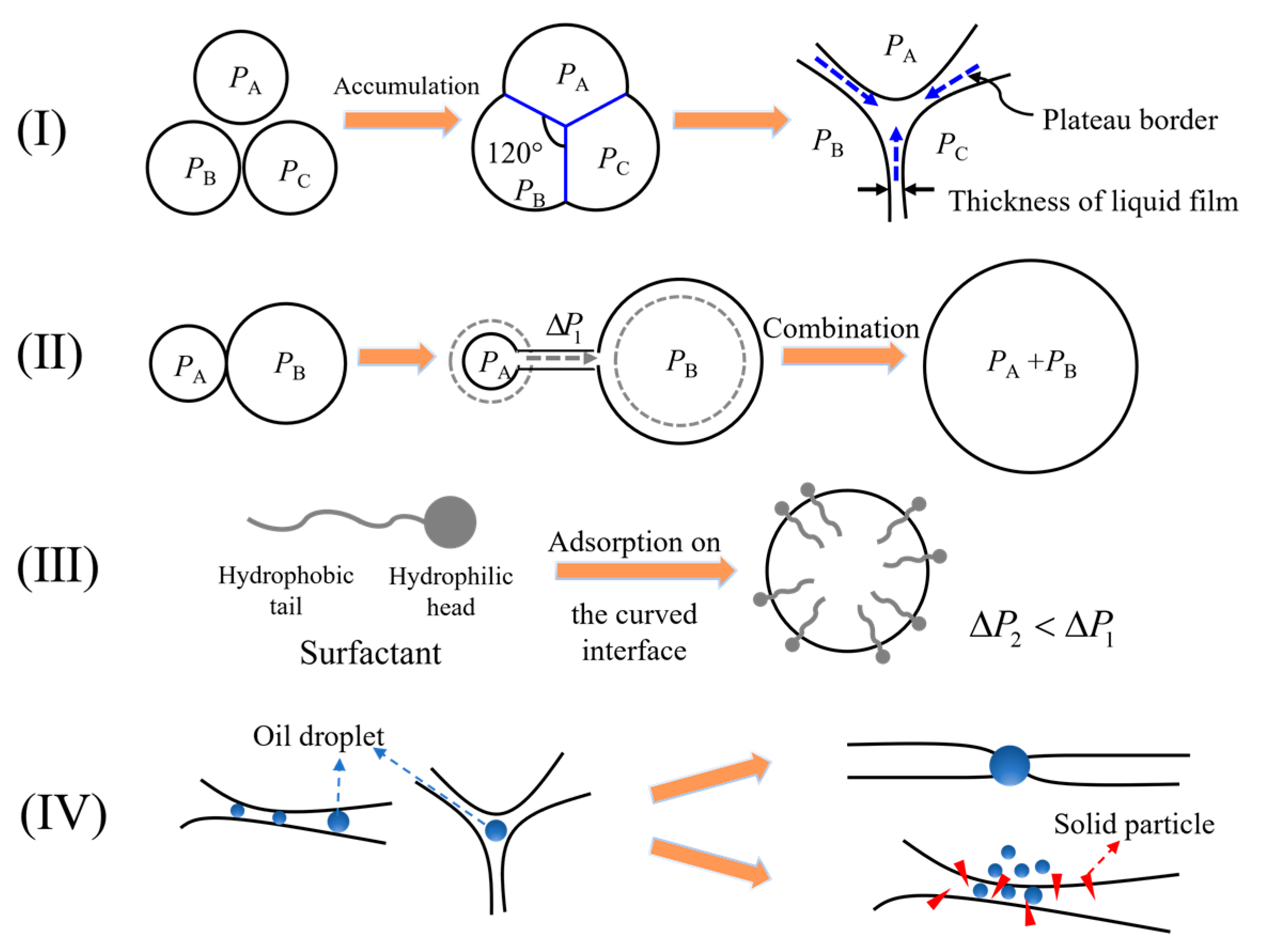
3.5. Mechanism of Defoamer in Grouts
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aslam, M.; Gao, Z.; Smith, G. Exploring factors for implementing lean construction for rapid initial successes in construction. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Xue, X.; Wang, Y.; Xue, W.; Tan, Y. A systematic overview of prefabricated construction policies in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dong, J.; Shen, L. A conceptual development framework for prefabricated construction supply chain management: An integrated overview. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, W.; Garmston, H. Compliance with building energy regulations for new-build dwellings. Energy 2012, 48, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boafo, F.E.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, J.-T. Performance of modular prefabricated architecture: Case study-based review and future pathways. Sustainability 2016, 8, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Einea, A.; Yamane, T.; Tadros, M.K. Grout-filled pipe splices for precast concrete construction. PCI J. 1995, 40, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Y.; Guo, Z.; Guan, D.; Zhang, X. Parametric study on a novel grouted rolling pipe splice for precast concrete construction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 166, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wang, K.; Wang, S.; Li, W.; Liu, W.; Du, D. Experimental bond behavior of deformed rebars in half-grouted sleeve connections with insufficient grouting defect. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 185, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, X.; Yan, Q. Performance of Grouting Sleeve-Connected Prefabricated Beams Subjected to Impact Loading. Buildings 2022, 12, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Takahashi, T.; Hanehara, S.; Matsuhisa, M. Effects of the chemical structure on the properties of polycarboxylate-type superplasticizer. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchikawa, H.; Hanehara, S.; Sawaki, D. The role of steric repulsive force in the dispersion of cement particles in fresh paste prepared with organic admixture. Cem. Concr. Res. 1997, 27, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Hirata, T.; Plank, J. 40 years of PCE superplasticizers-History, current state-of-the-art and an outlook. Cem. Concr. Res. 2022, 157, 106826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunstall, L.E.; Ley, M.T.; Scherer, G.W. Air entraining admixtures: Mechanisms, evaluations, and interactions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 150, 106557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alargova, R.G.; Warhadpande, D.S.; Paunov, V.N.; Velev, O.D. Foam superstabilization by polymer microrods. Langmuir 2004, 20, 10371–10374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandan, M.R.; Naskar, N.; Das, A.; Mukherjee, R.; Harikrishnan, G. Deducing multiple interfacial dynamics during polymeric foaming. Langmuir 2018, 34, 8024–8030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Robertson, R.E. Prevention of air void formation in polymer-modified cement mortar by pre-wetting. Cem. Concr. Res. 1997, 27, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, R.J. Experimental techniques for studying the structure of foams and froths. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 114, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arandigoyen, M.; Alvarez, J.I. Pore structure and mechanical properties of cement–lime mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denkov, N.D.; Marinova, K.G.; Tcholakova, S.S. Mechanistic understanding of the modes of action of foam control agents. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 206, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suja, V.C.; Kar, A.; Cates, W.; Remmert, S.; Fuller, G. Foam stability in filtered lubricants containing antifoams. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 567, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Cao, C.; Li, X.; Qian, J.; You, C. Preparation of Magnesium Ammonium Phosphate Mortar by Manufactured Limestone Sand Using Compound Defoaming Agents for Improved Strength and Impermeability. Buildings 2022, 12, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, D.; Lv, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Xue, G. Effects of Different Kinds of Defoamer on Properties of Geopolymer Mortar. Buildings 2022, 12, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JG/T 408-2019; Cementitious Grout for Sleeve of Rebar Splicing. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2019. (In Chinese)
- JGJ/T 70-2009; Standard for Test Method of Basic Properties of Construction Mortar. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2009. (In Chinese)
- Kim, H.; Jeon, J.; Lee, H.K. Workability, and mechanical, acoustic and thermal properties of lightweight aggregate concrete with a high volume of entrained air. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 29, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, H.A.; Yuan, Q.; Zuo, S. Air entrainment in fresh concrete and its effects on hardened concrete—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 274, 121835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, X.; Zhang, E.; Chen, Y.; Ma, R.; Gong, K.; Li, W.; Wang, X. Chemically Modified Silicone Oil with Enhanced Tribological and Anti-Foaming Properties. Lubricants 2022, 10, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.; John, V.M.; Ribeiro, J.L.; Roman, H. Pore size distribution of hydrated cement pastes modified with polymers. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorzelańczyk, T.; Hoła, J. Pore structure of self-compacting concretes made using different superplasticizers. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2011, 11, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Oxides | Na2O | SiO2 | K2O | CaO | P2O5 | Al2O3 | SO3 | MgO | Cl | Fe2O3 | CO2 | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | 0.18 | 20.61 | 0.85 | 57.23 | 0.07 | 6.67 | 3.73 | 3.90 | 0.05 | 0.62 | - | 4.09 |
| SF | 0.51 | 88.66 | 2.71 | 0.41 | - | 0.46 | 0.59 | 1.95 | - | 1.54 | 2.81 | - |
| CSA | 0.159 | 14.09 | 0.518 | 51.00 | 0.072 | 10.85 | 14.13 | 0.872 | 0.033 | 2.948 | 4.501 | 0.857 |
| PEA | 15.40 | 0.124 | - | 0.042 | - | 0.018 | 0.041 | - | 0.640 | 0.018 | 83.72 | - |
| No. | Cement/g | SF/g | Sand A/g | Sand B/g | CSA/g | PEA/g | ST/g | PCE/g | Defoamer/g% | W/B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GJ1 | 456 | 24 | 318 | 180 | 20 | 0.2 | 0.05 | 2.5 | 0 | 0.25 |
| GJ2 | 456 | 24 | 318 | 180 | 20 | 0.2 | 0.05 | 2.5 | 0.0025 | 0.25 |
| GJ3 | 456 | 24 | 318 | 180 | 20 | 0.2 | 0.05 | 2.5 | 0.005 | 0.25 |
| GJ4 | 456 | 24 | 318 | 180 | 20 | 0.2 | 0.05 | 2.5 | 0.0075 | 0.25 |
| GJ5 | 456 | 24 | 318 | 180 | 20 | 0.2 | 0.05 | 2.5 | 0.01 | 0.25 |
| GJ6 | 456 | 24 | 318 | 180 | 20 | 0.2 | 0.05 | 2.5 | 0.0125 | 0.25 |
| GJ7 | 456 | 24 | 318 | 180 | 20 | 0.2 | 0.05 | 2.5 | 0.015 | 0.25 |
| GJ8 | 456 | 24 | 318 | 180 | 20 | 0.2 | 0.05 | 2.5 | 0.02 | 0.25 |
| GJ9 | 456 | 24 | 318 | 180 | 20 | 0.2 | 0.05 | 2.5 | 0.025 | 0.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, C.; Ding, B.; Ou, Z.; Feng, R. Influence of Defoamer on the Properties and Pore Structure of Cementitious Grout for Rebar Sleeve Splicing. Buildings 2023, 13, 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13010170
Huang C, Ding B, Ou Z, Feng R. Influence of Defoamer on the Properties and Pore Structure of Cementitious Grout for Rebar Sleeve Splicing. Buildings. 2023; 13(1):170. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13010170
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Chunhua, Bo Ding, Zhihua Ou, and Ruiping Feng. 2023. "Influence of Defoamer on the Properties and Pore Structure of Cementitious Grout for Rebar Sleeve Splicing" Buildings 13, no. 1: 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13010170
APA StyleHuang, C., Ding, B., Ou, Z., & Feng, R. (2023). Influence of Defoamer on the Properties and Pore Structure of Cementitious Grout for Rebar Sleeve Splicing. Buildings, 13(1), 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13010170






