Abstract
This paper overviews the use of several waste materials for the construction and reconstruction of surface courses of asphalt pavements in the framework of sustainable perspectives that are adopted in pavement engineering. Based on a relevant literature search, the most commonly investigated alternative materials include waste plastic, crumb rubber, waste glass, steel slag, and Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP). Although recycling in pavement engineering is not a novelty, the strict performance requirements of the surface layers required to support a distress-resistant behavior possess continuous research challenges about the mechanical behavioral parameters, such as fatigue, rutting, moisture damage, and serviceability requirements, such as skid resistance. While studies in a laboratory environment mainly dominate, the importance of performance observations of real structures in the field is also pinpointed in an effort to provide a comprehensive overview of the so far knowledge status. Thereafter, this paper discusses peculiar issues and criteria for waste material selection that should balance performance requirements, local availabilities, and potential legislation concerns, thereby maximizing the economic or environmental advantages.
1. Introduction
Recycling in asphalt pavements dates back to 1915 with the Warren Brothers’ portable asphalt plant [1]. Thereafter, it was the oil crisis in the early 1970s that increased asphalt prices, and the related energy costs boosted a recycling perspective in pavement engineering [2,3]. In addition, the scarcity of raw materials for the construction and maintenance of roads has also raised the potential of using recycled materials in several layers of pavement structures [4]. Pavement surface layers provide a privileged domain of application for recycled and waste solid materials, considering that these layers are most frequently maintained or rehabilitated in the framework of the sustainable management of pavement infrastructure.
A major concern when using recycling materials is to avoid downgrading their quality [4,5,6]. This is much more intensive nowadays since socio-economic reasons and the need to minimize energy consumption force policy makers and road stakeholders to adopt circularity perspectives in their construction/reconstruction and asset management practices [7]. It is a widely held belief that recycled pavement materials help meet environmental requirements by limiting the need for new material resources, renewing the concept of “end-of-life”, an aspect that is also consistent with budgetary constraints [8]. Therefore, the inclusion of recycled materials seems to be in favor of a more sustainable construction and/or reconstruction process.
In recent decades, a significant trend has been observed concerning recycling or reusing solid waste materials in highway pavements, which can be categorized into pavement by-products, industrial by-products, and waste produced by the construction and demolition of buildings and road infrastructure [9,10,11,12,13]. Indicative examples include Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP) or simply Reclaimed Asphalt (RA), Electric Arc Furnace steel slag (EAFS), Blast Furnace slag (BFS), waste glass, and waste plastic that are used as either aggregate or binder substitutes in order to reduce the need for virgin materials. There are numerous research studies assessing these materials and their potential for inclusion into pavement structures, as well as their engineering performance features, e.g., [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. By far, RAP is the most popular waste material that can be rationally reused in roadway engineering [23,24] if its behavior and interaction with the new materials is better understood. RAP is obtained by milling or removing the asphalt layers from road pavements that are either being maintained or rehabilitated [20].
A critical concern when using non-conventional materials (i.e., recycled or waste materials) in pavement structures is the assessment of their suitability and contribution to pavement behavior. Such aspects shall be evaluated through experimental investigation and objective criteria, considering that each material might possess unique performance attributes to a layer’s mix or even to the overall structure [15]. It is deemed that the best method to evaluate the performance attributes of non-conventional materials and their impact on pavement performance is to perform detailed field inspections under real environmental and weather conditions or to conduct full-scale tests in Accelerated Pavement Testing (APT) facilities [15,25]. However, these procedures are labor intensive in both time and cost investments, while local factors affecting pavement performance may not be easily considered. Instead of becoming discouraged from systematically investigating such aspects, pavement engineers have usually invested in advanced laboratory testing and controlled performance simulations to familiarize themselves and disseminate related experience, which provides a fruitful precursor for field applications with considerable know-how.
In the meantime, as explained earlier, recycled and waste materials exhibit an increased potential for inclusion into the asphalt mix design of surface layers because of periodical surface interventions at in-service pavements [4,26]. In fact, road operators are not willing to proceed with costly in-depth interventions. So, once a pavement is designed and constructed to remain structurally sound in the long term, it is normally subject to surface treatments at periodical intervals that guarantee its serviceability. This is consistent with the concept of Long-Life Pavements (LLPs), where the concept is to design and construct pavements so that structural adequacy is guaranteed in the long term, and potential intervention needs to be focused on surface condition restoration. Such treatments can include routine maintenance actions (e.g., crack sealing) or minor rehabilitation measures (e.g., replacement of the surface layer). In the latter case, the privilege and/or local availability of alternative materials to be used for the reconstruction of pavement surface layers is highlighted.
Therefore, the present paper aims to give an overview of the related practices and current challenges encountered when incorporating non-conventional materials into pavement surface courses. Despite the availability of relevant review papers, this paper aims to shed light on specific research questions, including the following:
- What are the most frequently used waste materials in pavement engineering, especially for surface layer construction?
- What is the evidence so far from structural and functional performance features considering both laboratory and field experiments?
- What are the most common problems or gaps faced by researchers and practitioners in the domain of waste material reuse, and what are the future research trends toward a more holistic utilization of these?
Given the above remarks, in terms of its novelty, this paper aims to act as a constructive collection of material technology issues, performance observations, and “open” points for relevant comparative investigations of the reviewed waste materials by both researchers and practitioners.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. (i) A brief overview of the most commonly utilized non-conventional materials is performed in Section 2. (ii) RAP is further elaborated in Section 2.6 as one of the most popular materials used in pavement engineering, and several experimental findings or field observations regarding its use in surface layers are given for both its mechanical and functional behavior. (iii) Several research challenges, environmental aspects, limitations, and innovative applications are given in Section 3, and (iv) the main conclusions are set in Section 4.
2. Waste Materials for Building Asphalt Pavement Surfaces
2.1. Outline and Methods
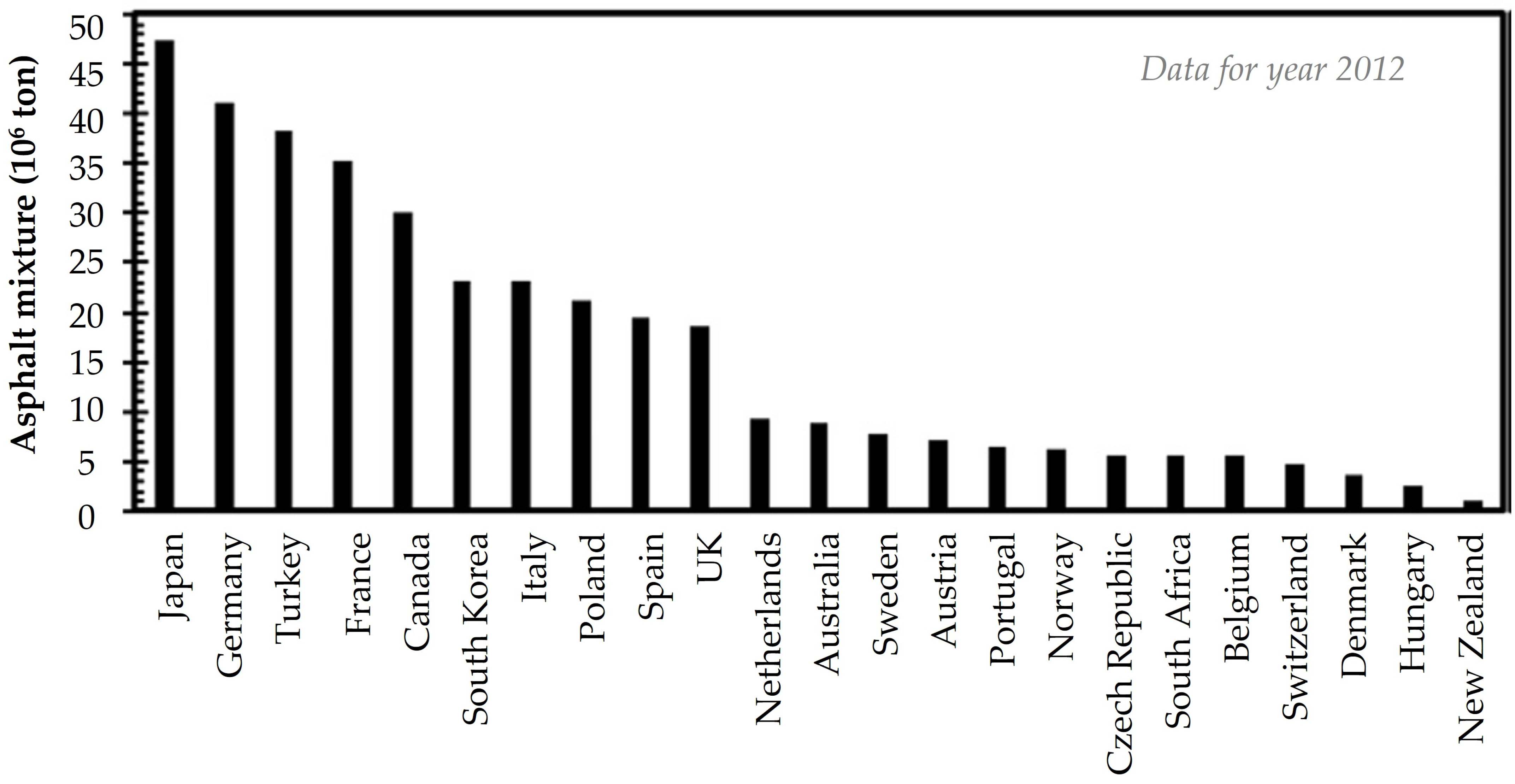
Asphalt manufacturing is ranked as the second most energy-intensive industry in the United States, with an annual Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA) mixture production of 500 Mt [21,27]. A worldwide production trend is given in Figure 1. More specifically, binder production and drying of aggregates are two energy-intensive processes [27]. Despite the advances in the Warm Mix Asphalt (WMA) technology that strives to reduce the energy consumption and Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions in asphalt pavements, additional costs are implied when modifying the current infrastructure status of mixing plants that are required for WMA. Thus, the use of waste materials is an indirect way to produce more sustainable asphalt mixtures, even with the traditional HMA concept [21,28].
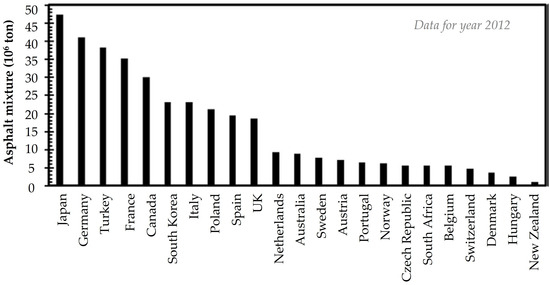
Figure 1.
Annual production quantities of asphalt mixtures [21,29].
Therefore, in order to have stable roads that are durable, skid resistant, and impervious to water intrusion, a wide variety of additives or non-conventional materials are added to the mix design with the view to extending the service life of the pavement [30]. Therefore, the mix design for the surface layer is a crucial stage for both the design phase and the operational service life of a pavement. Pavement surface performance envisages a distress-resistant behavior, which implies that both structural and functional features are of sufficient level. Common distresses that can appear on a pavement surface include top-down fatigue cracking (related to stiffness modulus and fatigue resistance [31,32]), rutting, moisture damage and stripping/raveling behavior, loss of smoothness or texture, and insufficient skid resistance. From a more holistic perspective, distressed pavement affects the vehicle’s rolling resistance and exhibits environmental, economic, and social implications. GHG emissions, noise level, road safety, storm water runoff, and solar reflectance are the basic variables associated with pavement surface performance too. Therefore, any kind of modification that is decided for conventional asphalt surface mixtures shall meet most of the above requirements of distress-resistant behavior. This justifies why detailed investigation continuously revives as an ongoing challenge for pavement science and engineering.
With respect to the survey methods, to retrieve the most commonly utilized alternative materials into pavement surface layers, the following procedure was followed. Since most articles are covered in the Scopus database compared to other ones (e.g., Web of Science), it was decided to employ an advanced search in Scopus. Relevant articles mainly falling within the last decade (i.e., 2014 and thereafter) were selected to capture the most recent trends on the recyclability of waste materials for pavement surfaces. Key indicators including the combination of the terms “waste materials, RAP, mix design, structural and functional performance assessment, surface layers, laboratory and field studies”, excluding the rest of the asphalt layers and/or base/subbase layers. Both research and review papers were evaluated by multiple publishers, including Elsevier, MDPI, Springer, Taylor and Francis, etc. To a lesser extent, some conference papers were also overviewed.
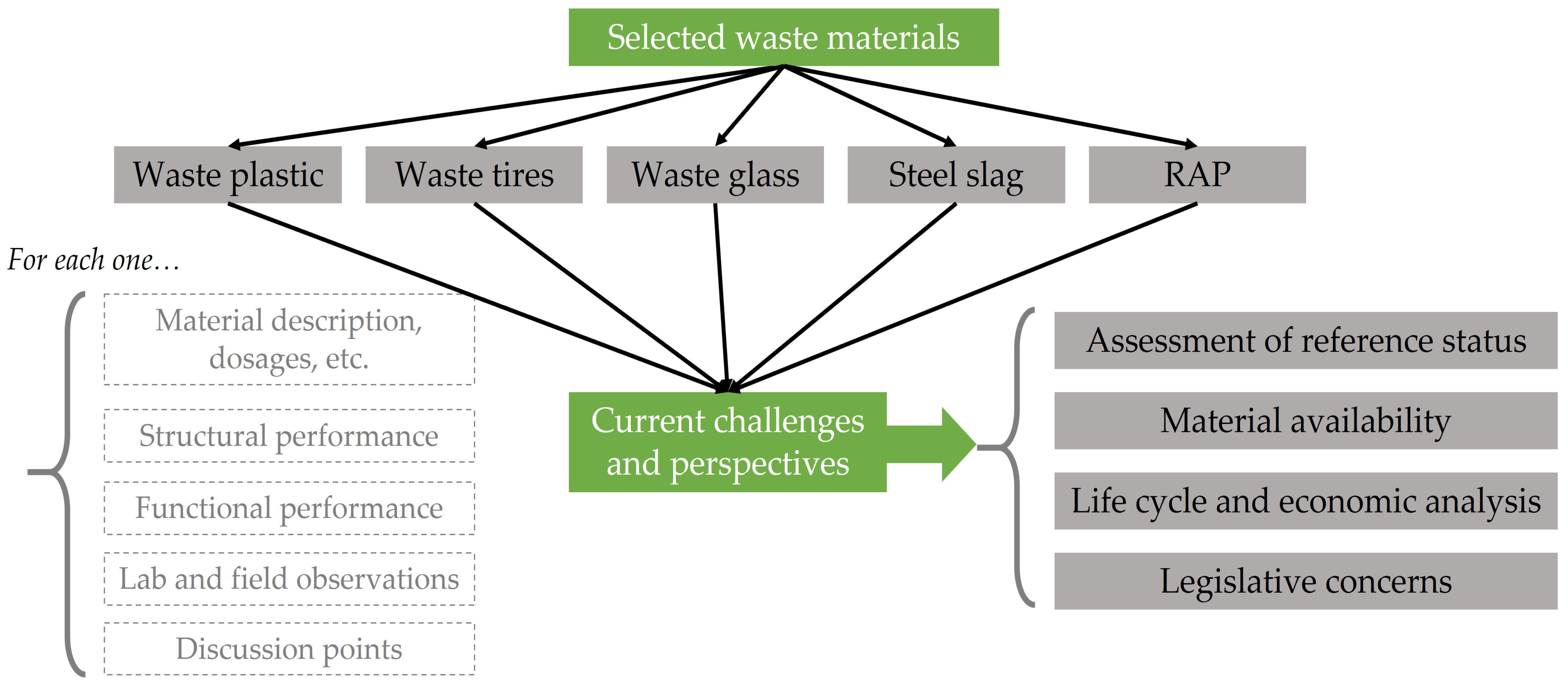
From the survey results, it was decided to focus on a specific spectrum of materials utilized as alternative and sustainable options for construction or reconstruction (i.e., maintenance and/or rehabilitation) and gather performance findings from the sufficiently gained knowledge in terms of both laboratory and field investigations. According to Table 1, the following materials were considered: waste plastic, waste tires, waste glass, steel slag, and RAP. Sufficient evidence exists in favor of their use [33,34,35]. Since much more attention has been paid to RAP, a relatively big subsection (i.e., No. 2.6) is dedicated to aspects concerning the use of RAP. Of course, each one of the presented materials is not uniformly used worldwide because of several factors including availability issues, legislation concerns, etc. Related discussion is provided in Section 3. Figure 2 illustrates the structure followed in this paper as a result of the methodological literature research.

Table 1.
Literature results for the considered alternative waste materials.
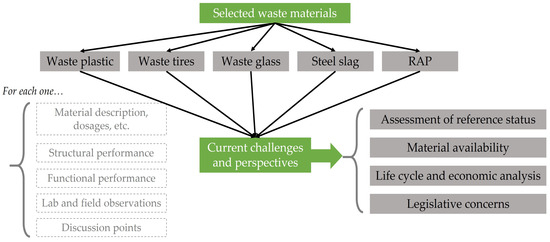
Figure 2.
The research framework of this paper.
Finally, it has to be mentioned for the sake of completeness that material technology has opened significant margins for research of even more alternative waste materials, like coal gangue and waste building aggregates [36,37]. Some of them are ideal for improving the self-healing properties of asphalt mixtures [37], something which is rather important for crack-resistant surface mixtures. However, because of the sparsity of the related studies, and considering the authors’ experience and perspective in pavement recycling issues, those materials were excluded from further investigation in this review paper.
2.2. Waste Plastic
The extensive amount of plastic waste worldwide requires innovative and viable recycling methods [16]. It has been reported that the world generates a million plastic bottles every minute [15]. Mashaan [38] reported that the annual consumption of plastic has globally jumped from about 5 million to 100 million tons within the second half of the last century. Hence, it can be considered that plastic has become one of the most important solid waste materials in recent decades. In the meantime, the recycling rate of waste plastic does not seem to be sufficient [6,32]. For example, in Australia, only 9% of the consumed plastic during 2017–2018 was recycled [17]. In 2016, approximately 69% of waste plastics in the majority of European Union countries were not recycled [32].
Waste plastics suffer from bio-decomposition quality, and thus limited options against being landfilled or combusted exist [39]. Both of these processes have been characterized as unhealthy for the environment, leading to land and air contamination [16]. Therefore, recycling plastic waste in many alternative ways (e.g., roadway engineering) helps decrease the negative impacts on ecosystems.
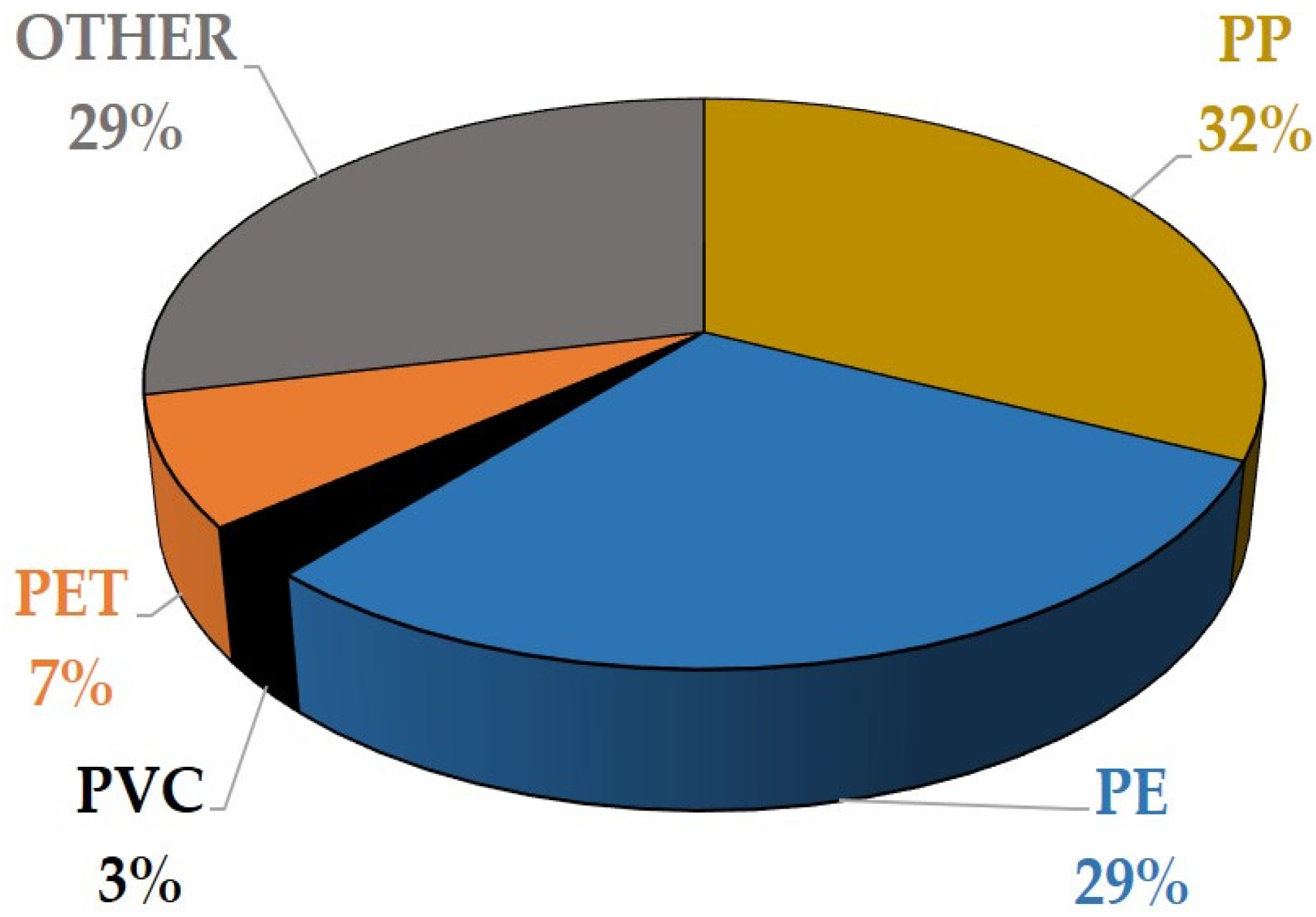
Waste plastics are normally classified into four main categories, as shown in Figure 3: (a) polypropylene (PP), (b) polyethylene (PE), (c) polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and (d) polyethylene terephthalate (PET) [16,32]. Plastic can be incorporated into the asphalt mix with two processes depending on the melting point of plastics, namely, (i) the wet process, where the plastic material with a low melting point is mixed with bitumen, and after, the aggregates are added, and (ii) the dry process, where plastic with a high melting point is mixed with the aggregates, and then bitumen is added [32,38].
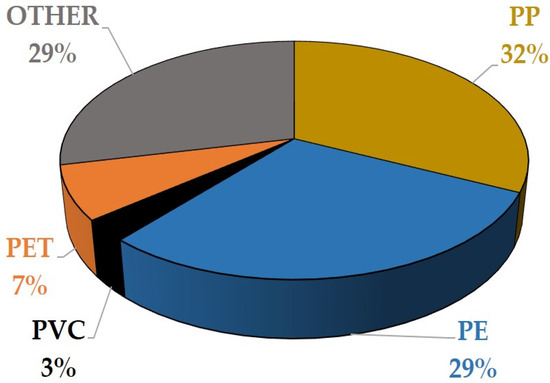
Figure 3.
Distribution of waste plastics in municipal solid waste, i.e., PP: polypropylene, PE: polyethylene, PVC: polyvinyl chloride, PET: polyethylene terephthalate (adapted from [16]).
According to the related studies, there is a general agreement that including waste plastic in asphalt mixtures with both processes improves the rutting resistance of the produced mixture for surface courses. Punith and Veeragavan [40] performed dynamic creep tests at mixtures, including PE, at a rate of 2.5–10% by the mass of the binder (wet process) and reported a better rutting performance compared to a control (i.e., unmodified) mixture. In the same context, using PE at a rate of 1–2% by the mass of the aggregates (dry process) has been commented as satisfactory in terms of rutting behavior [41,42]. PET-based and PV-based mixtures can also resist rutting [43,44]. While the dry process is more effective for the former case because of the high melting temperatures (i.e., around 250 °C [16]), both processes are suitable for the latter case since PVC exhibits a wider range of melting temperatures (i.e., around 100–300 °C [16,32]). Nevertheless, PVC-based mixtures are rarely investigated [32]. PP-based mixtures have been also found to be rutting resistant at 60 °C [41].
Regarding the moisture susceptibility of plastic-modified mixtures, it can be in generally reduced based on laboratory investigations on the tensile strength ratio (TSR). Specimens with (i) PE at a rate of less than 10% by the mass of the binder (wet process) [45,46] or of less than 0.5% by the mass of the aggregates (dry process) [47], (ii) PET at a rate of less than 6% by the mass of the binder [48] or of less than 1% by the mass of the aggregates [49], (iii) PVC at a rate of less than 10% by the mass of the binder and (iv) PP at an optimal rate of 2% by the mass of the binder [50] have been used to support the previous statement.
The stiffness modulus of a plastic-modified mixture generally increases compared to control mixtures with conventional materials. In most cases, the investigated temperatures ranged from 5 °C to 25 °C [41,46,49]. Noticeably, Giri et al. [42] revealed an interaction between PE and the testing temperature; higher stiffness for the modified mixture was observed at higher temperatures, whereas the opposite was reported for lower temperatures. Similar moduli have been reported for both conventional and PE-modified mixtures by Moghadas et al. [47].
In terms of fatigue resistance, improved performance has been consistently reported in the literature based mainly on the indirect tensile fatigue tests (ITFTs) at temperatures ranging from 15 to 20 °C [41,47,50]. Noticeably, the PET rate for the dry process might play a key role in controlling the fatigue resistance of the final mixture. Usman et al. [49] reported that PET contents of less than 0.5% by the mass of the mixture increase the fatigue resistance of the mixture, whereas the opposite happens for the PET rate at the range of 0.7–1% by the mass of the mixture. Finally, from an ad hoc case study, Russo et al. [51] reported superior performance of a plastic-modified asphalt mixture compared to a mixture that contained styrene–butadiene–styrene (SBS) polymer-modified asphalt. The conducted tests came from a full-scale laboratory investigation that included an indirect tensile strength test at 25 °C, Indirect Tensile Stiffness Modulus (ITSM) at 5, 20, and 40 °C, resistance to permanent deformation (Wheel Tracking Device (WTD) at 60 °C), and resistance to fatigue (ITFT at 20 °C).
2.3. Waste Tires
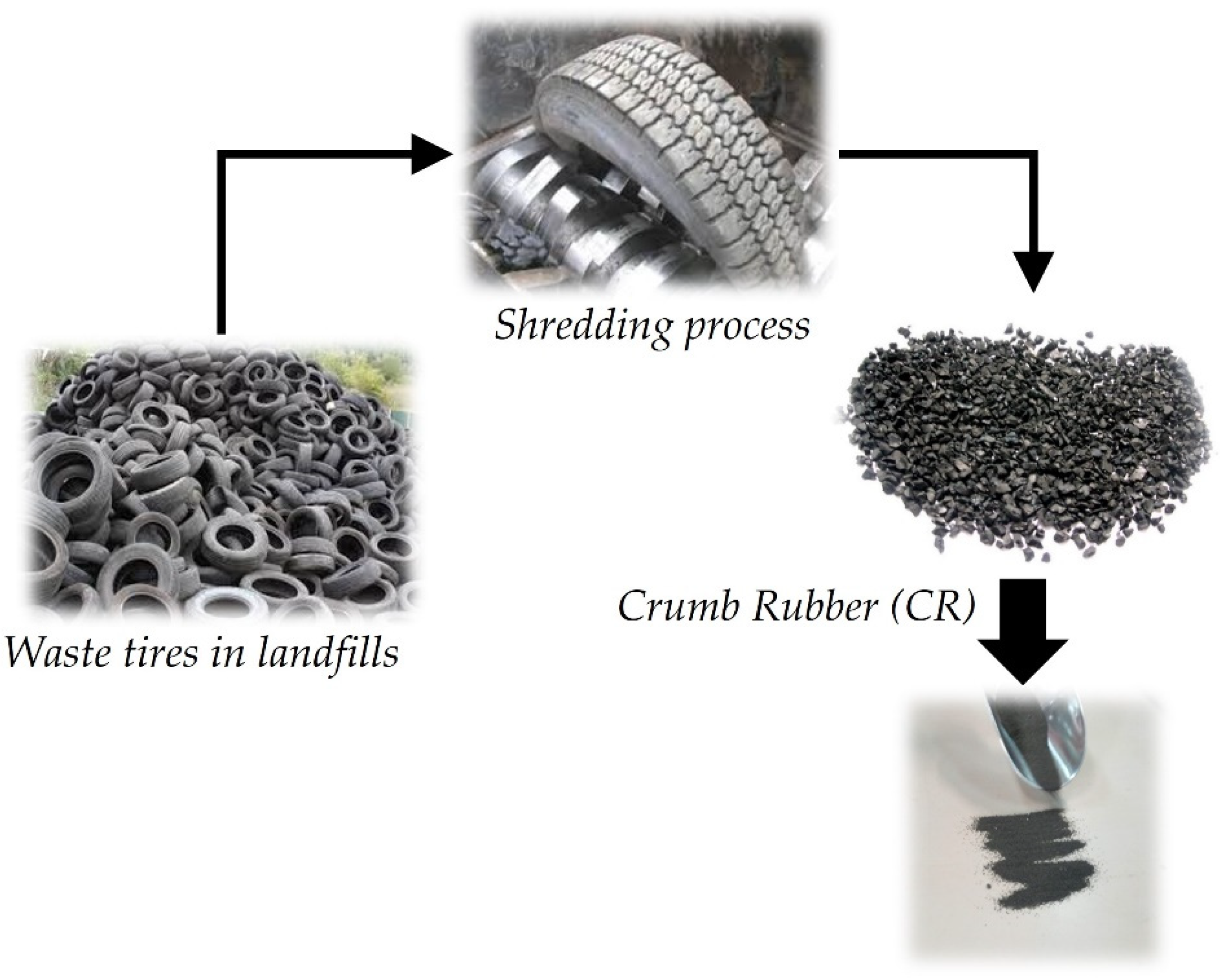
Waste tires can be considered in the design of asphalt mixtures after necessary processing in the form of crumb rubber (CR) according to Figure 4. CR is mostly used as a binder additive. Normally, waste tires end up in landfills. Despite the tire availability from old and aged cars, reclaiming waste tires for use in new ones is very limited due to the demanding process of re-vulcanizing rubber [52]. Therefore, alternative tire recycling solutions are in demand. Provided that CR’s contribution to the asphalt mixture performance is better understood, a sustainable opportunity appears so that waste tires can be fully recyclable into pavement structures [53,54]. The physical properties of CR can be found elsewhere [25].
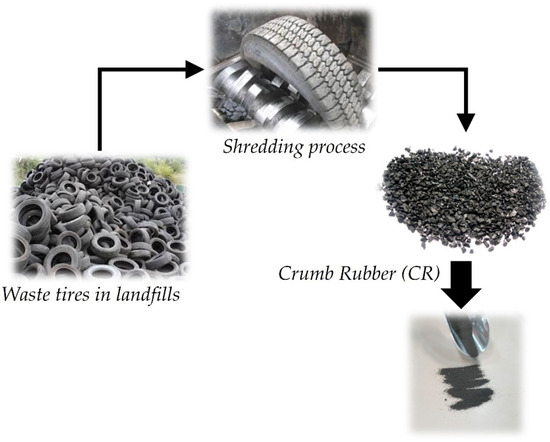
Figure 4.
Transformation of waste tires into CR.
Most of the related studies focus on the mechanical characterization of CR-modified mixtures, whereas only a few studies, as a slight exception, focus on serviceability and road safety issues by revealing skid resistance behavioral features. As per the binder performance, given the absence of relevant specifications and/or recommendations, the optimal dosage for CR addition has been reported to range from 5 to 20% by the mass of the binder [52,55,56]. From an extensive laboratory investigation, Cong et al. [57] demonstrated that adding CR into a binder increases the softening point, elastic recovery, viscosity, and complex modulus and decreases penetration and ductility.
As per the mechanical performance, CR-modified mixtures, either wet processed or dry processed, exhibit an improved performance against rutting development compared to control mixtures with conventional HMA [58,59,60,61]. The related investigations cover the case of both dense-graded mixtures [58,59] and porous mixtures [62]. Controversial results have been reported regarding the TSR of CR-modified mixtures. For wet-processed mixtures, dosages of up to 15% by the mass of the binder have been reported to improve the TSR [59,62], whereas, for more than 20%, the TSR might be reduced. Equivalent performance with conventional mixtures has also been mentioned [60,63]. On the contrary, Kim et al. [58] concluded that the TSR decreases for CR dosages ranging from 8 to 12%. Regarding the stiffness modulus of CR mixtures, different results appear, depending on the testing temperature and the air voids of the produced mixtures. The general tendency is that the addition of CR might increase the stiffness modulus. In more detail, at moderate temperatures (i.e., 20–25 °C), a higher modulus is observed [64]. For lower temperatures of less than 0 °C, the modulus of CR mixtures is lower than that of the control mixtures. For higher temperatures of up to 40 °C, higher moduli have been found for CR mixtures [61,65]. Finally, in terms of fatigue performance, it has been revealed from bending tests and indirect tensile tests that CR mixtures outperform at moderate temperatures in the range of 10–25 °C [58,60,64].
As per the functional performance, Eskandarsefat et al. [66] revealed that CR-modified dense-graded mixtures exhibited a slightly better performance in terms of macrotexture and skid resistance; however, there was an insignificant difference. Pomoni et al. [67] recently investigated the polishing patterns of newly fabricated and naturally aged CR-modified mixtures with dosages of 10% and 20% by the mass of the binder and found no consistent trend with respect to the impact of CR, indicating the need for further and more comprehensive investigations. Reductions in skid resistance have been reported by Putra et al. [68]; however, in their investigation, CR was added in RAP-based mixtures. Finally, the frictional performance of CR mixtures under the effect of simulated weather conditions has also been investigated, leading to remarks about comparable, and thus equivalent, behavior with the control mixtures of conventional materials [25].
At this point, two major issues regarding CR usage have to be mentioned. The first one relates to the increased energy costs for the production of traditional rubberized mixtures because of the higher mixing and compaction temperatures compared to unmodified mixtures [69]. This can be solved thanks to WMA technology that requires lower construction temperatures. Secondly, at elevated temperatures, e.g., 140–180 °C, during the transportation of the material, poor stability storage is observed because of the interaction conditions between the raw materials properties, including bitumen, CR characteristics, particle size, CR dosage, other potential additives, etc. [69,70]. Poor storage stability negatively affects the handling efficiency of storage and transport; the CR binder can suffer from segregation, thereby leading to durability problems of asphalt pavements. From a relevant sensitivity study on three sizes of crumb rubber particles (≤0.5 mm, ≤1 mm, and 1–2 mm), Vigneswaran et al. [70] reported that the smallest ones were the most effective in improving storage stability and minimizing phase separation of CR and the virgin asphalt binder. Related research in the domain of CR investigation is ongoing.
Overall, the incorporation of CR into mix design practices has become challenging. Venudharan et al. [55] reviewed the inclusion of waste rubber materials in gap-graded AC mixes, highlighting the need for more research to better elaborate on the CR impact. Moving forward, related studies are also performed, focusing mostly on the environmental perspective, including the impact of CR on the noise performance of pavements [55], the use of warm mix rubberized AC [71], and the combination of CR and RAP into WMA mixtures [3]. Undeniably, there are open challenges for the scientific community that can be easily detected in most of these studies. For instance, CR rates of more than 20% by the mass of the binder make the mixture’s performance inappropriate because of the binder’s brittleness. Another critical concern is that CR can absorb the lighter fractions of the mixed binder because of its porous structure [32]. Kedarissaty et al. [60] stated that pretreating CR can reduce the swelling potential. Therefore, it appears that CR will continue to attract research engineering interest in the coming years.
2.4. Waste Glass
Rashad [72] reported that the EU, China, and the US are the largest glass consumers worldwide, with quantities reaching values of 33, 32, and 20 million tons, respectively. By its nature, glass cannot be recycled; so, after the end-of-life of glass products, full glass reclamation for the production of new glass is not feasible. Thus, it can be treated as a viable alternative for manufacturing other materials. Additionally, being a non-biodegradable waste, it poses several threats in an area if left illegally at stockpiles and landfills [73]. Therefore, if WG can be used as an additive in construction engineering materials, including, among others, asphalt mixtures, then WG recycling can be accredited as a close-loop recycling method to some extent [21].
WG can be used as an aggregate substitute (for both coarse and fine aggregates) and/or as a filler substitute [21,74,75,76]. When used as a binder substitute, an increase in the softening point, penetration index, and viscosity has been reported to improve the temperature susceptibility of the modified binder [77,78]. From relevant laboratory investigations on mixtures with WG as an aggregate substitute, it was found that the use of WG reduces the effective binder content of asphalt mixtures [79], something that is expected to affect the overall mix design process. In particular, the Marshall Stability decreases, and the air voids increase when the rate of WG increases [80,81]. WG has a low absorption capacity, so the adhesion between binder and aggregates is reduced, affecting the aggregate interlock [15]. Another point is that the unabsorbed asphalt of mixtures with high contents of WG can make the mixture prone to asphalt bleeding [21], which is among the pavement surface distresses that act against road safety because of the skid resistance loss of surfaces with bleeding phenomena. Therefore, the maximum rate of WG should be controlled so that the mixture’s performance outperforms conventional mixtures. Arnold et al. [82] showed that the addition of up to 30% of glass waste by the mass of aggregates will not significantly change the mixture’s performance. On the other hand, more conservative estimations have been reported by Shafabakhsh and Sajed [83], who proposed the range of 10–15% for the WG rate in favor of a satisfactory mixture performance. Jamshidi and White [15] also propose the value of 15% as an upper limit for the WG rate.
As far as the structural performance of WG-based mixtures is related, Wu et al. [81] considered WG rates of up to 20% and demonstrated an increased rut depth based on the results of the testing process with Hamburg Wheel Tracking. Jamshidi et al. [21] reported that controlling the WG size can counterbalance any potential negative impact on rutting. In terms of moisture sensitivity, Hughes [84] did not detect any considerable change in the ITSR, but a minor stripping between glass particles and the binder was observed. A maximum glass size of 9.25 mm, associated with hydrated lime, was recommended to avoid stripping. Furthermore, no effect was reported on the stiffness characteristics of WG mixtures in terms of the indirect tensile strength and the resilient modulus [84]. This also coincides with a satisfactory fatigue-resistant performance at temperatures ranging from 5 to 25 °C, where a slight increase in fatigue life of around 4–5% has been observed [21]. An even higher increase of 35% has been reported elsewhere [77]. On the contrary, at even higher temperatures of around 40 °C, the fatigue life of WG-based mixtures has been commented to decrease. Finally, Airey et al. [79] proved that WG mixtures are less prone to aging, something that was commented as important enough for the use phase of pavements.
As far as the functional performance of pavements with WG-based mixtures, Su and Chen [85] have investigated the field performance of pavements with WG-based surface mixtures and observed higher skid resistance for both dry and wet conditions. In the same context, Gedik [77] commented that angular particles of recycled WG can act in favor of a skid-resistant pavement for wet and icy conditions. Moreover, the presence of WG particles on the surface increases light reflection, which acts in favor of better visibility for drivers at night (Figure 5) [85]. On the other hand, it was more recently stated that WG breakage due to traffic loading (polishing action) alerts for frequent maintenance planning to preserve the skid resistance capacity of pavements [21]. Therefore, it appears again that field demonstration examples and/or pilot road sections with alternative materials might be the most holistic solution to obtain a comprehensive understanding of pavement performance composed of alternative materials.

Figure 5.
Visibility improvement of pavement surfaces with WG particles.
Finally, some safety aspects have to be mentioned that are known to hinder the extensive use of WG in mixtures for surface courses. As vehicles travel over a pavement surface, they can dislodge glass particles that can cause damage to the vehicles and/or even injure pedestrians in urban road environments [75]. As such, there is a tendency not to “trust” WG for heavy-duty motorways where vehicles move at high speeds [21]. On the contrary, parking lots or low-volume roads seem to be a more appropriate domain for using WG.
2.5. Steel Slag
The steel industry represents a strategic and key contributor to the economy of several industrialized countries [86]. The EU produces steel slag at an annual quantity of 21.8 million tons [32,87], and 24% of this waste is temporarily stored and landfilled, thereby raising the potential of alternative reuses, like the inclusion of asphalt surface courses. In more detail, steel slag is a by-product of the steel-making process and is subdivided into Basic Oxygen Furnace Slag (BOFS) and Electric Arc Furnace Slag (EAFS), according to the method of steel production [88]. It is mainly composed of silica, alumina, titanium, iron sand, and calcium/magnesium oxides [89]. As a by-product, steel slag is typically used as an alternative aggregate material in asphalt concrete mixtures. Superior performance has been mentioned for slag-based mixtures that exhibit advantageous mechanical properties and improved skid resistance [14,88,89,90,91].
With respect to the mechanical properties, a satisfactory anti-rutting and moisture-resistant performance has been observed in mixtures where the coarse aggregate fraction was fully replaced by BOFS [92,93]. On the contrary, research has shown that using steel slag to replace the fine particles of aggregates could worsen the moisture-related performance of the mixture [91]. Improved performance against the development of permanent deformation has been acknowledged elsewhere, e.g., [94]. Pattanaik et al. [95] performed a sensitivity analysis of EAFS mixtures for porous pavements, considering dosages of 25–100% with an increment of 25%. They revealed satisfactory behavior for all dosages in terms of permanent deformation and moisture susceptibility, but the most optimal one corresponded to the dosage of 75%. Ameri et al. [96] recommended the use of EAFS for WMA mixes indicated limited moisture susceptibility and higher resilient modulus than conventional WMA mixes. Higher stiffness moduli and fatigue resistance for slag-based mixtures have been also reported by Pattanaik et al. [95] at a reference temperature of 20 °C, whereas higher moduli for a wider temperature range (−10, 5, 20, 40, and 54 °C) have been reported by Kim et al. [97] based on dynamic modulus testing. The fatigue performance of both BOFS- and EAFS-based mixtures has been characterized as sufficient and even improved compared to conventional mixtures [98]. Passetto and Baldo [99] stated that the presence of steel slag at a dosage of 50% improves the fatigue performance of asphalt mixtures based on test results from the four-point bending test and considered alternative approaches for fatigue characterization. It is mentioned that RAP was also included in their mixtures. Dondi et al. [89] conclude that because of its angular and rough-textured particles, steel slag contributes to a better interlocking mechanism of mixtures’ aggregates, thereby justifying its superior mechanical properties [100].
Additionally, the presence of steel slag in asphalt mixtures for surface courses is known to have a noticeable contribution to pavement’s frictional performance [88,91,101]. Autelitano and Giuliani [86] claim that the surface irregularities of steel aggregates, high toughness, abrasion, polishing resistance, and good affinity to the asphalt binder make EAFS mixtures an ideal choice in terms of the provided skid resistance and durability. These requirements are essential for wearing courses on motorways subject to high traffic- and climatic-induced stresses [13,102]. Based on microstructural analyses, Sofilic et al. [103] demonstrated a promising potential for using steel slag in surface treatments. Cui et al. [101] thoroughly investigated the use of slag in micro-surfacing (preventive maintenance measures) by focusing on frictional performance assessment with innovative laser scanning methods and digital processing. They revealed that the morphological differences between steel slag and natural aggregates of the mixture in conjunction with strong interlocking can help the mix design of micro-surfacing with simultaneously good skid resistance and improve traffic loading resistance. Considering data from field pavement performance, asphalt mixtures containing steel slag exhibit satisfactory performance in terms of skid resistance and surface texture in the long term [104,105]. Kehagia [88] reported that the British Pendulum Number (BPN) and the Mean Texture Depth (MTD) (sand patch method) were better on pavements with EAFS mixtures compared to conventional ones.
From the above remarks, it appears that using steel slag is a quite common approach for both traditional HMA and WMA, and it has been also investigated together with the use of RAP [100,106,107]. Despite the improved performance features, defining optimal rates seems to be again a critical issue for steel-based mixtures [86]. Skaf et al. [91] summarize two important challenges related to the high bulk-specific gravity of steel-based mixtures because of the presence of iron oxides and the impact on volumetric properties in case they have been used in high contents. The former relates to the likelihood of producing heavy mixtures, thereby increasing transportation costs and fuel consumption [86]. The latter implies that mixtures with high slag content have higher air voids, thereby raising the optimum binder content because of the high levels of absorption of slag and contradicting potential improvement on the mechanical properties [91]. In order to deal with such practical compatibility issues, although there is enough experimental evidence about the improvement of mix performance with high slag content, the actual optimal rate is much lower, e.g., in the area of 30%, according to several studies [108,109,110].
Overall, steel slag can be preferably used as a coarse aggregate substitute since problems could appear in terms of water sensitivity if it is used to substitute fine particles or filler [91]. Potential issues with the slag’s chemical composition can be dealt with before its incorporation into the new mixtures, including the removal of free calcium and magnesium oxides and the assessment of the slag’s expansion potential [32].
2.6. Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement
2.6.1. Overview
The main purpose of using RAP during pavement construction and reconstruction is to limit the need for natural resources and virgin aggregates. The process to obtain RAP through the milling process of existing pavements is illustrated in Figure 6. The ability to reuse RAP exhibits environmental benefits, including the reduction in (i) energy consumption, especially if RAP is combined with WMA [20,111,112,113,114], and (ii) GHG emissions during the production and construction process [114,115]. Transportation costs needed to obtain high-quality virgin aggregate are also lowered [3]. In the meantime, landfilling needs can be more rationally managed [116]. On these grounds, RAP has been investigated and widely used as an alternative material in road structures. RAP can be used in different pavement layers; as an alternative material for bases/subbases [117,118,119], where the material behavior is mainly nonlinear elastic [120], and for the asphalt layers, where the material behavior is mainly viscoelastic [121].

Figure 6.
Process to retrieve RAP.
However, different asphalt layers encompass different performance features and require adherence to specifications, with those materials intended to be used in surface or wearing courses having the most stringent requirements [32]. The strict requirements of asphalt surfaces include anti-skid and distress-resistant behavior. As such, the use of RAP in asphalt surface courses is still not prevalent, and the share rate of RAP is kept at relatively low levels [4,32]. Based on extensive research, Al-Qadi et al. [122] demonstrated that the proper preparation of RAP mixtures is a critical aspect of pavement performance and can behave satisfactorily with respect to rutting, thermal and fatigue resistance, and overall durability or longevity. Nevertheless, the maximum RAP content that can guarantee the aforementioned performance for asphalt surface courses consistently poses a major question and challenge for researchers and practitioners. This is because RAP, despite being a fully recyclable material, is reluctantly used at high contents [4,24].
According to a relevant report by the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) [123], using RAP up to 30% by mixture weight in the intermediate and surface layers does not compromise pavement performance compared to control mixtures with virgin aggregates. Similar remarks have been made by many researchers, reporting that optimal RAP rates range from 10 to 30% [124,125,126]. In the same context, Sabouri et al. [3] claim that RAP rates up to 15–20% are most comfortably selected by agencies and contractors considering experimental observations and pavement performance attributes in the field. Therefore, surface mixtures, including RAP, of more than 20–30% can be considered high RAP mixtures [4,127].
2.6.2. Challenges Related to the Use of RAP
The main challenges that are faced for higher RAP rates include the increased brittleness of the recycled mixture [23,128]. The aged-hardened binder of RAP has a different chemical composition than that of virgin binders [25]. Actually, as the RAP content increases, special care needs to be taken for the binder blend design. According to European standards [129], once RAP content is higher than 10% for surface courses, the virgin binder should be selected such that a logarithmic blending law for penetration and a linear blending law for the softening point are applied. In the US, for RAP contents greater than 20%, there are blending charts available to consider a wide temperature range for blending RAP and virgin binders. Lo Presti et al. [4] presented a novel approach and a detailed preliminary blend design for mixing RAP and virgin binders, which was the first step toward achieving even higher RAP contents that can reach the maximum rate of 100%.
The actual problem from the presence of high RAP is that the final mixtures become stiffer and thus more susceptible to fatigue and low-temperature cracking [3,111]. On the other hand, the increased stiffness of RAP mixtures makes them favorable against rutting [5,130]. To address the first aspect, the use of soft virgin binders to achieve a higher blending degree [131] or the use of rejuvenators for RAP binder modification is needed [24,132,133,134]. Rejuvenators can handle the issue of short-term aging because of the high temperatures needed to mix RAP and HMA and restore the chemical composition of the aged binder [131]. In addition, the stiffness of the aged binder is reduced, so a mixture’s fatigue performance can be improved, but the anti-rutting potential can be affected [128]. In the meantime, the blending efficiency of RAP, virgin binders, and/or binder additives (i.e., rejuvenator, recycling agent) can definitively control the performance outcome of the produced recycled mixture [4,128]. Therefore, a balanced mix design is most commonly needed to reach an optimal behavior of RAP mixtures [4,135,136].
The role of temperature is another critical parameter that should be considered for the preparation of RAP mixtures. The aged binder of RAP usually requires effort (i.e., high temperatures and aggregate heating) to improve the mixture’s workability and blending efficacy. There have been comments on potential environmental issues that this phenomenon can contradict the sustainability benefits of reducing the need for virgin materials [21]. High temperatures might increase the GHGs. For field practice and relevant applications, WMA technology can be a rational solution to this problem with many promising results so far [20,111].
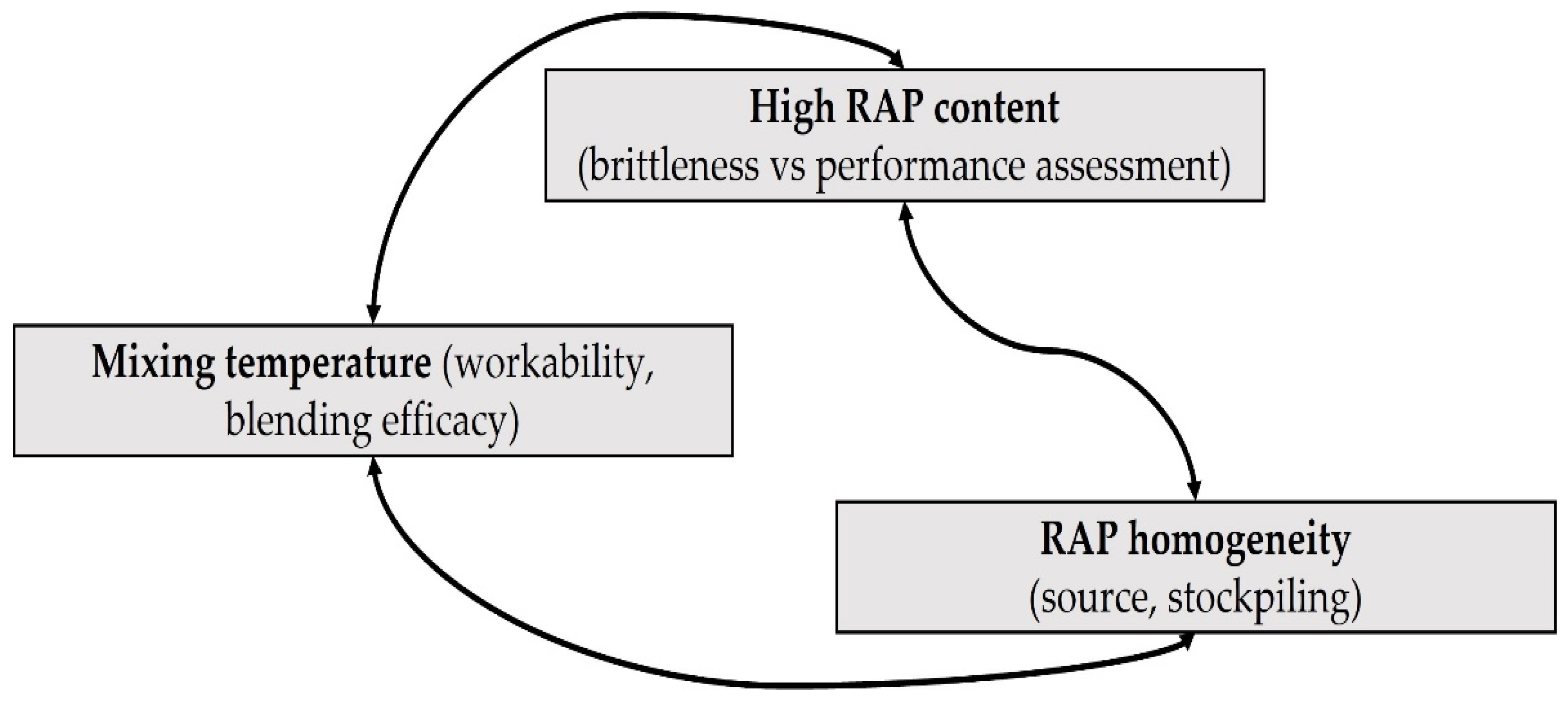
The mixture’s workability is also dependent on the homogeneity of the mixture, something that can, in turn, affect the whole performance of the pavement [137]. The intrinsic properties of RAP origin (i.e., binder type, filler used, age, and type of aggregate) and the handling process can drastically affect the homogeneity of the recycled mixture, including RAP [138]. On the same grounds, Mogawer et al. [139] confirmed that certain production factors, such as the source of RAP, the virgin binder penetration grade, production temperature, and plant type, can affect the material properties and, consequently, field performance. Additionally, RAP stockpiles exhibit considerable variations in the available gradations and can affect the way a recycled mixture conforms to the related specifications [137]. Antunes et al. [138] highlighted three important aspects to ensure mixture homogeneity: (a) fractioning RAP while being stockpiled, (b) uniformly applying the rejuvenator so that it can fully cover RAP particles, and (c) thoroughly blending the produced mixture. No matter the aging status of RAP, a simple fractioning and characterization of RAP bitumen and aggregate grading can make it possible to formulate a high RAP mixture. The role of the RAP feeding method in the mix plant has been highlighted elsewhere [140]. The aforementioned factors are collectively shown in Figure 7.

Figure 7.
The balance between three challenges for RAP mixtures.
Overall, so far, the research has revealed increased potentialities for using high RAP contents. Nevertheless, the final cost-effectiveness of the whole procedure poses some questions regarding the varying degree of awareness and readiness of the existing plant types and their related equipment on a worldwide scale. Consistent efforts might be needed in order to be able to reach a drastic increase in RAP in asphalt mixtures and maximize the related sustainability benefits. In particular, a technological change is needed for most of the existing asphalt plants, and local policies should be formulated in favor of innovative changes so that aspects related to RAP handling, RAP gradation, and quality should not appear as limitations [4].
2.6.3. Performance Features of RAP Mixtures
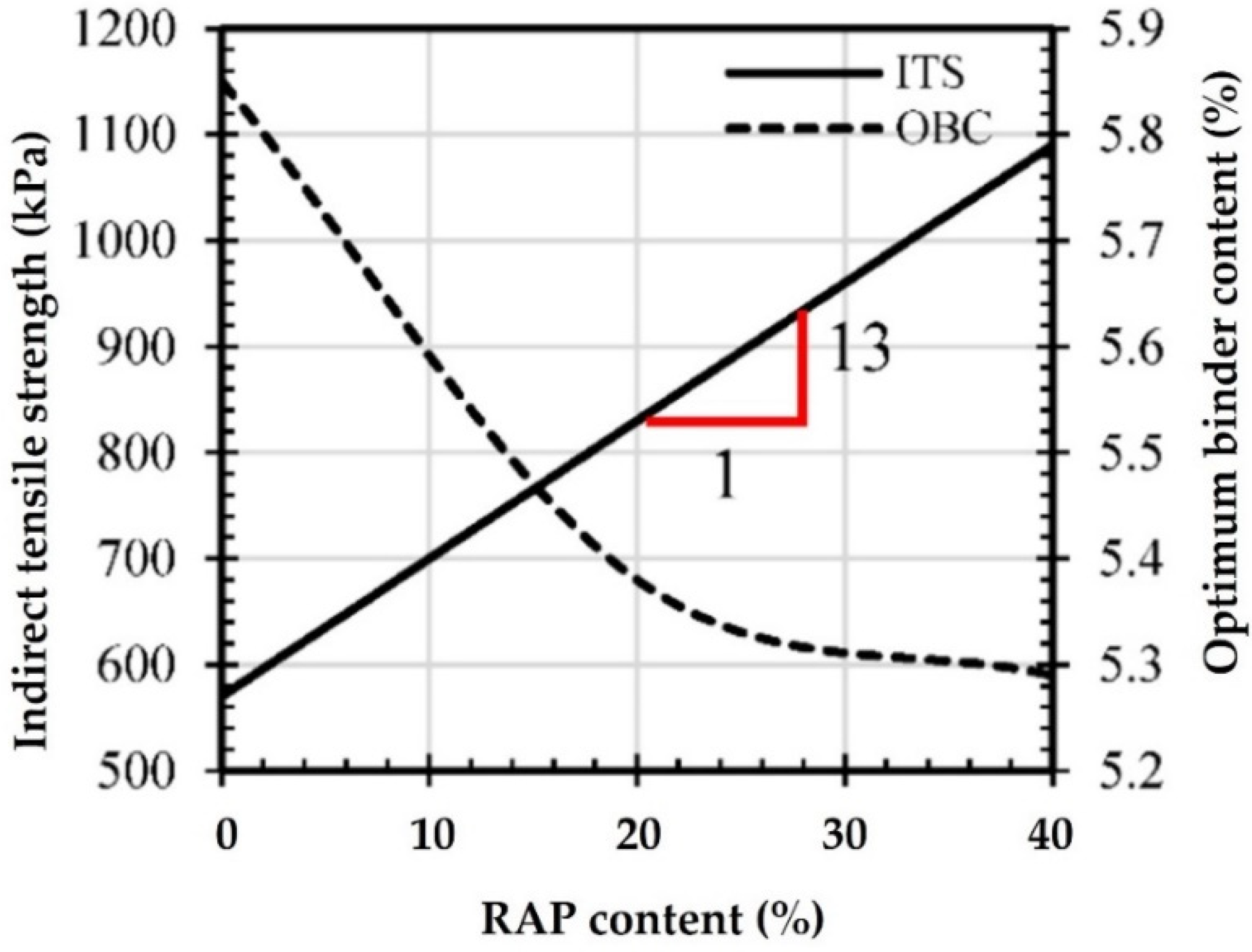
Focusing on the individual performance features of RAP mixtures, numerous experimental findings exist in the international literature. Due to the presence of the aged binder, the need for a new binder is thereby reduced, and the optimum new binder content (OBC) exhibits a descending trend (Figure 8) [21]. The stiffness characteristics of RAP mixtures are, in general, improved; the dynamic modulus and the indirect tensile strength are reported to increase (Figure 8) [141,142]. Carefully selecting rejuvenators can ensure a controlled cracking susceptibility [131].

Figure 8.
The impact of RAP on indirect tensile strength (ITS) (the red line and numbers denote the line slope) and the optimum binder content (OBC) [15].
Moving forward, insignificant differences between control mixtures and mixtures with 20–30% RAP have been reported by Maupin et al. [143] for fatigue and rutting behaviors, as well as for moisture damage potential. The authors used plant-produced mixtures and demonstrated that the addition of RAP undoubtedly raises the temperature grading, an aspect worthy of consideration in the mix design, as also previously implied. Similar remarks regarding the absence of blending problems and other mixture fabrication issues have been reported when using RAP up to 30% [144] for the same performance features (i.e., fatigue, rutting, and moisture damage). High RAP mixtures for wearing courses, including RAP between 20% and 50%, combined with WMA technology yielded a satisfactory performance in terms of durability, cracking, and rutting resistance [145]. Poursoltani and Hesami [146] investigated high RAP mixtures for micro-surfacing and proved that recycled mixtures met the design criteria of the International Slurry Surfacing Association (ISSA). Investigations for RAP contents from 40% to 100% showed improved performance against stripping near the vicinity of water, with the mixtures with 70% of RAP outperforming the other ones.
Of course, in the absence of strict guidelines and/or specifications, one should not be surprised by potentially controversial results that might argue against the use of RAP in surface courses. Based on LTPP data, Wang [147] commented that for distressed pavements with RAP overlays, the thickness of the overlay controls the performance efficacy of RAP mixtures. In particular, for thin overlays, RAP tends to weaken the pavement performance compared to overlays with virgin materials, whereas the opposite was observed for thick overlays. Gong et al. [148] claim that the use of RAP for the surface rehabilitation of pavements could adversely affect long-term pavement performance, but the impact on wheel path and non-wheel path longitudinal cracking appears to be limited. On the other hand, Hand et al. [149] pinpointed satisfactory field performance of low-volume roads in North Nevada with surface courses of 100% RAP based on the fact that these roads required little to no maintenance actions during their lifespan. Such remarks again highlight the importance of field observations that can shed further light on performance attributes of recycled mixtures and further ameliorate laboratory procedures aiming to better understand the impact of RAP on pavement performance.
Similar to the previous waste materials under investigation, related research about serviceability issues is limited to pavement surfaces with RAP mixtures [66,145,150]. Indicatively, based on limited material data, Wang et al. [150] reported a promising potential of using high RAP content asphalt mixtures in terms of skid resistance. Measurements with the British Pendulum Tester (BPT) on a laboratory scale yielded a friction increase against RAP content increase for micro-surfacing mixtures. It is noted that RAP contents of up to 80% were considered during this investigation. On the other hand, Pomoni et al. [67] investigated the predictability of the polishing behavior of RAP mixtures and found a lower friction coefficient compared to control HMA mixtures. Based on this, the authors commented on the sustainable potential of using RAP for constructing or reconstructing surface courses of low-volume roads. This is in agreement with long-term positive observations of other studies for low-volume roads with surfaces of RAP mixtures [149]. Sedthayutthaphong et al. [130] also explored the attenuation mechanism of skid resistance for RAP mixtures and claimed that the initial skid resistance depends on the properties of the blended asphalt binder, whereas the final skid resistance might depend on the virgin binder properties and the mixture’s gradation.
2.6.4. RAP Combination with Other Waste Materials
Being the most popular waste alternative material used in pavement engineering, RAP has been also investigated in conjunction with other waste materials [151]. Most of these investigations take place on a laboratory scale, aiming to act as a precursor for future expansion of large-scale experiments and pilot cases in the field. Some of the numerous studies are briefly presented hereinafter.
The use of RAP has been jointly investigated with CR and other additives, like Waste Engine Oils (WEOs) playing the role of rejuvenators. WEOs are known to enhance RAP mix workability and reduce the optimum binder content [152,153,154]. Khan et al. [155] have developed an arbitrary scale to rank the performance of RAP-WEO mixtures with CR as a binder modifier, and, based on laboratory tests, they concluded that the resilient modulus, indirect tensile fatigue, and moisture susceptibility were improved. The authors expressed their confidence in achieving higher RAP contents of up to 100% [155]. The fine particles of CR were used in the form of filler to modify dense-graded mixtures with RAP at 30% that were investigated in the laboratory for their mechanical properties and the field for their frictional properties [66]. It was observed that the Indirect Tensile Stiffness Modulus (ITSM) decreased at low temperatures because of the addition of CR and remained comparable to pure RAP mixtures at moderate and high temperatures.
In terms of serviceability features, if properly mixed and manufactured, CR-RAP mixtures exhibited improved micro- and macrotexture performance. Fakhri and Ahmadi [106] used (i) EAFS with (ii) RAP into WMA at rates of (i) 0 and 40% and (ii) 0%, 20%, and 40% respectively. Compared to the control mixtures (with EAFS and RAP at 0%), the modified mixtures tolerated a higher number of cycles in both dynamic creep and indirect tensile fatigue tests. The authors concluded that the environmental benefits gained from WMA technology can be magnified by jointly using EAFS and RAP [106]. Song et al. [156] investigated the use of glass fibers as an alternative means instead of rejuvenators to improve the fracture performance of RAP mixtures intended to be used for the design of ultra-thin friction courses (UTFCs). The inclusion of RAP and glass fibers revealed a better cracking resistance at low temperatures of around −10 °C and reduced cracking resistance at moderate temperatures of around 25 °C. The authors concluded that more tests are needed to ameliorate the adhesion potential of these two components by investigating different fiber lengths and distribution uniformity issues [156].
Overall, it appears that a lot of interest exists in using non-conventional materials for surface courses of asphalt pavements, something that is further justified considering that the most frequent Maintenance and Rehabilitation (M&R) actions usually focus on the very top of the pavement structure [26,157]. In many of these efforts, RAP remains the key material component that is normally preferred over other waste materials [158]. Therefore, related research on its use for surface courses consistently revives, although recycling itself is not a novelty [5].
2.6.5. RAP in Airfield Pavement Surfaces
The use of RAP for surface courses in airfield pavements is not as dominant compared to the case of highway pavements. Jamshidi and White [15] claim that the relevant reluctance is grounded in the long-term performance and durability concerns because of the severe aircraft loading conditions that make the runway pavement a high-risk environment [159]. Related remarks and experimental findings are presented below.
Relatively low RAP contents in the range of 5–10% have been used at two Australian airports without any negative impact on pavement performance, with the exception of reduced skid resistance in wet conditions [160]. Su et al. [161] investigated the use of RAP to build the asphalt surface course in a Japanese airport. After assessing the short- and long-term aging properties of the RAP binder, they performed a full-scale experiment with mixtures consisting of 40% and 70% RAP. Based on a three-year observation period, the performance of the trial sections with RAP mixtures was comparable to the control section (non-RAP mixture) in terms of both bearing capacity and evenness. Based on a collective assessment of laboratory findings and field observations, the use of RAP at a rate of 40% was favorable, apart from some moisture susceptibility issues. On the contrary, the authors did not recommend a high rate of 70% because of its poor fatigue resistance.
Overall, similar to roadways, many airports worldwide require frequent maintenance and/or minor rehabilitation measures. New construction might be limited, whereas the existing structures need to serve even heavier aircraft than those considered in the initial design [162]. However, the current construction specifications (AC150/5370-10H) of the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) do not permit the use of RAP in surface courses, apart from the case of pavement shoulders [163]. Based on this, the FAA has initiated a 10-year program to investigate recycling challenges for surface courses of airfield pavement combined with the benefits of WMA. Therefore, recycling opportunities for the construction or reconstruction of surface courses at airfield pavements should be further encouraged and investigated.
3. Challenges and Perspectives on the Use of Waste Materials
There is a common consensus that the use of waste materials can reduce the required quantities of virgin materials for HMA production (i.e., binder, aggregates), limit transportation costs for material procurement, ensure resource conservation, and address landfilling issues and debris accumulation [3]. Meanwhile, given on the one hand the strict performance requirements of surface courses in asphalt pavements, and, on the other hand, the diversity of material types and properties, there are several issues that one should consider before selecting waste materials. The present section gathers aspects to consider related to the use of waste materials in the surface courses of asphalt pavements.
3.1. Conventional Mixtures and Reference Status
First of all, related research should acknowledge the performance of asphalt mixtures with conventional materials and preparation techniques, which should be considered a reference status for the assessment of any kind of alternative mixtures. For waste materials that are expected to substitute the binder, special care needs to be taken with laboratory testing to evaluate their impact on the viscoelastic properties of the binder and the mixture [15]. It is practically implied that if a non-conventional material worsens the final mixture’s behavior, it should be probably rejected or at least used with caution, depending on several parameters, like the type of road, its traffic volume, the expected frequency for M&R actions, etc. Scientific research and more industrial experience from field applications definitely provide the strength to produce solid results.
3.2. Material Availability and Local Conditions
Thereafter, the available quantity of waste material is a determinant factor that could control its use. Waste materials could create landfilling problems at a local level (i.e., in a specific country, province, etc.) because of large volumes that might not be the first choice elsewhere (i.e., in a different country or province, etc.). By far, a considerable portion of RAP can be considered a raw material for asphalt surface courses on a worldwide scale for two dominant reasons that can account for the total road network.
The first is related to the heavy-duty pavements, where the ambition of road authorities and operators is to meet the challenges of maintaining LLPs. These pavements are designed and constructed so that their structural adequacy is guaranteed in the long term. However, the service life of wearing courses is usually limited, so interventions usually focus on restoring pavement surface condition and enhancing road users’ safety and comfort [53,67]. As a result, an increased amount of RAP becomes available from milling processes, thereby raising its potential for being envisaged as a secondary source of raw materials complimentary to virgin ones during reconstruction [5]. Thereafter, on the secondary road network, the majority of pavement infrastructure is in poor condition both in terms of structural integrity and serviceability [26]. However, such pavements usually serve low traffic volumes; therefore, in-depth rehabilitation needs tend to be neglected as impractical and costly. Cadar et al. [26] claim that Romanian pavements of a total length of around 24,000 km require rehabilitation at least in their wearing courses. In the meantime, virgin materials are not available everywhere in isolated regions [15], and costs for material production and transportation might be unaffordable [3]. As such, periodical surface restorations dominate again, thereby increasing the availability and the recyclability of RAP.
Therefore, RAP, as well as other waste materials, at the end-of-life disposal phase near a road network become a feasible alternative choice. In the same context, frequent interventions during roadway maintenance and reconstruction appear as an appealing way out for other waste materials (e.g., plastic, glass, etc.) to be effectively treated with a sustainable perspective. For instance, the disposal of plastic wastes and scrap tires is a social and environmental concern for many countries because of the non-biodegradable nature of these materials [164,165]. This issue leaves enough margin for consistent and ad hoc research initiatives that aim to provide viable alternatives that could engross a considerable part of the waste quantities. Of course, local conditions apply to each case. For instance, waste tires are more likely to be produced in areas where old cars are more intensively replaced by new ones. In particular, China is expected to double the number of new passenger cars from 2016 to 2024; so, recycling of the scrap tires of existing cars that are to be replaced becomes an issue [166]. On the other hand, the reutilization of scrap tires for new cars requires the exhaustive process of re-vulcanizing rubber [52]. As such, it is also important to perform a cost–benefit analysis so that it can be more holistically proved whether recycling for the pavement industry is a more privileged domain than recycling by other industries [32].
3.3. Life Cycle Analysis
The economic pillar of pavement recycling is an important aspect to consider. Costs refer to those affecting the road agencies and operators, as well as those related to the road users [15]. Comparisons with virgin material supply and recycled material processing should be performed, as well as an evaluation of the adaptiveness of existing production systems and equipment [4]. Such investigation can stimulate a targeted technological change and a radical improvement in the related specifications and/or recommendations. Prior to this, Life Cycle Analysis (LCA) appeared to be a comprehensive tool that is absolutely necessary for complementing performance analysis of recycled mixtures so that more robust decision making can be performed while adopting recycling perspectives [167,168,169,170].
Assaf and Abu Abdo [171] evaluated the environmental impact of recycled mixtures, including 0–40% RAP, for aggregate replacement and 0–20% waste plastic for binder replacement. From a design sensitivity analysis, they found that plastic is superior to RAP in terms of energy consumption and GHG emissions. According to [172], mix composition plays a critical role in the carbon footprint of alternative mixtures. The dosage of the older materials has a greater impact on carbon emissions than the percentage of the alternative materials used in the mixtures. Bizzaro et al. [173] reported a reduction rate of 55–64% for the carbon footprint of asphalt mixtures containing high RAP percentages (i.e., around 80–90%), whereas for lower RAP contents, the reduction can be even lower. For CR-based mixtures, reduction in carbon dioxide emissions is highly dependent on the selection of warm mix additives that can reduce the mixing temperature during mix production [174].
In terms of additional environmental benefits, the use of plastic reduced air acidification and photochemical smog, whereas RAP incorporation eliminated the costs of transporting waste milling products to landfills [171]. Mantalovas and Di Mino [168] introduced the concept of the Environmental Sustainability and Circularity Index (ESCI) to rank the individual levels of circularity of a material. They highlighted that mixtures with RAP at a rate of 90% exhibit the lowest environmental impacts; however, the impact of RAP on pavement performance could affect the service life of a surface course consisting of high RAP mixtures. Therefore, the ESCI is highly dependent on the exact composition of the individual components in a recycled mixture and not solely on the type of components (e.g., RAP or other waste materials).
Farina et al. [167] performed LCA of asphalt mixtures for wearing courses consisting of RAP and CR. They proposed that wet rubberized mixtures offered significant environmental benefits compared to conventional paving. Adding RAP in these mixtures revealed only slight additional enhancement in the environmental impact of the mixtures provided that a careful design and construction are performed. On the other hand, dry-processed CR mixtures do not lead to similar environmental benefits. Overall, it seems that LCA is sometimes, yet sparsely, adopted as a research initiative in the analysis, but the major obstacle to developing reliable LCA inventory data is the consideration of several assumptions, either conservative or not. As such, LCA needs to be systematically retrofitted by the consistent monitoring of production and a comparison of construction techniques.
Compared to LCA, studies involving recycled solid waste materials, like those presented in this review paper, Life Cycle Cost Analysis (LCCA) studies are, in general, rarer. In a comprehensive review, Li et al. [175] pinpointed two important factors that deserve consideration to guarantee a successful economic analysis: (i) the analysis period and (ii) the discount rate. First, the selection of a representative analysis period, so that the use phase can be well considered, is crucial. The analysis period may vary from 20 to 50 years, but its precise selection suffers from the subjectiveness of the decision makers [176]. For example, a short analysis period for the case of rubberized pavements does not reflect the long-term cost savings during the operation phase of the pavement, where M&R planning takes place. As per the discount rate, a range of 2.5% to 7% was reported in [170]; the selection of lower values corresponds to cases with high initial capital investments, whereas higher rates are preferrable for projects with higher future M&R costs. To sum up, strong recommendations to execute economic analysis are clearly pinpointed in the international literature [175,177] in order to supplement conventional LCA.
3.4. Legislative Issues
Finally, the use of candidate waste material should be performed in compliance with any kind of local regulations and potential legislative issues [32]. In particular, the reluctance to extensively use RAP in surface courses because of legislative restrictions has been already highlighted [4]. For example, Anthonissen et al. [178] reported that the use of RAP is not allowed in surface courses following the Flemish Road Standard SB250 v3.1 in Belgium. The use of waste glass is not permitted in surface courses at airport pavements (i.e., asphalt paved runways) because of the aircraft-induced shear loading conditions [15]. The potential of dislodging can cause damage to the moving aircraft.
Legislation can be even stricter for surface courses considering potential leachates from the use of waste materials and the noise induced from the tire–pavement interaction, which are especially crucial for urban environments, lighting requirements, climatic factors (e.g., albedo effect), and environmental considerations (e.g., carbonation, etc.). Such components shall not be excluded from the scope of investigating non-conventional materials in pavement structures and asphalt courses in particular [178].
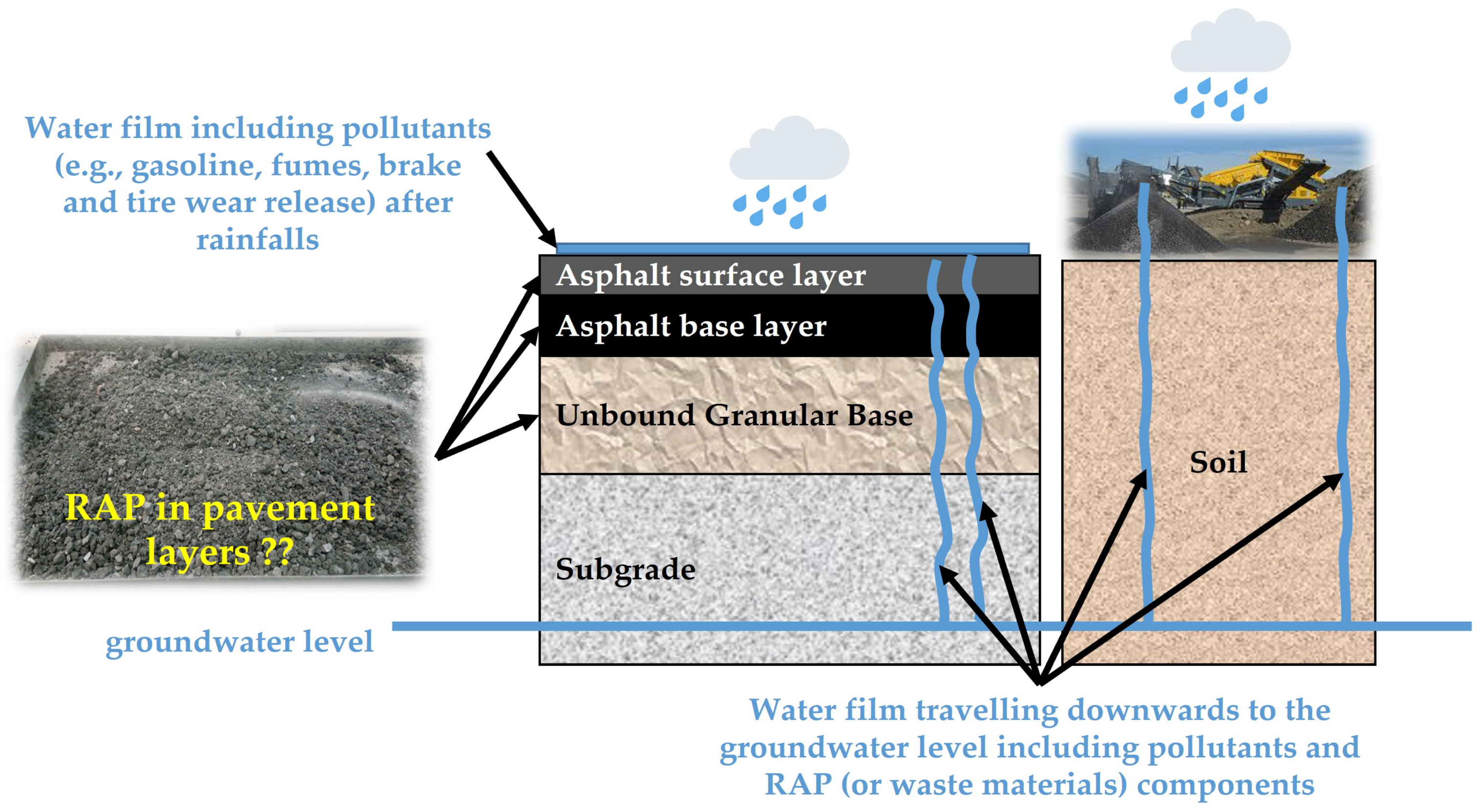
Indeed, a serious concern that is usually overlooked is the contaminant leaching from asphalt pavements to the underlying soils and groundwater aquifers, posing serious risks to ecosystems and the environment. This is a consistent concern related to the whole lifespan of a pavement, dating from the construction phase up to the end of the service life of the pavement [179]. Difficulties in the assessment of leaching potential arise from the fact that leaching can occur because of the use of waste materials in asphalt pavements, as well as from their disposal or stockpiling (Figure 9). Although there are both laboratory and field tests to assess the leaching potential, the latter ones are rare and difficult because of the long execution time needed to complete the assessment and make a complex interpretation.

Figure 9.
Illustration of the leaching action; the example of RAP use in pavements and/or RAP stockpiling.
Based on relevant investigations, it is highlighted that there is a need to consider as many of environmental conditions near the recycled pavement as possible, including, humidity, rainfall frequency, air temperature, and wind speed, for more accurate simulations. Finally, leaching should be assessed with the impact of the soil layers around the pavement and between the groundwater table and the pavement [179]. A joint consideration can help governments, industry, and academia to more effectively plan and design new test protocols and evaluation procedures.
It is deemed that the best approach to improve the current legislative system is to stimulate synergies between local governments, academia, and industry in order to develop relevant technical specifications about the use of waste materials in asphalt mixtures, including source selection, dosages, series of laboratory control tests, evaluation criteria, threshold values for quality acceptance, etc. Further to this, the organization of experimental campaigns in pilot sections of small lengths in situ could definitively enable the performance assessment of asphalt pavements with recycling materials in their surface courses under real traffic and environmental conditions. This factor can help improve and more robustly set legislative aspects for performance-based material requirements and specifications.
Finally, apart from the performance requirements, potential negative impacts on the health and safety of paving crews and working personnel should not be overlooked. Such factors can definitively induce additional legislative concerns surrounding the use of waste materials that should be accounted for [15].
3.5. Synopsis
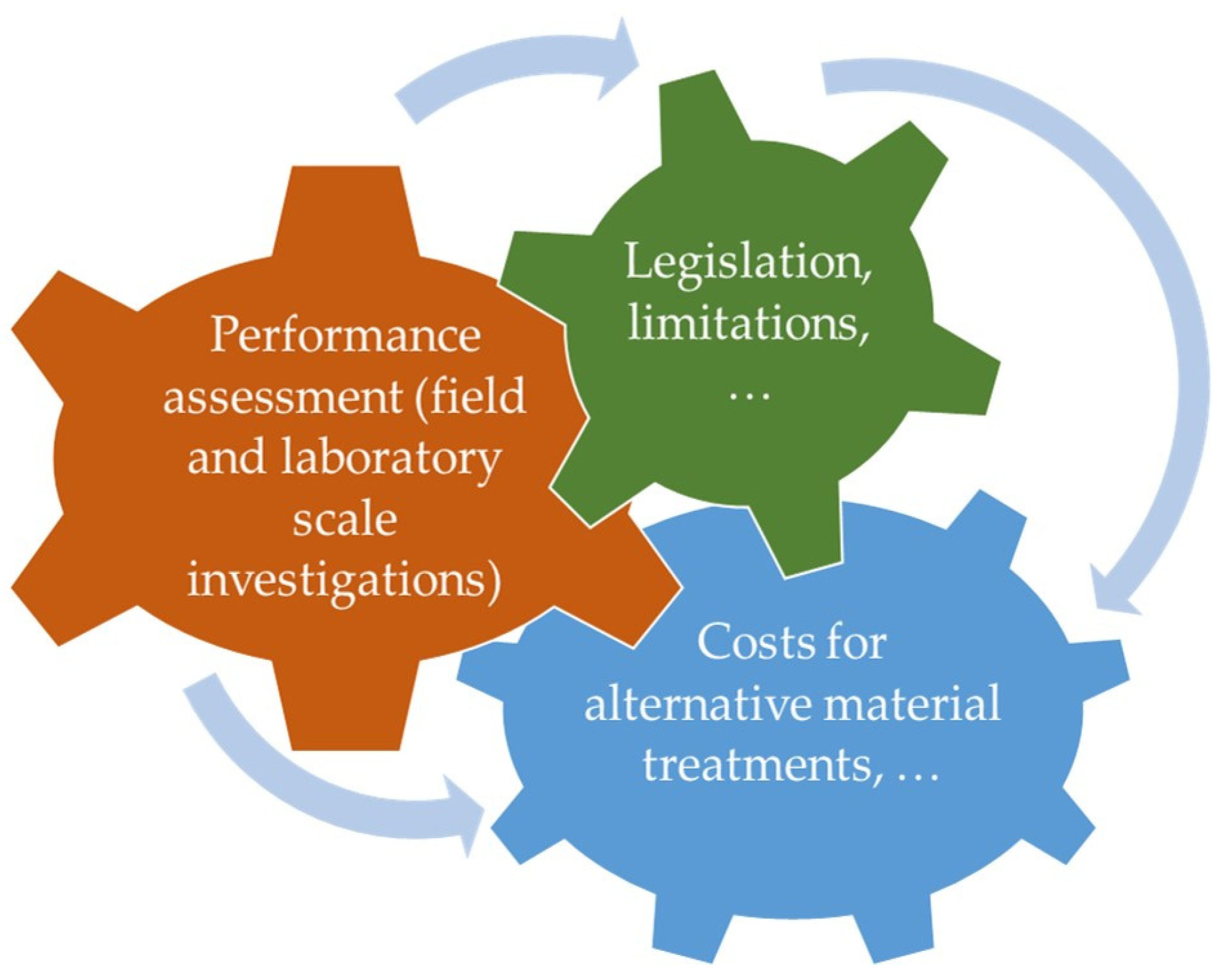
Selecting appropriate waste materials for pavement engineering should conform to performance requirements (i.e., aspects of mechanical behavior and serviceability issues), local availabilities, and potential legislation issues, and they should also maximize the economic or environmental advantages (Figure 10).

Figure 10.
Pillars for the optimal selection of waste materials.
Thereafter, the design and construction of pavement with asphalt courses of recycled materials should balance the majority of the previously mentioned factors [15]. Overall, long-term performance monitoring in the field coupled with laboratory investigations are the key pillars for guaranteeing effective selection and utilization of waste materials. Indeed, Mashaan et al. [17] highlighted the need to demonstrate the viability of mixtures with waste plastic, and, in particular, PET binders, considering field conditions. Other examples based on either short-term or long-term in situ performance monitoring (e.g., [51,85,104,149,180]) further support the criticality of field observations.
4. Conclusions
Recycling waste materials for use in pavement engineering is not something new. Recycling trends can vary in terms of both the material types and the utilized quantities inside the pavement structure. The main motivation for reutilizing waste materials includes the energy retrieval from waste materials, the sustainable practice of reducing the exploitation of natural resources (i.e., resource conservation), and the minimization of landfilling (i.e., transportation costs and required space for disposing of waste materials). In this respect, adopting a different “end-of-life” concept for waste products consolidates the circular economy perspectives among the pavement community.
However, when moving upwards within a pavement, and in particular in the surface course, pavement performance requirements become stricter, considering mechanical behavioral issues and serviceability aspects. This has been proved to limit the maximum rate of waste materials in the composition of the non-conventional mixture. Based on the presented literature findings, it appears that non-conventional mixtures, including waste plastic, crumb rubber, waste glass, steel slag, and RAP, exhibit an equivalent and even improved performance against fatigue, rutting, and moisture damage compared to control mixtures with conventional materials. It is noticed that the majority of the related studies focus on issues about the mechanical performance and the structural contribution of these materials. On the contrary, serviceability issues and functional requirements (i.e., texture, skid resistance, etc.) are more sparsely investigated, thereby receiving limited attention, despite the fact that surface layers are frequently replaced in the framework of an M&R plan.
Therefore, both the structural and functional contribution of non-conventional materials should raise more awareness in terms of sustainability practices in pavement engineering. On these grounds, potential controversies as per the performance of non-conventional mixtures justify why related research consistently revives. The importance of analyzing the full life cycle of pavement surface layers with non-conventional mixtures is also underlined. In the absence of relevant specifications and documented recommendations, research is pursued on an ongoing basis.
Another crucial remark to recall is that while most of the related research takes place in a controlled laboratory environment, the importance of field investigations and demonstration examples through pilot cases should be encouraged. Indeed, laboratory findings can act as a precursor for an optimal mix design, but the evaluation of the in situ performance can provide robust guidance and help the engineering community gain confidence toward a more strategic use of waste materials in asphalt surface courses. To this end, investing the in-place or in-plant recycling techniques for old asphalt pavements, considering both hot and cold procedures, and stimulating many cross-sectoral projects between researchers and practitioners can probably foster a symbiotic collaboration for the implementation of innovative technological processes that are able to transform alternative waste materials into valuable and cost-effective construction materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.G. and M.P.; methodology, K.G. and M.P.; literature review: K.G. and M.P.; writing—original draft preparation, K.G. and M.P.; writing—review and editing, K.G. and M.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Gannon, C.R.; Wombles, R.H.; Ramcy, C.A.; Daris, J.P.; Little, W.V. Recycling conventional and rubberized bituminous concrete pavement using recycling agents (a laboratory and field study). In Asphalt Paving Technology; Proceeding Association of Asphalt Technologists: Louisvile, KY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Imtiaz, A.; Lowel, C.W. Use of Waste materials in highway construction: State of the practice and evaluation of the selected waste products. J. Transp. Res. Rec. 1992, 1345, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Saberi, K.F.; Fakhri, M.; Azami, A. Evaluation of warm mix asphalt mixtures containing reclaimed asphalt pavement and crumb rubber. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Presti, D.; del Barco Carrion, A.J.; Airey, G.; Hajj, E. Towards 100% recycling of reclaimed asphalt in road surface courses: Binder design methodology and case studies. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 131, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, V.; Neves, J.; Freire, A.C. Performance Assessment of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP) in Road Surface Mixtures. Recycling 2021, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mino, G.; Vijayan, V.; Eskandarsefat, S.; Venturini, L.; Mantalovas, K. Investigating the Multi-Recyclability of Recycled Plastic-Modified Asphalt Mixtures. Infrastructures 2023, 8, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilli, A.; Balzi, A. Methodologic Recommendations to Implement Pavement Management Systems and Eco-Sustainable Solutions for Local Road Administrations. Infrastructures 2023, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, M.; Zaumanis, M.; Haritonovs, V. Asphalt Recycling Technologies: A Review on Limitations and Benefits. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 660, 012046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M.; Karimi, A.; Goli, A.; Hajikarimi, P.; Mohammadi, A.; Doctorsafaei, A.; Fini, E. Biobased Polyurethane: A Sustainable Asphalt Modifier with Improved Moisture Resistance. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2023, 36, 04023505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapsoba, N.; Sauzéat, C.; Di Benedetto, H.; Baaj, H.; Ech, M. Behaviour of asphalt mixtures containing reclaimed asphalt pavement and asphalt shingle. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2014, 15, 330–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Huang, B. Recycling of waste tire rubber in asphalt and portland cement concrete: An overview. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 67, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, A.; Ganjidoust, H.; Maghanaki, A.A. Use of plastic waste (poly-ethylene terephthalate) in asphalt concrete mixture as aggregate replacement. Waste Manag. Res. 2005, 23, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Zhong, J.; Zhu, J.; Wang, D. Influence of demolition waste used as recycled aggregate on performance of asphalt mixture. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2013, 14, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondón-Quintana, H.A.; Ruge-Cárdenas, J.C.; Patiño-Sánchez, D.F.; Vacca-Gamez, H.A.; Reyes-Lizcano, F.A.; Muniz de Farias, M. Blast Furnace Slag as a Substitute for the Fine Fraction of Aggregates in an Asphalt Mixture. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, A.; White, G. Evaluation of Performance and Challenges of Use of Waste Materials in Pavement Construction: A Critical Review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Long, Z.; You, Z.; Ge, D.; Yang, X.; Xu, F.; Hashemi, M.; Diab, A. Review of recycling waste plastics in asphalt paving materials. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2022, 9, 742–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashaan, N.S.; Chegenizadeh, A.; Nikraz, H.; Rezagholilou, A. Investigating the engineering properties of asphalt binder modified with waste plastic polymer. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 1569–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroni, F.; Flintsch, G.W.; Diefenderfer, B.K.; Diefenderfer, S.D. Application of Balanced Mix Design Methodology to Optimize Surface Mixes with High-RAP Content. Materials 2020, 13, 5638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meroni, F.; Flintsch, G.W.; Habbouche, J.; Diefenderfer, B.K.; Giustozzi, F. Three-level performance evaluation of high RAP asphalt surface mixes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 309, 125164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puccini, M.; Leandri, P.; Tasca, A.L.; Pistonesi, L.; Losa, M. Improving the Environmental Sustainability of Low Noise Pavements: Comparative Life Cycle Assessment of Reclaimed Asphalt and Crumb Rubber Based Warm Mix Technologies. Coatings 2019, 9, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, A.; Kurumisawa, K.; Nawa, T.; Igarashi, T. Performance of pavements incorporating waste glass: The current state of the art. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 64, 211–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Tanyu, B.F.; Dawson, A. Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP) as an Unbound Base Course Material: A Mechanistic Design Approach Based on Multi-stage Repeated Load Triaxial Tests. Transp. Geotech. 2022, 33, 100729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaumanis, M.; Cavalli, M.C.; Poulikakos, L.D. Effect of rejuvenator addition location in plant on mechanical and chemical properties of RAP binder. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2020, 21, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaumanis, M.; Mallick, R.B.; Frank, R. 100% Hot Mix Asphalt Recycling: Challenges and Benefits. Transp. Res. Procedia 2016, 14, 3493–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomoni, M.; Plati, C. Skid Resistance Performance of Asphalt Mixtures Containing Recycled Pavement Materials under Simulated Weather Conditions. Recycling 2022, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadar, R.D.; Boitor, R.M.; Dragomir, M.L. An Analysis of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement from a Single Source—Case Study: A Secondary Road in Romania. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, P.; Gambatese, J.-A. Energy consumption of asphalt and reinforced concrete pavement materials and construction. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2005, 11, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivilevičius, H.; Martišius, M. The Significance of the Factors Increasing the Asphalt Pavement Recycling Rate in the Country, Determined Using Multiple-Criteria Decision-Making Methods. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPAE. Municipal Solid Waste Generation and Disposal in the United States: Facts and Figures for 2012; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Jaber, M.; Al-shamayleh, R.A.; Ibrahim, R.; Alkhrissat, T.; Alqatamin, A. Mechanical properties evaluation of asphalt mixtures with variable contents of reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP). Results Eng. 2022, 14, 100463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedrigo, W.; Heller, L.F.; Brito, L.A.T.; Núñez, W.P. Fatigue of Cold Recycled Cement-Treated Pavement Layers: Experimental and Modeling Study. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, Z.; Mikhailenko, P.; Rafiq Kakar, M.; Bueno, M.; Hellweg, S.; Poulikakos, L.D. Urban mining for asphalt pavements: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandal, M.; Sood, H.; Gupta, P.K. A review study on sustainable utilisation of waste in bituminous layers of flexible pavement. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franesqui, M.A.; Yepes, J.; Valencia-Díaz, S. Sustainable Pavement Construction in Sensitive Environments: Low-Energy Asphalt with Local Waste Materials and Geomaterials. Buildings 2024, 14, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaro, N.S.A.; Sutanto, M.H.; Baloo, L.; Habib, N.Z.; Usman, A.; Yousafzai, A.K.; Ahmad, A.; Birniwa, A.H.; Jagaba, A.H.; Noor, A. A Comprehensive Overview of the Utilization of Recycled Waste Materials and Technologies in Asphalt Pavements: Towards Environmental and Sustainable Low-Carbon Roads. Processes 2023, 11, 2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cao, Y.; Sha, A.; Song, R.; Li, C.; Wang, Z. Prospective application of coal gangue as filler in fracture-healing behavior of asphalt mixture. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 373, 133738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Gao, X.; Xu, S.; Yang, X.; Tian, Q.; Liu, J. Microwave Heating Healing of Asphalt Mixture with Coal Gangue Powder and Basalt Aggregate. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashaan, N. Engineering Characterisation of Wearing Course Materials Modified with Waste Plastic. Recycling 2022, 7, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, R.S.; Marik, S. A review literature on the use of waste plastics and waste rubber tyres in pavement. Int. J. Core Eng. Manag. 2014, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Punith, V.S.; Veeraragavan, A. Behavior of asphalt concrete mixtures with reclaimed polyethylene as additive. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2007, 19, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastra-Gonzalez, P.; Calzada-Perez, M.A.; Castro-Fresno, D.; Vega-Zamanillo, A.; Indacoechea-Vega, I. Comparative analysis of the performance of asphalt concretes modified by dry way with polymeric waste. Construct. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, J.P.; Panda, M.; Sahoo, U.C. Performance of bituminous mixes containing treated recycled concrete aggregates and modified by waste polyethylene. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, M.; Nasr, D. Performance properties of devulcanized waste PET modified asphalt mixtures. Petrol. Sci. Technol. 2017, 35, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziari, H.; Nasiri, E.; Amini, A.; Ferdosian, O. The effect of EAF dust and waste PVC on moisture sensitivity, rutting resistance, and fatigue performance of asphalt binders and mixtures. Construct. Build. Mater. 2019, 203, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofteci, S. Effect of HDPE based wastes on the performance of modified asphalt mixtures. Procedia Eng. 2016, 161, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouali, M.; Derriche, Z.; Ghorbel, E.; Li, C. Plastic bag waste modified bitumen a possible solution to the Algerian road pavements. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2020, 21, 1713–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadas Nejad, F.; Arabani, M.; Hamedi, G.H.; Azarhoosh, A.R. Influence of using polymeric aggregate treatment on moisture damage in hot mix asphalt. Construct. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 1523–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherkhani, H.; Arshadi, M.R. Investigating the mechanical properties of asphalt concrete containing waste polyethylene terephthalate. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2019, 20, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, N.; Masirin, M.I.M.; Ahmad, K.A.; Ali, A.S.B. Application of recycled polyethylene terephthalate fiber in asphaltic mix for fatigue life improvement. In Proceedings of the 1st Global Civil Engineering Conference, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 25–28 July 2017; Pradhan, B., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 1401–1413. [Google Scholar]
- Karmakar, S.; Majhi, D.; Roy, T.K.; Chanda, D. Moisture damage analysis of bituminous mix by durability index utilizing waste plastic cup. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, F.; Eskandarsefat, S.; Venturini, L.; Viscione, N. A complete study on an asphalt concrete modified with graphene and recycled hard-plastics: A case study. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressi, S.; Fiorentini, N.; Huang, J.; Losa, M. Crumb rubber modifier in road asphalt pavements: State of the art and statistics. Coatings 2019, 9, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Presti, D. Recycled Tyre Rubber Modified Bitumens for road asphalt mixtures: A literature review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 863–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, F.; Marcobal, J.; Gallego, J. Laboratory evaluation of the mechanical properties of asphalt mixtures with rubber incorporated by the wet, dry, and semi-wet process. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 205, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venudharan, V.; Biligiri, K.P.; Sousa, J.B.; Way, G.B. Asphalt-rubber gap-graded mixture design practices: A state-of-the-art research review and future perspective. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2017, 18, 730–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedarisetty, S.; Biligri, K.P.; Sousa, J.B. Advanced rheological characterization of Reacted and Activated Rubber (RAR) modified asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 122, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, P.; Xun, P.; Xing, M.; Chen, S. Investigation of asphalt binder containing various crumb rubbers and asphalts. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 40, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, S.-J.; Yun, Y.-B.; Kim, K.W. The use of CRM-modified asphalt mixtures in Korea: Evaluation of high and ambient temperature performance. Construct. Build. Mater. 2014, 67, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Chen, L.Y.; Xue, L. Effect of crumb rubber modifier on pavement performance of wearing course asphalt mixture. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 168–170, 1145–1148. [Google Scholar]
- Kedarisetty, S.; Saha, G.; Biligiri, K.P.; Sousa, J.B. Reacted and activated rubber (RAR)-modified dense-graded asphalt mixtures: Design and performance evaluation. J. Test. Eval. 2018, 46, 2511–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, F.; Sol, M.; Rubio, M.C.; Segarra, M. The use of additives for the improvement of the mechanical behavior of high modulus asphalt mixes. Construct. Build. Mater. 2014, 70, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirini, B.; Imaninasab, R. Performance evaluation of rubberized and SBS modified porous asphalt mixtures. Construct. Build. Mater. 2016, 107, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, I.; Pasandín, A.R. Moisture damage resistance of hot-mix asphalt made with recycled concrete aggregates and crumb rubber. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, B.V.; Çolak, H. Laboratory comparison of the crumb-rubber and SBS modified bitumen and hot mix asphalt. Construct. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 3204–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, F.M.; Gamez, M.C.R. Influence of crumb rubber on the indirect tensile strength and stiffness modulus of hot bituminous mixes. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2012, 24, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandarsefat, S.; Sangiorgi, C.; Dondi, G.; Lamperti, R. Recycling asphalt pavement and tire rubber: A full laboratory and field scale study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 176, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomoni, M.; Plati, C.; Kane, M.; Loizos, A. Polishing behaviour of asphalt surface course containing recycled materials. Int. J. Transp. Sci. Technol. 2022, 11, 711–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, A.D.; Hadiwardoyo, S.P.; Sumabrata, R.J. Skid resistance performance against temperature change of hot-mix recycled asphalt pavement with added crumb rubber. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2114, 04112. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Erkens, S.; Skarpas, A. Experimental characterization of storage stability of crumb rubber modified bitumen with warm-mix additives. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 249, 118840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneswaran, S.; Yun, J.; Jeong, K.-D.; Lee, M.-S.; Lee, S.-J. Effect of Crumb Rubber Modifier Particle Size on Storage Stability of Rubberized Binders. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Apostolidis, P.; Scarpas, T. Review of warm mix rubberized asphalt concrete: Towards a sustainable paving technology. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 177, 302–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, A.M. Recycled waste glass as fine aggregate replacement in cementitious materials based on Portland cement. Constr. Build Mater. 2014, 72, 340–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khmiri, A.; Chaabouni, M.; Samet, B. Chemical behaviour of ground waste glass when used as partial cement replacement in mortars. Constr. Build Mater. 2013, 44, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalampokis, S.; Kalama, D.; Kesikidou, F.; Stefanidou, M.; Manthos, E. Assessment of Waste Glass Incorporation in Asphalt Concrete for Surface Layer Construction. Materials 2023, 16, 4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, J.; Kumar, B.; Gupta, A. Utilization of solid waste materials as alternative fillers in asphalt mixes: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 234, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmoorian, F.; Samali, B.; Yeaman, J.; Crabb, R. The Use of Glass to Optimize Bitumen Absorption of Hot Mix Asphalt Containing Recycled Construction Aggregates. Materials 2018, 11, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedik, A. An exploration into the utilization of recycled waste glass as a surrogate powder to crushed stone dust in asphalt pavement construction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 300, 123980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, A.; Ahmad, N.; Zaidi, B.; Khalid, R.A.; Hafeez, I.; Hussain, J.; Khitab, A.; Kırgız, M.S. GlasSphalt: A Borosilicate Based Sustainable Engineering Material for Asphalt Pavements. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airey, G.D.; Collop, A.C.; Thom, N.H. Mechanical performance of asphalt mixtures incorporating slag and glass secondary aggregates. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Asphalt Pavements for Southern Africa, Sun City, South Africa, 12–16 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Navarro, F.; Perez-Martinez, M.; Martín-Marín, J.; Sol-Sanchez, M.; Rubio-Gámez, M.-C. Mechanical performance of asphalt mixes incorporating waste glass. Balt. J. Road Bridge Eng. 2015, 10, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yang, W.; Xue, Y. Preparation and Properties of Glass-Asphalt Concrete; Key Laboratory for Silicate Materials Science and Engineering of Ministry of Education, Wuham University of Technology: Wuham, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, G.; Werkmeister, S.; Alabaster, D. The Effect of Adding Recycled Glass on the Performance of Base Course Aggregate. In NZ Transport Agency Research Report 351; New Zealand Transport Agency: Wellington, New Zealand, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Shafabakhsh, G.H.; Sajed, Y. Investigation of dynamic behavior of hot mix asphalt containing waste materials; case study: Glass cullet. J. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2014, 1, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, C.S. Feasibility of Using Recycled Glass in Asphalt Mixes; Report No. VTRC 90-R3; Virginia Transportation Research Council: Charlottesville, VA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Su, N.; Chen, J.S. Engineering properties of asphalt concrete made with recycled glass. Resou.r Conserv. Recycl. 2002, 35, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autelitano, F.; Giuliani, F. Optimization of electric arc furnace aggregates replacement in dense-graded asphalt wearing courses. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUROSLAG. Position Paper on the Status of Ferrous Slag; The European Slag Association, The European Steel Association: Duisburg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kehagia, F. Skid resistance performance of asphalt wearing courses with electric arc furnace slag aggregates. Waste Manag. Res. J. A Sustain. Circ. Econ. 2009, 27, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondi, G.; Mazzotta, F.; Lantieri, C.; Cuppi, F.; Vignali, V.; Sangiovanni, C. Use of Steel Slag as an Alternative to Aggregate and Filler in Road Pavements. Materials 2021, 14, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulikakos, L.D.; Papadaskalopoulou, C.; Hofko, B.; Gschösser, F.; Cannone Falchetto, A.; Bueno, M.; Arraigada, M.; Sousa, J.; Ruiz, R.; Petit, C.; et al. Harvesting the unexplored potential of European waste materials for road construction. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 116, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaf, M.; Manso, J.M.; Aragón, Á.; Fuente-Alonso, J.A.; Ortega-López, V. EAF slag in asphalt mixes: A brief review of its possible re-use. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 120, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-S.; Wei, S.-H. Engineering properties and performance of asphalt mixtures incorporating steel slag. Construct. Build. Mater. 2016, 128, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelian, S.; Manian, M.; Abtahi, S.M.; Goli, A. Moisture sensitivity and mechanical performance assessment of warm mix asphalt containing by-product steel slag. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 176, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwasola, E.A.; Hainin, M.R.; Aziz, M.A. Comparative evaluation of dense-graded and gap-graded asphalt mix incorporating electric arc furnace steel slag and copper mine tailings. J. Cleaner Prod. 2016, 122, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanaik, M.L.; Choudhary, R.; Kumar, B.; Kumar, A. Mechanical properties of open graded friction course mixtures with different contents of electric arc furnace steel slag as an alternative aggregate from steel industries. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2021, 22, 268–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, M.; Hesami, S.; Goli, H. Laboratory evaluation of warm mix asphalt mixtures containing electric arc furnace (EAF) steel slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Haeng Jo, S.; Kim, N.; Kim, H. Characteristics of hot mix asphalt containing steel slag aggregate according to temperature and void percentage. Construct. Build. Mater. 2018, 188, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazizadeh, M.J.; Farhad, H.; Kavussi, A.; Sadeghi, A. Evaluating the fatigue behavior of asphalt mixtures containing electric arc furnace and basic oxygen furnace slags using surface free energy estimation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 188, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasetto, M.; Baldo, N. Fatigue behavior characterization of bituminous mixtures made with reclaimed asphalt pavement and steel slag. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 53, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho, F.C.G.; Picado-Santos, L.G.; Capitão, S.D. Influence of recycled concrete and steel slag aggregates on warm-mix asphalt properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 185, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Wu, S.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, F. Enhancement mechanism of skid resistance in preventive maintenance of asphalt pavement by steel slag based on micro-surfacing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 239, 117870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiana, R.; Balzano, F.; Iuele, T.; Gallelli, V. Microtexture performance of EAF slags used as aggregate in asphalt mixes: A comparative study with surface properties of natural stones. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofilic, T.; Maldenovic, A.; Sofilic, U. Characterization of the EAF steel slag as aggregate for use in road construction. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2010, 19, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Liapis, I.; Likoydis, S. Use of electric arc furnace slag in thins skid-resistant surfacing. Proc. Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 48, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plati, C.; Pomoni, M.; Stergiou, T. From Mean Texture Depth to Mean Profile Depth: Exploring possibilities. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Bituminous Mixtures and Pavements (ICONFBMP), Thessaloniki, Greece, 12–14 June 2019; pp. 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, M.; Ahmadi, A. Recycling of RAP and steel slag aggregates into the warm mix asphalt: A performance evaluation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 147, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasetto, M.; Baldo, N. Dissipated energy analysis of four-point bending test on asphalt concretes made with steel slag and RAP. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2017, 10, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asi, I.M.; Qasrawi, H.Y.; Shalabi, F.I. Use of steel slag aggregate in asphalt concrete mixes. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2007, 34, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavussi, A.; Qazizadeh, M.J. Fatigue characterization of asphalt mixes containing electric arc furnace (EAF) steel slag subjected to long term aging. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 72, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiha, M.; El-Badawy, S.; Gabr, A. Modeling and performance evaluation of asphalt mixtures and aggregate bases containing steel slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 248, 118710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Riccardi, C.; Jafari, B.; Falchetto, A.C.; Wistuba, M.P. Investigation on the effect of high amount of Re-recycled RAP with Warm mix asphalt (WMA) technology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 312, 125395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Liu, H.; Jiao, Y.; Mo, L.; Tan, Y.; Wang, D.; Liang, M. Effect of WMA-RAP technology on pavement performance of asphalt mixture: A state-of-the-art review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 266, 121704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giani, M.I.; Dotelli, G.; Brandini, N.; Zampori, L. Comparative life cycle assessment of asphalt pavements using reclaimed asphalt, warm mix technology and cold in-place recycling. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 104, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, R.; Moliner, E.; Martínez, G.; Rubio, M.C. Life cycle assessment of hot mix asphalt and zeolite-based warm mix asphalt with reclaimed asphalt pavement. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2013, 74, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, H. Life cycle assessment of asphalt pavement recycling for greenhouse gas emission with temporal aspect. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 187, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmagarhe, A.; Lu, Q.; Alharthai, M.; Alamri, M.; Elnihum, A. Performance of Porous Asphalt Mixtures Containing Recycled Concrete Aggregate and Fly Ash. Materials 2022, 15, 6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montepara, A.; Tebaldi, G.; Marradi, A.; Betti, G. Effect on pavement performance of a subbase layer composed by natural aggregate and RAP. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 53, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binte Alam, T.; Abdelrahman, M.; Schram, S.A. Laboratory characterization of recycled asphalt pavement as a base layer. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2010, 11, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkyrtis, K. Pavement Analysis with the Consideration of Unbound Granular Material Nonlinearity. Designs 2023, 7, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loizos, A.; Spiliopoulos, K.; Cliatt, B.; Gkyrtis, K. Structural pavement responses using nonlinear finite element analysis of unbound materials. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Bearing Capacity of Roads, Railways and Airfields (BCRRA), Athens, Greece, 28–30 June 2017; pp. 1343–1350. [Google Scholar]
- Loizos, A.; Gkyrtis, K.; Plati, C. Modelling Asphalt Pavement Responses Based on Field and Laboratory Data. In Accelerated Pavement Testing to Transport Infrastructure Innovation; Chabot, A., Hornych, P., Harvey, J., Loria-Salazar, L., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 96, pp. 438–447. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Qadi, I.L.; Carpenter, S.H.; Roberts, G.F.; Ozer, H.; Aurangzeb, Q.; Elseifi, M.; Trepanier, J. Determination of Usable Residual Asphalt Binder in RAP; Research Report ICT-09-031; Illinois Center for Transportation: Rantoul, IL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Copeland, A. Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement in Asphalt Mixtures: State of the Practice; No. FHWA-HRT-11-021; Federal Highway Administration: McLean, VA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Valdés, G.; Pérez-Jiménez, F.; Miró, R.; Martínez, A.; Botella, R. Experimental study of recycled asphalt mixtures with high percentages of reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP). Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widyatmoko, I. Mechanistic-empirical mixture design for hot mix asphalt pavement recycling. Constr. Build Mater. 2008, 22, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Marasteanu, M.; Williams, R.; Clyne, T. Effect of RAP (proportion and type) and binder grade on the properties of asphalt mixtures. Transport Res. Rec. J. Transport Res. Board 2008, 2051, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austroads. Maximising the Re-Use of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement: Outcomes of Year Two: RAP Mix Design; AP-T286-15; Austroads: Sydney, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- del Barco Carrión, A.J.; Lo Presti, D.; Airey, G.D. Binder design of high RAP content hot and warm asphalt mixture wearing courses. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2015, 16, 460–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 13108-8; Bituminous Mixtures—Material Specifications—Part 8: Reclaimed Asphalt. BSI: Belgium, The Netherlands, 2006.
- Sedthayutthaphong, N.; Jitsangiam, P.; Nikraz, H.; Pra-ai, S.; Tantanee, S.; Nusit, K. The Influence of a Field-Aged Asphalt Binder and Aggregates on the Skid Resistance of Recycled Hot Mix Asphalt. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.X.; Saleh, M.; Nguyen, N.H.T. Effect of rejuvenator and mixing methods on behaviour of warm mix asphalt containing high RAP content. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 197, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, A.A.; Caputo, P.; Eskandarsefat, S.; Loise, V.; Porto, M.; Giorno, E.; Venturini, L.; Oliviero Rossi, C. Rejuvenating Agents vs. Fluxing Agents: Their Respective Mechanisms of Action on Bitumen Subjected to Multiple Aging Cycles. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izaks, R.; Haritonovs, V.; Klasa, I.; Zaumanis, M. Hot Mix Asphalt with High RAP Content. Procedia Eng. 2015, 114, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauste, R.; Moreno-Navarro, F.; Sol-Sánchez, M.; Rubio-Gámez, M. The Effect of the Nature of Rejuvenators on the Rheological Properties of Aged Asphalt Binders. In RILEM 252-CMB-Symposium on Chemo Mechanical Characterization of Bituminous Materials; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 220–225. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, N.H.; Taylor, A.; Willis, R. Effect of Rejuvenator on Performance Properties of HMA Mixtures with High RAP and RAS Contents; NCAT Report 12-05; National Center for Asphalt Technology at Auburn University: Auburn, AL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Canon Falla, G.; Blasl, A.; Millow, R.; Lo Presti, D. Mix design considerations for asphalt wearing courses with high reclaimed asphalt content. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Bituminous Mixtures and Pavements, Thessaloniki, Greece, 10–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Stroup-Gardiner, M.; Wagner, C. Use of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement in Superpave Hot-Mix Asphalt Applications. Transp. Res. Rec. 1999, 1681, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, V.; Freire, A.C.; Neves, J. Investigating aged binder mobilization and performance of RAP mixtures for surface courses. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 271, 121511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogawer, W.S.; Bennert, T.; Daniel, J.; Bonaquist, R.; Austerman, A.; Booshehrian, A. Performance Characteristics of Plant Produced High RAP Mixtures. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2012, 13, 183–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Rongmei Nuga, G.R.; Kumar, P.; Rai, P. Mix design, development, production and policies of recycled hot mix asphalt: A review. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. Engl. Ed. 2022, 9, 765–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, A.; Hamzah, M.O.; Kurumisawa, K.; Nawa, T.; Samali, B. Evaluation of sustainable technologies that upgrade the binder performance grade in asphalt pavement construction. J. Mater. Des. 2016, 95, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, S.; You, Z. Properties of Asphalt Mixtures with RAP in the Mechanistic-empirical pavement design of flexible pavements: A Preliminary Investigation. In Airfield and Highway Pavements; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2008; pp. 171–181. [Google Scholar]
- Maupin, G.W.; Diefenderfer, S.D.; Gillespie, J.S. Evaluation of Using Higher Percentages of Recycled Asphalt Pavement in Asphalt Mixes in Virginia; Virginia Transportation Research Council: Charlottesville, VA, USA, 2008; p. 29. [Google Scholar]
- Apeagyei, A.K.; Clark, T.M.; Rorrer, T.M. Stiffness of high-RAP asphalt mixtures: Virginia’s experience. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2013, 25, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.D.; Howard, I.L. Laboratory Investigation of High RAP Content Pavement Surface Layers; Final Report FHWA/MS-DOT-RD-10-212; Mississippi State University: Oktibbeha, MI, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Poursoltani, M.; Hesami, S. Performance evaluation of micro-surfacing mixture containing reclaimed asphalt pavement. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2020, 21, 1491–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. The effects of using reclaimed asphalt pavements (RAP) on the long-term performance of asphalt concrete overlays. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 120, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Huang, B.; Shu, X. Field performance evaluation of asphalt mixtures containing high percentage of RAP using LTPP data. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 176, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, A.J.T.; Ragavan, P.; Elias, N.G.; Hajj, E.Y.; Sebaaly, P.E. Evaluation of Low Volume Roads Surfaced with 100% RAP Millings. Materials 2022, 15, 7462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Shen, S.; Li, X.; Song, B. Micro-surfacing mixtures with reclaimed asphalt pavement: Mix design and performance evaluation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 201, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorashadizadeh, A.; Hajikarimi, P.; Rahi, M.; Maniei, S. Prediction of Rheological Properties of Asphalt Binder and Asphalt Mastic Containing Crumb Rubber Using Generalized Self-Consistent Micromechanical Model (GSCS). J. Transp. Res. 2024, 21, 329–338. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Dong, B.; Wang, W.; Zhao, G.; Guo, P.; Ma, Q. Effect of Waste Engine Oil and Waste Cooking Oil on Performance Improvement of Aged Asphalt. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Huang, B.; Moore, J.A.; Zhao, S. Influence of Waste Engine Oil on Asphalt Mixtures Containing Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 27, 04015042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiafico, S.; Di Benedetto, H.; Sauzéat, C.; Olard, F.; Pouget, S.; Planque, L. Relations between Linear Visco-Elastic Behaviour of Bituminous Mixtures Containing Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement and Colloidal Structure of Corresponding Binder Blends. Procedia Eng. 2016, 143, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.H.; Koting, S.; Katman, H.Y.B.; Ibrahim, M.R.; Babalghaith, A.M.; Asqool, O. Performance of High Content Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP) in Asphaltic Mix with Crumb Rubber Modifier and Waste Engine Oil as Rejuvenator. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zou, X.; Wu, H.; Zhan, Y. Effect of RAP and glass fiber on mode I fracture behaviors of ultra-thin friction course. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2022, 275, 108868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Balieu, R.; Kringos, N. Integrating sustainability into pavement maintenance effectiveness evaluation: A systematic review. Transp. Res. Part D 2022, 104, 103187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I. Use of Waste Materials in Highway Construction; Elsevier: London, UK, 1993; pp. 1–115. [Google Scholar]
- Gkyrtis, K.; Plati, C.; Loizos, A. A step toward improving management practices for airfield pavement infrastructures: A mechanistic-based analysis approach. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, G. Quantifying the impact of reclaimed asphalt pavement on airport asphalt surfaces. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 197, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.; Hachiya, Y.; Maekawa, R. Study on recycled asphalt concrete for use in surface course in airport pavement. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2009, 54, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkyrtis, K.; Armeni, A.; Loizos, A. A mechanistic perspective for airfield pavements evaluation focusing on the asphalt layers’ behaviour. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2023, 14, 5087–5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, N.; Kazmee, H.; Ricalde, L. Use of Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP) in Airport Pavements. In Proceedings of the RILEM International Symposium on Bituminous Materials, ISBM 2020, Lyon, France, 8–10 June 2020; RILEM Bookseries. Di Benedetto, H., Baaj, H., Chailleux, E., Tebaldi, G., Sauzéat, C., Mangiafico, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 27, pp. 1909–1916. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Leng, Z.; Lan, J.; Wang, W.; Yu, J.; Bai, Y.; Sreeram, A.; Hu, J. Sustainable Practice in Pavement Engineering through Value-Added Collective Recycling of Waste Plastic and Waste Tyre Rubber. Engineering 2021, 7, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Xiao, F.; Amirkhanian, S. Recent applications of waste solid materials in pavement engineering. Waste Manag. 2020, 108, 78–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Tire & Rubber Manufacturer’s Association (ETRMA). The ETRMA Statistics Report; European Tire & Rubber Manufacturer’s Association: Saint-Josse-ten-Noode, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Farina, A.; Zanetti, M.C.; Santagata, E.; Blengini, G.A. Life cycle assessment applied to bituminous mixtures containing recycled materials: Crumb rubber and reclaimed asphalt pavement. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 117, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantalovas, K.; Di Mino, G. Integrating Circularity in the Sustainability Assessment of Asphalt Mixtures. Sustainability 2020, 12, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttitta, G.; Giancontieri, G.; Parry, T.; Lo Presti, D. Modelling the Environmental and Economic Life Cycle Performance of Maximizing Asphalt Recycling on Road Pavement Surfaces in Europe. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, T.; Calmon, J.L.; Vieira, D.; Bravo, A.; Vieira, T. Life Cycle Assessment of Road Pavements That Incorporate Waste Reuse: A Systematic Review and Guidelines Proposal. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaf, H.; Abu Abdo, A. Life cycle assessment of incorporating recycled materials in pavement Design. J. King Saud Univ. Eng. Sci. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sha, C.; Ly, S.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Guo, M. Life Cycle Carbon Emissions and an Uncertainty Analysis of Recycled Asphalt Mixtures. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizarro, D.E.G.; Steinmann, Z.; Nieuwenhuijse, I.; Keijzer, E.; Hauck, M. Potential Carbon Footprint Reduction for Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement Innovations: LCA Methodology, Best Available Technology, and Near-Future Reduction Potential. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.-Z.; Chen, Z.-D.; Lin, K.-P.; Wang, C.-H. Estimation and Analysis of Energy Conservation and Emissions Reduction Effects of Warm-Mix Crumb Rubber-Modified Asphalts during Construction Period. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xiao, F.; Zhang, L.; Amirkhanian, S.N. Life cycle assessment and life cycle cost analysis of recycled solid waste materials in highway pavement: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 1182–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbay, K.; Jawad, D.; Parker, N.A.; Hussain, S. Life-cycle cost analysis: State of the practice versus state of the art. Transp. Res. Rec. 2004, 1864, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, U.; Whyte, A.; Al Jassmi, H.; Hasan, A. Lifecycle Cost Analysis of Recycled Asphalt Pavements: Determining Cost of Recycled Materials for an Urban Highway Section. CivilEng 2022, 3, 316–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthonissen, J.; Van den bergh, W.; Braet, J. Review and environmental impact assessment of green technologies for base courses in bituminous pavements. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2016, 60, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadgoleh, M.A.; Mohammadi, M.M.; Ghodrati, A.; Sharifi, S.S.; Palizban, S.M.M.; Ahmadi, A.; Vahidi, E.; Ayar, P. Characterization of contaminant leaching from asphalt pavements: A critical review of measurement methods, reclaimed asphalt pavement, porous asphalt, and waste-modified asphalt mixtures. Water Res. 2022, 219, 118584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho, F.C.G.; Silva, H.M.R.D.; Oliveira, J.R.M.; Moura, C.F.N.; Loureiro, C.D.A.; Silvestre, J.D.; Rodrigues, M.M.M. Mechanical and Environmental Performance of Asphalt Concrete with High Amounts of Recycled Concrete Aggregates (RCA) for Use in Surface Courses of Pavements. Sustainability 2024, 16, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).