Abstract
With the benefits of reduced travel time and alleviated traffic congestion, tunnel construction significantly enhances urban mobility. Meanwhile, tunnel construction accidents result in many casualties and property losses. To minimize accidents associated with tunnel construction while keeping its benefits, it is important to enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of training programs for construction workers. However, there is a lack of training evaluation systems specifically designed for tunnel construction workers, along with limited research on the effectiveness and efficiency of training programs for this group. This paper targets personnel from the China Railway 14th Bureau Group Company, aiming to evaluate a training program designed for tunnel construction workers. Three popular training approaches are proposed to evaluate the effectiveness and efficiency of training outcomes, including WeChat push safety construction knowledge (WP), the emergency drill (ED), and the unitive lecture (UL). Additionally, a concept of study is conducted to examine the performance of the proposed approaches in eighteen schemes that vary at different levels of training intensity by using VR (virtual reality), an electroencephalogram (EEG) system, and data enveloping analysis (DEA). The results show that the ED is the most effective training method, enabling industry professionals to respond effectively to unsafe situations by equipping them with critical skills through comprehensive training. Additionally, the ED has great potential for training tunnel construction workers via the provision of simulated experiences to enhance their safety preparedness.
1. Introduction
Safety concerns have been increasing for construction workers in the industry over the past few years [1,2,3]. It has been reported that one in every six fatal workplace accidents is associated with construction [4], where approximately 60,000 construction workers die annually while working on construction sites [5]. Additionally, a huge number of economic losses come from non-fatal construction accidents [6]. Tunnel construction safety remains a significant concern, which is constrained by factors including geological environments, sophisticated technology, construction techniques, and other influential factors when compared to surface projects. Many types of workers (i.e., steel workers, scaffolders, and machine operators) participate in construction sites, categorizing distinct risks that highly rely on different environments, locations, and times of day [7]. As a result of these considerations, more frequent and severe accidents in tunnel construction sites are caused than in other construction areas [8,9,10].
An abundance of studies have identified contributing factors for tunnel construction accidents, including challenging construction environments [11], complicated geological conditions [12,13], the organization and administration of the construction [14], etc., to ensure tunnel construction safety. Meanwhile, workers’ misbehavior has been verified as contributing significantly to construction accidents, accounting for about 80% of accidents [15,16]. Yang et al. explored the primary sources of risks in tunnel construction and their relationships, using grounded theory, the DEMATEL model, and structural equation modeling [8,17]. The research findings indicated that besides natural conditions, construction workers significantly contribute to tunnel construction accidents. The study of Petersen et al. highlighted the need to mitigate risky behaviors by employing effective training and management strategies that improve workers’ skills and safety awareness [18]. Therefore, it is important to pay more attention to personnel-related factors and prioritize improvements to enhance safety performance and minimize major losses [2,7,19]. Zielke et al. identified the potential of VR to the Texas Department of Transportation employees’ training and found that VR works well for workforce training [20]. Qing et al. designed an interactive VR training module for a work-zone flagger training course, and the results showed that it had great performance [21]. Park et al. incorporated VR into a training simulator for training transporter operators [22].
Management strategies to enhance workers’ safety management are categorized into four types; they are the employment of safety plans [23], ongoing education and training [24], focused emergency or accident response measures [25,26], and behavior-based safety (BBS) management [27]. Among these, providing training for tunnel construction workers is essential for improving their skill levels, safety awareness, and problem-solving skills. It results from the fact that many hotspot construction areas may not achieve safety levels solely through management and/or on-site learning. As a result, comprehensive safety training is important for equipping construction workers with professional knowledge and skills that are needed to proactively address potential risks [28]. Hasan Basri Başağa conducted a survey regarding construction workers’ needs in Turkey, and the results showed that 92.27% of workers required systematical occupational health and safety training or routine occupational health and safety training [29]. Meanwhile, employee training is the most important way to enhance occupational health and safety; it is necessary for all employees, regardless of their education level or age, to engage in practical training. The study of Tran et al. showed that the length of safety training and experience impacts an individual’s proficiency in recognizing hazardous environments [30]. Therefore, the effectiveness and efficiency of safety training for tunnel construction remains a critical concern, and Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) demonstrates a thorough, consistent, and effective training approach. It has been further investigated that proper training materials and methodologies can improve workers’ awareness of the potential hazards and dangerous situations in construction sites [31]. However, there is very little literature focused on evaluating the effectiveness and efficiency of training programs in transportation, especially for tunnel construction workers.
Dudley defined two types of training styles, including pedagogical and andragogical ones [32]. The pedagogical style is driven by external motivations such as competition and the fear of failure, while the andragogical style is characterized by self-directed learning, self-worth, recognition, and confidence. Although both of them have their unique benefits, it is unclear which style proves to be more effective in China. According to Han et al., low skill levels, inadequate technical knowledge, and a steep learning curve hinders construction workers’ safety performance [33]. To address the first two issues, effective training techniques should be introduced. At the same time, enhancing the efficiency of safety training aims to tackle the steep learning curve. Furnham suggested that adverse factors such as economic recession and limited training budgets impact safety training provided to construction workers [34]. A key challenge in addressing these constraints is finding ways to enhance training efficiency while working within these limited resources. However, the majority of studies for construction training only focus on identifying different safety training approaches and techniques [35,36,37,38,39] and exploring training outcomes for construction workers [40,41,42]. The existing literature on the efficacy and efficiency of training approaches is insufficient.
It is critical to investigate proper training techniques and efficient training schemes to enhance training outcomes for tunnel construction workers. This will lead to reduced costs in tunnel construction and the smooth progression of tunnel projects and has potential to bridge the effectiveness and efficiency gaps found in other construction safety training approaches. The literature lacks evaluation systems to determine whether construction personnel have adequate safety awareness and knowledge necessary for tunnel construction. Research has shown that virtual reality (VR) training enables workers to encounter risky tasks without facing real safety threats, making it a safe and economical training solution [43]. VR technology has been widely used in training construction workers [44,45,46]. The data envelopment analysis (DEA) method can be used to assess the input/output efficiency of an economic system that generates various outputs under multiple input resources and was first applied to the assessment of economic efficiency. The benefits include its ability to compute the relative efficiency of multiple input/output decision units, the elimination of the necessity to establish the index weight, and there being no need to carry out the normalized processing of line dimension [47]. Following its introduction, DEA has become a powerful method for assessing system operation efficiency. Consequently, it has found widespread application in evaluating input and output efficiency across numerous industries, including operational cost management [48], transportation [49,50,51], and healthcare [52,53,54].
Therefore, to overcome the limitations of current training evaluation systems, an innovated, integrated evaluation system that incorporates VR, an EEG, and DEA is proposed in this paper to assess the effectiveness and efficiency of training programs for tunnel construction workers. Three training methods, including WeChat push safety updates (WP), emergency drills (ED), and unitive lectures (UL), are implemented across eighteen training schemes within this program to identify how training intensity impacts the effectiveness of different types of training methods. Three research questions are raised as follows:
- (1)
- Do WP, ED, and UL work well within the training program? Which method has the best performance?
- (2)
- How do the three training methods work at different levels of training intensity?
- (3)
- Considering the limited training resources, how should safety training be implemented for tunnel construction workers in real engineering projects?
2. Methodology
All targeted training personnel were employees from the China Railway 14th Bureau Group Company. Prior to the start of the training program, the company provided an explanation of the research goals and assured the participants that all data would remain confidential and be used solely for research purposes. Each recruited participant signed a consent form before the official experiment began. All participants had been employed by the company for over a year (typically 12 to 14 months) but had not yet participated in tunnel construction projects.
Three pre-job training methods were chosen in this paper due to their proven effectiveness in enhancing professional skills, including WP, ED, and UL, as shown in Figure 1. Each method addresses different aspects of training for tunnel construction personnel, where WP is regarded as a widely used communication method, allowing for the timely dissemination of training materials and safety instructions, the ED provides simulated scenarios that enhance safety preparedness, and the UL delivers structured safety information to ensure a comprehensive understanding among personnel.

Figure 1.
Three chosen pre-job training methods.
The first method was WP, where safety information, guidelines, and accident reports were shared via WeChat by using graphics and short videos for easy access. The targeted training personnel had to screenshot and share the content in a WeChat group, with regular updates such as those occurring daily and every two days. The ED simulated real construction scenarios to improve emergency response skills, focusing on risks like personnel rescue and equipment failure. Sessions lasted from half a day to a full day, conducted once or twice a month in a realistic simulation tunnel environment. The UL presented structured safety information to the tunnel construction workers, covering emergency care, accident prevention, and protocols. Each two-hour lecture used case studies and videos, held one to three times a month and led by qualified trainers. After a month of systematic training, which was from 6 June 2021 to 6 July 2021, 227 employees (average age: 42; standard deviation: 10.2) successfully completed the company’s training requirements, resulting the development of 18 training schemes, as indicated in Table 1.

Table 1.
Tunnel construction personnel safety training schemes.
An electroencephalogram (EEG) system and VR equipment were used in this paper to evaluate the effectiveness of the three training methods across the eighteen schemes for the tunnel construction workers, as shown in Figure 2. The EEG system played an important role in evaluating the training outcomes by capturing the brainwave activity of the participants during various training sessions. Specifically, EEG waves were utilized to generate data that reflected the cognitive and emotional responses of the construction workers, providing insights into how effectively they were absorbing and retaining safety information. The raw EEG data collected from the participants were imported into MATLAB for comprehensive data processing and analysis. Additionally, VR equipment was employed to simulate realistic tunnel construction environments, enabling the participants to engage in immersive scenarios that mimicked potential risks and hazards they may encounter on the job.
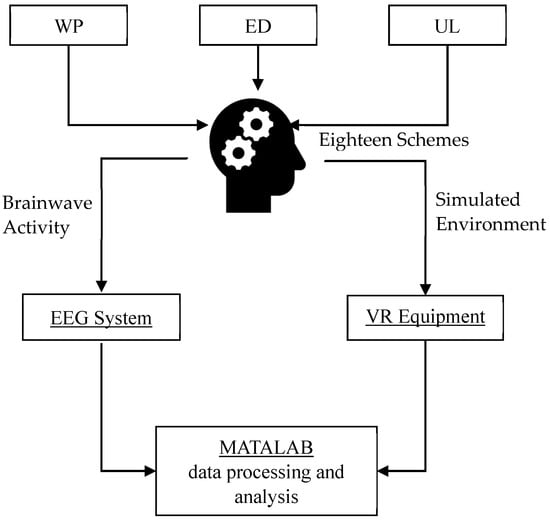
Figure 2.
Methodological framework.
Data envelopment analysis (DEA), introduced by Charnes et al. in 1978, is a non-parametric assessment technique that utilizes a mathematical programming model to evaluate the relative efficiency of departments or decision-making units (DMUs) with multiple inputs and outputs. DEA can be classified into two models: the BCC model, which accounts for variable returns to scale (where the output does not increase proportionally with the input), and the CCR model, which assumes constant returns to scale (where the output increases directly in proportion to the input). The BCC model was incorporated into the DEA model, in order to promote the effectiveness of training outcomes. The training intensity of the three training methods (WP, ED, and UL) were the input indices, while three indicators served as the output indices, including the SQ, IT, and EEG alpha-value. The average values of the measurement indicators from all participants were used as the three output index values across the eighteen decision schemes. For the WP indicator, the DEA model converted daily input data, ranging from 1 to 3 times per day, into monthly values of 30, 15, and 10 times, respectively. This adjustment reflected that higher values of the input and output indicators signified greater efficiency. Additionally, to transform the IT output indicator from a negative scale (where smaller values are preferred) to a positive scale (where larger values are better), we used a formula that calculated the percentage of remaining time after identifying a hazard, which represented the true value of the modified indicator. The data conversion is described below.
Here, represents the original data of the time it took for the construction workers to identify the risk source and represents the data after they were transformed into a positive indicator. Since each scene in this experiment lasted for two minutes, the theoretical maximum and minimum identification times were 120 s and 0 s, respectively. Consequently, max and min are defined as these two values. Table 2 displays the data that were entered into the DEA model.

Table 2.
Input and output indicators’ values of eighteen DMUs.
3. Results and Discussion
Table 3 lists the training outcomes for the participants across the three training methods after the three training methods were implemented across the eighteen training schemes. The p values for all training methods were less than 0.05, indicating their effectiveness on training outcomes. Among them, the ED had an F-value of 115.529 and an effect size of 0.354. The WP had an F-value of 17.023 and an effect size of 0.139. The UL had an F-value of 34.148 and an effect size of 0.254. The effectiveness of the training methods ranked from highest to lowest were the ED, UL, and WP, with higher F-values and effect sizes indicating greater positive impacts on the training outcomes. The results suggest that the ED and UL increased safety awareness of the tunnel construction workers in identifying risks, leading to improved risk detection and related remedies.

Table 3.
Significance analysis of training modes to EEG α-value.
The indicators, including the comprehensive technical efficiency (TE), pure technical efficiency (PTE), scale efficiency (SE), output changes with scale (VOWS), input redundancy (IR), and output redundancy (OR), across eighteen decision-making units (DMUs) are listed in Table 4; these are outputs from after running the DEAP 2.1 program. The values of the TE, PTE, and SE range from 0 to 1. The TE measures a DMU’s overall efficiency, incorporating both the SE and PTE. A TE value of 1 indicates the maximum output given current inputs, while a value below 1 suggests potential for increased efficiency. The PTE evaluates a DMU’s production efficiency under the assumption of an optimal size, ignoring size effects. It assesses the effective use of inputs based on existing technology and management, with a maximum value of 1 indicating optimal resource utilization. The SE measures how well a DMU is leveraging economies of scale. An SE value of 1 signifies that the scale is ideal, while a value below 1 suggests that the scale may be either too large or too small for optimal effectiveness.

Table 4.
DEA of eighteen training schemes.
Out of the eighteen DMUs in this paper, only the third, sixth, eighth, eleventh, and twelfth were found to be inefficient (TE < 1). This indicates that these five schemes could not achieve optimal training outcomes at the current intensity. Among them, the eleventh scheme showed potential for improvement in both the PTE and SE due to their values being very close to 1, suggesting that an enhanced training efficiency could be achieved by adjusting the scale and input ratios of the three training methods. Since its VOWS indicate decreasing returns to scale (drs), its training efficiency could be improved by reducing investment.
Additionally, the OR value for schemes 8 and 11 were more than 0, whereas all other schemes had an OR value equal to 0. To improve training outcomes for scheme 8, it is recommended to increase training satisfaction among tunnel construction personnel by 0.43 points and decrease the time spent on identifying risk training by 2.5%, and the EEG α-value should increase by 7.23 when identifying risk factors based on the available IR. For scheme 11, achieving optimal efficiency requires an increase in training satisfaction by 0.38 points. These findings suggest that training intensity could be optimized by reducing the frequency of ULs from twice a month to once a month for scheme 8 and, similarly, by decreasing the frequency of EDs and/or ULs from twice a month to once a month for scheme 11.
Therefore, employee safety throughout the tunnel construction process can be greatly increased by providing rational pre-job training. The effectiveness of the three training methods from high to low for Chinese tunnel construction workers are the ED, the UL, and WP.
Therefore, after providing participants from the China Railway 14th Bureau Group Company with eighteen various types of training schemes varying in severity, future research directions could involve conducting a VR simulation experiment and providing EEG systems focused on risk detection for other construction facilities to investigate the effectiveness of the three training methods across varied training schemes, such as signalized intersections and ramps
4. Conclusions
Pre-job training plays a crucial role in significantly enhancing employee safety during the tunnel construction process. For Chinese tunnel construction workers, three of the most prevalent training methods are emergency drills, unitive lectures, and WeChat push notifications that deliver essential safety knowledge tailored to tunnel construction. Emergency drills have emerged as the most effective training method due to their practical, hands-on approach and ability to simulate real-life scenarios that workers may encounter. Following closely in terms of effectiveness are unitive lectures, which provide clear and structured information while facilitating direct interaction between trainers and trainees. This engagement is crucial as it enhances the understanding and retention of safety rules and protocols. WeChat push notifications serve as a supplementary tool for reinforcing knowledge, yet they are less impactful compared to the other methods. While useful for delivering information, they lack the hands-on and interactive elements that are integral to effective learning.
By integrating these training approaches, particularly by prioritizing emergency drills and unitive lectures and incorporating digital tools, such as WeChat, for ongoing support, the build-up of a more knowledgeable and safety-conscious workforce in tunnel construction can be facilitated. This strategy not only enhances learning outcomes but also promotes a culture of safety that is very important for high-risk environments. The EEG system and VR equipment played an important role in evaluating the effectiveness of these training methods across the eighteen schemes for the tunnel construction personnel. The EEG system collected the brainwave activity of the participants when using the three training methods across the eighteen training schemes and generated EEG data that reflected the cognitive and emotional responses of the personnel. The participants wore VR equipment that simulated real tunnel construction environments, allowing them to experience realistic scenarios that reflected potential risks and hazards they might face on the job. The data collected from the EEG system and VR equipment were then input into MATLAB for detailed processing and analysis.
This paper further investigated the efficiency of eighteen different training schemes for tunnel workers using DEA. This analysis focused on three key efficiency measures, the TE, PTE, and SE, with values ranging from 0 to 1. The findings revealed that only five of the training schemes were inefficient, suggesting that there was considerable potential for improving the training effectiveness by adjusting the input scales and ratios.
Furthermore, specific schemes, particularly schemes 8 and 11, exhibited output redundancy. This indicates that these schemes could benefit from targeted enhancements to maximize their efficiency. Recommendations for their improvement include increasing training satisfaction among construction workers and optimizing processes related to risk identification. Implementing these adjustments could help these schemes reach the efficiency frontier, ultimately leading to safer working conditions and more effective training outcomes in tunnel construction.
The contributions of this paper are reflected in the following aspects:
- (1)
- This paper proposes an innovative integrated evaluation system that incorporates VR, the EEG system, and DEA to assess training effectiveness and efficiency for tunnel construction workers.
- (2)
- This paper explores how varying levels of training intensity affect the effectiveness of different training methods. This analysis contributes to a deeper understanding of how training can be tailored to enhance worker preparedness and safety in high-risk environments.
- (3)
- This paper provides practical strategies for implementing effective safety training for tunnel construction workers, particularly in the context of limited resources, offering valuable guidance for tunnel construction managers and safety officers.
Future research could focus on integrating both the EEG system and VR equipment for various training contexts, such as safe driving training and pavement construction worker training. By incorporating a driving simulator, VR experiments combined with EEG systems could be used to collect data on driving behaviors, particularly in relation to risk detection at facilities like signalized intersections and ramps.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.G. and Y.Y.; methodology, Y.Y.; validation, H.T., Y.Y. and W.L.; formal analysis, H.T.; investigation, H.T.; resources, Z.G.; data curation, Z.G.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.G.; writing—review and editing, H.T., Y.Y. and W.L.; visualization, H.T.; supervision, Y.Y. and W.L.; project administration, H.T., Y.Y. and W.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Zongyong Guo and Huadi Tao were employed by the company China Railway 14th Bureau Group Third Engineering Co., LTD. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Buniya, M.K.; Othman, I.; Sunindijo, R.Y.; Kineber, A.F.; Mussi, E.; Ahmad, H. Barriers to safety program implementation in the construction industry. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.D.; Guo, L.J.; Kim, J.; Xiong, S.P. Comparison of fatal occupational injuries in construction industry in the United States, South Korea, and China. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2019, 71, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, B.; Hu, Z.G.; Liu, Q.; Chen, S.; He, W.Q. Fatal accident patterns of building construction activities in China. Saf. Sci. 2019, 111, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A global alliance against forced labour. Int. Labour Rev. 2005, 144, 244–245.
- Wang, J.Y.; Zou, P.X.W.; Li, P.P. Critical factors and paths influencing construction workers’ safety risk tolerances. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2016, 93, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, Y.; Asilian-Mahabadi, H.; Hajizadeh, E.; Hassanzadeh-Rangi, N.; Bastani, H.; Behzadan, A.H. Factors influencing unsafe behaviors and accidents on construction sites: A review. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2014, 20, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.K.; Yang, S.J.; Liu, K.N.; Hua, K.C.; Yao, Q. Developing A Case-Based Reasoning Model for Safety Accident Pre-Control and Decision Making in the Construction Industry. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.; Easa, S.M.; Yan, X.B. Risk factors influencing tunnel construction safety: Structural equation model approach. Heliyon 2023, 9, e12924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.D.; Carlson, K. Occupational Safety Issues in Residential Construction Surveyed in Wisconsin, United States. Ind. Health 2014, 52, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhry, R.M. Behavior-based safety on construction sites: A case study. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2014, 70, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.Z.; Zhu, N.; Tian, Z.; Chen, Y.; Sun, B.H. Application of a trapezoidal fuzzy AHP method for work safety evaluation and early warning rating of hot and humid environments. Saf. Sci. 2012, 50, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; He, C.; Li, X.; Wang, B. Construction Schemes for Shallow and Asymmetrically Loaded Tunnels Crossing Below a Bridge. Int. J. Geomech. 2020, 20, 04020098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Peng, D.L.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, X.; He, C.Y.; Qi, X.; Zhao, K.Y.; Xiu, D.H.; Ju, N.P. Successful implementations of a real-time and intelligent early warning system for loess landslides on the Heifangtai terrace, China. Eng. Geol. 2020, 278, 105817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Ding, L.Y. Safety barrier warning system for underground construction sites using Internet-of-Things technologies. Autom. Constr. 2017, 83, 372–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriessen, J.H.T.H. Safe behaviour and safety motivation. J. Occup. Accid. 1978, 1, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Q.; Wu, X.Y.; Wang, X.Z.; Hu, S.H. Relationship between Social Capital, Safety Competency, and Safety Behaviors of Construction Workers. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2020, 146, 04020059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.; Easa, S.M.; Yan, X.B. Factors Affecting Road Tunnel Construction Accidents in China Based on Grounded Theory and DEMATEL. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, D.C. Human Error Reduction and Safety Management; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Moosa, M.H.; Oriet, L.P. Factors affecting safety performance in the construction industry: An empirical study using structural equation modelling. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2022, 28, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielke, M.; Zakhidov, D.; Defries, E.; Shringarpure, M.P.; Avila, R.; Keul, J.; Carpenterturner, D.; Hargrove, S.; Bateman, S.; Young, C. Using in situ research-based design to explore learning module effectiveness and usability in a virtual reality system for workforce training. Virtual Real. J. Virtual Real. Soc. 2024, 28, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Z.; Edara, P. Integrating Virtual Reality into Work Zone Flagger Training: Usability Analysis and Behavioral Assessment. Transp. Res. Rec. 2024, 2678, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-P.; Ham, S.-H.; Lee, W.-Y.; Yoo, B.-W. Development of transporter training simulator based on virtual reality and vehicle dynamics model. Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean. Eng. 2023, 15, 100547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Misra, S.C. Safety performance & evaluation framework in Indian construction industry. Saf. Sci. 2021, 134, 105023. [Google Scholar]
- Teo, E.A.L.; Ling, F.Y.Y.; Chong, A.F.W. Framework for project managers to manage construction safety. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2004, 23, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosly, I. Factors influencing safety performance in the construction industry of Saudi Arabia: An exploratory factor analysis. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2022, 28, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, F. Monitoring and Analysis of Construction Site Accidents by Using Accidents Analysis Management System in Turkey. J. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lu, M.J.; Hsu, S.C.; Gray, M.; Huang, T. Proactive behavior-based safety management for construction safety improvement. Saf. Sci. 2015, 75, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.F.; Gonzalez, V.A.; Yiu, T.W. The effectiveness of traditional tools and computer-aided technologies for health and safety training in the construction sector: A systematic review. Comput. Educ. 2019, 138, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basaga, H.B.; Temel, B.A.; Atasoy, M.; Yildirim, I. A study on the effectiveness of occupational health and safety trainings of construction workers in Turkey. Saf. Sci. 2018, 110, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, S.V.T.; Nguyen, T.L.; Chi, H.L.; Lee, D.; Park, C. Generative planning for construction safety surveillance camera installation in 4D BIM environment. Autom. Constr. 2022, 134, 104103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, Y. Occupational Safety and Health Administration Regulations. 2012. Available online: https://www.assembly.nl.ca/legislation/sr/regulations/rc120005.htm (accessed on 9 August 2024).
- Dudley, L. Andragogy vs. Pedagogy in Training. 2010. Available online: https://management.org/blogs/training-and-development/2010/03/30/andragogy-vs-pedagogy-in-training/ (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- Han, S.H.; Park, S.H.; Jin, E.J.; Kim, H.; Seong, Y.K. Critical Issues and Possible Solutions for Motivating Foreign Construction Workers. J. Manag. Eng. 2008, 24, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furnham, A. The Psychology Behavior at Work: The Individual in the Organization; Taylor & Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tay, J.; Safiena, S.; Lan, T.; Lim, M.S.; Goh, Y.M. Design for safety training for construction professionals: A digital game-based learning approach. Saf. Sci. 2024, 177, 106588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espina-Romero, L.C.; Franco, S.L.A.; Conde, H.O.D.; Guerrero-Alcedo, J.M.; Parra, D.E.R.; Ramírez, J.C.R. Soft skills in personnel training: Report of publications in scopus, topics explored and future research agenda. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Wong, M.O.; Pan, W. Virtual reality enhanced multi-role collaboration in crane-lift training for modular construction. Autom. Constr. 2023, 150, 104848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Shu, L.; Luo, X.W.; Yuan, M.Q.; Zheng, X.Z. Virtual reality technology in construction safety training: Extended technology acceptance model. Autom. Constr. 2022, 135, 104113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nykänen, M.; Puro, V.; Tiikkaja, M.; Kannisto, H.; Lantto, E.; Simpura, F.; Uusitalo, J.; Lukander, K.; Räsänen, T.; Heikkilä, T.; et al. Implementing and evaluating novel safety training methods for construction sector workers: Results of a randomized controlled trial. J. Saf. Res. 2020, 75, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Liu, Q.; Guo, X.; Xue, T.; Wang, Z. Identifying unsafe behaviors of construction workers through an unsupervised multi-anomaly GAN approach. Autom. Constr. 2024, 165, 105509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.W.; Luo, X.W. Differences between inexperienced and experienced safety supervisors in identifying construction hazards: Seeking insights for training the inexperienced. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2022, 52, 101602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teizer, J.; Cheng, T.; Fang, Y.H. Location tracking and data visualization technology to advance construction ironworkers’ education and training in safety and productivity. Autom. Constr. 2013, 35, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adami, P.; Rodrigues, P.B.; Woods, P.J.; Becerik-Gerber, B.; Soibelman, L.; Copur-Gencturk, Y.; Lucas, G. Effectiveness of VR-based training on improving construction workers’ knowledge, skills, and safety behavior in robotic teleoperation. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2021, 50, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akindele, N.; Taiwo, R.; Sarvari, H.; Oluleye, B.I.; Awodele, I.A.; Olaniran, T.O. A state-of-the-art analysis of virtual reality applications in construction health and safety. Results in Engineering 2024, 23, 102382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Dunston, P.S.; Proctor, R.W.; Wang, X.Y. Influence of training schedule on development of perceptual-motor control skills for construction equipment operators in a virtual training system. Autom. Constr. 2013, 35, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Shen, Q.C. Development and validation of a confined space rescue training prototype based on an immersive virtual reality serious game. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2022, 51, 101520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolghasemian, M.; Kanafi, A.G.; Daneshmand-Mehr, M. Simulation-Based Multiobjective Optimization of Open-Pit Mine Haulage System: A Modified-NBI Method and Meta Modeling Approach. Complexity 2022, 2022, 3540736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.A.; Salvador, C.V.M.; da Silva, A.V. Stochastic Data Envelopment Analysis applied to the 2015 Brazilian energy distribution benchmarking model. Decis. Anal. J. 2022, 3, 100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, J. Are electric vehicles more efficient? A slacks-based data envelopment analysis for European road passenger transportation. Energy 2023, 279, 128117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, H.T.K.; Asada, T.; Asada, T.; Arimura, M. Assessing transportation system efficiency in its relationship with urban housing: A data envelopment analysis. Asian Transp. Stud. 2022, 8, 100065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Gao, Y.; Li, M.J.; Wang, Y.M.; Liao, L.H. A new inverse data envelopment analysis approach to achieve China’s road transportation safety objectives. Saf. Sci. 2021, 142, 105362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Iqbal, A.; Zan, F.X.; Liu, X.M.; Dong, Z.J.; Jiang, C.C.; Chen, G.H. Integrated life cycle assessment with data envelopment analysis for enhancing medical waste management during a public health crisis. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 426, 139074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhwani, R.; Arya, A.; Jayaram, J. Greener healthcare operations during COVID-19 pandemic: A data envelopment analysis approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 452, 142043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.A.; Camanho, A.S. The ‘Healthcare Access and Quality Index’ revisited: A fuzzy data envelopment analysis approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 245, 123057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).