Exploring Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Internet of Things (IoT) Integration for Sustainable Building
Abstract
1. Introduction
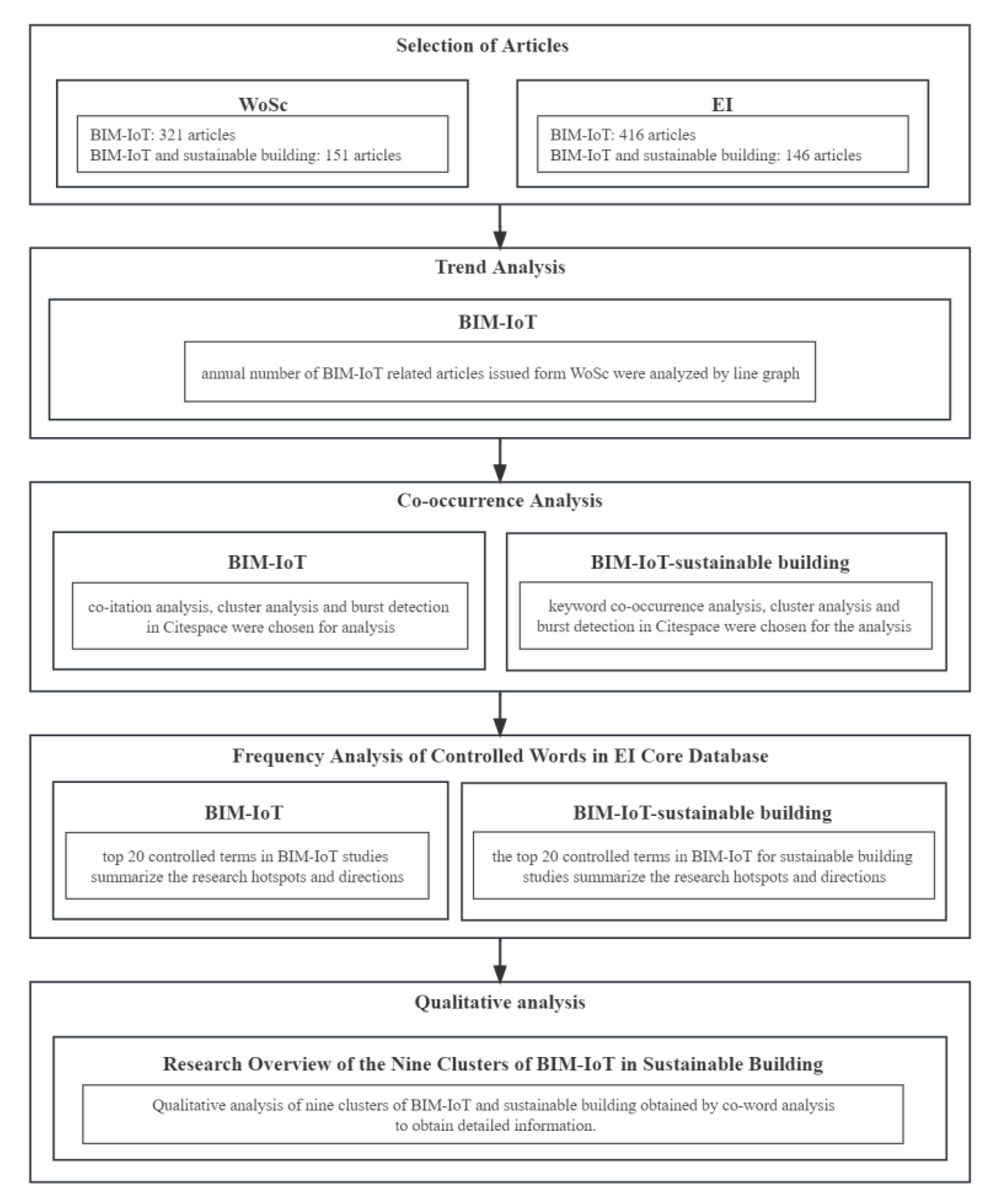
2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Results of the Macro Quantitative Analysis of Bibliometrics
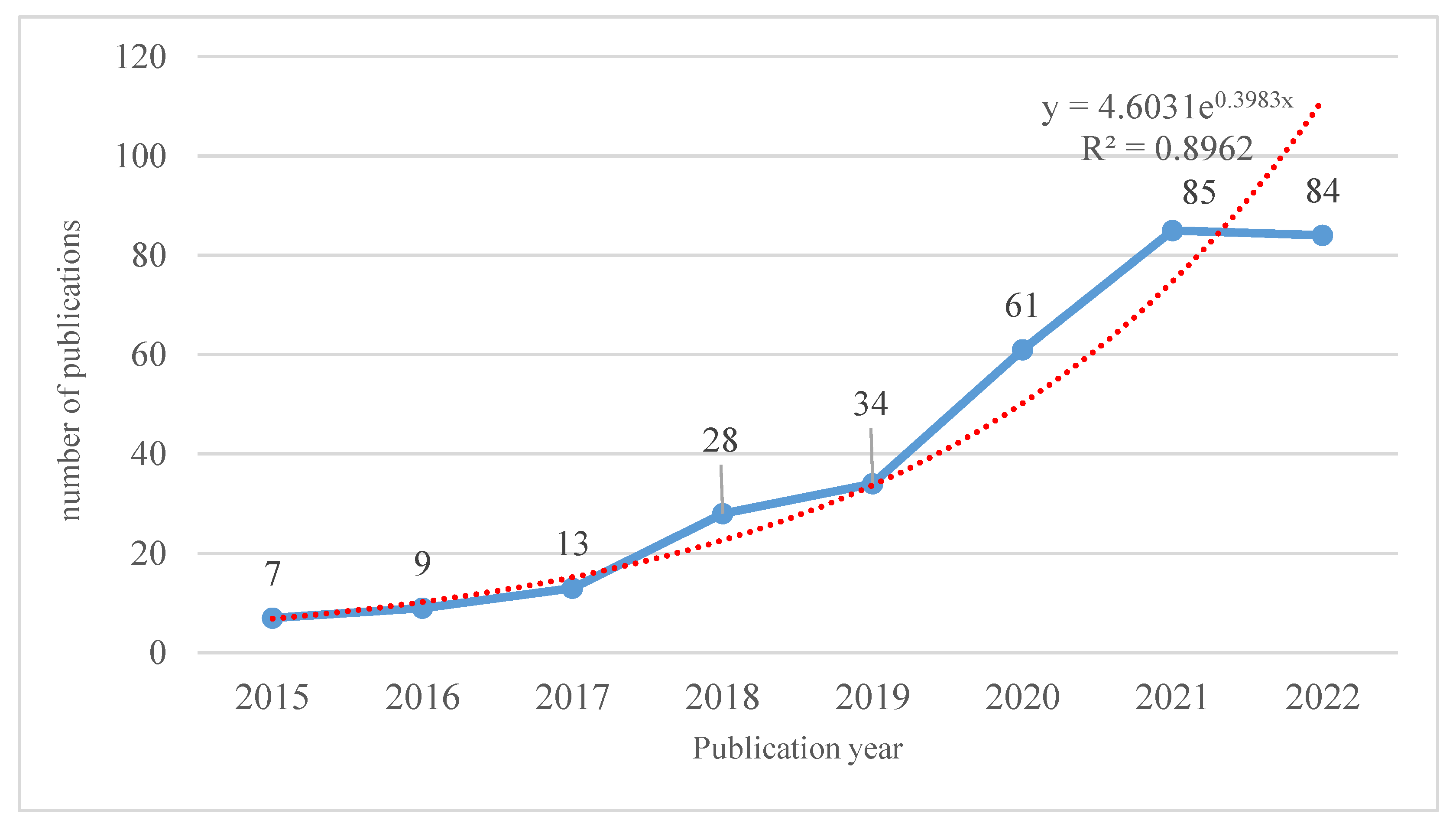
3.1.1. Trend Analysis and Co-Citation Analysis of Published Papers in WoSc Related to BIM–IoT Integration
- General Information
- Co-citation analysis
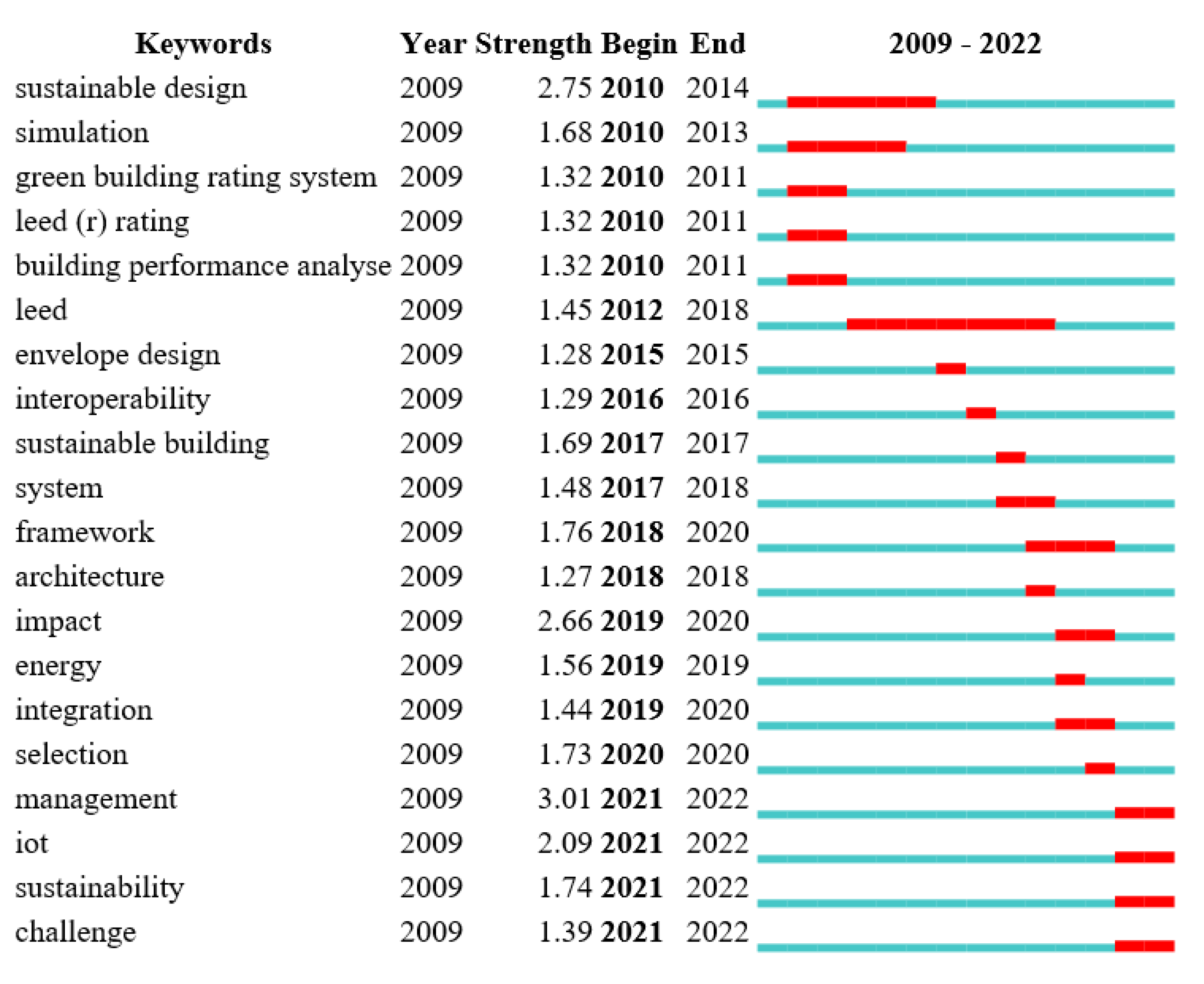
3.1.2. Co-Word Analysis of Published Papers in WoSc Related to BIM–IoT for Sustainable Building
- (1)
- Preparation Stage: optimization, framework, decision making, design, building design
- (2)
- Construction Stage: construction, construction project
- (3)
- Usage Stage: building metaverse, benefit
3.2. Frequency Analysis of Controlled Words in Engineering Index (EI) Core Database
- (1)
- Life Cycle: Life Cycle, Project Management, Decision Making, Energy Utilization, and Human Resource Management.
- (2)
- Smart City and Architecture: Architectural Design, Construction Industry (Construction), Office Buildings, Intelligent Buildings, and Smart City.
- (3)
- Internet of Things and other digital technologies: Internet of Things, Data Visualization(Visualization), Data Integration, Digital Storage, Semantics, and Three Dimensional Computer Graphics.
- (4)
- Information Management: Information Management and Information Theory.
- (1)
- Construction industry and building types: Construction Industry, Construction, Intelligent Buildings, Apartment Houses, and Office Buildings.
- (2)
- Design Related: Architectural Design, Structural Design, Eco-design, and Environmental Design.
- (3)
- Building Information Management and Decision Making: Decision Making, Information Theory, and Information Management.
- (4)
- Life Cycle and Sustainability: Life Cycle, Energy Efficiency, Environmental Impact, Sustainable Development, Project Management, Energy Utilization, Environmental Management, and Energy Conservation.
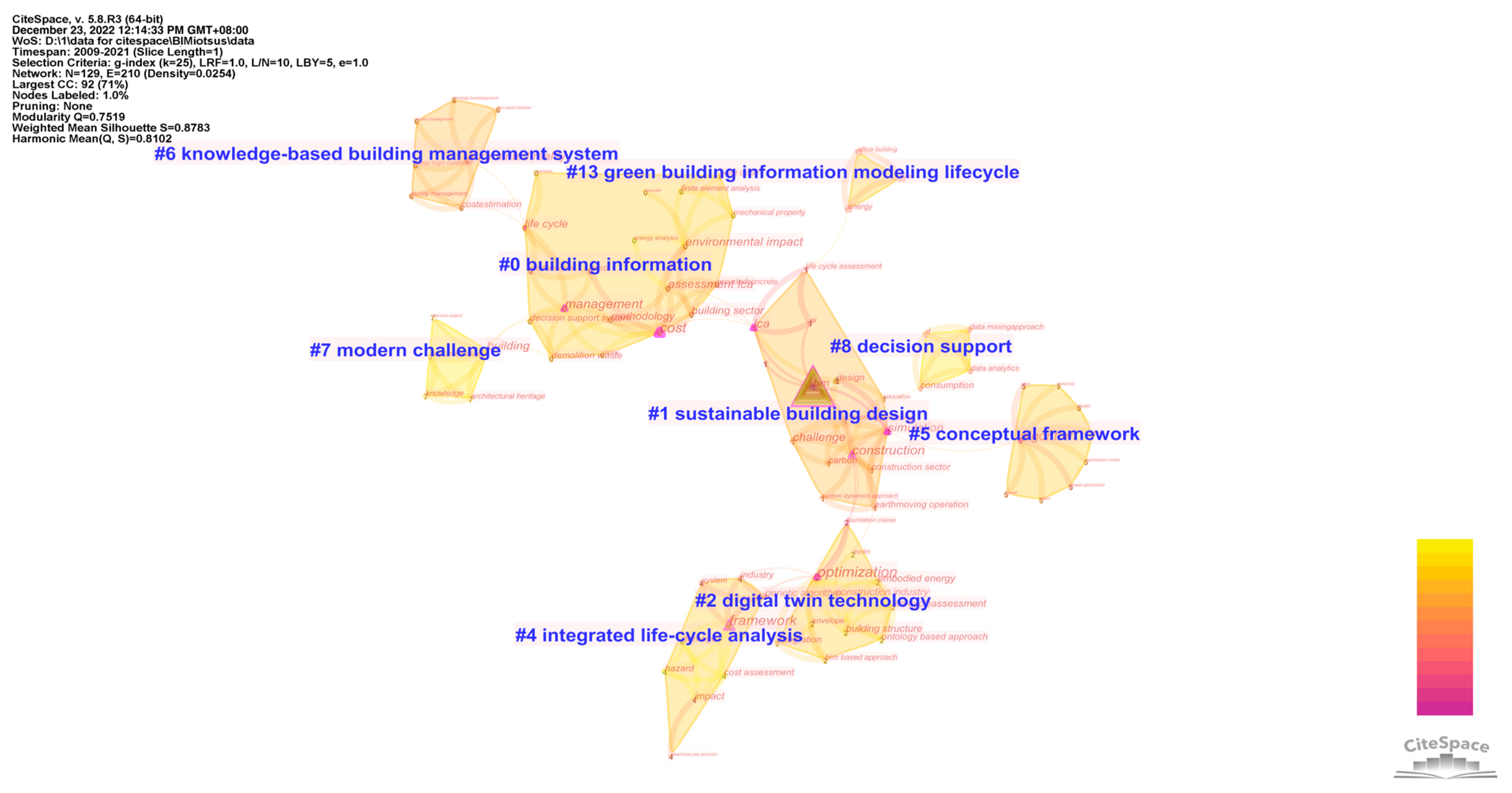
3.3. Results of the Micro Qualitative Analysis
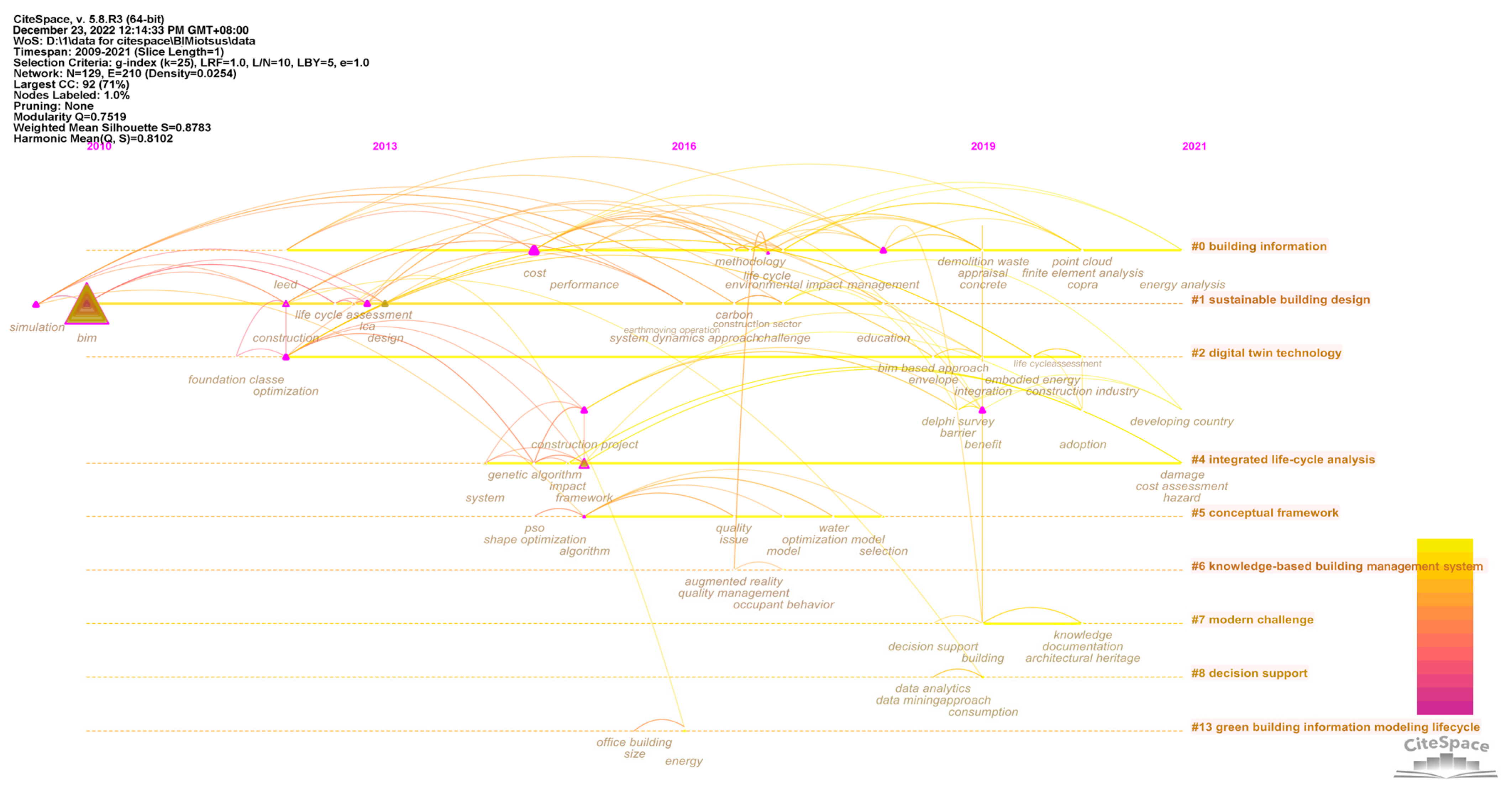
3.3.1. The Lifecycle Involved in The Nine Clusters in BIM–IoT-Sustainable Building
- (1)
- Preparation Stage (design and decision making): cluster #0 ‘building information’, cluster #1 ‘sustainable building design’, cluster #2 ‘digital twin technology’, cluster #4 ‘integrated life-cycle analysis’, cluster #5 ‘conceptual framework’, cluster #8 ‘decision support’, and cluster #13 ‘green building information modeling lifecycle’;
- (2)
- Construction Stage (construction): cluster #0 ‘building information’, cluster #2 ‘digital twin technology’, cluster #4 ‘integrated life-cycle analysis’, and cluster #13 ‘green building information modeling lifecycle’;
- (3)
- Usage Stage (operation, maintenance and refurbishment): cluster #1 ‘sustainable building design’, cluster #2 ‘digital twin technology’, cluster #4 ‘integrated life-cycle analysis’, cluster #6 ‘knowledge-based management system’, cluster #7 ‘modern challenge’, cluster #8 ‘decision support’, and cluster #13 ‘green building information modeling lifecycle’;
- (4)
- End Stage (deconstruction): cluster #2 ‘digital twin technology’, and cluster #13 ‘green building information modeling lifecycle’; and
- (5)
- Complete life cycle: cluster #2 ‘digital twin technology’, and cluster #13 ‘green building information modeling lifecycle’.
3.3.2. Research Overview of the Nine Clusters of BIM–IoT in Sustainable Building
- Cluster 0 building information
- Cluster 1 sustainable building design
- Cluster 2 digital twin technology
- Cluster 4 integrated life-cycle analysis
- Cluster 5 conceptual framework
- Cluster 6 knowledge-based management system
- Cluster 7 modern challenge
- Cluster 8 decision support
- Cluster 13 green building information modeling lifecycle
4. Discussion
4.1. The Necessity of Clarifying the Scope of the Definition of Sustainable Building
4.2. Change of Research Topics in the BIM-IoT Integration Field in the Timeline
4.3. Impact of Emerging Information Technology on Sustainable Building
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haarstad, H. Constructing the Sustainable City: Examining the Role of Sustainability in the ‘Smart City’ Discourse. J. Environ. Policy Plan. 2017, 19, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apanaviciene, R.; Vanagas, A.; Fokaides, P.A. Smart Building Integration into a Smart City (SBISC): Development of a New Evaluation Framework. Energies 2020, 13, 2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chi, Z.; Osmani, M.; Demian, P. Blockchain and Building Information Management (BIM) for Sustainable Building Development within the Context of Smart Cities. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckman, A.H.; Mayfield, M.; Beck, S.B.M. What Is a Smart Building? Smart Sustain. Built Environ. 2014, 3, 92–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawari, N.O.; Ravindran, S. Blockchain and the Built Environment: Potentials and Limitations. J. Build. Eng. 2019, 25, 100832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, S.; Nanayakkara, S.; Rodrigo, M.N.N.; Senaratne, S.; Weinand, R. Blockchain Technology: Is It Hype or Real in the Construction Industry? J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2020, 17, 100125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Adeli, H. Sustainable Building Design. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2014, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, R.; Stengel, J.; Schultmann, F. Building Information Modeling (BIM) for Existing Buildings—Literature Review and Future Needs. Autom. Constr. 2014, 38, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Huber, D.; Akinci, B.; Lipman, R.; Lytle, A. Automatic Reconstruction of As-Built Building Information Models from Laser-Scanned Point Clouds: A Review of Related Techniques. Autom. Constr. 2010, 19, 829–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.-J.; Ren, Z.-J.; Lu, H.; Wu, J.-F. The Progress and Trend of BIM Research: A Bibliometrics-Based Visualization Analysis. Autom. Constr. 2021, 124, 103558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, C.; Fisher, D. An Outline of the Building Description System. Res. Rep. 1974, 50. [Google Scholar]
- Frequently Asked Questions About the National BIM Standard-United StatesTM|National BIM Standard—United States. Available online: https://www.nationalbimstandard.org/faqs#faq1 (accessed on 15 May 2022).
- Wang, M.; Wang, C.C.; Sepasgozar, S.; Zlatanova, S. A Systematic Review of Digital Technology Adoption in Off-Site Construction: Current Status and Future Direction towards Industry 4.0. Buildings 2020, 10, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.K.W.; Ge, J.; He, S.X. Digitisation in Facilities Management: A Literature Review and Future Research Directions. Autom. Constr. 2018, 92, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhang, J. Present and Future of Integrated Applications of BIM, Cloud Computing, Big Data and Internet of Things. J. Graph. 2018, 39, 806–816. [Google Scholar]
- Uckelmann, D.; Harrison, M.; Michahelles, F. Architecting the Internet of Things; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, C.; Sun, G. Principles of the Internet of Things and Industry Applications; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2013; pp. 320–323. [Google Scholar]
- Štefanič, M.; Stankovski, V. A Review of Technologies and Applications for Smart Construction. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Civ. Eng. 2019, 172, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannino, A.; Dejaco, M.C.; Re Cecconi, F. Building Information Modelling and Internet of Things Integration for Facility Management—Literature Review and Future Needs. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Kamaruzzaman, S.N.; Aziz, N.M. Green Building Construction: A Systematic Review of BIM Utilization. Buildings 2022, 12, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, U. Clarifying the New Interpretations of the Concept of Sustainable Building. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2013, 8, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, N.; Kim, D.H. Iot task management mechanism based on predictive optimization for efficient energy consumption in smart residential buildings. Energy Build. 2022, 257, 111762. [Google Scholar]
- Karthick Raghunath, K.M.; Koti, M.S.; Sivakami, R.; Vinoth Kumar, V.; NagaJyothi, G.; Muthukumaran, V. Utilization of IoT-assisted computational strategies in wireless sensor networks for smart infrastructure management. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 2022, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Shelden, D.R.; Eastman, C.M.; Pishdad-Bozorgi, P.; Gao, X. A Review of Building Information Modeling (BIM) and the Internet of Things (IoT) Devices Integration: Present Status and Future Trends. Autom. Constr. 2019, 101, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagnino, A.; Montanaro, T.; Lazoi, M.; Sergi, I.; Corallo, A.; Patrono, L. Building Information Modeling and Internet of Things Integration for Smart and Sustainable Environments: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Liang, X.; Kong, L.; Shen, X.; Wu, T. Assessment of the Toxicity of Quantum Dots through Biliometric Analysis. Int J Env. Res Public Health 2021, 18, 5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Hu, Z.; Liu, S.; Tseng, H. Emerging Trends in Regenerative Medicine: A Scientometric Analysis in CiteSpace. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2012, 12, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, H. Literature Review as a Research Methodology: An Overview and Guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 104, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, G.P. Smart Cities Research in Portugal and Spain: An Exploratory Biliometric Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2018 13th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI), Caceres, Spain, 13–16 June 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, D.; Ma, H. Exploring the Evolution of Scientific Data Research Themes in China from the Perspective of Keywords Frequency Change. J. Mod. Inf. 2018, 38, 141–146, 161. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.; Hou, H.; Ren, P.; Hu, Z. Selection of Research Front Detection Methods Based on Bibliographic Coupling and Co-citation. J. Intell. 2018, 37, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Small, H. Co-Citation in the Scientific Literature: A New Measure of the Relationship between Two Documents. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 1973, 24, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ma, F. On paradigm of research knowledge management:A bibliometric analysis. J. Manag. Sci. China 2007, 10, 65–75. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.; Yuan, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, Q. From Digital to Sustainable: A Scientometric Review of Smart City Literature between 1990 and 2019. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Web of Science. Available online: https://www.webofscience.com/wos/alldb/basic-search (accessed on 23 November 2022).
- Engineering Village—Quick Search. Available online: https://www.engineeringvillage.com/search/quick.url (accessed on 23 November 2022).
- Li, J.; Chen, C. Citespace: Text Mining and Visualization in Scientific Literature, 2nd ed.; Capital University of Economics & Business Press: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, Z.; Hu, Z.; Wang, X. The methodology function of Cite Space mapping knowledge domains. Stud. Sci. Sci. 2015, 33, 242–253. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, Z.; Hu, Z. Principle and Application of Analyzing a Citation Space; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Forcael, E.; Ferrari, I.; Opazo-Vega, A.; Pulido-Arcas, J.A. Construction 4.0: A Literature Review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boton, C.; Rivest, L.; Ghnaya, O.; Chouchen, M. What Is at the Root of Construction 4.0: A Systematic Review of the Recent Research Effort. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 28, 2331–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, S.A.; Oyedele, L.O.; Akinade, O.O.; Bilal, M.; Davila Delgado, J.M.; Akanbi, L.A.; Ajayi, A.O.; Owolabi, H.A. Cloud Computing in Construction Industry: Use Cases, Benefits and Challenges. Autom. Constr. 2021, 122, 103441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panteli, C.; Kylili, A.; Fokaides, P.A. Building Information Modelling Applications in Smart Buildings: From Design to Commissioning and beyond A Critical Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 265, 121766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boje, C.; Guerriero, A.; Kubicki, S.; Rezgui, Y. Towards a Semantic Construction Digital Twin: Directions for Future Research. Autom. Constr. 2020, 114, 103179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, B.; Buda, A.; Nurminen, A.; Främling, K. A Framework for Integrating BIM and IoT through Open Standards. Autom. Constr. 2018, 95, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Z.; Xue, F.; Li, X.; Hong, J.; Shen, G.Q. An Internet of Things-Enabled BIM Platform for on-Site Assembly Services in Prefabricated Construction. Autom. Constr. 2018, 89, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerik-Gerber, B.; Jazizadeh, F.; Li, N.; Calis, G. Application Areas and Data Requirements for BIM-Enabled Facilities Management. J. Constr. Eng. Manage. 2012, 138, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Oyedele, L.O.; Qadir, J.; Munir, K.; Ajayi, S.O.; Akinade, O.O.; Owolabi, H.A.; Alaka, H.A.; Pasha, M. Big Data in the Construction Industry: A Review of Present Status, Opportunities, and Future Trends. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2016, 30, 500–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.Y.; Peng, Y.; Xue, F.; Fang, J.; Zou, W.; Luo, H.; Thomas Ng, S.; Lu, W.; Shen, G.Q.P.; Huang, G.Q. Prefabricated Construction Enabled by the Internet-of-Things. Autom. Constr. 2017, 76, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Lu, W.; Peng, Y.; Rowlinson, S.; Huang, G.Q. Bridging BIM and Building: From a Literature Review to an Integrated Conceptual Framework. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2015, 33, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irizarry, J.; Karan, E.P.; Jalaei, F. Integrating BIM and GIS to Improve the Visual Monitoring of Construction Supply Chain Management. Autom. Constr. 2013, 31, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motamedi, A.; Hammad, A.; Asen, Y. Knowledge-assisted BIM-based visual analytics for failure root cause detection in facilities management. Autom. Constr. 2014, 43, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottaccioli, L.; Aliberti, A.; Ugliotti, F.; Patti, E.; Osello, A.; Macii, E.; Acquaviva, A. Building Energy Modelling and Monitoring by Integration of IoT Devices and Building Information Models. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 41st Annual Computer Software and Applications Conference (COMPSAC), Turin, Italy, 4–8 July 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodhead, R.; Stephenson, P.; Morrey, D. Digital Construction: From Point Solutions to IoT Ecosystem. Autom. Constr. 2018, 93, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Ke, P. The Research on Hotspots and Foreground of International Library &Information Science (2014–2015): Full Sample Analysis of 27 SSCI Core Journals. J. Acad. Libr. 2017, 35, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Gubbi, J.; Buyya, R.; Marusic, S.; Palaniswami, M. Internet of Things (IoT): A vision, architectural elements, and future directions. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2013, 39, 1645–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar, S. Building Information Modeling (BIM): Trends, Benefits, Risks, and Challenges for the AEC Industry. Leadersh. Manag. Eng. 2011, 11, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar, S.; Khalfan, M.; Maqsood, T. Building Information Modeling (BIM): Now and Beyond. Australas. J. Constr. Econ. Build. 2015, 12, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, Z.; Arslan, M.; Kiani, A.K.; Azhar, S. CoSMoS: A BIM and Wireless Sensor Based Integrated Solution for Worker Safety in Confined Spaces. Autom. Constr. 2014, 45, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yang, T.; Hu, K. Visualization Analysis on Knowledge Graph of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Treating Lung Cancer Based on Cite Space. Mod. Tradit. Chin. Med. Mater. Med.-World Sci. Technol. 2020, 22, 3549–3557. [Google Scholar]
- Zabalza Bribián, I.; Aranda Usón, A.; Scarpellini, S. Life Cycle Assessment in Buildings: State-of-the-Art and Simplified LCA Methodology as a Complement for Building Certification. Build. Environ. 2009, 44, 2510–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Osmani, M. Integration of Digital Economy and Circular Economy: Current Status and Future Directions. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwepe, L.; Aigbavboa, C. A Theoretical Review of Building Life Cycle Stages and Their Related Environmental Impacts. J. Civ. Eng. Environ. Technol. 2015, 2, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, J.K.W.; Zhou, J. Enhancing Environmental Sustainability over Building Life Cycles through Green BIM: A Review. Autom. Constr. 2015, 57, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong-Chao, S.; Ying-Jing, T.U.N.; Jian-Sha, L.U. State-of-the-Art of Research on Manufacturing Execution System Based on Bibliometrics. China Mech. Eng. 2011, 22, 1605. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q. Review on the Word Frequency Analysis Employed to Discover the Development of Science Research in China. Doc. Inf. Knowl. 2011, 2, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis, M.; Antucheviciene, J.; Migilinskas, D. Assessment of Buildings Redevelopment Possibilities Using MCDM and BIM Techniques. Procedia Eng. 2017, 172, 846–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, R.; Mimendi, L. Digitisation of Bamboo Culms for Structural Applications. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 29, 101193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalesi, H.; Balali, A.; Valipour, A.; Antucheviciene, J.; Migilinskas, D.; Zigmund, V. Application of Hybrid SWARA–BIM in Reducing Reworks of Building Construction Projects from the Perspective of Time. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, L.C.A.; César, S.F.; Cunha, R.D.A.; Kiperstok, A. Getting Environmental Information from Construction Cost Databases: Applications in Brazilian Courses and Environmental Assessment. Sustainability 2019, 11, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanlande, R.; Nicolle, C.; Cruz, C. IFC and Building Lifecycle Management. Autom. Constr. 2008, 18, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eadie, R.; Browne, M.; Odeyinka, H.; McKeown, C.; McNiff, S. BIM Implementation throughout the UK Construction Project Lifecycle: An Analysis. Autom. Constr. 2013, 36, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harter, H.; Singh, M.M.; Schneider-Marin, P.; Lang, W.; Geyer, P. Uncertainty Analysis of Life Cycle Energy Assessment in Early Stages of Design. Energy Build. 2020, 208, 109635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Aibinu, A.; Thaheem, M.J. BIM-Based Iterative Tool for Sustainable Building Design: A Conceptual Framework. Procedia Eng. 2017, 180, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jrade, A.; Jalaei, F. Integrating Building Information Modelling with Sustainability to Design Building Projects at the Conceptual Stage. Build. Simul. 2013, 6, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani Asl, M.; Zarrinmehr, S.; Yan, W. Towards BIM-Based Parametric Building Energy Performance Optimization. In Proceedings of the Association for Computer Aided Design in Architecture (ACADIA), Cambridge, ON, Canada, 24–27 October 2013; pp. 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Starynina, J.; Ustinovichius, L. A Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Synthesis Method to Determine the Most Effective Option for Modernising a Public Building. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2020, 26, 1237–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kylili, A.; Fokaides, P.A. Policy Trends for the Sustainability Assessment of Construction Materials: A Review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 35, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Meng, X.; Tam, C. Building Information Modeling Based Building Design Optimization for Sustainability. Energy Build. 2015, 105, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Edwards, D.J.; Hosseini, M.R. Patterns and Trends in Internet of Things (IoT) Research: Future Applications in the Construction Industry. ECAM 2020, 28, 457–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Tao, F. Digital Twin and Big Data Towards Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0: 360 Degree Comparison. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 3585–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Ma, T.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Han, C. A BIM-IoT and intelligent compaction integrated framework for advanced road compaction quality monitoring and management. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 100, 107981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eneyew, D.D.; Capretz, M.A.; Bitsuamlak, G.T. Towards Smart Building Digital Twins: BIM and IoT Data Integration. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 130487–130506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajavi, S.H.; Motlagh, N.H.; Jaribion, A.; Werner, L.C.; Holmstrom, J. Digital Twin: Vision, Benefits, Boundaries, and Creation for Buildings. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 147406–147419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, N. From the Design of Green Buildings to Resilience Management of Building Stocks. Build. Res. Inf. 2018, 46, 578–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, E.; Pauwels, P.; Svidt, K.; Jensen, R.L. Towards Data-Driven Sustainable Design: Decision Support Based on Knowledge Discovery in Disparate Building Data. Archit. Eng. Des. Manag. 2019, 15, 334–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeles, K.; Patsialis, D.; Taflanidis, A.A.; Kijewski-Correa, T.L.; Buccellato, A.; Vardeman, C. Advancing the Design of Resilient and Sustainable Buildings: An Integrated Life-Cycle Analysis. J. Struct. Eng. 2021, 147, 04020341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, M.; Azab, S.; Metawie, M. BIM-Based Approach for Optimizing Life Cycle Costs of Sustainable Buildings. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 188, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.X.; Zhu, Y.; Passe, U. Modeling and Data Infrastructure for Human-Centric Design and Operation of Sustainable, Healthy Buildings through a Case Study. Build. Environ. 2020, 170, 106518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GhaffarianHoseini, A.; Zhang, T.; Nwadigo, O.; GhaffarianHoseini, A.; Naismith, N.; Tookey, J.; Raahemifar, K. Application of ND BIM Integrated Knowledge-Based Building Management System (BIM-IKBMS) for Inspecting Post-Construction Energy Efficiency. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 935–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aamodt, A.; Plaza, E. Case-Based Reasoning: Foundational Issues, Methodological Variations, and System Approaches. AI Commun. 1994, 7, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motawa, I.; Almarshad, A. A Knowledge-Based BIM System for Building Maintenance. Autom. Constr. 2013, 29, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diara, F.; Rinaudo, F. Open source hbim for cultural heritage: A project proposal. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, XLII–2, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prizeman, O.; Pezzica, C.; Taher, A.; Boughanmi, M. Networking Historic Environmental Standards to Address Modern Challenges for Sustainable Conservation in HBIM. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heylighen, A.; Martin, W.M.; Cavallin, H. Building Stories Revisited: Unlocking the Knowledge Capital of Architectural Practice. Archit. Eng. Des. Manag. 2007, 3, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, M.F.; Esmanioto, F.; Huber, N.; Loures, E.R.; Canciglieri, O. A Systematic Literature Review of Interoperability in the Green Building Information Modeling Lifecycle. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 223, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, L.C.; Kamsu-Foguem, B. BIM-Oriented Data Mining for Thermal Performance of Prefabricated Buildings. Ecol. Inform. 2019, 51, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Sensing Information Modelling for Smart City. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Smart City/SocialCom/SustainCom (SmartCity), Chengdu, China, 19–21 December 2015; pp. 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.-B.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Fan, C.-X.; Sun, J.-J. Internet of Things: Summarize on Concepts, Architecture and Key Technology Problem. J. Beijing Univ. Posts Telecommun. 2010, 33, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Madakam, S.; Lake, V.; Lake, V.; Lake, V. Internet of Things (IoT): A Literature Review. J. Comput. Commun. 2015, 3, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruíz-Zafra, Á.; Benghazi, K.; Noguera, M. IFC+: Towards the integration of IoT into early stages of building design. Autom. Constr. 2022, 136, 104129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Osmani, M. The Relationship between Sustainable Built Environment, Art Therapy and Therapeutic Design in Promoting Health and Well-Being. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Švajlenka, J. Aspects of the Internal Environment Buildings in the Context of IoT. In Integrating IoT and AI for Indoor Air Quality Assessment; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 55–72. [Google Scholar]
- Zeiger, F.; Huber, M.F. Demonstration Abstract: Participatory Sensing Enabled Environmental Monitoring in Smart Cities. In Proceedings of the IPSN-14 Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, Berlin, Germany, 15–17 April 2014; pp. 337–338. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, B.N.; Khan, M.; Han, K. Towards Sustainable Smart Cities: A Review of Trends, Architectures, Components, and Open Challenges in Smart Cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 38, 697–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baracho, R.; Junior, M.P.C.; Almeida, M.B. Ontologia, Internet Das Coisas e Modelagem Da Informação Da Construção (BIM): Estudo Exploratório e a Inter-Relação Entre as Tecnologias(Ontology, Internet of Things, and Building Information Modeling (BIM): An Exploratory Study and the Interrelations Between Technologies). In Proceedings of the ONTOBRAS, Brasília, Brazil, 28–30 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wen, F.; Sun, Z.; Guo, X.; He, T.; Lee, C. Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Sensing Technologies in the 5G/Internet of Things Era: From Virtual Reality/Augmented Reality to the Digital Twin. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2022, 4, 2100228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onungwa, I.; Olugu-Uduma, N.; Shelden, D.R. Cloud BIM Technology as a Means of Collaboration and Project Integration in Smart Cities. SAGE Open 2021, 11, 21582440211033250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xiong, W. Internet of Things Technology and Application, 2nd ed.; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2020; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Elefante, C. The Greenest Building Is... One That Is Already Built. Forum J. 2012, 27, 62–72. [Google Scholar]
- Pavón, R.M.; Alberti, M.G.; Álvarez, A.A.A.; del Rosario Chiyón Carrasco, I. Use of BIM-FM to Transform Large Conventional Public Buildings into Efficient and Smart Sustainable Buildings. Energies 2021, 14, 3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
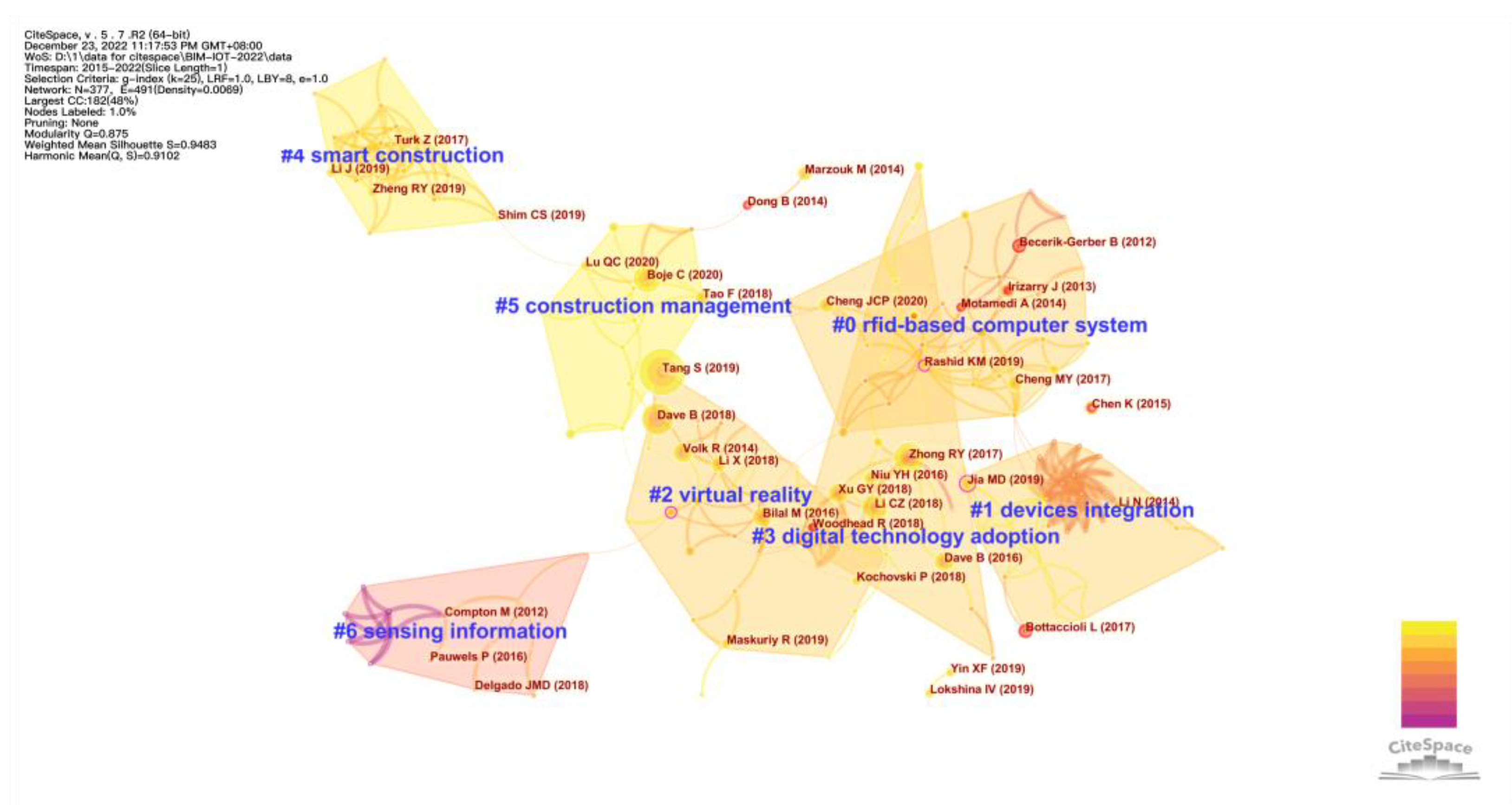
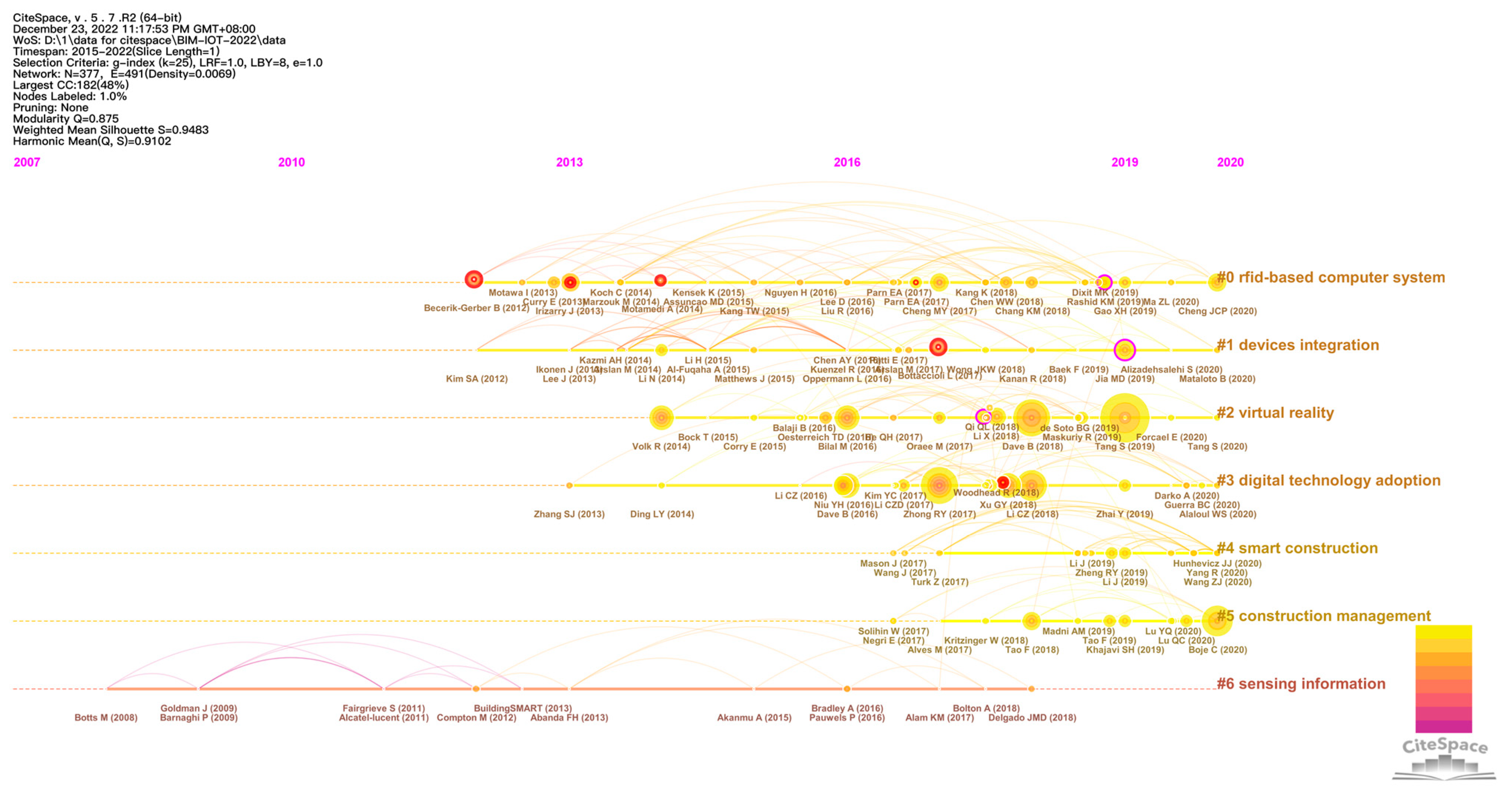

| Cluster | Size | Silhouette | Mean (Cited Year) | Label (LSI) | Label (LLR) | Label (MI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 33 | 0.951 | 2016 | building information modeling | rfid-based computer system | facility management |
| 1 | 23 | 0.969 | 2015 | future trends | devices integration | sustainable environment |
| 2 | 27 | 0.918 | 2017 | virtual reality | virtual reality | airport project delivery |
| 3 | 22 | 0.944 | 2017 | Internet | digital technology adoption | wearable sensing device |
| 4 | 19 | 0.967 | 2019 | smart construction | smart construction | construction information flow |
| 5 | 15 | 0.922 | 2018 | Integration | construction management | advanced project management |
| 6 | 14 | 0.94 | 2013 | sensing information | sensing information | semantic construction |
| Centrality | Count | Year | Keywords |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.20 | 25 | 2012 | Construction |
| 0.19 | 16 | 2015 | Framework |
| 0.18 | 11 | 2012 | Optimization |
| 0.15 | 4 | 2015 | Construction project |
| 0.12 | 1 | 2022 | Building Metaverse |
| 0.11 | 2 | 2015 | Decision Making |
| 0.11 | 4 | 2015 | Construction Industry |
| 0.10 | 3 | 2019 | Building Design |
| 0.10 | 5 | 2019 | Benefit |
| 0.10 | 21 | 2013 | Design |
| BIM-IoT | BIM-IoT-Sustainable Building | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Controlled Vocabulary | Count | Controlled Vocabulary | Count |
| Architectural Design | 312 | Architectural Design | 162 |
| Internet of Things | 271 | Intelligent Buildings | 135 |
| Information Management | 128 | Sustainable Development | 134 |
| Information Theory | 97 | Information Theory | 65 |
| Construction Industry | 78 | Life Cycle | 49 |
| Project Management | 69 | Energy Efficiency | 43 |
| Life Cycle | 68 | Construction Industry | 40 |
| Construction | 57 | Eco-design | 38 |
| Intelligent Buildings | 54 | Decision Making | 34 |
| Office Buildings | 43 | Construction | 28 |
| Decision Making | 41 | Energy Utilization | 24 |
| Smart City | 28 | Office Buildings | 22 |
| Data Visualization | 23 | Project Management | 20 |
| Data Integration | 22 | Environmental Impact | 16 |
| Visualization | 21 | Structural Design | 16 |
| Semantics | 20 | Environmental Design | 13 |
| Digital Storage | 19 | Information Management | 13 |
| Energy Utilization | 19 | Energy Conservation | 12 |
| Human Resource Management | 19 | Environmental Management | 12 |
| Three Dimensional Computer Graphics | 19 | Apartment Houses | 8 |
| Cluster Name | Life Cycle Stages | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preparation Stage | Construction Stage | Usage Stage | End Stage | |||||||||
| Design | Decision- Making | Manufacturing | Procurement | Construction | Transport | Operations | Maintenance | Refurbishment | Deconstruction | Disposal | Reuse or Recycling | |
| #0 building information | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| #1 sustainable building design | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| #2 digital twin technology | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| #4 integrated life-cycle analysis | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| #5 conceptual framework | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| #6 knowledge-based management system | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| #7 modern challenge | 1 | |||||||||||
| #8 decision support | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| #13 green building information modeling lifecycle | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Cui, J.; Osmani, M.; Demian, P. Exploring Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Internet of Things (IoT) Integration for Sustainable Building. Buildings 2023, 13, 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13020288
Chen Y, Wang X, Liu Z, Cui J, Osmani M, Demian P. Exploring Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Internet of Things (IoT) Integration for Sustainable Building. Buildings. 2023; 13(2):288. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13020288
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yali, Xiaozi Wang, Zhen Liu, Jia Cui, Mohamed Osmani, and Peter Demian. 2023. "Exploring Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Internet of Things (IoT) Integration for Sustainable Building" Buildings 13, no. 2: 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13020288
APA StyleChen, Y., Wang, X., Liu, Z., Cui, J., Osmani, M., & Demian, P. (2023). Exploring Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Internet of Things (IoT) Integration for Sustainable Building. Buildings, 13(2), 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13020288








