Structural Behaviour of FRP-Reinforced Tubular T-Joint Subjected to Combined In-Plane Bending and Axial Load
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Finite Element Simulation Steps
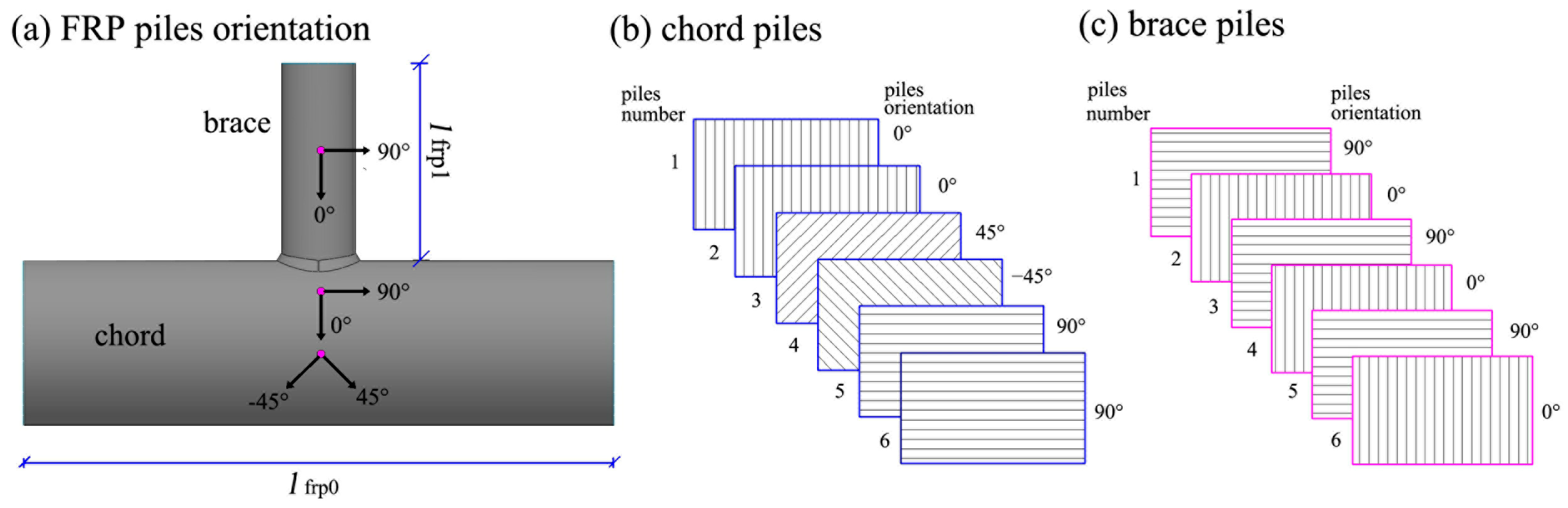
2.1. Modelling
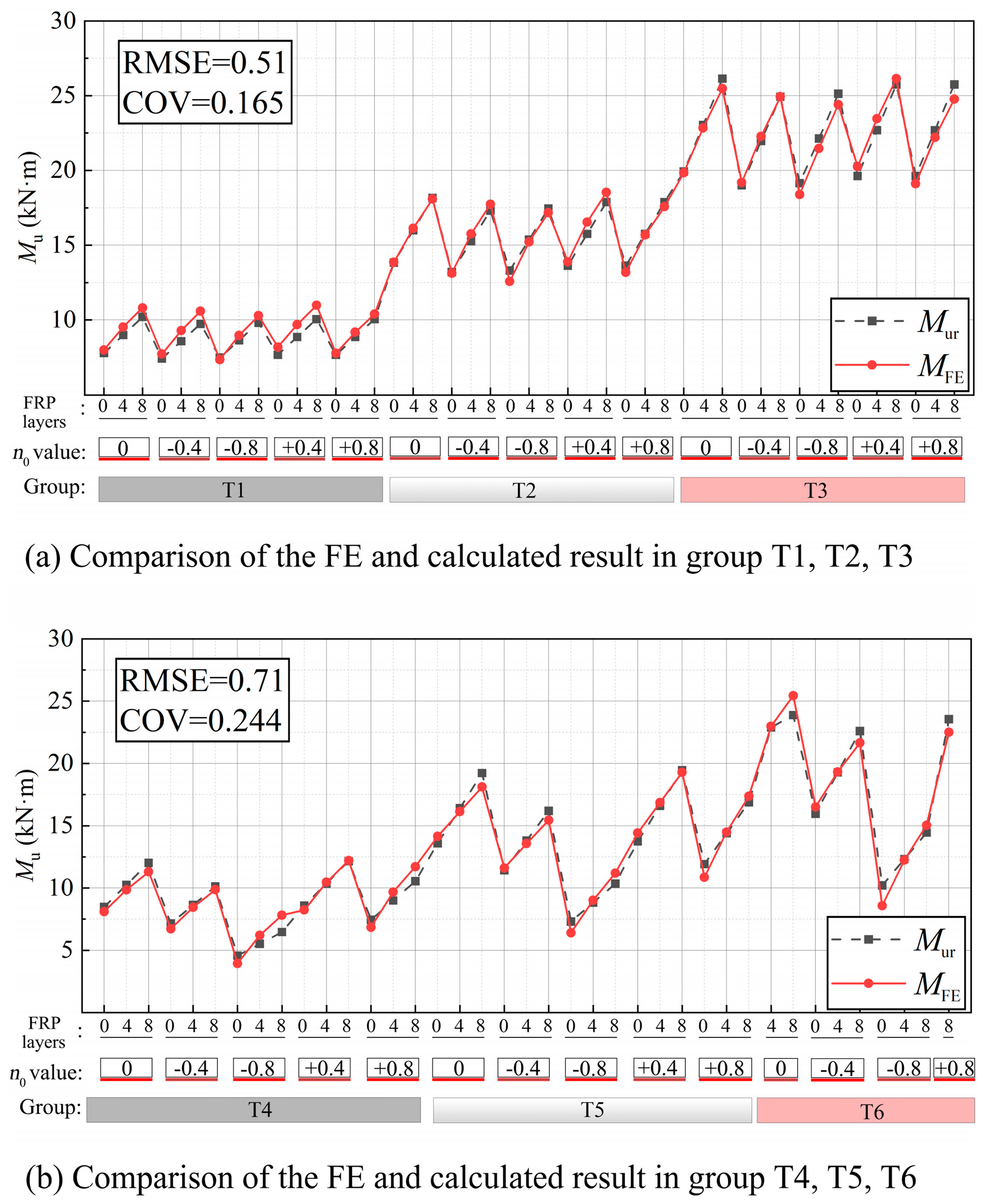
2.2. Verification Study
3. Parametric Investigation
3.1. Specimen Programme
3.2. Numerical Model, Loading Protocol, and Strength Definition
4. Typical Failure Phenomena
4.1. Distribution of Failure Mode
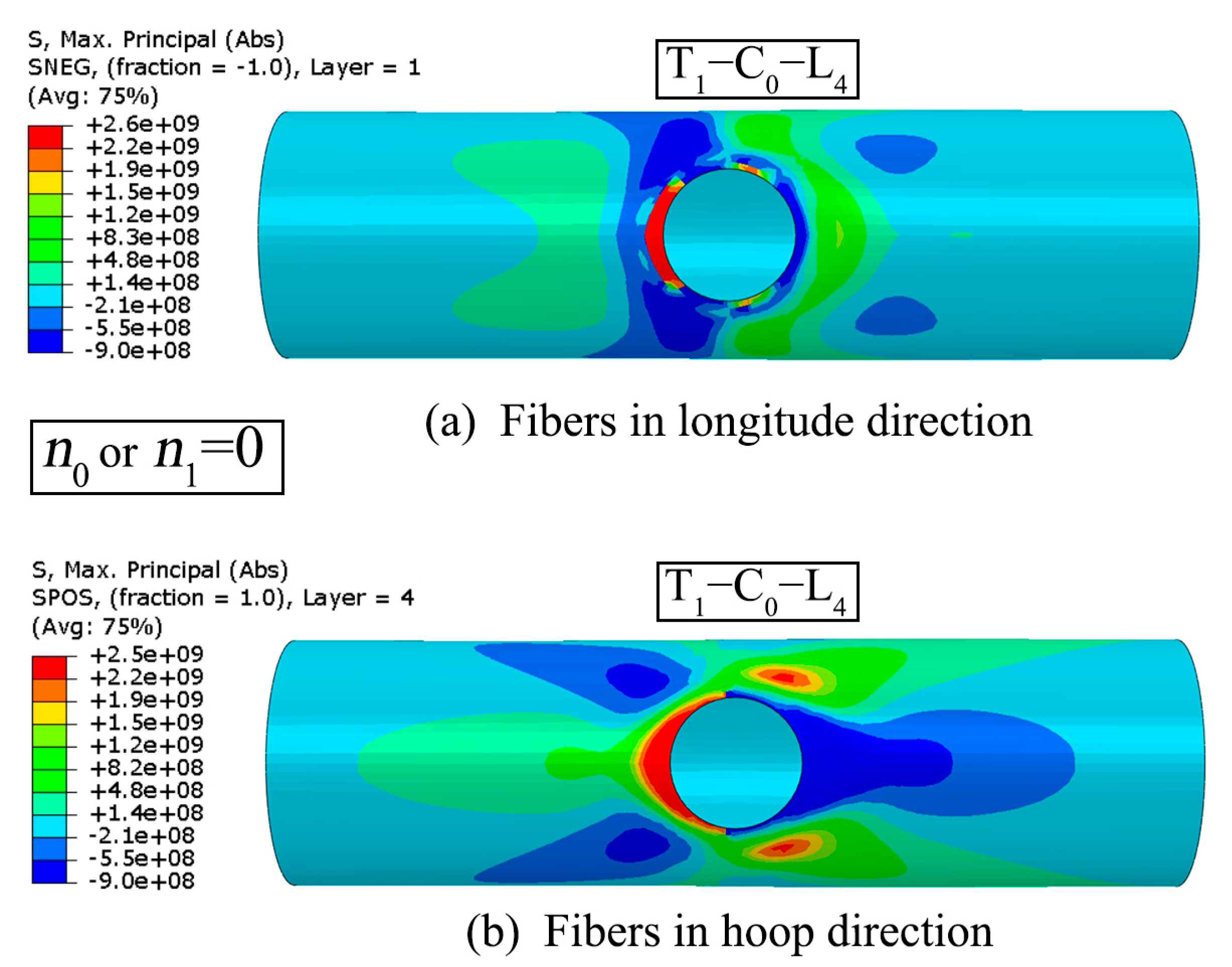
4.2. Chord Plastic Failure (T1-C0-L4)
4.3. Brace Plastic Failure (T6-B+0.4-L4)
4.4. Brace Buckling Failure (T6-B0-L0)
5. Effects of Diverse Loading Strategies on FRP-Reinforced Joint
5.1. General
5.2. IPB Moment
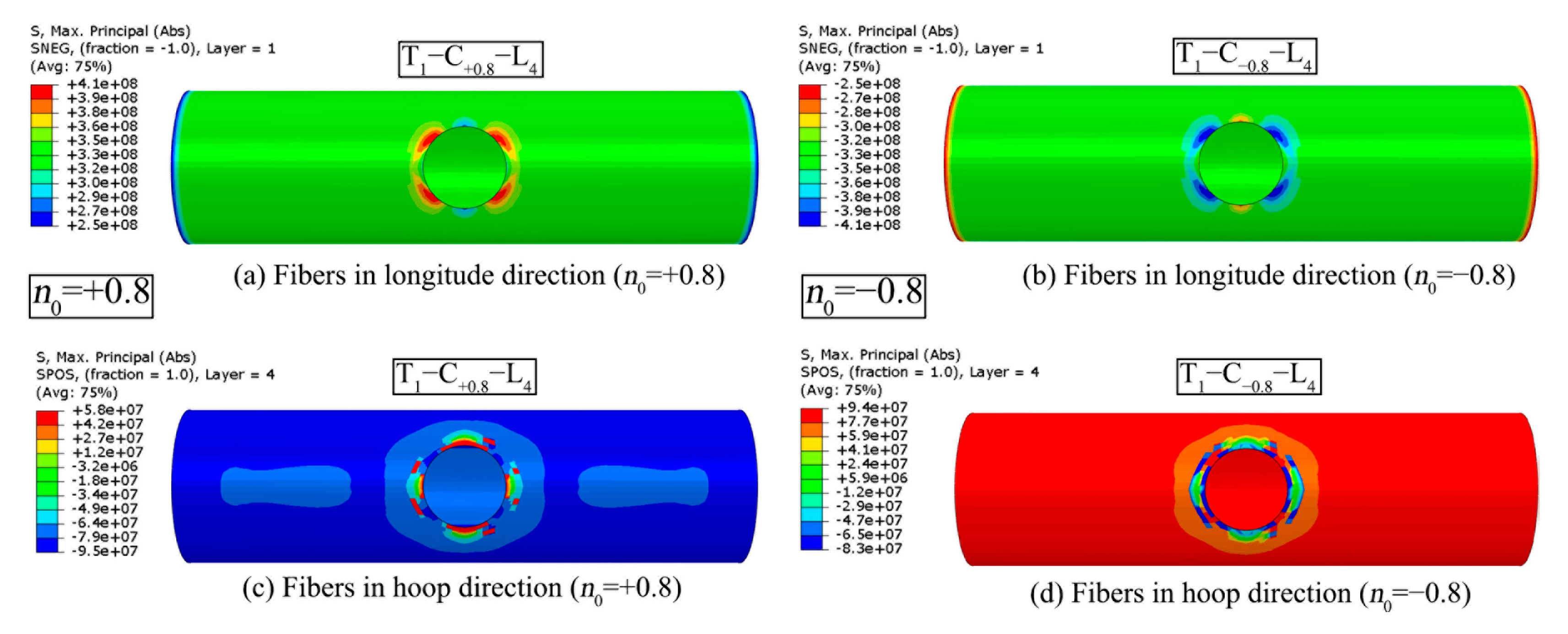
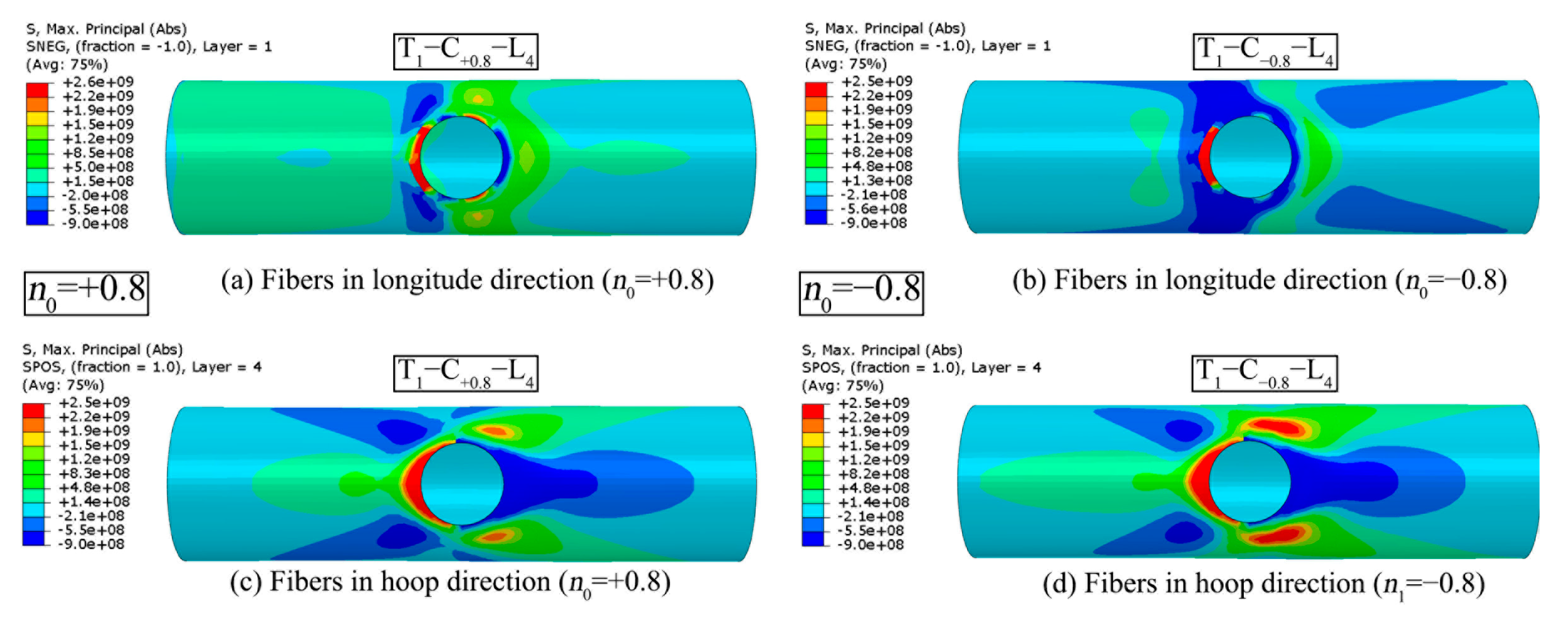
5.3. Chord AX and IPB Moment
5.4. Brace AX and IPB Moment
6. Results
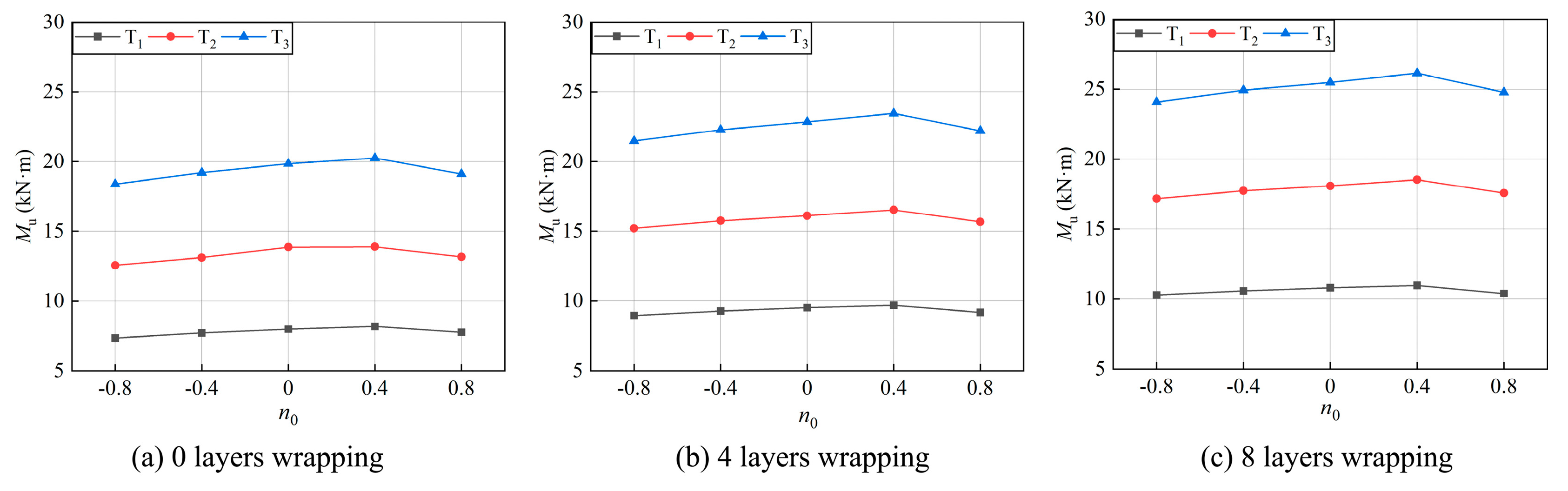
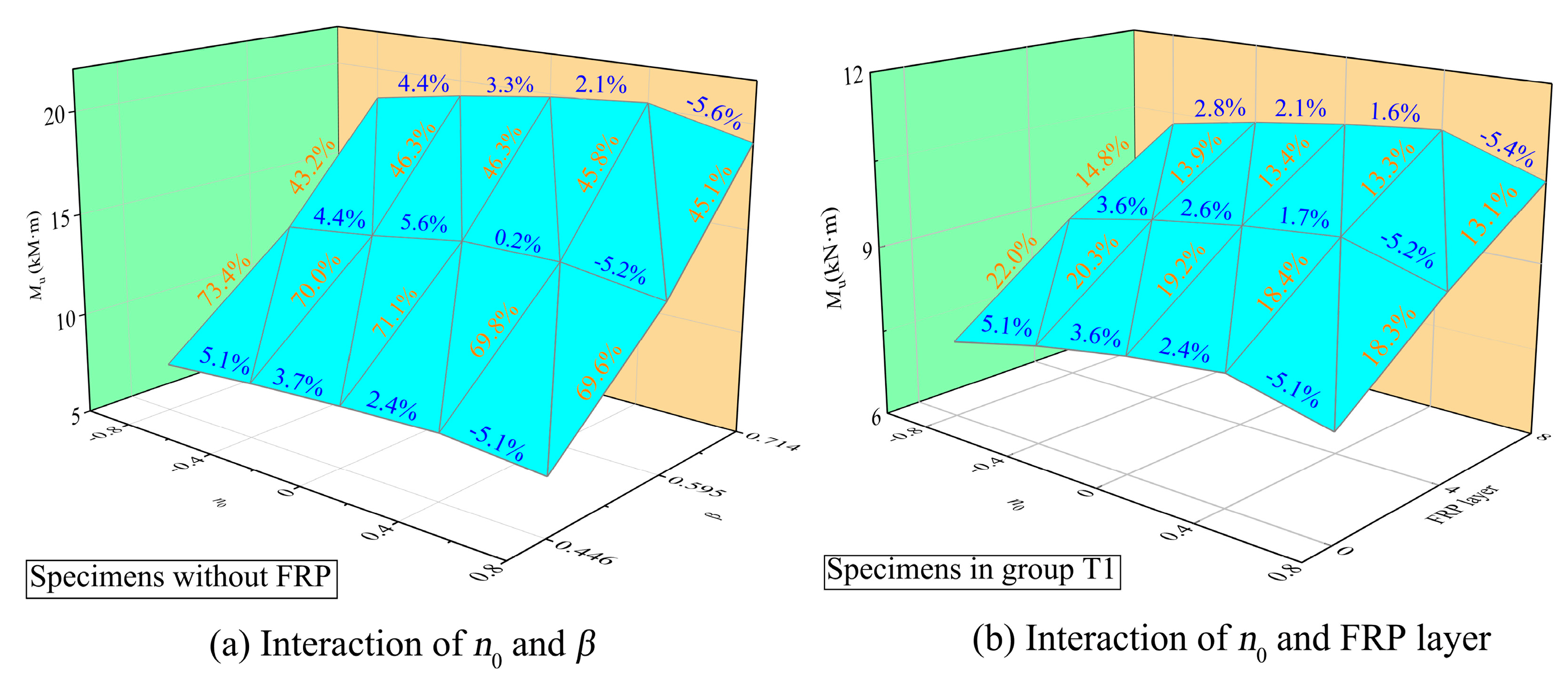
6.1. Effect of n0, β, and FRP Layer-Count on Joint Strength
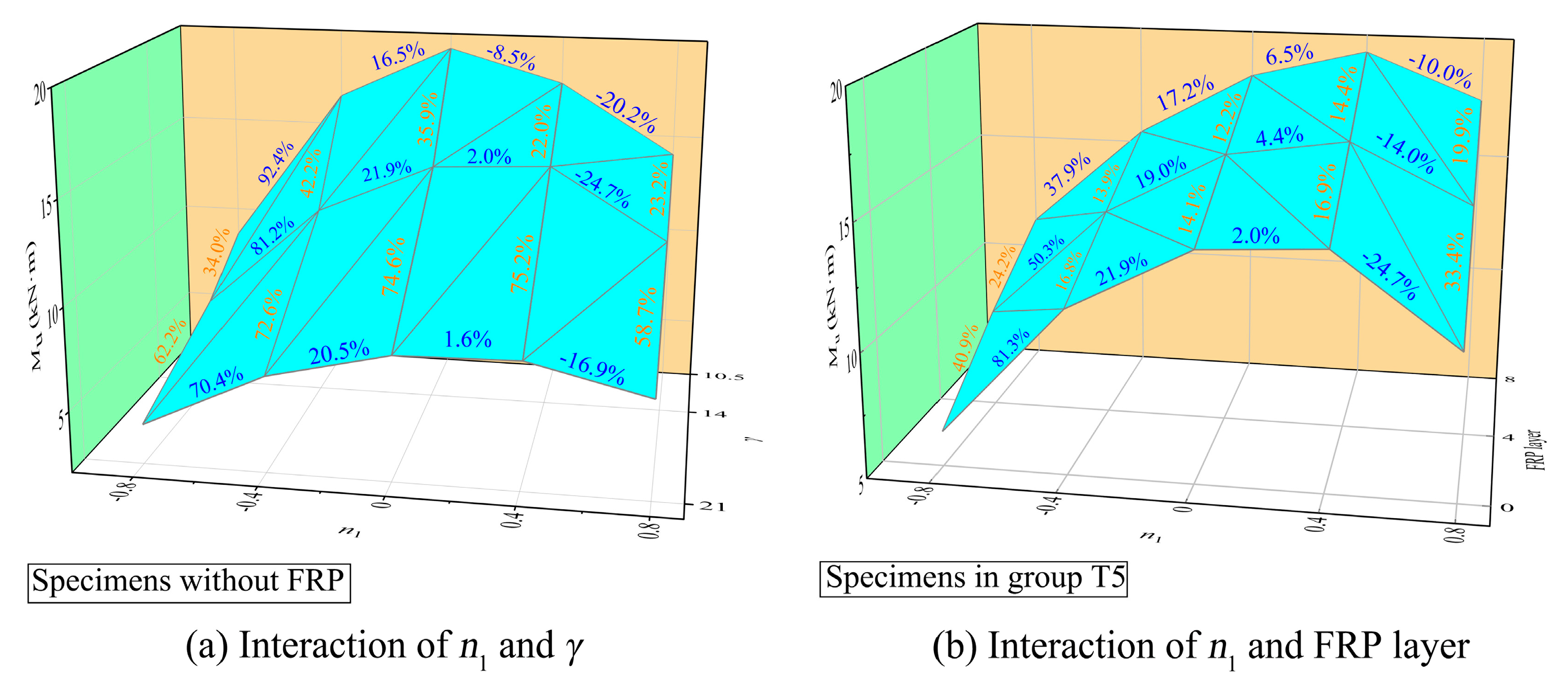
6.2. Effect of n1, γ, and FRP Layer-Count on Joint Strength
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
- (1)
- There are three main failure modes: chord plastic failure, brace plastic failure, and brace buckling failure. A small γ promotes brace-related joint failure, and the combination of IPB and brace tension can cause plastic failure of the brace. However, a sufficient number of FRP layers can make chord plasticity the main failure mode. The increase in FRP reinforcement could compensate for the thinner brace thickness and yield results equivalent to those obtained with joints with a larger γ.
- (2)
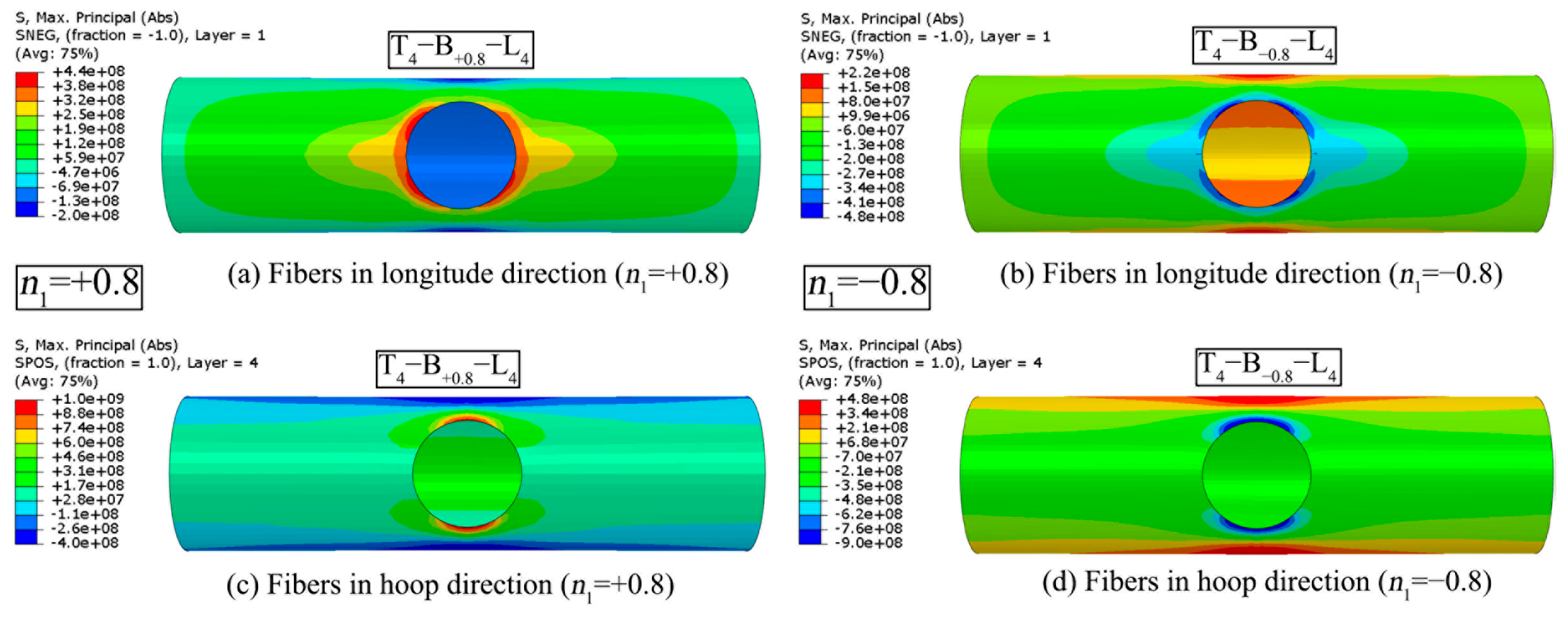
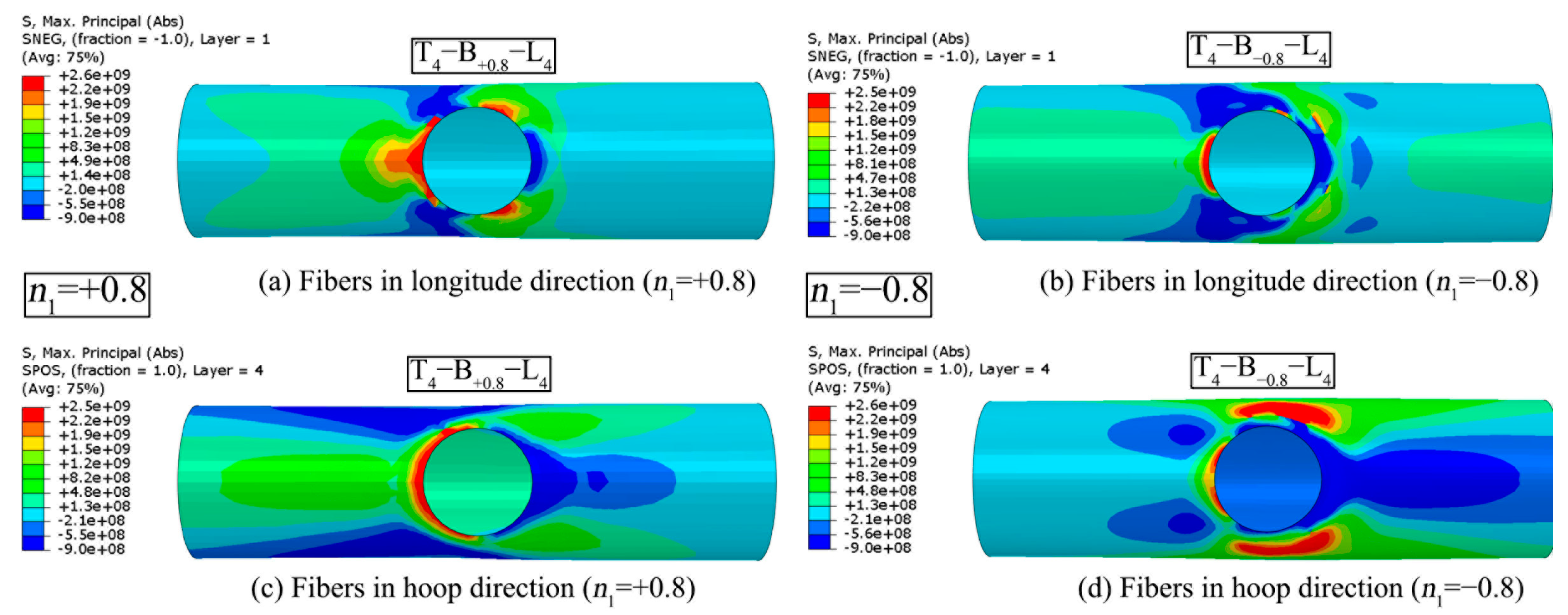
- FRP reinforcement restricts the deformation of joints under complex load patterns. Under axial compression of the chord or brace, the fibres in both the longitudinal and hoop directions of the chord will take on more responsibilities for tensile stress in the crown area. Under axial tension of the chord or brace, more fibre tension appears on the chord side wall. The FRP composite serves more efficient stiffeners for the joint subjected to combined IPB moment and brace AX than the combination of IPB and chord AX.
- (3)
- A relatively independent influence of chord AX, β, and FRP layer count is observed on the IPB resistance of the T-joint. Under the IPB moment and brace AX, the FRP composite exhibited a relatively minor reinforcement effect on the T-joint. However, the resistance is sensitive to the proportional brace AX for joints with small γ; adding FRP layers can weaken the influence of the proportional brace AX.
- (4)
- A modified strength equation for IPB resistance is proposed, incorporating the contribution of FRP reinforcement and the impact of brace AX on joint strength. The prototypical function of the chord loads in CIDECT [2] is improved with FRP reinforcement.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gibstein, M.B. The Static Strength of T-Joints Subjected to In-Plane Bending; Det Norske Veritas Report; DNV: Bærum, Norway, 1976; pp. 76–137. [Google Scholar]
- Wardenier, J.; Kurobane, Y.; Packer, J.A.; Van der Vegte, G.J.; Zhao, X.L. Design Guide for Circular Hollow Section (CHS) Joints under Predominantly Static Loading; CIDECT: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Hu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Tong, G.; Liu, Q.; Pan, Y. Effects of chord pre-load on strength of CHS X-joints stiffened with external ring stiffeners and gusset plates. Eng. Struct. 2019, 195, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soh, A.K.; Soh, C.K.; Hoon, K. Stress analysis of reinforced tubular joints subjected to different load types. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Struct. Build. 1994, 104, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Guo, J.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Q. Finite element analysis of corrosion tubular T-joint repaired with grouted clamp. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2023, 2023, 6634023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, K.; Kumaraswamidhas, L.A.; Das, R.R. Detailed investigation of adhesive fillet tubular T-joint of laminated FRP composite tube under axial compressive load. Weld. World 2020, 64, 1279–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassiraei, H.; Rezadoost, P. Local joint flexibility of tubular T/Y-joints retrofitted with GFRP under in-plane bending moment. Mar. Struct. 2021, 77, 102936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipen, K.R.; Pratiksha, H.W.; Ashwini, K.; Mavinkere, R.S.; Suchart, S.; Anish, K.; Abdullah, M.A.; Naresh, K.; Velmurugan, R.; Gupta, N.K. Impact of fiber reinforced polymer composites on structural joints of tubular sections: A review. Thin Wall. Struct. 2022, 180, 109967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesani, M.; Bahaari, M.R.; Shokrieh, M.M. Numerical investigation of FRP-strengthened tubular T-joints under axial compressive loads. Compos. Struct. 2013, 100, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesani, M.; Bahaari, M.R.; Shokrieh, M.M. Experimental investigation of FRP-strengthened tubular T-joints under axial compressive loads. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 53, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Yang, B.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y. Experimental and numerical investigations of the compressive behavior of carbon fiber-reinforced polymer-strengthened tubular steel T-joints. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 2020, 14, 1215–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassiraei, H.; Rezadoost, P. Probabilistic analysis of the SCFs in tubular T/Y-joints reinforced with FRP under axial, in-plane bending, and out-of-plane bending loads. Structures 2022, 35, 1078–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, A.S.; Bahaari, M.R.; Lesani, M. Stress concentration factors in FRP-strengthened offshore steel tubular T-joints under various brace loadings. Structures 2019, 20, 779–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Tong, L.; He, L.; Zhao, X.L. Experimental and numerical investigation on behavior of CFRP-strengthened circular hollow section gap K-joints. Thin Wall. Struct. 2016, 102, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavvar, E.; Hosseini, A.S.; Lotfollahi-Yaghin, M.A. Stress concentration factors in steel tubular KT-connections with FRP-Wrapping under bending moments. Structures 2021, 33, 4743–4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Xu, J.; Chen, Z.; Roy, K.; Chen, B.; Lim, J.B. Numerical investigation and design rules for stress concentration factors of stainless-steel hybrid tubular joints. Thin Wall. Struct. 2021, 163, 107783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone, T.J.; Yura, J.A.; Hoadley, P.W. Ultimate strength of tubular joints: Chord stress effects. In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 7–9 May 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Packer, J.A.; Yang, G.J. Yield line analysis of RHS connections with axial loads. J. Constr. Steel Res. 1998, 48, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.T.; Moffat, D.G.; Mistry, J. Strength of DT tubular joints with brace and chord compression. J. Struct. Eng. 1998, 124, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saadi, A.U.; Aravinthan, T.; Lokuge, W. Structural applications of fibre reinforced polymer (FRP) composite tubes: A review of columns members. Compos. Struct. 2018, 204, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, D.; Yu, T.; Teng, J.G.; Zhao, X.L. CFRP strengthening of rectangular steel tubes subjected to end bearing loads: Effect of adhesive properties and finite element modelling. Thin Wall. Struct. 2009, 47, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.G.; Yu, T.; Fernando, D. Strengthening of steel structures with fibre-reinforced polymer composites. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2012, 78, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Shao, Y.; Hassanein, M.F.; Xiong, C.; Zhu, H. Static strengths of preloaded circular hollow section stub columns strengthened with carbon fibre reinforced polymer. Steel Compos. Struct. 2023, 47, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, H.; Zhao, X.L. CFRP strengthened butt-welded very high strength (VHS) circular steel tubes. Thin Wall. Struct. 2004, 42, 963–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadei, J.C.; Stratford, T.J.; Duckett, W.G.; Hollaway, L.C. Strengthening Metallic Structures Using Externally Bonded Fibre-Reinforced Polymers; CIRIA: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Moy, S.S. FRP Composites: Life Extension and Strengthening of Metallic Structures; Thomas Telford: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, P.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X. Study on dynamic behavior of tubular T-joints subjected to out-of-plane impact loading. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2022, 198, 107556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Chen, X.; Yang, B.; Guo, J.; Liu, Y. Finite element analysis on the residual bearing capacity of axially preloaded tubular T-joints subjected to impacts. Structures 2021, 31, 286–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.B.; Chen, Z.M.; Zhou, Z. Experimental on static bearing capacity of corroded T-joints strengthened with CFRP. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2020, 37, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.F.; Chung, K.F.; Ban, H.; Nethercot, D.A. Structural testing and numerical modelling of T-joints between cold-formed S690 circular hollow sections under brace in-plane bending. Eng. Struct. 2022, 250, 113317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassault Systèmes Simulia Corp. Abaqus 6.11 Analysis User’s Manual; Dassault: Paris, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, M.; Chung, K.F.; Young, B. Design of cold-formed high strength steel tubular T-joints under compression loads. Thin Wall. Struct. 2021, 164, 107573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashin, Z. Fatigue failure criteria for unidirectional fibre composites. J. Appl. Mech. 1980, 47, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 50017-2017; Standard for Design of Steel Structures. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2017. (In Chinese)
- Lu, L.H.; Wardenier, J. Ultimate deformation criteria for uniplanar connections between I-beams and RHS columns under in-plane bending. In Proceedings of the International Ocean and Polar Engineering Conference, Osaka, Japan, 10 April 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Hoadley, P.W. Ultimate Strength of Tubular Joints Subjected to Combined Loads. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Texas, Austin, TX, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Nassiraei, H.; Rezadoost, P. SCFs in tubular X-connections retrofitted with FRP under in-plane bending load. Compos. Struct. 2021, 274, 114314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbuckle, J.L. IBM SPSS Amos 20 User’s Guide; Amos Development Corporation & SPSS Inc.: Whitingham, VT, USA, 2011; pp. 226–229. [Google Scholar]





| Model | Chord/mm | Brace/mm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d0 | t0 | l0 | d1 | t1 | l1 | |
| T-1/T-1-C | 168 | 5 | 1960 | 95 | 4 | 536 |
| M-T2 | 250 | 10 | 1199 | 150 | 6 | 600 |
| Model | Member | Young’ Modulus E/GPa | Yield Strength fy/MPa | Tensile Strength fu/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-1/T-1-C | Chord | 202 | 386 | 523 |
| Brace | 204 | 349 | 521 | |
| M-T2 | Chord | 201 | 766 | 828 |
| Brace | 202 | 757 | 811 |
| Group | Specimen | Chord/mm | Brace/mm | β | γ | Axial Load Proportion | FRP Layers | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-Cn0/Bn1-Llayer | d0 | t0 | l0 | d1 | t1 | l1 | Chord (n0) | Brace (n1) | ||||
| T1 | T1-C0/+0.4/+0.8/−0.4/−0.8-L0/4/8 | 168 | 6 | 1500 | 75 | 5 | 410 | 0.446 | 14 | 0/+0.4/+0.8/−0.4/−0.8 | 0 | 0/4/8 |
| T2 | T2-C0/+0.4/+0.8/−0.4/−0.8-L0/4/8 | 168 | 6 | 1500 | 100 | 5 | 416 | 0.595 | 14 | 0/+0.4/+0.8/−0.4/−0.8 | 0 | 0/4/8 |
| T3 | T3-C0/+0.4/+0.8/−0.4/−0.8-L0/4/8 | 168 | 6 | 1500 | 120 | 5 | 416 | 0.714 | 14 | 0/+0.4/+0.8/−0.4/−0.8 | 0 | 0/4/8 |
| T4 | T4-B0/+0.4/+0.8/−0.4/−0.8-L0/4/8 | 168 | 4 | 1500 | 100 | 5 | 416 | 0.595 | 21 | 0 | 0/+0.4/+0.8/−0.4/−0.8 | 0/4/8 |
| T5 | T5-B0/+0.4/+0.8/−0.4/−0.8-L0/4/8 | 168 | 6 | 1500 | 100 | 5 | 416 | 0.595 | 14 | 0 | 0/+0.4/+0.8/−0.4/−0.8 | 0/4/8 |
| T6 | T6-B0/+0.4/+0.8/−0.4/−0.8-L0/4/8 | 168 | 8 | 1500 | 100 | 5 | 416 | 0.595 | 10.5 | 0 | 0/+0.4/+0.8/−0.4/−0.8 | 0/4/8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Guo, J. Structural Behaviour of FRP-Reinforced Tubular T-Joint Subjected to Combined In-Plane Bending and Axial Load. Buildings 2024, 14, 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14020412
Deng P, Chen Y, Zhu Z, Liu Y, Zhao S, Guo J. Structural Behaviour of FRP-Reinforced Tubular T-Joint Subjected to Combined In-Plane Bending and Axial Load. Buildings. 2024; 14(2):412. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14020412
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Peng, Yunkai Chen, Zhongyi Zhu, Yan Liu, Shiqi Zhao, and Jian Guo. 2024. "Structural Behaviour of FRP-Reinforced Tubular T-Joint Subjected to Combined In-Plane Bending and Axial Load" Buildings 14, no. 2: 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14020412
APA StyleDeng, P., Chen, Y., Zhu, Z., Liu, Y., Zhao, S., & Guo, J. (2024). Structural Behaviour of FRP-Reinforced Tubular T-Joint Subjected to Combined In-Plane Bending and Axial Load. Buildings, 14(2), 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14020412









