Investigation on Minute Holes of Woven Fabrics for Wide-Band Micro-Perforated Sound Absorbers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Structures
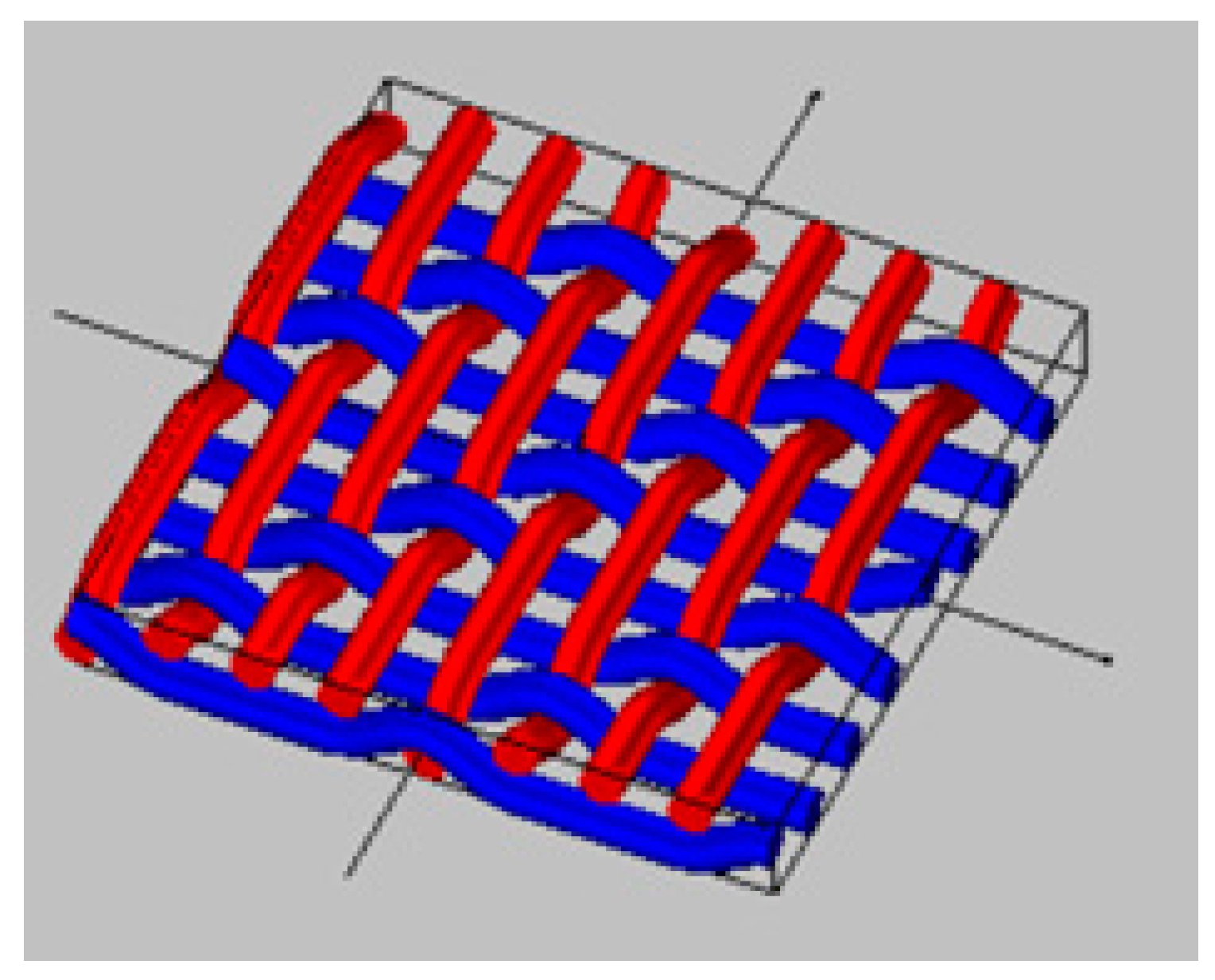
2.1. Material and Structure of Woven Fabrics
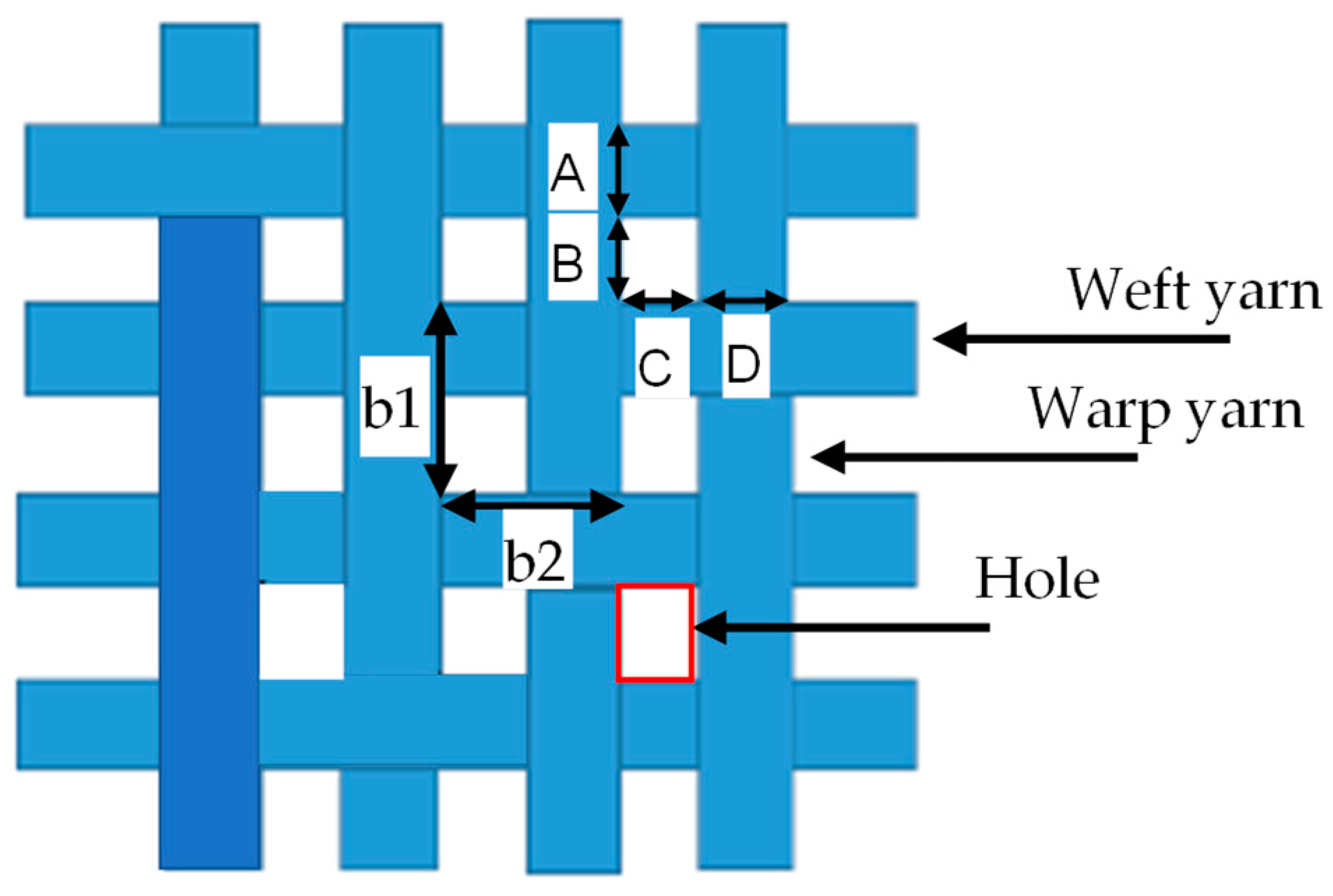
2.2. Textile Parameters and Perforation Properties
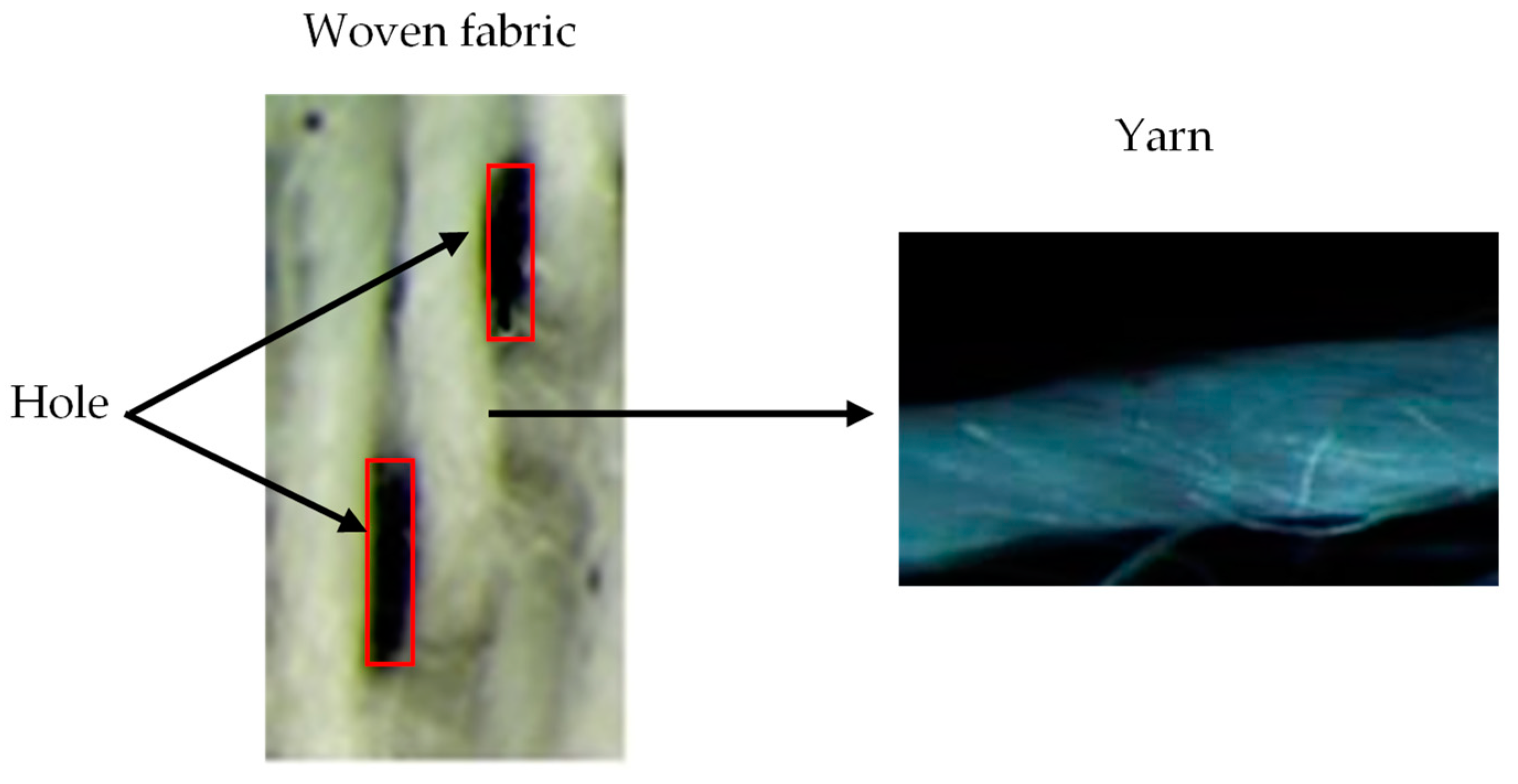
2.3. Yarns Properties and MPP Structure
3. Methods
3.1. Geometrical Characterization
3.2. Flow Resistance Measurement
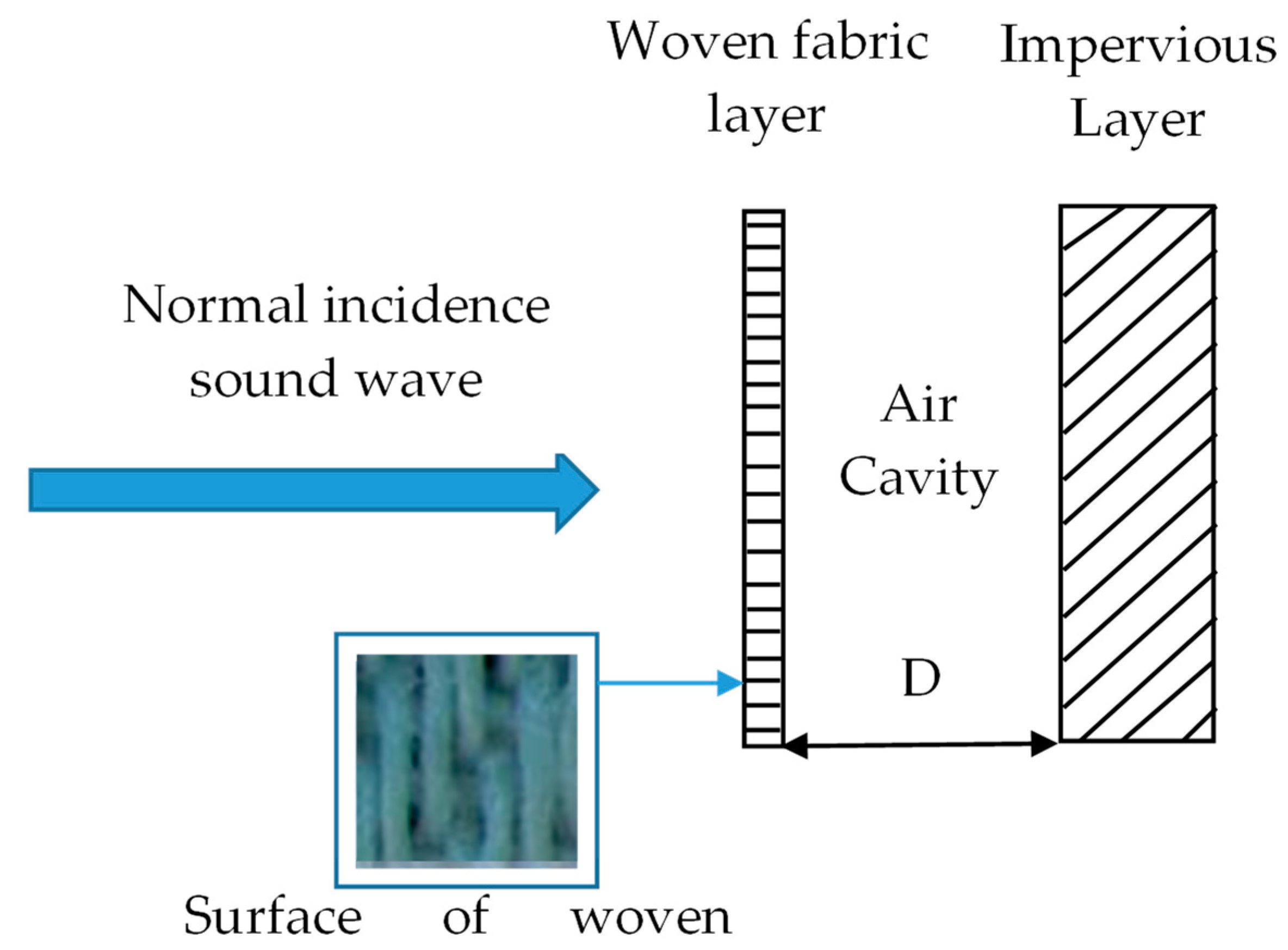
3.3. Acoustic Characterization
4. Results and Discussions
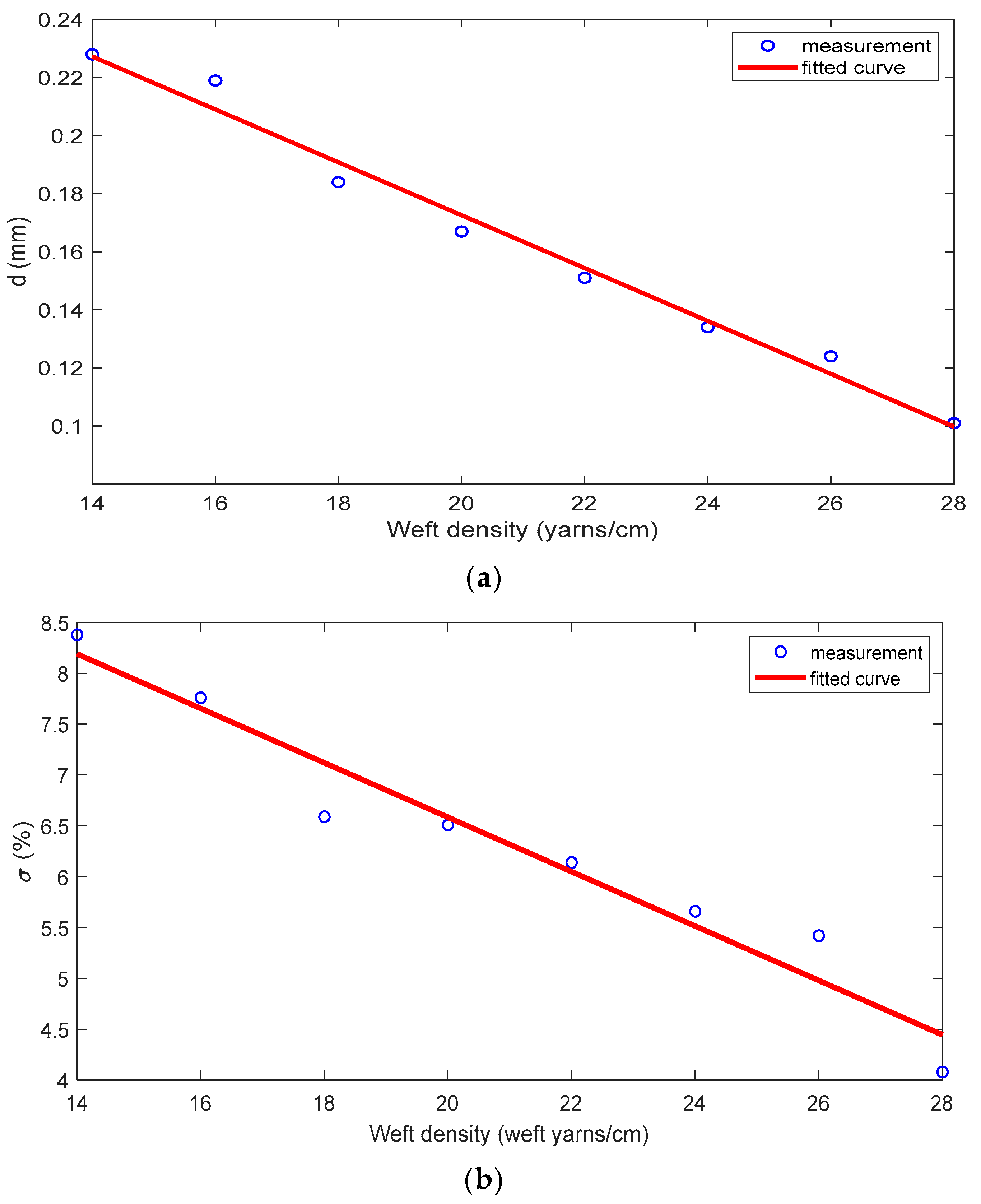
4.1. Relationship of Weft Density and Hole Diameter
4.2. Flow Resistance Characteristics
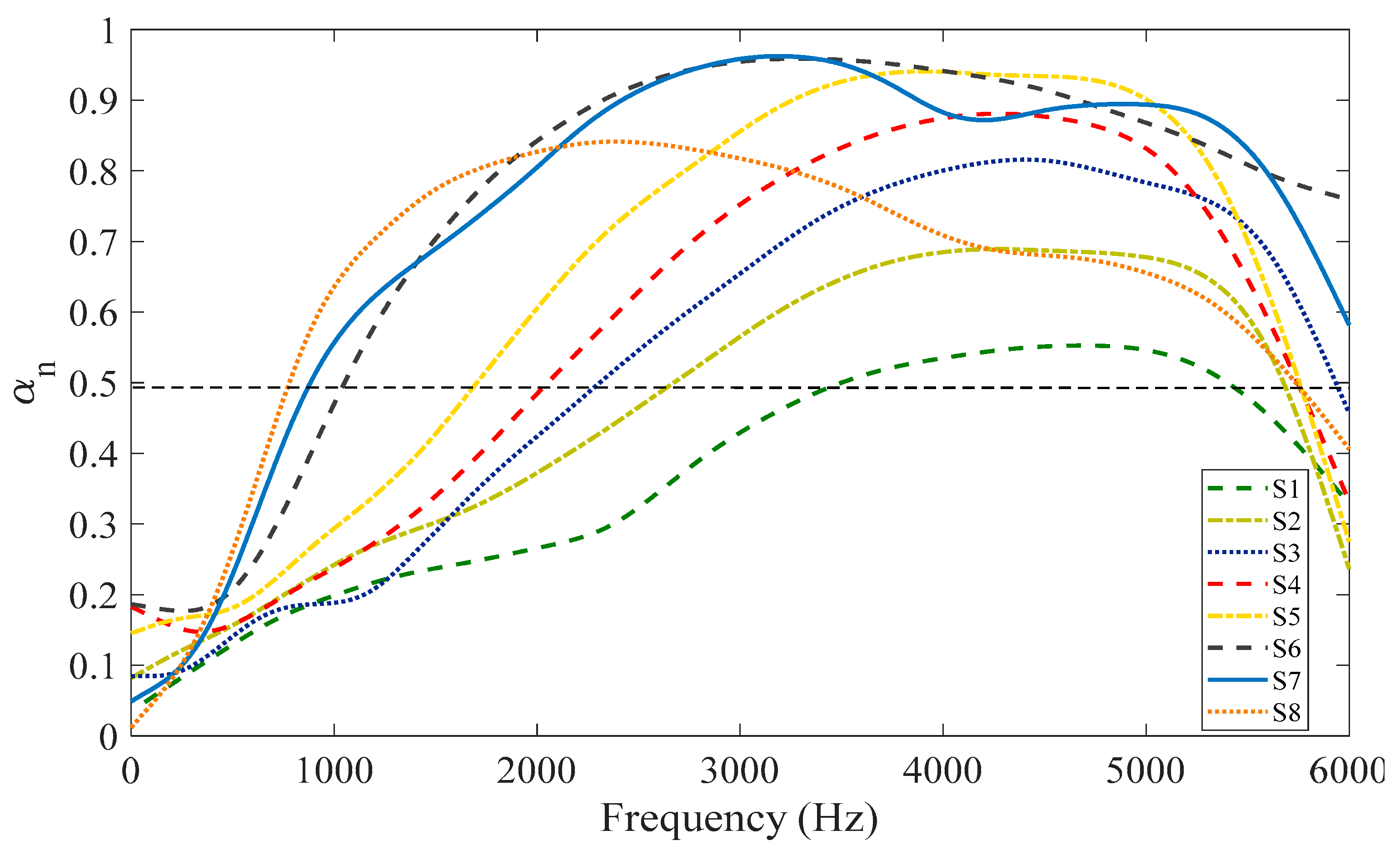
4.3. Absorption Characteristics
4.3.1. Perforation Variation
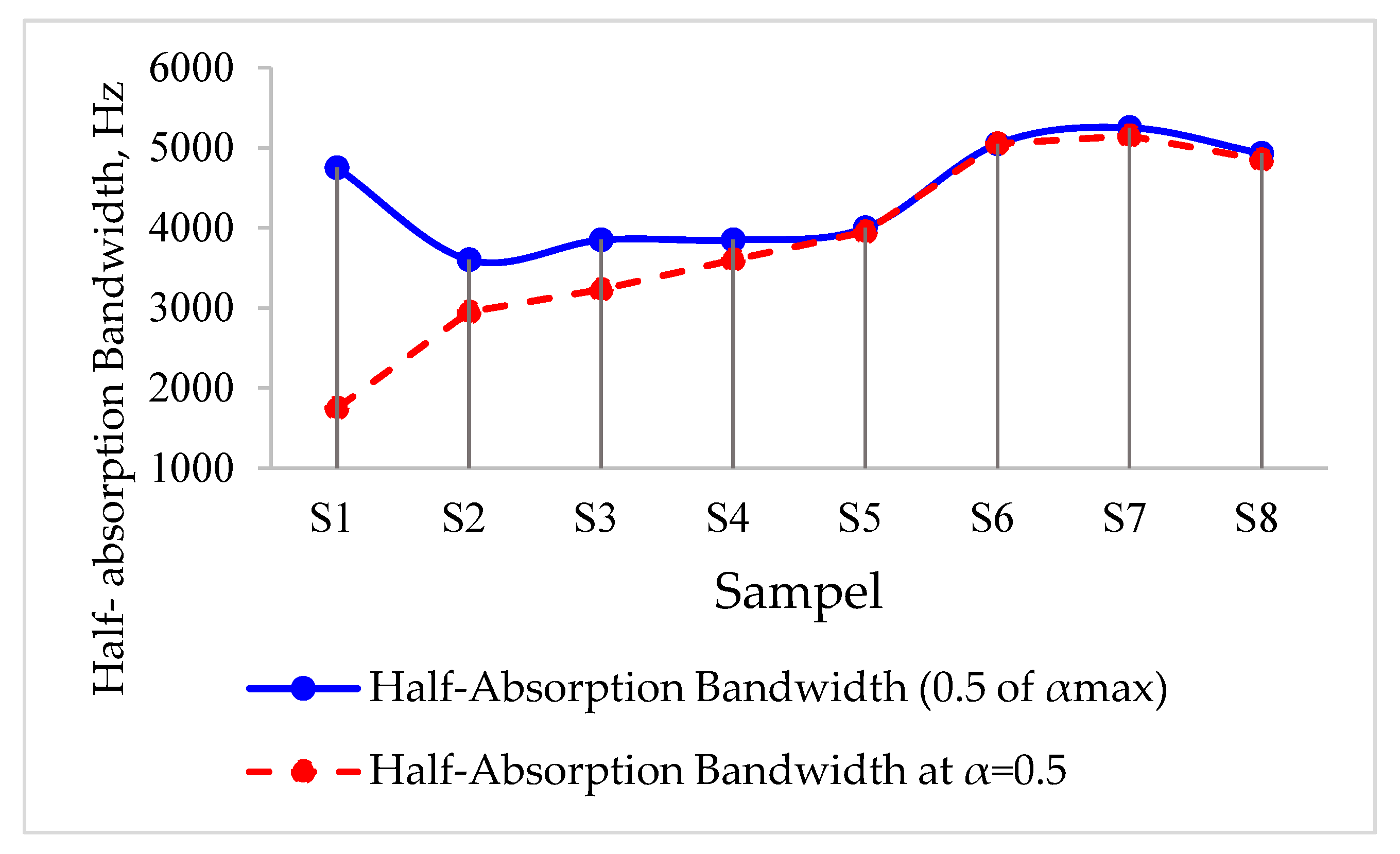
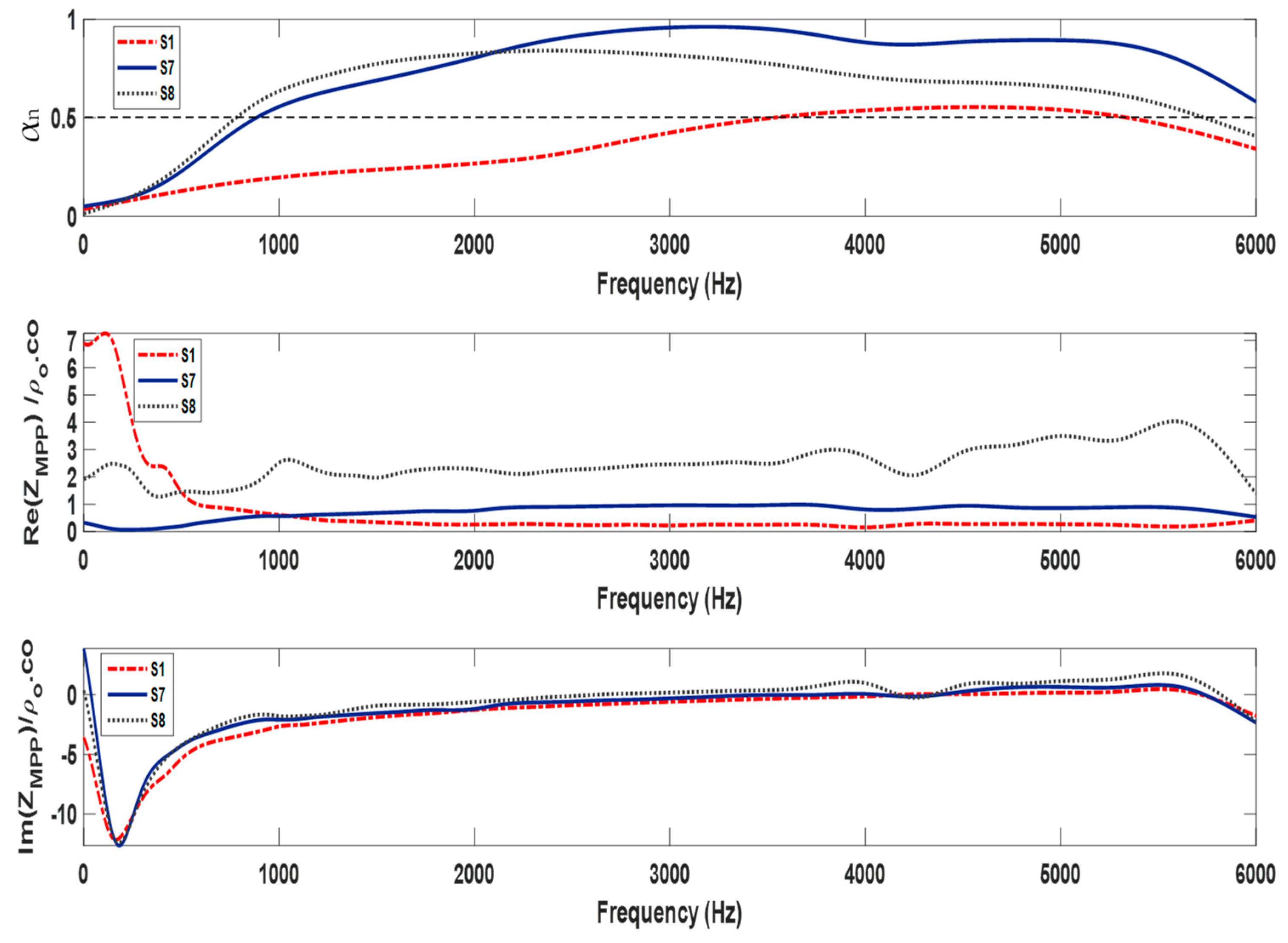
4.3.2. Surface Impedance Behavior
5. Comparison with Existing Theory
5.1. Absorption Mechanism
5.2. Theoretical Model
5.3. Validation Results
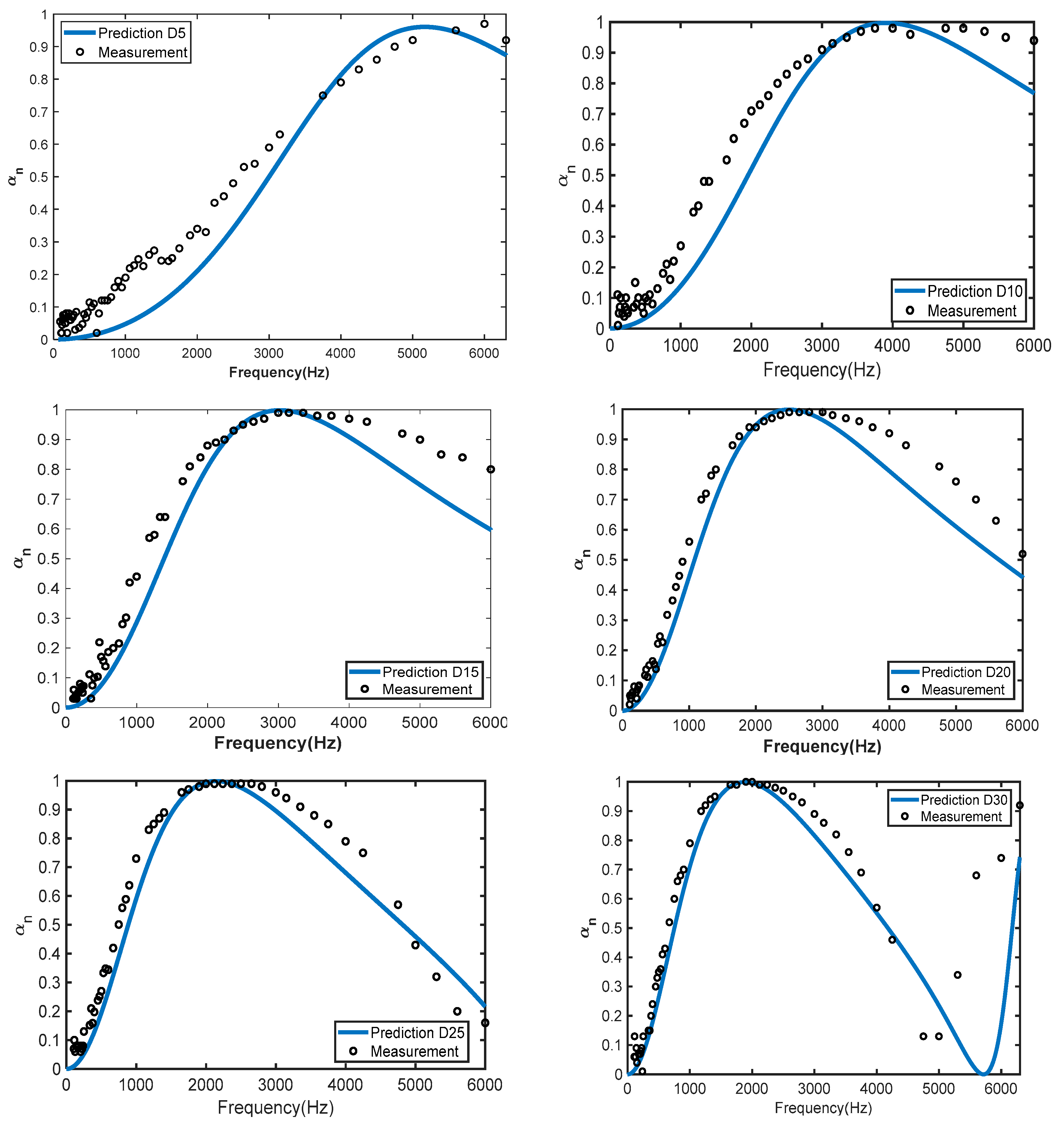
5.3.1. Effect of Backing Air Cavity Depth
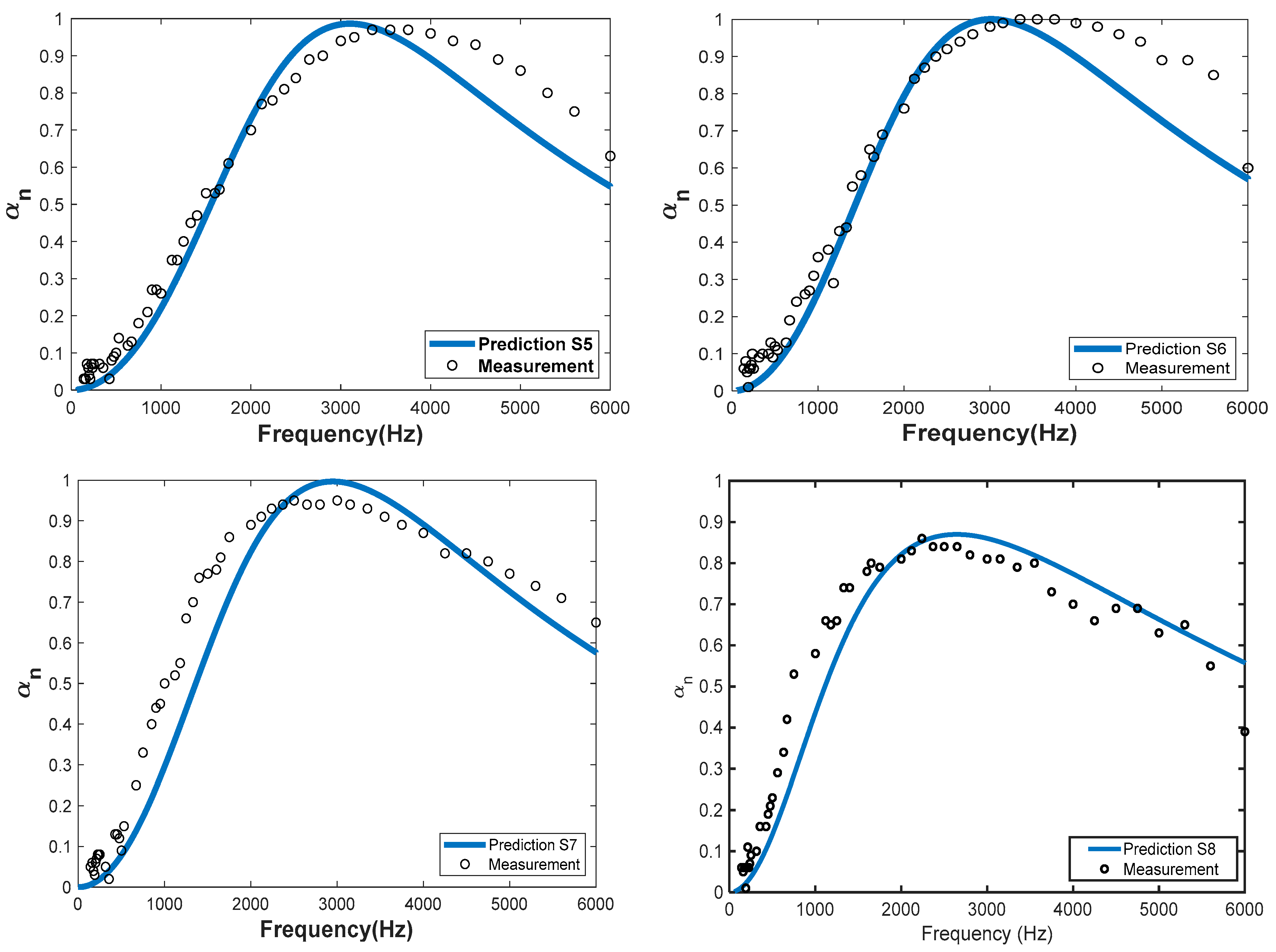
5.3.2. Effect of perforation ratio
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fuchs, H.V.; Zha, X. Acrylic-glass sound absorbers in the plenum of the deutscher bundestag. Appl. Acoust. 1997, 51, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwono, J.; Prasetiyo, I.; Andreas, S.; William, A. The Design of MPP and its Application to Enhance the Acoustics of a Real Auditorium. In Proceedings of the INTER-NOISE and NOISE-CON Congress and Conference Proceedings Internoise, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi, K.; Hanyu, T.; Okuzono, T.; Sakagami, K.; Yairi, M.; Harada, S.; Takahashi, S.; Ueda, Y. Implementation experiment of a honeycomb backed MPP sound absorbing panel in a meeting room. In Proceedings of the 25th International Congress on Sound and Vibration, Hiroshima, Japan, 8–12 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Herrin, D.W.; Seybert, A.F. Application of Micro-Perforated Panels to Attenuate Noise in a Duct; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cobo, P.; Ruiz, H.; Alvarez, J. Double-Layer Microperforated Panel/Porous Absorber as Liner for Anechoic Closing of the Test Section in Wind Tunnels. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2010, 96, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maa, D.-Y. Potential of microperforated panel absorber. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1998, 104, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maa, D.-Y. Microperforated Panel Wideband Absrbers. Noise Control. Eng. J. 1987, 29, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, Q.; Kang, L.; Liu, B. Design of Multiple Parallel-Arranged Perforated Panel Absorbers for Low Frequency Sound Absorption. Materials 2019, 12, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verdière, K.; Panneton, R.; Elkoun, S.; Dupont, T.; Leclaire, P. Prediction of acoustic properties of parallel assemblies by means of transfer matrix method. Proc. Mtgs. Acoust. 2013, 19, 065011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.J.; Zhang, J.; Sun, N.; Kong, D.Y.; Zhang, X.X. Pilot study on wideband sound absorber obtained by adopting a serial-parallel coupling manner. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 124, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakagami, K.; Kobatake, S.; Kano, K.I.; Morimoto, M.; Yairi, M. Sound absorption characteristics of a single microperforated panel absorber backed by a porous absorbent layer. Acoust. Aust. 2011, 39, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhan, J.; Fard, M.; Davy, J.L. Acoustic measurement of a 3D printed micro-perforated panel combined with a porous material. Measurement 2017, 104, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraj, L.; Jeyanthi, S.; Mailan Chinnapandi, L.B. Sound absorption of Multilayer Micro perforated Panel with Helmholtz Resonator Mount. In Proceedings of the INTER-NOISE and NOISE-CON Congress and Conference Proceedings, Madrid, Spain, 16–19 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gai, X.-L.; Xing, T.; Cai, Z.-N.; Wang, F.; Li, X.-H.; Zhang, B.; Guan, X.-W. Developing a microperforated panel with ultra-micro holes by heat shrinkable materials. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 152, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.J.; Kong, D.Y.; Liu, S.M.; Sun, S.M.; Zhao, Z. Investigation on micro-perforated panel absorber with ultra-micro perforations. Appl. Acoust. 2013, 74, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.J.; Kong, D.Y.; Fei, J.T. A note on the fabrication methods of flexible ultra micro-perforated panels. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 90, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, P.; Montero de Espinosa, F. Proposal of cheap microperforated panel absorbers manufactured by infiltration. Appl. Acoust. 2013, 74, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.J.; Cui, K.; Liu, S.M.; Li, Z.B.; Kong, D.Y.; Sun, S.M. Development of broadband ultra micro-perforated panels based on MEMS technology. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 535, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.H.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, L.J.; Du, L.D.; Xiao, L.; Fang, Z.; Zhao, J.J.; Xuan, Y.D. Two Fabrication Schematics of Silicon Micro Perforated Panel Based on MEMS Technology. Key Eng. Mater. 2012, 503, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, H.; Cobo, P.; Dupont, T.; Martin, B.; Leclaire, P. Acoustic properties of plates with unevenly distributed macroperforations backed by woven meshes. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 132, 3138–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, X.; Kong, D.; Yan, X. Facile dip-coating method to prepare micro-perforated fabric acoustic absorber. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 130, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Kong, D.; Yan, X. Multiple regression analysis of a woven fabric sound absorber. Text. Res. J. 2018, 89, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieren, R. Sound absorption modeling of thin woven fabrics backed by an air cavity. Text. Res. J. 2012, 82, 864–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieren, R.; Heutschi, K. Predicting sound absorption coefficients of lightweight multilayer curtains using the equivalent circuit method. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 92, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieren, R.; Schäffer, B.; Schoenwald, S.; Eggenschwiler, K. Sound absorption of textile curtains—Theoretical models and validations by experiments and simulations. Text. Res. J. 2016, 88, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetiyo, I.; Muqowi, E.; Putra, A.; Novenbrianty, M.; Desendra, G.; Adhika, D.R. Modelling sound absorption of tunable double layer woven fabrics. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 157, 107008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetiyo, I.; Desendra, G.; Hermanto, M.N.; Andhika, D.R. On Woven Fabric Sound Absorption Prediction. Arch. Acoust. 2018, 43, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onursal, O.; Mehmet, C. Design of a single layer micro-perforated sound absorber by finite element analysis. Appl. Acoust. 2010, 71, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Desendra, G.; Prasetiyo, I.; Hermanto, M.N.; Andhika, D.R. Experimental investigation of fabric-based micro perforated panel absorber. In Proceedings of the Regional Conference on Acoustics and Vibration 2017 (RECAV 2017), Bali, Indonesia, 27–28 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 5084; Textiles—Determination of Thickness of Textiles and Textiles Products. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996.
- Tang, X.; Jeong, C.-H.; Yan, X. Prediction of sound absorption based on specific airflow resistance and air permeability of textiles. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 144, EL100–EL104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ISO 10534-2; Acoustics—Determination of Sound Absorption Coefficient and Impedance in Impedances Tubes. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001.
- Hunter, L.; Fan, J. 11—Waterproofing and breathability of fabrics and garments. In Engineering Apparel Fabrics and Garments; Fan, J., Hunter, L., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 283–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkowska, D.; Kaleta, A. Structure and Properties of Microporous Polyurethane Membranes Designed for Textile-Polymeric Composite Systems. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2005, 13, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.J.; Jeong, J.H.; Sohn, J.-Y. Sound absorption characteristics of PTFE membrane Material and their application to a multi-purpose stadium. Build. Serv. Eng. Res. Technol. 2009, 30, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razak, H.A.; Chua, C.S.; Toyoda, H. Weatherability of coated fabrics as roofing material in tropical environment. Build. Environ. 2004, 39, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens, J.; Zanelli, A. Structural Membranes for Refurbishment of the Architectural Heritage. Procedia Eng. 2016, 155, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chilton, J. 7—Tensile structures—Textiles for architecture and design. In Textiles, Polymers and Composites for Buildings; Pohl, G., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2010; pp. 229–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monjo-Carrió, J.; Tejera, J. 12—The use of textile materials for architectural membranes. In Fibrous and Composite Materials for Civil Engineering Applications; Fangueiro, R., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 325–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raleigh, J. Theory of Sound II; MacMillan: New York, NY, USA, 1929. [Google Scholar]
- Crandall, I.B. Theory of Vibration System and Sound; D.Van Nostrand Company: New York, NY, USA, 1926. [Google Scholar]
- Morse, P.M.; Ingard, K.U. Theoretical Acoustics; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; He, W.; Peng, X.; Xin, F.; Lu, T.J. Sound absorption theory for micro-perforated panel with petal-shaped perforations. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 148, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
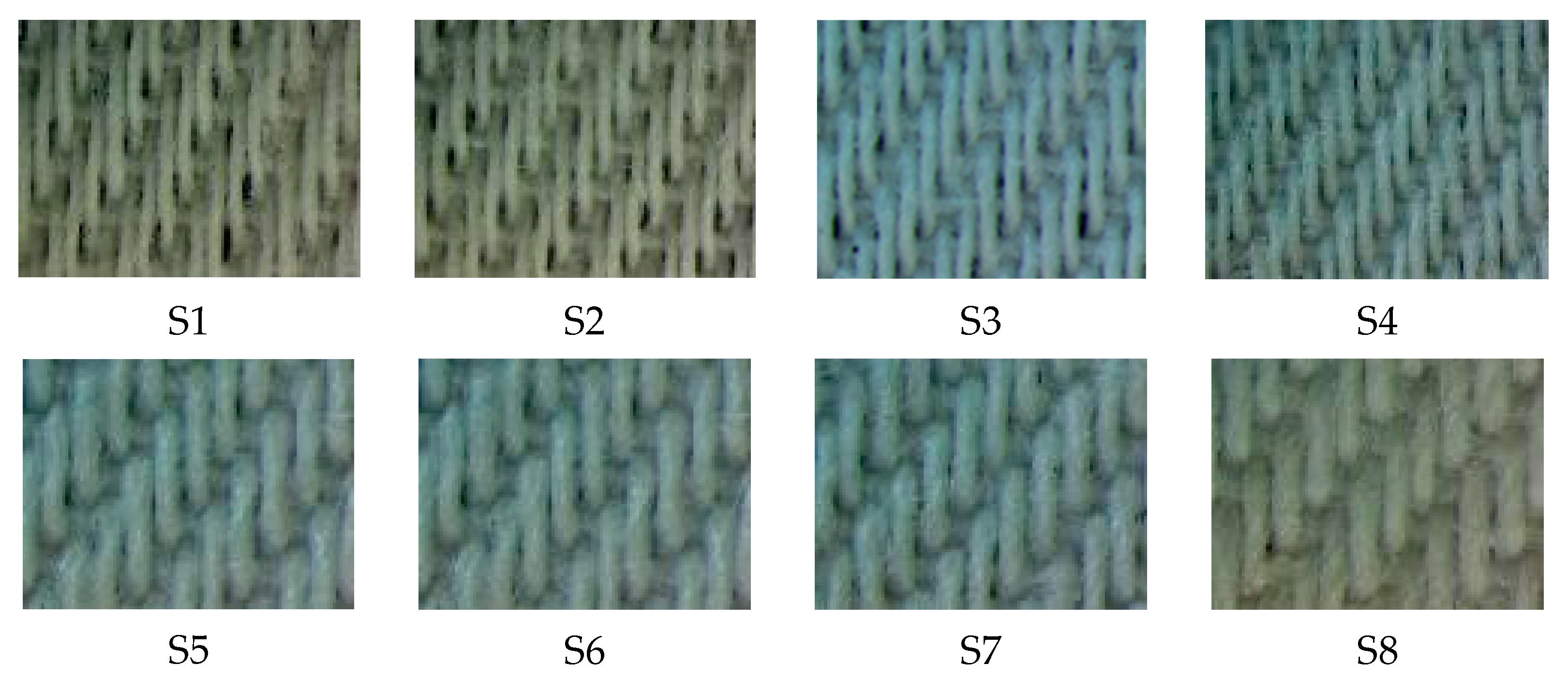


| Sample (S) | Warp Density (yarn/cm) | Weft Density (yarn/cm) |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | 39 | 14 |
| S2 | 39 | 16 |
| S3 | 39 | 18 |
| S4 | 39 | 20 |
| S5 | 39 | 22 |
| S6 | 39 | 24 |
| S7 | 39 | 26 |
| S8 | 39 | 28 |
| Sample (S) | Hole Diameter (d) (mm) | Perforation Ratio σ (%) (Equation (3)) |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.218 | 7.37 |
| S2 | 0.206 | 7.33 |
| S3 | 0.189 | 7.16 |
| S4 | 0.170 | 6.85 |
| S5 | 0.151 | 6.35 |
| S6 | 0.135 | 5.74 |
| S7 | 0.121 | 5.14 |
| S8 | 0.103 | 4.25 |
| Sample (S) | Hole Diameter (d) (mm) | Air Permeability (mm/s) | Airflow Resistance (Pa s/m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.218 | 1878 | 170.7 |
| S2 | 0.206 | 1477 | 217.1 |
| S3 | 0.189 | 1109 | 289.1 |
| S4 | 0.170 | 877.4 | 365.4 |
| S5 | 0.151 | 634.4 | 505.4 |
| S6 | 0.135 | 434.8 | 737.4 |
| S7 | 0.121 | 357.2 | 897.6 |
| S8 | 0.103 | 222.1 | 1443.7 |
| Samples | The peak of Sound Absorption Coefficient (αmax) | Half-Absorption Bandwidth | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Δα0.5, Hz (a) | α = 0.5, Hz (b) | ||
| S1 | 0.55 | 4750 | 1750 |
| S2 | 0.70 | 3600 | 2950 |
| S3 | 0.84 | 3850 | 3230 |
| S4 | 0.89 | 3850 | 3600 |
| S5 | 0.95 | 4000 | 3950 |
| S6 | 0.96 | 5050 | 5050 |
| S7 | 0.98 | 5250 | 5150 |
| S8 | 0.86 | 4930 | 4850 |
| Samples | Difference of Hole Diameter (mm) | Percentage of the Peak Difference of Sound Absorption Coefficient (%) | Percentage of a Difference the Half-Absorption Bandwidth, Δα0.5 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1–S2 | 0.012 | 27 | 69 |
| S1–S3 | 0.029 | 53 | 85 |
| S1–S4 | 0.047 | 62 | 106 |
| S1–S5 | 0.066 | 73 | 126 |
| S1–S6 | 0.083 | 75 | 189 |
| S1–S7 | 0.097 | 78 | 194 |
| S1–S8 | 0.115 | 56 | 177 |
| Sample | RMSE | Sample | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| D5 | 0.17 | D20 | 0.07 |
| D10 | 0.10 | D25 | 0.07 |
| D15 | 0.09 | D30 | 0.14 |
| Sample | RMSE | Sample | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.06 | S5 | 0.07 |
| S2 | 0.05 | S6 | 0.08 |
| S3 | 0.06 | S7 | 0.11 |
| S4 | 0.06 | S8 | 0.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gunawan; Prasetiyo, I.; Yuliarto, B.; Putra, A.; Irianto. Investigation on Minute Holes of Woven Fabrics for Wide-Band Micro-Perforated Sound Absorbers. Buildings 2023, 13, 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13030663
Gunawan, Prasetiyo I, Yuliarto B, Putra A, Irianto. Investigation on Minute Holes of Woven Fabrics for Wide-Band Micro-Perforated Sound Absorbers. Buildings. 2023; 13(3):663. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13030663
Chicago/Turabian StyleGunawan, Iwan Prasetiyo, Brian Yuliarto, Azma Putra, and Irianto. 2023. "Investigation on Minute Holes of Woven Fabrics for Wide-Band Micro-Perforated Sound Absorbers" Buildings 13, no. 3: 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13030663
APA StyleGunawan, Prasetiyo, I., Yuliarto, B., Putra, A., & Irianto. (2023). Investigation on Minute Holes of Woven Fabrics for Wide-Band Micro-Perforated Sound Absorbers. Buildings, 13(3), 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13030663








